AI
-
 KAIST Successfully Implements 3D Brain-Mimicking Platform with 6x Higher Precision
<(From left) Dr. Dongjo Yoon, Professor Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, (upper right) Professor Yoonkey Nam, Dr. Soo Jee Kim>
Existing three-dimensional (3D) neuronal culture technology has limitations in brain research due to the difficulty of precisely replicating the brain's complex multilayered structure and the lack of a platform that can simultaneously analyze both structure and function. A KAIST research team has successfully developed an integrated platform that can implement brain-like layered neuronal structures using 3D printing technology and precisely measure neuronal activity within them.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of July that a joint research team led by Professors Je-Kyun Park and Yoonkey Nam from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed an integrated platform capable of fabricating high-resolution 3D multilayer neuronal networks using low-viscosity natural hydrogels with mechanical properties similar to brain tissue, and simultaneously analyzing their structural and functional connectivity.
Conventional bioprinting technology uses high-viscosity bioinks for structural stability, but this limits neuronal proliferation and neurite growth. Conversely, neural cell-friendly low-viscosity hydrogels are difficult to precisely pattern, leading to a fundamental trade-off between structural stability and biological function. The research team completed a sophisticated and stable brain-mimicking platform by combining three key technologies that enable the precise creation of brain structure with dilute gels, accurate alignment between layers, and simultaneous observation of neuronal activity.
The three core technologies are: ▲ 'Capillary Pinning Effect' technology, which enables the dilute gel (hydrogel) to adhere firmly to a stainless steel mesh (micromesh) to prevent it from flowing, thereby reproducing brain structures with six times greater precision (resolution of 500 μm or less) than conventional methods; ▲ the '3D Printing Aligner,' a cylindrical design that ensures the printed layers are precisely stacked without misalignment, guaranteeing the accurate assembly of multilayer structures and stable integration with microelectrode chips; and ▲ 'Dual-mode Analysis System' technology, which simultaneously measures electrical signals from below and observes cell activity with light (calcium imaging) from above, allowing for the simultaneous verification of the functional operation of interlayer connections through multiple methods.
< Figure 1. Platform integrating brain-structure-mimicking neural network model construction and functional measurement technology>
The research team successfully implemented a three-layered mini-brain structure using 3D printing with a fibrin hydrogel, which has elastic properties similar to those of the brain, and experimentally verified the process of actual neural cells transmitting and receiving signals within it.
Cortical neurons were placed in the upper and lower layers, while the middle layer was left empty but designed to allow neurons to penetrate and connect through it. Electrical signals were measured from the lower layer using a microsensor (electrode chip), and cell activity was observed from the upper layer using light (calcium imaging). The results showed that when electrical stimulation was applied, neural cells in both upper and lower layers responded simultaneously. When a synapse-blocking agent (synaptic blocker) was introduced, the response decreased, proving that the neural cells were genuinely connected and transmitting signals.
Professor Je-Kyun Park of KAIST explained, "This research is a joint development achievement of an integrated platform that can simultaneously reproduce the complex multilayered structure and function of brain tissue. Compared to existing technologies where signal measurement was impossible for more than 14 days, this platform maintains a stable microelectrode chip interface for over 27 days, allowing the real-time analysis of structure-function relationships. It can be utilized in various brain research fields such as neurological disease modeling, brain function research, neurotoxicity assessment, and neuroprotective drug screening in the future."
<Figure 2. Integration process of stacked bioprinting technology and microelectrode chip>
The research, in which Dr. Soo Jee Kim and Dr. Dongjo Yoon from KAIST's Department of Bio and Brain Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal 'Biosensors and Bioelectronics' on June 11, 2025.
※Paper: Hybrid biofabrication of multilayered 3D neuronal networks with structural and functional interlayer connectivity
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2025.117688
2025.07.16 View 79
KAIST Successfully Implements 3D Brain-Mimicking Platform with 6x Higher Precision
<(From left) Dr. Dongjo Yoon, Professor Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, (upper right) Professor Yoonkey Nam, Dr. Soo Jee Kim>
Existing three-dimensional (3D) neuronal culture technology has limitations in brain research due to the difficulty of precisely replicating the brain's complex multilayered structure and the lack of a platform that can simultaneously analyze both structure and function. A KAIST research team has successfully developed an integrated platform that can implement brain-like layered neuronal structures using 3D printing technology and precisely measure neuronal activity within them.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of July that a joint research team led by Professors Je-Kyun Park and Yoonkey Nam from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed an integrated platform capable of fabricating high-resolution 3D multilayer neuronal networks using low-viscosity natural hydrogels with mechanical properties similar to brain tissue, and simultaneously analyzing their structural and functional connectivity.
Conventional bioprinting technology uses high-viscosity bioinks for structural stability, but this limits neuronal proliferation and neurite growth. Conversely, neural cell-friendly low-viscosity hydrogels are difficult to precisely pattern, leading to a fundamental trade-off between structural stability and biological function. The research team completed a sophisticated and stable brain-mimicking platform by combining three key technologies that enable the precise creation of brain structure with dilute gels, accurate alignment between layers, and simultaneous observation of neuronal activity.
The three core technologies are: ▲ 'Capillary Pinning Effect' technology, which enables the dilute gel (hydrogel) to adhere firmly to a stainless steel mesh (micromesh) to prevent it from flowing, thereby reproducing brain structures with six times greater precision (resolution of 500 μm or less) than conventional methods; ▲ the '3D Printing Aligner,' a cylindrical design that ensures the printed layers are precisely stacked without misalignment, guaranteeing the accurate assembly of multilayer structures and stable integration with microelectrode chips; and ▲ 'Dual-mode Analysis System' technology, which simultaneously measures electrical signals from below and observes cell activity with light (calcium imaging) from above, allowing for the simultaneous verification of the functional operation of interlayer connections through multiple methods.
< Figure 1. Platform integrating brain-structure-mimicking neural network model construction and functional measurement technology>
The research team successfully implemented a three-layered mini-brain structure using 3D printing with a fibrin hydrogel, which has elastic properties similar to those of the brain, and experimentally verified the process of actual neural cells transmitting and receiving signals within it.
Cortical neurons were placed in the upper and lower layers, while the middle layer was left empty but designed to allow neurons to penetrate and connect through it. Electrical signals were measured from the lower layer using a microsensor (electrode chip), and cell activity was observed from the upper layer using light (calcium imaging). The results showed that when electrical stimulation was applied, neural cells in both upper and lower layers responded simultaneously. When a synapse-blocking agent (synaptic blocker) was introduced, the response decreased, proving that the neural cells were genuinely connected and transmitting signals.
Professor Je-Kyun Park of KAIST explained, "This research is a joint development achievement of an integrated platform that can simultaneously reproduce the complex multilayered structure and function of brain tissue. Compared to existing technologies where signal measurement was impossible for more than 14 days, this platform maintains a stable microelectrode chip interface for over 27 days, allowing the real-time analysis of structure-function relationships. It can be utilized in various brain research fields such as neurological disease modeling, brain function research, neurotoxicity assessment, and neuroprotective drug screening in the future."
<Figure 2. Integration process of stacked bioprinting technology and microelectrode chip>
The research, in which Dr. Soo Jee Kim and Dr. Dongjo Yoon from KAIST's Department of Bio and Brain Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal 'Biosensors and Bioelectronics' on June 11, 2025.
※Paper: Hybrid biofabrication of multilayered 3D neuronal networks with structural and functional interlayer connectivity
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2025.117688
2025.07.16 View 79 -
 Professor Jung-woo' Choi ‘s Team Comes in First at the World's Top Acoustic AI Challenge
<Photo1. (From left) Ph.D candidate Yong-hoo Kwon, M.S candidate Do-hwan Kim, Professor Jung-woo Choi, Dr. Dong-heon Lee>
'Acoustic separation and classification technology' is a next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) core technology that enables the early detection of abnormal sounds in areas such as drones, fault detection of factory pipelines, and border surveillance systems, or allows for the separation and editing of spatial audio by sound source when producing AR/VR content.
On the 11th of July, a research team led by Professor Jung-woo Choi of KAIST's Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering won first place in the 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' task of the 'DCASE2025 Challenge,' the world's most prestigious acoustic detection and analysis competition.
This year’s challenge featured 86 teams competing across six tasks. In this competition, the KAIST research team achieved the best performance in their first-ever participation to Task 4. Professor Jung-woo Choi’s research team consisted of Dr. Dong-heon, Lee, Ph.D. candidate Young-hoo Kwon, and M.S. candidate Do-hwan Kim.
Task 4 titled 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' is a highly demanding task requiring the analysis of spatial information in multi-channel audio signals with overlapping sound sources. The goal was to separate individual sounds and classify them into 18 predefined categories. The research team plans to present their technology at the DCASE workshop in Barcelona this October.
<Figure 1. Example of an acoustic scene with multiple mixed sounds>
Early this year, Dr. Dong-heon Lee developed a state-of-the-art sound source separation AI that combines Transformer and Mamba architectures. During the competition, centered around researcher Young-hoo Kwon, they completed a ‘chain-of-inference architecture' AI model that performs sound source separation and classification again, using the waveforms and types of the initially separated sound sources as clues. This AI model is inspired by human’s auditory scene analysis mechanism that isolates individual sounds by focusing on incomplete clues such as sound type, rhythm, or direction, when listening to complex sounds.
Through this, the team was the only participant to achieve double-digit performance (11 dB) in 'Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi)*,' which is the measure for ranking how well the AI separated and classified sounds, proving their technical excellence.
Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi): Measures how much clearer (less distorted) the desired sound is separated and classified compared to the original audio, in dB (decibels). A higher number indicates more accurate and cleaner sound separation.
Prof. Jung-woo Choi remarked, "The research team has showcased world-leading acoustic separation AI models for the past three years, and I am delighted that these results have been officially recognized." He added, "I am proud of every member of the research team for winning first place through focused research, despite the significant increase in difficulty and having only a few weeks for development."
<Figure 2. Time-frequency patterns of sound sources separated from a mixed source>
The IEEE DCASE Challenge 2025 was held online, with submissions accepted from April 1 to June 15 and results announced on June 30. Since its launch in 2013, the DCASE Challenge has served as a premier global platform of IEEE Signal Processing Society for showcasing cutting-edge AI models in acoustic signal processing.
This research was supported by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Project and STEAM Research Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, as well as support from the Future Defense Research Center, funded by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration and the Agency for Defense Development.
2025.07.13 View 69
Professor Jung-woo' Choi ‘s Team Comes in First at the World's Top Acoustic AI Challenge
<Photo1. (From left) Ph.D candidate Yong-hoo Kwon, M.S candidate Do-hwan Kim, Professor Jung-woo Choi, Dr. Dong-heon Lee>
'Acoustic separation and classification technology' is a next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) core technology that enables the early detection of abnormal sounds in areas such as drones, fault detection of factory pipelines, and border surveillance systems, or allows for the separation and editing of spatial audio by sound source when producing AR/VR content.
On the 11th of July, a research team led by Professor Jung-woo Choi of KAIST's Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering won first place in the 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' task of the 'DCASE2025 Challenge,' the world's most prestigious acoustic detection and analysis competition.
This year’s challenge featured 86 teams competing across six tasks. In this competition, the KAIST research team achieved the best performance in their first-ever participation to Task 4. Professor Jung-woo Choi’s research team consisted of Dr. Dong-heon, Lee, Ph.D. candidate Young-hoo Kwon, and M.S. candidate Do-hwan Kim.
Task 4 titled 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' is a highly demanding task requiring the analysis of spatial information in multi-channel audio signals with overlapping sound sources. The goal was to separate individual sounds and classify them into 18 predefined categories. The research team plans to present their technology at the DCASE workshop in Barcelona this October.
<Figure 1. Example of an acoustic scene with multiple mixed sounds>
Early this year, Dr. Dong-heon Lee developed a state-of-the-art sound source separation AI that combines Transformer and Mamba architectures. During the competition, centered around researcher Young-hoo Kwon, they completed a ‘chain-of-inference architecture' AI model that performs sound source separation and classification again, using the waveforms and types of the initially separated sound sources as clues. This AI model is inspired by human’s auditory scene analysis mechanism that isolates individual sounds by focusing on incomplete clues such as sound type, rhythm, or direction, when listening to complex sounds.
Through this, the team was the only participant to achieve double-digit performance (11 dB) in 'Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi)*,' which is the measure for ranking how well the AI separated and classified sounds, proving their technical excellence.
Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi): Measures how much clearer (less distorted) the desired sound is separated and classified compared to the original audio, in dB (decibels). A higher number indicates more accurate and cleaner sound separation.
Prof. Jung-woo Choi remarked, "The research team has showcased world-leading acoustic separation AI models for the past three years, and I am delighted that these results have been officially recognized." He added, "I am proud of every member of the research team for winning first place through focused research, despite the significant increase in difficulty and having only a few weeks for development."
<Figure 2. Time-frequency patterns of sound sources separated from a mixed source>
The IEEE DCASE Challenge 2025 was held online, with submissions accepted from April 1 to June 15 and results announced on June 30. Since its launch in 2013, the DCASE Challenge has served as a premier global platform of IEEE Signal Processing Society for showcasing cutting-edge AI models in acoustic signal processing.
This research was supported by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Project and STEAM Research Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, as well as support from the Future Defense Research Center, funded by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration and the Agency for Defense Development.
2025.07.13 View 69 -
 KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation Landmark
KAIST announced on July 10th that it held a groundbreaking ceremony on July 9th for the expansion of its Creative Learning Building. This project, which celebrates the university's 50th anniversary, will become a significant donation-funded landmark and marks the official start of its construction.
<(From left) President Kwang Hyung Lee, Former President Sung-Chul Shin>
The groundbreaking ceremony was attended by key donors who graced the occasion, including KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, former President Sung-Chul Shin, Alumni Association President Yoon-Tae Lee, as well as parents and faculty member.
The Creative Learning Building serves as a primary space where KAIST undergraduate and graduate students attend lectures, functioning as a central hub for a variety of classes and talks. It also houses student support departments, including the Student Affairs Office, establishing itself as a student-centric complex that integrates educational, counseling, and welfare functions.
This expansion is more than just an increase in educational facilities; it's being developed as a "donation landmark" embodying KAIST's identity and future vision. Designed with a focus on creative convergence education, this project aims to create a new educational hub that organically combines education, exchange, and welfare functions
The campaign included over 230 participants, including KAIST alumni Byung-gyu Chang, Chairman of Krafton, former Alumni Association President Ki-chul Cha, Dr. Kun-mo Chung (former Minister of Science and Technology), as well as faculty members, parents, and current students. They collectively raised 6.5 billion KRW in donations. The total cost for this expansion project is 9 billion KRW, encompassing a gross floor area of 3,222.92㎡ across five above-ground floors, with completion targeted for September 2026.
2025.07.10 View 132
KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation Landmark
KAIST announced on July 10th that it held a groundbreaking ceremony on July 9th for the expansion of its Creative Learning Building. This project, which celebrates the university's 50th anniversary, will become a significant donation-funded landmark and marks the official start of its construction.
<(From left) President Kwang Hyung Lee, Former President Sung-Chul Shin>
The groundbreaking ceremony was attended by key donors who graced the occasion, including KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, former President Sung-Chul Shin, Alumni Association President Yoon-Tae Lee, as well as parents and faculty member.
The Creative Learning Building serves as a primary space where KAIST undergraduate and graduate students attend lectures, functioning as a central hub for a variety of classes and talks. It also houses student support departments, including the Student Affairs Office, establishing itself as a student-centric complex that integrates educational, counseling, and welfare functions.
This expansion is more than just an increase in educational facilities; it's being developed as a "donation landmark" embodying KAIST's identity and future vision. Designed with a focus on creative convergence education, this project aims to create a new educational hub that organically combines education, exchange, and welfare functions
The campaign included over 230 participants, including KAIST alumni Byung-gyu Chang, Chairman of Krafton, former Alumni Association President Ki-chul Cha, Dr. Kun-mo Chung (former Minister of Science and Technology), as well as faculty members, parents, and current students. They collectively raised 6.5 billion KRW in donations. The total cost for this expansion project is 9 billion KRW, encompassing a gross floor area of 3,222.92㎡ across five above-ground floors, with completion targeted for September 2026.
2025.07.10 View 132 -
 Professor Moon-Jeong Choi Appointed as an Advisor for the ITU's 'AI for Good Global Summit'
Professor Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy has been appointed as an advisor for "Innovate for Impact" at the AI for Good Global Summit, organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN).
The ITU is the UN's oldest specialized agency in the field of information and communication technology (ICT) and serves as a crucial body for coordinating global ICT policies and standards.
This advisory committee was formed to explore global cooperation strategies for realizing the social value of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and promoting sustainable development. Experts from around the world are participating as committee members, with Professor Choi being the sole Korean representative.
<Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy>
The AI for Good Global Summit is taking place in Geneva, Switzerland from July 8 to 11. It is organized by the ITU in collaboration with approximately 40 other UN-affiliated organizations. The summit aims to address global challenges facing humanity through the use of AI technology, focusing on key agenda items such as identifying AI application cases, discussing international policies and technical standards, and strengthening global partnerships.
As an "Innovate for Impact" advisor, Professor Choi will evaluate AI application cases from various countries, participating in case analyses primarily focused on public interest and social impact. The summit will move beyond discussions of technical performance to focus on how AI can contribute to the public good, with diverse case studies from around the world being debated. Notably, during a policy panel discussion at the summit, Professor Choi will discuss policy frameworks for AI transparency, inclusivity, and fairness under the theme of "Responsible AI Development."
Professor Choi commented, "I believe the social impact of technology mirrors the values and systems of each nation. As a society's core values permeate technology, the way AI is developed and used varies significantly from country to country. These differences lead to diverse manifestations of AI's impact on society." She further emphasized, "Korea's vision of becoming an AI powerhouse should not merely be about technological superiority, but rather about enhancing social capital through human-centered AI and realizing communal values that enable us to live together."
Professor Moon-Jeong Choi currently serves as the Dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy. She is also an external director for the National Information Society Agency (2023-present) and chair of the Korea-OECD Digital Society Initiative (2024-present).
For more information about the AI for Good Global Summit, please visit the official website: https://aiforgood.itu.int.
2025.07.08 View 210
Professor Moon-Jeong Choi Appointed as an Advisor for the ITU's 'AI for Good Global Summit'
Professor Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy has been appointed as an advisor for "Innovate for Impact" at the AI for Good Global Summit, organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN).
The ITU is the UN's oldest specialized agency in the field of information and communication technology (ICT) and serves as a crucial body for coordinating global ICT policies and standards.
This advisory committee was formed to explore global cooperation strategies for realizing the social value of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and promoting sustainable development. Experts from around the world are participating as committee members, with Professor Choi being the sole Korean representative.
<Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy>
The AI for Good Global Summit is taking place in Geneva, Switzerland from July 8 to 11. It is organized by the ITU in collaboration with approximately 40 other UN-affiliated organizations. The summit aims to address global challenges facing humanity through the use of AI technology, focusing on key agenda items such as identifying AI application cases, discussing international policies and technical standards, and strengthening global partnerships.
As an "Innovate for Impact" advisor, Professor Choi will evaluate AI application cases from various countries, participating in case analyses primarily focused on public interest and social impact. The summit will move beyond discussions of technical performance to focus on how AI can contribute to the public good, with diverse case studies from around the world being debated. Notably, during a policy panel discussion at the summit, Professor Choi will discuss policy frameworks for AI transparency, inclusivity, and fairness under the theme of "Responsible AI Development."
Professor Choi commented, "I believe the social impact of technology mirrors the values and systems of each nation. As a society's core values permeate technology, the way AI is developed and used varies significantly from country to country. These differences lead to diverse manifestations of AI's impact on society." She further emphasized, "Korea's vision of becoming an AI powerhouse should not merely be about technological superiority, but rather about enhancing social capital through human-centered AI and realizing communal values that enable us to live together."
Professor Moon-Jeong Choi currently serves as the Dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy. She is also an external director for the National Information Society Agency (2023-present) and chair of the Korea-OECD Digital Society Initiative (2024-present).
For more information about the AI for Good Global Summit, please visit the official website: https://aiforgood.itu.int.
2025.07.08 View 210 -
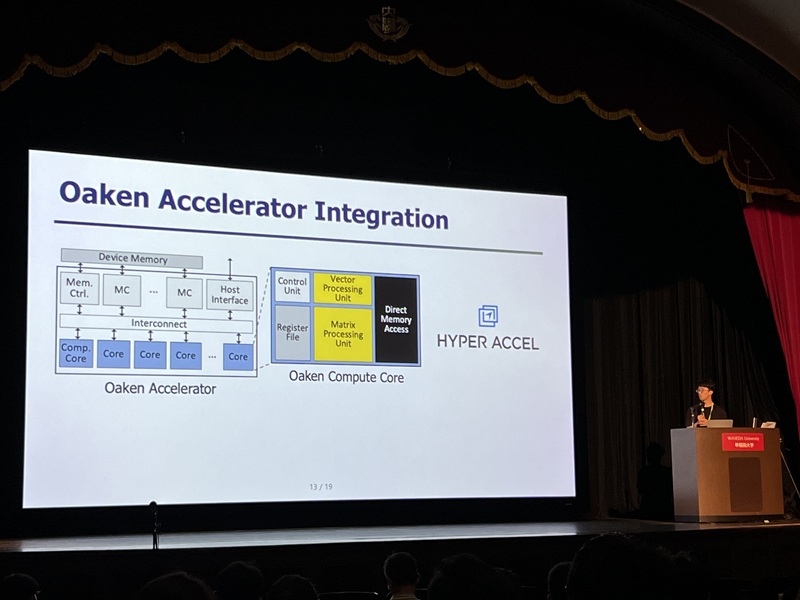 Development of Core NPU Technology to Improve ChatGPT Inference Performance by Over 60%
Latest generative AI models such as OpenAI's ChatGPT-4 and Google's Gemini 2.5 require not only high memory bandwidth but also large memory capacity. This is why generative AI cloud operating companies like Microsoft and Google purchase hundreds of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs. As a solution to address the core challenges of building such high-performance AI infrastructure, Korean researchers have succeeded in developing an NPU (Neural Processing Unit)* core technology that improves the inference performance of generative AI models by an average of over 60% while consuming approximately 44% less power compared to the latest GPUs.
*NPU (Neural Processing Unit): An AI-specific semiconductor chip designed to rapidly process artificial neural networks.
On the 4th, Professor Jongse Park's research team from KAIST School of Computing, in collaboration with HyperAccel Inc. (a startup founded by Professor Joo-Young Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering), announced that they have developed a high-performance, low-power NPU (Neural Processing Unit) core technology specialized for generative AI clouds like ChatGPT.
The technology proposed by the research team has been accepted by the '2025 International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA 2025)', a top-tier international conference in the field of computer architecture.
The key objective of this research is to improve the performance of large-scale generative AI services by lightweighting the inference process, while minimizing accuracy loss and solving memory bottleneck issues. This research is highly recognized for its integrated design of AI semiconductors and AI system software, which are key components of AI infrastructure.
While existing GPU-based AI infrastructure requires multiple GPU devices to meet high bandwidth and capacity demands, this technology enables the configuration of the same level of AI infrastructure using fewer NPU devices through KV cache quantization*. KV cache accounts for most of the memory usage, thereby its quantization significantly reduces the cost of building generative AI clouds.
*KV Cache (Key-Value Cache) Quantization: Refers to reducing the data size in a type of temporary storage space used to improve performance when operating generative AI models (e.g., converting a 16-bit number to a 4-bit number reduces data size by 1/4).
The research team designed it to be integrated with memory interfaces without changing the operational logic of existing NPU architectures. This hardware architecture not only implements the proposed quantization algorithm but also adopts page-level memory management techniques* for efficient utilization of limited memory bandwidth and capacity, and introduces new encoding technique optimized for quantized KV cache.
*Page-level memory management technique: Virtualizes memory addresses, as the CPU does, to allow consistent access within the NPU.
Furthermore, when building an NPU-based AI cloud with superior cost and power efficiency compared to the latest GPUs, the high-performance, low-power nature of NPUs is expected to significantly reduce operating costs.
Professor Jongse Park stated, "This research, through joint work with HyperAccel Inc., found a solution in generative AI inference lightweighting algorithms and succeeded in developing a core NPU technology that can solve the 'memory problem.' Through this technology, we implemented an NPU with over 60% improved performance compared to the latest GPUs by combining quantization techniques that reduce memory requirements while maintaining inference accuracy, and hardware designs optimized for this".
He further emphasized, "This technology has demonstrated the possibility of implementing high-performance, low-power infrastructure specialized for generative AI, and is expected to play a key role not only in AI cloud data centers but also in the AI transformation (AX) environment represented by dynamic, executable AI such as 'Agentic AI'."
This research was presented by Ph.D. student Minsu Kim and Dr. Seongmin Hong from HyperAccel Inc. as co-first authors at the '2025 International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA)' held in Tokyo, Japan, from June 21 to June 25. ISCA, a globally renowned academic conference, received 570 paper submissions this year, with only 127 papers accepted (an acceptance rate of 22.7%).
※Paper Title: Oaken: Fast and Efficient LLM Serving with Online-Offline Hybrid KV Cache Quantization
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3695053.3731019
Meanwhile, this research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Excellent Young Researcher Program, the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP), and the AI Semiconductor Graduate School Support Project.
2025.07.07 View 601
Development of Core NPU Technology to Improve ChatGPT Inference Performance by Over 60%
Latest generative AI models such as OpenAI's ChatGPT-4 and Google's Gemini 2.5 require not only high memory bandwidth but also large memory capacity. This is why generative AI cloud operating companies like Microsoft and Google purchase hundreds of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs. As a solution to address the core challenges of building such high-performance AI infrastructure, Korean researchers have succeeded in developing an NPU (Neural Processing Unit)* core technology that improves the inference performance of generative AI models by an average of over 60% while consuming approximately 44% less power compared to the latest GPUs.
*NPU (Neural Processing Unit): An AI-specific semiconductor chip designed to rapidly process artificial neural networks.
On the 4th, Professor Jongse Park's research team from KAIST School of Computing, in collaboration with HyperAccel Inc. (a startup founded by Professor Joo-Young Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering), announced that they have developed a high-performance, low-power NPU (Neural Processing Unit) core technology specialized for generative AI clouds like ChatGPT.
The technology proposed by the research team has been accepted by the '2025 International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA 2025)', a top-tier international conference in the field of computer architecture.
The key objective of this research is to improve the performance of large-scale generative AI services by lightweighting the inference process, while minimizing accuracy loss and solving memory bottleneck issues. This research is highly recognized for its integrated design of AI semiconductors and AI system software, which are key components of AI infrastructure.
While existing GPU-based AI infrastructure requires multiple GPU devices to meet high bandwidth and capacity demands, this technology enables the configuration of the same level of AI infrastructure using fewer NPU devices through KV cache quantization*. KV cache accounts for most of the memory usage, thereby its quantization significantly reduces the cost of building generative AI clouds.
*KV Cache (Key-Value Cache) Quantization: Refers to reducing the data size in a type of temporary storage space used to improve performance when operating generative AI models (e.g., converting a 16-bit number to a 4-bit number reduces data size by 1/4).
The research team designed it to be integrated with memory interfaces without changing the operational logic of existing NPU architectures. This hardware architecture not only implements the proposed quantization algorithm but also adopts page-level memory management techniques* for efficient utilization of limited memory bandwidth and capacity, and introduces new encoding technique optimized for quantized KV cache.
*Page-level memory management technique: Virtualizes memory addresses, as the CPU does, to allow consistent access within the NPU.
Furthermore, when building an NPU-based AI cloud with superior cost and power efficiency compared to the latest GPUs, the high-performance, low-power nature of NPUs is expected to significantly reduce operating costs.
Professor Jongse Park stated, "This research, through joint work with HyperAccel Inc., found a solution in generative AI inference lightweighting algorithms and succeeded in developing a core NPU technology that can solve the 'memory problem.' Through this technology, we implemented an NPU with over 60% improved performance compared to the latest GPUs by combining quantization techniques that reduce memory requirements while maintaining inference accuracy, and hardware designs optimized for this".
He further emphasized, "This technology has demonstrated the possibility of implementing high-performance, low-power infrastructure specialized for generative AI, and is expected to play a key role not only in AI cloud data centers but also in the AI transformation (AX) environment represented by dynamic, executable AI such as 'Agentic AI'."
This research was presented by Ph.D. student Minsu Kim and Dr. Seongmin Hong from HyperAccel Inc. as co-first authors at the '2025 International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA)' held in Tokyo, Japan, from June 21 to June 25. ISCA, a globally renowned academic conference, received 570 paper submissions this year, with only 127 papers accepted (an acceptance rate of 22.7%).
※Paper Title: Oaken: Fast and Efficient LLM Serving with Online-Offline Hybrid KV Cache Quantization
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3695053.3731019
Meanwhile, this research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Excellent Young Researcher Program, the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP), and the AI Semiconductor Graduate School Support Project.
2025.07.07 View 601 -
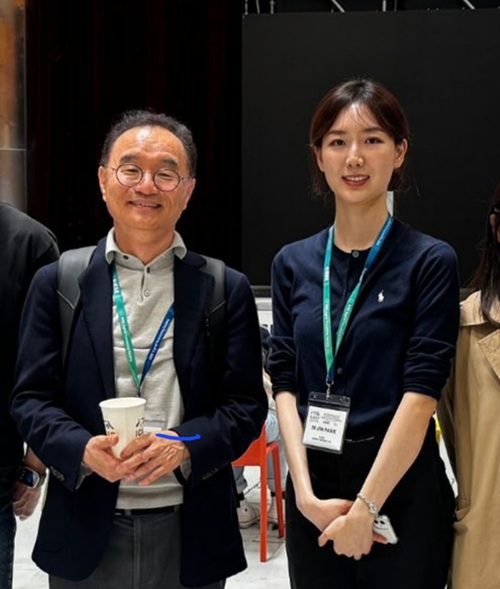 KAIST researcher Se Jin Park develops 'SpeechSSM,' opening up possibilities for a 24-hour AI voice assistant.
<(From Left)Prof. Yong Man Ro and Ph.D. candidate Sejin Park>
Se Jin Park, a researcher from Professor Yong Man Ro’s team at KAIST, has announced 'SpeechSSM', a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech that sounds natural and remains consistent.
An efficient processing technique based on linear sequence modeling overcomes the limitations of existing spoken language models, enabling high-quality speech generation without time constraints.
It is expected to be widely used in podcasts, audiobooks, and voice assistants due to its ability to generate natural, long-duration speech like humans.
Recently, Spoken Language Models (SLMs) have been spotlighted as next-generation technology that surpasses the limitations of text-based language models by learning human speech without text to understand and generate linguistic and non-linguistic information. However, existing models showed significant limitations in generating long-duration content required for podcasts, audiobooks, and voice assistants. Now, KAIST researcher has succeeded in overcoming these limitations by developing 'SpeechSSM,' which enables consistent and natural speech generation without time constraints.
KAIST(President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of July that Ph.D. candidate Sejin Park from Professor Yong Man Ro's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed 'SpeechSSM,' a spoken. a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech.
This research is set to be presented as an oral paper at ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning) 2025, one of the top machine learning conferences, selected among approximately 1% of all submitted papers. This not only proves outstanding research ability but also serves as an opportunity to once again demonstrate KAIST's world-leading AI research capabilities.
A major advantage of Spoken Language Models (SLMs) is their ability to directly process speech without intermediate text conversion, leveraging the unique acoustic characteristics of human speakers, allowing for the rapid generation of high-quality speech even in large-scale models.
However, existing models faced difficulties in maintaining semantic and speaker consistency for long-duration speech due to increased 'speech token resolution' and memory consumption when capturing very detailed information by breaking down speech into fine fragments.
To solve this problem, Se Jin Park developed 'SpeechSSM,' a spoken language model using a Hybrid State-Space Model, designed to efficiently process and generate long speech sequences.
This model employs a 'hybrid structure' that alternately places 'attention layers' focusing on recent information and 'recurrent layers' that remember the overall narrative flow (long-term context). This allows the story to flow smoothly without losing coherence even when generating speech for a long time. Furthermore, memory usage and computational load do not increase sharply with input length, enabling stable and efficient learning and the generation of long-duration speech.
SpeechSSM effectively processes unbounded speech sequences by dividing speech data into short, fixed units (windows), processing each unit independently, and then combining them to create long speech.
Additionally, in the speech generation phase, it uses a 'Non-Autoregressive' audio synthesis model (SoundStorm), which rapidly generates multiple parts at once instead of slowly creating one character or one word at a time, enabling the fast generation of high-quality speech.
While existing models typically evaluated short speech models of about 10 seconds, Se Jin Park created new evaluation tasks for speech generation based on their self-built benchmark dataset, 'LibriSpeech-Long,' capable of generating up to 16 minutes of speech.
Compared to PPL (Perplexity), an existing speech model evaluation metric that only indicates grammatical correctness, she proposed new evaluation metrics such as 'SC-L (semantic coherence over time)' to assess content coherence over time, and 'N-MOS-T (naturalness mean opinion score over time)' to evaluate naturalness over time, enabling more effective and precise evaluation.
Through these new evaluations, it was confirmed that speech generated by the SpeechSSM spoken language model consistently featured specific individuals mentioned in the initial prompt, and new characters and events unfolded naturally and contextually consistently, despite long-duration generation. This contrasts sharply with existing models, which tended to easily lose their topic and exhibit repetition during long-duration generation.
PhD candidate Sejin Park explained, "Existing spoken language models had limitations in long-duration generation, so our goal was to develop a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech for actual human use." She added, "This research achievement is expected to greatly contribute to various types of voice content creation and voice AI fields like voice assistants, by maintaining consistent content in long contexts and responding more efficiently and quickly in real time than existing methods."
This research, with Se Jin Park as the first author, was conducted in collaboration with Google DeepMind and is scheduled to be presented as an oral presentation at ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning) 2025 on July 16th.
Paper Title: Long-Form Speech Generation with Spoken Language Models
DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.18603
Ph.D. candidate Se Jin Park has demonstrated outstanding research capabilities as a member of Professor Yong Man Ro's MLLM (multimodal large language model) research team, through her work integrating vision, speech, and language. Her achievements include a spotlight paper presentation at 2024 CVPR (Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition) and an Outstanding Paper Award at 2024 ACL (Association for Computational Linguistics).
For more information, you can refer to the publication and accompanying demo: SpeechSSM Publications.
2025.07.04 View 639
KAIST researcher Se Jin Park develops 'SpeechSSM,' opening up possibilities for a 24-hour AI voice assistant.
<(From Left)Prof. Yong Man Ro and Ph.D. candidate Sejin Park>
Se Jin Park, a researcher from Professor Yong Man Ro’s team at KAIST, has announced 'SpeechSSM', a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech that sounds natural and remains consistent.
An efficient processing technique based on linear sequence modeling overcomes the limitations of existing spoken language models, enabling high-quality speech generation without time constraints.
It is expected to be widely used in podcasts, audiobooks, and voice assistants due to its ability to generate natural, long-duration speech like humans.
Recently, Spoken Language Models (SLMs) have been spotlighted as next-generation technology that surpasses the limitations of text-based language models by learning human speech without text to understand and generate linguistic and non-linguistic information. However, existing models showed significant limitations in generating long-duration content required for podcasts, audiobooks, and voice assistants. Now, KAIST researcher has succeeded in overcoming these limitations by developing 'SpeechSSM,' which enables consistent and natural speech generation without time constraints.
KAIST(President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of July that Ph.D. candidate Sejin Park from Professor Yong Man Ro's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed 'SpeechSSM,' a spoken. a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech.
This research is set to be presented as an oral paper at ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning) 2025, one of the top machine learning conferences, selected among approximately 1% of all submitted papers. This not only proves outstanding research ability but also serves as an opportunity to once again demonstrate KAIST's world-leading AI research capabilities.
A major advantage of Spoken Language Models (SLMs) is their ability to directly process speech without intermediate text conversion, leveraging the unique acoustic characteristics of human speakers, allowing for the rapid generation of high-quality speech even in large-scale models.
However, existing models faced difficulties in maintaining semantic and speaker consistency for long-duration speech due to increased 'speech token resolution' and memory consumption when capturing very detailed information by breaking down speech into fine fragments.
To solve this problem, Se Jin Park developed 'SpeechSSM,' a spoken language model using a Hybrid State-Space Model, designed to efficiently process and generate long speech sequences.
This model employs a 'hybrid structure' that alternately places 'attention layers' focusing on recent information and 'recurrent layers' that remember the overall narrative flow (long-term context). This allows the story to flow smoothly without losing coherence even when generating speech for a long time. Furthermore, memory usage and computational load do not increase sharply with input length, enabling stable and efficient learning and the generation of long-duration speech.
SpeechSSM effectively processes unbounded speech sequences by dividing speech data into short, fixed units (windows), processing each unit independently, and then combining them to create long speech.
Additionally, in the speech generation phase, it uses a 'Non-Autoregressive' audio synthesis model (SoundStorm), which rapidly generates multiple parts at once instead of slowly creating one character or one word at a time, enabling the fast generation of high-quality speech.
While existing models typically evaluated short speech models of about 10 seconds, Se Jin Park created new evaluation tasks for speech generation based on their self-built benchmark dataset, 'LibriSpeech-Long,' capable of generating up to 16 minutes of speech.
Compared to PPL (Perplexity), an existing speech model evaluation metric that only indicates grammatical correctness, she proposed new evaluation metrics such as 'SC-L (semantic coherence over time)' to assess content coherence over time, and 'N-MOS-T (naturalness mean opinion score over time)' to evaluate naturalness over time, enabling more effective and precise evaluation.
Through these new evaluations, it was confirmed that speech generated by the SpeechSSM spoken language model consistently featured specific individuals mentioned in the initial prompt, and new characters and events unfolded naturally and contextually consistently, despite long-duration generation. This contrasts sharply with existing models, which tended to easily lose their topic and exhibit repetition during long-duration generation.
PhD candidate Sejin Park explained, "Existing spoken language models had limitations in long-duration generation, so our goal was to develop a spoken language model capable of generating long-duration speech for actual human use." She added, "This research achievement is expected to greatly contribute to various types of voice content creation and voice AI fields like voice assistants, by maintaining consistent content in long contexts and responding more efficiently and quickly in real time than existing methods."
This research, with Se Jin Park as the first author, was conducted in collaboration with Google DeepMind and is scheduled to be presented as an oral presentation at ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning) 2025 on July 16th.
Paper Title: Long-Form Speech Generation with Spoken Language Models
DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.18603
Ph.D. candidate Se Jin Park has demonstrated outstanding research capabilities as a member of Professor Yong Man Ro's MLLM (multimodal large language model) research team, through her work integrating vision, speech, and language. Her achievements include a spotlight paper presentation at 2024 CVPR (Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition) and an Outstanding Paper Award at 2024 ACL (Association for Computational Linguistics).
For more information, you can refer to the publication and accompanying demo: SpeechSSM Publications.
2025.07.04 View 639 -
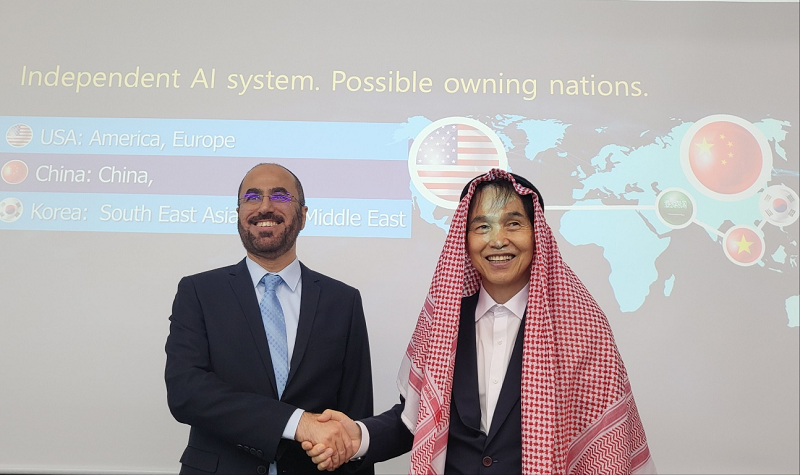 King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership
<From left> President Abdulla Al-Salman(King Saud University), President Kwang Hyung Lee(KAIST)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) and King Saud University (President Abdulla Al-Salman) held a meeting on July 3 at the KAIST Campus in Seoul and agreed to pursue strategic cooperation in AI and digital platform development. The global AI landscape is increasingly polarized between closed models developed by the U.S. and China’s nationally focused technology ecosystems. In this context, many neutral countries have consistently called for an alternative third model that promotes both technological diversity and open access. President Lee has previously advocated for a "Tripartite Platform Strategy" (三分之計), proposing an international collaboration framework based on open-source principles to be free from binary digital power structures and foster cooperative coexistence.
This KAIST-KSU collaboration represents a step toward developing a new, inclusive AI model. The collaboration aims to establish an innovative multilateral framework, especially within the MENA, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, by building an open-source-based AI alliance. Both institutions bring complementary strengths to the table. Saudi Arabia possesses large-scale capital and digital infrastructure, while Korea leads in core AI and semiconductor technologies, applied research, and talent cultivation.
Together, the two nations aim to establish a sustainable collaboration model that creates a virtuous cycle of investment, technology, and talent. This initiative is expected to contribute to the development of an open AI platform and promote diversity in the global AI ecosystem.
During the meeting, the two sides discussed key areas of future cooperation, including:
· Joint development of open-source AI technologies and digital platforms
· Launch of a KAIST-KSU dual graduate degree program
· Expansion of exchange programs for students, faculty, and researchers
· Collaborative research in basic science and STEM disciplines
In particular, the two institutions discussed to establish a joint AI research center to co-develop open AI models and explore practical industrial applications. The goal is to broaden access to AI technology and create an inclusive innovation environment for more countries and institutions.
President Abdulla Al-Salman stated, "Under Saudi Vision 2030, we are driving innovation in science and technology through new leadership, openness, and strategic investment. This partnership with KAIST will serve as a critical foundation for building a competitive AI ecosystem in the Middle East."
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "By combining Saudi Arabia's leadership, market, and investment capacity with KAIST's technological innovation and the rich talent pools from both countries, we will significantly contribute to diversifying the global AI ecosystem."
Both leaders further noted, "Through joint research leading to an independent AI model, our two institutions could establish a new axis beyond the existing US-China digital order—realizing a 'Tripartite AI Strategy' that will propel us into global markets extending far beyond the MENA and ASEAN regions."
KAIST and KSU plan to formalize this agreement by signing an MOU in the near future, followed by concrete actions such as launching the joint research institute and global talent development programs. This collaboration was initiated under the Korea Foundation’s Distinguished Guests Invitation Program, overseen by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and is expected to grow into a long-term strategic partnership with continued support from KF.
About King Saud University (KSU)
Founded in 1957, KSU is Saudi Arabia’s first and leading national university. As a top research-oriented institution in the Middle East, it has achieved international recognition in fields such as AI, energy, and biotechnology. It plays a central role in nurturing talent and driving innovation aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and is expanding global partnerships to further strengthen its research capabilities.
About the Korea Foundation (KF)
Established in 1991 under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Korea Foundation is a public diplomacy institution dedicated to strengthening international understanding and friendship with Korea. KF plays a key role in expanding Korea’s soft power through academic and cultural exchange, people-to-people networks, and global Korean studies programs. Its Distinguished Guests Invitation Program fosters strategic partnerships with global leaders in government, academia, and industry.
2025.07.04 View 486
King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership
<From left> President Abdulla Al-Salman(King Saud University), President Kwang Hyung Lee(KAIST)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) and King Saud University (President Abdulla Al-Salman) held a meeting on July 3 at the KAIST Campus in Seoul and agreed to pursue strategic cooperation in AI and digital platform development. The global AI landscape is increasingly polarized between closed models developed by the U.S. and China’s nationally focused technology ecosystems. In this context, many neutral countries have consistently called for an alternative third model that promotes both technological diversity and open access. President Lee has previously advocated for a "Tripartite Platform Strategy" (三分之計), proposing an international collaboration framework based on open-source principles to be free from binary digital power structures and foster cooperative coexistence.
This KAIST-KSU collaboration represents a step toward developing a new, inclusive AI model. The collaboration aims to establish an innovative multilateral framework, especially within the MENA, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, by building an open-source-based AI alliance. Both institutions bring complementary strengths to the table. Saudi Arabia possesses large-scale capital and digital infrastructure, while Korea leads in core AI and semiconductor technologies, applied research, and talent cultivation.
Together, the two nations aim to establish a sustainable collaboration model that creates a virtuous cycle of investment, technology, and talent. This initiative is expected to contribute to the development of an open AI platform and promote diversity in the global AI ecosystem.
During the meeting, the two sides discussed key areas of future cooperation, including:
· Joint development of open-source AI technologies and digital platforms
· Launch of a KAIST-KSU dual graduate degree program
· Expansion of exchange programs for students, faculty, and researchers
· Collaborative research in basic science and STEM disciplines
In particular, the two institutions discussed to establish a joint AI research center to co-develop open AI models and explore practical industrial applications. The goal is to broaden access to AI technology and create an inclusive innovation environment for more countries and institutions.
President Abdulla Al-Salman stated, "Under Saudi Vision 2030, we are driving innovation in science and technology through new leadership, openness, and strategic investment. This partnership with KAIST will serve as a critical foundation for building a competitive AI ecosystem in the Middle East."
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "By combining Saudi Arabia's leadership, market, and investment capacity with KAIST's technological innovation and the rich talent pools from both countries, we will significantly contribute to diversifying the global AI ecosystem."
Both leaders further noted, "Through joint research leading to an independent AI model, our two institutions could establish a new axis beyond the existing US-China digital order—realizing a 'Tripartite AI Strategy' that will propel us into global markets extending far beyond the MENA and ASEAN regions."
KAIST and KSU plan to formalize this agreement by signing an MOU in the near future, followed by concrete actions such as launching the joint research institute and global talent development programs. This collaboration was initiated under the Korea Foundation’s Distinguished Guests Invitation Program, overseen by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and is expected to grow into a long-term strategic partnership with continued support from KF.
About King Saud University (KSU)
Founded in 1957, KSU is Saudi Arabia’s first and leading national university. As a top research-oriented institution in the Middle East, it has achieved international recognition in fields such as AI, energy, and biotechnology. It plays a central role in nurturing talent and driving innovation aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and is expanding global partnerships to further strengthen its research capabilities.
About the Korea Foundation (KF)
Established in 1991 under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Korea Foundation is a public diplomacy institution dedicated to strengthening international understanding and friendship with Korea. KF plays a key role in expanding Korea’s soft power through academic and cultural exchange, people-to-people networks, and global Korean studies programs. Its Distinguished Guests Invitation Program fosters strategic partnerships with global leaders in government, academia, and industry.
2025.07.04 View 486 -
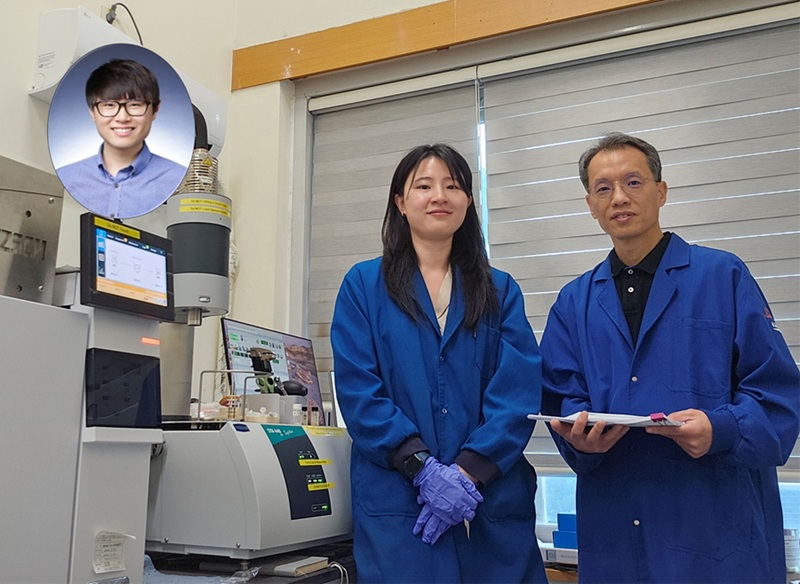 KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine Contamination
<(From the Right) Professor Ho Jin Ryu, Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center>
Managing radioactive waste is one of the core challenges in the use of nuclear energy. In particular, radioactive iodine poses serious environmental and health risks due to its long half-life (15.7 million years in the case of I-129), high mobility, and toxicity to living organisms. A Korean research team has successfully used artificial intelligence to discover a new material that can remove iodine for nuclear environmental remediation. The team plans to push forward with commercialization through various industry-academia collaborations, from iodine-adsorbing powders to contaminated water treatment filters.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2of July that Professor Ho Jin Ryu's research team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Juhwan Noh of the Digital Chemistry Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young Kook Lee), which operates under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Youngsik Kim), developed a technique using AI to discover new materials that effectively remove radioactive iodine contaminants.
Recent studies show that radioactive iodine primarily exists in aqueous environments in the form of iodate (IO₃⁻). However, existing silver-based adsorbents have weak chemical adsorption strength for iodate, making them inefficient. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new adsorbent materials that can effectively remove iodate.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu’s team used a machine learning-based experimental strategy to identify optimal iodate adsorbents among compounds called Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs), which contain various metal elements.
The multi-metal LDH developed in this study – Cu₃(CrFeAl), based on copper, chromium, iron, and aluminum—showed exceptional adsorption performance, removing over 90% of iodate. This achievement was made possible by efficiently exploring a vast compositional space using AI-driven active learning, which would be difficult to search through conventional trial-and-error experiments.
<Picture2. Concept of Developed AI-Based Technology for Exploring New Materials for Radioactive Contamination Removal>
The research team focused on the fact that LDHs, like high-entropy materials, can incorporate a wide range of metal compositions and possess structures favorable for anion adsorption. However, due to the overwhelming number of possible metal combinations in multi-metal LDHs, identifying the optimal composition through traditional experimental methods has been nearly impossible.
To overcome this, the team employed AI (machine learning). Starting with experimental data from 24 binary and 96 ternary LDH compositions, they expanded their search to include quaternary and quinary candidates. As a result, they were able to discover the optimal material for iodate removal by testing only 16% of the total candidate materials.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu stated, “This study shows the potential of using artificial intelligence to efficiently identify radioactive decontamination materials from a vast pool of new material candidates, which is expected to accelerate research for developing new materials for nuclear environmental cleanup.”
The research team has filed a domestic patent application for the developed powder technology and is currently proceeding with an international patent application. They plan to enhance the material’s performance under various conditions and pursue commercialization through industry-academia cooperation in the development of filters for treating contaminated water.
Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center, participated as the co-first authors of the study. The results were published online on May 26 in the internationally renowned environmental publication Journal of Hazardous Materials.
※ Paper title: Discovery of multi-metal-layered double hydroxides for decontamination of iodate by machine learning-assisted experiments ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138735
This research was supported by the Nuclear Energy Research Infrastructure Program and the Nano-Materials Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.03 View 832
KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine Contamination
<(From the Right) Professor Ho Jin Ryu, Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center>
Managing radioactive waste is one of the core challenges in the use of nuclear energy. In particular, radioactive iodine poses serious environmental and health risks due to its long half-life (15.7 million years in the case of I-129), high mobility, and toxicity to living organisms. A Korean research team has successfully used artificial intelligence to discover a new material that can remove iodine for nuclear environmental remediation. The team plans to push forward with commercialization through various industry-academia collaborations, from iodine-adsorbing powders to contaminated water treatment filters.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2of July that Professor Ho Jin Ryu's research team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Juhwan Noh of the Digital Chemistry Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young Kook Lee), which operates under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Youngsik Kim), developed a technique using AI to discover new materials that effectively remove radioactive iodine contaminants.
Recent studies show that radioactive iodine primarily exists in aqueous environments in the form of iodate (IO₃⁻). However, existing silver-based adsorbents have weak chemical adsorption strength for iodate, making them inefficient. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new adsorbent materials that can effectively remove iodate.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu’s team used a machine learning-based experimental strategy to identify optimal iodate adsorbents among compounds called Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs), which contain various metal elements.
The multi-metal LDH developed in this study – Cu₃(CrFeAl), based on copper, chromium, iron, and aluminum—showed exceptional adsorption performance, removing over 90% of iodate. This achievement was made possible by efficiently exploring a vast compositional space using AI-driven active learning, which would be difficult to search through conventional trial-and-error experiments.
<Picture2. Concept of Developed AI-Based Technology for Exploring New Materials for Radioactive Contamination Removal>
The research team focused on the fact that LDHs, like high-entropy materials, can incorporate a wide range of metal compositions and possess structures favorable for anion adsorption. However, due to the overwhelming number of possible metal combinations in multi-metal LDHs, identifying the optimal composition through traditional experimental methods has been nearly impossible.
To overcome this, the team employed AI (machine learning). Starting with experimental data from 24 binary and 96 ternary LDH compositions, they expanded their search to include quaternary and quinary candidates. As a result, they were able to discover the optimal material for iodate removal by testing only 16% of the total candidate materials.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu stated, “This study shows the potential of using artificial intelligence to efficiently identify radioactive decontamination materials from a vast pool of new material candidates, which is expected to accelerate research for developing new materials for nuclear environmental cleanup.”
The research team has filed a domestic patent application for the developed powder technology and is currently proceeding with an international patent application. They plan to enhance the material’s performance under various conditions and pursue commercialization through industry-academia cooperation in the development of filters for treating contaminated water.
Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center, participated as the co-first authors of the study. The results were published online on May 26 in the internationally renowned environmental publication Journal of Hazardous Materials.
※ Paper title: Discovery of multi-metal-layered double hydroxides for decontamination of iodate by machine learning-assisted experiments ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138735
This research was supported by the Nuclear Energy Research Infrastructure Program and the Nano-Materials Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.03 View 832 -
 2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Concludes Successfully in Silicon Valley
< A group photo taken at the 2025 GESS Special Lecture.Vice President So Young Kim from the International Office, VC Jay Eum from GFT Ventures, Professor Byungchae Jin from the Impact MBA Program at the Business School, and Research Assistant Professor Sooa Lee from the Office of Global Initiative>
The “2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2025 KAIST GESS),” organized by the Office of Global Initiative of the KAIST International Office (Vice President So Young Kim), successfully concluded. Now in its fourth year, the program was designed to provide KAIST students with firsthand experience of the world’s leading startup ecosystem in Silicon Valley, USA, and to strengthen their practical capabilities to take on challenges on the global stage.
This year’s 2025 KAIST GESS welcomed approximately 40 participants, including 24 undergraduate and graduate students selected through document screening, interviews, team presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations, as well as 16 Impact MBA students from the College of Business. The selected undergraduate and graduate participants underwent two months of pre-program training and received mentoring from experienced entrepreneurs to refine their business models and elevate their project ideas. Meanwhile, Impact MBA students joined the Silicon Valley program onsite, attending key lectures and networking sessions to broaden their understanding of the global startup ecosystem.
From June 22nd, participants spent seven days in Silicon Valley completing the global entrepreneurship curriculum. The program was operated in cooperation with major organizations including the KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, Korea-US AI Semiconductor Innovation Center (K-ASIC), and Plug and Play Tech Center. Local experts delivered lectures on topics such as “Startup Culture,” “Learning from Failures” and “Networks and Capital.”
Participants also had the opportunity to visit startups led by KAIST alumni and local entrepreneurs, gaining valuable insights from firsthand stories about global entrepreneurship. Companies visited included Medic Life Sciences (CEO Kyuho Han) and ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim). Through these visits, participants received practical advice on market entry strategies and overcoming challenges in the global arena.
As part of their first onsite schedule, KAIST students attended an interactive fireside chat titled “Global Entrepreneurship and AI,” where they engaged in in-depth discussions on the future of AI-driven global startups. The session featured three distinguished speakers: Jay Kim, Head of US Business Development at Hyper Accel; Chandra Shekhar Dhir, AI/ML Director at JPMorgan Chase’s Machine Learning Center of Excellence; and Taesu Kim, co-founder of AI voice synthesis startup Neosapience and KAIST alumnus. Taesu Kim shared, “Facing serious health issues made me reflect on my life, and after recovering, I wanted to pursue something that could create a real impact on society, which led me to start my own company.” He also advised students to “take time at important turning points in life to deeply think about what you truly want to do and how you can contribute to society.
In line with the core value of ‘paying it forward’—a fundamental principle of global entrepreneurship learned in Silicon Valley—GESS participants engaged in a community service project titled “Let’s Play with AI+Tech,” organized in collaboration with the Sunnyvale community and Foothill College. Leveraging their strong foundation in AI, KAIST students designed and led a hands-on ‘Doodle AI’ educational program to make foundational AI concepts accessible and engaging for underrepresented local elementary school children and their parents, fostering meaningful community interaction.
On the final day of the 2025 KAIST GESS, a pitch competition was held with participation from Silicon Valley venture capitalists and accelerators. Participants presented their business models, developed over the two-month program, to a panel of judges. The winning team was eaureco, and Si Li Sara Aow (Civil and Environmental Engineering) shared, “GESS was a valuable opportunity to test and hone practical entrepreneurship skills beyond mere networking.” She added, “At first, I lacked confidence, but challenging myself to pitch in the final presentation gave me the courage to take one step closer to global entrepreneurship. Pitching in Silicon Valley, the heart of global startups, was an invaluable experience that will shape my path as a global entrepreneur.”
The program concluded with a special lecture by Jay Eum, a seasoned Silicon Valley venture capitalist and a judging panel member for GESS over the past three years. He shared key insights on startup success from an investor’s perspective, advising, “The journey of entrepreneurship is never easy, but the sooner you start, the better.” He further encouraged participants to “focus on solving problems in local markets, but do not fear challenging global markets,” inspiring them with courage and actionable advice.
So Young Kim, Director of the KAIST Office of Global Initiative, said, “We hope the 2025 KAIST GESS serves as a stepping stone for KAIST students to grow into influential entrepreneurs on the global stage,” adding, “This program is also expected to further enhance KAIST’s international reputation.”
Byungchae Jin, Faculty Chair of the KAIST Impact MBA, College of Business, highlighted the program's educational benefits, stating, “Engaging directly with local entrepreneurs and gaining practical experience in Silicon Valley's startup environment provide students with hands-on learning and significant inspiration.”
The 2025 KAIST GESS was jointly hosted by the KAIST Office of Global Initiative, Impact MBA, and Startup KAIST. Moving forward, KAIST plans to continue expanding its field-based global entrepreneurship education by linking with key global hubs like Silicon Valley, fostering next-generation global leaders who will lead innovation and challenge the status quo.
2025.07.01 View 851
2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Concludes Successfully in Silicon Valley
< A group photo taken at the 2025 GESS Special Lecture.Vice President So Young Kim from the International Office, VC Jay Eum from GFT Ventures, Professor Byungchae Jin from the Impact MBA Program at the Business School, and Research Assistant Professor Sooa Lee from the Office of Global Initiative>
The “2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2025 KAIST GESS),” organized by the Office of Global Initiative of the KAIST International Office (Vice President So Young Kim), successfully concluded. Now in its fourth year, the program was designed to provide KAIST students with firsthand experience of the world’s leading startup ecosystem in Silicon Valley, USA, and to strengthen their practical capabilities to take on challenges on the global stage.
This year’s 2025 KAIST GESS welcomed approximately 40 participants, including 24 undergraduate and graduate students selected through document screening, interviews, team presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations, as well as 16 Impact MBA students from the College of Business. The selected undergraduate and graduate participants underwent two months of pre-program training and received mentoring from experienced entrepreneurs to refine their business models and elevate their project ideas. Meanwhile, Impact MBA students joined the Silicon Valley program onsite, attending key lectures and networking sessions to broaden their understanding of the global startup ecosystem.
From June 22nd, participants spent seven days in Silicon Valley completing the global entrepreneurship curriculum. The program was operated in cooperation with major organizations including the KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, Korea-US AI Semiconductor Innovation Center (K-ASIC), and Plug and Play Tech Center. Local experts delivered lectures on topics such as “Startup Culture,” “Learning from Failures” and “Networks and Capital.”
Participants also had the opportunity to visit startups led by KAIST alumni and local entrepreneurs, gaining valuable insights from firsthand stories about global entrepreneurship. Companies visited included Medic Life Sciences (CEO Kyuho Han) and ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim). Through these visits, participants received practical advice on market entry strategies and overcoming challenges in the global arena.
As part of their first onsite schedule, KAIST students attended an interactive fireside chat titled “Global Entrepreneurship and AI,” where they engaged in in-depth discussions on the future of AI-driven global startups. The session featured three distinguished speakers: Jay Kim, Head of US Business Development at Hyper Accel; Chandra Shekhar Dhir, AI/ML Director at JPMorgan Chase’s Machine Learning Center of Excellence; and Taesu Kim, co-founder of AI voice synthesis startup Neosapience and KAIST alumnus. Taesu Kim shared, “Facing serious health issues made me reflect on my life, and after recovering, I wanted to pursue something that could create a real impact on society, which led me to start my own company.” He also advised students to “take time at important turning points in life to deeply think about what you truly want to do and how you can contribute to society.
In line with the core value of ‘paying it forward’—a fundamental principle of global entrepreneurship learned in Silicon Valley—GESS participants engaged in a community service project titled “Let’s Play with AI+Tech,” organized in collaboration with the Sunnyvale community and Foothill College. Leveraging their strong foundation in AI, KAIST students designed and led a hands-on ‘Doodle AI’ educational program to make foundational AI concepts accessible and engaging for underrepresented local elementary school children and their parents, fostering meaningful community interaction.
On the final day of the 2025 KAIST GESS, a pitch competition was held with participation from Silicon Valley venture capitalists and accelerators. Participants presented their business models, developed over the two-month program, to a panel of judges. The winning team was eaureco, and Si Li Sara Aow (Civil and Environmental Engineering) shared, “GESS was a valuable opportunity to test and hone practical entrepreneurship skills beyond mere networking.” She added, “At first, I lacked confidence, but challenging myself to pitch in the final presentation gave me the courage to take one step closer to global entrepreneurship. Pitching in Silicon Valley, the heart of global startups, was an invaluable experience that will shape my path as a global entrepreneur.”
The program concluded with a special lecture by Jay Eum, a seasoned Silicon Valley venture capitalist and a judging panel member for GESS over the past three years. He shared key insights on startup success from an investor’s perspective, advising, “The journey of entrepreneurship is never easy, but the sooner you start, the better.” He further encouraged participants to “focus on solving problems in local markets, but do not fear challenging global markets,” inspiring them with courage and actionable advice.
So Young Kim, Director of the KAIST Office of Global Initiative, said, “We hope the 2025 KAIST GESS serves as a stepping stone for KAIST students to grow into influential entrepreneurs on the global stage,” adding, “This program is also expected to further enhance KAIST’s international reputation.”
Byungchae Jin, Faculty Chair of the KAIST Impact MBA, College of Business, highlighted the program's educational benefits, stating, “Engaging directly with local entrepreneurs and gaining practical experience in Silicon Valley's startup environment provide students with hands-on learning and significant inspiration.”
The 2025 KAIST GESS was jointly hosted by the KAIST Office of Global Initiative, Impact MBA, and Startup KAIST. Moving forward, KAIST plans to continue expanding its field-based global entrepreneurship education by linking with key global hubs like Silicon Valley, fostering next-generation global leaders who will lead innovation and challenge the status quo.
2025.07.01 View 851 -
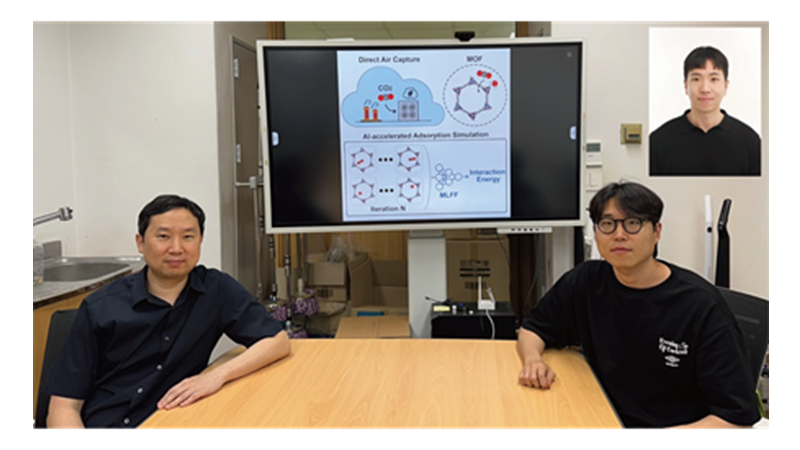 KAIST Develops AI to Easily Find Promising Materials That Capture Only CO₂
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jihan Kim, Ph.D. candidate Yunsung Lim and Dr. Hyunsoo Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
In order to help prevent the climate crisis, actively reducing already-emitted CO₂ is essential. Accordingly, direct air capture (DAC) — a technology that directly extracts only CO₂ from the air — is gaining attention. However, effectively capturing pure CO₂ is not easy due to water vapor (H₂O) present in the air. KAIST researchers have successfully used AI-driven machine learning techniques to identify the most promising CO₂-capturing materials among metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a key class of materials studied for this technology.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 29th of June that a research team led by Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, in collaboration with a team at Imperial College London, has developed a machine-learning-based simulation method that can quickly and accurately screen MOFs best suited for atmospheric CO₂ capture.
< Figure 1. Concept diagram of Direct Air Capture (DAC) technology and carbon capture using Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are promising porous materials capable of capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, drawing attention as a core material for DAC technology. >
To overcome the difficulty of discovering high-performance materials due to the complexity of structures and the limitations of predicting intermolecular interactions, the research team developed a machine learning force field (MLFF) capable of precisely predicting the interactions between CO₂, water (H₂O), and MOFs. This new method enables calculations of MOF adsorption properties with quantum-mechanics-level accuracy at vastly faster speeds than before.
Using this system, the team screened over 8,000 experimentally synthesized MOF structures, identifying more than 100 promising candidates for CO₂ capture. Notably, this included new candidates that had not been uncovered by traditional force-field-based simulations. The team also analyzed the relationships between MOF chemical structure and adsorption performance, proposing seven key chemical features that will help in designing new materials for DAC.
< Figure 2. Concept diagram of adsorption simulation using Machine Learning Force Field (MLFF). The developed MLFF is applicable to various MOF structures and allows for precise calculation of adsorption properties by predicting interaction energies during repetitive Widom insertion simulations. It is characterized by simultaneously achieving high accuracy and low computational cost compared to conventional classical force fields. >
This research is recognized as a significant advance in the DAC field, greatly enhancing materials design and simulation by precisely predicting MOF-CO₂ and MOF-H₂O interactions.
The results of this research, with Ph.D. candidate Yunsung Lim and Dr. Hyunsoo Park of KAIST as co-first authors, were published in the international academic journal Matter on June 12.
※Paper Title: Accelerating CO₂ direct air capture screening for metal–organic frameworks with a transferable machine learning force field
※DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2025.102203
This research was supported by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO₂ Management Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT's Global C.L.E.A.N. Project.
2025.06.29 View 1011
KAIST Develops AI to Easily Find Promising Materials That Capture Only CO₂
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jihan Kim, Ph.D. candidate Yunsung Lim and Dr. Hyunsoo Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
In order to help prevent the climate crisis, actively reducing already-emitted CO₂ is essential. Accordingly, direct air capture (DAC) — a technology that directly extracts only CO₂ from the air — is gaining attention. However, effectively capturing pure CO₂ is not easy due to water vapor (H₂O) present in the air. KAIST researchers have successfully used AI-driven machine learning techniques to identify the most promising CO₂-capturing materials among metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a key class of materials studied for this technology.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 29th of June that a research team led by Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, in collaboration with a team at Imperial College London, has developed a machine-learning-based simulation method that can quickly and accurately screen MOFs best suited for atmospheric CO₂ capture.
< Figure 1. Concept diagram of Direct Air Capture (DAC) technology and carbon capture using Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are promising porous materials capable of capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, drawing attention as a core material for DAC technology. >
To overcome the difficulty of discovering high-performance materials due to the complexity of structures and the limitations of predicting intermolecular interactions, the research team developed a machine learning force field (MLFF) capable of precisely predicting the interactions between CO₂, water (H₂O), and MOFs. This new method enables calculations of MOF adsorption properties with quantum-mechanics-level accuracy at vastly faster speeds than before.
Using this system, the team screened over 8,000 experimentally synthesized MOF structures, identifying more than 100 promising candidates for CO₂ capture. Notably, this included new candidates that had not been uncovered by traditional force-field-based simulations. The team also analyzed the relationships between MOF chemical structure and adsorption performance, proposing seven key chemical features that will help in designing new materials for DAC.
< Figure 2. Concept diagram of adsorption simulation using Machine Learning Force Field (MLFF). The developed MLFF is applicable to various MOF structures and allows for precise calculation of adsorption properties by predicting interaction energies during repetitive Widom insertion simulations. It is characterized by simultaneously achieving high accuracy and low computational cost compared to conventional classical force fields. >
This research is recognized as a significant advance in the DAC field, greatly enhancing materials design and simulation by precisely predicting MOF-CO₂ and MOF-H₂O interactions.
The results of this research, with Ph.D. candidate Yunsung Lim and Dr. Hyunsoo Park of KAIST as co-first authors, were published in the international academic journal Matter on June 12.
※Paper Title: Accelerating CO₂ direct air capture screening for metal–organic frameworks with a transferable machine learning force field
※DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2025.102203
This research was supported by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO₂ Management Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT's Global C.L.E.A.N. Project.
2025.06.29 View 1011 -
 Military Combatants Usher in an Era of Personalized Training with New Materials
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Steve Park of Materials Science and Engineering, Kyusoon Pak, Ph.D. Candidate (Army Major) >
Traditional military training often relies on standardized methods, which has limited the provision of optimized training tailored to individual combatants' characteristics or specific combat situations. To address this, our research team developed an e-textile platform, securing core technology that can reflect the unique traits of individual combatants and various combat scenarios. This technology has proven robust enough for battlefield use and is economical enough for widespread distribution to a large number of troops.
On June 25th, Professor Steve Park's research team at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a flexible, wearable electronic textile (E-textile) platform using an innovative technology that 'draws' electronic circuits directly onto fabric.
The wearable e-textile platform developed by the research team combines 3D printing technology with new materials engineering design to directly print flexible and highly durable sensors and electrodes onto textile substrates. This enables the collection of precise movement and human body data from individual combatants, which can then be used to propose customized training models.
Existing e-textile fabrication methods were often complex or limited in their ability to provide personalized customization. To overcome these challenges, the research team adopted an additive manufacturing technology called 'Direct Ink Writing (DIW)' 3D printing.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of e-textile manufactured with Direct Ink Writing (DIW) printing technology on various textiles, including combat uniforms >
This technology involves directly dispensing and printing special ink, which functions as sensors and electrodes, onto textile substrates in desired patterns. This allows for flexible implementation of various designs without the complex process of mask fabrication. This is expected to be an effective technology that can be easily supplied to hundreds of thousands of military personnel.
The core of this technology lies in the development of high-performance functional inks based on advanced materials engineering design. The research team combined styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) polymer, which provides flexibility, with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) for electrical conductivity. They developed a tensile/bending sensor ink that can stretch up to 102% and maintain stable performance even after 10,000 repetitive tests. This means that accurate data can be consistently obtained even during the strenuous movements of combatants.
< Figure 2. Measurement of human movement and breathing patterns using e-textile >
Furthermore, new material technology was applied to implement 'interconnect electrodes' that electrically connect the upper and lower layers of the fabric. The team developed an electrode ink combining silver (Ag) flakes with rigid polystyrene (PS) polymer, precisely controlling the impregnation level (how much the ink penetrates the fabric) to effectively connect both sides or multiple layers of the fabric. This secures the technology for producing multi-layered wearable electronic systems integrating sensors and electrodes.
< Figure 3. Experimental results of recognizing unknown objects after machine learning six objects using a smart glove >
The research team proved the platform's performance through actual human movement monitoring experiments. They printed the developed e-textile on major joint areas of clothing (shoulders, elbows, knees) and measured movements and posture changes during various exercises such as running, jumping jacks, and push-ups in real-time.
Additionally, they demonstrated the potential for applications such as monitoring breathing patterns using a smart mask and recognizing objects through machine learning and perceiving complex tactile information by printing multiple sensors and electrodes on gloves. These results show that the developed e-textile platform is effective in precisely understanding the movement dynamics of combatants.
This research is an important example demonstrating how cutting-edge new material technology can contribute to the advancement of the defense sector. Major Kyusoon Pak of the Army, who participated in this research, considered required objectives such as military applicability and economic feasibility for practical distribution from the research design stage.
< Figure 4. Experimental results showing that a multi-layered e-textile glove connected with interconnect electrodes can measure tensile/bending signals and pressure signals at a single point >
Major Pak stated, "Our military is currently facing both a crisis and an opportunity due to the decrease in military personnel resources caused by the demographic cliff and the advancement of science and technology. Also, respect for life in the battlefield is emerging as a significant issue. This research aims to secure original technology that can provide customized training according to military branch/duty and type of combat, thereby enhancing the combat power and ensuring the survivability of our soldiers."
He added, "I hope this research will be evaluated as a case that achieved both scientific contribution and military applicability."
This research, where Kyusoon Pak, Ph.D. Candidate (Army Major) from KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participated as the first author and Professor Steve Park supervised, was published on May 27, 2025, in `npj Flexible Electronics (top 1.8% in JCR field)', an international academic journal in the electrical, electronic, and materials engineering fields.
* Paper Title: Fabrication of Multifunctional Wearable Interconnect E-textile Platform Using Direct Ink Writing (DIW) 3D Printing
* DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-025-00414-7
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.25 View 1237
Military Combatants Usher in an Era of Personalized Training with New Materials
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Steve Park of Materials Science and Engineering, Kyusoon Pak, Ph.D. Candidate (Army Major) >
Traditional military training often relies on standardized methods, which has limited the provision of optimized training tailored to individual combatants' characteristics or specific combat situations. To address this, our research team developed an e-textile platform, securing core technology that can reflect the unique traits of individual combatants and various combat scenarios. This technology has proven robust enough for battlefield use and is economical enough for widespread distribution to a large number of troops.
On June 25th, Professor Steve Park's research team at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a flexible, wearable electronic textile (E-textile) platform using an innovative technology that 'draws' electronic circuits directly onto fabric.
The wearable e-textile platform developed by the research team combines 3D printing technology with new materials engineering design to directly print flexible and highly durable sensors and electrodes onto textile substrates. This enables the collection of precise movement and human body data from individual combatants, which can then be used to propose customized training models.
Existing e-textile fabrication methods were often complex or limited in their ability to provide personalized customization. To overcome these challenges, the research team adopted an additive manufacturing technology called 'Direct Ink Writing (DIW)' 3D printing.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of e-textile manufactured with Direct Ink Writing (DIW) printing technology on various textiles, including combat uniforms >
This technology involves directly dispensing and printing special ink, which functions as sensors and electrodes, onto textile substrates in desired patterns. This allows for flexible implementation of various designs without the complex process of mask fabrication. This is expected to be an effective technology that can be easily supplied to hundreds of thousands of military personnel.
The core of this technology lies in the development of high-performance functional inks based on advanced materials engineering design. The research team combined styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) polymer, which provides flexibility, with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) for electrical conductivity. They developed a tensile/bending sensor ink that can stretch up to 102% and maintain stable performance even after 10,000 repetitive tests. This means that accurate data can be consistently obtained even during the strenuous movements of combatants.
< Figure 2. Measurement of human movement and breathing patterns using e-textile >
Furthermore, new material technology was applied to implement 'interconnect electrodes' that electrically connect the upper and lower layers of the fabric. The team developed an electrode ink combining silver (Ag) flakes with rigid polystyrene (PS) polymer, precisely controlling the impregnation level (how much the ink penetrates the fabric) to effectively connect both sides or multiple layers of the fabric. This secures the technology for producing multi-layered wearable electronic systems integrating sensors and electrodes.
< Figure 3. Experimental results of recognizing unknown objects after machine learning six objects using a smart glove >
The research team proved the platform's performance through actual human movement monitoring experiments. They printed the developed e-textile on major joint areas of clothing (shoulders, elbows, knees) and measured movements and posture changes during various exercises such as running, jumping jacks, and push-ups in real-time.
Additionally, they demonstrated the potential for applications such as monitoring breathing patterns using a smart mask and recognizing objects through machine learning and perceiving complex tactile information by printing multiple sensors and electrodes on gloves. These results show that the developed e-textile platform is effective in precisely understanding the movement dynamics of combatants.
This research is an important example demonstrating how cutting-edge new material technology can contribute to the advancement of the defense sector. Major Kyusoon Pak of the Army, who participated in this research, considered required objectives such as military applicability and economic feasibility for practical distribution from the research design stage.
< Figure 4. Experimental results showing that a multi-layered e-textile glove connected with interconnect electrodes can measure tensile/bending signals and pressure signals at a single point >
Major Pak stated, "Our military is currently facing both a crisis and an opportunity due to the decrease in military personnel resources caused by the demographic cliff and the advancement of science and technology. Also, respect for life in the battlefield is emerging as a significant issue. This research aims to secure original technology that can provide customized training according to military branch/duty and type of combat, thereby enhancing the combat power and ensuring the survivability of our soldiers."
He added, "I hope this research will be evaluated as a case that achieved both scientific contribution and military applicability."
This research, where Kyusoon Pak, Ph.D. Candidate (Army Major) from KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participated as the first author and Professor Steve Park supervised, was published on May 27, 2025, in `npj Flexible Electronics (top 1.8% in JCR field)', an international academic journal in the electrical, electronic, and materials engineering fields.
* Paper Title: Fabrication of Multifunctional Wearable Interconnect E-textile Platform Using Direct Ink Writing (DIW) 3D Printing
* DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-025-00414-7
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.25 View 1237 -
 KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse
* Focusing on nurturing talent and dedicating to R&D to become a G3 AI powerhouse (Top 3 AI Nations).
* Leading the realization of an "AI-driven Basic Society for All" and developing technologies that leverage AI to overcome the crisis in Korea's manufacturing sector.
* 50 years ago, South Korea emerged as a scientific and technological powerhouse from the ashes, with KAIST at its core, contributing to the development of scientific and technological talent, innovative technology, national industrial growth, and the creation of a startup innovation ecosystem.
As public interest in AI and science and technology has significantly grown with the inauguration of the new government, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced its plan, on June 24th, to transform into an "AI-centric, Value-Creating Science and Technology University" that leads national innovation based on science and technology and spearheads solutions to global challenges.
At a time when South Korea is undergoing a major transition to a technology-driven society, KAIST, drawing on its half-century of experience as a "Starter Kit" for national development, is preparing to leap beyond being a mere educational and research institution to become a global innovation hub that creates new social value.
In particular, KAIST has presented a vision for realizing an "AI-driven Basic Society" where all citizens can utilize AI without alienation, enabling South Korea to ascend to the top three AI nations (G3). To achieve this, through the "National AI Research Hub" project (headed by Kee Eung Kim), led by KAIST representing South Korea, the institution is dedicated to enhancing industrial competitiveness and effectively solving social problems based on AI technology.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee >
KAIST's research achievements in the AI field are garnering international attention. In the top three machine learning conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 1st in Asia over the past five years (2020-2024). During the same period, based on the number of papers published in top conferences in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 4th in Asia. Furthermore, KAIST has consistently demonstrated unparalleled research capabilities, ranking 1st globally in the average number of papers accepted at ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Conference), the world's most prestigious academic conference on semiconductor integrated circuits, for 19 years (2006-2024).
KAIST is continuously expanding its research into core AI technologies, including hyper-scale AI models (Korean LLM), neuromorphic semiconductors, and low-power AI processors, as well as various application areas such as autonomous driving, urban air mobility (UAM), precision medicine, and explainable AI (XAI).
In the manufacturing sector, KAIST's AI technologies are also driving on-site innovation. Professor Young Jae Jang's team has enhanced productivity in advanced manufacturing fields like semiconductors and displays through digital twins utilizing manufacturing site data and AI-based prediction technology. Professor Song Min Kim's team developed ultra-low power wireless tag technology capable of tracking locations with sub-centimeter precision, accelerating the implementation of smart factories. Technologies such as industrial process optimization and equipment failure prediction developed by INEEJI Co., Ltd., founded by Professor Jaesik Choi, are being rapidly applied in real industrial settings, yielding results. INEEJI was designated as a national strategic technology in the 'Explainable AI (XAI)' field by the government in March.
< Researchers performing data analysis for AI research >
Practical applications are also emerging in the robotics sector, which is closely linked to AI. Professor Jemin Hwangbo's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering garnered attention by newly developing RAIBO 2, a quadrupedal robot usable in high-risk environments such as disaster relief and rough terrain exploration. Professor Kyoung Chul Kong's team and Angel Robotics Co., Ltd. developed the WalkOn Suit exoskeleton robot, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with complete lower body paralysis or walking disabilities.
Additionally, remarkable research is ongoing in future core technology areas such as AI semiconductors, quantum cryptography communication, ultra-small satellites, hydrogen fuel cells, next-generation batteries, and biomimetic sensors. Notably, space exploration technology based on small satellites, asteroid exploration projects, energy harvesting, and high-speed charging technologies are gaining attention.
Particularly in advanced bio and life sciences, KAIST is collaborating with Germany's Merck company on various research initiatives, including synthetic biology and mRNA. KAIST is also contributing to the construction of a 430 billion won Merck Bio-Center in Daejeon, thereby stimulating the local economy and creating jobs.
Based on these cutting-edge research capabilities, KAIST continues to expand its influence not only within the industry but also on the global stage. It has established strategic partnerships with leading universities worldwide, including MIT, Stanford University, and New York University (NYU). Notably, KAIST and NYU have established a joint campus in New York to strengthen human exchange and collaborative research. Active industry-academia collaborations with global companies such as Google, Intel, and TSMC are also ongoing, playing a pivotal role in future technology development and the creation of an innovation ecosystem.
These activities also lead to a strong startup ecosystem that drives South Korean industries. The flow of startups, which began with companies like Qnix Computer, Nexon, and Naver, has expanded to a total of 1,914 companies to date. Their cumulative assets amount to 94 trillion won, with sales reaching 36 trillion won and employing approximately 60,000 people. Over 90% of these are technology-based startups originating from faculty and student labs, demonstrating a model that makes a tangible economic contribution based on science and technology.
< Students at work >
Having consistently generated diverse achievements, KAIST has already produced approximately 80,000 "KAISTians" who have created innovation through challenge and failure, and is currently recruiting new talent to continue driving innovation that transforms South Korea and the world.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "KAIST will establish itself as a global leader in science and technology, designing the future of South Korea and humanity and creating tangible value." He added, "We will focus on talent nurturing and research and development to realize the new government's national agenda of becoming a G3 AI powerhouse."
He further stated, "KAIST's vision for the AI field, in which it places particular emphasis, is to strive for a society where everyone can freely utilize AI. We will contribute to significantly boosting productivity by recovering manufacturing competitiveness through AI and actively disseminating physical AI, AI robots, and AI mobility technologies to industrial sites."
2025.06.24 View 1491
KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse
* Focusing on nurturing talent and dedicating to R&D to become a G3 AI powerhouse (Top 3 AI Nations).
* Leading the realization of an "AI-driven Basic Society for All" and developing technologies that leverage AI to overcome the crisis in Korea's manufacturing sector.
* 50 years ago, South Korea emerged as a scientific and technological powerhouse from the ashes, with KAIST at its core, contributing to the development of scientific and technological talent, innovative technology, national industrial growth, and the creation of a startup innovation ecosystem.
As public interest in AI and science and technology has significantly grown with the inauguration of the new government, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced its plan, on June 24th, to transform into an "AI-centric, Value-Creating Science and Technology University" that leads national innovation based on science and technology and spearheads solutions to global challenges.
At a time when South Korea is undergoing a major transition to a technology-driven society, KAIST, drawing on its half-century of experience as a "Starter Kit" for national development, is preparing to leap beyond being a mere educational and research institution to become a global innovation hub that creates new social value.
In particular, KAIST has presented a vision for realizing an "AI-driven Basic Society" where all citizens can utilize AI without alienation, enabling South Korea to ascend to the top three AI nations (G3). To achieve this, through the "National AI Research Hub" project (headed by Kee Eung Kim), led by KAIST representing South Korea, the institution is dedicated to enhancing industrial competitiveness and effectively solving social problems based on AI technology.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee >
KAIST's research achievements in the AI field are garnering international attention. In the top three machine learning conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 1st in Asia over the past five years (2020-2024). During the same period, based on the number of papers published in top conferences in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 4th in Asia. Furthermore, KAIST has consistently demonstrated unparalleled research capabilities, ranking 1st globally in the average number of papers accepted at ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Conference), the world's most prestigious academic conference on semiconductor integrated circuits, for 19 years (2006-2024).
KAIST is continuously expanding its research into core AI technologies, including hyper-scale AI models (Korean LLM), neuromorphic semiconductors, and low-power AI processors, as well as various application areas such as autonomous driving, urban air mobility (UAM), precision medicine, and explainable AI (XAI).
In the manufacturing sector, KAIST's AI technologies are also driving on-site innovation. Professor Young Jae Jang's team has enhanced productivity in advanced manufacturing fields like semiconductors and displays through digital twins utilizing manufacturing site data and AI-based prediction technology. Professor Song Min Kim's team developed ultra-low power wireless tag technology capable of tracking locations with sub-centimeter precision, accelerating the implementation of smart factories. Technologies such as industrial process optimization and equipment failure prediction developed by INEEJI Co., Ltd., founded by Professor Jaesik Choi, are being rapidly applied in real industrial settings, yielding results. INEEJI was designated as a national strategic technology in the 'Explainable AI (XAI)' field by the government in March.
< Researchers performing data analysis for AI research >
Practical applications are also emerging in the robotics sector, which is closely linked to AI. Professor Jemin Hwangbo's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering garnered attention by newly developing RAIBO 2, a quadrupedal robot usable in high-risk environments such as disaster relief and rough terrain exploration. Professor Kyoung Chul Kong's team and Angel Robotics Co., Ltd. developed the WalkOn Suit exoskeleton robot, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with complete lower body paralysis or walking disabilities.
Additionally, remarkable research is ongoing in future core technology areas such as AI semiconductors, quantum cryptography communication, ultra-small satellites, hydrogen fuel cells, next-generation batteries, and biomimetic sensors. Notably, space exploration technology based on small satellites, asteroid exploration projects, energy harvesting, and high-speed charging technologies are gaining attention.
Particularly in advanced bio and life sciences, KAIST is collaborating with Germany's Merck company on various research initiatives, including synthetic biology and mRNA. KAIST is also contributing to the construction of a 430 billion won Merck Bio-Center in Daejeon, thereby stimulating the local economy and creating jobs.
Based on these cutting-edge research capabilities, KAIST continues to expand its influence not only within the industry but also on the global stage. It has established strategic partnerships with leading universities worldwide, including MIT, Stanford University, and New York University (NYU). Notably, KAIST and NYU have established a joint campus in New York to strengthen human exchange and collaborative research. Active industry-academia collaborations with global companies such as Google, Intel, and TSMC are also ongoing, playing a pivotal role in future technology development and the creation of an innovation ecosystem.
These activities also lead to a strong startup ecosystem that drives South Korean industries. The flow of startups, which began with companies like Qnix Computer, Nexon, and Naver, has expanded to a total of 1,914 companies to date. Their cumulative assets amount to 94 trillion won, with sales reaching 36 trillion won and employing approximately 60,000 people. Over 90% of these are technology-based startups originating from faculty and student labs, demonstrating a model that makes a tangible economic contribution based on science and technology.
< Students at work >
Having consistently generated diverse achievements, KAIST has already produced approximately 80,000 "KAISTians" who have created innovation through challenge and failure, and is currently recruiting new talent to continue driving innovation that transforms South Korea and the world.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "KAIST will establish itself as a global leader in science and technology, designing the future of South Korea and humanity and creating tangible value." He added, "We will focus on talent nurturing and research and development to realize the new government's national agenda of becoming a G3 AI powerhouse."
He further stated, "KAIST's vision for the AI field, in which it places particular emphasis, is to strive for a society where everyone can freely utilize AI. We will contribute to significantly boosting productivity by recovering manufacturing competitiveness through AI and actively disseminating physical AI, AI robots, and AI mobility technologies to industrial sites."
2025.06.24 View 1491