ACT
-
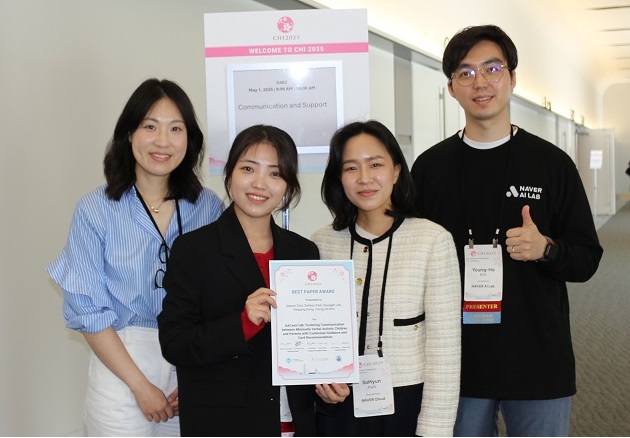 “For the First Time, We Shared a Meaningful Exchange”: KAIST Develops an AI App for Parents and Minimally Verbal Autistic Children Connect
• KAIST team up with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center Develop ‘AAcessTalk’, an AI-driven Communication Tool bridging the gap Between Children with Autism and their Parents
• The project earned the prestigious Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025, the Premier International Conference in Human-Computer Interaction
• Families share heartwarming stories of breakthrough communication and newfound understanding.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hwajung Hong and Doctoral candidate Dasom Choi of the Department of Industrial Design with SoHyun Park and Young-Ho Kim of Naver Cloud AI Lab >
For many families of minimally verbal autistic (MVA) children, communication often feels like an uphill battle. But now, thanks to a new AI-powered app developed by researchers at KAIST in collaboration with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center, parents are finally experiencing moments of genuine connection with their children.
On the 16th, the KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) research team, led by Professor Hwajung Hong of the Department of Industrial Design, announced the development of ‘AAcessTalk,’ an artificial intelligence (AI)-based communication tool that enables genuine communication between children with autism and their parents.
This research was recognized for its human-centered AI approach and received international attention, earning the Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025*, an international conference held in Yokohama, Japan.*ACM CHI (ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025: One of the world's most prestigious academic conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
This year, approximately 1,200 papers were selected out of about 5,000 submissions, with the Best Paper Award given to only the top 1%. The conference, which drew over 5,000 researchers, was the largest in its history, reflecting the growing interest in ‘Human-AI Interaction.’
Called AACessTalk, the app offers personalized vocabulary cards tailored to each child’s interests and context, while guiding parents through conversations with customized prompts. This creates a space where children’s voices can finally be heard—and where parents and children can connect on a deeper level.
Traditional augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools have relied heavily on fixed card systems that often fail to capture the subtle emotions and shifting interests of children with autism. AACessTalk breaks new ground by integrating AI technology that adapts in real time to the child’s mood and environment.
< Figure. Schematics of AACessTalk system. It provides personalized vocabulary cards for children with autism and context-based conversation guides for parents to focus on practical communication. Large ‘Turn Pass Button’ is placed at the child’s side to allow the child to lead the conversation. >
Among its standout features is a large ‘Turn Pass Button’ that gives children control over when to start or end conversations—allowing them to lead with agency. Another feature, the “What about Mom/Dad?” button, encourages children to ask about their parents’ thoughts, fostering mutual engagement in dialogue, something many children had never done before.
One parent shared, “For the first time, we shared a meaningful exchange.” Such stories were common among the 11 families who participated in a two-week pilot study, where children used the app to take more initiative in conversations and parents discovered new layers of their children’s language abilities.
Parents also reported moments of surprise and joy when their children used unexpected words or took the lead in conversations, breaking free from repetitive patterns. “I was amazed when my child used a word I hadn’t heard before. It helped me understand them in a whole new way,” recalled one caregiver.
Professor Hwajung Hong, who led the research at KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, emphasized the importance of empowering children to express their own voices. “This study shows that AI can be more than a communication aid—it can be a bridge to genuine connection and understanding within families,” she said.
Looking ahead, the team plans to refine and expand human-centered AI technologies that honor neurodiversity, with a focus on bringing practical solutions to socially vulnerable groups and enriching user experiences.
This research is the result of KAIST Department of Industrial Design doctoral student Dasom Choi's internship at NAVER AI Lab.* Thesis Title: AACessTalk: Fostering Communication between Minimally Verbal Autistic Children and Parents with Contextual Guidance and Card Recommendation* DOI: 10.1145/3706598.3713792* Main Author Information: Dasom Choi (KAIST, NAVER AI Lab, First Author), SoHyun Park (NAVER AI Lab) , Kyungah Lee (Dodakim Child Development Center), Hwajung Hong (KAIST), and Young-Ho Kim (NAVER AI Lab, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the NAVER AI Lab internship program and grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea: the Doctoral Student Research Encouragement Grant (NRF-2024S1A5B5A19043580) and the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program for the Development of a Generative AI-Based Augmentative and Alternative Communication System for Autism Spectrum Disorder (RS-2024-00458557).
2025.05.19 View 296
“For the First Time, We Shared a Meaningful Exchange”: KAIST Develops an AI App for Parents and Minimally Verbal Autistic Children Connect
• KAIST team up with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center Develop ‘AAcessTalk’, an AI-driven Communication Tool bridging the gap Between Children with Autism and their Parents
• The project earned the prestigious Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025, the Premier International Conference in Human-Computer Interaction
• Families share heartwarming stories of breakthrough communication and newfound understanding.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hwajung Hong and Doctoral candidate Dasom Choi of the Department of Industrial Design with SoHyun Park and Young-Ho Kim of Naver Cloud AI Lab >
For many families of minimally verbal autistic (MVA) children, communication often feels like an uphill battle. But now, thanks to a new AI-powered app developed by researchers at KAIST in collaboration with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center, parents are finally experiencing moments of genuine connection with their children.
On the 16th, the KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) research team, led by Professor Hwajung Hong of the Department of Industrial Design, announced the development of ‘AAcessTalk,’ an artificial intelligence (AI)-based communication tool that enables genuine communication between children with autism and their parents.
This research was recognized for its human-centered AI approach and received international attention, earning the Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025*, an international conference held in Yokohama, Japan.*ACM CHI (ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025: One of the world's most prestigious academic conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
This year, approximately 1,200 papers were selected out of about 5,000 submissions, with the Best Paper Award given to only the top 1%. The conference, which drew over 5,000 researchers, was the largest in its history, reflecting the growing interest in ‘Human-AI Interaction.’
Called AACessTalk, the app offers personalized vocabulary cards tailored to each child’s interests and context, while guiding parents through conversations with customized prompts. This creates a space where children’s voices can finally be heard—and where parents and children can connect on a deeper level.
Traditional augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools have relied heavily on fixed card systems that often fail to capture the subtle emotions and shifting interests of children with autism. AACessTalk breaks new ground by integrating AI technology that adapts in real time to the child’s mood and environment.
< Figure. Schematics of AACessTalk system. It provides personalized vocabulary cards for children with autism and context-based conversation guides for parents to focus on practical communication. Large ‘Turn Pass Button’ is placed at the child’s side to allow the child to lead the conversation. >
Among its standout features is a large ‘Turn Pass Button’ that gives children control over when to start or end conversations—allowing them to lead with agency. Another feature, the “What about Mom/Dad?” button, encourages children to ask about their parents’ thoughts, fostering mutual engagement in dialogue, something many children had never done before.
One parent shared, “For the first time, we shared a meaningful exchange.” Such stories were common among the 11 families who participated in a two-week pilot study, where children used the app to take more initiative in conversations and parents discovered new layers of their children’s language abilities.
Parents also reported moments of surprise and joy when their children used unexpected words or took the lead in conversations, breaking free from repetitive patterns. “I was amazed when my child used a word I hadn’t heard before. It helped me understand them in a whole new way,” recalled one caregiver.
Professor Hwajung Hong, who led the research at KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, emphasized the importance of empowering children to express their own voices. “This study shows that AI can be more than a communication aid—it can be a bridge to genuine connection and understanding within families,” she said.
Looking ahead, the team plans to refine and expand human-centered AI technologies that honor neurodiversity, with a focus on bringing practical solutions to socially vulnerable groups and enriching user experiences.
This research is the result of KAIST Department of Industrial Design doctoral student Dasom Choi's internship at NAVER AI Lab.* Thesis Title: AACessTalk: Fostering Communication between Minimally Verbal Autistic Children and Parents with Contextual Guidance and Card Recommendation* DOI: 10.1145/3706598.3713792* Main Author Information: Dasom Choi (KAIST, NAVER AI Lab, First Author), SoHyun Park (NAVER AI Lab) , Kyungah Lee (Dodakim Child Development Center), Hwajung Hong (KAIST), and Young-Ho Kim (NAVER AI Lab, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the NAVER AI Lab internship program and grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea: the Doctoral Student Research Encouragement Grant (NRF-2024S1A5B5A19043580) and the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program for the Development of a Generative AI-Based Augmentative and Alternative Communication System for Autism Spectrum Disorder (RS-2024-00458557).
2025.05.19 View 296 -
 KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 571
KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 571 -
 KAIST & CMU Unveils Amuse, a Songwriting AI-Collaborator to Help Create Music
Wouldn't it be great if music creators had someone to brainstorm with, help them when they're stuck, and explore different musical directions together? Researchers of KAIST and Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) have developed AI technology similar to a fellow songwriter who helps create music.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) has developed an AI-based music creation support system, Amuse, by a research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with CMU. The research was presented at the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), one of the world’s top conferences in human-computer interaction, held in Yokohama, Japan from April 26 to May 1. It received the Best Paper Award, given to only the top 1% of all submissions.
< (From left) Professor Chris Donahue of Carnegie Mellon University, Ph.D. Student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering >
The system developed by Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s research team, Amuse, is an AI-based system that converts various forms of inspiration such as text, images, and audio into harmonic structures (chord progressions) to support composition.
For example, if a user inputs a phrase, image, or sound clip such as “memories of a warm summer beach”, Amuse automatically generates and suggests chord progressions that match the inspiration.
Unlike existing generative AI, Amuse is differentiated in that it respects the user's creative flow and naturally induces creative exploration through an interactive method that allows flexible integration and modification of AI suggestions.
The core technology of the Amuse system is a generation method that blends two approaches: a large language model creates music code based on the user's prompt and inspiration, while another AI model, trained on real music data, filters out awkward or unnatural results using rejection sampling.
< Figure 1. Amuse system configuration. After extracting music keywords from user input, a large language model-based code progression is generated and refined through rejection sampling (left). Code extraction from audio input is also possible (right). The bottom is an example visualizing the chord structure of the generated code. >
The research team conducted a user study targeting actual musicians and evaluated that Amuse has high potential as a creative companion, or a Co-Creative AI, a concept in which people and AI collaborate, rather than having a generative AI simply put together a song.
The paper, in which a Ph.D. student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Carnegie Mellon University Professor Chris Donahue participated, demonstrated the potential of creative AI system design in both academia and industry. ※ Paper title: Amuse: Human-AI Collaborative Songwriting with Multimodal Inspirations DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713818
※ Research demo video: https://youtu.be/udilkRSnftI?si=FNXccC9EjxHOCrm1
※ Research homepage: https://nmsl.kaist.ac.kr/projects/amuse/
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “Recent generative AI technology has raised concerns in that it directly imitates copyrighted content, thereby violating the copyright of the creator, or generating results one-way regardless of the creator’s intention. Accordingly, the research team was aware of this trend, paid attention to what the creator actually needs, and focused on designing an AI system centered on the creator.”
He continued, “Amuse is an attempt to explore the possibility of collaboration with AI while maintaining the initiative of the creator, and is expected to be a starting point for suggesting a more creator-friendly direction in the development of music creation tools and generative AI systems in the future.”
This research was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea with funding from the government (Ministry of Science and ICT). (RS-2024-00337007)
2025.05.07 View 1438
KAIST & CMU Unveils Amuse, a Songwriting AI-Collaborator to Help Create Music
Wouldn't it be great if music creators had someone to brainstorm with, help them when they're stuck, and explore different musical directions together? Researchers of KAIST and Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) have developed AI technology similar to a fellow songwriter who helps create music.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) has developed an AI-based music creation support system, Amuse, by a research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with CMU. The research was presented at the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), one of the world’s top conferences in human-computer interaction, held in Yokohama, Japan from April 26 to May 1. It received the Best Paper Award, given to only the top 1% of all submissions.
< (From left) Professor Chris Donahue of Carnegie Mellon University, Ph.D. Student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering >
The system developed by Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s research team, Amuse, is an AI-based system that converts various forms of inspiration such as text, images, and audio into harmonic structures (chord progressions) to support composition.
For example, if a user inputs a phrase, image, or sound clip such as “memories of a warm summer beach”, Amuse automatically generates and suggests chord progressions that match the inspiration.
Unlike existing generative AI, Amuse is differentiated in that it respects the user's creative flow and naturally induces creative exploration through an interactive method that allows flexible integration and modification of AI suggestions.
The core technology of the Amuse system is a generation method that blends two approaches: a large language model creates music code based on the user's prompt and inspiration, while another AI model, trained on real music data, filters out awkward or unnatural results using rejection sampling.
< Figure 1. Amuse system configuration. After extracting music keywords from user input, a large language model-based code progression is generated and refined through rejection sampling (left). Code extraction from audio input is also possible (right). The bottom is an example visualizing the chord structure of the generated code. >
The research team conducted a user study targeting actual musicians and evaluated that Amuse has high potential as a creative companion, or a Co-Creative AI, a concept in which people and AI collaborate, rather than having a generative AI simply put together a song.
The paper, in which a Ph.D. student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Carnegie Mellon University Professor Chris Donahue participated, demonstrated the potential of creative AI system design in both academia and industry. ※ Paper title: Amuse: Human-AI Collaborative Songwriting with Multimodal Inspirations DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713818
※ Research demo video: https://youtu.be/udilkRSnftI?si=FNXccC9EjxHOCrm1
※ Research homepage: https://nmsl.kaist.ac.kr/projects/amuse/
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “Recent generative AI technology has raised concerns in that it directly imitates copyrighted content, thereby violating the copyright of the creator, or generating results one-way regardless of the creator’s intention. Accordingly, the research team was aware of this trend, paid attention to what the creator actually needs, and focused on designing an AI system centered on the creator.”
He continued, “Amuse is an attempt to explore the possibility of collaboration with AI while maintaining the initiative of the creator, and is expected to be a starting point for suggesting a more creator-friendly direction in the development of music creation tools and generative AI systems in the future.”
This research was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea with funding from the government (Ministry of Science and ICT). (RS-2024-00337007)
2025.05.07 View 1438 -
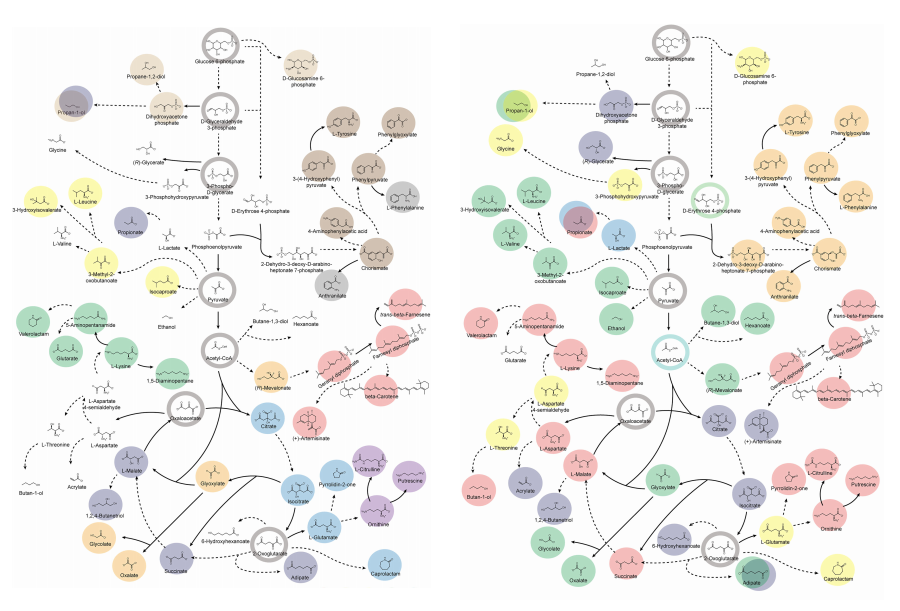 KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 1759
KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 1759 -
 No More Touch Issues on Rainy Days! KAIST Develops Human-Like Tactile Sensor
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled machines to handle delicate objects like eggs with precision, thanks to highly integrated pressure sensors that provide detailed tactile feedback. However, even the most advanced robots struggle to accurately detect pressure in complex environments involving water, bending, or electromagnetic interference. A research team at KAIST has successfully developed a pressure sensor that operates stably without external interference, even on wet surfaces like a smartphone screen covered in water, achieving human-level tactile sensitivity.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of March that a research team led by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a high-resolution pressure sensor that remains unaffected by external interference such as "ghost touches" caused by moisture on touchscreens.
Capacitive pressure sensors, widely used in touch systems due to their simple structure and durability, are essential components of human-machine interface (HMI) technologies in smartphones, wearable devices, and robots. However, they are prone to malfunctions caused by water droplets, electromagnetic interference, and curves.
To address these issues, the research team investigated the root causes of interference in capacitive pressure sensors. They identified that the "fringe field" generated at the sensor’s edges is particularly susceptible to external disturbances.
The researchers concluded that, to fundamentally resolve this issue, suppressing the fringe field was necessary. Through theoretical analysis, they determined that reducing the electrode spacing to the nanometer scale could effectively minimize the fringe field to below a few percent.
Utilizing proprietary micro/nanofabrication techniques, the team developed a nanogap pressure sensor with an electrode spacing of 900 nanometers (nm). This newly developed sensor reliably detected pressure regardless of the material exerting force and remained unaffected by bending or electromagnetic interference.
Furthermore, the team successfully implemented an artificial tactile system utilizing the developed sensor’s characteristics. Human skin contains specialized pressure receptors called Merkel’s disks. To artificially mimic them, the exclusive detection of pressure was necessary, but hadn’t been achieved by conventional sensors.
Professor Yoon’s research team overcame these challenges, developing a sensor achieving a density comparable to Merkel’s discs and enabling wireless, high-precision pressure sensing.
To explore potential applications, the researcher also developed a force touch pad system, demonstrating its ability to capture pressure magnitude and distribution with high resolution and without interference.
Professor Yoon stated, “Our nanogap pressure sensor operates reliably even in rainy conditions or sweaty environments, eliminating common touch malfunctions. We believe this innovation will significantly enhance everyday user experiences.”
He added, “This technology has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including precision tactile sensors for robotics, medical wearable devices, and next-generation augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) interfaces.”
The study was led by Jae-Soon Yang (Ph.D.), Myung-Kun Chung (Ph.D. candidate), and Jae-Young Yoo (Assistant Professor at Sungkyunkwan University, a KAIST Ph.D. graduate). The research findings were published in Nature Communications on February 27, 2025. (Paper title: “Interference-Free Nanogap Pressure Sensor Array with High Spatial Resolution for Wireless Human-Machine Interface Applications”, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57232-8)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and Leading Research Center Support Program.
2025.03.14 View 1881
No More Touch Issues on Rainy Days! KAIST Develops Human-Like Tactile Sensor
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled machines to handle delicate objects like eggs with precision, thanks to highly integrated pressure sensors that provide detailed tactile feedback. However, even the most advanced robots struggle to accurately detect pressure in complex environments involving water, bending, or electromagnetic interference. A research team at KAIST has successfully developed a pressure sensor that operates stably without external interference, even on wet surfaces like a smartphone screen covered in water, achieving human-level tactile sensitivity.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of March that a research team led by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a high-resolution pressure sensor that remains unaffected by external interference such as "ghost touches" caused by moisture on touchscreens.
Capacitive pressure sensors, widely used in touch systems due to their simple structure and durability, are essential components of human-machine interface (HMI) technologies in smartphones, wearable devices, and robots. However, they are prone to malfunctions caused by water droplets, electromagnetic interference, and curves.
To address these issues, the research team investigated the root causes of interference in capacitive pressure sensors. They identified that the "fringe field" generated at the sensor’s edges is particularly susceptible to external disturbances.
The researchers concluded that, to fundamentally resolve this issue, suppressing the fringe field was necessary. Through theoretical analysis, they determined that reducing the electrode spacing to the nanometer scale could effectively minimize the fringe field to below a few percent.
Utilizing proprietary micro/nanofabrication techniques, the team developed a nanogap pressure sensor with an electrode spacing of 900 nanometers (nm). This newly developed sensor reliably detected pressure regardless of the material exerting force and remained unaffected by bending or electromagnetic interference.
Furthermore, the team successfully implemented an artificial tactile system utilizing the developed sensor’s characteristics. Human skin contains specialized pressure receptors called Merkel’s disks. To artificially mimic them, the exclusive detection of pressure was necessary, but hadn’t been achieved by conventional sensors.
Professor Yoon’s research team overcame these challenges, developing a sensor achieving a density comparable to Merkel’s discs and enabling wireless, high-precision pressure sensing.
To explore potential applications, the researcher also developed a force touch pad system, demonstrating its ability to capture pressure magnitude and distribution with high resolution and without interference.
Professor Yoon stated, “Our nanogap pressure sensor operates reliably even in rainy conditions or sweaty environments, eliminating common touch malfunctions. We believe this innovation will significantly enhance everyday user experiences.”
He added, “This technology has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including precision tactile sensors for robotics, medical wearable devices, and next-generation augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) interfaces.”
The study was led by Jae-Soon Yang (Ph.D.), Myung-Kun Chung (Ph.D. candidate), and Jae-Young Yoo (Assistant Professor at Sungkyunkwan University, a KAIST Ph.D. graduate). The research findings were published in Nature Communications on February 27, 2025. (Paper title: “Interference-Free Nanogap Pressure Sensor Array with High Spatial Resolution for Wireless Human-Machine Interface Applications”, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57232-8)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and Leading Research Center Support Program.
2025.03.14 View 1881 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 2761
KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 2761 -
 KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 2257
KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 2257 -
 KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 22318
KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 22318 -
 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7431
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7431 -
 KAIST Wins CES 2025 Innovation Award, Showcasing Innovative Technologies
KAIST will showcase innovative technologies at the world’s largest technology fair, the Consumer Electronics Show (CES 2025). In addition, KAIST startups VIRNECT Inc., Standard Energy Inc., A2US Inc., and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards.
< Image 1. 3D-Graphical Profile of CES 2025 KAIST Exhibition Booth >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 31st that it will operate a 140㎡ standalone booth at CES Eureka Park, which will be held in Las Vegas, USA from January 7th to 10th next year, to showcase KAIST's innovative technologies to global companies and investors.
KAIST startups VIRNECT, Standard Energy, A2US, and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards. ▴VIRNECT won the Innovation Award in the ‘Industrial Equipment and Machinery’ category for ‘VisionX’, an AI-based smart glass for industrial sites; ▴Standard Energy Co., Ltd. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Smart City’ category for developing the world’s first vanadium-ion battery; ▴A2US won the Innovation Award in the ‘Environment & Energy’ category for its portable air purifier that eliminates bacteria, odors, and fine dust in the air with just water droplets; ▴Panmnesia, Inc. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Computer Peripherals and Accessories’ category for its ‘CXL-based GPU Memory Expansion Kit’ that can drastically reduce the cost of building AI infrastructure.
< Image 2. (From left on the top row) VIRNECT, Standard Energy, (From left on the bottom row) A2US, Panmnesia, Inc. >
This exhibition will feature 15 startups that are standing out in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, mobility, and sustainability. In particular, AI-based deep tech startups in various industries such as logistics, architecture, and medicine will take up half of the total, showcasing the companies’ innovative AI technologies.
Polyphenol Factory Co.,Ltd introduces ‘Grabity’, a hair loss shampoo launched domestically, which applies the patented ingredient ‘LiftMax 308™’ that forms an instantaneous protective layer on the hair during the shampooing process. A real-time demonstration will be held at this exhibition hall so that visitors can experience the effects of the ingredient directly, and plans to enter the global market starting with the launch on Amazon in the US in January 2025.
VIRNECT will present ‘VisionX’, a prototype that won the Innovation Award this time. The product provides a chatbot AI through an AI voice interface, and has a function that allows users to check the status of the equipment in real time through conversations with the AI and receive troubleshooting guidance through voice conversations, so users can experience it directly at the KAIST Hall.
‘Standard Energy’ plans to exhibit ‘Energy Tile’, an indoor ESS that utilizes the world’s first vanadium ion battery (hereinafter referred to as VIB). VIB is absolutely safe from fire and has high installation flexibility, so it can be applied to smart cities and AI data centers.
‘A2US’ is the only company in the world that has hydroxyl radical water production technology, and won the Innovation Award for its first product, an air purifier. In the future, it is expected to be widely commercialized in air and water purification, smart farms, food tech, and semiconductor cleaning using safe and environmentally friendly hydroxyl radical water.
Panmnesia, Inc. won the CES Innovation Award for its GPU memory expansion solution equipped with its CXL 3.1 IP. By connecting a memory expansion device using Panmnesia’s CXL IP, the GPU’s memory capacity can be expanded to the terabyte level. Following the Innovation Award for ‘CXL-equipped AI Accelerator’ at CES 2024 last year, it is the only company to have won the Innovation Award for its AI-oriented CXL solution for two consecutive years.
In addition, technologies from a total of 15 companies will be introduced, including ▴Omelet ▴NEXTWAVE ▴Planby Technologies ▴Cosmo Bee ▴ImpactAI ▴Roen Surgical ▴DIDEN Roboticss ▴Autopedia ▴OAQ ▴HydroXpand ▴BOOKEND ▴Sterri.
On the central stage of the KAIST Hall, KAIST students selected as CES Student Supporters will conduct interviews with participating companies and promote the companies' innovative technologies and solutions. On the 8th, from 5 PM to 7 PM, a KAIST NIGHT event will be held where pre-invited investors and participating companies can network.
Keon Jae Lee, the head of the Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “Through CES 2025, we will showcase innovative technologies and solutions from startups based on KAIST’s deep science and deep tech, and lead commercialization in cutting-edge technology fields such as AI, robotics, mobility, and environment/energy. KAIST plans to further promote technology commercialization by supporting the growth and marketing of innovative startups through the Institute of Technology Value Creation and by strengthening global networks and expanding cooperation opportunities.”
2024.12.31 View 3874
KAIST Wins CES 2025 Innovation Award, Showcasing Innovative Technologies
KAIST will showcase innovative technologies at the world’s largest technology fair, the Consumer Electronics Show (CES 2025). In addition, KAIST startups VIRNECT Inc., Standard Energy Inc., A2US Inc., and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards.
< Image 1. 3D-Graphical Profile of CES 2025 KAIST Exhibition Booth >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 31st that it will operate a 140㎡ standalone booth at CES Eureka Park, which will be held in Las Vegas, USA from January 7th to 10th next year, to showcase KAIST's innovative technologies to global companies and investors.
KAIST startups VIRNECT, Standard Energy, A2US, and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards. ▴VIRNECT won the Innovation Award in the ‘Industrial Equipment and Machinery’ category for ‘VisionX’, an AI-based smart glass for industrial sites; ▴Standard Energy Co., Ltd. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Smart City’ category for developing the world’s first vanadium-ion battery; ▴A2US won the Innovation Award in the ‘Environment & Energy’ category for its portable air purifier that eliminates bacteria, odors, and fine dust in the air with just water droplets; ▴Panmnesia, Inc. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Computer Peripherals and Accessories’ category for its ‘CXL-based GPU Memory Expansion Kit’ that can drastically reduce the cost of building AI infrastructure.
< Image 2. (From left on the top row) VIRNECT, Standard Energy, (From left on the bottom row) A2US, Panmnesia, Inc. >
This exhibition will feature 15 startups that are standing out in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, mobility, and sustainability. In particular, AI-based deep tech startups in various industries such as logistics, architecture, and medicine will take up half of the total, showcasing the companies’ innovative AI technologies.
Polyphenol Factory Co.,Ltd introduces ‘Grabity’, a hair loss shampoo launched domestically, which applies the patented ingredient ‘LiftMax 308™’ that forms an instantaneous protective layer on the hair during the shampooing process. A real-time demonstration will be held at this exhibition hall so that visitors can experience the effects of the ingredient directly, and plans to enter the global market starting with the launch on Amazon in the US in January 2025.
VIRNECT will present ‘VisionX’, a prototype that won the Innovation Award this time. The product provides a chatbot AI through an AI voice interface, and has a function that allows users to check the status of the equipment in real time through conversations with the AI and receive troubleshooting guidance through voice conversations, so users can experience it directly at the KAIST Hall.
‘Standard Energy’ plans to exhibit ‘Energy Tile’, an indoor ESS that utilizes the world’s first vanadium ion battery (hereinafter referred to as VIB). VIB is absolutely safe from fire and has high installation flexibility, so it can be applied to smart cities and AI data centers.
‘A2US’ is the only company in the world that has hydroxyl radical water production technology, and won the Innovation Award for its first product, an air purifier. In the future, it is expected to be widely commercialized in air and water purification, smart farms, food tech, and semiconductor cleaning using safe and environmentally friendly hydroxyl radical water.
Panmnesia, Inc. won the CES Innovation Award for its GPU memory expansion solution equipped with its CXL 3.1 IP. By connecting a memory expansion device using Panmnesia’s CXL IP, the GPU’s memory capacity can be expanded to the terabyte level. Following the Innovation Award for ‘CXL-equipped AI Accelerator’ at CES 2024 last year, it is the only company to have won the Innovation Award for its AI-oriented CXL solution for two consecutive years.
In addition, technologies from a total of 15 companies will be introduced, including ▴Omelet ▴NEXTWAVE ▴Planby Technologies ▴Cosmo Bee ▴ImpactAI ▴Roen Surgical ▴DIDEN Roboticss ▴Autopedia ▴OAQ ▴HydroXpand ▴BOOKEND ▴Sterri.
On the central stage of the KAIST Hall, KAIST students selected as CES Student Supporters will conduct interviews with participating companies and promote the companies' innovative technologies and solutions. On the 8th, from 5 PM to 7 PM, a KAIST NIGHT event will be held where pre-invited investors and participating companies can network.
Keon Jae Lee, the head of the Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “Through CES 2025, we will showcase innovative technologies and solutions from startups based on KAIST’s deep science and deep tech, and lead commercialization in cutting-edge technology fields such as AI, robotics, mobility, and environment/energy. KAIST plans to further promote technology commercialization by supporting the growth and marketing of innovative startups through the Institute of Technology Value Creation and by strengthening global networks and expanding cooperation opportunities.”
2024.12.31 View 3874 -
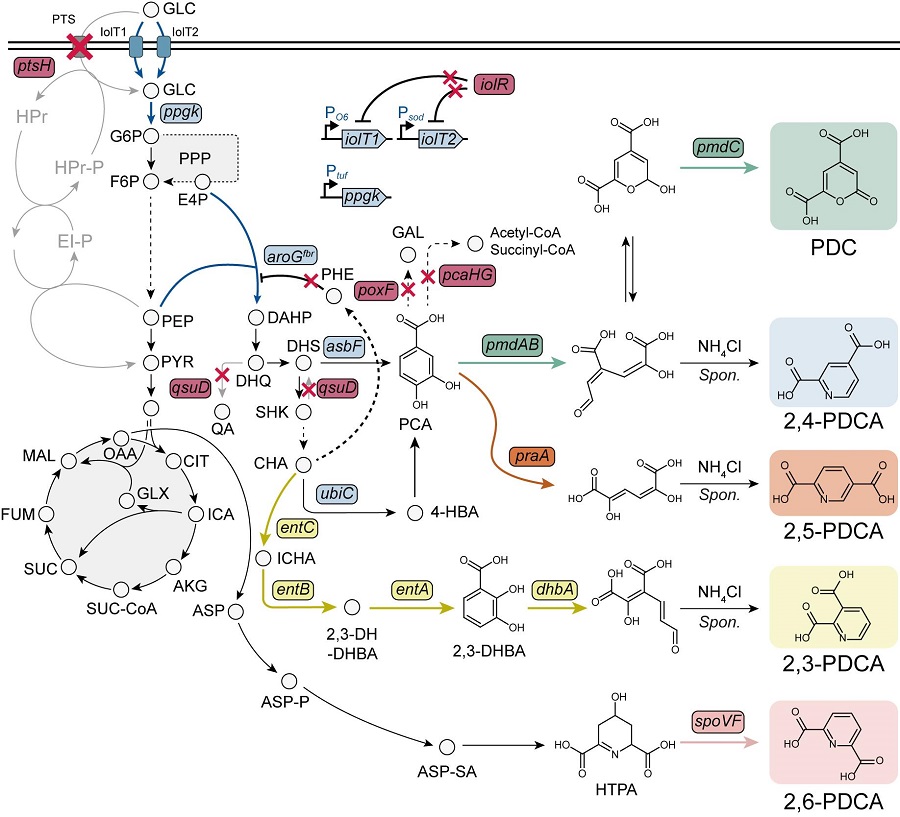 KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 6638
KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 6638 -
 KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 5272
KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 5272