ACM
-
 KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 604
KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 604 -
 KAIST & CMU Unveils Amuse, a Songwriting AI-Collaborator to Help Create Music
Wouldn't it be great if music creators had someone to brainstorm with, help them when they're stuck, and explore different musical directions together? Researchers of KAIST and Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) have developed AI technology similar to a fellow songwriter who helps create music.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) has developed an AI-based music creation support system, Amuse, by a research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with CMU. The research was presented at the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), one of the world’s top conferences in human-computer interaction, held in Yokohama, Japan from April 26 to May 1. It received the Best Paper Award, given to only the top 1% of all submissions.
< (From left) Professor Chris Donahue of Carnegie Mellon University, Ph.D. Student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering >
The system developed by Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s research team, Amuse, is an AI-based system that converts various forms of inspiration such as text, images, and audio into harmonic structures (chord progressions) to support composition.
For example, if a user inputs a phrase, image, or sound clip such as “memories of a warm summer beach”, Amuse automatically generates and suggests chord progressions that match the inspiration.
Unlike existing generative AI, Amuse is differentiated in that it respects the user's creative flow and naturally induces creative exploration through an interactive method that allows flexible integration and modification of AI suggestions.
The core technology of the Amuse system is a generation method that blends two approaches: a large language model creates music code based on the user's prompt and inspiration, while another AI model, trained on real music data, filters out awkward or unnatural results using rejection sampling.
< Figure 1. Amuse system configuration. After extracting music keywords from user input, a large language model-based code progression is generated and refined through rejection sampling (left). Code extraction from audio input is also possible (right). The bottom is an example visualizing the chord structure of the generated code. >
The research team conducted a user study targeting actual musicians and evaluated that Amuse has high potential as a creative companion, or a Co-Creative AI, a concept in which people and AI collaborate, rather than having a generative AI simply put together a song.
The paper, in which a Ph.D. student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Carnegie Mellon University Professor Chris Donahue participated, demonstrated the potential of creative AI system design in both academia and industry. ※ Paper title: Amuse: Human-AI Collaborative Songwriting with Multimodal Inspirations DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713818
※ Research demo video: https://youtu.be/udilkRSnftI?si=FNXccC9EjxHOCrm1
※ Research homepage: https://nmsl.kaist.ac.kr/projects/amuse/
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “Recent generative AI technology has raised concerns in that it directly imitates copyrighted content, thereby violating the copyright of the creator, or generating results one-way regardless of the creator’s intention. Accordingly, the research team was aware of this trend, paid attention to what the creator actually needs, and focused on designing an AI system centered on the creator.”
He continued, “Amuse is an attempt to explore the possibility of collaboration with AI while maintaining the initiative of the creator, and is expected to be a starting point for suggesting a more creator-friendly direction in the development of music creation tools and generative AI systems in the future.”
This research was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea with funding from the government (Ministry of Science and ICT). (RS-2024-00337007)
2025.05.07 View 1453
KAIST & CMU Unveils Amuse, a Songwriting AI-Collaborator to Help Create Music
Wouldn't it be great if music creators had someone to brainstorm with, help them when they're stuck, and explore different musical directions together? Researchers of KAIST and Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) have developed AI technology similar to a fellow songwriter who helps create music.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) has developed an AI-based music creation support system, Amuse, by a research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with CMU. The research was presented at the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), one of the world’s top conferences in human-computer interaction, held in Yokohama, Japan from April 26 to May 1. It received the Best Paper Award, given to only the top 1% of all submissions.
< (From left) Professor Chris Donahue of Carnegie Mellon University, Ph.D. Student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering >
The system developed by Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s research team, Amuse, is an AI-based system that converts various forms of inspiration such as text, images, and audio into harmonic structures (chord progressions) to support composition.
For example, if a user inputs a phrase, image, or sound clip such as “memories of a warm summer beach”, Amuse automatically generates and suggests chord progressions that match the inspiration.
Unlike existing generative AI, Amuse is differentiated in that it respects the user's creative flow and naturally induces creative exploration through an interactive method that allows flexible integration and modification of AI suggestions.
The core technology of the Amuse system is a generation method that blends two approaches: a large language model creates music code based on the user's prompt and inspiration, while another AI model, trained on real music data, filters out awkward or unnatural results using rejection sampling.
< Figure 1. Amuse system configuration. After extracting music keywords from user input, a large language model-based code progression is generated and refined through rejection sampling (left). Code extraction from audio input is also possible (right). The bottom is an example visualizing the chord structure of the generated code. >
The research team conducted a user study targeting actual musicians and evaluated that Amuse has high potential as a creative companion, or a Co-Creative AI, a concept in which people and AI collaborate, rather than having a generative AI simply put together a song.
The paper, in which a Ph.D. student Yewon Kim and Professor Sung-Ju Lee of KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering and Carnegie Mellon University Professor Chris Donahue participated, demonstrated the potential of creative AI system design in both academia and industry. ※ Paper title: Amuse: Human-AI Collaborative Songwriting with Multimodal Inspirations DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713818
※ Research demo video: https://youtu.be/udilkRSnftI?si=FNXccC9EjxHOCrm1
※ Research homepage: https://nmsl.kaist.ac.kr/projects/amuse/
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “Recent generative AI technology has raised concerns in that it directly imitates copyrighted content, thereby violating the copyright of the creator, or generating results one-way regardless of the creator’s intention. Accordingly, the research team was aware of this trend, paid attention to what the creator actually needs, and focused on designing an AI system centered on the creator.”
He continued, “Amuse is an attempt to explore the possibility of collaboration with AI while maintaining the initiative of the creator, and is expected to be a starting point for suggesting a more creator-friendly direction in the development of music creation tools and generative AI systems in the future.”
This research was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea with funding from the government (Ministry of Science and ICT). (RS-2024-00337007)
2025.05.07 View 1453 -
 KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 5283
KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 5283 -
 “3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
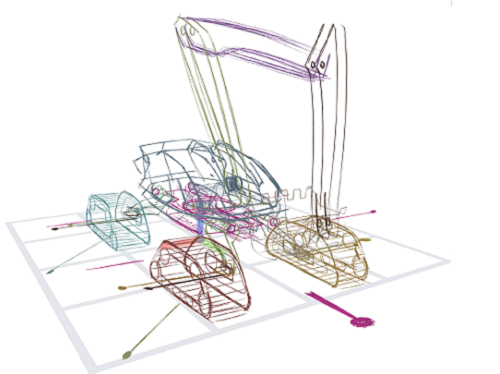
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 9932
“3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 9932 -
 Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 12801
Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 12801 -
 Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 8525
Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 8525 -
 Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 7686
Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 7686 -
 Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11743
Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11743 -
 Professor Dongsu Han Named Program Chair for ACM CoNEXT 2020
Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed as the program chair for the 16th Association for Computing Machinery’s International Conference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies (ACM CoNEXT 2020). Professor Han is the first program chair to be appointed from an Asian institution.
ACM CoNEXT is hosted by ACM SIGCOMM, ACM's Special Interest Group on Data Communications, which specializes in the field of communication and computer networks.
Professor Han will serve as program co-chair along with Professor Anja Feldmann from the Max Planck Institute for Informatics. Together, they have appointed 40 world-leading researchers as program committee members for this conference, including Professor Song Min Kim from KAIST School of Electrical Engineering.
Paper submissions for the conference can be made by the end of June, and the event itself is to take place from the 1st to 4th of December.
Conference Website: https://conferences2.sigcomm.org/co-next/2020/#!/home
(END)
2020.06.02 View 10768
Professor Dongsu Han Named Program Chair for ACM CoNEXT 2020
Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed as the program chair for the 16th Association for Computing Machinery’s International Conference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies (ACM CoNEXT 2020). Professor Han is the first program chair to be appointed from an Asian institution.
ACM CoNEXT is hosted by ACM SIGCOMM, ACM's Special Interest Group on Data Communications, which specializes in the field of communication and computer networks.
Professor Han will serve as program co-chair along with Professor Anja Feldmann from the Max Planck Institute for Informatics. Together, they have appointed 40 world-leading researchers as program committee members for this conference, including Professor Song Min Kim from KAIST School of Electrical Engineering.
Paper submissions for the conference can be made by the end of June, and the event itself is to take place from the 1st to 4th of December.
Conference Website: https://conferences2.sigcomm.org/co-next/2020/#!/home
(END)
2020.06.02 View 10768 -
 AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 17798
AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 17798 -
 Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 25805
Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 25805 -
 Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 28291
Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 28291