Jun-Bo+Yoon
-
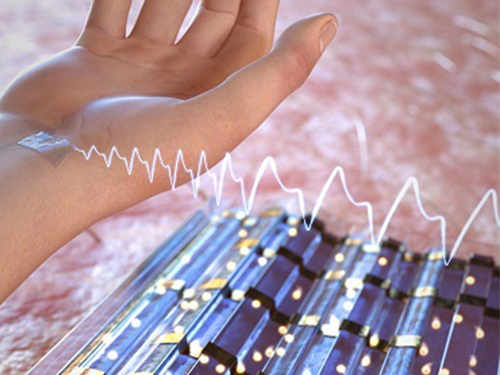 High-Performance Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor for Wearable Devices
Researchers reported a high-performance and transparent nanoforce touch sensor by developing a thin, flexible, and transparent hierarchical nanocomposite (HNC) film. The research team says their sensor simultaneously features all the necessary characters for industrial-grade application: high sensitivity, transparency, bending insensitivity, and manufacturability.
Force touch sensors that recognize the location and pressure of external stimuli have received considerable attention for various applications, such as wearable devices, flexible displays, and humanoid robots. For decades, huge amounts of research and development have been devoted to improving pressure sensitivity to realize industrial-grade sensing devices. However, it remains a challenge to apply force touch sensors in flexible applications because sensing performance is subject to change and degraded by induced mechanical stress and deformation when the device is bent.
To overcome these issues, the research team focused on the development of non-air gap sensors to break away from the conventional technology where force touch sensors need to have air-gaps between electrodes for high sensitivity and flexibility.
The proposed non air-gap force touch sensor is based on a transparent nanocomposite insulator containing metal nanoparticles which can maximize the capacitance change in dielectrics according to the pressure, and a nanograting substrate which can increase transparency as well as sensitivity by concentrating pressure. As a result, the team succeeded in fabricating a highly sensitive, transparent, flexible force touch sensor that is mechanically stable against repetitive pressure.
Furthermore, by placing the sensing electrodes on the same plane as the neutral plane, the force touch sensor can operate, even when bending to the radius of the ballpoint pen, without changes in performance levels.
The proposed force touch has also satisfied commercial considerations in mass production such as large-area uniformity, production reproducibility, and reliability according to temperature and long-term use.
Finally, the research team applied the developed sensor to a pulse-monitoring capable healthcare wearable device and detected a real-time human pulse. In addition, the research team confirmed with HiDeep, Inc. that a seven-inch large-area sensor can be integrated into a commercial smartphone.
The team of Professor Jun-Bo Yoon, PhD student Jae-Young Yoo, and Dr. Min-Ho Seo from the School of Electrical Engineering carried out this study that was featured as a back cover in Advanced Functional Materials Journal.
PhD student Jae-Young Yoo who led this research said, "We successfully developed an industrial-grade force touch sensor by using a simple structure and fabrication process. We expect it to be widely used in user touch interfaces and wearable devices."
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and also supported by the Open Innovation Lab Cooperation Project funded by the National Nano Fab Center.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of a transparent, flexible force touch sensor (upper image) and sensitivity enhancement by using stress concentration (lower image).
2018.10.15 View 7596
High-Performance Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor for Wearable Devices
Researchers reported a high-performance and transparent nanoforce touch sensor by developing a thin, flexible, and transparent hierarchical nanocomposite (HNC) film. The research team says their sensor simultaneously features all the necessary characters for industrial-grade application: high sensitivity, transparency, bending insensitivity, and manufacturability.
Force touch sensors that recognize the location and pressure of external stimuli have received considerable attention for various applications, such as wearable devices, flexible displays, and humanoid robots. For decades, huge amounts of research and development have been devoted to improving pressure sensitivity to realize industrial-grade sensing devices. However, it remains a challenge to apply force touch sensors in flexible applications because sensing performance is subject to change and degraded by induced mechanical stress and deformation when the device is bent.
To overcome these issues, the research team focused on the development of non-air gap sensors to break away from the conventional technology where force touch sensors need to have air-gaps between electrodes for high sensitivity and flexibility.
The proposed non air-gap force touch sensor is based on a transparent nanocomposite insulator containing metal nanoparticles which can maximize the capacitance change in dielectrics according to the pressure, and a nanograting substrate which can increase transparency as well as sensitivity by concentrating pressure. As a result, the team succeeded in fabricating a highly sensitive, transparent, flexible force touch sensor that is mechanically stable against repetitive pressure.
Furthermore, by placing the sensing electrodes on the same plane as the neutral plane, the force touch sensor can operate, even when bending to the radius of the ballpoint pen, without changes in performance levels.
The proposed force touch has also satisfied commercial considerations in mass production such as large-area uniformity, production reproducibility, and reliability according to temperature and long-term use.
Finally, the research team applied the developed sensor to a pulse-monitoring capable healthcare wearable device and detected a real-time human pulse. In addition, the research team confirmed with HiDeep, Inc. that a seven-inch large-area sensor can be integrated into a commercial smartphone.
The team of Professor Jun-Bo Yoon, PhD student Jae-Young Yoo, and Dr. Min-Ho Seo from the School of Electrical Engineering carried out this study that was featured as a back cover in Advanced Functional Materials Journal.
PhD student Jae-Young Yoo who led this research said, "We successfully developed an industrial-grade force touch sensor by using a simple structure and fabrication process. We expect it to be widely used in user touch interfaces and wearable devices."
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and also supported by the Open Innovation Lab Cooperation Project funded by the National Nano Fab Center.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of a transparent, flexible force touch sensor (upper image) and sensitivity enhancement by using stress concentration (lower image).
2018.10.15 View 7596 -
 Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 7159
Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 7159 -
 A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 10923
A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 10923