Byungjoo+Lee
-
 Play Games With No Latency
One of the most challenging issues for game players looks to be resolved soon with the introduction of a zero-latency gaming environment. A KAIST team developed a technology that helps game players maintain zero-latency performance. The new technology transforms the shapes of game design according to the amount of latency.
Latency in human-computer interactions is often caused by various factors related to the environment and performance of the devices, networks, and data processing. The term ‘lag’ is used to refer to any latency during gaming which impacts the user’s performance.
Professor Byungjoo Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology in collaboration with Aalto University in Finland presented a mathematical model for predicting players' behavior by understanding the effects of latency on players. This cognitive model is capable of predicting the success rate of a user when there is latency in a 'moving target selection' task which requires button input in a time constrained situation.
The model predicts the players’ task success rate when latency is added to the gaming environment. Using these predicted success rates, the design elements of the game are geometrically modified to help players maintain similar success rates as they would achieve in a zero-latency environment. In fact, this research succeeded in modifying the pillar heights of the Flappy Bird game, allowing the players to maintain their gaming performance regardless of the added latency.
Professor Lee said, "This technique is unique in the sense that it does not interfere with a player's gaming flow, unlike traditional methods which manipulate the game clock by the amount of latency. This study can be extended to various games such as reducing the size of obstacles in the latent computing environment.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University and led by PhD candidate Injung Lee, was presented during the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems last month in Glasgow in the UK.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2017R1C1B2002101, 2018R1A5A7025409), and the Aalto University Seed Funding Granted to the GamerLab respectively.
Figure 1. Overview of Geometric Compensation
Publication:
Injung Lee, Sunjun Kim, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Geometrically Compensating Effect of End-to-End Latency in Moving-Target Selection Games. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) . ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 560, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300790
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/TTi7dipAKJs
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Injung Lee, PhD Candidate
edndn@kaist.ac.kr
PhD Candidate
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Postdoc. Sunjun Kim, MD, PhD
kuaa.net@gmail.com
Postdoctoral Researcher
User Interfaces Group
Aalto University
https://www.aalto.fi Espoo 02150, Finland
(END)
2019.06.11 View 48362
Play Games With No Latency
One of the most challenging issues for game players looks to be resolved soon with the introduction of a zero-latency gaming environment. A KAIST team developed a technology that helps game players maintain zero-latency performance. The new technology transforms the shapes of game design according to the amount of latency.
Latency in human-computer interactions is often caused by various factors related to the environment and performance of the devices, networks, and data processing. The term ‘lag’ is used to refer to any latency during gaming which impacts the user’s performance.
Professor Byungjoo Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology in collaboration with Aalto University in Finland presented a mathematical model for predicting players' behavior by understanding the effects of latency on players. This cognitive model is capable of predicting the success rate of a user when there is latency in a 'moving target selection' task which requires button input in a time constrained situation.
The model predicts the players’ task success rate when latency is added to the gaming environment. Using these predicted success rates, the design elements of the game are geometrically modified to help players maintain similar success rates as they would achieve in a zero-latency environment. In fact, this research succeeded in modifying the pillar heights of the Flappy Bird game, allowing the players to maintain their gaming performance regardless of the added latency.
Professor Lee said, "This technique is unique in the sense that it does not interfere with a player's gaming flow, unlike traditional methods which manipulate the game clock by the amount of latency. This study can be extended to various games such as reducing the size of obstacles in the latent computing environment.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University and led by PhD candidate Injung Lee, was presented during the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems last month in Glasgow in the UK.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2017R1C1B2002101, 2018R1A5A7025409), and the Aalto University Seed Funding Granted to the GamerLab respectively.
Figure 1. Overview of Geometric Compensation
Publication:
Injung Lee, Sunjun Kim, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Geometrically Compensating Effect of End-to-End Latency in Moving-Target Selection Games. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) . ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 560, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300790
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/TTi7dipAKJs
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Injung Lee, PhD Candidate
edndn@kaist.ac.kr
PhD Candidate
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Postdoc. Sunjun Kim, MD, PhD
kuaa.net@gmail.com
Postdoctoral Researcher
User Interfaces Group
Aalto University
https://www.aalto.fi Espoo 02150, Finland
(END)
2019.06.11 View 48362 -
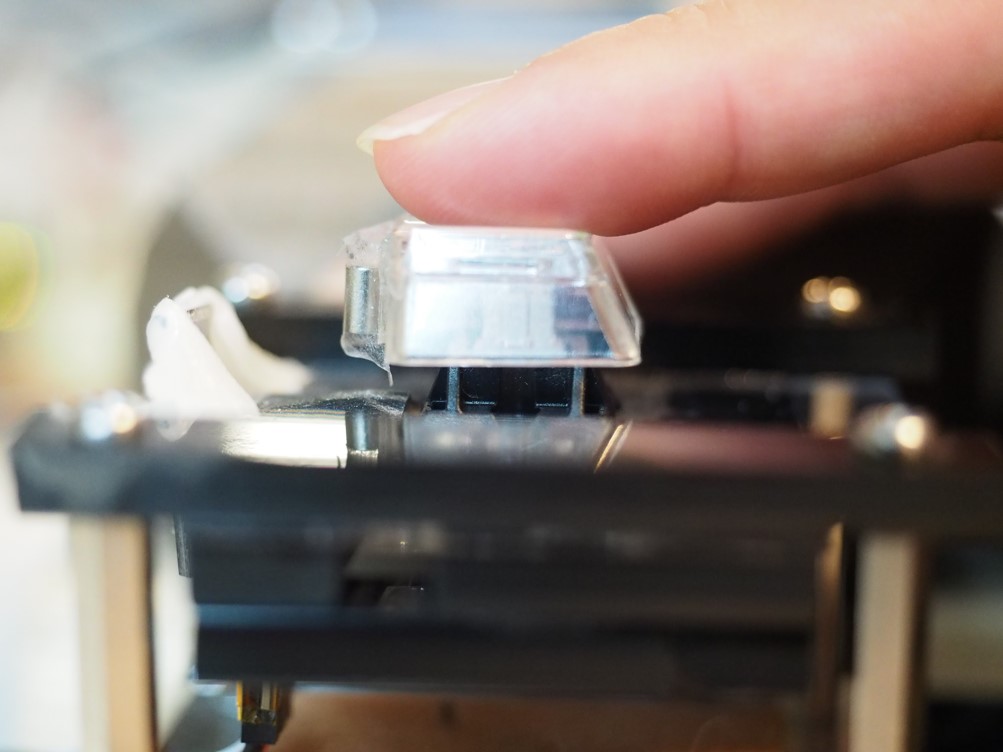 A New Theory Improves Button Designs
Pressing a button appears effortless. People easily dismisses how challenging it is. Researchers at KAIST and Aalto University in Finland, created detailed simulations of button-pressing with the goal of producing human-like presses.
The researchers argue that the key capability of the brain is a probabilistic model. The brain learns a model that allows it to predict a suitable motor command for a button. If a press fails, it can pick a very good alternative and try it out. "Without this ability, we would have to learn to use every button like it was new," tells Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST.
After successfully activating the button, the brain can tune the motor command to be more precise, use less energy and to avoid stress or pain. "These factors together, with practice, produce the fast, minimum-effort, elegant touch people are able to perform."
The brain uses probabilistic models also to extract information optimally from the sensations that arise when the finger moves and its tip touches the button. It "enriches" the ephemeral sensations optimally based on prior experience to estimate the time the button was impacted. For example, tactile sensation from the tip of the finger a better predictor for button activation than proprioception (angle position) and visual feedback.
Best performance is achieved when all sensations are considered together. To adapt, the brain must fuse their information using prior experiences. Professor Lee explains, "We believe that the brain picks up these skills over repeated button pressings that start already as a child. What appears easy for us now has been acquired over years."
The research was triggered by admiration of our remarkable capability to adapt button-pressing. Professor Antti Oulasvirta at Aalto University said, "We push a button on a remote controller differently than a piano key. The press of a skilled user is surprisingly elegant when looked at terms of timing, reliability, and energy use. We successfully press buttons without ever knowing the inner workings of a button. It is essentially a black box to our motor system. On the other hand, we also fail to activate buttons, and some buttons are known to be worse than others."
Previous research has shown that touch buttons are worse than push-buttons, but there has not been adequate theoretical explanation.
"In the past, there has been very little attention to buttons, although we use them all the time" says Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University. The new theory and simulations can be used to design better buttons.
"One exciting implication of the theory is that activating the button at the moment when the sensation is strongest will help users better rhythm their keypresses."
To test this hypothesis, the researchers created a new method for changing the way buttons are activated. The technique is called Impact Activation. Instead of activating the button at first contact, it activates it when the button cap or finger hits the floor with maximum impact.
The technique was 94% better in rapid tapping than the regular activation method for a push-button (Cherry MX switch) and 37% than a regular touchscreen button using a capacitive touch sensor. The technique can be easily deployed in touchscreens. However, regular physical keyboards do not offer the required sensing capability, although special products exist (e.g., the Wooting keyboard) on which it can be implemented.
The simulations shed new light on what happens during a button press. One problem the brain must overcome is that muscles do not activate as perfectly as we will, but every press is slightly different. Moreover, a button press is very fast, occurring within 100 milliseconds, and is too fast for correcting movement. The key to understanding button-pressing is therefore to understand how the brain adapts based on the limited sensations that are the residue of the brief press event.
The researchers also used the simulation to explain differences among physical and touchscreen-based button types. Both physical and touch buttons provide clear tactile signals from the impact of the tip with the button floor. However, with the physical button this signal is more pronounced and longer.
"Where the two button types also differ is the starting height of the finger, and this makes a difference," explains Professor Lee. "When we pull up the finger from the touchscreen, it will end up at different height every time. Its down-press cannot be as accurately controlled in time as with a push-button where the finger can rest on top of the key cap."
Three scientific articles, "Neuromechanics of a Button Press", "Impact activation improves rapid button pressing", and "Moving target selection: A cue integration model", will be presented at the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Montréal, Canada, in April 2018.
2018.03.22 View 8188
A New Theory Improves Button Designs
Pressing a button appears effortless. People easily dismisses how challenging it is. Researchers at KAIST and Aalto University in Finland, created detailed simulations of button-pressing with the goal of producing human-like presses.
The researchers argue that the key capability of the brain is a probabilistic model. The brain learns a model that allows it to predict a suitable motor command for a button. If a press fails, it can pick a very good alternative and try it out. "Without this ability, we would have to learn to use every button like it was new," tells Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST.
After successfully activating the button, the brain can tune the motor command to be more precise, use less energy and to avoid stress or pain. "These factors together, with practice, produce the fast, minimum-effort, elegant touch people are able to perform."
The brain uses probabilistic models also to extract information optimally from the sensations that arise when the finger moves and its tip touches the button. It "enriches" the ephemeral sensations optimally based on prior experience to estimate the time the button was impacted. For example, tactile sensation from the tip of the finger a better predictor for button activation than proprioception (angle position) and visual feedback.
Best performance is achieved when all sensations are considered together. To adapt, the brain must fuse their information using prior experiences. Professor Lee explains, "We believe that the brain picks up these skills over repeated button pressings that start already as a child. What appears easy for us now has been acquired over years."
The research was triggered by admiration of our remarkable capability to adapt button-pressing. Professor Antti Oulasvirta at Aalto University said, "We push a button on a remote controller differently than a piano key. The press of a skilled user is surprisingly elegant when looked at terms of timing, reliability, and energy use. We successfully press buttons without ever knowing the inner workings of a button. It is essentially a black box to our motor system. On the other hand, we also fail to activate buttons, and some buttons are known to be worse than others."
Previous research has shown that touch buttons are worse than push-buttons, but there has not been adequate theoretical explanation.
"In the past, there has been very little attention to buttons, although we use them all the time" says Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University. The new theory and simulations can be used to design better buttons.
"One exciting implication of the theory is that activating the button at the moment when the sensation is strongest will help users better rhythm their keypresses."
To test this hypothesis, the researchers created a new method for changing the way buttons are activated. The technique is called Impact Activation. Instead of activating the button at first contact, it activates it when the button cap or finger hits the floor with maximum impact.
The technique was 94% better in rapid tapping than the regular activation method for a push-button (Cherry MX switch) and 37% than a regular touchscreen button using a capacitive touch sensor. The technique can be easily deployed in touchscreens. However, regular physical keyboards do not offer the required sensing capability, although special products exist (e.g., the Wooting keyboard) on which it can be implemented.
The simulations shed new light on what happens during a button press. One problem the brain must overcome is that muscles do not activate as perfectly as we will, but every press is slightly different. Moreover, a button press is very fast, occurring within 100 milliseconds, and is too fast for correcting movement. The key to understanding button-pressing is therefore to understand how the brain adapts based on the limited sensations that are the residue of the brief press event.
The researchers also used the simulation to explain differences among physical and touchscreen-based button types. Both physical and touch buttons provide clear tactile signals from the impact of the tip with the button floor. However, with the physical button this signal is more pronounced and longer.
"Where the two button types also differ is the starting height of the finger, and this makes a difference," explains Professor Lee. "When we pull up the finger from the touchscreen, it will end up at different height every time. Its down-press cannot be as accurately controlled in time as with a push-button where the finger can rest on top of the key cap."
Three scientific articles, "Neuromechanics of a Button Press", "Impact activation improves rapid button pressing", and "Moving target selection: A cue integration model", will be presented at the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Montréal, Canada, in April 2018.
2018.03.22 View 8188