School+of+Computing
-
 SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6817
SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6817 -
 Startup Elice Donates 300 Million KRW to School of Computing
Elice hopes to create a virtuous circle that bridges the educational gap
Elice, a student startup from the School of Computing has committed to donate 300 million KRW to KAIST. Jae-Won Kim, CEO of the coding education company, established the startup with his colleagues in 2015. Since then, more than 100 companies, including 17 of Korea’s top 20 companies such as SK and LG have used Elice' digital coding platform to educate employees. More than 200,000 employees have completed the online training with completion rates over 80%.
Kim said during the donation ceremony that he hopes to fund the renovation of the School of Computing building and that he will continue to work on expanding platforms that will help make communication between educators and students more interactive. He explained, “We are making this contribution to create a virtuous circle that bridges the educational gap and improves the quality of education."
President Kwang Hyung Lee was pleased to welcome the student startup’s donation, saying, "Software talent is one of the most precious resources we should foster for the nation’s future. I am thrilled to see that a startup that was founded here on the KAIST campus has grown into a great company that provides excellent coding education for our society.”
Professor Alice Oh, who was the advisor for Kim and his colleagues when they launched the startup, joined the ceremony along with the founding members from KAIST including CPO Su-In Kim, CTO Chong-Kuk Park, and team leader Chang-Hyun Lee.
2021.12.13 View 6004
Startup Elice Donates 300 Million KRW to School of Computing
Elice hopes to create a virtuous circle that bridges the educational gap
Elice, a student startup from the School of Computing has committed to donate 300 million KRW to KAIST. Jae-Won Kim, CEO of the coding education company, established the startup with his colleagues in 2015. Since then, more than 100 companies, including 17 of Korea’s top 20 companies such as SK and LG have used Elice' digital coding platform to educate employees. More than 200,000 employees have completed the online training with completion rates over 80%.
Kim said during the donation ceremony that he hopes to fund the renovation of the School of Computing building and that he will continue to work on expanding platforms that will help make communication between educators and students more interactive. He explained, “We are making this contribution to create a virtuous circle that bridges the educational gap and improves the quality of education."
President Kwang Hyung Lee was pleased to welcome the student startup’s donation, saying, "Software talent is one of the most precious resources we should foster for the nation’s future. I am thrilled to see that a startup that was founded here on the KAIST campus has grown into a great company that provides excellent coding education for our society.”
Professor Alice Oh, who was the advisor for Kim and his colleagues when they launched the startup, joined the ceremony along with the founding members from KAIST including CPO Su-In Kim, CTO Chong-Kuk Park, and team leader Chang-Hyun Lee.
2021.12.13 View 6004 -
 ‘Urban Green Space Affects Citizens’ Happiness’
Study finds the relationship between green space, the economy, and happiness
A recent study revealed that as a city becomes more economically developed, its citizens’ happiness becomes more directly related to the area of urban green space.
A joint research project by Professor Meeyoung Cha of the School of Computing and her collaborators studied the relationship between green space and citizen happiness by analyzing big data from satellite images of 60 different countries.
Urban green space, including parks, gardens, and riversides not only provides aesthetic pleasure, but also positively affects our health by promoting physical activity and social interactions. Most of the previous research attempting to verify the correlation between urban green space and citizen happiness was based on few developed countries. Therefore, it was difficult to identify whether the positive effects of green space are global, or merely phenomena that depended on the economic state of the country. There have also been limitations in data collection, as it is difficult to visit each location or carry out investigations on a large scale based on aerial photographs.
The research team used data collected by Sentinel-2, a high-resolution satellite operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) to investigate 90 green spaces from 60 different countries around the world. The subjects of analysis were cities with the highest population densities (cities that contain at least 10% of the national population), and the images were obtained during the summer of each region for clarity. Images from the northern hemisphere were obtained between June and September of 2018, and those from the southern hemisphere were obtained between December of 2017 and February of 2018.
The areas of urban green space were then quantified and crossed with data from the World Happiness Report and GDP by country reported by the United Nations in 2018. Using these data, the relationships between green space, the economy, and citizen happiness were analyzed.
The results showed that in all cities, citizen happiness was positively correlated with the area of urban green space regardless of the country’s economic state. However, out of the 60 countries studied, the happiness index of the bottom 30 by GDP showed a stronger correlation with economic growth. In countries whose gross national income (GDP per capita) was higher than 38,000 USD, the area of green space acted as a more important factor affecting happiness than economic growth. Data from Seoul was analyzed to represent South Korea, and showed an increased happiness index with increased green areas compared to the past.
The authors point out their work has several policy-level implications. First, public green space should be made accessible to urban dwellers to enhance social support. If public safety in urban parks is not guaranteed, its positive role in social support and happiness may diminish. Also, the meaning of public safety may change; for example, ensuring biological safety will be a priority in keeping urban parks accessible during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Second, urban planning for public green space is needed for both developed and developing countries. As it is challenging or nearly impossible to secure land for green space after the area is developed, urban planning for parks and green space should be considered in developing economies where new cities and suburban areas are rapidly expanding.
Third, recent climate changes can present substantial difficulty in sustaining urban green space. Extreme events such as wildfires, floods, droughts, and cold waves could endanger urban forests while global warming could conversely accelerate tree growth in cities due to the urban heat island effect. Thus, more attention must be paid to predict climate changes and discovering their impact on the maintenance of urban green space.
“There has recently been an increase in the number of studies using big data from satellite images to solve social conundrums,” said Professor Cha. “The tool developed for this investigation can also be used to quantify the area of aquatic environments like lakes and the seaside, and it will now be possible to analyze the relationship between citizen happiness and aquatic environments in future studies,” she added.
Professor Woo Sung Jung from POSTECH and Professor Donghee Wohn from the New Jersey Institute of Technology also joined this research. It was reported in the online issue of EPJ Data Science on May 30.
-PublicationOh-Hyun Kwon, Inho Hong, Jeasurk Yang, Donghee Y. Wohn, Woo-Sung Jung, andMeeyoung Cha, 2021. Urban green space and happiness in developed countries. EPJ Data Science. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-021-00278-7
-ProfileProfessor Meeyoung ChaData Science Labhttps://ds.ibs.re.kr/
School of Computing
KAIST
2021.06.21 View 13552
‘Urban Green Space Affects Citizens’ Happiness’
Study finds the relationship between green space, the economy, and happiness
A recent study revealed that as a city becomes more economically developed, its citizens’ happiness becomes more directly related to the area of urban green space.
A joint research project by Professor Meeyoung Cha of the School of Computing and her collaborators studied the relationship between green space and citizen happiness by analyzing big data from satellite images of 60 different countries.
Urban green space, including parks, gardens, and riversides not only provides aesthetic pleasure, but also positively affects our health by promoting physical activity and social interactions. Most of the previous research attempting to verify the correlation between urban green space and citizen happiness was based on few developed countries. Therefore, it was difficult to identify whether the positive effects of green space are global, or merely phenomena that depended on the economic state of the country. There have also been limitations in data collection, as it is difficult to visit each location or carry out investigations on a large scale based on aerial photographs.
The research team used data collected by Sentinel-2, a high-resolution satellite operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) to investigate 90 green spaces from 60 different countries around the world. The subjects of analysis were cities with the highest population densities (cities that contain at least 10% of the national population), and the images were obtained during the summer of each region for clarity. Images from the northern hemisphere were obtained between June and September of 2018, and those from the southern hemisphere were obtained between December of 2017 and February of 2018.
The areas of urban green space were then quantified and crossed with data from the World Happiness Report and GDP by country reported by the United Nations in 2018. Using these data, the relationships between green space, the economy, and citizen happiness were analyzed.
The results showed that in all cities, citizen happiness was positively correlated with the area of urban green space regardless of the country’s economic state. However, out of the 60 countries studied, the happiness index of the bottom 30 by GDP showed a stronger correlation with economic growth. In countries whose gross national income (GDP per capita) was higher than 38,000 USD, the area of green space acted as a more important factor affecting happiness than economic growth. Data from Seoul was analyzed to represent South Korea, and showed an increased happiness index with increased green areas compared to the past.
The authors point out their work has several policy-level implications. First, public green space should be made accessible to urban dwellers to enhance social support. If public safety in urban parks is not guaranteed, its positive role in social support and happiness may diminish. Also, the meaning of public safety may change; for example, ensuring biological safety will be a priority in keeping urban parks accessible during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Second, urban planning for public green space is needed for both developed and developing countries. As it is challenging or nearly impossible to secure land for green space after the area is developed, urban planning for parks and green space should be considered in developing economies where new cities and suburban areas are rapidly expanding.
Third, recent climate changes can present substantial difficulty in sustaining urban green space. Extreme events such as wildfires, floods, droughts, and cold waves could endanger urban forests while global warming could conversely accelerate tree growth in cities due to the urban heat island effect. Thus, more attention must be paid to predict climate changes and discovering their impact on the maintenance of urban green space.
“There has recently been an increase in the number of studies using big data from satellite images to solve social conundrums,” said Professor Cha. “The tool developed for this investigation can also be used to quantify the area of aquatic environments like lakes and the seaside, and it will now be possible to analyze the relationship between citizen happiness and aquatic environments in future studies,” she added.
Professor Woo Sung Jung from POSTECH and Professor Donghee Wohn from the New Jersey Institute of Technology also joined this research. It was reported in the online issue of EPJ Data Science on May 30.
-PublicationOh-Hyun Kwon, Inho Hong, Jeasurk Yang, Donghee Y. Wohn, Woo-Sung Jung, andMeeyoung Cha, 2021. Urban green space and happiness in developed countries. EPJ Data Science. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-021-00278-7
-ProfileProfessor Meeyoung ChaData Science Labhttps://ds.ibs.re.kr/
School of Computing
KAIST
2021.06.21 View 13552 -
 Professor Kyu-Young Whang Donates Toward the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building
Distinguished Professor Kyu-Young Whang from the School of Computing made a gift of 100 million KRW toward the construction of the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building during a ceremony on November 3 at the Daejeon campus. "As a member of the first class of KAIST, I feel very delighted to play a part in the fundraising campaign for the 50th anniversary celebration. This is also a token of appreciation to my alma mater and I look forward to alumni and the KAIST community joining this campaign," said Professor Emeritus Whang. KAIST will name the Kyu-Young Whang and Jonghae Song Christian Seminar Room at the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building. The ground will be broken in 2022 for construction of the building.
2020.11.04 View 7522
Professor Kyu-Young Whang Donates Toward the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building
Distinguished Professor Kyu-Young Whang from the School of Computing made a gift of 100 million KRW toward the construction of the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building during a ceremony on November 3 at the Daejeon campus. "As a member of the first class of KAIST, I feel very delighted to play a part in the fundraising campaign for the 50th anniversary celebration. This is also a token of appreciation to my alma mater and I look forward to alumni and the KAIST community joining this campaign," said Professor Emeritus Whang. KAIST will name the Kyu-Young Whang and Jonghae Song Christian Seminar Room at the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building. The ground will be broken in 2022 for construction of the building.
2020.11.04 View 7522 -
 A Global Campaign of ‘Facts before Rumors’ on COVID-19 Launched
- A KAIST data scientist group responds to facts and rumors on COVID-19 for global awareness of the pandemic. -
Like the novel coronavirus, rumors have no borders. The world is fighting to contain the pandemic, but we also have to deal with the appalling spread of an infodemic that is as contagious as the virus. This infodemic, a pandemic of false information, is bringing chaos and extreme fear to the general public.
Professor Meeyoung Cha’s group at the School of Computing started a global campaign called ‘Facts before Rumors,’ to prevent the spread of false information from crossing borders. She explained, “We saw many rumors that had already been fact-checked long before in China and South Korea now begin to circulate in other countries, sometimes leading to detrimental results. We launched an official campaign, Facts before Rumors, to deliver COVID-19-related facts to countries where the number of cases is now increasing.” She released the first set of facts on March 26 via her Twitter account @nekozzang.
Professor Cha, a data scientist who has focused on detecting global fake news, is now part of the COVID-19 AI Task Force at the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST. She is also leading the Data Science Group at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) as Chief Investigator.
Her research group worked in collaboration with the College of Nursing at Ewha Woman’s University to identify 15 claims about COVID-19 that circulated on social networks (SNS) and among the general public. The team fact-checked these claims based on information from the WHO and CDCs of Korea and the US. The research group is now working on translating the list of claims into Portuguese, Spanish, Persian, Chinese, Amharic, Hindi, and Vietnamese. Delivering facts before rumors, the team says, will help contain the disease and prevent any harm caused by misinformation.
The pandemic, which spread in China and South Korea before arriving in Europe and the US, is now moving into South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. “We would like to play a part in preventing the further spread of the disease with the provision of only scientifically vetted, truthful facts,” said the team.
For this campaign, Professor Cha’s team investigated more than 200 rumored claims on COVID-19 in China during the early days of the pandemic. These claims spread in different levels: while some were only relevant locally or in larger regions of China, others propagated in Asia and are now spreading to countries that are currently most affected by the disease.
For example, the false claim which publicized that ‘Fireworks can help tame the virus in the air’ only spread in China. Other claims such as ‘Eating garlic helps people overcome the disease’ or ‘Gargling with salt water prevents the contraction of the disease,’ spread around the world even after being proved groundless.
The team noted, however, that the times at which these claims propagate are different from one country to another. “This opens up an opportunity to debunk rumors in some countries, even before they start to emerge,” said Professor Cha.
Kun-Woo Kim, a master’s candidate in the Department of Industrial Design who joined this campaign and designed the Facts before Rumors chart also expressed his hope that this campaign will help reduce the number of victims. He added, “I am very grateful to our scientists who quickly responded to the Fact Check in these challenging times.”
2020.03.27 View 14436
A Global Campaign of ‘Facts before Rumors’ on COVID-19 Launched
- A KAIST data scientist group responds to facts and rumors on COVID-19 for global awareness of the pandemic. -
Like the novel coronavirus, rumors have no borders. The world is fighting to contain the pandemic, but we also have to deal with the appalling spread of an infodemic that is as contagious as the virus. This infodemic, a pandemic of false information, is bringing chaos and extreme fear to the general public.
Professor Meeyoung Cha’s group at the School of Computing started a global campaign called ‘Facts before Rumors,’ to prevent the spread of false information from crossing borders. She explained, “We saw many rumors that had already been fact-checked long before in China and South Korea now begin to circulate in other countries, sometimes leading to detrimental results. We launched an official campaign, Facts before Rumors, to deliver COVID-19-related facts to countries where the number of cases is now increasing.” She released the first set of facts on March 26 via her Twitter account @nekozzang.
Professor Cha, a data scientist who has focused on detecting global fake news, is now part of the COVID-19 AI Task Force at the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST. She is also leading the Data Science Group at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) as Chief Investigator.
Her research group worked in collaboration with the College of Nursing at Ewha Woman’s University to identify 15 claims about COVID-19 that circulated on social networks (SNS) and among the general public. The team fact-checked these claims based on information from the WHO and CDCs of Korea and the US. The research group is now working on translating the list of claims into Portuguese, Spanish, Persian, Chinese, Amharic, Hindi, and Vietnamese. Delivering facts before rumors, the team says, will help contain the disease and prevent any harm caused by misinformation.
The pandemic, which spread in China and South Korea before arriving in Europe and the US, is now moving into South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. “We would like to play a part in preventing the further spread of the disease with the provision of only scientifically vetted, truthful facts,” said the team.
For this campaign, Professor Cha’s team investigated more than 200 rumored claims on COVID-19 in China during the early days of the pandemic. These claims spread in different levels: while some were only relevant locally or in larger regions of China, others propagated in Asia and are now spreading to countries that are currently most affected by the disease.
For example, the false claim which publicized that ‘Fireworks can help tame the virus in the air’ only spread in China. Other claims such as ‘Eating garlic helps people overcome the disease’ or ‘Gargling with salt water prevents the contraction of the disease,’ spread around the world even after being proved groundless.
The team noted, however, that the times at which these claims propagate are different from one country to another. “This opens up an opportunity to debunk rumors in some countries, even before they start to emerge,” said Professor Cha.
Kun-Woo Kim, a master’s candidate in the Department of Industrial Design who joined this campaign and designed the Facts before Rumors chart also expressed his hope that this campaign will help reduce the number of victims. He added, “I am very grateful to our scientists who quickly responded to the Fact Check in these challenging times.”
2020.03.27 View 14436 -
 Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 41648
Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 41648 -
 Sound-based Touch Input Technology for Smart Tables and Mirrors
(from left: MS candidate Anish Byanjankar, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim and Professor Insik Shin)
Time passes so quickly, especially in the morning. Your hands are so busy brushing your teeth and checking the weather on your smartphone. You might wish that your mirror could turn into a touch screen and free up your hands. That wish can be achieved very soon. A KAIST team has developed a smartphone-based touch sound localization technology to facilitate ubiquitous interactions, turning objects like furniture and mirrors into touch input tools.
This technology analyzes touch sounds generated from a user’s touch on a surface and identifies the location of the touch input. For instance, users can turn surrounding tables or walls into virtual keyboards and write lengthy e-mails much more conveniently by using only the built-in microphone on their smartphones or tablets. Moreover, family members can enjoy a virtual chessboard or enjoy board games on their dining tables.
Additionally, traditional smart devices such as smart TVs or mirrors, which only provide simple screen display functions, can play a smarter role by adding touch input function support (see the image below).
Figure 1.Examples of using touch input technology: By using only smartphone, you can use surrounding objects as a touch screen anytime and anywhere.
The most important aspect of enabling the sound-based touch input method is to identify the location of touch inputs in a precise manner (within about 1cm error). However, it is challenging to meet these requirements, mainly because this technology can be used in diverse and dynamically changing environments. Users may use objects like desks, walls, or mirrors as touch input tools and the surrounding environments (e.g. location of nearby objects or ambient noise level) can be varied. These environmental changes can affect the characteristics of touch sounds.
To address this challenge, Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing and his team focused on analyzing the fundamental properties of touch sounds, especially how they are transmitted through solid surfaces.
On solid surfaces, sound experiences a dispersion phenomenon that makes different frequency components travel at different speeds. Based on this phenomenon, the team observed that the arrival time difference (TDoA) between frequency components increases in proportion to the sound transmission distance, and this linear relationship is not affected by the variations of surround environments.
Based on these observations, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim proposed a novel sound-based touch input technology that records touch sounds transmitted through solid surfaces, then conducts a simple calibration process to identify the relationship between TDoA and the sound transmission distance, finally achieving accurate touch input localization.
The accuracy of the proposed system was then measured. The average localization error was lower than about 0.4 cm on a 17-inch touch screen. Particularly, it provided a measurement error of less than 1cm, even with a variety of objects such as wooden desks, glass mirrors, and acrylic boards and when the position of nearby objects and noise levels changed dynamically. Experiments with practical users have also shown positive responses to all measurement factors, including user experience and accuracy.
Professor Shin said, “This is novel touch interface technology that allows a touch input system just by installing three to four microphones, so it can easily turn nearby objects into touch screens.”
The proposed system was presented at ACM SenSys, a top-tier conference in the field of mobile computing and sensing, and was selected as a best paper runner-up in November 2018.
(The demonstration video of the sound-based touch input technology)
2018.12.26 View 9974
Sound-based Touch Input Technology for Smart Tables and Mirrors
(from left: MS candidate Anish Byanjankar, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim and Professor Insik Shin)
Time passes so quickly, especially in the morning. Your hands are so busy brushing your teeth and checking the weather on your smartphone. You might wish that your mirror could turn into a touch screen and free up your hands. That wish can be achieved very soon. A KAIST team has developed a smartphone-based touch sound localization technology to facilitate ubiquitous interactions, turning objects like furniture and mirrors into touch input tools.
This technology analyzes touch sounds generated from a user’s touch on a surface and identifies the location of the touch input. For instance, users can turn surrounding tables or walls into virtual keyboards and write lengthy e-mails much more conveniently by using only the built-in microphone on their smartphones or tablets. Moreover, family members can enjoy a virtual chessboard or enjoy board games on their dining tables.
Additionally, traditional smart devices such as smart TVs or mirrors, which only provide simple screen display functions, can play a smarter role by adding touch input function support (see the image below).
Figure 1.Examples of using touch input technology: By using only smartphone, you can use surrounding objects as a touch screen anytime and anywhere.
The most important aspect of enabling the sound-based touch input method is to identify the location of touch inputs in a precise manner (within about 1cm error). However, it is challenging to meet these requirements, mainly because this technology can be used in diverse and dynamically changing environments. Users may use objects like desks, walls, or mirrors as touch input tools and the surrounding environments (e.g. location of nearby objects or ambient noise level) can be varied. These environmental changes can affect the characteristics of touch sounds.
To address this challenge, Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing and his team focused on analyzing the fundamental properties of touch sounds, especially how they are transmitted through solid surfaces.
On solid surfaces, sound experiences a dispersion phenomenon that makes different frequency components travel at different speeds. Based on this phenomenon, the team observed that the arrival time difference (TDoA) between frequency components increases in proportion to the sound transmission distance, and this linear relationship is not affected by the variations of surround environments.
Based on these observations, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim proposed a novel sound-based touch input technology that records touch sounds transmitted through solid surfaces, then conducts a simple calibration process to identify the relationship between TDoA and the sound transmission distance, finally achieving accurate touch input localization.
The accuracy of the proposed system was then measured. The average localization error was lower than about 0.4 cm on a 17-inch touch screen. Particularly, it provided a measurement error of less than 1cm, even with a variety of objects such as wooden desks, glass mirrors, and acrylic boards and when the position of nearby objects and noise levels changed dynamically. Experiments with practical users have also shown positive responses to all measurement factors, including user experience and accuracy.
Professor Shin said, “This is novel touch interface technology that allows a touch input system just by installing three to four microphones, so it can easily turn nearby objects into touch screens.”
The proposed system was presented at ACM SenSys, a top-tier conference in the field of mobile computing and sensing, and was selected as a best paper runner-up in November 2018.
(The demonstration video of the sound-based touch input technology)
2018.12.26 View 9974 -
 AI-based Digital Watermarking to Beat Fake News
(from left: PhD candidates Ji-Hyeon Kang, Seungmin Mun, Sangkeun Ji and Professor Heung-Kyu Lee)
The illegal use of images has been a prevalent issue along with the rise of distributing fake news, which all create social and economic problems. Here, a KAIST team succeeded in embedding and detecting digital watermarks based on deep neural learning artificial intelligence, which adaptively responds to a variety of attack types, such as removing watermarks and hacking. Their research shows that this technology reached a level of reliability for technology commercialization.
Conventional watermarking technologies show limitations in terms of practicality, technology scalability, and usefulness because they require a predetermined set of conditions, such as the attack type and intensity. They are designed and implemented in a way to satisfy specific conditions.
In addition to those limitations, the technology itself is vulnerable to security issues because upgraded hacking technologies are constantly emerging, such as watermark removal, copying, and substitution.
Professor Heung-Kyu Lee from the School of Computing and his team provided a web service that responds to new attacks through deep neural learning artificial intelligence. It also serves as a two-dimensional image watermarking technique based on neural networks with high security derived from the nonlinear characteristics of artificial neural networks. To protect images from varying viewpoints, the service offers a depth-image-based rendering (DIBR) three-dimensional image watermarking technique.
Lastly, they provided a stereoscopic three-dimensional (S3D) image watermarking technique that minimizes visual fatigue due to the embedded watermarks. Their two-dimensional image watermarking technology is the first of its kind to be based upon artificial neural works. It acquires robustness through educating the artificial neural networking on various attack scenarios.
At the same time, the team has greatly improved on existing security vulnerabilities by acquiring high security against watermark hacking through the deep structure of artificial neural networks. They have also developed a watermarking technique embedded whenever needed to provide proof during possible disagreements.
Users can upload their images to the web service and insert the watermarks. When necessary, they can detect the watermarks for proof in any dispute.
Moreover, this technology provides services, including simulation tools, watermark adjustment, and image quality comparisons before and after the watermark is embedded.
This study maximized the usefulness of watermarking technology by facilitating additional editing and demonstrating robustness against hacking.
Hence, this technology can be applied in a variety of contents for certification, authentication, distinction tracking, and copyrights. It can contribute to spurring the content industry and promoting a digital society by reducing the socio-economic losses caused by the use of various illegal image materials in the future.
Professor Lee said, “Disputes related to images are now beyond the conventional realm of copyrights. Recently, their interest has rapidly expanded due to the issues of authentication, certification, integrity inspection, and distribution tracking because of the fake video problem. We will lead digital watermarking research that can overcome the technical limitations of conventional watermarking techniques.”
This technology has only been conducted in labs thus far, but it is now open to the public after years of study. His team has been conducting a test run on the webpage (click).Moving forward from testing the technology under specific lab conditions, it will be applied to a real environment setting where constant changes pervade.
1. Figure. 2D image using the watermarking technique: a) original image b) watermark-embedded image c) signal from the embedded watermark
Figure 2. Result of watermark detection according to the password
Figure 3. Example of a center image using the DIBR 3D image watermarking technique: a) original image b) depth image c) watermark-embedded image d) signal from the embedded watermark
Figure 4. Example of using the S3D image watermarking technique: a) original left image b) original right image c) watermark-embedded left image d) watermark-embedded right image e) signal from the embedded watermark (left) f) signal from the embedded watermark (right)
2018.12.05 View 5648
AI-based Digital Watermarking to Beat Fake News
(from left: PhD candidates Ji-Hyeon Kang, Seungmin Mun, Sangkeun Ji and Professor Heung-Kyu Lee)
The illegal use of images has been a prevalent issue along with the rise of distributing fake news, which all create social and economic problems. Here, a KAIST team succeeded in embedding and detecting digital watermarks based on deep neural learning artificial intelligence, which adaptively responds to a variety of attack types, such as removing watermarks and hacking. Their research shows that this technology reached a level of reliability for technology commercialization.
Conventional watermarking technologies show limitations in terms of practicality, technology scalability, and usefulness because they require a predetermined set of conditions, such as the attack type and intensity. They are designed and implemented in a way to satisfy specific conditions.
In addition to those limitations, the technology itself is vulnerable to security issues because upgraded hacking technologies are constantly emerging, such as watermark removal, copying, and substitution.
Professor Heung-Kyu Lee from the School of Computing and his team provided a web service that responds to new attacks through deep neural learning artificial intelligence. It also serves as a two-dimensional image watermarking technique based on neural networks with high security derived from the nonlinear characteristics of artificial neural networks. To protect images from varying viewpoints, the service offers a depth-image-based rendering (DIBR) three-dimensional image watermarking technique.
Lastly, they provided a stereoscopic three-dimensional (S3D) image watermarking technique that minimizes visual fatigue due to the embedded watermarks. Their two-dimensional image watermarking technology is the first of its kind to be based upon artificial neural works. It acquires robustness through educating the artificial neural networking on various attack scenarios.
At the same time, the team has greatly improved on existing security vulnerabilities by acquiring high security against watermark hacking through the deep structure of artificial neural networks. They have also developed a watermarking technique embedded whenever needed to provide proof during possible disagreements.
Users can upload their images to the web service and insert the watermarks. When necessary, they can detect the watermarks for proof in any dispute.
Moreover, this technology provides services, including simulation tools, watermark adjustment, and image quality comparisons before and after the watermark is embedded.
This study maximized the usefulness of watermarking technology by facilitating additional editing and demonstrating robustness against hacking.
Hence, this technology can be applied in a variety of contents for certification, authentication, distinction tracking, and copyrights. It can contribute to spurring the content industry and promoting a digital society by reducing the socio-economic losses caused by the use of various illegal image materials in the future.
Professor Lee said, “Disputes related to images are now beyond the conventional realm of copyrights. Recently, their interest has rapidly expanded due to the issues of authentication, certification, integrity inspection, and distribution tracking because of the fake video problem. We will lead digital watermarking research that can overcome the technical limitations of conventional watermarking techniques.”
This technology has only been conducted in labs thus far, but it is now open to the public after years of study. His team has been conducting a test run on the webpage (click).Moving forward from testing the technology under specific lab conditions, it will be applied to a real environment setting where constant changes pervade.
1. Figure. 2D image using the watermarking technique: a) original image b) watermark-embedded image c) signal from the embedded watermark
Figure 2. Result of watermark detection according to the password
Figure 3. Example of a center image using the DIBR 3D image watermarking technique: a) original image b) depth image c) watermark-embedded image d) signal from the embedded watermark
Figure 4. Example of using the S3D image watermarking technique: a) original left image b) original right image c) watermark-embedded left image d) watermark-embedded right image e) signal from the embedded watermark (left) f) signal from the embedded watermark (right)
2018.12.05 View 5648 -
 Adding Smart to Science Museum
KAIST and the National Science Museum (NSM) created an Exhibition Research Center for Smart Science to launch exhibitions that integrate emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoTs), and artificial intelligence (AI).
There has been a great demand for a novel technology for better, user-oriented exhibition services. The NSM continuously faces the problem of not having enough professional guides. Additionally, there have been constant complaints about its current mobile application for exhibitions not being very effective.
To tackle these problems, the new center was founded, involving 11 institutes and universities. Sponsored by the National Research Foundation, it will oversee 15 projects in three areas: exhibition-based technology, exhibition operational technology, and exhibition content.
The group first aims to provide a location-based exhibition guide system service, which allows it to incorporate various technological services, such as AR/VR to visitors. An indoor locating system named KAILOS, which was developed by KAIST, will be applied to this service. They will also launch a mobile application service that provides audio-based exhibition guides.
To further cater to visitors’ needs, the group plans to apply a user-centered ecosystem, a living lab concept to create pleasant environment for visitors.
“Every year, hundred thousands of young people visit the National Science Museum. I believe that the exhibition guide system has to be innovative, using cutting-edge IT technology in order to help them cherish their dreams and inspirations through science,” Jeong Heoi Bae, President of Exhibition and Research Bureau of NSM, emphasized.
Professor Dong Soo Han from the School of Computing, who took the position of research head of the group, said, “We will systematically develop exhibition technology and contents for the science museum to create a platform for smart science museums. It will be the first time to provide an exhibition guide system that integrates AR/VR with an indoor location system.”
The center will first apply the new system to the NSM and then expand it to 167 science museums and other regional museums.
2018.09.04 View 10800
Adding Smart to Science Museum
KAIST and the National Science Museum (NSM) created an Exhibition Research Center for Smart Science to launch exhibitions that integrate emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoTs), and artificial intelligence (AI).
There has been a great demand for a novel technology for better, user-oriented exhibition services. The NSM continuously faces the problem of not having enough professional guides. Additionally, there have been constant complaints about its current mobile application for exhibitions not being very effective.
To tackle these problems, the new center was founded, involving 11 institutes and universities. Sponsored by the National Research Foundation, it will oversee 15 projects in three areas: exhibition-based technology, exhibition operational technology, and exhibition content.
The group first aims to provide a location-based exhibition guide system service, which allows it to incorporate various technological services, such as AR/VR to visitors. An indoor locating system named KAILOS, which was developed by KAIST, will be applied to this service. They will also launch a mobile application service that provides audio-based exhibition guides.
To further cater to visitors’ needs, the group plans to apply a user-centered ecosystem, a living lab concept to create pleasant environment for visitors.
“Every year, hundred thousands of young people visit the National Science Museum. I believe that the exhibition guide system has to be innovative, using cutting-edge IT technology in order to help them cherish their dreams and inspirations through science,” Jeong Heoi Bae, President of Exhibition and Research Bureau of NSM, emphasized.
Professor Dong Soo Han from the School of Computing, who took the position of research head of the group, said, “We will systematically develop exhibition technology and contents for the science museum to create a platform for smart science museums. It will be the first time to provide an exhibition guide system that integrates AR/VR with an indoor location system.”
The center will first apply the new system to the NSM and then expand it to 167 science museums and other regional museums.
2018.09.04 View 10800 -
 Multi-Device Mobile Platform for App Functionality Sharing
Case 1. Mr. Kim, an employee, logged on to his SNS account using a tablet PC at the airport while traveling overseas. However, a malicious virus was installed on the tablet PC and some photos posted on his SNS were deleted by someone else.
Case 2. Mr. and Mrs. Brown are busy contacting credit card and game companies, because his son, who likes games, purchased a million dollars worth of game items using his smartphone.
Case 3. Mr. Park, who enjoys games, bought a sensor-based racing game through his tablet PC. However, he could not enjoy the racing game on his tablet because it was not comfortable to tilt the device for game control.
The above cases are some of the various problems that can arise in modern society where diverse smart devices, including smartphones, exist. Recently, new technology has been developed to easily solve these problems. Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing has developed ‘Mobile Plus,’ which is a mobile platform that can share the functionalities of applications between smart devices.
This is a novel technology that allows applications to easily share their functionalities without needing any modifications. Smartphone users often use Facebook to log in to another SNS account like Instagram, or use a gallery app to post some photos on their SNS. These examples are possible, because the applications share their login and photo management functionalities.
The functionality sharing enables users to utilize smartphones in various and convenient ways and allows app developers to easily create applications. However, current mobile platforms such as Android or iOS only support functionality sharing within a single mobile device. It is burdensome for both developers and users to share functionalities across devices because developers would need to create more complex applications and users would need to install the applications on each device.
To address this problem, Professor Shin’s research team developed platform technology to support functionality sharing between devices. The main concept is using virtualization to give the illusion that the applications running on separate devices are on a single device. They succeeded in this virtualization by extending a RPC (Remote Procedure Call) scheme to multi-device environments.
This virtualization technology enables the existing applications to share their functionalities without needing any modifications, regardless of the type of applications. So users can now use them without additional purchases or updates. Mobile Plus can support hardware functionalities like cameras, microphones, and GPS as well as application functionalities such as logins, payments, and photo sharing. Its greatest advantage is its wide range of possible applications.
Professor Shin said, "Mobile Plus is expected to have great synergy with smart home and smart car technologies. It can provide novel user experiences (UXs) so that users can easily utilize various applications of smart home/vehicle infotainment systems by using a smartphone as their hub."
This research was published at ACM MobiSys, an international conference on mobile computing that was hosted in the United States on June 21.
Figure1. Users can securely log on to SNS accounts by using their personal devices
Figure 2. Parents can control impulse shopping of their children.
Figure 3. Users can enjoy games more and more by using the smartphone as a controller.
2017.08.09 View 10905
Multi-Device Mobile Platform for App Functionality Sharing
Case 1. Mr. Kim, an employee, logged on to his SNS account using a tablet PC at the airport while traveling overseas. However, a malicious virus was installed on the tablet PC and some photos posted on his SNS were deleted by someone else.
Case 2. Mr. and Mrs. Brown are busy contacting credit card and game companies, because his son, who likes games, purchased a million dollars worth of game items using his smartphone.
Case 3. Mr. Park, who enjoys games, bought a sensor-based racing game through his tablet PC. However, he could not enjoy the racing game on his tablet because it was not comfortable to tilt the device for game control.
The above cases are some of the various problems that can arise in modern society where diverse smart devices, including smartphones, exist. Recently, new technology has been developed to easily solve these problems. Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing has developed ‘Mobile Plus,’ which is a mobile platform that can share the functionalities of applications between smart devices.
This is a novel technology that allows applications to easily share their functionalities without needing any modifications. Smartphone users often use Facebook to log in to another SNS account like Instagram, or use a gallery app to post some photos on their SNS. These examples are possible, because the applications share their login and photo management functionalities.
The functionality sharing enables users to utilize smartphones in various and convenient ways and allows app developers to easily create applications. However, current mobile platforms such as Android or iOS only support functionality sharing within a single mobile device. It is burdensome for both developers and users to share functionalities across devices because developers would need to create more complex applications and users would need to install the applications on each device.
To address this problem, Professor Shin’s research team developed platform technology to support functionality sharing between devices. The main concept is using virtualization to give the illusion that the applications running on separate devices are on a single device. They succeeded in this virtualization by extending a RPC (Remote Procedure Call) scheme to multi-device environments.
This virtualization technology enables the existing applications to share their functionalities without needing any modifications, regardless of the type of applications. So users can now use them without additional purchases or updates. Mobile Plus can support hardware functionalities like cameras, microphones, and GPS as well as application functionalities such as logins, payments, and photo sharing. Its greatest advantage is its wide range of possible applications.
Professor Shin said, "Mobile Plus is expected to have great synergy with smart home and smart car technologies. It can provide novel user experiences (UXs) so that users can easily utilize various applications of smart home/vehicle infotainment systems by using a smartphone as their hub."
This research was published at ACM MobiSys, an international conference on mobile computing that was hosted in the United States on June 21.
Figure1. Users can securely log on to SNS accounts by using their personal devices
Figure 2. Parents can control impulse shopping of their children.
Figure 3. Users can enjoy games more and more by using the smartphone as a controller.
2017.08.09 View 10905 -
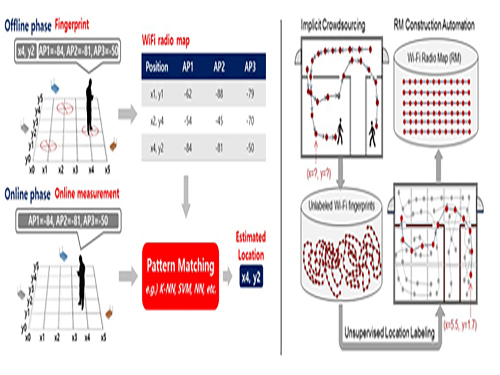 Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 10716
Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 10716 -
 KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8776
KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8776