research
< 20190725112532_34433_1854745074.jpg >
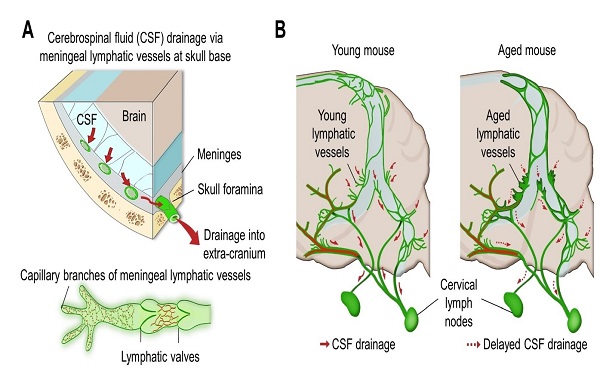
(Figure: Schematic images of location and features of meningeal lymphatic vessels and their changes associated with ageing.)
Just see what happens when your neighborhood’s waste disposal system is out of service. Not only do the piles of trash stink but they can indeed hinder the area’s normal functioning. That is also the case when the brain’s waste management is on the blink.
The buildup of toxic proteins in the brain causes a massive damage to the nerves, leading to cognitive dysfunction and increased probability of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Though the brain drains its waste via the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), little has been understood about an accurate route for the brain’s cleansing mechanism.
Medical scientists led by Professor Gou Young Koh at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering have reported the basal side of the skull as the major route, so called “hotspot” for CSF drainage.
They found that basal meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) function as the main plumbing pipes for CSF. They confirmed macromolecules in the CSF mainly runs through the basal mLVs. Notably, the team also revealed that the brain’s major drainage system, specifically basal mLVs are impaired with aging. Their findings have been reported in the journal Nature on July 24.
Throughout our body, excess fluids and waste products are removed from tissues via lymphatic vessels. It was only recently discovered that the brain also has a lymphatic drainage system. mLVs are supposed to carry waste from the brain tissue fluid and the CSF down the deep cervical lymph nodes for disposal. Still scientist are left with one perplexing question — where is the main exit for the CSF? Though mLVs in the upper part of the skull (dorsal meningeal lymphatic vessels) were reported as the brain’s clearance pathways in 2014, no substantial drainage mechanism was observed in that section.
“As a hidden exit for CSF, we looked into the mLVs trapped within complex structures at the base of the skull,” says Dr. Ji Hoon Ahn, the first author of this study. The researchers used several techniques to characterize the basal mLVs in detail. They used a genetically engineered lymphatic-reporter mouse model to visualize mLVs under a fluorescence microscope. By performing a careful examination of the mice skull, they found distinctive features of basal mLVs that make them suitable for CSF uptake and drainage. Just like typical functional lymphatic vessels, basal mLVs are found to have abundant lymphatic vessel branches with finger-like protrusions. Additionally, valves inside the basal mLVs allow the flow to go in one direction. In particular, they found that the basal mLVs are closely located to the CSF. Dr. Hyunsoo Cho, the first author of this study explains, “All up, it seemed a solid case that basal mLVs are the brain’s main clearance pathways.
The researchers verified such specialized morphologic characteristics of basal mLVs indeed facilitate the CSF uptake and drainage. Using CSF contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a rat model, they found that CSF is drained preferentially through the basal mLVs. They also utilized a lymphatic-reporter mouse model and discovered that fluorescence-tagged tracer injected into the brain itself or the CSF is cleared mainly through the basal mLVs. Jun-Hee Kim, the first author of this study notes, “We literally saw that the brain clearance mechanism utilizing basal outflow route to exit the skull.
It has long been suggested that CSF turnover and drainage declines with ageing. However, alteration of mLVs associated with ageing is poorly understood. In this study, the researchers observed changes of mLVs in young (3-month-old) and aged (24~27-months-old) mice. They found that the structure of the basal mLVs and their lymphatic valves in aged mice become severely flawed, thus hampering CSF clearance. The corresponding author of this study, Dr. Koh says, “By characterizing the precise route for fluids leaving the brain, this study improves our understanding on how waste is cleared from the brain. Our findings also provide further insights into the role of impaired CSF clearance in the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.”
Many current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease target abnormally accumulated proteins, such as beta-amyloid. By mapping out a precise route for the brain’s waste clearance system, this study may be able to help find ways to improve the brain’s cleansing function. Such breakthrough might become quite a sensational strategy for eliminating the buildup of aging-related toxic proteins. “It definitely warrants more extensive investigation of mLVs in patients with age-related neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical investigation,” adds Professor Koh.
-
research “One Experiment Is All It Takes”: KAIST Team Revolutionizes Drug Interaction Testing, Replacing 60,000 Studies
A groundbreaking new method developed by researchers at KAIST and Chungnam National University could drastically streamline drug interaction testing — replacing dozens of traditional experiments with just one. The research, led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences & IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group and Professor Sang Kyum Kim of Chungnam National University's College of Pharmacy, introduces a novel analysis technique called 50-BOA, published in Natu
2025-06-16 -
research KAIST Predicts Diseases by Early Detection of Aging Signals in Liver Tissue
- KAIST-KRIBB Develops ‘FiNi-seq’ Technology to Capture Characteristics of Fibrotic Microenvironments Accumulated in Liver Tissue and Dynamic Changes of Early Aging Cells - Elucidation of the Spatial Ecosystem of Aged Liver Tissue, where Reprogramming of Senescent Cells and Immune Exhaustion Progresses, at the Single-Cell Genome and Epigenome Levels < (From left) Professor Jong-Eun Park of KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), Dr. Chuna Kim of K
2025-06-12 -
research KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues. · The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA. · The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the
2025-06-10 -
research KAIST Develops Virtual Staining Technology for 3D Histopathology
Moving beyond traditional methods of observing thinly sliced and stained cancer tissues, a collaborative international research team led by KAIST has successfully developed a groundbreaking technology. This innovation uses advanced optical techniques combined with an artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithm to create realistic, virtually stained 3D images of cancer tissue without the need for serial sectioning nor staining. This breakthrough is anticipated to pave the way for next-g
2025-05-26 -
research KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic. KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor
2025-03-24