research

< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST >
A research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Dr. So Young Choi, Dr. In Jin Cho, Da-Hee Ahn, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported the 30-year history of metabolic engineering, highlighting examples of recent progress in the field and contributions to sustainability and health. Their paper “Metabolic engineering for sustainability and health” was published online in the 40th anniversary special issue of Trends in Biotechnology on January 10, 2023.
Metabolic engineering, a discipline of engineering that modifies cell phenotypes through molecular and genetic-level manipulations to improve cellular activities, has been studied since the early 1990s, and has progressed significantly over the past 30 years. In particular, metabolic engineering has enabled the engineering of microorganisms for the development of microbial cell factories capable of efficiently producing chemicals and materials as well as degrading recalcitrant contaminants.
This review article revisited how metabolic engineering has advanced over the past 30 years, from the advent of genetic engineering techniques such as recombinant DNA technologies to recent breakthroughs in systems metabolic engineering and data science aided by artificial intelligence. The research team highlighted momentous events and achievements in metabolic engineering, providing both trends and future directions in the field. Metabolic engineering’s contributions to bio-based sustainable chemicals and clean energy, health, and bioremediation were also reviewed. Finally, the research team shared their perspectives on the future challenges impacting metabolic engineering than must be overcome in order to achieve advancements in sustainability and health.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Replacing fossil resource-based chemical processes with bio-based sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels, and materials using metabolic engineering has become our essential task for the future. By looking back on the 30+ years of metabolic engineering, we aimed to highlight the contributions of metabolic engineering to achieve sustainability and good health.” He added, “Metabolic engineering will play an increasingly important role as a key solution to the climate crisis, environmental pollution, food and energy shortages, and health problems in aging societies.”
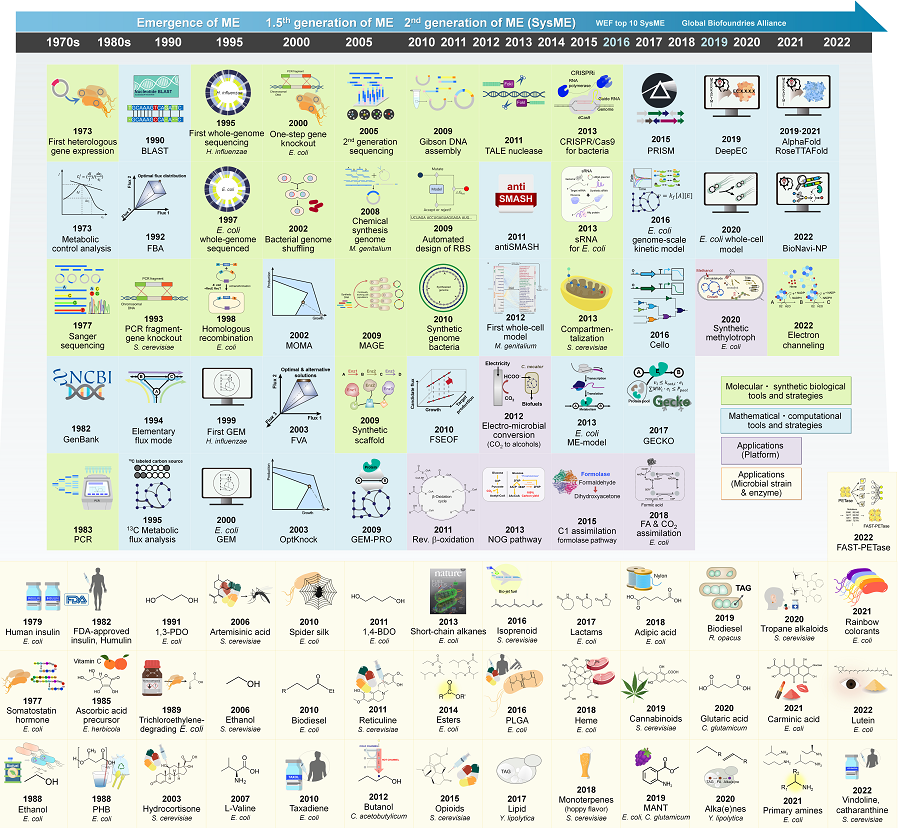
< Figure: Metabolic Engineering Timeline >
-
research KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum. On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioPro
2024-03-05 -
research KAIST presents strategies for environmentally friendly and sustainable polyamides production
- Provides current research trends in bio-based polyamide production - Research on bio-based polyamides production gains importance for achieving a carbon-neutral society Global industries focused on carbon neutrality, under the slogan "Net-Zero," are gaining increasing attention. In particular, research on microbial production of polymers, replacing traditional chemical methods with biological approaches, is actively progressing. Polyamides, represented by nylon, are linear polymers wide
2023-12-21 -
research KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons - Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develo
2023-11-09 -
research A KAIST Research Team Produces Eco-Friendly Nylon with Engineered Bacterium
With worsening climate change and environmental issues, in recent years, there has been increased interest in the eco-friendly production of polymers like nylon. On August 10, Dr. Taehee Han from a KAIST research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the successful development of a microbial strain that produces valerolactam, a monomer of nylon-5. Valerolactam is an important monomer that constitutes nylon-5 and
2023-08-24 -
research KAIST presents a microbial cell factory as a source of eco-friendly food and cosmetic coloring
Despite decades of global population growth, global food crisis seems to be at hand yet again because the food productivity is cut severely due to prolonged presence of abnormal weather from intensifying climate change and global food supply chain is deteriorated due to international conflicts such as wars exacerbating food shortages and nutritional inequality around the globe. At the same time, however, as awareness of the environment and sustainability rises, an increase in demand for more eco
2023-07-28