research
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections — the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger — are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
“Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases,” said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures.”
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
“Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity,” Professor Chung said. “Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain.”
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
“Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity,” Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group’s preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
“Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders,” Professor Chung said. “It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute basic research program.
Other contributors include Joon-Hyuk Lee and Se Young Lee, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); Ji-young Kim, Hyoeun Lee and Hyungju Park; Research Group for Neurovascular Unit, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI); Seulgi Noh, and Ji Young Mun, Research Group for Neural Circuit, KBRI. Kim, Noh and Park are also affiliated with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
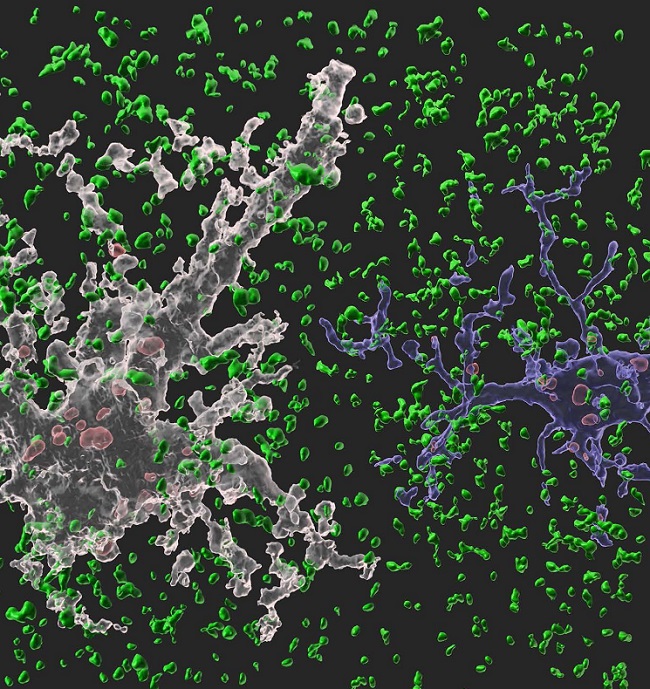
< Image: A 3-D animated image showing our synapse phagocytosis reporter in mouse hippocampus. Presynapses in green, astrocytes in white, and microglia in blue. Phagocytosed presynapses by glia were shown in red. >
-Profile
Professor Won-Suk Chung
Department of Biological Sciences
Gliabiology Lab (https://www.kaistglia.org/)
KAIST
-Publication
"Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis"
-
research Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now. A KAIST resea
2025-05-15 -
research Editing Parkinson's Disease – KAIST Makes World's First Discovery of an Inflammatory RNA Editing Enzyme through Co-work with UCL Researchers
< Professor Minee Choi of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (top left). Professor Sonia Gandhi (top right) and Professor Klenerman of the University College London (bottom right) > Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder in which the α-synuclein protein abnormally aggregates within brain cells, causing neuronal damage. Through international collaboration, researchers at KAIST have revealed that RNA editing plays a crucial role in regulating neuroi
2025-05-02 -
event KAIST to Collaborate with AT&C to Take Dominance over Dementia
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST Dean of the College of Natural Sciences Daesoo Kim, KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, AT&C Chairman Ki Tae Lee, AT&C CEO Jong-won Lee > KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 9th that it signed a memorandum of understanding for a comprehensive mutual cooperation with AT&C (CEO Jong-won Lee) at its Seoul Dogok Campus to expand research investment and industry-academia cooperation in preparation for the future cutting-edge digital
2025-01-09 -
event KAIST Opens Newly Expanded Center for Contemplative Research in Collaboration with Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 2nd that it would hold an opening ceremony for the expanded KAIST Center for Contemplative Research (Director Wan Doo Kim) at the Creativity Learning Building on its Daejeon campus on January 3 (Friday). Established in 2018 with the mission of "integrating meditation and science for the happiness and prosperity of humanity," the KAIST Center for Contemplative Research has been expanding its scope of research into the n
2025-01-03 -
research KAIST Unveils New Possibilities for Treating Intractable Brain Tumors
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, and Dr. Keun Bon Ku > Immunotherapy, which enhances the immune system's T cell response to eliminate cancer cells, has emerged as a key approach in cancer treatment. However, in the case of glioblastoma, an aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumor, numerous clinical trials have failed to confirm their efficacy. Korean researchers have recently analyzed the mechanisms that cause T cell exhaus
2024-11-15