research
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee demonstrates the transfer printing of a large number of micro-sized inorganic semiconductor chips via the selective modulation of micro-vacuum force.
MicroLEDs are a light source for next-generation displays that utilize inorganic LED chips with a size of less than 100 μm. MicroLEDs have attracted a great deal of attention due to their superior electrical/optical properties, reliability, and stability compared to conventional displays such as LCD, OLED, and QD. To commercialize microLEDs, transfer printing technology is essential for rearranging microLED dies from a growth substrate onto the final substrate with a desired layout and precise alignment. However, previous transfer methods still have many challenges such as the need for additional adhesives, misalignment, low transfer yield, and chip damage.
Professor Lee’s research team has developed a micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer printing (µVAST) technology to transfer a large number of microLED chips by adjusting the micro-vacuum suction force.
The key technology relies on a laser-induced etching (LIE) method for forming 20 μm-sized micro-hole arrays with a high aspect ratio on glass substrates at fabrication speed of up to 7,000 holes per second. The LIE-drilled glass is connected to the vacuum channels, controlling the micro-vacuum force at desired hole arrays to selectively pick up and release the microLEDs. The micro-vacuum assisted transfer printing accomplishes a higher adhesion switchability compared to previous transfer methods, enabling the assembly of micro-sized semiconductors with various heterogeneous materials, sizes, shapes, and thicknesses onto arbitrary substrates with high transfer yields.
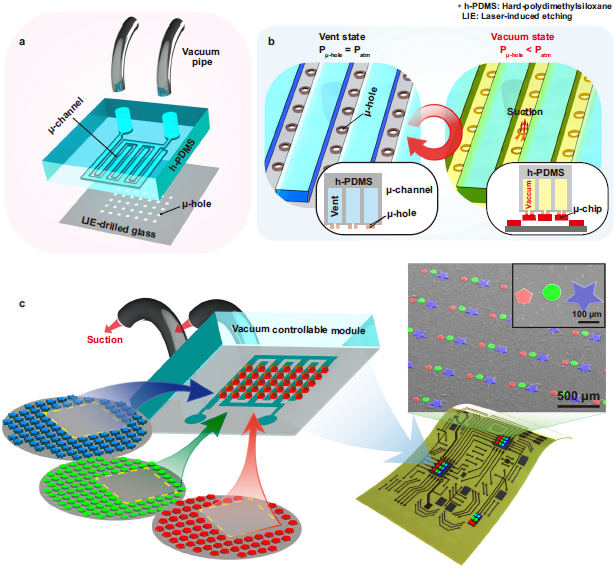
< Figure 01. Concept of micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer printing (μVAST). >
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The micro-vacuum assisted transfer provides an interesting tool for large-scale, selective integration of microscale high-performance inorganic semiconductors. Currently, we are investigating the transfer printing of commercial microLED chips with an ejector system for commercializing next-generation displays (Large screen TVs, flexible/stretchable devices) and wearable phototherapy patches.”
This result titled “Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force” was published in Nature Communications on November 26th, 2023. (DOI: 10.1038/S41467-023-43342-8)
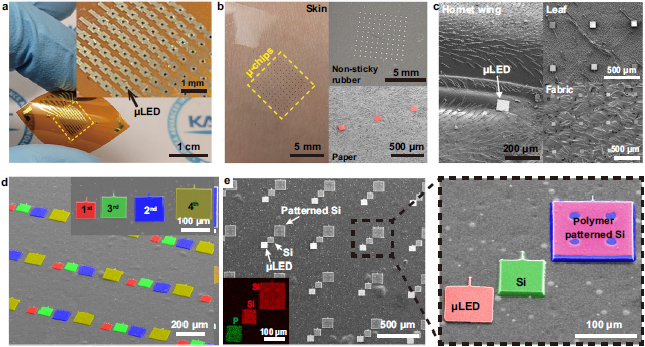
< Figure 02. Universal transfer printing of thin-film semiconductors via μVAST. >
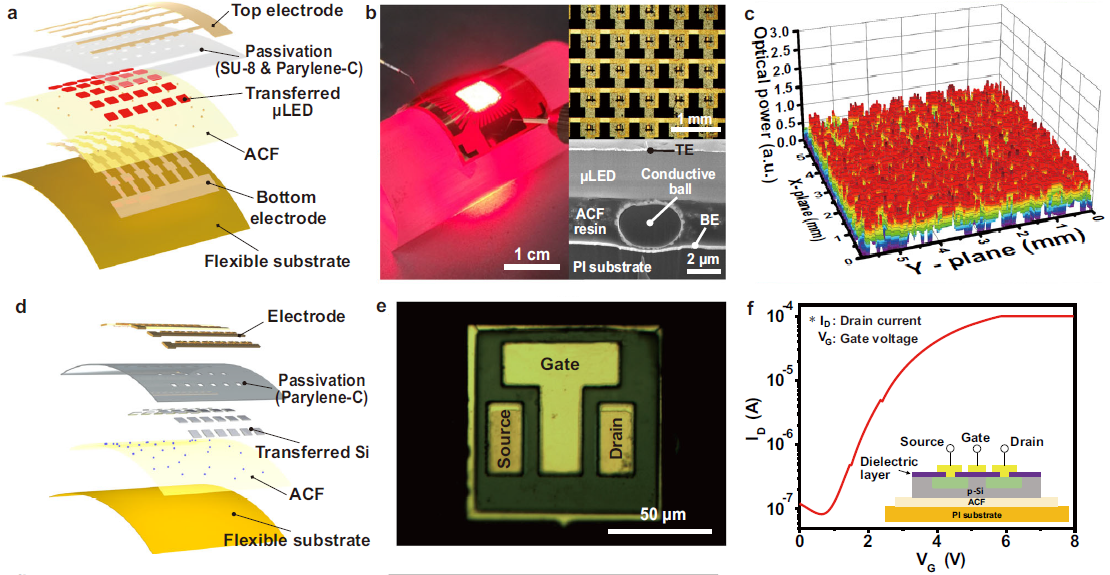
< Figure 03. Flexible devices fabricated by μVAST. >
Title: Entire process including LIE and µVAST
Vimeo link: https://vimeo.com/894430416?share=copy
-
research KAIST and Mainz Researchers Unveil 3D Magnon Control, Charting a New Course for Neuromorphic and Quantum Technologies
< Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics (left), Dr. Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany (right) > What if the magnon Hall effect, which processes information using magnons (spin waves) capable of current-free information transfer with magnets, could overcome its current limitation of being possible only on a 2D plane? If magnons could be utilized in 3D space, they would enable flexible design, including 3D circuits, and be applicable in various fields such as nex
2025-05-22 -
event KAIST School of Computing Unveils 'KRAFTON Building,' A Symbol of Collective Generosity
< (From the fifth from the left) Provost and Executive Vice President Gyun Min Lee, Auditor Eun Woo Lee, President Kwang-Hyung Lee, Dean of the School of Computing Seok-Young Ryu, former Krafton member and donor Woong-Hee Cho, Krafton Chairman Byung-Gyu Chang > KAIST announced on May 20th the completion of the expansion building for its School of Computing, the "KRAFTON Building." The project began in June 2021 with an ₩11 billion donation from KRAFTON and its employees, eventually gr
2025-05-21 -
event Life Springs at KAIST: A Tale of Two Special Campus Families
A Gift of Life on Teachers' Day: Baby Geese Born at KAIST Pond On Teachers' Day, a meaningful miracle of life arrived at the KAIST campus. A pair of geese gave birth to two goslings by the duck pond. < On Teachers' Day, a pair of geese and their goslings leisurely swim in the pond. > The baby goslings, covered in yellow down, began exploring the pond's edge, scurrying about, while their aunt geese steadfastly stood by. Their curious glances, watchful gazes, playful hops on water
2025-05-21 -
event <Big Coins> Exhibition: Where Coins and Imagination Collide - Held at SUPEX Hall, KAIST Seoul Campus
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 19th the opening of the solo exhibition, “Big Coins,” by photographer and media artist Hojun Ji (Adjunct Professor, Department of Industrial Design) at the SUPEX Hall in the Business School of the Seoul Campus. The exhibition will run from May 19th to the end of February of the following year. This exhibition at the KAIST Seoul Campus Business School presents artworks with an insightful perspective, inviting diverse interpretations
2025-05-20 -
research “For the First Time, We Shared a Meaningful Exchange”: KAIST Develops an AI App for Parents and Minimally Verbal Autistic Children Connect
• KAIST team up with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center Develop ‘AAcessTalk’, an AI-driven Communication Tool bridging the gap Between Children with Autism and their Parents • The project earned the prestigious Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025, the Premier International Conference in Human-Computer Interaction • Families share heartwarming stories of breakthrough communication and newfound understanding. < Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hw
2025-05-19