-
 Yang-Hann Kim named recipient of the Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education by the Acoustical Society of America
Courtesy of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA)
Press release issued by ASA on October 8, 2015:
Yang-Hann Kim named recipient of the Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education by the Acoustical Society of America
Melville (NY), 8 October 2015—Yang-Hann Kim, Professor at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology), Daejeon, has been named recipient of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA) Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education. The Rossing Prize is awarded to an individual who has made significant contributions toward furthering acoustics education through distinguished teaching, creation of educational materials, textbook writing and other activities. The Prize will be presented at the 170th meeting of the ASA on 4 November 2015 in Jacksonville, Florida.
“It is my great honor to receive the Rossing Prize, which has been given to outstanding scholar members of ASA since 2003. I never dreamed to be one of them.” said Kim. “I must express my deep respect and love to my friend Thomas Rossing: I have known him more than 20 years, always respect what he has done for teaching, writing books, and pioneering work in musical acoustics.”
Yang-Hann Kim is a Fellow of the Acoustical Society of America. He received a Ph.D. from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. His main research interests in acoustics began with “sound visualization” resulted in the development of the “sound camera” which makes any sound visible instantly. Then he moved to “sound manipulation.” Using his manipulation technology, one can move any sound in space and time, positioning sound, and can create a private sound zone. Sound Visualization and Manipulation, (Wiley, 2013), summarizes these two fields. Dr. Kim’s textbook, Sound Propagation: An Impedance Based Approach (John Wiley and Sons, 2010), is well acknowledged by the associated professional communities as one of best acoustics textbooks. Using his teaching experience at KAIST, he created a YouTube lecture on acoustics and vibration which is also available in MOOC (Massive Open Online Course). He has also presented lectures to over 500 engineers and technicians for the past 30 years.
###
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America—the world’s leading journal on acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The Society also holds two major scientific meetings per year. For more information about the Society visit our website, www.acousticalsociety.org.
2015.10.06 View 11133
Yang-Hann Kim named recipient of the Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education by the Acoustical Society of America
Courtesy of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA)
Press release issued by ASA on October 8, 2015:
Yang-Hann Kim named recipient of the Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education by the Acoustical Society of America
Melville (NY), 8 October 2015—Yang-Hann Kim, Professor at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology), Daejeon, has been named recipient of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA) Rossing Prize in Acoustics Education. The Rossing Prize is awarded to an individual who has made significant contributions toward furthering acoustics education through distinguished teaching, creation of educational materials, textbook writing and other activities. The Prize will be presented at the 170th meeting of the ASA on 4 November 2015 in Jacksonville, Florida.
“It is my great honor to receive the Rossing Prize, which has been given to outstanding scholar members of ASA since 2003. I never dreamed to be one of them.” said Kim. “I must express my deep respect and love to my friend Thomas Rossing: I have known him more than 20 years, always respect what he has done for teaching, writing books, and pioneering work in musical acoustics.”
Yang-Hann Kim is a Fellow of the Acoustical Society of America. He received a Ph.D. from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. His main research interests in acoustics began with “sound visualization” resulted in the development of the “sound camera” which makes any sound visible instantly. Then he moved to “sound manipulation.” Using his manipulation technology, one can move any sound in space and time, positioning sound, and can create a private sound zone. Sound Visualization and Manipulation, (Wiley, 2013), summarizes these two fields. Dr. Kim’s textbook, Sound Propagation: An Impedance Based Approach (John Wiley and Sons, 2010), is well acknowledged by the associated professional communities as one of best acoustics textbooks. Using his teaching experience at KAIST, he created a YouTube lecture on acoustics and vibration which is also available in MOOC (Massive Open Online Course). He has also presented lectures to over 500 engineers and technicians for the past 30 years.
###
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America—the world’s leading journal on acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The Society also holds two major scientific meetings per year. For more information about the Society visit our website, www.acousticalsociety.org.
2015.10.06 View 11133 -
 Professor Kyung-Won Chung Receives the 2015 Design Value Awards
The Design Management Institute (DMI) announced eleven winners of its 2015 Design Value Awards.
Professor Kyung-Won Chung of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST took one of the four First Place Design Value Awards. The award ceremony was held on September 28, 2015, at the Royal Sonesta Hotel in Boston.
DMI is an international organization that has actively advocated for the strategic value of design, sponsoring research, publishing academic papers, connecting members across disciplines and the globe, and sharing best design practices.
Commemorating its 40th anniversary, DMI created the inaugural Design Value Awards this year, which honors the contributions of design teams who have delivered significant value through design or design management practices.
There were four categories of the awards: first, second, and third prize, and Honorable Mention. The first place had four winners; both the second and third took two winners each. The honorable mention included three awardees.
The award noted Professor Chung's contributions to the development of design management theory and practices in Korea and his dedication to elevate KAIST’s industrial design department to one of the 30 leading design institutions in the world during his 30-year career at the university.
DMI also appointed Professor Chung a Life Fellow.
Professor Chung said,
“I am greatly honored to receive such a significant award, the equivalent of the Academy Awards in the field of design. I hope this award will encourage the further development of the Korean design industry to lead the global design community.”
He has served in various important positions in public and private organizations, including as the president of the Korea Institute of Design Promotion, Vice Mayor of Design for the City of Seoul, Advisor to the Design Division of Samsung Electronics, and a member of organizing committee of the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design.
2015.10.04 View 8441
Professor Kyung-Won Chung Receives the 2015 Design Value Awards
The Design Management Institute (DMI) announced eleven winners of its 2015 Design Value Awards.
Professor Kyung-Won Chung of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST took one of the four First Place Design Value Awards. The award ceremony was held on September 28, 2015, at the Royal Sonesta Hotel in Boston.
DMI is an international organization that has actively advocated for the strategic value of design, sponsoring research, publishing academic papers, connecting members across disciplines and the globe, and sharing best design practices.
Commemorating its 40th anniversary, DMI created the inaugural Design Value Awards this year, which honors the contributions of design teams who have delivered significant value through design or design management practices.
There were four categories of the awards: first, second, and third prize, and Honorable Mention. The first place had four winners; both the second and third took two winners each. The honorable mention included three awardees.
The award noted Professor Chung's contributions to the development of design management theory and practices in Korea and his dedication to elevate KAIST’s industrial design department to one of the 30 leading design institutions in the world during his 30-year career at the university.
DMI also appointed Professor Chung a Life Fellow.
Professor Chung said,
“I am greatly honored to receive such a significant award, the equivalent of the Academy Awards in the field of design. I hope this award will encourage the further development of the Korean design industry to lead the global design community.”
He has served in various important positions in public and private organizations, including as the president of the Korea Institute of Design Promotion, Vice Mayor of Design for the City of Seoul, Advisor to the Design Division of Samsung Electronics, and a member of organizing committee of the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design.
2015.10.04 View 8441 -
 Nikon Instruments Korea Donates a Fund to KAIST's Department of Biological Sciences
Representatives from Nikon Instruments Korea Co., Ltd., a producer of microscopes and measuring instruments, visited the KAIST campus on September 25, 2015, and donated USD 9,000 to the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
A small ceremony to mark the donation took place at the department’s conference room.
In the picture from left to right were Professor Won-Do Heo, Department Head Byung-Ha Oh, Professor Sangyong Jon, President Sam-Sup Jang of Korea Instech, and Director Ik-Soo Yoo of Nikon Instruments Korea.
The department announced that the fund would be used to build its new research center to house the state-of-the-art research equipment and tools for the development of new medicine.
2015.10.03 View 5925
Nikon Instruments Korea Donates a Fund to KAIST's Department of Biological Sciences
Representatives from Nikon Instruments Korea Co., Ltd., a producer of microscopes and measuring instruments, visited the KAIST campus on September 25, 2015, and donated USD 9,000 to the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
A small ceremony to mark the donation took place at the department’s conference room.
In the picture from left to right were Professor Won-Do Heo, Department Head Byung-Ha Oh, Professor Sangyong Jon, President Sam-Sup Jang of Korea Instech, and Director Ik-Soo Yoo of Nikon Instruments Korea.
The department announced that the fund would be used to build its new research center to house the state-of-the-art research equipment and tools for the development of new medicine.
2015.10.03 View 5925 -
 Professor Junehwa Song Appointed as the General Chair of the Organizing Committee of ACM SenSys
Professor Junehwa Song from the Schooling of Computing at KAIST has been appointed the general chair of the organizing committee of ACM SenSys—the American Computing Machine (ACM) Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems.
ACM SenSys held its first conference in 2003 to promote research on wireless sensor networks and embedded systems. Since then, it has expanded into an influential international conference especially with the increasing importance in sensor technologies. Recently the committee has expanded its field of interest to mobile sensors, the Internet of Things, smart device system, and security.
Professor Song is considered a world-renown researcher in mobile and ubiquitous computing system. He presented numerous research papers at various conferences organized by ACM. He is also a member of the editorial committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Transactions on Mobile Computing journal. For his achievements in the field and flair for coordinating and planning conferences, he is now the first Korean researcher to be appointed the chair of ACM SenSys.
Professor Song said that, as the chair, he would help discover new technology in and applications of networked, wireless sensors that would meet the demands of our modern society.
The 13th ACM SenSys will take place in Seoul—the first one to be held in Asia. The event will begin on November 1, 2015 and last four days. More information about this year’s event can be found at http://sensys.acm.org/2015/.
2015.10.02 View 8891
Professor Junehwa Song Appointed as the General Chair of the Organizing Committee of ACM SenSys
Professor Junehwa Song from the Schooling of Computing at KAIST has been appointed the general chair of the organizing committee of ACM SenSys—the American Computing Machine (ACM) Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems.
ACM SenSys held its first conference in 2003 to promote research on wireless sensor networks and embedded systems. Since then, it has expanded into an influential international conference especially with the increasing importance in sensor technologies. Recently the committee has expanded its field of interest to mobile sensors, the Internet of Things, smart device system, and security.
Professor Song is considered a world-renown researcher in mobile and ubiquitous computing system. He presented numerous research papers at various conferences organized by ACM. He is also a member of the editorial committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Transactions on Mobile Computing journal. For his achievements in the field and flair for coordinating and planning conferences, he is now the first Korean researcher to be appointed the chair of ACM SenSys.
Professor Song said that, as the chair, he would help discover new technology in and applications of networked, wireless sensors that would meet the demands of our modern society.
The 13th ACM SenSys will take place in Seoul—the first one to be held in Asia. The event will begin on November 1, 2015 and last four days. More information about this year’s event can be found at http://sensys.acm.org/2015/.
2015.10.02 View 8891 -
 The 2015 Rock Festival on Campus
The Undergraduate Student Association of KAIST hosted a fall rock festival on campus on October 3-4, 2015. The festival, which began in 2011, included students and local citizens who enjoyed rock music, arts and crafts, independent films, and flea market.
President Kang-In Kim of the student association said,
“We are pleased to offer a place where KAIST students and the local community come together and have fun. We will try to continue this event in the future, making it a tradition of KAIST.”
2015.10.01 View 3306
The 2015 Rock Festival on Campus
The Undergraduate Student Association of KAIST hosted a fall rock festival on campus on October 3-4, 2015. The festival, which began in 2011, included students and local citizens who enjoyed rock music, arts and crafts, independent films, and flea market.
President Kang-In Kim of the student association said,
“We are pleased to offer a place where KAIST students and the local community come together and have fun. We will try to continue this event in the future, making it a tradition of KAIST.”
2015.10.01 View 3306 -
 POSTECH-KAIST Science War
The 14th POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) and KAIST Science War took place at the KAIST campus in Daejeon on September 18-19, 2015.
Students from both universities participated in the two-day sports and science event.
The Science War has been held every September since 2002 to encourage interaction among students of the two schools. Following the rule that puts the hosting school second in the title, this year it is called the “POSTECH-KAIST War.”
The competition consists of seven events: hacking, a science quiz bowl and AI (artificial intelligence) for the science section, LOL (League of Legends) for the e-Sports section, and lastly, baseball, basketball and football for the sports section.
Of the seven events, the school that wins four or more events is declared the winner. Thus far, KAIST has had seven wins and five losses.
In addition, the cheering squads and clubs of both schools participated. They were KAIST’s ELKA, Twilight, Infinite, and MindFreak, as well as POSTECH’s Cheero, Bremen, Stiller, and P-Funk perform.
2015.09.30 View 5555
POSTECH-KAIST Science War
The 14th POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) and KAIST Science War took place at the KAIST campus in Daejeon on September 18-19, 2015.
Students from both universities participated in the two-day sports and science event.
The Science War has been held every September since 2002 to encourage interaction among students of the two schools. Following the rule that puts the hosting school second in the title, this year it is called the “POSTECH-KAIST War.”
The competition consists of seven events: hacking, a science quiz bowl and AI (artificial intelligence) for the science section, LOL (League of Legends) for the e-Sports section, and lastly, baseball, basketball and football for the sports section.
Of the seven events, the school that wins four or more events is declared the winner. Thus far, KAIST has had seven wins and five losses.
In addition, the cheering squads and clubs of both schools participated. They were KAIST’s ELKA, Twilight, Infinite, and MindFreak, as well as POSTECH’s Cheero, Bremen, Stiller, and P-Funk perform.
2015.09.30 View 5555 -
 Professor Sang-Min Bae receives the 2015 IDEA Awards
Professor Sang-min Bae of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST garnered one silver and two bronze awards from the 2015 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Along with iF Design Award and Red Dot Design Awards, the IDEA is regarded as one of the world’s most respected recognition in the field of design.
Trash to Bin (T2B), a silver winner in the category of Social Impact Design, is a trash bin made of 1.87 lb (0.85 kg) of discarded papers. Using one-hundred percent recycled paper pulp, each T2B costs under $5 for production. The bin can be fully waterproofed for at least six hours. While satisfying with the industry safety standards, this environmentally-friendly bin can be produced on a large scale using litter energy, but offering the exact same benefit of a general garbage can.
Roll-Di, one of the two bronze winners, is a direction indicator that tells which string of screen curtains should be pulled to make the curtain go up or down. As shown in the picture below, Roll-Di can be installed at the bottom of the string, and the “up and down” arrows show which side of the string needs to be pulled to achieve the desired position of the curtain. This simple, yet handy solution to the problem that people frequently make the mistake of pulling the wrong string provides users with greater convenience.
The other bronze winner is Printing Solar-cell, an organic cartridge module that prints solar-cells using a domestic, ink-jet printer. With Printing Solar-cell, users can design their own cell patterns and charge their electronics anywhere holding the printed solar-cell on a copy paper.
Professor Bae said, “I’ve always tried to design something that is useful for people in need. I consider the IDEA awards an encouragement to keep up with my work toward that goal.”
Trash to Bin
Roll-Di
Printing Solar-cell
2015.09.30 View 9608
Professor Sang-Min Bae receives the 2015 IDEA Awards
Professor Sang-min Bae of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST garnered one silver and two bronze awards from the 2015 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Along with iF Design Award and Red Dot Design Awards, the IDEA is regarded as one of the world’s most respected recognition in the field of design.
Trash to Bin (T2B), a silver winner in the category of Social Impact Design, is a trash bin made of 1.87 lb (0.85 kg) of discarded papers. Using one-hundred percent recycled paper pulp, each T2B costs under $5 for production. The bin can be fully waterproofed for at least six hours. While satisfying with the industry safety standards, this environmentally-friendly bin can be produced on a large scale using litter energy, but offering the exact same benefit of a general garbage can.
Roll-Di, one of the two bronze winners, is a direction indicator that tells which string of screen curtains should be pulled to make the curtain go up or down. As shown in the picture below, Roll-Di can be installed at the bottom of the string, and the “up and down” arrows show which side of the string needs to be pulled to achieve the desired position of the curtain. This simple, yet handy solution to the problem that people frequently make the mistake of pulling the wrong string provides users with greater convenience.
The other bronze winner is Printing Solar-cell, an organic cartridge module that prints solar-cells using a domestic, ink-jet printer. With Printing Solar-cell, users can design their own cell patterns and charge their electronics anywhere holding the printed solar-cell on a copy paper.
Professor Bae said, “I’ve always tried to design something that is useful for people in need. I consider the IDEA awards an encouragement to keep up with my work toward that goal.”
Trash to Bin
Roll-Di
Printing Solar-cell
2015.09.30 View 9608 -
 Brain Cognitive Engineering Experts from Korea and Abroad Gather at KAIST
The symposium presents recent and future research trends in brain and cognitive engineering.
KAIST hosted the Brain Cognitive Engineering Symposium on September 24, 2015, at the Dream Hall of the Chung Moon Soul building on campus. Around 100 experts in the field of neuroscience participated.
Organized by the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, the symposium celebrated the establishment of the Brain Cognitive Engineering Program at the university and examined the recent research trends in neuroscience.
Six neuroscience experts presented their research and held discussions.
Professor Paul M. Thompson of the University of Southern California (USC), a renowned scientist in neurology imaging genetics, gave a speech entitled “The ENIGMA Project: Mapping Disease and Genetic Effects on the Human Brain in 30,000 People Worldwide.”
Professor Jae-seung Jeong of KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Director Sung-Gi Kim of IBS Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research, Professor Sung-Hwan Lee of Korea University’s Department of Brain Engineering, Professor Cheil-Moon of DGIST’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Science, and Professor Jun-Tani of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering also participated in the symposium.
Participants discussed the most recent findings in the field of brain science such as the education and research trends of brain cognitive engineering, trends of the world’s brain integrated science, the prospects of brain cognitive engineering program, brain activities that induce blood flow and fMRI, activity production in the brain cortex model as well as the development of functional hierarchy for the motor visual perception, and the neurorobotics research.
Professor Jeong said that “this symposium is a place for examination of the most recent research findings in the field of neuroscience as well as for discussion of its education,”and that “it would be an important opportunity for learning research on brain’s basic mechanisms as well as its applications.”
2015.09.25 View 9868
Brain Cognitive Engineering Experts from Korea and Abroad Gather at KAIST
The symposium presents recent and future research trends in brain and cognitive engineering.
KAIST hosted the Brain Cognitive Engineering Symposium on September 24, 2015, at the Dream Hall of the Chung Moon Soul building on campus. Around 100 experts in the field of neuroscience participated.
Organized by the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, the symposium celebrated the establishment of the Brain Cognitive Engineering Program at the university and examined the recent research trends in neuroscience.
Six neuroscience experts presented their research and held discussions.
Professor Paul M. Thompson of the University of Southern California (USC), a renowned scientist in neurology imaging genetics, gave a speech entitled “The ENIGMA Project: Mapping Disease and Genetic Effects on the Human Brain in 30,000 People Worldwide.”
Professor Jae-seung Jeong of KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Director Sung-Gi Kim of IBS Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research, Professor Sung-Hwan Lee of Korea University’s Department of Brain Engineering, Professor Cheil-Moon of DGIST’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Science, and Professor Jun-Tani of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering also participated in the symposium.
Participants discussed the most recent findings in the field of brain science such as the education and research trends of brain cognitive engineering, trends of the world’s brain integrated science, the prospects of brain cognitive engineering program, brain activities that induce blood flow and fMRI, activity production in the brain cortex model as well as the development of functional hierarchy for the motor visual perception, and the neurorobotics research.
Professor Jeong said that “this symposium is a place for examination of the most recent research findings in the field of neuroscience as well as for discussion of its education,”and that “it would be an important opportunity for learning research on brain’s basic mechanisms as well as its applications.”
2015.09.25 View 9868 -
 KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8705
KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8705 -
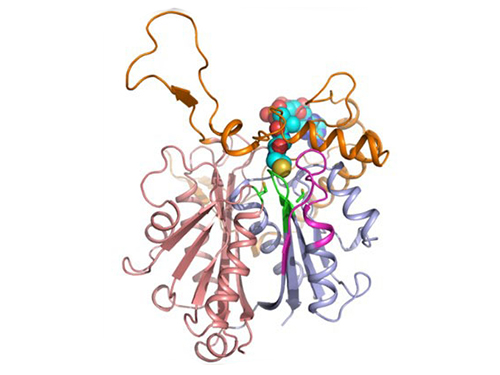 Discovery of Redox-Switch of KEenzyme Involved in N-Butanol Biosynthesis
Research teams at KAIST and Kyungpook National University (KNU) have succeeded in uncovering the redox-switch of thiolase, a key enzyme for n-butanol production in Clostridium acetobutylicum, one of the best known butanol-producing bacteria.
Biological n-butanol production was first reported by Louis Pasteur in 1861, and the bioprocess was industrialized usingClostridium acetobutylicum. The fermentation process by Clostridium strains has been known to be the most efficient one for n-butanol production. Due to growing world-wide issues such as energy security and climate change, the biological production of n-butanol has been receiving much renewed interest. This is because n-butanol possesses much better fuel characteristics compared to ethanol, such as higher energy content (29.2 MJ/L vs 19.6 MJ/L), less corrosiveness, less hygroscopy, and the ease with which it can be blended with gasoline and diesel.
In the paper published in Nature Communications, a broad-scope, online-only, and open access journal issued by the Nature Publishing Group (NPG), on September 22, 2015, Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at the School of Life Sciences, KNU, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, have proved that the redox-switch of thiolase plays a role in a regulation of metabolic flux in C. acetobutylicum by using in silico modeling and simulation tools.
The research team has redesigned thiolase with enhanced activity on the basis of the 3D structure of the wild-type enzyme. To reinforce a metabolic flux toward butanol production, the metabolic network of C. acetobutylicum strain was engineered with the redesigned enzyme. The combination of the discovery of 3D enzyme structure and systems metabolic engineering approaches resulted in increased n-butanol production in C. acetobutylicum, which allows the production of this important industrial chemical to be cost competitive.
Professors Kim and Lee said, "We have reported the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase-a key enzyme involved in n-butanol biosynthesis, for the first time. Further study will be done to produce butanol more economically on the basis of the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase."
This work was published online in Nature Communications on September 22, 2015.
Reference: Kim et al. "Redox-switch regulatory mechanism of thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum," Nature Communications
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Advanced Biomass Center through the Global Frontier Research Program of the MEST, Korea.
For further information, contact Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, +82-42-350-3930); and Dr. Kyung-Jin Kim, Professor, KNU, Daegu, Korea (kkim@knu.ac.kr, +82-53-950-6088).
Figure 1: A redox-switch of thiolase involves in butanol biosynthesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Thiolase condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules for initiating four carbon flux towards butanol.
Figure 2: Thiolase catalyzes the condensation reaction of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA. Two catalytic cysteine residues at 88th and 378th are oxidized and formed an intermolecular disulfide bond in an oxidized status, which results in inactivation of the enzyme for n-butanol biosynthesis. The intermolecular disulfide bond is broken enabling the n-butanol biosynthesis, when the environment status is reduced.
2015.09.23 View 11772
Discovery of Redox-Switch of KEenzyme Involved in N-Butanol Biosynthesis
Research teams at KAIST and Kyungpook National University (KNU) have succeeded in uncovering the redox-switch of thiolase, a key enzyme for n-butanol production in Clostridium acetobutylicum, one of the best known butanol-producing bacteria.
Biological n-butanol production was first reported by Louis Pasteur in 1861, and the bioprocess was industrialized usingClostridium acetobutylicum. The fermentation process by Clostridium strains has been known to be the most efficient one for n-butanol production. Due to growing world-wide issues such as energy security and climate change, the biological production of n-butanol has been receiving much renewed interest. This is because n-butanol possesses much better fuel characteristics compared to ethanol, such as higher energy content (29.2 MJ/L vs 19.6 MJ/L), less corrosiveness, less hygroscopy, and the ease with which it can be blended with gasoline and diesel.
In the paper published in Nature Communications, a broad-scope, online-only, and open access journal issued by the Nature Publishing Group (NPG), on September 22, 2015, Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at the School of Life Sciences, KNU, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, have proved that the redox-switch of thiolase plays a role in a regulation of metabolic flux in C. acetobutylicum by using in silico modeling and simulation tools.
The research team has redesigned thiolase with enhanced activity on the basis of the 3D structure of the wild-type enzyme. To reinforce a metabolic flux toward butanol production, the metabolic network of C. acetobutylicum strain was engineered with the redesigned enzyme. The combination of the discovery of 3D enzyme structure and systems metabolic engineering approaches resulted in increased n-butanol production in C. acetobutylicum, which allows the production of this important industrial chemical to be cost competitive.
Professors Kim and Lee said, "We have reported the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase-a key enzyme involved in n-butanol biosynthesis, for the first time. Further study will be done to produce butanol more economically on the basis of the 3D structure of C. acetobutylicum thiolase."
This work was published online in Nature Communications on September 22, 2015.
Reference: Kim et al. "Redox-switch regulatory mechanism of thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum," Nature Communications
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Advanced Biomass Center through the Global Frontier Research Program of the MEST, Korea.
For further information, contact Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, +82-42-350-3930); and Dr. Kyung-Jin Kim, Professor, KNU, Daegu, Korea (kkim@knu.ac.kr, +82-53-950-6088).
Figure 1: A redox-switch of thiolase involves in butanol biosynthesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Thiolase condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules for initiating four carbon flux towards butanol.
Figure 2: Thiolase catalyzes the condensation reaction of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA. Two catalytic cysteine residues at 88th and 378th are oxidized and formed an intermolecular disulfide bond in an oxidized status, which results in inactivation of the enzyme for n-butanol biosynthesis. The intermolecular disulfide bond is broken enabling the n-butanol biosynthesis, when the environment status is reduced.
2015.09.23 View 11772 -
 KAIST Makes a List of Top Ten Most Innovative Universities around the World
Reuters News released a list of the World’s Top 100 Most Innovative Universities on September 15, 2015.
Nine of the top ten universities on the list were American institutions. KAIST took tenth place, the only non-American and Asian university to do so.
Stanford University ranked first, followed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in second, and Harvard University in third.
The inaugural Reuters Top 100 survey based its rankings on ten criteria: patent volume, patent successes, global patents, patent citations, patent citation impact, percent of patents cited, patent to article citation impact, industry article citation impact, percent of industry collaborative articles, and the total number of science papers.
Japan had nine universities in the survey, more than all countries except for the United States. South Korea has a total of eight universities on the list including Pohang University of Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Yonsei University, and Hanyang University.
For the full details of the survey, see
http://www.reuters.com/article/2015/09/15/idUSL1N11K16Q20150915.
2015.09.23 View 4977
KAIST Makes a List of Top Ten Most Innovative Universities around the World
Reuters News released a list of the World’s Top 100 Most Innovative Universities on September 15, 2015.
Nine of the top ten universities on the list were American institutions. KAIST took tenth place, the only non-American and Asian university to do so.
Stanford University ranked first, followed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in second, and Harvard University in third.
The inaugural Reuters Top 100 survey based its rankings on ten criteria: patent volume, patent successes, global patents, patent citations, patent citation impact, percent of patents cited, patent to article citation impact, industry article citation impact, percent of industry collaborative articles, and the total number of science papers.
Japan had nine universities in the survey, more than all countries except for the United States. South Korea has a total of eight universities on the list including Pohang University of Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Yonsei University, and Hanyang University.
For the full details of the survey, see
http://www.reuters.com/article/2015/09/15/idUSL1N11K16Q20150915.
2015.09.23 View 4977 -
 Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy at KAIST Creates the Next Generation Open Forum 2045
Open forums for envisioning the next 30 years for Korea from the perspective of young people will be held in five metropolitan cities in Korea. Organized by KAIST and hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the Committee for the 70th Anniversary of Korean Liberation, the Next Generation Open Forum 2045 invites young people to shape the future image of Korea for the upcoming 100th anniversary of Korean liberation. It will start off with its first event on September 22 in the Millennium Hall of Konkuk University in Seoul.
In this event, a panel and invited guests will discuss employment issues with a view to ameliorating problems prevalent in the society. A robotics scientist, Dr. JK Han will address the impact of robot automation on the job issue as a keynote speaker, and a performance featuring human-size robot actor will follow his talk to celebrate the opening of the event.
Invited guests can actively participate in the discussion by suggesting their opinions on job issue of the future and by voting on their smartphone apps during the event. Every opinion conveyed during the discussion will be printed and put in a time capsule, which will be opened in 2045 for the celebration of 100th anniversary of Korean liberation.
The Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy of KAIST will organize events in five cities including Daegu, Daejeon, Busan, and Gwangju with topics including education, science and technology, unification diplomacy, and culture. The event will end with a symposium held in Seoul. Perspective applicants can apply for free to the Next Generation Open Forum 2045 on the official website of the Committee for the 70th Anniversary of Korean Liberation.
2015.09.22 View 5584
Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy at KAIST Creates the Next Generation Open Forum 2045
Open forums for envisioning the next 30 years for Korea from the perspective of young people will be held in five metropolitan cities in Korea. Organized by KAIST and hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the Committee for the 70th Anniversary of Korean Liberation, the Next Generation Open Forum 2045 invites young people to shape the future image of Korea for the upcoming 100th anniversary of Korean liberation. It will start off with its first event on September 22 in the Millennium Hall of Konkuk University in Seoul.
In this event, a panel and invited guests will discuss employment issues with a view to ameliorating problems prevalent in the society. A robotics scientist, Dr. JK Han will address the impact of robot automation on the job issue as a keynote speaker, and a performance featuring human-size robot actor will follow his talk to celebrate the opening of the event.
Invited guests can actively participate in the discussion by suggesting their opinions on job issue of the future and by voting on their smartphone apps during the event. Every opinion conveyed during the discussion will be printed and put in a time capsule, which will be opened in 2045 for the celebration of 100th anniversary of Korean liberation.
The Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy of KAIST will organize events in five cities including Daegu, Daejeon, Busan, and Gwangju with topics including education, science and technology, unification diplomacy, and culture. The event will end with a symposium held in Seoul. Perspective applicants can apply for free to the Next Generation Open Forum 2045 on the official website of the Committee for the 70th Anniversary of Korean Liberation.
2015.09.22 View 5584