R
-
 Professor Jinwoo Shin Receives the Bloomberg Scientific Research Award
Professor Jinwoo Shin (https://sites.google.com/site/mijirim/) of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been selected as one of the three winners to receive the first Bloomberg Scientific Research Award this month. The newly created award is presented to researchers in computer science who conduct high-quality research in such areas as machine learning, natural language processing, machine translation, statistics, and theory.
Professor Shin submitted his research proposal entitled “Scalable Probabilistic Deep Leaning,” and the award will support funding his research for one year. For details, please click on the link below for an article released by Bloomberg News, announcing the winners of the award:
Bloomberg News, April 28, 2015
“Announcing the Winners of the Bloomberg’s First Scientific Research Program”
https://3blmedia.com/News/Announcing-Winners-Bloombergs-First-Scientific-Research-Program
2015.04.30 View 9351
Professor Jinwoo Shin Receives the Bloomberg Scientific Research Award
Professor Jinwoo Shin (https://sites.google.com/site/mijirim/) of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been selected as one of the three winners to receive the first Bloomberg Scientific Research Award this month. The newly created award is presented to researchers in computer science who conduct high-quality research in such areas as machine learning, natural language processing, machine translation, statistics, and theory.
Professor Shin submitted his research proposal entitled “Scalable Probabilistic Deep Leaning,” and the award will support funding his research for one year. For details, please click on the link below for an article released by Bloomberg News, announcing the winners of the award:
Bloomberg News, April 28, 2015
“Announcing the Winners of the Bloomberg’s First Scientific Research Program”
https://3blmedia.com/News/Announcing-Winners-Bloombergs-First-Scientific-Research-Program
2015.04.30 View 9351 -
 Jong Hoon Kim, a former president of Bell Labs, speaks at KAIST
Dr. Jong-Hoon Kim, who was the youngest person to serve as the President of Bell Labs and selected as one of the ten most influential Asian-Americans, will give a lecture at KAIST at 5 pm on April 28, 2015 in the KI building.
In 1992, Dr. Kim founded a telecommunication company, Yurie System. After listing the company on NASDAQ, he sold the company to Lucent Technologies for USD one billion. Dr. Kim served as the President of Lucent Technologies, taught as the University of Maryland, and subsequently served as the President of Bell Labs. He is currently the President of Kiswe Mobile.
In his lecture entitled “Aim High, Take Action,” Dr. Kim will share his personal stories and speak about ways young people can set goals for future and put those into practice. He will focus on his experiences in the United States to list his own company, Yurie System, on NASDAQ and to sell the company as well as the management innovations, which he brought about during his presidency at Bell Labs.
KAIST and Kiswe Mobile have been cooperating on a project, "Global Entrepreneurship by Doing," since 2014 to foster entrepreneurship in Korean youth. While working for Kiswe Mobile in the United States, KAIST students will have an opportunity to conduct project management, market research, and marketing, and to build local networks.
The details of the program can be found on the website of the KAIST Center for Science-based Entrepreneurship, http://eship.kaist.ac.kr.
2015.04.27 View 6895
Jong Hoon Kim, a former president of Bell Labs, speaks at KAIST
Dr. Jong-Hoon Kim, who was the youngest person to serve as the President of Bell Labs and selected as one of the ten most influential Asian-Americans, will give a lecture at KAIST at 5 pm on April 28, 2015 in the KI building.
In 1992, Dr. Kim founded a telecommunication company, Yurie System. After listing the company on NASDAQ, he sold the company to Lucent Technologies for USD one billion. Dr. Kim served as the President of Lucent Technologies, taught as the University of Maryland, and subsequently served as the President of Bell Labs. He is currently the President of Kiswe Mobile.
In his lecture entitled “Aim High, Take Action,” Dr. Kim will share his personal stories and speak about ways young people can set goals for future and put those into practice. He will focus on his experiences in the United States to list his own company, Yurie System, on NASDAQ and to sell the company as well as the management innovations, which he brought about during his presidency at Bell Labs.
KAIST and Kiswe Mobile have been cooperating on a project, "Global Entrepreneurship by Doing," since 2014 to foster entrepreneurship in Korean youth. While working for Kiswe Mobile in the United States, KAIST students will have an opportunity to conduct project management, market research, and marketing, and to build local networks.
The details of the program can be found on the website of the KAIST Center for Science-based Entrepreneurship, http://eship.kaist.ac.kr.
2015.04.27 View 6895 -
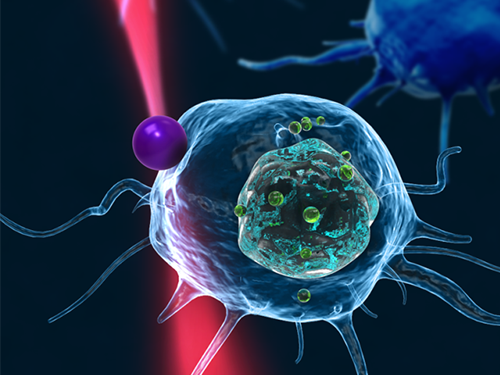 Fast, Accurate 3D Imaging to Track Optically-Trapped Particles
KAIST researchers published an article on the development of a novel technique to precisely track the 3-D positions of optically-trapped particles having complicated geometry in high speed in the April 2015 issue of Optica.
Optical tweezers have been used as an invaluable tool for exerting micro-scale force on microscopic particles and manipulating three-dimensional (3-D) positions of particles. Optical tweezers employ a tightly-focused laser whose beam diameter is smaller than one micrometer (1/100 of hair thickness), which generates attractive force on neighboring microscopic particles moving toward the beam focus. Controlling the positions of the beam focus enabled researchers to hold the particles and move them freely to other locations so they coined the name “optical tweezers.”
To locate the optically-trapped particles by a laser beam, optical microscopes have usually been employed. Optical microscopes measure light signals scattered by the optically-trapped microscopic particles and the positions of the particles in two dimensions. However, it was difficult to quantify the particles’ precise positions along the optic axis, the direction of the beam, from a single image, which is analogous to the difficulty of determining the front and rear positions of objects when closing an eye due to a lack of depth perception. Furthermore, it became more difficult to measure precisely 3-D positions of particles when scattered light signals were distorted by optically-trapped particles having complicated shapes or other particles occlude the target object along the optic axis.
Professor YongKeun Park and his research team in the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) employed an optical diffraction tomography (ODT) technique to measure 3-D positions of optically-trapped particles in high speed. The principle of ODT is similar to X-ray CT imaging commonly used in hospitals for visualizing the internal organs of patients. Like X-ray CT imaging, which takes several images from various illumination angles, ODT measures 3-D images of optically-trapped particles by illuminating them with a laser beam in various incidence angles.
The KAIST team used optical tweezers to trap a glass bead with a diameter of 2 micrometers, and moved the bead toward a white blood cell having complicated internal structures. The team measured the 3-D dynamics of the white blood cell as it responded to an approaching glass bead via ODT in the high acquisition rate of 60 images per second. Since the white blood cell screens the glass bead along an optic axis, a conventionally-used optical microscope could not determine the 3-D positions of the glass bead. In contrast, the present method employing ODT localized the 3-D positions of the bead precisely as well as measured the composition of the internal materials of the bead and the white blood cell simultaneously.
Professor Park said, “Our technique has the advantage of measuring the 3-D positions and internal structures of optically-trapped particles in high speed without labelling exogenous fluorescent agents and can be applied in various fields including physics, optics, nanotechnology, and medical science.”
Kyoohyun Kim, the lead author of this paper (“Simultaneous 3D Visualization and Position Tracking of Optically Trapped Particles Using Optical Diffraction Tomography”), added, “This ODT technique can also apply to cellular-level surgeries where optical tweezers are used to manipulate intracellular organelles and to display in real time and in 3-D the images of the reaction of the cell membrane and nucleus during the operation or monitoring the recovery process of the cells from the surgery.”
The research results were published as the cover article in the April 2014 issue of Optica, the newest journal launched last year by the Optical Society of America (OSA) for rapid dissemination of high-impact results related to optics.
Figure 1: This picture shows the concept image of tweezing an optically-trapped glass bead on the cellular membrane of a white blood cell.
Figure 2: High-speed 3-D images produced from optical diffraction tomography technique
2015.04.24 View 12821
Fast, Accurate 3D Imaging to Track Optically-Trapped Particles
KAIST researchers published an article on the development of a novel technique to precisely track the 3-D positions of optically-trapped particles having complicated geometry in high speed in the April 2015 issue of Optica.
Optical tweezers have been used as an invaluable tool for exerting micro-scale force on microscopic particles and manipulating three-dimensional (3-D) positions of particles. Optical tweezers employ a tightly-focused laser whose beam diameter is smaller than one micrometer (1/100 of hair thickness), which generates attractive force on neighboring microscopic particles moving toward the beam focus. Controlling the positions of the beam focus enabled researchers to hold the particles and move them freely to other locations so they coined the name “optical tweezers.”
To locate the optically-trapped particles by a laser beam, optical microscopes have usually been employed. Optical microscopes measure light signals scattered by the optically-trapped microscopic particles and the positions of the particles in two dimensions. However, it was difficult to quantify the particles’ precise positions along the optic axis, the direction of the beam, from a single image, which is analogous to the difficulty of determining the front and rear positions of objects when closing an eye due to a lack of depth perception. Furthermore, it became more difficult to measure precisely 3-D positions of particles when scattered light signals were distorted by optically-trapped particles having complicated shapes or other particles occlude the target object along the optic axis.
Professor YongKeun Park and his research team in the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) employed an optical diffraction tomography (ODT) technique to measure 3-D positions of optically-trapped particles in high speed. The principle of ODT is similar to X-ray CT imaging commonly used in hospitals for visualizing the internal organs of patients. Like X-ray CT imaging, which takes several images from various illumination angles, ODT measures 3-D images of optically-trapped particles by illuminating them with a laser beam in various incidence angles.
The KAIST team used optical tweezers to trap a glass bead with a diameter of 2 micrometers, and moved the bead toward a white blood cell having complicated internal structures. The team measured the 3-D dynamics of the white blood cell as it responded to an approaching glass bead via ODT in the high acquisition rate of 60 images per second. Since the white blood cell screens the glass bead along an optic axis, a conventionally-used optical microscope could not determine the 3-D positions of the glass bead. In contrast, the present method employing ODT localized the 3-D positions of the bead precisely as well as measured the composition of the internal materials of the bead and the white blood cell simultaneously.
Professor Park said, “Our technique has the advantage of measuring the 3-D positions and internal structures of optically-trapped particles in high speed without labelling exogenous fluorescent agents and can be applied in various fields including physics, optics, nanotechnology, and medical science.”
Kyoohyun Kim, the lead author of this paper (“Simultaneous 3D Visualization and Position Tracking of Optically Trapped Particles Using Optical Diffraction Tomography”), added, “This ODT technique can also apply to cellular-level surgeries where optical tweezers are used to manipulate intracellular organelles and to display in real time and in 3-D the images of the reaction of the cell membrane and nucleus during the operation or monitoring the recovery process of the cells from the surgery.”
The research results were published as the cover article in the April 2014 issue of Optica, the newest journal launched last year by the Optical Society of America (OSA) for rapid dissemination of high-impact results related to optics.
Figure 1: This picture shows the concept image of tweezing an optically-trapped glass bead on the cellular membrane of a white blood cell.
Figure 2: High-speed 3-D images produced from optical diffraction tomography technique
2015.04.24 View 12821 -
 Professor Sang Ouk Kim Receives the POSCO Academic Award
Professor Sang Ouk Kim of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the 2015 POSCO Academic Award. The award ceremony took place at the annual conference of the Korean Institute of Metals and Materials on April 23, 2015.
The POSCO Academic Award has been presented to the Institute's researchers and academics in recognition of their contributions to the advancement of metals and materials engineering in Korea.
Professor Kim is known for his pioneering work in manipulating the properties (work function, conductivity, surface energy, chemo-responsiveness, etc.) of carbon-based materials using double-element doping. Through his research, Professor Kim showed that carbon materials could be extremely useful in various areas including solar batteries and flexible devices. His work has been recognized and published in such journals as Advanced Materials, which invited him to write a review paper on his research in its 25th anniversary issue in 2014, along with world-renowned scholars including the Nobel laureate Alan Heeger.
Professor Kim has published a total of 143 Science Citation Index papers in journals like Nature, Science, Nature Materials, Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, Nano Letters, and Physical Review Letters. According to Scopus, a bibliographic database containing abstracts and citations for academic journal articles, he has been cited 6,456 times and has the h-index of 44, an index describing the scientific productivity and impact of a researcher.
2015.04.22 View 11317
Professor Sang Ouk Kim Receives the POSCO Academic Award
Professor Sang Ouk Kim of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the 2015 POSCO Academic Award. The award ceremony took place at the annual conference of the Korean Institute of Metals and Materials on April 23, 2015.
The POSCO Academic Award has been presented to the Institute's researchers and academics in recognition of their contributions to the advancement of metals and materials engineering in Korea.
Professor Kim is known for his pioneering work in manipulating the properties (work function, conductivity, surface energy, chemo-responsiveness, etc.) of carbon-based materials using double-element doping. Through his research, Professor Kim showed that carbon materials could be extremely useful in various areas including solar batteries and flexible devices. His work has been recognized and published in such journals as Advanced Materials, which invited him to write a review paper on his research in its 25th anniversary issue in 2014, along with world-renowned scholars including the Nobel laureate Alan Heeger.
Professor Kim has published a total of 143 Science Citation Index papers in journals like Nature, Science, Nature Materials, Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, Nano Letters, and Physical Review Letters. According to Scopus, a bibliographic database containing abstracts and citations for academic journal articles, he has been cited 6,456 times and has the h-index of 44, an index describing the scientific productivity and impact of a researcher.
2015.04.22 View 11317 -
 KAIST's Alumni Announces Its Vision to Raise Development Funds
The 40th anniversary of the Graduation and Homecoming Day took place at Seoul campus on April 18, 2015.
KAIST’s alumni announced its long-term vision called “Honor KAIST” to raise the development fund of USD 1 billion by 2100 at the 40th anniversary of “The First Master’s Graduation and Homecoming Day.” The anniversary ceremony took place at the Seoul campus on April 18, 2015. President Steve Kang, Man-Ki Paik, President of KAIST Alumni Association, and the first graduates of KAIST master’s program attended the event.
The first 106 master’s graduates of KAIST, the Class of 1975, received their degrees from eight departments. About 18 professors, including Dr. KunMo Chung, who taught the Class of 1975, and 52 graduates such as Suk-Joong Kang, Sik-Chol Kwon, Youngkyu Do, Sung Joo Park, Joon-Taik Park, Hyung-Kang Shin, Dong-Yol Yang, Seong Ihl Woo, Jae Kyu Lee, In-Won Lee, Byoung-Kyu Choi, and Kyu-Young Hwang participated in the homecoming event that proceeded with the tour of Seoul campus and the ceremony to deliver the first donation by the graduates.
The graduates involved in the vision campaign declared: “KAIST graduates have great pride in having taken part in advancing science and technology in Korea and are grateful for the education given by the nation. There is still a long way ahead for KAIST and Korea. The alumni should work together to help shaping the future of KAIST with great interest and affection for the institution.” They also urged KAIST graduates to donate more for their alma mater: “Let us try to participate in donating USD 100,000 in our lifetime!” The graduates added, “Having donations up to USD 1 billion helped MIT become a great university. We should take the lead in aiming to collect such amount by 2100 for KAIST.”
President Kang addressed the ceremony and said in his speech, “The Honor KAIST Development Funds will serve as the foundation for the university’s continuous, strong growth. Every member of KAIST will work in harmony to transfer KAIST into one of the top ten research universities in the world.” He continued, “The funds will be used to further future strategies of KAIST such as high impact Nobel-prize level research and innovative education.”
Contributors will receive benefits including an honorary lifetime email account entitled “Honor.KAIST” and will have their names listed on “The Honor KAIST” website and “The Honor KAIST” commemorative wall.
Picture 1: The First Master’s Graduation and Homecoming Day 2015
Picture 2: President Steve Kang (right) and President Man-Ki Paik of the KAIST Alumni Association
2015.04.22 View 10123
KAIST's Alumni Announces Its Vision to Raise Development Funds
The 40th anniversary of the Graduation and Homecoming Day took place at Seoul campus on April 18, 2015.
KAIST’s alumni announced its long-term vision called “Honor KAIST” to raise the development fund of USD 1 billion by 2100 at the 40th anniversary of “The First Master’s Graduation and Homecoming Day.” The anniversary ceremony took place at the Seoul campus on April 18, 2015. President Steve Kang, Man-Ki Paik, President of KAIST Alumni Association, and the first graduates of KAIST master’s program attended the event.
The first 106 master’s graduates of KAIST, the Class of 1975, received their degrees from eight departments. About 18 professors, including Dr. KunMo Chung, who taught the Class of 1975, and 52 graduates such as Suk-Joong Kang, Sik-Chol Kwon, Youngkyu Do, Sung Joo Park, Joon-Taik Park, Hyung-Kang Shin, Dong-Yol Yang, Seong Ihl Woo, Jae Kyu Lee, In-Won Lee, Byoung-Kyu Choi, and Kyu-Young Hwang participated in the homecoming event that proceeded with the tour of Seoul campus and the ceremony to deliver the first donation by the graduates.
The graduates involved in the vision campaign declared: “KAIST graduates have great pride in having taken part in advancing science and technology in Korea and are grateful for the education given by the nation. There is still a long way ahead for KAIST and Korea. The alumni should work together to help shaping the future of KAIST with great interest and affection for the institution.” They also urged KAIST graduates to donate more for their alma mater: “Let us try to participate in donating USD 100,000 in our lifetime!” The graduates added, “Having donations up to USD 1 billion helped MIT become a great university. We should take the lead in aiming to collect such amount by 2100 for KAIST.”
President Kang addressed the ceremony and said in his speech, “The Honor KAIST Development Funds will serve as the foundation for the university’s continuous, strong growth. Every member of KAIST will work in harmony to transfer KAIST into one of the top ten research universities in the world.” He continued, “The funds will be used to further future strategies of KAIST such as high impact Nobel-prize level research and innovative education.”
Contributors will receive benefits including an honorary lifetime email account entitled “Honor.KAIST” and will have their names listed on “The Honor KAIST” website and “The Honor KAIST” commemorative wall.
Picture 1: The First Master’s Graduation and Homecoming Day 2015
Picture 2: President Steve Kang (right) and President Man-Ki Paik of the KAIST Alumni Association
2015.04.22 View 10123 -
 KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 9468
KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 9468 -
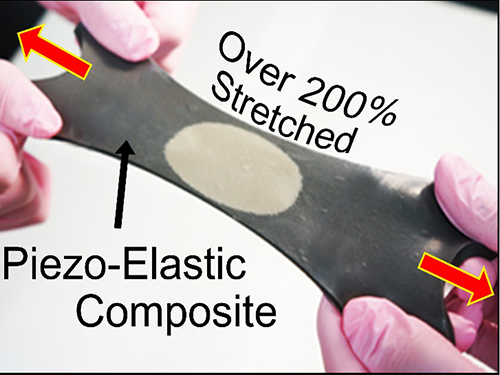 KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 14917
KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 14917 -
 KAIST Hosts a Symposium on IPR
KAIST’s Graduate School of Future Strategy (http://futures.kaist.ac.kr) hosted a symposium entitled “Future Strategies to Grow Korea as the Hub for the World’s Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs)” under the theme of “Patent Laws and a Revised Bill for the Code of Civil Procedures” in the National Assembly’s Memorial Hall on April 9, 2015.
Experts who attended the symposium included Professor James Dator, Director of the Hawaii Research Center for Futures Studies, Sang-Wook Han, a lawyer and Vice President of Korea Intellectual Property Protection Association (KIPRA), and Min Seo, a former Chairman of Civil Law Revision Commission of the Ministry of Justice, Korea.
The event consisted of special lectures, patent law presentations, a revised bill for the code of civil procedures in patent law, and a general discussion forum. Professor Dator, the keynote speaker, addressed the future of intellectual property. San-Wook Han (KIPRA) talked about new and effective changes in Korean patent law such as the compensation against IPR violations and the reduction of legal burden of proof in IPR disputes. Min Seo from the Ministry of Justice moderated a panel of eight members, which offered an in-depth discussion on the revised bill.
A ceremony for “The Third Future Strategy Award” was also held at the symposium. Yeon-Soo Park, former Administrator of the National Emergency Management Agency, received the award for his work on the Northeast Asian International Business Center City Project which enabled the construction of Incheon International Airport and Songdo International City.
2015.04.09 View 11969
KAIST Hosts a Symposium on IPR
KAIST’s Graduate School of Future Strategy (http://futures.kaist.ac.kr) hosted a symposium entitled “Future Strategies to Grow Korea as the Hub for the World’s Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs)” under the theme of “Patent Laws and a Revised Bill for the Code of Civil Procedures” in the National Assembly’s Memorial Hall on April 9, 2015.
Experts who attended the symposium included Professor James Dator, Director of the Hawaii Research Center for Futures Studies, Sang-Wook Han, a lawyer and Vice President of Korea Intellectual Property Protection Association (KIPRA), and Min Seo, a former Chairman of Civil Law Revision Commission of the Ministry of Justice, Korea.
The event consisted of special lectures, patent law presentations, a revised bill for the code of civil procedures in patent law, and a general discussion forum. Professor Dator, the keynote speaker, addressed the future of intellectual property. San-Wook Han (KIPRA) talked about new and effective changes in Korean patent law such as the compensation against IPR violations and the reduction of legal burden of proof in IPR disputes. Min Seo from the Ministry of Justice moderated a panel of eight members, which offered an in-depth discussion on the revised bill.
A ceremony for “The Third Future Strategy Award” was also held at the symposium. Yeon-Soo Park, former Administrator of the National Emergency Management Agency, received the award for his work on the Northeast Asian International Business Center City Project which enabled the construction of Incheon International Airport and Songdo International City.
2015.04.09 View 11969 -
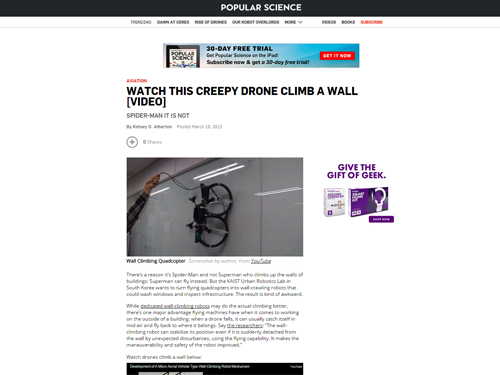 Wall Climbing Quadcopter by KAIST Urban Robotics Lab
Popular Science, an American monthly magazine devoted to general readers of science and technology, published “Watch This Creepy Drone Climb A Wall” online describing a drone that can fly and climb walls on March 19, 2015. The drone is the product of research conducted by Professor Hyun Myung of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST. The flying quadcopters can turn into wall-crawling robots, or vice versa, when carrying out such assignments as cleaning windows or inspecting a building’s infrastructure. Professor Myung leads the KAIST Urban Robotics Lab (http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/). For a link to the article, see http://www.popsci.com/watch-drone-climb-wall-video.
Another Popular Science article (posted on April 3, 2015), entitled “South Korea Gets Ready for Drone-on-Drone Warfare with North Korea,” describes a combat system of drones against hostile drones. Professor Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Engineering Department at KAIST developed the anti-drone system. He currently heads the Unmanned System Research Group, FDCL, http://unmanned.kaist.ac.kr/) and the Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration, aNd Defense (C-FRIEND).
2015.04.07 View 13714
Wall Climbing Quadcopter by KAIST Urban Robotics Lab
Popular Science, an American monthly magazine devoted to general readers of science and technology, published “Watch This Creepy Drone Climb A Wall” online describing a drone that can fly and climb walls on March 19, 2015. The drone is the product of research conducted by Professor Hyun Myung of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST. The flying quadcopters can turn into wall-crawling robots, or vice versa, when carrying out such assignments as cleaning windows or inspecting a building’s infrastructure. Professor Myung leads the KAIST Urban Robotics Lab (http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/). For a link to the article, see http://www.popsci.com/watch-drone-climb-wall-video.
Another Popular Science article (posted on April 3, 2015), entitled “South Korea Gets Ready for Drone-on-Drone Warfare with North Korea,” describes a combat system of drones against hostile drones. Professor Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Engineering Department at KAIST developed the anti-drone system. He currently heads the Unmanned System Research Group, FDCL, http://unmanned.kaist.ac.kr/) and the Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration, aNd Defense (C-FRIEND).
2015.04.07 View 13714 -
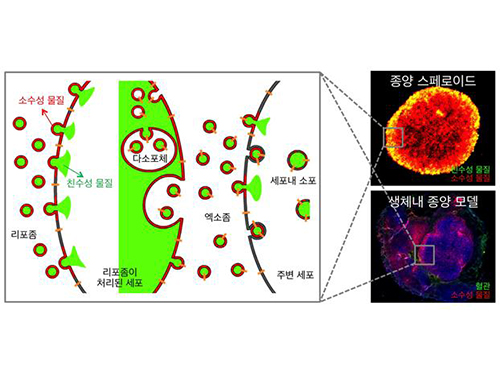 Anti-Cancer Therapy Delivering Drug to an Entire Tumor Developed
KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Professor Ji-Ho Park and his team successfully developed a new highly efficacious anti-cancer nanotechnology by delivering anti-cancer drugs uniformly to an entire tumor. Their research results were published in Nano Letters online on March 31, 2015.
To treat inoperable tumors, anti-cancer medicine is commonly used. However, efficient drug delivery to tumor cells is often difficult, treating an entire tumor with drugs even more so.
Using the existing drug delivery systems, including nanotechnology, a drug can be delivered only to tumor cells near blood vessels, leaving cells at the heart of a tumor intact. Since most drugs are injected into the bloodstream, tumor recurrence post medication is frequent.
Therefore, the team used liposomes that can fuse to the cell membrane and enter the cell. Once inside liposomes the drug can travel into the bloodstream, enter tumor cells near blood vessels, where they are loaded to exosomes, which are naturally occurring nanoparticles in the body. Since exosomes can travel between cells, the drug can be delivered efficiently into inner cells of the tumor.
Exosomes, which are secreted by cells that exist in the tumor microenvironment, is known to have an important role in tumor progression and metastasis since they transfer biological materials between cells. The research team started the investigation recognizing the possibility of delivering the anti-cancer drug to the entire tumor using exosomes.
The team injected the light-sensitive anti-cancer drug using their new delivery technique into experimental mice. The researchers applied light to the tumor site to activate the anti-cancer treatment and analyzed a tissue sample. They observed the effects of the anti-cancer drug in the entire tumor tissue.
The team’s results establish a ground-breaking foothold in drug delivery technology development that can be tailored to specific diseases by understanding its microenvironment. The work paves the way to more effective drug delivery systems for many chronic diseases, including cancer tumors that were difficult to treat due to the inability to penetrate deep into the tissue.
The team is currently conducting experiments with other anti-cancer drugs, which are being developed by pharmaceutical companies, using their tumor-penetrating drug delivery nanotechnology, to identify its effects on malignant tumors.
Professor Park said, “This research is the first to apply biological nanoparticles, exosomes that are continuously secreted and can transfer materials to neighboring cells, to deliver drugs directly to the heart of tumor.”
Picture: Incorporation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds into membrane vesicles by engineering the parental cells via synthetic liposomes.
2015.04.07 View 13063
Anti-Cancer Therapy Delivering Drug to an Entire Tumor Developed
KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Professor Ji-Ho Park and his team successfully developed a new highly efficacious anti-cancer nanotechnology by delivering anti-cancer drugs uniformly to an entire tumor. Their research results were published in Nano Letters online on March 31, 2015.
To treat inoperable tumors, anti-cancer medicine is commonly used. However, efficient drug delivery to tumor cells is often difficult, treating an entire tumor with drugs even more so.
Using the existing drug delivery systems, including nanotechnology, a drug can be delivered only to tumor cells near blood vessels, leaving cells at the heart of a tumor intact. Since most drugs are injected into the bloodstream, tumor recurrence post medication is frequent.
Therefore, the team used liposomes that can fuse to the cell membrane and enter the cell. Once inside liposomes the drug can travel into the bloodstream, enter tumor cells near blood vessels, where they are loaded to exosomes, which are naturally occurring nanoparticles in the body. Since exosomes can travel between cells, the drug can be delivered efficiently into inner cells of the tumor.
Exosomes, which are secreted by cells that exist in the tumor microenvironment, is known to have an important role in tumor progression and metastasis since they transfer biological materials between cells. The research team started the investigation recognizing the possibility of delivering the anti-cancer drug to the entire tumor using exosomes.
The team injected the light-sensitive anti-cancer drug using their new delivery technique into experimental mice. The researchers applied light to the tumor site to activate the anti-cancer treatment and analyzed a tissue sample. They observed the effects of the anti-cancer drug in the entire tumor tissue.
The team’s results establish a ground-breaking foothold in drug delivery technology development that can be tailored to specific diseases by understanding its microenvironment. The work paves the way to more effective drug delivery systems for many chronic diseases, including cancer tumors that were difficult to treat due to the inability to penetrate deep into the tissue.
The team is currently conducting experiments with other anti-cancer drugs, which are being developed by pharmaceutical companies, using their tumor-penetrating drug delivery nanotechnology, to identify its effects on malignant tumors.
Professor Park said, “This research is the first to apply biological nanoparticles, exosomes that are continuously secreted and can transfer materials to neighboring cells, to deliver drugs directly to the heart of tumor.”
Picture: Incorporation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds into membrane vesicles by engineering the parental cells via synthetic liposomes.
2015.04.07 View 13063 -
 Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 14403
Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 14403 -
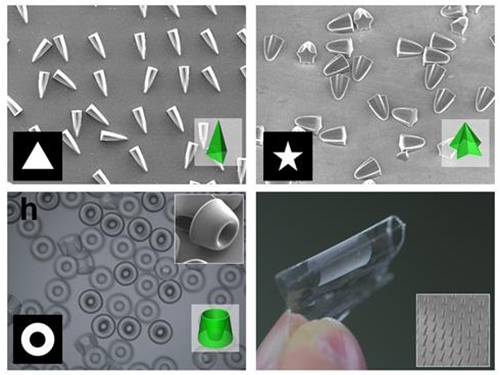 Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 11734
Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 11734