-
 Public Lectures on the Korean Language and Alphabet
The School of Humanities and Social Sciences at KAIST will offer public lectures on the Korean language and alphabet, Hangul, from March 22, 2016 to April 26, 2016.
The lectures, which are entitled “The Riddle of Hangul,” will take place on campus in Daejeon.
A total of six lectures will be held on such topics as the origin of Korean, the grammar of ancient Korean in the Chosun Dynasty (1392-1897), and subsequent developments in contemporary Korean.
Professor Jung-Hoon Kim, who is responsible for organizing the public lecture program, said, “The audience will have an interesting opportunity to understand the history of Korean and its mechanism, while reviewing the unique spelling system of Hangul. I hope many people will show up for these wonderful classes.”
For further information and registration, please visit: http://hss.kaist.ac.kr. All lectures, available only in Korean, are free and open to the public.
2016.03.15 View 10050
Public Lectures on the Korean Language and Alphabet
The School of Humanities and Social Sciences at KAIST will offer public lectures on the Korean language and alphabet, Hangul, from March 22, 2016 to April 26, 2016.
The lectures, which are entitled “The Riddle of Hangul,” will take place on campus in Daejeon.
A total of six lectures will be held on such topics as the origin of Korean, the grammar of ancient Korean in the Chosun Dynasty (1392-1897), and subsequent developments in contemporary Korean.
Professor Jung-Hoon Kim, who is responsible for organizing the public lecture program, said, “The audience will have an interesting opportunity to understand the history of Korean and its mechanism, while reviewing the unique spelling system of Hangul. I hope many people will show up for these wonderful classes.”
For further information and registration, please visit: http://hss.kaist.ac.kr. All lectures, available only in Korean, are free and open to the public.
2016.03.15 View 10050 -
 KAIST Offers Online Science Magnet High School Program
The Global Institute for Talented Education at KAIST has begun providing middle and high school students with in-depth online science education.
The institute receives applications until March 20, 2016. For details, please refer to the website: http://talented.kaist.ac.kr.
The program will run from March 21, 2016 to June 13, 2016.
Any middle and high school student can take courses on mathematics, science (physics, chemistry and biology), and information system (C language and Python computer language) based on their levels and needs. A total of 23 courses will be offered at the level of the first year of middle school to the second year of high school.
The online lecturers are drawn from science-magnet high schools nationwide. They will lead the classes to become more interactive with students, encouraging discussions and questions and answers.
KAIST students will also take part as tutors, helping the middle and high school students better understand the basic concept of the subjects they undertake and and to think creatively to solve problems.
About 500 top students will be chosen from the online course applicants to participate in a science camp hosted by KAIST during summer and winter vacations.
2016.03.14 View 5583
KAIST Offers Online Science Magnet High School Program
The Global Institute for Talented Education at KAIST has begun providing middle and high school students with in-depth online science education.
The institute receives applications until March 20, 2016. For details, please refer to the website: http://talented.kaist.ac.kr.
The program will run from March 21, 2016 to June 13, 2016.
Any middle and high school student can take courses on mathematics, science (physics, chemistry and biology), and information system (C language and Python computer language) based on their levels and needs. A total of 23 courses will be offered at the level of the first year of middle school to the second year of high school.
The online lecturers are drawn from science-magnet high schools nationwide. They will lead the classes to become more interactive with students, encouraging discussions and questions and answers.
KAIST students will also take part as tutors, helping the middle and high school students better understand the basic concept of the subjects they undertake and and to think creatively to solve problems.
About 500 top students will be chosen from the online course applicants to participate in a science camp hosted by KAIST during summer and winter vacations.
2016.03.14 View 5583 -
 KAIST Identifies 27 Research Topics on Local Community
In tandem with the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology and Daejeon Civic Society Research Center, the Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations at KAIST conducted a study on social challenges facing the local community and identified 27 research issues that could be solved with the help of science and technology.
The results of the study were released on March 10, 2016.
The research team prepared a report in an effort to encourage universities, research centers, and local citizens to cooperate in investigating social issues and finding their solutions.
The 27 issues were first chosen by pre-surveys and in-depth interviews with local citizens, and then discussed through public and expert workshops. Among the issues were environment, agriculture, energy, culture, public safety, family, and social integration. The team presented industrial complexes, agricultural facilities, and factories in rural areas were the most urgent issues of social concern within a city and province.
Hong-Gyu Lee, Director of the Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations, said,
“The most serious problem that should be tackled in Daejon City is the chronic stench and garbage odor coming from industrial complexes, while environmental damages arisen from the development of new agricultural technology and factories are the major challenge in rural areas of Chungnam Province. This report is meaningful because citizens, universities, and research institutions worked together to find important issues related to the development of local community and explored solutions to solve those issues with the advancement of science and technology.”
2016.03.12 View 5601
KAIST Identifies 27 Research Topics on Local Community
In tandem with the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology and Daejeon Civic Society Research Center, the Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations at KAIST conducted a study on social challenges facing the local community and identified 27 research issues that could be solved with the help of science and technology.
The results of the study were released on March 10, 2016.
The research team prepared a report in an effort to encourage universities, research centers, and local citizens to cooperate in investigating social issues and finding their solutions.
The 27 issues were first chosen by pre-surveys and in-depth interviews with local citizens, and then discussed through public and expert workshops. Among the issues were environment, agriculture, energy, culture, public safety, family, and social integration. The team presented industrial complexes, agricultural facilities, and factories in rural areas were the most urgent issues of social concern within a city and province.
Hong-Gyu Lee, Director of the Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations, said,
“The most serious problem that should be tackled in Daejon City is the chronic stench and garbage odor coming from industrial complexes, while environmental damages arisen from the development of new agricultural technology and factories are the major challenge in rural areas of Chungnam Province. This report is meaningful because citizens, universities, and research institutions worked together to find important issues related to the development of local community and explored solutions to solve those issues with the advancement of science and technology.”
2016.03.12 View 5601 -
 Dr. Demis Hassabis, the Developer of AlphaGo, Lectures at KAIST
AlphaGo, a computer program developed by Google DeepMind in London to play the traditional Chinese board game Go, had five matches against Se-Dol Lee, a professional Go player in Korea from March 8-15, 2016. AlphaGo won four out of the five games, a significant test result showcasing the advancement achieved in the field of general-purpose artificial intelligence (GAI), according to the company.
Dr. Demis Hassabis, the Chief Executive Officer of Google DeepMind, visited KAIST on March 11, 2016 and gave an hour-long talk to students and faculty. In the lecture, which was entitled “Artificial Intelligence and the Future,” he introduced an overview of GAI and some of its applications in Atari video games and Go.
He said that the ultimate goal of GAI was to become a useful tool to help society solve some of the biggest and most pressing problems facing humanity, from climate change to disease diagnosis.
2016.03.11 View 5094
Dr. Demis Hassabis, the Developer of AlphaGo, Lectures at KAIST
AlphaGo, a computer program developed by Google DeepMind in London to play the traditional Chinese board game Go, had five matches against Se-Dol Lee, a professional Go player in Korea from March 8-15, 2016. AlphaGo won four out of the five games, a significant test result showcasing the advancement achieved in the field of general-purpose artificial intelligence (GAI), according to the company.
Dr. Demis Hassabis, the Chief Executive Officer of Google DeepMind, visited KAIST on March 11, 2016 and gave an hour-long talk to students and faculty. In the lecture, which was entitled “Artificial Intelligence and the Future,” he introduced an overview of GAI and some of its applications in Atari video games and Go.
He said that the ultimate goal of GAI was to become a useful tool to help society solve some of the biggest and most pressing problems facing humanity, from climate change to disease diagnosis.
2016.03.11 View 5094 -
 KAIST Ranks Third in the World's Top Universities for Attracting Industry Funding
The Times Higher Education released its World University Rankings online, naming the 20 best institutions that secured the largest amount of research funding from the private sector, on March 8, 2016.
The rankings were based on the 2013 record of industry-sector investments made per academic of an institution.
According to the list, KAIST ranked third with a figure of $254,700.
Germany’s Ludwig Maximilian University (Munich) took first place ($400,000), while the United State’s Duke University placed second ($290,000).
For a full list of the rankings, go to https://www.timeshighereducation.com/world-university-rankings/funding-for-innovation-ranking-2016.
2016.03.08 View 4086
KAIST Ranks Third in the World's Top Universities for Attracting Industry Funding
The Times Higher Education released its World University Rankings online, naming the 20 best institutions that secured the largest amount of research funding from the private sector, on March 8, 2016.
The rankings were based on the 2013 record of industry-sector investments made per academic of an institution.
According to the list, KAIST ranked third with a figure of $254,700.
Germany’s Ludwig Maximilian University (Munich) took first place ($400,000), while the United State’s Duke University placed second ($290,000).
For a full list of the rankings, go to https://www.timeshighereducation.com/world-university-rankings/funding-for-innovation-ranking-2016.
2016.03.08 View 4086 -
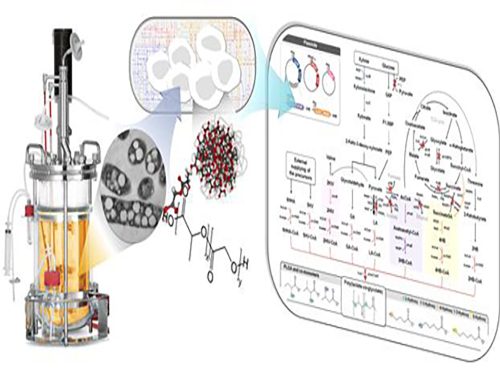 Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 12854
Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 12854 -
 K-Glass 3 Offers Users a Keyboard to Type Text
KAIST researchers upgraded their smart glasses with a low-power multicore processor to employ stereo vision and deep-learning algorithms, making the user interface and experience more intuitive and convenient.
K-Glass, smart glasses reinforced with augmented reality (AR) that were first developed by KAIST in 2014, with the second version released in 2015, is back with an even stronger model. The latest version, which KAIST researchers are calling K-Glass 3, allows users to text a message or type in key words for Internet surfing by offering a virtual keyboard for text and even one for a piano.
Currently, most wearable head-mounted displays (HMDs) suffer from a lack of rich user interfaces, short battery lives, and heavy weight. Some HMDs, such as Google Glass, use a touch panel and voice commands as an interface, but they are considered merely an extension of smartphones and are not optimized for wearable smart glasses. Recently, gaze recognition was proposed for HMDs including K-Glass 2, but gaze cannot be realized as a natural user interface (UI) and experience (UX) due to its limited interactivity and lengthy gaze-calibration time, which can be up to several minutes.
As a solution, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo and his team from the Electrical Engineering Department recently developed K-Glass 3 with a low-power natural UI and UX processor. This processor is composed of a pre-processing core to implement stereo vision, seven deep-learning cores to accelerate real-time scene recognition within 33 milliseconds, and one rendering engine for the display.
The stereo-vision camera, located on the front of K-Glass 3, works in a manner similar to three dimension (3D) sensing in human vision. The camera’s two lenses, displayed horizontally from one another just like depth perception produced by left and right eyes, take pictures of the same objects or scenes and combine these two different images to extract spatial depth information, which is necessary to reconstruct 3D environments. The camera’s vision algorithm has an energy efficiency of 20 milliwatts on average, allowing it to operate in the Glass more than 24 hours without interruption.
The research team adopted deep-learning-multi core technology dedicated for mobile devices. This technology has greatly improved the Glass’s recognition accuracy with images and speech, while shortening the time needed to process and analyze data. In addition, the Glass’s multi-core processor is advanced enough to become idle when it detects no motion from users. Instead, it executes complex deep-learning algorithms with a minimal power to achieve high performance.
Professor Yoo said, “We have succeeded in fabricating a low-power multi-core processer that consumes only 126 milliwatts of power with a high efficiency rate. It is essential to develop a smaller, lighter, and low-power processor if we want to incorporate the widespread use of smart glasses and wearable devices into everyday life. K-Glass 3’s more intuitive UI and convenient UX permit users to enjoy enhanced AR experiences such as a keyboard or a better, more responsive mouse.”
Along with the research team, UX Factory, a Korean UI and UX developer, participated in the K-Glass 3 project.
These research results entitled “A 126.1mW Real-Time Natural UI/UX Processor with Embedded Deep-Learning Core for Low-Power Smart Glasses” (lead author: Seong-Wook Park, a doctoral student in the Electrical Engineering Department, KAIST) were presented at the 2016 IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) that took place January 31-February 4, 2016 in San Francisco, California.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/If_anx5NerQ
Figure 1: K-Glass 3
K-Glass 3 is equipped with a stereo camera, dual microphones, a WiFi module, and eight batteries to offer higher recognition accuracy and enhanced augmented reality experiences than previous models.
Figure 2: Architecture of the Low-Power Multi-Core Processor
K-Glass 3’s processor is designed to include several cores for pre-processing, deep-learning, and graphic rendering.
Figure 3: Virtual Text and Piano Keyboard
K-Glass 3 can detect hands and recognize their movements to provide users with such augmented reality applications as a virtual text or piano keyboard.
2016.02.26 View 14270
K-Glass 3 Offers Users a Keyboard to Type Text
KAIST researchers upgraded their smart glasses with a low-power multicore processor to employ stereo vision and deep-learning algorithms, making the user interface and experience more intuitive and convenient.
K-Glass, smart glasses reinforced with augmented reality (AR) that were first developed by KAIST in 2014, with the second version released in 2015, is back with an even stronger model. The latest version, which KAIST researchers are calling K-Glass 3, allows users to text a message or type in key words for Internet surfing by offering a virtual keyboard for text and even one for a piano.
Currently, most wearable head-mounted displays (HMDs) suffer from a lack of rich user interfaces, short battery lives, and heavy weight. Some HMDs, such as Google Glass, use a touch panel and voice commands as an interface, but they are considered merely an extension of smartphones and are not optimized for wearable smart glasses. Recently, gaze recognition was proposed for HMDs including K-Glass 2, but gaze cannot be realized as a natural user interface (UI) and experience (UX) due to its limited interactivity and lengthy gaze-calibration time, which can be up to several minutes.
As a solution, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo and his team from the Electrical Engineering Department recently developed K-Glass 3 with a low-power natural UI and UX processor. This processor is composed of a pre-processing core to implement stereo vision, seven deep-learning cores to accelerate real-time scene recognition within 33 milliseconds, and one rendering engine for the display.
The stereo-vision camera, located on the front of K-Glass 3, works in a manner similar to three dimension (3D) sensing in human vision. The camera’s two lenses, displayed horizontally from one another just like depth perception produced by left and right eyes, take pictures of the same objects or scenes and combine these two different images to extract spatial depth information, which is necessary to reconstruct 3D environments. The camera’s vision algorithm has an energy efficiency of 20 milliwatts on average, allowing it to operate in the Glass more than 24 hours without interruption.
The research team adopted deep-learning-multi core technology dedicated for mobile devices. This technology has greatly improved the Glass’s recognition accuracy with images and speech, while shortening the time needed to process and analyze data. In addition, the Glass’s multi-core processor is advanced enough to become idle when it detects no motion from users. Instead, it executes complex deep-learning algorithms with a minimal power to achieve high performance.
Professor Yoo said, “We have succeeded in fabricating a low-power multi-core processer that consumes only 126 milliwatts of power with a high efficiency rate. It is essential to develop a smaller, lighter, and low-power processor if we want to incorporate the widespread use of smart glasses and wearable devices into everyday life. K-Glass 3’s more intuitive UI and convenient UX permit users to enjoy enhanced AR experiences such as a keyboard or a better, more responsive mouse.”
Along with the research team, UX Factory, a Korean UI and UX developer, participated in the K-Glass 3 project.
These research results entitled “A 126.1mW Real-Time Natural UI/UX Processor with Embedded Deep-Learning Core for Low-Power Smart Glasses” (lead author: Seong-Wook Park, a doctoral student in the Electrical Engineering Department, KAIST) were presented at the 2016 IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) that took place January 31-February 4, 2016 in San Francisco, California.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/If_anx5NerQ
Figure 1: K-Glass 3
K-Glass 3 is equipped with a stereo camera, dual microphones, a WiFi module, and eight batteries to offer higher recognition accuracy and enhanced augmented reality experiences than previous models.
Figure 2: Architecture of the Low-Power Multi-Core Processor
K-Glass 3’s processor is designed to include several cores for pre-processing, deep-learning, and graphic rendering.
Figure 3: Virtual Text and Piano Keyboard
K-Glass 3 can detect hands and recognize their movements to provide users with such augmented reality applications as a virtual text or piano keyboard.
2016.02.26 View 14270 -
 KAIST Commencement 2016
KAIST hosted its 2016 commencement ceremony on February 19, 2016 at the Sports Complex on campus.
KAIST celebrated the event with five thousand participants including graduating students, faculty, guests, Vice Minister Nam-Ki Hong of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, Chairman Jang-Moo Lee of KAIST's Board of Trustees, and President Jeong-Sik Ko of the KAIST Alumni Association.
President Patrick Aebischer of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland, and the former Speaker of the National Assembly of Korea Chang-Hee Kang received honorary doctorates in science and technology for their contributions to the advancement of science and engineering in education and research.
KAIST granted 570 doctoral degrees, 1,329 master’s degrees, and 867 bachelor degrees on this day.
Yoon-Bum Lee of the Chemistry Department graduated with honors; Woo-Young Jin of the Mathematical Sciences Department received the Chairman’s Award of the KAIST Board and Eun-Hee Yoo of the Biological Sciences Department for the KAIST Presidential Award. Min-Hyun Cho and Yoon-Seok Chang were recipients of the President’s Award of the KAIST Alumni Association and the President’s Award of the University Supporting Association, respectively.
President Steve Kang addressed the ceremony and congratulated the graduates, saying,
“Now, your task is to make significant contributions to your communities: be leaders in your fields and remain active members of society. Given your academic knowledge and vision for the future, I encourage you to dream big.”
2016.02.23 View 43576
KAIST Commencement 2016
KAIST hosted its 2016 commencement ceremony on February 19, 2016 at the Sports Complex on campus.
KAIST celebrated the event with five thousand participants including graduating students, faculty, guests, Vice Minister Nam-Ki Hong of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, Chairman Jang-Moo Lee of KAIST's Board of Trustees, and President Jeong-Sik Ko of the KAIST Alumni Association.
President Patrick Aebischer of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland, and the former Speaker of the National Assembly of Korea Chang-Hee Kang received honorary doctorates in science and technology for their contributions to the advancement of science and engineering in education and research.
KAIST granted 570 doctoral degrees, 1,329 master’s degrees, and 867 bachelor degrees on this day.
Yoon-Bum Lee of the Chemistry Department graduated with honors; Woo-Young Jin of the Mathematical Sciences Department received the Chairman’s Award of the KAIST Board and Eun-Hee Yoo of the Biological Sciences Department for the KAIST Presidential Award. Min-Hyun Cho and Yoon-Seok Chang were recipients of the President’s Award of the KAIST Alumni Association and the President’s Award of the University Supporting Association, respectively.
President Steve Kang addressed the ceremony and congratulated the graduates, saying,
“Now, your task is to make significant contributions to your communities: be leaders in your fields and remain active members of society. Given your academic knowledge and vision for the future, I encourage you to dream big.”
2016.02.23 View 43576 -
 KAIST Graduate Han Receives a 2016 PECASE Award
President Barack Obama of the United States (US) announced 105 recipients of the 2016 Presidential Early Career Awards for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) on February 18. Among the awardees was a graduate from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
Dr. Jin-Woo Han has worked as a research scientist at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Ames Research Center since graduating from KAIST in 2010. This year, he is the only awardee who received a doctoral degree from a Korean university to become a recipient of the highest honor bestowed by the US government on science and engineering professionals in the early stages of their independent research careers.
The awards ceremony will take place in early spring at the White House in Washington, D.C.
Dr. Han has been involved in the development of radiation tolerant semiconductor devices as well as radiation and gas sensors under Dr. Meyya Meyyappan, Chief Scientist of the Center for Nanotechnology at NASA Ames Research Center.
KAIST and the NASA Ames Research Center made a research collaboration agreement in 2008, under which KAIST has sent 12 post-doctoral fellows to the center to date.
The PECASE awards, established in 1996 by President Bill Clinton, are coordinated by the Office of Science and Technology Policy within the Executive Office of the US President. Awardees are selected for their pursuit of innovative research at the frontiers of science and technology and their commitment to community services as demonstrated through scientific leadership, public education, or community outreach.
2016.02.23 View 10805
KAIST Graduate Han Receives a 2016 PECASE Award
President Barack Obama of the United States (US) announced 105 recipients of the 2016 Presidential Early Career Awards for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) on February 18. Among the awardees was a graduate from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
Dr. Jin-Woo Han has worked as a research scientist at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Ames Research Center since graduating from KAIST in 2010. This year, he is the only awardee who received a doctoral degree from a Korean university to become a recipient of the highest honor bestowed by the US government on science and engineering professionals in the early stages of their independent research careers.
The awards ceremony will take place in early spring at the White House in Washington, D.C.
Dr. Han has been involved in the development of radiation tolerant semiconductor devices as well as radiation and gas sensors under Dr. Meyya Meyyappan, Chief Scientist of the Center for Nanotechnology at NASA Ames Research Center.
KAIST and the NASA Ames Research Center made a research collaboration agreement in 2008, under which KAIST has sent 12 post-doctoral fellows to the center to date.
The PECASE awards, established in 1996 by President Bill Clinton, are coordinated by the Office of Science and Technology Policy within the Executive Office of the US President. Awardees are selected for their pursuit of innovative research at the frontiers of science and technology and their commitment to community services as demonstrated through scientific leadership, public education, or community outreach.
2016.02.23 View 10805 -
 Workshop on Techniques in Prediction Analysis for the Industry
There has been growing interest in the value and the application of “big data” in recent years. To meet this interest, a workshop was held to discuss the possibility and the future of prediction analysis, which is the next big step in data mining after big data.
On February 25 in COEX, Seoul, the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering at KAIST held the 4th knowledge service workshop on “Techniques in Prediction Analysis for the Industry.”
Predication analysis is a technique that can predict the future based on the understanding of the past and the present through analyzing “big data.” If “big data” is fuel in figurative sense, the prediction analysis serves as the engine.
The Department seeks to help those companies interested in data mining by introducing fundamentals and some application examples to the executives of companies who are interested in implementation of the technique.
The lecture was delivered by six professors from the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering and the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST.
Thomas Miller, the author of Modeling Techniques in Predictive Analytics, covered the contents of his book at the event. Professor Moon-Yong Yi, Chair of the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering, said, “This conference will be important to companies that are considering the implementation of the prediction analysis as well as to students who are interested in the field.”
2016.02.22 View 6004
Workshop on Techniques in Prediction Analysis for the Industry
There has been growing interest in the value and the application of “big data” in recent years. To meet this interest, a workshop was held to discuss the possibility and the future of prediction analysis, which is the next big step in data mining after big data.
On February 25 in COEX, Seoul, the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering at KAIST held the 4th knowledge service workshop on “Techniques in Prediction Analysis for the Industry.”
Predication analysis is a technique that can predict the future based on the understanding of the past and the present through analyzing “big data.” If “big data” is fuel in figurative sense, the prediction analysis serves as the engine.
The Department seeks to help those companies interested in data mining by introducing fundamentals and some application examples to the executives of companies who are interested in implementation of the technique.
The lecture was delivered by six professors from the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering and the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST.
Thomas Miller, the author of Modeling Techniques in Predictive Analytics, covered the contents of his book at the event. Professor Moon-Yong Yi, Chair of the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering, said, “This conference will be important to companies that are considering the implementation of the prediction analysis as well as to students who are interested in the field.”
2016.02.22 View 6004 -
 KAIST Confers Two Honorary Doctorates at Its 2016 Commencement
KAIST awarded two honorary doctoral degrees at this year’s commencement which took place on February 19, 2016.
Chang-Hee Kang (pictured on the left below), a former Speaker of the National Assembly of Korea and a serving member of the current Assembly, as well as Patrick Aebischer (pictured on the right), the President of the Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland, received honorary doctorates in science and technology.
National Assemblyman Kang was born in 1946 and grew up in Daejeon. He graduated from the Korea Military Academy in 1969, and received a master’s degree in management from Kyungnam University, Korea, in 1980.
He began his distinguished political career with his first election to the 11th National Assembly in 1983. Since then, he has been reelected to the Assembly five times, becoming a leading politician representing Daejeon and Chungchong Province for the past 35 years.
Throughout his career in public service, he served in various important offices, such as Chief Secretary for the Prime Minster of Korea, Chairman of the Telecommunications, Science and Technology Committee for the National Assembly, and the first Minister of Science and Technology of Korea.
Assemblyman Kang has always been a strong advocate for the important role that science and technology continue to play in the growth of Korea. He has worked on many of the critical issues relating to science and research in the nation, including the establishment of the Ministry of Science and Technology in the Korean government, the legislation of special law for science and technology innovation, and the adoption of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) for the national standard of personal communication services.
In his acceptance speech for the degree, Assemblyman Kang said, “As a member of the science and technology community, and as a part of KAIST, I will strive harder to further advance the science and technology field of Korea.”
President Patrick Aebischer was born in 1954 in Fribourg, Switzerland. He was raised in a family of artists, from which his ingenuity, a character he has often displayed as a researcher, was nurtured.
He received a doctorate in medicine from the University of Geneva in 1980, and three years later, obtained a doctorate in neuroscience from the University of Fribourg.
He started his teaching and research career at Brown University in the United States in 1984, where he was eventually promoted to Associate Professor in medical sciences. After living nearly a decade in the United States, President Aebischer returned to Switzerland and became a professor at the Lausanne University Medical School, while serving at the same time as the Director of its Surgical Research Division and Gene Therapy Center.
President Aebischer was appointed by the Swiss Federal Council to lead EPFL in 1999, one of the two most prestigious science and technology universities in the nation. From March 2000, he has served as the President of EPFL.
Under his leadership, EPFL has flourished and expanded its reach across the globe. The university’s core expertise, engineering, has successfully evolved. In addition to engineering, it now offers some of the best programs in natural and life sciences, finance, and management in the world.
His endeavors to promote “disruptive innovations” for the advancement of his own institution, as well as for the whole community of science and research, have led him to introduce many reforms and changes “to push the envelope” on behalf of higher education in science and technology.
In his acceptance speech, President Aebischer said, “I strongly believe that the future belongs to forward-looking and entrepreneurial universities, such as KAIST—to be able to offer a unique education aimed at finding solutions to the global issues such as climate change, dwindling natural resources, aging, cyber-security, and migration amongst others.”
2016.02.19 View 5699
KAIST Confers Two Honorary Doctorates at Its 2016 Commencement
KAIST awarded two honorary doctoral degrees at this year’s commencement which took place on February 19, 2016.
Chang-Hee Kang (pictured on the left below), a former Speaker of the National Assembly of Korea and a serving member of the current Assembly, as well as Patrick Aebischer (pictured on the right), the President of the Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland, received honorary doctorates in science and technology.
National Assemblyman Kang was born in 1946 and grew up in Daejeon. He graduated from the Korea Military Academy in 1969, and received a master’s degree in management from Kyungnam University, Korea, in 1980.
He began his distinguished political career with his first election to the 11th National Assembly in 1983. Since then, he has been reelected to the Assembly five times, becoming a leading politician representing Daejeon and Chungchong Province for the past 35 years.
Throughout his career in public service, he served in various important offices, such as Chief Secretary for the Prime Minster of Korea, Chairman of the Telecommunications, Science and Technology Committee for the National Assembly, and the first Minister of Science and Technology of Korea.
Assemblyman Kang has always been a strong advocate for the important role that science and technology continue to play in the growth of Korea. He has worked on many of the critical issues relating to science and research in the nation, including the establishment of the Ministry of Science and Technology in the Korean government, the legislation of special law for science and technology innovation, and the adoption of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) for the national standard of personal communication services.
In his acceptance speech for the degree, Assemblyman Kang said, “As a member of the science and technology community, and as a part of KAIST, I will strive harder to further advance the science and technology field of Korea.”
President Patrick Aebischer was born in 1954 in Fribourg, Switzerland. He was raised in a family of artists, from which his ingenuity, a character he has often displayed as a researcher, was nurtured.
He received a doctorate in medicine from the University of Geneva in 1980, and three years later, obtained a doctorate in neuroscience from the University of Fribourg.
He started his teaching and research career at Brown University in the United States in 1984, where he was eventually promoted to Associate Professor in medical sciences. After living nearly a decade in the United States, President Aebischer returned to Switzerland and became a professor at the Lausanne University Medical School, while serving at the same time as the Director of its Surgical Research Division and Gene Therapy Center.
President Aebischer was appointed by the Swiss Federal Council to lead EPFL in 1999, one of the two most prestigious science and technology universities in the nation. From March 2000, he has served as the President of EPFL.
Under his leadership, EPFL has flourished and expanded its reach across the globe. The university’s core expertise, engineering, has successfully evolved. In addition to engineering, it now offers some of the best programs in natural and life sciences, finance, and management in the world.
His endeavors to promote “disruptive innovations” for the advancement of his own institution, as well as for the whole community of science and research, have led him to introduce many reforms and changes “to push the envelope” on behalf of higher education in science and technology.
In his acceptance speech, President Aebischer said, “I strongly believe that the future belongs to forward-looking and entrepreneurial universities, such as KAIST—to be able to offer a unique education aimed at finding solutions to the global issues such as climate change, dwindling natural resources, aging, cyber-security, and migration amongst others.”
2016.02.19 View 5699 -
 GSIS Graduates Its First Doctor
The Graduate School of Information Security at KAIST (GSIS) granted its first doctoral degree to Il-Goo Lee at the university’s 2016 commencement on February 19, 2016.
Lee received the degree for his dissertation entitled “Interference-Aware Secure Communications for Wireless LANs.”
He explained the background of his research:
“As we use wireless technology more and more in areas of the Internet of Things (IoT), unmanned vehicles, and drones, information security will become an issue of major concern. I would like to contribute to the advancement of communications technology to help minimize wireless interference between devices while ensuring their optimal performance.”
Based on his research, he developed a communications technique to increase wireless devices’ energy efficiency and the level of their security, and created a prototype to showcase that technique.
He plans to continue his research in the development of the next generation WiFi chip sets to protect the information security of IoT and wireless devices.
Since its establishment in March 2011, KAIST’s GSIS has conferred 50 master’s and one doctoral degrees.
2016.02.18 View 10674
GSIS Graduates Its First Doctor
The Graduate School of Information Security at KAIST (GSIS) granted its first doctoral degree to Il-Goo Lee at the university’s 2016 commencement on February 19, 2016.
Lee received the degree for his dissertation entitled “Interference-Aware Secure Communications for Wireless LANs.”
He explained the background of his research:
“As we use wireless technology more and more in areas of the Internet of Things (IoT), unmanned vehicles, and drones, information security will become an issue of major concern. I would like to contribute to the advancement of communications technology to help minimize wireless interference between devices while ensuring their optimal performance.”
Based on his research, he developed a communications technique to increase wireless devices’ energy efficiency and the level of their security, and created a prototype to showcase that technique.
He plans to continue his research in the development of the next generation WiFi chip sets to protect the information security of IoT and wireless devices.
Since its establishment in March 2011, KAIST’s GSIS has conferred 50 master’s and one doctoral degrees.
2016.02.18 View 10674