initiative
-
 KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9867
KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9867 -
 2013 International Forum on Eco-Friendly Vehicle and System
Leaders in transportation technology gathered at KAIST to discuss commercialization & standardization and to encourage the exchange of research progress, strategy, and future initiatives in transportation technology.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST hosted the 2013 International Forum on Eco-friendly Vehicles and Systems (IFEV) in Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute Building from October 21 to 22.
About 50 leaders in the field of future transportation from academic institutes and industries including Dr. Soon-Man Hong, President of Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI), Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam, Professor at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Mr. Mike Schagrin, the Intelligent Transportation Systems Program Manager of the US Department of Transportation (retired) participated in the 4th annual IFEV.
The commercialization & standardization session and a technical session were followed by the plenary meeting of the forum.
Dr. Hong, the keynote speaker, introduced the High Capacity Double Deck High Speed Train, Near Surface Subway System, and Urban Railway System with Wireless Power Transfer Technology under the title “Korea’s Policy and Technology Initiative for Enhancing Green Transport Systems.”
Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam presented “Electric Vehicle Trends & the POSTECH E-Car Research Center Power Train Design,” followed by Mr. Mike Schagrin who spoke about “Going Green with Connected Automation.”
Dr. Omer C. Onar from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) shared recent research on “ORNL Development in Stationary and Dynamic Wireless Charging.”
In the commercialization session, Faical Turki of Vahle, Germany, presented “Wireless Inductive Battery Chargers,” and Professor Kazuyuki Ouchi from Tokyo University presented “Wind Challenger, the Next Generation Hybrid Vessels.”
In the technical session, presentations and discussions were performed on future ground vehicles and railroad technology, intelligent transportation systems and strategy, and policy on eco-friendly vehicle technology, including Professor In-Soo Suh of the Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST who presented on “Armadillo-T: 4WD Micro Electric EV with a Foldable Body Concept.”
On the second day of IFEV 2013, representatives of the European Union’s Safe and Green Road Vehicles (SAGE) consortium discussed connectivity in road transportation as a means of improving safety, efficiency and convenience in future safe and green vehicles with collaboration from Korean transportation organizations such as the Korea Transport Institute and Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute.
Professor Suh, who organized the forum, said, “This forum will serve as an excellent opportunity to discuss and share R&BD progress in the green transportation field. “Details can be found at http://gt.kaist.ac.kr/ifev2013/.
2013.11.15 View 13787
2013 International Forum on Eco-Friendly Vehicle and System
Leaders in transportation technology gathered at KAIST to discuss commercialization & standardization and to encourage the exchange of research progress, strategy, and future initiatives in transportation technology.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST hosted the 2013 International Forum on Eco-friendly Vehicles and Systems (IFEV) in Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute Building from October 21 to 22.
About 50 leaders in the field of future transportation from academic institutes and industries including Dr. Soon-Man Hong, President of Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI), Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam, Professor at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Mr. Mike Schagrin, the Intelligent Transportation Systems Program Manager of the US Department of Transportation (retired) participated in the 4th annual IFEV.
The commercialization & standardization session and a technical session were followed by the plenary meeting of the forum.
Dr. Hong, the keynote speaker, introduced the High Capacity Double Deck High Speed Train, Near Surface Subway System, and Urban Railway System with Wireless Power Transfer Technology under the title “Korea’s Policy and Technology Initiative for Enhancing Green Transport Systems.”
Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam presented “Electric Vehicle Trends & the POSTECH E-Car Research Center Power Train Design,” followed by Mr. Mike Schagrin who spoke about “Going Green with Connected Automation.”
Dr. Omer C. Onar from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) shared recent research on “ORNL Development in Stationary and Dynamic Wireless Charging.”
In the commercialization session, Faical Turki of Vahle, Germany, presented “Wireless Inductive Battery Chargers,” and Professor Kazuyuki Ouchi from Tokyo University presented “Wind Challenger, the Next Generation Hybrid Vessels.”
In the technical session, presentations and discussions were performed on future ground vehicles and railroad technology, intelligent transportation systems and strategy, and policy on eco-friendly vehicle technology, including Professor In-Soo Suh of the Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST who presented on “Armadillo-T: 4WD Micro Electric EV with a Foldable Body Concept.”
On the second day of IFEV 2013, representatives of the European Union’s Safe and Green Road Vehicles (SAGE) consortium discussed connectivity in road transportation as a means of improving safety, efficiency and convenience in future safe and green vehicles with collaboration from Korean transportation organizations such as the Korea Transport Institute and Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute.
Professor Suh, who organized the forum, said, “This forum will serve as an excellent opportunity to discuss and share R&BD progress in the green transportation field. “Details can be found at http://gt.kaist.ac.kr/ifev2013/.
2013.11.15 View 13787 -
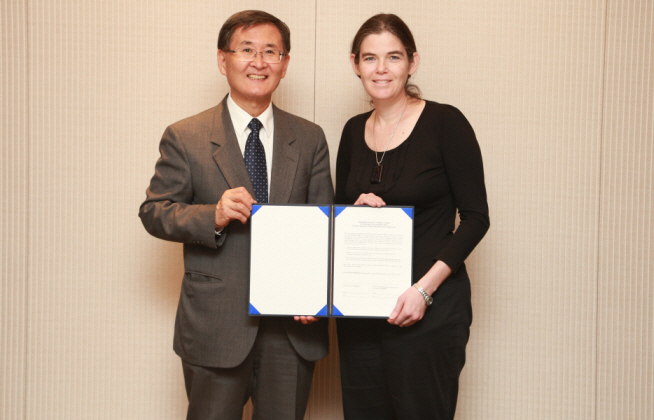 KAIST's classes now available to take from all around the world
Signed a partnership agreement with Coursera to provide millions of people with online courses in science and technology.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), a world-leading research university focusing on science, engineering and technology, joined a new, online platform for open access that serves the needs of Korean and global learners.
KAIST and Coursera, the world"s largest provider of massive open online courses (MOOCs), agreed on October 14th, 2013 to partner for the provision of internet-based open learning, through which the university expects to reinforce its current education initiative, Education 3.0.Steve Kang, president of KAIST, was upbeat about the partnership."We know the benefits and importance of online education that will significantly impact the landscape of today"s higher education. Hopefully, our partnership with Coursera will expand our initiative to continuously provide quality education globally."
With its network of 107 prestigious partner universities and public institutions worldwide, Coursera offers 482 free online courses across a wide field of humanities, science, engineering, and business to 5 million students around the globe.
KAIST will be able to utilize top-notch online courses and lecture contents available on the company"s website. The university can also supply its online courses to the global community, allowing the faculty"s top quality lectures to reach hundreds and thousands of students and adult learners throughout the world.Incorporating advanced information and communications technology, KAIST has implemented a new, smart education program, Education 3.0, since 2012 to effectively meet the growing demands of creating a better and more interactive learning and teaching environment for students and faculty. Under Education 3.0, students study online and meet in groups with a professor for discussions and problem solving.
Tae-Eog Lee, Director of the Center for Excellence in Learning & Teaching at KAIST, said:"We received a phenomenal response from students and professors to the courses made available under Education 3.0. For this year alone, we are offering 60 courses, such classes as calculus, general biology, basic programming, design and communication, bioengineering fundamentals, and logic and artificial intelligence."
Professor Lee added:"It has turned out that our education initiative is not only useful to our students but also quite popular among learners outside the university and Korea. It"s a great thing that KAIST can contribute to the world"s concerted efforts to provide equal opportunities for learning. At the same time, we look forward to seeing the benefits of MOOC-based content being used in our classrooms."
Founded in 2012 by two eminent Stanford University professors, Coursera has held a strong lead in MOOCs. Unlike the traditional online education model, open courseware (OCW), designed for simply sharing lecture materials including videos, slides, and data through the internet, MOOCs develop and evaluate courses, lecture contents, and delivery quality to meet high academic standards—In order to earn credits, subscribers (universities and students) are required to submit course registration, specification, and description; student attendance roster; homework and assignments; and assessment.
Daphne Koller, co-founder of Coursera, commented on the partnership agreement with KAIST:"We are honored to have so many brilliant minds working together to expand educational opportunities globally. To be able to offer courses from professors at the forefront of their fields to millions of people is truly remarkable, and our students remind us daily of the value of spreading this knowledge globally."
Among the partner universities and institutions are Stanford University, California Institute of Technology, Columbia University, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, the National University of Singapore, the University of Tokyo, the World Bank, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
President Steve Kang (in the left) singed a partnership agreement with Dr. Daphne Koller (in the right), president and CEO of Coursera.
2013.11.04 View 10692
KAIST's classes now available to take from all around the world
Signed a partnership agreement with Coursera to provide millions of people with online courses in science and technology.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), a world-leading research university focusing on science, engineering and technology, joined a new, online platform for open access that serves the needs of Korean and global learners.
KAIST and Coursera, the world"s largest provider of massive open online courses (MOOCs), agreed on October 14th, 2013 to partner for the provision of internet-based open learning, through which the university expects to reinforce its current education initiative, Education 3.0.Steve Kang, president of KAIST, was upbeat about the partnership."We know the benefits and importance of online education that will significantly impact the landscape of today"s higher education. Hopefully, our partnership with Coursera will expand our initiative to continuously provide quality education globally."
With its network of 107 prestigious partner universities and public institutions worldwide, Coursera offers 482 free online courses across a wide field of humanities, science, engineering, and business to 5 million students around the globe.
KAIST will be able to utilize top-notch online courses and lecture contents available on the company"s website. The university can also supply its online courses to the global community, allowing the faculty"s top quality lectures to reach hundreds and thousands of students and adult learners throughout the world.Incorporating advanced information and communications technology, KAIST has implemented a new, smart education program, Education 3.0, since 2012 to effectively meet the growing demands of creating a better and more interactive learning and teaching environment for students and faculty. Under Education 3.0, students study online and meet in groups with a professor for discussions and problem solving.
Tae-Eog Lee, Director of the Center for Excellence in Learning & Teaching at KAIST, said:"We received a phenomenal response from students and professors to the courses made available under Education 3.0. For this year alone, we are offering 60 courses, such classes as calculus, general biology, basic programming, design and communication, bioengineering fundamentals, and logic and artificial intelligence."
Professor Lee added:"It has turned out that our education initiative is not only useful to our students but also quite popular among learners outside the university and Korea. It"s a great thing that KAIST can contribute to the world"s concerted efforts to provide equal opportunities for learning. At the same time, we look forward to seeing the benefits of MOOC-based content being used in our classrooms."
Founded in 2012 by two eminent Stanford University professors, Coursera has held a strong lead in MOOCs. Unlike the traditional online education model, open courseware (OCW), designed for simply sharing lecture materials including videos, slides, and data through the internet, MOOCs develop and evaluate courses, lecture contents, and delivery quality to meet high academic standards—In order to earn credits, subscribers (universities and students) are required to submit course registration, specification, and description; student attendance roster; homework and assignments; and assessment.
Daphne Koller, co-founder of Coursera, commented on the partnership agreement with KAIST:"We are honored to have so many brilliant minds working together to expand educational opportunities globally. To be able to offer courses from professors at the forefront of their fields to millions of people is truly remarkable, and our students remind us daily of the value of spreading this knowledge globally."
Among the partner universities and institutions are Stanford University, California Institute of Technology, Columbia University, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, the National University of Singapore, the University of Tokyo, the World Bank, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
President Steve Kang (in the left) singed a partnership agreement with Dr. Daphne Koller (in the right), president and CEO of Coursera.
2013.11.04 View 10692 -
 Joint Research Center on EEWS with Hyundai Heavy Industries Plans to Open
The research center will conduct collaborative R&D projects on energy, environment, water, and sustainability for the next five years.Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), the world’s largest shipbuilding company, signed an MOU with KAIST for future business development and joint research collaboration.
KAIST and HHI signed an MOU as an agreement to establish the “HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center (HK Research Center) on June 21st.”
The major mission of the HK Research Center is to build a strong base for creating future businesses through developing fundamental, core technology in the field of EEWS and designing business models based on the new technology.
Toward this goal, HHI will sponsor the R&D budget and operation expenses of the research center for the next five years.
Prior to the signing of the MOU, a delegation from HHI, led by the Vice President, Mr. Si-Young Hwang, visited the Office of EEWS Initiative at KAIST and held a workshop. During the workshop, HHI and KAIST agreed to collaborate in fields such as LNG-propelled ships, solar power generation, energy storage, fuel cells, and CO2 capture.
KAIST has run a EEWS graduate program that receives government grants over the last five years, with a research emphasis on energy, environment, water, and sustainability, which are crucial issues to humankind in the 21st century. The EEWS program achieved 24 core technological developments and educates more than 200 masters- and PhD-degree students annually.
The EEWS program also emphasizes commercializing its research outcomes. Through the annual Business Planning Competition and Investment Drive, there have been eight new companies founded by alumni and professors over the last five years of the program. The HK Research Center will be an excellent foundation for future education and research in EEWS.
Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of the HK Research Center and the director of the EEWS Initiative, said, “This event is a benchmarking example of Industry-KAIST collaboration. We hope that the HK Research Center will be a place for disruptive innovations to translate into creative business opportunities.”
MOU signed for Hyundai Heavy Industries-KAIST EEWS Research Center
2013.07.15 View 10006
Joint Research Center on EEWS with Hyundai Heavy Industries Plans to Open
The research center will conduct collaborative R&D projects on energy, environment, water, and sustainability for the next five years.Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), the world’s largest shipbuilding company, signed an MOU with KAIST for future business development and joint research collaboration.
KAIST and HHI signed an MOU as an agreement to establish the “HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center (HK Research Center) on June 21st.”
The major mission of the HK Research Center is to build a strong base for creating future businesses through developing fundamental, core technology in the field of EEWS and designing business models based on the new technology.
Toward this goal, HHI will sponsor the R&D budget and operation expenses of the research center for the next five years.
Prior to the signing of the MOU, a delegation from HHI, led by the Vice President, Mr. Si-Young Hwang, visited the Office of EEWS Initiative at KAIST and held a workshop. During the workshop, HHI and KAIST agreed to collaborate in fields such as LNG-propelled ships, solar power generation, energy storage, fuel cells, and CO2 capture.
KAIST has run a EEWS graduate program that receives government grants over the last five years, with a research emphasis on energy, environment, water, and sustainability, which are crucial issues to humankind in the 21st century. The EEWS program achieved 24 core technological developments and educates more than 200 masters- and PhD-degree students annually.
The EEWS program also emphasizes commercializing its research outcomes. Through the annual Business Planning Competition and Investment Drive, there have been eight new companies founded by alumni and professors over the last five years of the program. The HK Research Center will be an excellent foundation for future education and research in EEWS.
Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of the HK Research Center and the director of the EEWS Initiative, said, “This event is a benchmarking example of Industry-KAIST collaboration. We hope that the HK Research Center will be a place for disruptive innovations to translate into creative business opportunities.”
MOU signed for Hyundai Heavy Industries-KAIST EEWS Research Center
2013.07.15 View 10006 -
 Professor Jay H. Lee to receive the 2013 AIChE CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award
Professor Jay H. Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has won the 2013 Computing in Chemical Engineering Award of AIChE"s CAST Division (AIChE, American Institute of Chemical Engineers and CAST, Computing & Systems Technology Division).
The CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award, sponsored by The Dow Chemical Company, is annually given to an individual who has made outstanding contributions in the application of computing and systems technology to chemical engineering.Professor Lee has been recognized for his pioneering research contributions for “novel paradigms for much improved and robust model predictive control in industrial processes.” He is currently the Head of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Director of Brain Korea (BK) 21 Program at the department. BK21 is the Korean government’s initiative to support the growth of research universities in the nation and foster highly trained master’s and doctoral students as well as researchers.
The CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award will be presented to Professor Jay H. Lee at the CAST Division dinner to be held at the AIChE Annual Meeting this November in San Francisco, where he will also deliver the after dinner lecture associated with this award.
2013.06.12 View 11544
Professor Jay H. Lee to receive the 2013 AIChE CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award
Professor Jay H. Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has won the 2013 Computing in Chemical Engineering Award of AIChE"s CAST Division (AIChE, American Institute of Chemical Engineers and CAST, Computing & Systems Technology Division).
The CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award, sponsored by The Dow Chemical Company, is annually given to an individual who has made outstanding contributions in the application of computing and systems technology to chemical engineering.Professor Lee has been recognized for his pioneering research contributions for “novel paradigms for much improved and robust model predictive control in industrial processes.” He is currently the Head of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Director of Brain Korea (BK) 21 Program at the department. BK21 is the Korean government’s initiative to support the growth of research universities in the nation and foster highly trained master’s and doctoral students as well as researchers.
The CAST Computing in Chemical Engineering Award will be presented to Professor Jay H. Lee at the CAST Division dinner to be held at the AIChE Annual Meeting this November in San Francisco, where he will also deliver the after dinner lecture associated with this award.
2013.06.12 View 11544 -
 Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16564
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16564 -
 KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
Source: IDTechEX, Feb. 28, 2011
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
28 Feb 2011
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by researchers at KAIST (Korea Advance Institute of Science & Technology).
The research, led by KAIST"s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of "Advanced Materials".
Professor Bae"s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae"s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, "Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further."
http://www.printedelectronicsworld.com/articles/kaist_paves_the_way_to_commercialize_flexible_display_screens_00003144.asp?sessionid=1
2011.03.01 View 15897
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
Source: IDTechEX, Feb. 28, 2011
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
28 Feb 2011
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by researchers at KAIST (Korea Advance Institute of Science & Technology).
The research, led by KAIST"s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of "Advanced Materials".
Professor Bae"s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae"s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, "Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further."
http://www.printedelectronicsworld.com/articles/kaist_paves_the_way_to_commercialize_flexible_display_screens_00003144.asp?sessionid=1
2011.03.01 View 15897 -
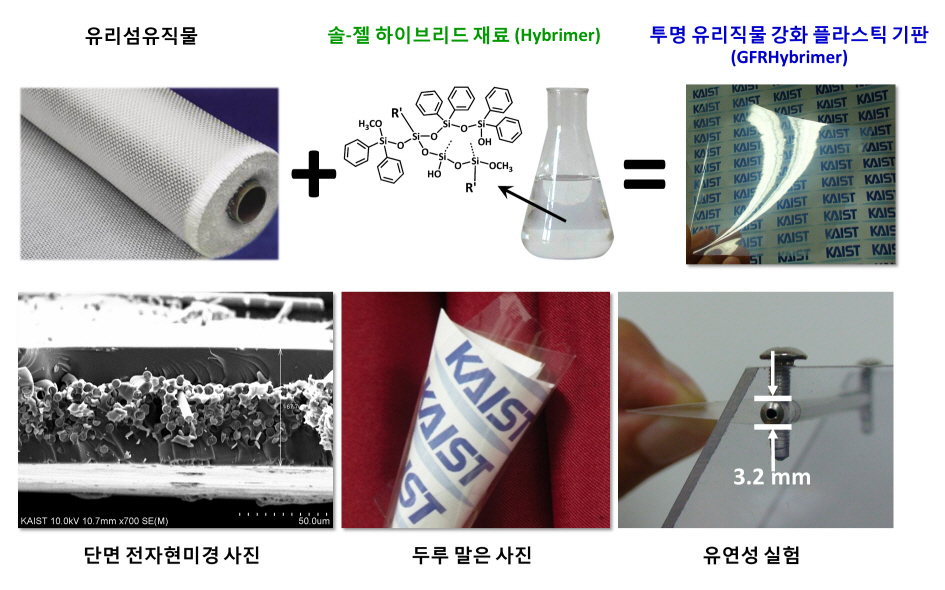 KAIST developed a plastic film board less sensitive to heat.
The research result was made the cover of magazine, Advanced Materials and is accredited to paving the way to commercialize flexible display screens and solar power cells.
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by Korean researchers.
The research, led by KAIST’s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of ‘Advanced Materials’ which is the leading magazine in the field of materials science.
Professor Bae’s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae’s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, “Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further.”
2011.01.05 View 16591
KAIST developed a plastic film board less sensitive to heat.
The research result was made the cover of magazine, Advanced Materials and is accredited to paving the way to commercialize flexible display screens and solar power cells.
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by Korean researchers.
The research, led by KAIST’s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of ‘Advanced Materials’ which is the leading magazine in the field of materials science.
Professor Bae’s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae’s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, “Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further.”
2011.01.05 View 16591 -
 International Workshop on EEWS 2010 was held.
On October 7 and 8th at Fusion Hall of KI Building, KAIST, the 2010 International Workshop on EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) was held.
The third to be held, forty national and international academic professionals including Mark Shannon, professor at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Domen Kazunari, Tokyo University professor, Dong Sub Kim, CTO of SK Energy and Doyoung Seung, Senior Vice President of GS Caltex, participated at this year’s workshop.
In twelve sessions, themes including Artificial Photosynthesis, Wireless Power Transfer, Green Aviation, Safe Nuclear Fuel Reuse, Fuel Cells in Action, LED 2.0, Foundation of Energy-Water Nexus, and Flexible Battery & Solar Cell were presented and discussed.
“Through this workshop, current EEWS policy and research progress from different countries and the future of related technologies will be foreseen,” said Jae Kyu Lee, Dean of KAIST EEWS Initiative. “I hope it became an opportunity to create cooperative relationships with leading researchers.”
EEWS is a research project conducted by KAIST to solve global issues that mankind faces today such as depletion of energy, environmental pollution, water shortage, and sustainability.
2010.10.15 View 18886
International Workshop on EEWS 2010 was held.
On October 7 and 8th at Fusion Hall of KI Building, KAIST, the 2010 International Workshop on EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) was held.
The third to be held, forty national and international academic professionals including Mark Shannon, professor at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Domen Kazunari, Tokyo University professor, Dong Sub Kim, CTO of SK Energy and Doyoung Seung, Senior Vice President of GS Caltex, participated at this year’s workshop.
In twelve sessions, themes including Artificial Photosynthesis, Wireless Power Transfer, Green Aviation, Safe Nuclear Fuel Reuse, Fuel Cells in Action, LED 2.0, Foundation of Energy-Water Nexus, and Flexible Battery & Solar Cell were presented and discussed.
“Through this workshop, current EEWS policy and research progress from different countries and the future of related technologies will be foreseen,” said Jae Kyu Lee, Dean of KAIST EEWS Initiative. “I hope it became an opportunity to create cooperative relationships with leading researchers.”
EEWS is a research project conducted by KAIST to solve global issues that mankind faces today such as depletion of energy, environmental pollution, water shortage, and sustainability.
2010.10.15 View 18886 -
 International Center was built to promote greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
On July 9, 2010, KAIST held an opening ceremony for the construction of International Center. The Center will serve as an internal and external liaison for the university, providing a source of assistance to faculty, administrators, and students on matters related to international activities and initiatives. It will also pursue greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
The facility accommodates various meetings, exhibitions, library, language services, and other amenities. The International Cooperation Team of KAIST will be moved into this building and provide a variety of services, such as immigration regulations, cultural adjustment, employment, to assist international students, scholars, faculty, and staff at KAIST, as well as Korean students seeking opportunities to study, work, or travel abroad. An international nursery school will also be inside the building so that foreign faculty and students with children can have convenience and quality child care while they are teaching or studying.
At the center will be held many different kinds of international event—one among them is KAIST-ONE, a festival held twice a year in spring and fall to introduce and share culture, education, and food of the global community at KAIST.
2010.07.19 View 13158
International Center was built to promote greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
On July 9, 2010, KAIST held an opening ceremony for the construction of International Center. The Center will serve as an internal and external liaison for the university, providing a source of assistance to faculty, administrators, and students on matters related to international activities and initiatives. It will also pursue greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
The facility accommodates various meetings, exhibitions, library, language services, and other amenities. The International Cooperation Team of KAIST will be moved into this building and provide a variety of services, such as immigration regulations, cultural adjustment, employment, to assist international students, scholars, faculty, and staff at KAIST, as well as Korean students seeking opportunities to study, work, or travel abroad. An international nursery school will also be inside the building so that foreign faculty and students with children can have convenience and quality child care while they are teaching or studying.
At the center will be held many different kinds of international event—one among them is KAIST-ONE, a festival held twice a year in spring and fall to introduce and share culture, education, and food of the global community at KAIST.
2010.07.19 View 13158 -
 The 8th International Conference on Metabolic Engineering was held on June 13-18, 2010 in Jeju Island, South Korea.
From left to right, top row: Distinguished Professor and the conference chair Sang Yup Lee, Sang-Hyup Kim - Secretary to the President of Korea, Dr. Jay Keasling, Dr. Greg Stephanopoulos. Left to right, bottom row: Dr. William Provine, Dr. Terry Papoutsakis, Dr, Jens Nielsen, Dr. Lars Nielsen.
The importance of industrial biotechnology that produces chemicals and materials from renewable biomass is increasing due to climate change and the dearth of natural resources. Industrial biotechnology refers to a technology that allows sustainable bio-based production of chemicals and materials that could enrich human"s lives using microorganisms. This is where metabolic engineering comes into play for successful application of microorganisms, in which they are engineered in our intended way for improved production capability.
The 8th International Conference on Metabolic Engineering, the longest running conference of its kind, was held on June 13-18, 2010 at the International Convention Center in Jeju Island, South Korea. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST, Dean of College of Life Science and Bioengineering and Co-Director of Institute for the BioCentury, chaired the conference with the main theme of "metabolic engineering for green growth."
With 300 delegates selected by the committee, papers on production of biofuels, chemicals, biopolymers, and pharmaceutics and the development of fundamental metabolic engineering techniques were presented at the conference along with examples of successful commercialization of products developed by several global companies.
Sang Hyup Kim, Secretary to the President of Korea, gave an opening plenary lecture entitled "Korean green growth initiative," to inform experts from around the globe of the leadership on green growth in Korea. Young Hoon Park, President of Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB, Korea) delivered his congratulatory address.
Sang Hyup Kim said, "Hosting an international conference in Korea on metabolic engineering, which forms a core technology necessary for the development of environmentally friendly processes for producing chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass, is very meaningful as green growth is a big issue around the globe. This is a great chance to show the excellence of Korea"s green growth associated technology to experts in metabolic engineering and industrial biotechnology."
A total of 47 invited lectures in this conference included recent and important topics, for instance, "Synthetic biology for synthetic fuels" by Dr. Jay Keasling from the Joint BioEnergy Institute (USA), "Microbial oil production from renewable feedstocks" by Dr. Greg Stephanopoulos from MIT (USA), "Yeast as a platform cell factory for production of fuels and chemicals" by Dr. Jens Nielsen from Chalmers University (Sweden), "Mammalian synthetic biology - from tools to therapies" by Dr. Martin Fussengger from ETH (Switzerland), "Building, modeling, and applications of metabolic and transcriptional regulatory networks at a genome-scale" by Dr. Bernhard Palsson from the University of California - San Diego (USA), "Genome analysis and engineering Eschericha coli for sucrose utilization" by Dr. Lars Nielsen from the University of Queensland (Australia), "Artificial microorganisms by synthetic biology" by Dr. Daniel Gibson from JCVI (USA), and "Metabolomics and its applications" by Dr. Masaru Tomita from Keio University (Japan). From Korea, Dr. Jin Hwan Park from the research group of Dr. Sang Yup Lee at KAIST presented "Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for amino acid production," and Dr. Ji Hyun Kim from KRIBB presented "Genome sequencing and omics systems analysis of the protein cell factory of Escherichia coli".
Global companies involved in biorefinery presented their recent research outcomes with emphasis on commercialized technologies. They included "Metabolic and process engineering for commercial outcomes" by Dr. William Provine from DuPont (USA), "Direct production of 1,4-butanediol from renewable feedstocks" by Dr. Mark Burk from Genomatica (USA), "Development of an economically sustainable bioprocess for the production of bio 1,2-propanediol" by Dr. Francis Voelker from Metabolic Explorer (France), "Biotechnology to the bottom-line: low pH lactic acid production at industrial scale" by Dr. Pirkko Suominen from Cargill (USA), "Bioisoprene™: traditional monomer, traditional chemistry, sustainable source" by Dr. Gregg Whited from Danisco (USA) and "Efficient production of pharmaceuticals by engineered fungi" by Dr. Roel Bovenberg from DSM (Netherlands).
This biennial conference also presented the International Metabolic Engineering Award (expanded version of the previous Merck Metabolic Engineering Award) to the best metabolic engineer in the world. The 2010 International Metabolic Engineering Award went to Dr. E. Terry Papoutsakis from the University of Delaware (USA) who has contributed to the production of biobutanol through the metabolic engineering of Clostridia in the last three decades, and he gave an award lecture. Dr. Sang Yup Lee, the current chair of the upcoming conference, was the previous recipient of this award at the last metabolic engineering conference in 2008.
In addition to the invited lectures, a total of 156 carefully selected poster papers were chosen for presentation, and awards were presented to the best posters after rigorous review by the committee members. Such awards included "The 2010 Metabolic Engineering Best Poster Award" and the "2010 Young Metabolic Engineer Award" from the Metabolic Engineering conference, and prestigious international journal awards, including "Wiley Biotechnology Journal Best Poster Award", "Wiley Biotechnology and Bioengineering Best Poster Award" and "Elsevier Metabolic Engineering Best Paper Award." Dr. Catherine Goodman, a senior editor of Nature Chemical Biology, also presented the "Nature Chemical Biology Best Poster Award on Metabolic Engineering."
Regarding this conference, Dr. Sang Yup Lee, the conference chair, said, "This conference is the best international conference in the field of metabolic engineering, which is held every two years, and Korea is the first Asian country to host it. All the experts and students spend time together from early breakfast to late poster sessions, which is a distinct feature of this conference. Although the number of delegates had typically been limited to 200, around 300 delegates were selected this year to accept more attendees from many people who have been interested in metabolic engineering. Also, it is very fitting that "green growth" is the main topic of this conference because Korea is playing a key role in this field. I"m grateful to the Lotte Scholarship Foundation, COFCO, GS Caltex, Bioneer, US DOE, US NSF, Daesang, CJ Cheiljedang, Genomatica and DuPont who provided us with generous financial support that allowed the successful organization of this conference."
The conference was organized by the Systems Biology Research Project Team supported by the Ministry of Eduction, Science and Technology (MEST), Microbial Frontier Research Project Group, World Class University Project Group at KAIST, Institute for the BioCentury at KAIST, Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering, and the Engineering Conference International (ECI) of the United States.
Inquiries: Professor Sang Yup Lee (+82-42-350-3930), industrialbio@gmail.com
2010.06.25 View 21472
The 8th International Conference on Metabolic Engineering was held on June 13-18, 2010 in Jeju Island, South Korea.
From left to right, top row: Distinguished Professor and the conference chair Sang Yup Lee, Sang-Hyup Kim - Secretary to the President of Korea, Dr. Jay Keasling, Dr. Greg Stephanopoulos. Left to right, bottom row: Dr. William Provine, Dr. Terry Papoutsakis, Dr, Jens Nielsen, Dr. Lars Nielsen.
The importance of industrial biotechnology that produces chemicals and materials from renewable biomass is increasing due to climate change and the dearth of natural resources. Industrial biotechnology refers to a technology that allows sustainable bio-based production of chemicals and materials that could enrich human"s lives using microorganisms. This is where metabolic engineering comes into play for successful application of microorganisms, in which they are engineered in our intended way for improved production capability.
The 8th International Conference on Metabolic Engineering, the longest running conference of its kind, was held on June 13-18, 2010 at the International Convention Center in Jeju Island, South Korea. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST, Dean of College of Life Science and Bioengineering and Co-Director of Institute for the BioCentury, chaired the conference with the main theme of "metabolic engineering for green growth."
With 300 delegates selected by the committee, papers on production of biofuels, chemicals, biopolymers, and pharmaceutics and the development of fundamental metabolic engineering techniques were presented at the conference along with examples of successful commercialization of products developed by several global companies.
Sang Hyup Kim, Secretary to the President of Korea, gave an opening plenary lecture entitled "Korean green growth initiative," to inform experts from around the globe of the leadership on green growth in Korea. Young Hoon Park, President of Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB, Korea) delivered his congratulatory address.
Sang Hyup Kim said, "Hosting an international conference in Korea on metabolic engineering, which forms a core technology necessary for the development of environmentally friendly processes for producing chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass, is very meaningful as green growth is a big issue around the globe. This is a great chance to show the excellence of Korea"s green growth associated technology to experts in metabolic engineering and industrial biotechnology."
A total of 47 invited lectures in this conference included recent and important topics, for instance, "Synthetic biology for synthetic fuels" by Dr. Jay Keasling from the Joint BioEnergy Institute (USA), "Microbial oil production from renewable feedstocks" by Dr. Greg Stephanopoulos from MIT (USA), "Yeast as a platform cell factory for production of fuels and chemicals" by Dr. Jens Nielsen from Chalmers University (Sweden), "Mammalian synthetic biology - from tools to therapies" by Dr. Martin Fussengger from ETH (Switzerland), "Building, modeling, and applications of metabolic and transcriptional regulatory networks at a genome-scale" by Dr. Bernhard Palsson from the University of California - San Diego (USA), "Genome analysis and engineering Eschericha coli for sucrose utilization" by Dr. Lars Nielsen from the University of Queensland (Australia), "Artificial microorganisms by synthetic biology" by Dr. Daniel Gibson from JCVI (USA), and "Metabolomics and its applications" by Dr. Masaru Tomita from Keio University (Japan). From Korea, Dr. Jin Hwan Park from the research group of Dr. Sang Yup Lee at KAIST presented "Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for amino acid production," and Dr. Ji Hyun Kim from KRIBB presented "Genome sequencing and omics systems analysis of the protein cell factory of Escherichia coli".
Global companies involved in biorefinery presented their recent research outcomes with emphasis on commercialized technologies. They included "Metabolic and process engineering for commercial outcomes" by Dr. William Provine from DuPont (USA), "Direct production of 1,4-butanediol from renewable feedstocks" by Dr. Mark Burk from Genomatica (USA), "Development of an economically sustainable bioprocess for the production of bio 1,2-propanediol" by Dr. Francis Voelker from Metabolic Explorer (France), "Biotechnology to the bottom-line: low pH lactic acid production at industrial scale" by Dr. Pirkko Suominen from Cargill (USA), "Bioisoprene™: traditional monomer, traditional chemistry, sustainable source" by Dr. Gregg Whited from Danisco (USA) and "Efficient production of pharmaceuticals by engineered fungi" by Dr. Roel Bovenberg from DSM (Netherlands).
This biennial conference also presented the International Metabolic Engineering Award (expanded version of the previous Merck Metabolic Engineering Award) to the best metabolic engineer in the world. The 2010 International Metabolic Engineering Award went to Dr. E. Terry Papoutsakis from the University of Delaware (USA) who has contributed to the production of biobutanol through the metabolic engineering of Clostridia in the last three decades, and he gave an award lecture. Dr. Sang Yup Lee, the current chair of the upcoming conference, was the previous recipient of this award at the last metabolic engineering conference in 2008.
In addition to the invited lectures, a total of 156 carefully selected poster papers were chosen for presentation, and awards were presented to the best posters after rigorous review by the committee members. Such awards included "The 2010 Metabolic Engineering Best Poster Award" and the "2010 Young Metabolic Engineer Award" from the Metabolic Engineering conference, and prestigious international journal awards, including "Wiley Biotechnology Journal Best Poster Award", "Wiley Biotechnology and Bioengineering Best Poster Award" and "Elsevier Metabolic Engineering Best Paper Award." Dr. Catherine Goodman, a senior editor of Nature Chemical Biology, also presented the "Nature Chemical Biology Best Poster Award on Metabolic Engineering."
Regarding this conference, Dr. Sang Yup Lee, the conference chair, said, "This conference is the best international conference in the field of metabolic engineering, which is held every two years, and Korea is the first Asian country to host it. All the experts and students spend time together from early breakfast to late poster sessions, which is a distinct feature of this conference. Although the number of delegates had typically been limited to 200, around 300 delegates were selected this year to accept more attendees from many people who have been interested in metabolic engineering. Also, it is very fitting that "green growth" is the main topic of this conference because Korea is playing a key role in this field. I"m grateful to the Lotte Scholarship Foundation, COFCO, GS Caltex, Bioneer, US DOE, US NSF, Daesang, CJ Cheiljedang, Genomatica and DuPont who provided us with generous financial support that allowed the successful organization of this conference."
The conference was organized by the Systems Biology Research Project Team supported by the Ministry of Eduction, Science and Technology (MEST), Microbial Frontier Research Project Group, World Class University Project Group at KAIST, Institute for the BioCentury at KAIST, Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering, and the Engineering Conference International (ECI) of the United States.
Inquiries: Professor Sang Yup Lee (+82-42-350-3930), industrialbio@gmail.com
2010.06.25 View 21472 -
 President of Israel visited KAIST on June 9, 2010.
President of Israel, Shimon Peres, visited KAIST today on June 9, 2010 to witness the development of science and technology in Korea and explore ways of establishing collaboration and cooperation with industries and universities between Korea and Israel. President Peres led a delegation consisted of the Israeli Mister of Industry, Trade, and Labor, the Minister of Communication, and 60 business leaders from the top companies in the security, infrastructure, communication, high-tech, and water industries.
Upon their arrival to the campus, the Israeli delegation was greeted by KAIST’s humanoid robot, “HUBO,” and then moved to its branch campus, IT Convergence Campus, for a ride of Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) that has been developed by KAIST. The OLEV receives the necessary power through the cable lines buried underground, so it can be provided with a constant and continuous supply of electricity while running or stopping.
Between roads and OLEVs is nothing but space. There is no electrical wires intricately crossed underbody of the electric car or above the road. The pick-up equipment installed beneath the body of the electric car collects magnetic fields created around the underground cables, which then converts the filed into electricity. The OLEV’s wireless, non-contact charging system made it possible for a battery currently used for hybrid or pure electric cars on the market to be smaller and cheaper.
President Peres expressed a great interest in the technology applied to the OLVE, quoting, “the OLEV system is indeed very impressive.” He talked about efforts being made in Israel with respect to the development of electric cars. The country plans to replace the conventional transportation system with electric cars by constructing a network of battery exchange stations and roadside charge points which allow the cars to be charged whenever they are parked.
“Despite the different approach taken by the two nations for the development of electric cars, I believe that transforming the automobile industry from combustion engine to electric system is the right direction we should all follow. Without addressing the current transportation system that heavily dependent on natural resources, we will not be able to promote “green growth on a global scale,” added President Peres.
In addition to electric cars, President Peres took up a considerable portion of his time to exchange ideas on how to expand cooperative relations between universities in Korea and Israel, specifically in the area of space, biotechnology, nanotechnology, high-tech, renewable and alternative energy, and the EEWS initiatives that have been implemented by KAIST to find answers to global issues such as climate change and depletion of natural resources. The EEWS stands for energy, environment, water, and sustainability.
In response, the president of KAIST pledged to set up a stronger and greater tie with research universities in Israel, particularly called for more collaboration between KAIST and Technion-Israel Institute of Technology.
Also, the Israeli delegation had a tour for several Korean research and development centers in Daedeok Innopolis, located in the City of Daejeon, which is the 2nd largest science and research complex in Korea.
Shimon Peres, the 9th president of Israel, held many of important government positions in Israel, among other things, Prime Minster and Minister of Defense. He won Nobel Peace Prize in 1994, together with Yitzhak Rabin and Yasser Arafat for the conclusion of a peace agreement, Oslo Accords, between Israel and Palestine Liberation Organization.
2010.06.09 View 18932
President of Israel visited KAIST on June 9, 2010.
President of Israel, Shimon Peres, visited KAIST today on June 9, 2010 to witness the development of science and technology in Korea and explore ways of establishing collaboration and cooperation with industries and universities between Korea and Israel. President Peres led a delegation consisted of the Israeli Mister of Industry, Trade, and Labor, the Minister of Communication, and 60 business leaders from the top companies in the security, infrastructure, communication, high-tech, and water industries.
Upon their arrival to the campus, the Israeli delegation was greeted by KAIST’s humanoid robot, “HUBO,” and then moved to its branch campus, IT Convergence Campus, for a ride of Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) that has been developed by KAIST. The OLEV receives the necessary power through the cable lines buried underground, so it can be provided with a constant and continuous supply of electricity while running or stopping.
Between roads and OLEVs is nothing but space. There is no electrical wires intricately crossed underbody of the electric car or above the road. The pick-up equipment installed beneath the body of the electric car collects magnetic fields created around the underground cables, which then converts the filed into electricity. The OLEV’s wireless, non-contact charging system made it possible for a battery currently used for hybrid or pure electric cars on the market to be smaller and cheaper.
President Peres expressed a great interest in the technology applied to the OLVE, quoting, “the OLEV system is indeed very impressive.” He talked about efforts being made in Israel with respect to the development of electric cars. The country plans to replace the conventional transportation system with electric cars by constructing a network of battery exchange stations and roadside charge points which allow the cars to be charged whenever they are parked.
“Despite the different approach taken by the two nations for the development of electric cars, I believe that transforming the automobile industry from combustion engine to electric system is the right direction we should all follow. Without addressing the current transportation system that heavily dependent on natural resources, we will not be able to promote “green growth on a global scale,” added President Peres.
In addition to electric cars, President Peres took up a considerable portion of his time to exchange ideas on how to expand cooperative relations between universities in Korea and Israel, specifically in the area of space, biotechnology, nanotechnology, high-tech, renewable and alternative energy, and the EEWS initiatives that have been implemented by KAIST to find answers to global issues such as climate change and depletion of natural resources. The EEWS stands for energy, environment, water, and sustainability.
In response, the president of KAIST pledged to set up a stronger and greater tie with research universities in Israel, particularly called for more collaboration between KAIST and Technion-Israel Institute of Technology.
Also, the Israeli delegation had a tour for several Korean research and development centers in Daedeok Innopolis, located in the City of Daejeon, which is the 2nd largest science and research complex in Korea.
Shimon Peres, the 9th president of Israel, held many of important government positions in Israel, among other things, Prime Minster and Minister of Defense. He won Nobel Peace Prize in 1994, together with Yitzhak Rabin and Yasser Arafat for the conclusion of a peace agreement, Oslo Accords, between Israel and Palestine Liberation Organization.
2010.06.09 View 18932