Technology
-
 Professor Lee's Research Selected as Top 100 National R&D Projects
A research project, led by Research Professor Ju Yong Lee from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence, was selected as one of the Top 100 National Research and Development Projects 2017.
This research project, titled LTE-A-based Single RF Small Base Station supporting Multiple Streams, developed 300Mbps low power, low complexity and broadband small base station technology that supports 4x4 MIMO (Multiple Input and Multiple Output) by proposing a new antenna structure and a new RF (Radio Frequency) structure based on LTE-A. Professors from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Dong Ho Cho, Songcheol Hong, and Yong Hoon Lee also collaborated on the project.
The existing heterodyne method of communication systems generates the problems of increasing unit price and system complexity.
In this project, however, Professor Lee directly modulated the baseband signal from the RF stage through an impedance loading-based RF chip. This method was designed to facilitate low power as well as low complexity while supporting broadband service. Based on this, his team developed source technology for RF that can be applied to fourth and even fifth generation networks.
Furthermore, this base station is smallest among the small-cell stations so far, providing an eco-friendly installation environment. It contributes to the market for fifth generation mobile communications by reducing power consumption significantly yet providing high-capacity services.
Professor Lee said, “This technology will contribute to creating a new market and additional jobs because business based on the fifth mobile generation can provide multi-functional services, including multiband. Requiring low power and providing high-capacity services anywhere at any time will enhance national competence and reduce costs for establishing a next generation mobile communication system. It is expected that this technology will help with disseminating mobile communication infrastructure through expanding information and communication system as well as the infrastructure of island areas.”
2017.11.08 View 9396
Professor Lee's Research Selected as Top 100 National R&D Projects
A research project, led by Research Professor Ju Yong Lee from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence, was selected as one of the Top 100 National Research and Development Projects 2017.
This research project, titled LTE-A-based Single RF Small Base Station supporting Multiple Streams, developed 300Mbps low power, low complexity and broadband small base station technology that supports 4x4 MIMO (Multiple Input and Multiple Output) by proposing a new antenna structure and a new RF (Radio Frequency) structure based on LTE-A. Professors from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Dong Ho Cho, Songcheol Hong, and Yong Hoon Lee also collaborated on the project.
The existing heterodyne method of communication systems generates the problems of increasing unit price and system complexity.
In this project, however, Professor Lee directly modulated the baseband signal from the RF stage through an impedance loading-based RF chip. This method was designed to facilitate low power as well as low complexity while supporting broadband service. Based on this, his team developed source technology for RF that can be applied to fourth and even fifth generation networks.
Furthermore, this base station is smallest among the small-cell stations so far, providing an eco-friendly installation environment. It contributes to the market for fifth generation mobile communications by reducing power consumption significantly yet providing high-capacity services.
Professor Lee said, “This technology will contribute to creating a new market and additional jobs because business based on the fifth mobile generation can provide multi-functional services, including multiband. Requiring low power and providing high-capacity services anywhere at any time will enhance national competence and reduce costs for establishing a next generation mobile communication system. It is expected that this technology will help with disseminating mobile communication infrastructure through expanding information and communication system as well as the infrastructure of island areas.”
2017.11.08 View 9396 -
 Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 10278
Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 10278 -
 In Jin Cho Earned the Best Poster Prize at ME Summit 2017
In Jin Cho, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST received the best poster prize at the International Metabolic Engineering Summit 2017 held on October 24 in Beijing, China.
The International Metabolic Engineering Summit is a global conference where scientists and corporate researchers in the field of metabolic engineering present their latest research outcomes and build networks.
At this year’s summit, about 500 researchers from around the world participated in active academic exchanges, including giving keynote speeches and presenting posters.
During the poster session, the summit selects one person for the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award, two for Microbial Cell Factories Poster Awards, and three for Biotechnology Journal Poster Awards among the posters presented by graduate students, post-doctoral fellows and researchers. Cho received the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award. Her winning poster is on the biotransformation of p-xylene to terephthalic acid using engineered Escherichia coli.
Terephthalic acid is generally produced by p-xylene oxidation; however, this process requires a high temperature and pressure as well as a toxic catalyst during the reaction process.
Cho and Ziwei Luo, a Ph.D. student at KAIST, co-conducted the research and developed a successful biological conversion process. Compared to the existing chemical process, it does not require a high temperature and pressure; and it is environmentally friendly with a relatively high conversion rate of approximately 97%.
Cho’s advisor, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Further research on glucose-derived terephthalic acid will enable us to produce biomass-based eco-friendly terephthalic acid through engineered Escherichia coli.”
2017.10.31 View 10210
In Jin Cho Earned the Best Poster Prize at ME Summit 2017
In Jin Cho, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST received the best poster prize at the International Metabolic Engineering Summit 2017 held on October 24 in Beijing, China.
The International Metabolic Engineering Summit is a global conference where scientists and corporate researchers in the field of metabolic engineering present their latest research outcomes and build networks.
At this year’s summit, about 500 researchers from around the world participated in active academic exchanges, including giving keynote speeches and presenting posters.
During the poster session, the summit selects one person for the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award, two for Microbial Cell Factories Poster Awards, and three for Biotechnology Journal Poster Awards among the posters presented by graduate students, post-doctoral fellows and researchers. Cho received the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award. Her winning poster is on the biotransformation of p-xylene to terephthalic acid using engineered Escherichia coli.
Terephthalic acid is generally produced by p-xylene oxidation; however, this process requires a high temperature and pressure as well as a toxic catalyst during the reaction process.
Cho and Ziwei Luo, a Ph.D. student at KAIST, co-conducted the research and developed a successful biological conversion process. Compared to the existing chemical process, it does not require a high temperature and pressure; and it is environmentally friendly with a relatively high conversion rate of approximately 97%.
Cho’s advisor, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Further research on glucose-derived terephthalic acid will enable us to produce biomass-based eco-friendly terephthalic acid through engineered Escherichia coli.”
2017.10.31 View 10210 -
 KAIST and KOICA Invited Dominican Republic Officials for Workshop
KAIST will host a two-week workshop for Dominican Republic officials and scholars in collaboration with KOICA (Korea International Cooperation Agency) beginning October 23 at KAIST.
The workshop aims to encourage academia-industry cooperation as one of the Projects for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology at KOICA. Dominican participants including the assistant minister of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology (MESCYT) and deans of engineering colleges at major universities will enjoy lectures from experts and visit enterprises known for excellent academia-industry collaboration.
According to the Center for Overseas Development, at which Professor WonJoon Kim in the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST holds the position of director, the workshop is designed to develop human resources in the science and technology (S&T) area, share knowledge on research and development in the field of academia-industry cooperation, and help the participants acquire know-how for managing partnerships between related organizations and industries.
During the workshop, KAIST plans to transfer know-how and share knowledge on its academia-industry cooperation R&D system, in hopes that the workshop will help the Dominican Republic foster its manpower in higher education. The workshop organizers hope that the officers and scholars will be able to apply what they will learn for establishing and carrying out detailed action plans for academia-industry cooperation policies in an effective manner.
“This workshop provides an opportunity to learn about the development of S&T in Korea, academia-industry cooperation R&D, and fostering manpower in advanced S&T. Through the knowledge sharing, we can have a better understanding of academia-industry cooperation as well as education on advanced manpower,” said Pedro Antonio Eduardo, the assistant minister of MESCYT.
He added, “I hope that this workshop will further detailed cooperation between the two countries for Korean high-tech enterprises’ overseas expansion and advanced manpower education. The development model in Korea has many essential elements, so learning its engine for growth and polytechnic manpower education will help develop my country’s industry sector.”
The Project for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology is one of the official development assistance projects running from last year until 2019. It promotes R&D activities for S&T in the Dominican Republic, encouraging academia-industry cooperation by improving trainers in charge of advanced manpower education.
2017.10.30 View 8294
KAIST and KOICA Invited Dominican Republic Officials for Workshop
KAIST will host a two-week workshop for Dominican Republic officials and scholars in collaboration with KOICA (Korea International Cooperation Agency) beginning October 23 at KAIST.
The workshop aims to encourage academia-industry cooperation as one of the Projects for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology at KOICA. Dominican participants including the assistant minister of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology (MESCYT) and deans of engineering colleges at major universities will enjoy lectures from experts and visit enterprises known for excellent academia-industry collaboration.
According to the Center for Overseas Development, at which Professor WonJoon Kim in the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST holds the position of director, the workshop is designed to develop human resources in the science and technology (S&T) area, share knowledge on research and development in the field of academia-industry cooperation, and help the participants acquire know-how for managing partnerships between related organizations and industries.
During the workshop, KAIST plans to transfer know-how and share knowledge on its academia-industry cooperation R&D system, in hopes that the workshop will help the Dominican Republic foster its manpower in higher education. The workshop organizers hope that the officers and scholars will be able to apply what they will learn for establishing and carrying out detailed action plans for academia-industry cooperation policies in an effective manner.
“This workshop provides an opportunity to learn about the development of S&T in Korea, academia-industry cooperation R&D, and fostering manpower in advanced S&T. Through the knowledge sharing, we can have a better understanding of academia-industry cooperation as well as education on advanced manpower,” said Pedro Antonio Eduardo, the assistant minister of MESCYT.
He added, “I hope that this workshop will further detailed cooperation between the two countries for Korean high-tech enterprises’ overseas expansion and advanced manpower education. The development model in Korea has many essential elements, so learning its engine for growth and polytechnic manpower education will help develop my country’s industry sector.”
The Project for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology is one of the official development assistance projects running from last year until 2019. It promotes R&D activities for S&T in the Dominican Republic, encouraging academia-industry cooperation by improving trainers in charge of advanced manpower education.
2017.10.30 View 8294 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 11983
Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 11983 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 12414
Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 12414 -
 Hyosung R&DB Labs to Teach Special Class on High Molecule Chemistry for the Fall Semester
The Department of Chemistry in collaboration with the Hyosung Group’s R&DB Labs will open a ‘special class on high molecule chemistry’ for Masters and Ph.D. candidates. The class, led by researchers at Hyosung’s R&D think tank, will provide the latest market and technology trends in the molecule chemical industry during the fall semester.
Hyosung joined this special industry program in an effort to enhance students’ hands-on understanding of new technologies that will emerge in the global market. During the semester, Hyosung plans to present the technology portfolios on their brand new materials of TAC film, membrane, and carbon fiber as well as the existing products leading the world in market share such as spandex, tire cords.
Hyosung plans to recruit students who previously took courses led by Hyosung researchers. President Tu-Won Chang of Hyosung R&DB said, “This program is designed to foster highly qualified R&D personnel especially catering to our company’s needs and market demands. We will continue to share our company’s market analysis and R&D know-how with outstanding universities.
2017.09.07 View 5371
Hyosung R&DB Labs to Teach Special Class on High Molecule Chemistry for the Fall Semester
The Department of Chemistry in collaboration with the Hyosung Group’s R&DB Labs will open a ‘special class on high molecule chemistry’ for Masters and Ph.D. candidates. The class, led by researchers at Hyosung’s R&D think tank, will provide the latest market and technology trends in the molecule chemical industry during the fall semester.
Hyosung joined this special industry program in an effort to enhance students’ hands-on understanding of new technologies that will emerge in the global market. During the semester, Hyosung plans to present the technology portfolios on their brand new materials of TAC film, membrane, and carbon fiber as well as the existing products leading the world in market share such as spandex, tire cords.
Hyosung plans to recruit students who previously took courses led by Hyosung researchers. President Tu-Won Chang of Hyosung R&DB said, “This program is designed to foster highly qualified R&D personnel especially catering to our company’s needs and market demands. We will continue to share our company’s market analysis and R&D know-how with outstanding universities.
2017.09.07 View 5371 -
 KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 7718
KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 7718 -
 Professor Dae-Sik Im to Head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office at the Ministry of Science & ICT
(Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences)
Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences, a renowned molecular cell biologist, was named to head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office in the Ministry of Science and ICT on August 31. He will be responsible for the oversight of national R&D projects as well as budget deliberation. Joining the KAIST faculty in 2002, he led the Creative Research Center of Cell Division and Differentiation at KAIST.
Announcing the nomination of Professor Im, Cheong Wa Dae spokesman Park Soo-Hyun said, “Professor Im will be the best person to lead the innovation of the research infrastructure system for basic research studies. We believe that his expertise and leadership will make a significant impact in enhancing the nation’s science and technology competitiveness. This vice minister position in the Ministry of Science and ICT was newly created in an effort to enhance national science and technology initiatives by President Moon Jae-In.
Professor Im said at the news conference, “I would like to make a sustainable, as well as credible, system ensuring the ingenuity of scientists in Korean labs. To this end, I will make every effort to enhance Korea’s innovative research environment in a way to maximize research achievements.”
2017.09.03 View 9561
Professor Dae-Sik Im to Head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office at the Ministry of Science & ICT
(Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences)
Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences, a renowned molecular cell biologist, was named to head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office in the Ministry of Science and ICT on August 31. He will be responsible for the oversight of national R&D projects as well as budget deliberation. Joining the KAIST faculty in 2002, he led the Creative Research Center of Cell Division and Differentiation at KAIST.
Announcing the nomination of Professor Im, Cheong Wa Dae spokesman Park Soo-Hyun said, “Professor Im will be the best person to lead the innovation of the research infrastructure system for basic research studies. We believe that his expertise and leadership will make a significant impact in enhancing the nation’s science and technology competitiveness. This vice minister position in the Ministry of Science and ICT was newly created in an effort to enhance national science and technology initiatives by President Moon Jae-In.
Professor Im said at the news conference, “I would like to make a sustainable, as well as credible, system ensuring the ingenuity of scientists in Korean labs. To this end, I will make every effort to enhance Korea’s innovative research environment in a way to maximize research achievements.”
2017.09.03 View 9561 -
 KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 15070
KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 15070 -
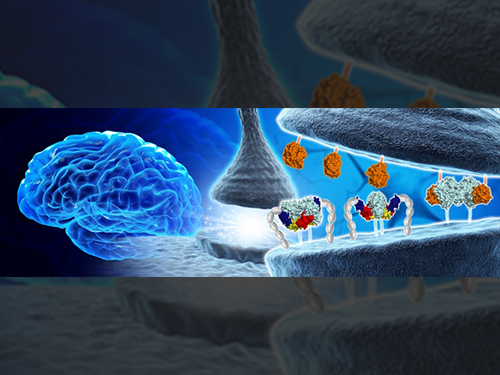 Structural Insights into the Modulation of Synaptic Adhesion by MDGA for Synaptogenesis
Synapses connected by various synaptic adhesion molecules are communication spaces between neurons for transmitting information. Among various synaptic adhesion molecules, neuroligins are arguably the most widely studied class of postsynaptic adhesion molecules, which mainly interact with presynaptic neurexins to induce excitatory or inhibitory synapse development. Recently, the membrane-associated mucin (MAM) domain-containing GPI anchor protein 1 (MDGA1) has been characterized as a key suppressor of Neuroligin-2/Neurexin-1β-mediated inhibitory synapse development, but how it acts remains a mystery.
In a recent issue of Neuron, published on June 21, 2017, a research team led by Professor Ho Min Kim at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering of KAIST reported the three-dimensional structure of MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex and mechanistic insights into how MDGAs negatively modulate synapse development governed by Neurexins/Neuroligins trans -synaptic adhesion complex.
MDGA1 consists of six Ig-like domains, fibronectin type III repeat domain, and MAM domain . The crystal structure of MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex reveals that they form the 2:2 hetero-tetrameric complex and only the Ig1-Ig2 domains of MDGA1 are involved in interactions with Neuroligin-2. The structural comparison between the MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 and Neurexin-1β/Neuroligin-1 complexes intriguingly indicates that the Neuroligin-2 region binding to MDGA1 largely overlaps with that of Neurexin-1β, but the interaction interface of the MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex is much larger than that of the Neurexin-1β/Neuroligin-1 complex. This explains why Neuroligin-2 binds stronger to MDGA1 than Neurexin-1β, and how the favored MDGA1 binding to Neuroligin-2 sterically blocks the interaction between Neuroligin-2 and Neurexin-1β, which is critical for the suppression of inhibitory synapse development.
“Although we found that MDGA Ig domains (Ig 1 and Ig 2) are sufficient to form a complex with NL2, other extracellular domains, including Ig 3–6, FN III, and MAM domains, may also contribute to stable cis-interactions between MDGA1 and Neuroligin-2 by providing conformational flexibility. Therefore, further structural analysis of full-length MDGA will be required,” Professor Kim said.
Neuroligin-2 specifically promotes the development of inhibitory synapses, whereas neuroligin-1 promotes the development of excitatory synapses. Recently, not only MDGA1, but also MDGA2 have emerged as synaptic regulators for the development of excitatory or inhibitory synapses. In vitro biochemical analysis in this research clearly demonstrates that Neuroligin-1 and Neuroligin-2 bind to both MDGA1 and MDGA2 with comparable affinity. However, pull-down assays using detergent-solubilized mouse brain membrane fractions show the specific interaction of MDGA1 with Neuroligin-2, but not with Neuroligin-1. “This suggests that unidentified processes may dictate the selective association of MDGA1 with Neuroligin-2 in vivo , ” explained Professor Jaewon Ko at the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
A balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses is crucial to healthy cognition and behavior. Mutations in neuroligins, neurexins, and MDGAs, which can disrupt the excitatory/inhibitory balance, are associated with neuropsychiatric diseases such as autism and schizophrenia. Jung A Kim at KAIST, first author in this study, said, “Our discovery from integrative investigations are an important first step both for a better understanding of Neuroligin/Neurexin synaptic adhesion pathways and MDGA-mediated regulation of synapse development as well as the development of potential new therapies for autism, schizophrenia, and epilepsy.”
2017.07.10 View 9204
Structural Insights into the Modulation of Synaptic Adhesion by MDGA for Synaptogenesis
Synapses connected by various synaptic adhesion molecules are communication spaces between neurons for transmitting information. Among various synaptic adhesion molecules, neuroligins are arguably the most widely studied class of postsynaptic adhesion molecules, which mainly interact with presynaptic neurexins to induce excitatory or inhibitory synapse development. Recently, the membrane-associated mucin (MAM) domain-containing GPI anchor protein 1 (MDGA1) has been characterized as a key suppressor of Neuroligin-2/Neurexin-1β-mediated inhibitory synapse development, but how it acts remains a mystery.
In a recent issue of Neuron, published on June 21, 2017, a research team led by Professor Ho Min Kim at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering of KAIST reported the three-dimensional structure of MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex and mechanistic insights into how MDGAs negatively modulate synapse development governed by Neurexins/Neuroligins trans -synaptic adhesion complex.
MDGA1 consists of six Ig-like domains, fibronectin type III repeat domain, and MAM domain . The crystal structure of MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex reveals that they form the 2:2 hetero-tetrameric complex and only the Ig1-Ig2 domains of MDGA1 are involved in interactions with Neuroligin-2. The structural comparison between the MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 and Neurexin-1β/Neuroligin-1 complexes intriguingly indicates that the Neuroligin-2 region binding to MDGA1 largely overlaps with that of Neurexin-1β, but the interaction interface of the MDGA1/Neuroligin-2 complex is much larger than that of the Neurexin-1β/Neuroligin-1 complex. This explains why Neuroligin-2 binds stronger to MDGA1 than Neurexin-1β, and how the favored MDGA1 binding to Neuroligin-2 sterically blocks the interaction between Neuroligin-2 and Neurexin-1β, which is critical for the suppression of inhibitory synapse development.
“Although we found that MDGA Ig domains (Ig 1 and Ig 2) are sufficient to form a complex with NL2, other extracellular domains, including Ig 3–6, FN III, and MAM domains, may also contribute to stable cis-interactions between MDGA1 and Neuroligin-2 by providing conformational flexibility. Therefore, further structural analysis of full-length MDGA will be required,” Professor Kim said.
Neuroligin-2 specifically promotes the development of inhibitory synapses, whereas neuroligin-1 promotes the development of excitatory synapses. Recently, not only MDGA1, but also MDGA2 have emerged as synaptic regulators for the development of excitatory or inhibitory synapses. In vitro biochemical analysis in this research clearly demonstrates that Neuroligin-1 and Neuroligin-2 bind to both MDGA1 and MDGA2 with comparable affinity. However, pull-down assays using detergent-solubilized mouse brain membrane fractions show the specific interaction of MDGA1 with Neuroligin-2, but not with Neuroligin-1. “This suggests that unidentified processes may dictate the selective association of MDGA1 with Neuroligin-2 in vivo , ” explained Professor Jaewon Ko at the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
A balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses is crucial to healthy cognition and behavior. Mutations in neuroligins, neurexins, and MDGAs, which can disrupt the excitatory/inhibitory balance, are associated with neuropsychiatric diseases such as autism and schizophrenia. Jung A Kim at KAIST, first author in this study, said, “Our discovery from integrative investigations are an important first step both for a better understanding of Neuroligin/Neurexin synaptic adhesion pathways and MDGA-mediated regulation of synapse development as well as the development of potential new therapies for autism, schizophrenia, and epilepsy.”
2017.07.10 View 9204 -
 KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 11453
KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 11453