-
 KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 13003
KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 13003 -
 Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
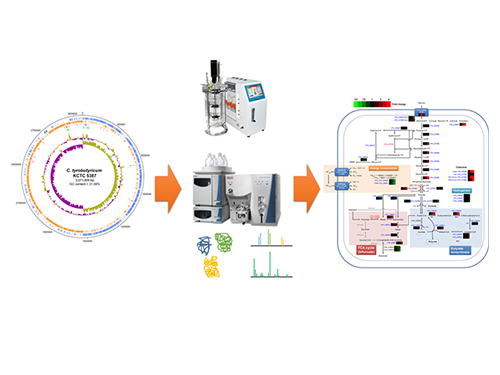
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10978
Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10978 -
 Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
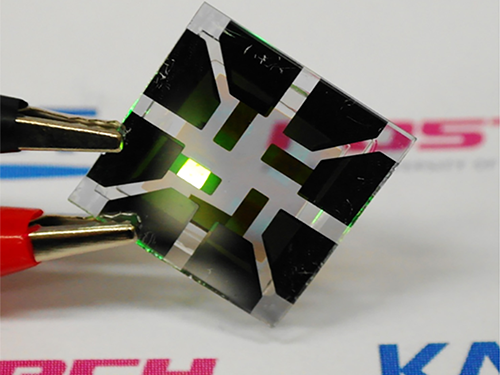
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 14388
Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 14388 -
 Special Lecture by Professor Sung-Hou Kim of UC Berkeley
As part of its special lecture series, the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has invited Professor Sung-Hou Kim of the Department of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, to lecture on his research in structural biology. He will speak twice on May 23 and 30, respectively, on the topics “Origin of Universe and Earth—A Narrative” and “Origin of Life and Human Species—A Narrative.”
Professor Kim's research addresses the structural basis of molecules to reveal how they communicate with each other to activate or inhibit particular processes in cell growth, cell differentiation, and cancer. Using the single-crystal X-ray diffraction technology, he discovered, for the first time in the world, the three-dimensional (3-D) structure of a transfer RNA (t-RNA) and received much praise for this work from the scientific community. Since then, he has been cited as a candidate for a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for many years.
He also examined the 3-D structures of a RAS protein in normal and cancer cells and identified the mutations of the RAS protein as a cause for cancer. His work has assisted in the development of target drugs for cancer treatment. In recent years, he has adopted a computational biology approach to study the structure and function of biological genomics, with which he has tried to predict disease-sensitive genes.
Professor Kim graduated from Seoul National University in 1962 and received his Ph.D. degree in chemistry from the University of Pittsburgh in the United States in 1966. He worked at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as a senior research scientist, and has taught at UC Berkeley since 1978.
2016.05.23 View 7215
Special Lecture by Professor Sung-Hou Kim of UC Berkeley
As part of its special lecture series, the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has invited Professor Sung-Hou Kim of the Department of Chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, to lecture on his research in structural biology. He will speak twice on May 23 and 30, respectively, on the topics “Origin of Universe and Earth—A Narrative” and “Origin of Life and Human Species—A Narrative.”
Professor Kim's research addresses the structural basis of molecules to reveal how they communicate with each other to activate or inhibit particular processes in cell growth, cell differentiation, and cancer. Using the single-crystal X-ray diffraction technology, he discovered, for the first time in the world, the three-dimensional (3-D) structure of a transfer RNA (t-RNA) and received much praise for this work from the scientific community. Since then, he has been cited as a candidate for a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for many years.
He also examined the 3-D structures of a RAS protein in normal and cancer cells and identified the mutations of the RAS protein as a cause for cancer. His work has assisted in the development of target drugs for cancer treatment. In recent years, he has adopted a computational biology approach to study the structure and function of biological genomics, with which he has tried to predict disease-sensitive genes.
Professor Kim graduated from Seoul National University in 1962 and received his Ph.D. degree in chemistry from the University of Pittsburgh in the United States in 1966. He worked at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as a senior research scientist, and has taught at UC Berkeley since 1978.
2016.05.23 View 7215 -
 KAIST Researchers Receive the 2016 IEEE William R. Bennett Prize
A research team led by Professors Yung Yi and Song Chong from the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been awarded the 2016 William R. Bennett Prize of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is the most prestigious award in the field of communications network. The IEEE bestows the honor annually and selects winning papers from among those published in the past three years for its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews.
The IEEE award ceremony will take place on May 24, 2016 at the IEEE International Conference on Communications in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The team members include Dr. Kyoung-Han Lee, a KAIST graduate, who is currently a professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea, Dr. Joo-Hyun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Ohio State University in the United States, and In-Jong Rhee, a vice president of the Mobile Division at Samsung Electronics. The same KAIST team previously received the award back in 2013, making them the second recipient ever to win the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize twice.
Past winners include Professors Robert Gallager of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Sachin Katti of Stanford University, and Ion Stoica of the University of California at Berkeley.
The research team received the Bennett award for their work on “Mobile Data Offloading: How Much Can WiFi Deliver?” Their research paper has been cited more than 500 times since its publication in 2013. They proposed an original method to effectively offload the cellular network and maximize the Wi-Fi network usage by analyzing the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life.
2016.05.02 View 14007
KAIST Researchers Receive the 2016 IEEE William R. Bennett Prize
A research team led by Professors Yung Yi and Song Chong from the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been awarded the 2016 William R. Bennett Prize of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is the most prestigious award in the field of communications network. The IEEE bestows the honor annually and selects winning papers from among those published in the past three years for its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews.
The IEEE award ceremony will take place on May 24, 2016 at the IEEE International Conference on Communications in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The team members include Dr. Kyoung-Han Lee, a KAIST graduate, who is currently a professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea, Dr. Joo-Hyun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Ohio State University in the United States, and In-Jong Rhee, a vice president of the Mobile Division at Samsung Electronics. The same KAIST team previously received the award back in 2013, making them the second recipient ever to win the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize twice.
Past winners include Professors Robert Gallager of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Sachin Katti of Stanford University, and Ion Stoica of the University of California at Berkeley.
The research team received the Bennett award for their work on “Mobile Data Offloading: How Much Can WiFi Deliver?” Their research paper has been cited more than 500 times since its publication in 2013. They proposed an original method to effectively offload the cellular network and maximize the Wi-Fi network usage by analyzing the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life.
2016.05.02 View 14007 -
 President Sung-Mo Kang Receives the Jang Young-sil Award
On April 22, 2016, President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST became the 18th recipient of the Jang Young-sil Award. The Jang Young-sil Memorial Association of Korea awarded the prize to him at the Korea Press Center in Seoul.
The award, created in 1999 by the Jang Young-sil Memorial Association of Korea to recognize those scientists who have made significant contributions to the development of Korean science and technology, is bestowed annually.
Jang Young-sil was a highly regarded Korean scientist and astronomer during the Joseon Dynasty (1392-1897), whose major inventions were a sundial, a water clock, and a rain gauge.
In the award ceremony, the association said that President Kang had devoted much of his life to the advancement of science education and research, globally and nationally, as an educator, scholar, administrator, and researcher and that his accomplishments have served as an example of leadership for young scientists.
In his acceptance speech, President Kang expressed his gratitude for the award and said,
“I am honored to receive an award in the name of our great ancestor scientist Jang Young-sil who, despite his low birth as a peasant, rose to become an excellent scientist and built a remarkable legacy of science for Korea. While cherishing his spirit, creativity and grit, I will continue to working hard to foster outstanding scientists and engineers who are needed not only by Korea but also by the global community.”
In the photo, Dr. Gun-Mo Chung (pictured on the right), the former Minister of Science and Technology of Korea presents the Jang Young-sil Award to President Sung-Mo Kang (left).
2016.04.22 View 5825
President Sung-Mo Kang Receives the Jang Young-sil Award
On April 22, 2016, President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST became the 18th recipient of the Jang Young-sil Award. The Jang Young-sil Memorial Association of Korea awarded the prize to him at the Korea Press Center in Seoul.
The award, created in 1999 by the Jang Young-sil Memorial Association of Korea to recognize those scientists who have made significant contributions to the development of Korean science and technology, is bestowed annually.
Jang Young-sil was a highly regarded Korean scientist and astronomer during the Joseon Dynasty (1392-1897), whose major inventions were a sundial, a water clock, and a rain gauge.
In the award ceremony, the association said that President Kang had devoted much of his life to the advancement of science education and research, globally and nationally, as an educator, scholar, administrator, and researcher and that his accomplishments have served as an example of leadership for young scientists.
In his acceptance speech, President Kang expressed his gratitude for the award and said,
“I am honored to receive an award in the name of our great ancestor scientist Jang Young-sil who, despite his low birth as a peasant, rose to become an excellent scientist and built a remarkable legacy of science for Korea. While cherishing his spirit, creativity and grit, I will continue to working hard to foster outstanding scientists and engineers who are needed not only by Korea but also by the global community.”
In the photo, Dr. Gun-Mo Chung (pictured on the right), the former Minister of Science and Technology of Korea presents the Jang Young-sil Award to President Sung-Mo Kang (left).
2016.04.22 View 5825 -
 KAIST and McKinsey Korea Agreed to Cultivate Management Leaders
KAIST and McKinsey Korea signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) for the “Joint Research on Innovative Instructional Method to Cultivate Future Management Leaders” on April 8, 2016, at the SUPEX Management Hall of KAIST Management School in Seoul.
Under the MOU, both organizations will cooperate in the following research areas: management strategies to overcome the low growth of Korean economy, instructional methods to foster leaders in the field of business and management, and innovative management systems for business.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to work with McKinsey, a worldwide management consulting firm, to foster leaders in science and business. As we see more demanding challenges of managing and leading science-based businesses today, this alliance is indeed timely and will be very helpful.”
2016.04.15 View 5984
KAIST and McKinsey Korea Agreed to Cultivate Management Leaders
KAIST and McKinsey Korea signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) for the “Joint Research on Innovative Instructional Method to Cultivate Future Management Leaders” on April 8, 2016, at the SUPEX Management Hall of KAIST Management School in Seoul.
Under the MOU, both organizations will cooperate in the following research areas: management strategies to overcome the low growth of Korean economy, instructional methods to foster leaders in the field of business and management, and innovative management systems for business.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to work with McKinsey, a worldwide management consulting firm, to foster leaders in science and business. As we see more demanding challenges of managing and leading science-based businesses today, this alliance is indeed timely and will be very helpful.”
2016.04.15 View 5984 -
 KAIST, NTU, and Technion Collaborate for Research in Emerging Fields
KAIST, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) of Singapore, and Technion of Israel signed an agreement on April 11, 2016 in Seoul to create a five-year joint research program for some of the most innovative and entrepreneurial areas: robotics, medical technologies, satellites, materials science and engineering, and entrepreneurship. Under the agreement, the universities will also offer dual degree opportunities, exchange visits, and internships.
In the picture from the left, Bertil Andersson of NTU, Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, and Peretz Lavie of Technion hold the signed memorandum of understanding.
2016.04.14 View 12092
KAIST, NTU, and Technion Collaborate for Research in Emerging Fields
KAIST, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) of Singapore, and Technion of Israel signed an agreement on April 11, 2016 in Seoul to create a five-year joint research program for some of the most innovative and entrepreneurial areas: robotics, medical technologies, satellites, materials science and engineering, and entrepreneurship. Under the agreement, the universities will also offer dual degree opportunities, exchange visits, and internships.
In the picture from the left, Bertil Andersson of NTU, Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, and Peretz Lavie of Technion hold the signed memorandum of understanding.
2016.04.14 View 12092 -
 KAIST Hosts the 2016 IPFGRU
More than 120 senior representatives from 65 universities around the world will convene this month in Seoul to discuss the social responsibilities of higher education and strategic global partnerships among academia, research, and industry to advance socio-economic values.
Higher education as a driver of change to address the social and global challenges facing humanity in the 21st century has never been as important as it is today.
KAIST will raise the topic of higher education as a driver of social change, innovation, and entrepreneurship with the heads of global universities at its seventh international forum to be held on April 11-12, 2016 at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
The 2016 International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities (IPFGRU) will bring over 120 presidents and vice presidents of 65 research universities and institutes from 36 nations together to discuss the theme of “Social Responsibilities of Higher Education and Strategic Global Partnership.”
Presidents Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, Jacques Biot of École Polytechnique in France, and Peretz Lavie of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology will address the conference as plenary speakers.
President Kang will speak about KAIST’s initiatives to produce creative talents through student-centered education, entrepreneurship curricula, and the integration of humanities into cutting-edge research programs. His presentation, titled “The Fostering of Creative Talents and the Social Responsibility of Research Universities in the New Era,” introduces KAIST’s educational philosophy which can be represented as π. A broad range of understanding in basic disciplines (the horizontal line) is supported with one prong of in-depth knowledge in a chosen field and the other in entrepreneurial spirit.
KAIST graduates have demonstrated extraordinary leadership in research, academia, business, and public service. Nearly 25% of the research and development personnel at Samsung Electronics are KAIST Ph.D. holders. President Kang also describes KAIST’s latest endeavor to turn a university-led entrepreneurial activity into a stable business based on research outcomes and campus innovations. The K-School, a one-year master’s degree program on entrepreneurship and innovation, has just launched and is expecting to receive its first batch of students this fall. The K-School is envisioned to continue the university’s legacy as a major feeder for startups in Korea.
President Lavie will give a talk on “Fostering an Innovation and Entrepreneurship (I&E) Ecosystem in Israel,” in which he describes how the Technion-Israel Institute has become integral to the foundation of the nation’s I&E platform. Since its establishment in 1912, the university has become a key player in the growth of Israel’s industry, science, and technology while nurturing the majority of the nation’s top-notch researchers, innovators, and entrepreneurs. Technion graduates have created more than 2,000 companies in Israel alone, generating 100,000 jobs and USD 30 billion through mergers and acquisitions.
President Biot will offer his insights into how the future of global research universities will be widely impacted by the emergence of disruptions triggered by the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In his speech entitled “How to Prepare Our Universities for the New Era of Industry 4.0,” he emphasizes that universities should take multi-disciplinary approaches to tackle societal challenges given the complexity of today’s problems ranging from climate change to energy crises, pandemic diseases, and poverty. He argues that universities should identify the needs of students in “Generation Z” who, from birth, have been heavily exposed to the Internet and digital technologies and, thus, universities should develop new educational systems (i.e., University 4.0.) to better prepare these students to cope with Industry 4.0.
The IPFGRU consists of presentations and discussions addressing the following sub-topics:
- Seeking a New Model of Research Universities in a New Era: This session will explore the role of research universities as both innovation drivers and growth engines in an age of robotics, globalization, and digitally-driven markets. In addition, speakers will discuss how to prepare universities for the Industry 4.0 era, and how multidisciplinary approaches and open innovations will play a large part in facilitating translational research and technology transfer.
- Shared Challenges and Responsibilities from a Global Perspective: Universities will share their strategies, policies, and practices to respond to critical issues facing local and global communities such as youth unemployment, the environment, energy, inequality, and entrepreneurship.
- Strategic Global Partnerships for Sustainable Development: Panelists will discuss how to build productive and sustainable partnerships that can generate synergies between education and research.
- Insights into Higher Education: Trends and Development: Participants will examine how universities can stay relevant in an increasingly competitive higher education sector and can assist students to better adapt to opportunities and challenges posed by the new industry of digital transformation and exponentially-growing technologies.
Sung-Hyon Myaeng, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST and a Co-chair of the 2016 IPFGRU said,
“The IPFGRU was established in 2008 to promote excellence and innovation in higher education with presidents of leading research universities and key policy-makers in the private and public sectors from across the world. Since then, it has served as one of the largest university gatherings in Asia, allowing participants to cooperate and share their expertise, ideas, and best practices taking place in academia, industry, and government.”
“This year’s meeting has recorded the largest number of universities participating, including 28 European schools, 20 Asian institutions, and 8 schools from the Americas, which I believe reflects a sense of urgency that global universities share. One way or another, we must adapt to the rapidly transforming educational and research environment encompassing higher learning,” added Myaeng.
For more information, go to http://forum.kaist.ac.kr.
2016.04.08 View 9853
KAIST Hosts the 2016 IPFGRU
More than 120 senior representatives from 65 universities around the world will convene this month in Seoul to discuss the social responsibilities of higher education and strategic global partnerships among academia, research, and industry to advance socio-economic values.
Higher education as a driver of change to address the social and global challenges facing humanity in the 21st century has never been as important as it is today.
KAIST will raise the topic of higher education as a driver of social change, innovation, and entrepreneurship with the heads of global universities at its seventh international forum to be held on April 11-12, 2016 at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
The 2016 International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities (IPFGRU) will bring over 120 presidents and vice presidents of 65 research universities and institutes from 36 nations together to discuss the theme of “Social Responsibilities of Higher Education and Strategic Global Partnership.”
Presidents Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, Jacques Biot of École Polytechnique in France, and Peretz Lavie of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology will address the conference as plenary speakers.
President Kang will speak about KAIST’s initiatives to produce creative talents through student-centered education, entrepreneurship curricula, and the integration of humanities into cutting-edge research programs. His presentation, titled “The Fostering of Creative Talents and the Social Responsibility of Research Universities in the New Era,” introduces KAIST’s educational philosophy which can be represented as π. A broad range of understanding in basic disciplines (the horizontal line) is supported with one prong of in-depth knowledge in a chosen field and the other in entrepreneurial spirit.
KAIST graduates have demonstrated extraordinary leadership in research, academia, business, and public service. Nearly 25% of the research and development personnel at Samsung Electronics are KAIST Ph.D. holders. President Kang also describes KAIST’s latest endeavor to turn a university-led entrepreneurial activity into a stable business based on research outcomes and campus innovations. The K-School, a one-year master’s degree program on entrepreneurship and innovation, has just launched and is expecting to receive its first batch of students this fall. The K-School is envisioned to continue the university’s legacy as a major feeder for startups in Korea.
President Lavie will give a talk on “Fostering an Innovation and Entrepreneurship (I&E) Ecosystem in Israel,” in which he describes how the Technion-Israel Institute has become integral to the foundation of the nation’s I&E platform. Since its establishment in 1912, the university has become a key player in the growth of Israel’s industry, science, and technology while nurturing the majority of the nation’s top-notch researchers, innovators, and entrepreneurs. Technion graduates have created more than 2,000 companies in Israel alone, generating 100,000 jobs and USD 30 billion through mergers and acquisitions.
President Biot will offer his insights into how the future of global research universities will be widely impacted by the emergence of disruptions triggered by the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In his speech entitled “How to Prepare Our Universities for the New Era of Industry 4.0,” he emphasizes that universities should take multi-disciplinary approaches to tackle societal challenges given the complexity of today’s problems ranging from climate change to energy crises, pandemic diseases, and poverty. He argues that universities should identify the needs of students in “Generation Z” who, from birth, have been heavily exposed to the Internet and digital technologies and, thus, universities should develop new educational systems (i.e., University 4.0.) to better prepare these students to cope with Industry 4.0.
The IPFGRU consists of presentations and discussions addressing the following sub-topics:
- Seeking a New Model of Research Universities in a New Era: This session will explore the role of research universities as both innovation drivers and growth engines in an age of robotics, globalization, and digitally-driven markets. In addition, speakers will discuss how to prepare universities for the Industry 4.0 era, and how multidisciplinary approaches and open innovations will play a large part in facilitating translational research and technology transfer.
- Shared Challenges and Responsibilities from a Global Perspective: Universities will share their strategies, policies, and practices to respond to critical issues facing local and global communities such as youth unemployment, the environment, energy, inequality, and entrepreneurship.
- Strategic Global Partnerships for Sustainable Development: Panelists will discuss how to build productive and sustainable partnerships that can generate synergies between education and research.
- Insights into Higher Education: Trends and Development: Participants will examine how universities can stay relevant in an increasingly competitive higher education sector and can assist students to better adapt to opportunities and challenges posed by the new industry of digital transformation and exponentially-growing technologies.
Sung-Hyon Myaeng, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST and a Co-chair of the 2016 IPFGRU said,
“The IPFGRU was established in 2008 to promote excellence and innovation in higher education with presidents of leading research universities and key policy-makers in the private and public sectors from across the world. Since then, it has served as one of the largest university gatherings in Asia, allowing participants to cooperate and share their expertise, ideas, and best practices taking place in academia, industry, and government.”
“This year’s meeting has recorded the largest number of universities participating, including 28 European schools, 20 Asian institutions, and 8 schools from the Americas, which I believe reflects a sense of urgency that global universities share. One way or another, we must adapt to the rapidly transforming educational and research environment encompassing higher learning,” added Myaeng.
For more information, go to http://forum.kaist.ac.kr.
2016.04.08 View 9853 -
 Next-Generation Holographic Microscope for 3D Live Cell Imaging
KAIST researchers have developed a revolutionary bio-medical imaging tool, the HT-1, to view and analyze cells, which is commercially available.
Professor YongKeun Park of the Physics Department at KAIST and his research team have developed a powerful method for 3D imaging of live cells without staining. The researchers announced the launch of their new microscopic tool, the holotomography (HT)-1, to the global marketplace through a Korean start-up that Professor Park co-founded, TomoCube (www.tomocube.com).
Professor Park is a leading researcher in the field of biophotonics and has dedicated much of his research career to working on digital holographic microscopy technology. He collaborated with TomoCube’s R&D team to develop a state-of-the-art, 2D/3D/4D holographic microscope that would allow a real-time label-free visualization of biological cells and tissues.
The HT is an optical analogy of X-ray computed tomography (CT). Both X-ray CT and HT share the same physical principle—the inverse of wave scattering. The difference is that HT uses laser illumination whereas X-ray CT uses X-ray beams. From the measurement of multiple 2D holograms of a cell, coupled with various angles of laser illuminations, the 3D refractive index (RI) distribution of the cell can be reconstructed. The reconstructed 3D RI map provides structural and chemical information of the cell including mass, morphology, protein concentration, and dynamics of the cellular membrane.
The HT enables users to quantitatively and non-invasively investigate the intrinsic properties of biological cells, for example, dry mass and protein concentration. Some of the research team’s breakthroughs that have leveraged HT’s unique and special capabilities can be found in several recent publications, including a lead article on the simultaneous 3D visualization and position tracking of optically trapped particles which was published in Optica on April 20, 2015.
Current fluorescence confocal microscopy techniques require the use of exogenous labeling agents to render high-contrast molecular information. Therefore, drawbacks include possible photo-bleaching, photo-toxicity, and interference with normal molecular activities. Immune or stem cells that need to be reinjected into the body are considered particularly difficult to employ with fluorescence microscopy.
“As one of the two currently available, high-resolution tomographic microscopes in the world, I believe that the HT-1 is the best in class regarding specifications and functionality. Users can see 3D/4D live images of cells, without fixing, coating or staining cells. Sample preparation times are reduced from a few days or hours to just a few minutes,” said Professor Park.
Two Korean hospitals, Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang and Boramae Hospital in Seoul, are using this microscope currently. The research team has also introduced the HT-1 at the Photonics West Exhibition 2016 that took place on February 16-18 in San Francisco, USA.
Professor Park added, “Our technology has set a new paradigm for cell observation under a microscope. I expect that this tomographic microscopy will be more widely used in future in various areas of pharmaceuticals, neuroscience, immunology, hematology, and cell biology.”
Figure 1: HT-1 and Its Specifications
Figure 2: 3D Images of Representative Biological Cells Taken with the HT-1
2016.03.29 View 13200
Next-Generation Holographic Microscope for 3D Live Cell Imaging
KAIST researchers have developed a revolutionary bio-medical imaging tool, the HT-1, to view and analyze cells, which is commercially available.
Professor YongKeun Park of the Physics Department at KAIST and his research team have developed a powerful method for 3D imaging of live cells without staining. The researchers announced the launch of their new microscopic tool, the holotomography (HT)-1, to the global marketplace through a Korean start-up that Professor Park co-founded, TomoCube (www.tomocube.com).
Professor Park is a leading researcher in the field of biophotonics and has dedicated much of his research career to working on digital holographic microscopy technology. He collaborated with TomoCube’s R&D team to develop a state-of-the-art, 2D/3D/4D holographic microscope that would allow a real-time label-free visualization of biological cells and tissues.
The HT is an optical analogy of X-ray computed tomography (CT). Both X-ray CT and HT share the same physical principle—the inverse of wave scattering. The difference is that HT uses laser illumination whereas X-ray CT uses X-ray beams. From the measurement of multiple 2D holograms of a cell, coupled with various angles of laser illuminations, the 3D refractive index (RI) distribution of the cell can be reconstructed. The reconstructed 3D RI map provides structural and chemical information of the cell including mass, morphology, protein concentration, and dynamics of the cellular membrane.
The HT enables users to quantitatively and non-invasively investigate the intrinsic properties of biological cells, for example, dry mass and protein concentration. Some of the research team’s breakthroughs that have leveraged HT’s unique and special capabilities can be found in several recent publications, including a lead article on the simultaneous 3D visualization and position tracking of optically trapped particles which was published in Optica on April 20, 2015.
Current fluorescence confocal microscopy techniques require the use of exogenous labeling agents to render high-contrast molecular information. Therefore, drawbacks include possible photo-bleaching, photo-toxicity, and interference with normal molecular activities. Immune or stem cells that need to be reinjected into the body are considered particularly difficult to employ with fluorescence microscopy.
“As one of the two currently available, high-resolution tomographic microscopes in the world, I believe that the HT-1 is the best in class regarding specifications and functionality. Users can see 3D/4D live images of cells, without fixing, coating or staining cells. Sample preparation times are reduced from a few days or hours to just a few minutes,” said Professor Park.
Two Korean hospitals, Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang and Boramae Hospital in Seoul, are using this microscope currently. The research team has also introduced the HT-1 at the Photonics West Exhibition 2016 that took place on February 16-18 in San Francisco, USA.
Professor Park added, “Our technology has set a new paradigm for cell observation under a microscope. I expect that this tomographic microscopy will be more widely used in future in various areas of pharmaceuticals, neuroscience, immunology, hematology, and cell biology.”
Figure 1: HT-1 and Its Specifications
Figure 2: 3D Images of Representative Biological Cells Taken with the HT-1
2016.03.29 View 13200 -
 Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activated by KAIST and UPenn Teams
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik of the Chemistry Department at KAIST and his team collaborated with an international team to discover a novel chemical reaction, carbon-hydrogen borylation using methane, and their research results were published in the March 25th issue of Science.
For details, please refer to the following press release from the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS) in Korea and the University of Pennsylvania in the United States.
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activation Achieved for the First Time
The Institute for Basic Science, March 24, 2016
Penn Chemists Lay Groundwork for Countless New, Cleaner Uses of Methane
University of Pennsylvania, March 24, 2016
2016.03.25 View 9954
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activated by KAIST and UPenn Teams
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik of the Chemistry Department at KAIST and his team collaborated with an international team to discover a novel chemical reaction, carbon-hydrogen borylation using methane, and their research results were published in the March 25th issue of Science.
For details, please refer to the following press release from the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS) in Korea and the University of Pennsylvania in the United States.
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activation Achieved for the First Time
The Institute for Basic Science, March 24, 2016
Penn Chemists Lay Groundwork for Countless New, Cleaner Uses of Methane
University of Pennsylvania, March 24, 2016
2016.03.25 View 9954 -
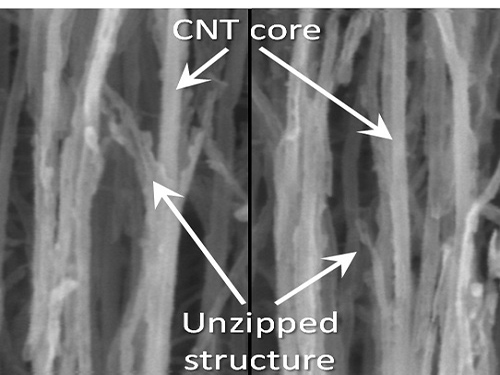 KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 9195
KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 9195