-
 KAIST Named Asia's Most Innovative University by Thomson Reuters
Thomson Reuters ranked KAIST first among Asia’s top most innovative universities in a list that it released on August 30, 2016. Seventy-five Asian universities received this distinction.
Thomson Reuters created the list to identify those educational institutions that are “doing the most to advance science, invent new technologies, and help drive the global economy.”
The rankings were based on data drawn from each academic institution's research papers and patent filing information as evaluated by the Intellectual Property & Science division of Thomson Reuters.
Thomson Reuters described KAIST as producing "original and influential research" and noted that other organizations cited its patent portfolios as "significant prior art in their own patent applications, a strong indicator that the university has an outsized impact on global research and development."
For details, please go to the link below:
Asia’s Most Innovative Universities
Reuters
August 30, 2016
http://www.reuters.com/article/us-asiapac-reuters-ranking-innovative-un-idUSKCN1152B7#listing
2016.08.31 View 5843
KAIST Named Asia's Most Innovative University by Thomson Reuters
Thomson Reuters ranked KAIST first among Asia’s top most innovative universities in a list that it released on August 30, 2016. Seventy-five Asian universities received this distinction.
Thomson Reuters created the list to identify those educational institutions that are “doing the most to advance science, invent new technologies, and help drive the global economy.”
The rankings were based on data drawn from each academic institution's research papers and patent filing information as evaluated by the Intellectual Property & Science division of Thomson Reuters.
Thomson Reuters described KAIST as producing "original and influential research" and noted that other organizations cited its patent portfolios as "significant prior art in their own patent applications, a strong indicator that the university has an outsized impact on global research and development."
For details, please go to the link below:
Asia’s Most Innovative Universities
Reuters
August 30, 2016
http://www.reuters.com/article/us-asiapac-reuters-ranking-innovative-un-idUSKCN1152B7#listing
2016.08.31 View 5843 -
 Professor Lee to Head the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology
Emeritus Professor In Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was appointed to the post of President of the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAiT) in Ethiopia. His term will begin on August 1, 2016 and end on July 31, 2018, which can be extended up to five years.
AAiT is an affiliated institute of Addis Ababa University, a distinguished national university in Ethiopia, and specializes in education and research in engineering and technology. There are currently 5,500 undergraduate and 4,500 graduate students enrolled at the institute.
The Ethiopian government has recognized the importance of science and technology for the future of the country. The government intends to develop AAiT into a distinguished research university similar to KAIST, and thus sought advice from KAIST to recommend an administrator who will head AAiT. Upon recommendation by KAIST President Steve Kang, Professor Lee was appointed.
Professor Lee graduated from Seoul National University with bachelor's and master’s degrees in aeronautical engineering and earned his Ph.D. in aeronautics from Stanford University.
He has served as the President of The Korean Society for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, the Director of the KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center, and a Research Associate at NASA Ames Research Center.
2016.08.03 View 9018
Professor Lee to Head the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology
Emeritus Professor In Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was appointed to the post of President of the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAiT) in Ethiopia. His term will begin on August 1, 2016 and end on July 31, 2018, which can be extended up to five years.
AAiT is an affiliated institute of Addis Ababa University, a distinguished national university in Ethiopia, and specializes in education and research in engineering and technology. There are currently 5,500 undergraduate and 4,500 graduate students enrolled at the institute.
The Ethiopian government has recognized the importance of science and technology for the future of the country. The government intends to develop AAiT into a distinguished research university similar to KAIST, and thus sought advice from KAIST to recommend an administrator who will head AAiT. Upon recommendation by KAIST President Steve Kang, Professor Lee was appointed.
Professor Lee graduated from Seoul National University with bachelor's and master’s degrees in aeronautical engineering and earned his Ph.D. in aeronautics from Stanford University.
He has served as the President of The Korean Society for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, the Director of the KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center, and a Research Associate at NASA Ames Research Center.
2016.08.03 View 9018 -
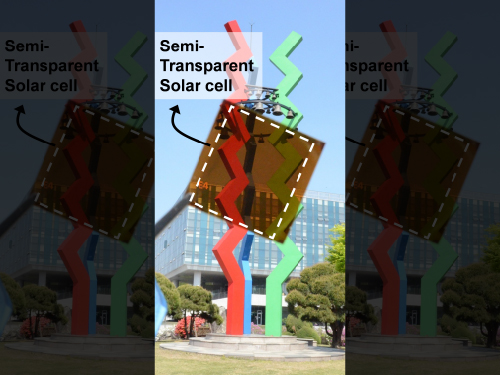 KAIST Team Develops Semi-Transparent Solar Cells with Thermal Mirror Capability
A research team led by KAIST and Sungkyunkwan University professors has created semi-transparent perovskite solar cells that demonstrate high-power conversion efficiency and transmit visible light while blocking infrared light, making them great candidates for solar windows.
Modern architects prefer to build exteriors designed with glass mainly from artistic or cost perspectives. Scientists, however, go one step further and see opportunities from its potential ability to harness solar energy. Researchers have thus explored ways to make solar cells transparent or semi-transparent as a substitute material for glass, but this has proven to be a challenging task because solar cells need to absorb sunlight to generate electricity, and when they are transparent, it reduces their energy efficiency.
Typical solar cells today are made of crystalline silicon, but it is difficult to make them translucent. Semi-transparent solar cells under development use, for example, organic or dye-sensitized materials, but compared to crystalline silicon-based cells, their power-conversion efficiencies are relatively low. Perovskites are hybrid organic-inorganic halide-based photovoltaic materials, which are cheap to produce and easy to manufacture. They have recently received much attention as the efficiency of perovskite solar cells has rapidly increased to the level of silicon technologies in the past few years.
Using perovskites, a Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and Professor Nam-Gyu Park of the Chemical Engineering School at Sungkyunkwan University developed a semi-transparent solar cell that is highly efficient and, additionally, functions very effectively as a thermal-mirror.
The team has developed a top transparent electrode (TTE) that works well with perovskite solar cells. In most cases, a key to success in realizing semi-transparent solar cells is to find a TTE that is compatible with a given photoactive material system, which is also the case for perovskite solar cells. The proposed TTE is based on a multilayer stack consisting of a metal film sandwiched between a high refractive-index (high-index) layer and an interfacial buffer layer. This TTE, placed as a top-most layer, can be prepared without damaging ingredients used in perovskite solar cells. Unlike conventional transparent electrodes focusing only on transmitting visible light, the proposed TTE plays the dual role of passing through visible light while reflecting infrared rays. The semi-transparent solar cells made with the proposed TTEs exhibited average power conversion efficiency as high as 13.3% with 85.5% infrared rejection.
The team believes that if the semi-transparent perovskite solar cells are scaled up for practical applications, they can be used in solar windows for buildings and automobiles, which not only generate electrical energy but also enable the smart heat management for indoor environments, thereby utilizing solar energy more efficiently and effectively.
This result was published as a cover article in the July 20, 2016 issue of Advanced Energy Materials. The research paper is entitled “Empowering Semi-transparent Solar Cells with Thermal-mirror Functionality.” (DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502466)
The team designed the transparent electrode (TE) stack in three layers: A thin-film of silver (Ag) is placed in between the bottom interfacial layer of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) and the top high-index dielectric layer of zinc sulfide (ZnS). Such a tri-layer approach has been known as a means to increase the overall visible-light transmittance of metallic thin films via index matching technique, which is essentially the same technique used for anti-reflection coating of glasses except that the present case involves a metallic layer.
Traditionally, when a TE is based on a metal film, such as Ag, the film should be extremely thin, e.g., 7-12 nanometers (nm), to obtain transparency and, accordingly, to transmit visible light. However, the team took a different approach in this research. They made the Ag TE two or three times thicker (12-24 nm) than conventional metal films and, as a result, it reflected more infrared light. The high refractive index of the ZnS layer plays an essential role in keeping the visible light transmittance of the proposed TTE high even with the relatively thick Ag film when its thickness is carefully optimized for maximal destructive interference, leading to low reflectance (and thus high transmittance) within its visible light range.
The team confirmed the semi-transparent perovskite solar cell’s thermal-mirror function through an experiment in which a halogen lamp illuminated an object for five minutes through three mediums: a window of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and the proposed semi-transparent perovskite solar cell. An infrared (IR) camera took thermal images of the object as well as that of each window’s surface. The object’s temperature, when exposed through the glass window, rose to 36.8 Celsius degrees whereas both the tinting film and the cell allowed the object to remain below 27 Celsius degrees. The tinting film absorbs light to block solar energy, so the film’s surface became hot as it was continuously exposed to the lamp light, but the proposed semi-transparent solar cell stayed cool since it rejects solar heat energy by reflection, rather than by absorption. The total solar energy rejection (TSER) of the proposed cell was as high as 89.6%.
Professor Yoo of KAIST said, “The major contributions of this work are to find transparent electrode technology suitable for translucent perovskite cells and to provide a design approach to fully harness the potential it can further deliver as a heat mirror in addition to its main role as an electrode. The present work can be further fine-tuned to include colored solar cells and to incorporate flexible or rollable form factors, as they will allow for greater design freedom and thus offer more opportunities for them to be integrated into real-world objects and structures such as cars, buildings, and houses.”
The lead authors are Hoyeon Kim and Jaewon Ha, both Ph.D. candidates in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, and Hui-Seon Kim, a student in the School of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University. This research was supported mainly by the Climate Change Research Hub Program of KAIST.
Picture 1: Semi-transparent Perovskite Solar Cell
This picture shows a prototype of a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell with thermal-mirror functionality.
Picture 2: A Heat Rejection Performance Comparison Experiment
This picture presents thermal images taken by an infrared camera for comparing the heat rejection performance of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell after being illuminated by a halogen lamp for five minutes.
2016.08.02 View 12850
KAIST Team Develops Semi-Transparent Solar Cells with Thermal Mirror Capability
A research team led by KAIST and Sungkyunkwan University professors has created semi-transparent perovskite solar cells that demonstrate high-power conversion efficiency and transmit visible light while blocking infrared light, making them great candidates for solar windows.
Modern architects prefer to build exteriors designed with glass mainly from artistic or cost perspectives. Scientists, however, go one step further and see opportunities from its potential ability to harness solar energy. Researchers have thus explored ways to make solar cells transparent or semi-transparent as a substitute material for glass, but this has proven to be a challenging task because solar cells need to absorb sunlight to generate electricity, and when they are transparent, it reduces their energy efficiency.
Typical solar cells today are made of crystalline silicon, but it is difficult to make them translucent. Semi-transparent solar cells under development use, for example, organic or dye-sensitized materials, but compared to crystalline silicon-based cells, their power-conversion efficiencies are relatively low. Perovskites are hybrid organic-inorganic halide-based photovoltaic materials, which are cheap to produce and easy to manufacture. They have recently received much attention as the efficiency of perovskite solar cells has rapidly increased to the level of silicon technologies in the past few years.
Using perovskites, a Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and Professor Nam-Gyu Park of the Chemical Engineering School at Sungkyunkwan University developed a semi-transparent solar cell that is highly efficient and, additionally, functions very effectively as a thermal-mirror.
The team has developed a top transparent electrode (TTE) that works well with perovskite solar cells. In most cases, a key to success in realizing semi-transparent solar cells is to find a TTE that is compatible with a given photoactive material system, which is also the case for perovskite solar cells. The proposed TTE is based on a multilayer stack consisting of a metal film sandwiched between a high refractive-index (high-index) layer and an interfacial buffer layer. This TTE, placed as a top-most layer, can be prepared without damaging ingredients used in perovskite solar cells. Unlike conventional transparent electrodes focusing only on transmitting visible light, the proposed TTE plays the dual role of passing through visible light while reflecting infrared rays. The semi-transparent solar cells made with the proposed TTEs exhibited average power conversion efficiency as high as 13.3% with 85.5% infrared rejection.
The team believes that if the semi-transparent perovskite solar cells are scaled up for practical applications, they can be used in solar windows for buildings and automobiles, which not only generate electrical energy but also enable the smart heat management for indoor environments, thereby utilizing solar energy more efficiently and effectively.
This result was published as a cover article in the July 20, 2016 issue of Advanced Energy Materials. The research paper is entitled “Empowering Semi-transparent Solar Cells with Thermal-mirror Functionality.” (DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502466)
The team designed the transparent electrode (TE) stack in three layers: A thin-film of silver (Ag) is placed in between the bottom interfacial layer of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) and the top high-index dielectric layer of zinc sulfide (ZnS). Such a tri-layer approach has been known as a means to increase the overall visible-light transmittance of metallic thin films via index matching technique, which is essentially the same technique used for anti-reflection coating of glasses except that the present case involves a metallic layer.
Traditionally, when a TE is based on a metal film, such as Ag, the film should be extremely thin, e.g., 7-12 nanometers (nm), to obtain transparency and, accordingly, to transmit visible light. However, the team took a different approach in this research. They made the Ag TE two or three times thicker (12-24 nm) than conventional metal films and, as a result, it reflected more infrared light. The high refractive index of the ZnS layer plays an essential role in keeping the visible light transmittance of the proposed TTE high even with the relatively thick Ag film when its thickness is carefully optimized for maximal destructive interference, leading to low reflectance (and thus high transmittance) within its visible light range.
The team confirmed the semi-transparent perovskite solar cell’s thermal-mirror function through an experiment in which a halogen lamp illuminated an object for five minutes through three mediums: a window of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and the proposed semi-transparent perovskite solar cell. An infrared (IR) camera took thermal images of the object as well as that of each window’s surface. The object’s temperature, when exposed through the glass window, rose to 36.8 Celsius degrees whereas both the tinting film and the cell allowed the object to remain below 27 Celsius degrees. The tinting film absorbs light to block solar energy, so the film’s surface became hot as it was continuously exposed to the lamp light, but the proposed semi-transparent solar cell stayed cool since it rejects solar heat energy by reflection, rather than by absorption. The total solar energy rejection (TSER) of the proposed cell was as high as 89.6%.
Professor Yoo of KAIST said, “The major contributions of this work are to find transparent electrode technology suitable for translucent perovskite cells and to provide a design approach to fully harness the potential it can further deliver as a heat mirror in addition to its main role as an electrode. The present work can be further fine-tuned to include colored solar cells and to incorporate flexible or rollable form factors, as they will allow for greater design freedom and thus offer more opportunities for them to be integrated into real-world objects and structures such as cars, buildings, and houses.”
The lead authors are Hoyeon Kim and Jaewon Ha, both Ph.D. candidates in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, and Hui-Seon Kim, a student in the School of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University. This research was supported mainly by the Climate Change Research Hub Program of KAIST.
Picture 1: Semi-transparent Perovskite Solar Cell
This picture shows a prototype of a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell with thermal-mirror functionality.
Picture 2: A Heat Rejection Performance Comparison Experiment
This picture presents thermal images taken by an infrared camera for comparing the heat rejection performance of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell after being illuminated by a halogen lamp for five minutes.
2016.08.02 View 12850 -
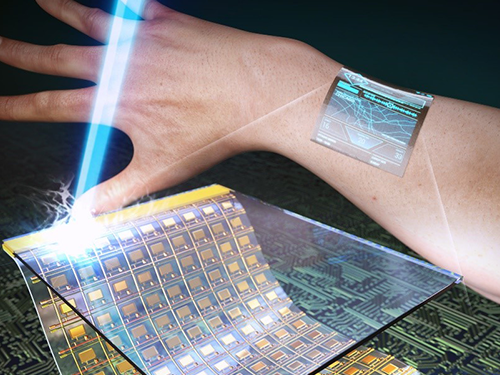 KAIST Develops Transparent Oxide Thin-Film Transistors
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) era, strong demand has grown for wearable and transparent displays that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR) and skin-like thin flexible devices. However, previous flexible transparent displays have posed real challenges to overcome, which are, among others, poor transparency and low electrical performance. To improve the transparency and performance, past research efforts have tried to use inorganic-based electronics, but the fundamental thermal instabilities of plastic substrates have hampered the high temperature process, an essential step necessary for the fabrication of high performance electronic devices.
As a solution to this problem, a research team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Sang-Hee Ko Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the KAIST has developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors (TFT) for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off (ILLO) method. Professor Lee’s team previously demonstrated the ILLO technology for energy-harvesting (Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014) and flexible memory (Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014) devices.
The research team fabricated a high-performance oxide TFT array on top of a sacrificial laser-reactive substrate. After laser irradiation from the backside of the substrate, only the oxide TFT arrays were separated from the sacrificial substrate as a result of reaction between laser and laser-reactive layer, and then subsequently transferred onto ultrathin plastics ( thickness). Finally, the transferred ultrathin-oxide driving circuit for the flexible display was attached conformally to the surface of human skin to demonstrate the possibility of the wearable application. The attached oxide TFTs showed high optical transparency of 83% and mobility of even under several cycles of severe bending tests.
Professor Lee said, “By using our ILLO process, the technological barriers for high performance transparent flexible displays have been overcome at a relatively low cost by removing expensive polyimide substrates. Moreover, the high-quality oxide semiconductor can be easily transferred onto skin-like or any flexible substrate for wearable application.”
These research results, entitled “Skin-Like Oxide Thin-Film Transistors for Transparent Displays,”
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201601296/abstract) were the lead article published in the July 2016 online issue of Wiley’s Advanced Functional Materials.
###
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014, Highly-efficient, Flexible Piezoelectric PZT Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201305659/abstract)
[2] Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014, Flexible Crossbar-structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substartes via Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract)
Picture 1: A Schamatic Image of Ultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This image shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors produced via the ILLO process.
Picture 2: Application of Uultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This picture shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors attached to a jumper sleeve and human skin.
2016.08.01 View 12786
KAIST Develops Transparent Oxide Thin-Film Transistors
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) era, strong demand has grown for wearable and transparent displays that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR) and skin-like thin flexible devices. However, previous flexible transparent displays have posed real challenges to overcome, which are, among others, poor transparency and low electrical performance. To improve the transparency and performance, past research efforts have tried to use inorganic-based electronics, but the fundamental thermal instabilities of plastic substrates have hampered the high temperature process, an essential step necessary for the fabrication of high performance electronic devices.
As a solution to this problem, a research team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Sang-Hee Ko Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the KAIST has developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors (TFT) for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off (ILLO) method. Professor Lee’s team previously demonstrated the ILLO technology for energy-harvesting (Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014) and flexible memory (Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014) devices.
The research team fabricated a high-performance oxide TFT array on top of a sacrificial laser-reactive substrate. After laser irradiation from the backside of the substrate, only the oxide TFT arrays were separated from the sacrificial substrate as a result of reaction between laser and laser-reactive layer, and then subsequently transferred onto ultrathin plastics ( thickness). Finally, the transferred ultrathin-oxide driving circuit for the flexible display was attached conformally to the surface of human skin to demonstrate the possibility of the wearable application. The attached oxide TFTs showed high optical transparency of 83% and mobility of even under several cycles of severe bending tests.
Professor Lee said, “By using our ILLO process, the technological barriers for high performance transparent flexible displays have been overcome at a relatively low cost by removing expensive polyimide substrates. Moreover, the high-quality oxide semiconductor can be easily transferred onto skin-like or any flexible substrate for wearable application.”
These research results, entitled “Skin-Like Oxide Thin-Film Transistors for Transparent Displays,”
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201601296/abstract) were the lead article published in the July 2016 online issue of Wiley’s Advanced Functional Materials.
###
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014, Highly-efficient, Flexible Piezoelectric PZT Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201305659/abstract)
[2] Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014, Flexible Crossbar-structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substartes via Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract)
Picture 1: A Schamatic Image of Ultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This image shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors produced via the ILLO process.
Picture 2: Application of Uultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This picture shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors attached to a jumper sleeve and human skin.
2016.08.01 View 12786 -
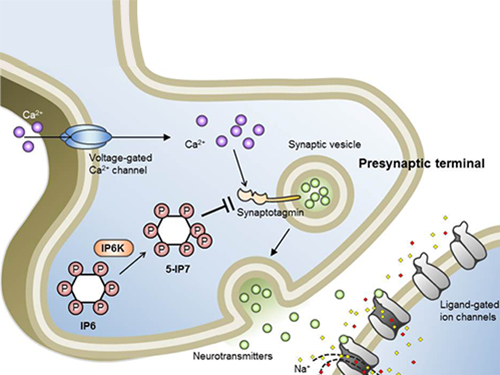 Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12130
Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12130 -
 'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5353
'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5353 -
 ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 8741
ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 8741 -
 Professor Kun-pyo Lee Appointed Honorary Fellow of the Design Research Society
Founded in the United Kingdom (UK) in 1966, the Design Research Society is an international academic organization that promotes excellence in design and supports the interests of the design research community.
Professor Kun-pyo Lee of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST received his honorary fellowship from the Society at its 50th international conference held from June 27, 2016 to July 3, 2016 in Brighton, UK.
The Society recognized Professor Lee’s academic achievements and his contribution to the advancement of design research nationally and globally. To date, only eight researchers have received honorary fellowships from the Society, and he is the first Asian to become an honorary fellow.
Professor Lee has worked at KAIST for more than 30 years as a professor in industrial engineering and served on various important positions such as the president of the Korean Society of Design Science, the president of the International Association of Societies of Design Research, an executive vice president of the Corporate Design Center at LG Electronics, and an advisory board member for Human-centered Design Network in Japan and UXnet in the United States.
By introducing the concept of user experience (UX) in Korea for the first time, he developed this field while focusing on user-centered designs to optimize interactive digital products as well as interaction design to create mental and physical interfaces between people and interactive digital products, services, and systems.
Professor Lee said, “I am pleased to become an honorary fellow of the Design Research Society. For quiet some time, industrial design remained in the domain of practical studies, lacking the kind of support needed to grow as an independent academic and research discipline, but this has changed rapidly in recent years. I will continue to remain actively involved in the development of industrial design engineering in Korea and the world.”
2016.07.19 View 8438
Professor Kun-pyo Lee Appointed Honorary Fellow of the Design Research Society
Founded in the United Kingdom (UK) in 1966, the Design Research Society is an international academic organization that promotes excellence in design and supports the interests of the design research community.
Professor Kun-pyo Lee of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST received his honorary fellowship from the Society at its 50th international conference held from June 27, 2016 to July 3, 2016 in Brighton, UK.
The Society recognized Professor Lee’s academic achievements and his contribution to the advancement of design research nationally and globally. To date, only eight researchers have received honorary fellowships from the Society, and he is the first Asian to become an honorary fellow.
Professor Lee has worked at KAIST for more than 30 years as a professor in industrial engineering and served on various important positions such as the president of the Korean Society of Design Science, the president of the International Association of Societies of Design Research, an executive vice president of the Corporate Design Center at LG Electronics, and an advisory board member for Human-centered Design Network in Japan and UXnet in the United States.
By introducing the concept of user experience (UX) in Korea for the first time, he developed this field while focusing on user-centered designs to optimize interactive digital products as well as interaction design to create mental and physical interfaces between people and interactive digital products, services, and systems.
Professor Lee said, “I am pleased to become an honorary fellow of the Design Research Society. For quiet some time, industrial design remained in the domain of practical studies, lacking the kind of support needed to grow as an independent academic and research discipline, but this has changed rapidly in recent years. I will continue to remain actively involved in the development of industrial design engineering in Korea and the world.”
2016.07.19 View 8438 -
 Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11402
Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11402 -
 KAIST and KTH Establish a Dual Degree Program in Nuclear Engineering
Professor Man-Sung Im, head of the Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Department at KAIST and Director Waclaw Gudowski of the Physics Department at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm (KTH), Sweden, agreed to establish a dual master’s degree program in the field of nuclear and quantum engineering, and signed the agreement on July 4, 2016 at the Faculty Club on the KAIST campus.
Following the first joint degree program in mechanical engineering in 2014, this is the second dual degree program created between the two universities.
Under the agreement, which will be effective beginning in the 2016 fall semester, KAIST and KTH will exchange students, confer students dual degrees when they earn the required number of credits, and support financial aid for exchange students.
Dean Im said, “The two schools have enjoyed an excellent reputation in nuclear and quantum engineering, and offering students more opportunities to study abroad at the other university will produce synergistic effects for the growth of the two schools' education and research.”
Founded in 1827, KTH is regarded one of the most prestigious universities in Northern Europe.
Professor Man-Sung Im of KAIST’s Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (pictured on the left) and Director Waclaw Gudowski of KTH’s Physics Department are shaking hands after signing the agreement for the dual master’s degree program.
2016.07.05 View 9221
KAIST and KTH Establish a Dual Degree Program in Nuclear Engineering
Professor Man-Sung Im, head of the Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Department at KAIST and Director Waclaw Gudowski of the Physics Department at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm (KTH), Sweden, agreed to establish a dual master’s degree program in the field of nuclear and quantum engineering, and signed the agreement on July 4, 2016 at the Faculty Club on the KAIST campus.
Following the first joint degree program in mechanical engineering in 2014, this is the second dual degree program created between the two universities.
Under the agreement, which will be effective beginning in the 2016 fall semester, KAIST and KTH will exchange students, confer students dual degrees when they earn the required number of credits, and support financial aid for exchange students.
Dean Im said, “The two schools have enjoyed an excellent reputation in nuclear and quantum engineering, and offering students more opportunities to study abroad at the other university will produce synergistic effects for the growth of the two schools' education and research.”
Founded in 1827, KTH is regarded one of the most prestigious universities in Northern Europe.
Professor Man-Sung Im of KAIST’s Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (pictured on the left) and Director Waclaw Gudowski of KTH’s Physics Department are shaking hands after signing the agreement for the dual master’s degree program.
2016.07.05 View 9221 -
 Synthesized Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, who is also the Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and his research team have recently published their research results entitled "Lanthanum-catalysed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons in a Zeolite Template" on June 29, 2016 in Nature on a new method to synthesize carbons having graphene structures with 3D periodic micropores, a trait resulted from using a zeolite as a template for the synthesis. The research team expects this technology to find a range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts.
Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, which was discovered more than a decade ago, has led to myriad research that seeks to unlock its vast potential. Zeolites, commonly used microporous solid catalysts in the petrochemical industry, have recently attracted attention in the field of material science as a template for carbon synthesis. Zeolites’ individual crystal is distinguished by its unique 1 nanometer (nm)-size pore structures. These structures facilitate the accommodation of carbon nanotubes inside zeolites. In their paper, the research team showed that these nanoporous systems are an ideal template for the carbon synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) graphene architecture, but zeolite pores are too small to accommodate bulky molecular compounds like polyaromatic and furfuryl alcohol that are often used in carbon synthesis. Small molecules like ethylene and acetylene can be used as a carbon source to achieve successful carbonization within zeolite pores, but it comes at a great cost. The high temperatures required for the synthesis cause reactions of carbons being deposited randomly on the external surfaces of zeolites as well as their internal pore walls, resulting in coke deposition and consequently, causing serious diffusion limitations in the zeolite pores.
The team from the IBS Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials solved this conundrum with a novel approach. First author Dr. KIM Kyoungsoo explains: “The zeolite-template carbon synthesis has existed for a long time, but the problem with temperatures has foiled many scientists from extracting their full potential. Here, our team sought to find the answer by embedding lanthanum ions (La3+), a silvery-white metal element, in zeolite pores. This lowers the temperature required for the carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. Graphene-like sp2 carbon structures can be selectively formed inside the zeolite template, without carbon deposition at the external surfaces. After the zeolite template is removed, the carbon framework exhibits the electrical conductivity two orders of magnitude higher than amorphous mesoporous carbon, which is a pretty astonishing result. This highly efficient synthesis strategy based on the lanthanum ions renders the carbon framework to be formed in pores with a less than 1 nm diameter, just like as easily reproducible as in mesoporous templates. This provides a general method to synthesize carbon nanostructures with various topologies corresponding to the template zeolite pore topologies, such as FAU, EMT, beta, LTL, MFI, and LTA. Also, all the synthesis can be readily scaled up, which is important for practical applications in areas of batteries, fuel storage, and other zeolite-like catalyst supports.”
The research team began their experiment by utilizing La3+ ions. Dr. KIM elucidates why this silvery-white element proved so beneficial to the team, “La3+ ions are unreducible under carbonization process condition, so they can stay inside the zeolite pores instead of moving to the outer zeolite surface in the form of reduced metal particles. Within the pores, they can stabilize ethylene and the pyrocondensation intermediately to form a carbon framework in zeolites.”
In order to test this hypothesis, the team compared the amount of carbon deposited in La3+-containing form of Y zeolite (LaY) sample against a host of other samples such as NaY and HY. The experimental results indicate that all the LaY, NaY, and HY zeolite samples show rapid carbon deposition at 800°C. However, as the temperature decreases, there appears to be a dramatic difference between the different ionic forms of zeolites. At 600°C, the LaY zeolite is still active as a carbon deposition template. In contrast, both NaY and HY lose their carbon deposition functions almost completely.
The results, according to their paper published in Nature, highlight a catalytic effect of lanthanum for carbonization. By making graphene with 3D periodic nanoporous architectures, it promises a wide range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts but due to the lack of efficient synthetic strategies, such applications have not yet been successful. By taking advantage of the pore-selective carbon filling at decreased temperatures, the synthesis can readily be scaled up for studies requiring bulk quantities of carbon, in particular high electrical conductivity, which is a highly sought aspect for the production of batteries.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/lkNiHiB8lBk
Image 1: (Top to Bottom) Zeolite Template: Microporous Aluminosilicate; Zeolite ion exchanged with La3+ ions in aqueous solution; and Zeolite Template with La3+ ions
Image 2: (Top to Bottom) Catalytic carbonization progressed at La3+ ions-exchanged sites using ethylene as a carbon precursor. Carbon is highlighted in grey; Zeolite template removed in an acid solution (HF/ HCl); Microporous 3D graphene-like carbon
2016.07.01 View 9618
Synthesized Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, who is also the Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and his research team have recently published their research results entitled "Lanthanum-catalysed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons in a Zeolite Template" on June 29, 2016 in Nature on a new method to synthesize carbons having graphene structures with 3D periodic micropores, a trait resulted from using a zeolite as a template for the synthesis. The research team expects this technology to find a range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts.
Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, which was discovered more than a decade ago, has led to myriad research that seeks to unlock its vast potential. Zeolites, commonly used microporous solid catalysts in the petrochemical industry, have recently attracted attention in the field of material science as a template for carbon synthesis. Zeolites’ individual crystal is distinguished by its unique 1 nanometer (nm)-size pore structures. These structures facilitate the accommodation of carbon nanotubes inside zeolites. In their paper, the research team showed that these nanoporous systems are an ideal template for the carbon synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) graphene architecture, but zeolite pores are too small to accommodate bulky molecular compounds like polyaromatic and furfuryl alcohol that are often used in carbon synthesis. Small molecules like ethylene and acetylene can be used as a carbon source to achieve successful carbonization within zeolite pores, but it comes at a great cost. The high temperatures required for the synthesis cause reactions of carbons being deposited randomly on the external surfaces of zeolites as well as their internal pore walls, resulting in coke deposition and consequently, causing serious diffusion limitations in the zeolite pores.
The team from the IBS Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials solved this conundrum with a novel approach. First author Dr. KIM Kyoungsoo explains: “The zeolite-template carbon synthesis has existed for a long time, but the problem with temperatures has foiled many scientists from extracting their full potential. Here, our team sought to find the answer by embedding lanthanum ions (La3+), a silvery-white metal element, in zeolite pores. This lowers the temperature required for the carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. Graphene-like sp2 carbon structures can be selectively formed inside the zeolite template, without carbon deposition at the external surfaces. After the zeolite template is removed, the carbon framework exhibits the electrical conductivity two orders of magnitude higher than amorphous mesoporous carbon, which is a pretty astonishing result. This highly efficient synthesis strategy based on the lanthanum ions renders the carbon framework to be formed in pores with a less than 1 nm diameter, just like as easily reproducible as in mesoporous templates. This provides a general method to synthesize carbon nanostructures with various topologies corresponding to the template zeolite pore topologies, such as FAU, EMT, beta, LTL, MFI, and LTA. Also, all the synthesis can be readily scaled up, which is important for practical applications in areas of batteries, fuel storage, and other zeolite-like catalyst supports.”
The research team began their experiment by utilizing La3+ ions. Dr. KIM elucidates why this silvery-white element proved so beneficial to the team, “La3+ ions are unreducible under carbonization process condition, so they can stay inside the zeolite pores instead of moving to the outer zeolite surface in the form of reduced metal particles. Within the pores, they can stabilize ethylene and the pyrocondensation intermediately to form a carbon framework in zeolites.”
In order to test this hypothesis, the team compared the amount of carbon deposited in La3+-containing form of Y zeolite (LaY) sample against a host of other samples such as NaY and HY. The experimental results indicate that all the LaY, NaY, and HY zeolite samples show rapid carbon deposition at 800°C. However, as the temperature decreases, there appears to be a dramatic difference between the different ionic forms of zeolites. At 600°C, the LaY zeolite is still active as a carbon deposition template. In contrast, both NaY and HY lose their carbon deposition functions almost completely.
The results, according to their paper published in Nature, highlight a catalytic effect of lanthanum for carbonization. By making graphene with 3D periodic nanoporous architectures, it promises a wide range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts but due to the lack of efficient synthetic strategies, such applications have not yet been successful. By taking advantage of the pore-selective carbon filling at decreased temperatures, the synthesis can readily be scaled up for studies requiring bulk quantities of carbon, in particular high electrical conductivity, which is a highly sought aspect for the production of batteries.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/lkNiHiB8lBk
Image 1: (Top to Bottom) Zeolite Template: Microporous Aluminosilicate; Zeolite ion exchanged with La3+ ions in aqueous solution; and Zeolite Template with La3+ ions
Image 2: (Top to Bottom) Catalytic carbonization progressed at La3+ ions-exchanged sites using ethylene as a carbon precursor. Carbon is highlighted in grey; Zeolite template removed in an acid solution (HF/ HCl); Microporous 3D graphene-like carbon
2016.07.01 View 9618 -
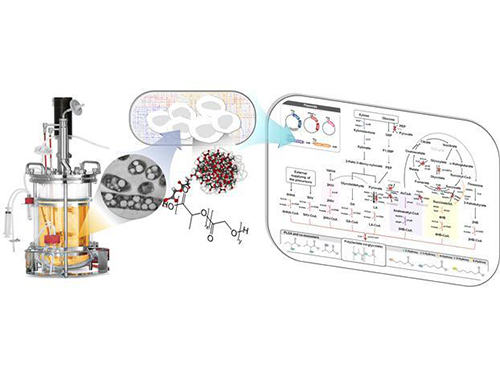 Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11451
Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11451