Platform
-
 KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13092
KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13092 -
 KAIST GSAI and SNUBH Join Hands for AI in Healthcare
< Dean Song Chong (left) and Director Chang Wan Oh (right)
at the KAIST GSAI - SNUBH MOU Signing Ceremony >
The Graduate School of AI (GSAI) at KAIST and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to cooperate in AI education and research in the field of healthcare last month. The two institutions have agreed to collaborate on research and technology development through the implementation of academic and personnel exchange programs.
The GSAI, opened in August 2019 as Korea’s first AI graduate school, has been in the forefront of nurturing top-tier AI specialists in the era of Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school employs a two-track strategy that not only provides students with core AI-related courses on machine learning, data mining, computer vision, and natural language processing, but also a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies. Its faculty members are "the cream of the crop” in their early 40s, achieving world-class performance in their respective fields.
SNUBH opened the Healthcare Innovation Park in 2016, the first hospital-led convergence research complex among Korean medical institutions. It is leading future medical research in five specialized areas: medical devices, healthcare ICT, human genetics, nano-machines, and regenerative medicine.
The Dean of the GSAI, Song Chong, said, “We have set the stage for a cooperative platform for continuous and efficient joint education and research by the two institutions.” He expressed his excitement, saying, “Through this platform and our expertise in AI engineering and medicine, we will lead future AI-based medical technology.”
The Director of the SNUBH Research Division, Chang Wan Oh, stressed that “the mutual cooperation between the two institutions will become a crucial turning point in AI education and research, which is at the core of future healthcare.” He added, “Through a high level of cooperation, we will have the ability to bring about global competitiveness and innovation.”
(END)
2019.12.27 View 9460
KAIST GSAI and SNUBH Join Hands for AI in Healthcare
< Dean Song Chong (left) and Director Chang Wan Oh (right)
at the KAIST GSAI - SNUBH MOU Signing Ceremony >
The Graduate School of AI (GSAI) at KAIST and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to cooperate in AI education and research in the field of healthcare last month. The two institutions have agreed to collaborate on research and technology development through the implementation of academic and personnel exchange programs.
The GSAI, opened in August 2019 as Korea’s first AI graduate school, has been in the forefront of nurturing top-tier AI specialists in the era of Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school employs a two-track strategy that not only provides students with core AI-related courses on machine learning, data mining, computer vision, and natural language processing, but also a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies. Its faculty members are "the cream of the crop” in their early 40s, achieving world-class performance in their respective fields.
SNUBH opened the Healthcare Innovation Park in 2016, the first hospital-led convergence research complex among Korean medical institutions. It is leading future medical research in five specialized areas: medical devices, healthcare ICT, human genetics, nano-machines, and regenerative medicine.
The Dean of the GSAI, Song Chong, said, “We have set the stage for a cooperative platform for continuous and efficient joint education and research by the two institutions.” He expressed his excitement, saying, “Through this platform and our expertise in AI engineering and medicine, we will lead future AI-based medical technology.”
The Director of the SNUBH Research Division, Chang Wan Oh, stressed that “the mutual cooperation between the two institutions will become a crucial turning point in AI education and research, which is at the core of future healthcare.” He added, “Through a high level of cooperation, we will have the ability to bring about global competitiveness and innovation.”
(END)
2019.12.27 View 9460 -
 KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 8850
KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 8850 -
 Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 9902
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 9902 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 11580
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 11580 -
 AI Graduate School to Take the Lead in Shaping the Future of AI
KAIST opened its AI Graduate School on August 26 with its first cohort of 22 Master’s and 10 PhD students for the 2019 fall semester. The new graduate school will provide students with a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies, and will offer 18 courses this semester.
KAIST was selected as one of the first three AI graduate schools that the Korean government will financially endorse to nurture top-tier AI specialists. The government will provide 9 billion KRW and KAIST will invest an additional 4.2 billion KRW in the school over the next five years.
KAIST aims to foster top-tiered AI engineers who will work for advancing emergent technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school will produce original technologies by driving high-risk, innovative AI research projects and will be the main supplier of highly competent engineers who will lead the industry and advance the global market.
KAIST has a long history of AI research and has a top-level AI education and research infrastructure. In 1990, KAIST launched the first AI research center in Korea. Since then, KAIST has taken the lead in the field by making breakthroughs in intelligent sensing information systems and AI platforms. About 20 percent of the faculty members at KAIST, or about 120 professors, are conducting AI-related research while offering 136 AI-related courses.
The Dean of the AI Graduate School, Song Chong, said, “Our faculty members are the cream of the crop and are all in their early 40s. Although we started with only eight professors, we will employ 20 full-time professors by 2023 and will spare no effort to make the world’s best AI research hub and develop the brightest minds.”
Dean Chong said that three professors are already listed in the top ten when measured by the number of publications from the top two AI conferences, Neural Information Processing System (NIPS) and ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning). KAIST has several highly recognized faculty members who have published more than 10 NIPS/ICML papers over nine years, winning numerous awards including the ACM Sigmetrics Rising Star Award, Google AI Focused Research Award, and INFORMS Applied Probability Best Publication Award.
The number of students attempting to gain admission to the school is also very high. The admission office said that the percentage of applicants being offered admission stood at 9.1 percent. From next year, the school plans to increase the number of enrollments to 40 Master’s and 20 PhD students.
The school will also open the AI Graduate School Research Center in Songnam City next month and expand its collaboration with local companies in the Songnam and Pangyo region, both emerging techno and ICT valleys. With the placement of 60 research personnel in the center, the school plans to play a leading role in building the companies’ technical competitiveness.
The government’s keen interest was well highlighted with the attendance of many dignitaries including the Mayor of Daejeon City Tae-Jong Huh, Vice Minister of Science and ICT Won-Ki Min, and National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed the importance of AI as a growth engine, saying, “AI will be a game changer and a key enabler of major industries. But the winner takes all in industry. Therefore, without producing the world’s top technology, we will not survive in the global market. To foster highly competitive specialists who will take the lead in this industry, we will educate students who can converge multiple disciplines and contribute to national growth and beyond in the years ahead.”
2019.08.27 View 7017
AI Graduate School to Take the Lead in Shaping the Future of AI
KAIST opened its AI Graduate School on August 26 with its first cohort of 22 Master’s and 10 PhD students for the 2019 fall semester. The new graduate school will provide students with a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies, and will offer 18 courses this semester.
KAIST was selected as one of the first three AI graduate schools that the Korean government will financially endorse to nurture top-tier AI specialists. The government will provide 9 billion KRW and KAIST will invest an additional 4.2 billion KRW in the school over the next five years.
KAIST aims to foster top-tiered AI engineers who will work for advancing emergent technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school will produce original technologies by driving high-risk, innovative AI research projects and will be the main supplier of highly competent engineers who will lead the industry and advance the global market.
KAIST has a long history of AI research and has a top-level AI education and research infrastructure. In 1990, KAIST launched the first AI research center in Korea. Since then, KAIST has taken the lead in the field by making breakthroughs in intelligent sensing information systems and AI platforms. About 20 percent of the faculty members at KAIST, or about 120 professors, are conducting AI-related research while offering 136 AI-related courses.
The Dean of the AI Graduate School, Song Chong, said, “Our faculty members are the cream of the crop and are all in their early 40s. Although we started with only eight professors, we will employ 20 full-time professors by 2023 and will spare no effort to make the world’s best AI research hub and develop the brightest minds.”
Dean Chong said that three professors are already listed in the top ten when measured by the number of publications from the top two AI conferences, Neural Information Processing System (NIPS) and ICML (International Conference on Machine Learning). KAIST has several highly recognized faculty members who have published more than 10 NIPS/ICML papers over nine years, winning numerous awards including the ACM Sigmetrics Rising Star Award, Google AI Focused Research Award, and INFORMS Applied Probability Best Publication Award.
The number of students attempting to gain admission to the school is also very high. The admission office said that the percentage of applicants being offered admission stood at 9.1 percent. From next year, the school plans to increase the number of enrollments to 40 Master’s and 20 PhD students.
The school will also open the AI Graduate School Research Center in Songnam City next month and expand its collaboration with local companies in the Songnam and Pangyo region, both emerging techno and ICT valleys. With the placement of 60 research personnel in the center, the school plans to play a leading role in building the companies’ technical competitiveness.
The government’s keen interest was well highlighted with the attendance of many dignitaries including the Mayor of Daejeon City Tae-Jong Huh, Vice Minister of Science and ICT Won-Ki Min, and National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed the importance of AI as a growth engine, saying, “AI will be a game changer and a key enabler of major industries. But the winner takes all in industry. Therefore, without producing the world’s top technology, we will not survive in the global market. To foster highly competitive specialists who will take the lead in this industry, we will educate students who can converge multiple disciplines and contribute to national growth and beyond in the years ahead.”
2019.08.27 View 7017 -
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Donates His Prize Money
The honoree of the 2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Award, Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang donated his prize money of one hundred million KRW to the Chemistry Department Scholarship Fund and the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex Management Fund during a donation ceremony last week.
Professor Chang won the award last month in recognition of his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. Professor Chang, a world renowned chemist, has been recognized for his highly selective catalytic systems, allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals.
“All my achievements are the results of my students’ hard work and dedication. I feel very fortunate to have such talented team members. I want to express my sincere gratitude for such a great research environment that we have worked together in so far,” said Professor Chang at the ceremony.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “Not only will Professor Chang’s donation make a significant contribution to the Department of Chemistry, but also to the improvement of the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex’s management, which directly links to the health and welfare of the KAIST community.”
Professor Chang currently holds the position of distinguished professor at KAIST and director of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations in the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). He previously received the Kyung-Ahm Academic Award in 2013 and the Korea Toray Science Award in 2018. All these prize money also went to the school.
(END)
2019.08.26 View 9079
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Donates His Prize Money
The honoree of the 2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Award, Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang donated his prize money of one hundred million KRW to the Chemistry Department Scholarship Fund and the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex Management Fund during a donation ceremony last week.
Professor Chang won the award last month in recognition of his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. Professor Chang, a world renowned chemist, has been recognized for his highly selective catalytic systems, allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals.
“All my achievements are the results of my students’ hard work and dedication. I feel very fortunate to have such talented team members. I want to express my sincere gratitude for such a great research environment that we have worked together in so far,” said Professor Chang at the ceremony.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “Not only will Professor Chang’s donation make a significant contribution to the Department of Chemistry, but also to the improvement of the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex’s management, which directly links to the health and welfare of the KAIST community.”
Professor Chang currently holds the position of distinguished professor at KAIST and director of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations in the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). He previously received the Kyung-Ahm Academic Award in 2013 and the Korea Toray Science Award in 2018. All these prize money also went to the school.
(END)
2019.08.26 View 9079 -
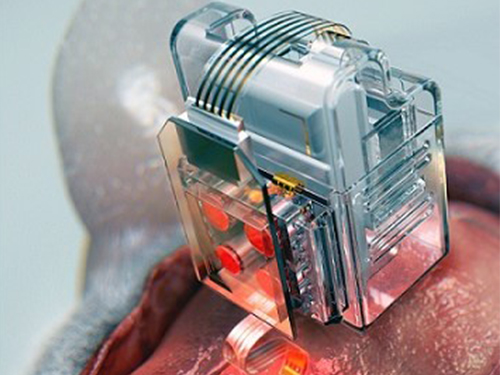 Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 33610
Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 33610 -
 Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 40990
Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 40990 -
 Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 38993
Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 38993 -
 Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 13400
Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 13400 -
 Micropatch Made of DNA
Researchers reported the fabrication of microstructure arrays of DNA materials using topographic control. This method provides a platform for forming multiscale hierarchical orientations of soft and biomaterials using a process of simple shearing and controlled evaporation on a patterned substrate. This approach enables the potential of patterning applications using DNA or other anisotropic biomaterials.
DNA is one of the most abundant biomaterials found in all living organisms in nature. It has unique characteristics of fine feature size and liquid crystalline phase, enabling to create various kinds of microstructure DNA arrays. Based on these characteristics, DNA has been used as a building block for “origami” and textile art at the nanometer scale.
A KAIST research team led by Professors Dong Ki Yoon and Hyungsoo Kim fabricated a DNA-based micropatch using the “coffee ring effect” and its multi-angle control technology, which was published online in Nature Communications on June 7.
The research team used cheap DNA material extracted from salmon to realize the micropatch structure with well-aligned knit or ice cream cone shapes. When the DNA material in an aqueous solution is rubbed between two solid substrates while water is evaporating, DNA chains are unidirectionally aligned to make a thin film such as in LCD display devices. The DNA chains can make more complex microstructures such as knit or a texture with ice cream cone shapes when the same procedure is carried out in topographical patterns like microposts (Figure 1). This can be applied to make metamaterials by mixing with functionalized gold nanorods to show plasmonic color.
Plasmon resonance is a phenomenon in which electrons vibrate uniformly on the surface of a substrate made of metal, reacting only to light that matches a specific energy to enhance the clarity and expression of colors. For this, the most important factor is the orientation in which the gold nanorods align. That is, when the rods are aligned side by side in one direction, the optical and electrical characteristics are maximized. The research team focused on this point and made the DNA micropatch as a frame to orient the gold nanorods in a unique shape and fabricated a plasmonic color film (Figure 2).
Professor Yoon said this study is meaningful in that it deals with the evaporation phenomenon, which has not been studied much in the field of polymers and biopolymers in terms of basic science. He explained, “This will also help maximize the efficiency of polymeric materials that can be orientated in coating, 2D, and 3D printing applications. Furthermore, DNA that exists infinitely in nature can be expected to have industrial application value as a new material since it can easily form complexes with other materials as described in this study.”
(Figure 1. The DNA micropatch using topographic control. (a) The experimental scheme.
(b) Enlarged image of (e). (c-e) Different micropatches made of DNA using different shearing directions.)
(Figure 2. The knit-like structures made of DNA-gold nanorod complex. (a,b) Optical
and polarized optical microscopy images. (c-f) Plasmonic colors reflected from aligned DNA-gold nanorod complex depending on the sample rotation.)
2019.07.01 View 35199
Micropatch Made of DNA
Researchers reported the fabrication of microstructure arrays of DNA materials using topographic control. This method provides a platform for forming multiscale hierarchical orientations of soft and biomaterials using a process of simple shearing and controlled evaporation on a patterned substrate. This approach enables the potential of patterning applications using DNA or other anisotropic biomaterials.
DNA is one of the most abundant biomaterials found in all living organisms in nature. It has unique characteristics of fine feature size and liquid crystalline phase, enabling to create various kinds of microstructure DNA arrays. Based on these characteristics, DNA has been used as a building block for “origami” and textile art at the nanometer scale.
A KAIST research team led by Professors Dong Ki Yoon and Hyungsoo Kim fabricated a DNA-based micropatch using the “coffee ring effect” and its multi-angle control technology, which was published online in Nature Communications on June 7.
The research team used cheap DNA material extracted from salmon to realize the micropatch structure with well-aligned knit or ice cream cone shapes. When the DNA material in an aqueous solution is rubbed between two solid substrates while water is evaporating, DNA chains are unidirectionally aligned to make a thin film such as in LCD display devices. The DNA chains can make more complex microstructures such as knit or a texture with ice cream cone shapes when the same procedure is carried out in topographical patterns like microposts (Figure 1). This can be applied to make metamaterials by mixing with functionalized gold nanorods to show plasmonic color.
Plasmon resonance is a phenomenon in which electrons vibrate uniformly on the surface of a substrate made of metal, reacting only to light that matches a specific energy to enhance the clarity and expression of colors. For this, the most important factor is the orientation in which the gold nanorods align. That is, when the rods are aligned side by side in one direction, the optical and electrical characteristics are maximized. The research team focused on this point and made the DNA micropatch as a frame to orient the gold nanorods in a unique shape and fabricated a plasmonic color film (Figure 2).
Professor Yoon said this study is meaningful in that it deals with the evaporation phenomenon, which has not been studied much in the field of polymers and biopolymers in terms of basic science. He explained, “This will also help maximize the efficiency of polymeric materials that can be orientated in coating, 2D, and 3D printing applications. Furthermore, DNA that exists infinitely in nature can be expected to have industrial application value as a new material since it can easily form complexes with other materials as described in this study.”
(Figure 1. The DNA micropatch using topographic control. (a) The experimental scheme.
(b) Enlarged image of (e). (c-e) Different micropatches made of DNA using different shearing directions.)
(Figure 2. The knit-like structures made of DNA-gold nanorod complex. (a,b) Optical
and polarized optical microscopy images. (c-f) Plasmonic colors reflected from aligned DNA-gold nanorod complex depending on the sample rotation.)
2019.07.01 View 35199