engineering
-
 KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 16237
KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 16237 -
 KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 12591
KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 12591 -
 Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 8952
Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 8952 -
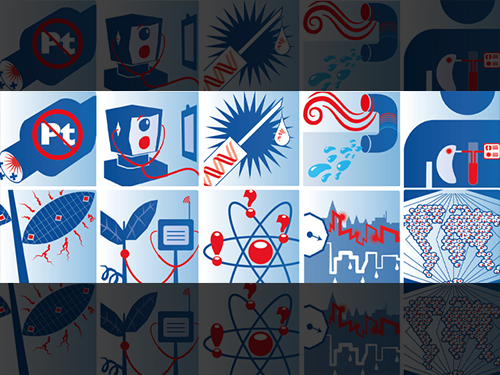 Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 13977
Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 13977 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Elected to the NAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was elected as a foreign associate to the US National Academy of Sciences (NAS) on May 2. The National Academy of Sciences elected 84 new members and 21 foreign associates in recognition of their distinguished and continuing achievements in their original research. Election to the Academy is widely regarded as one of the highest honors that a scientist can receive.
Professor Lee was also elected in 2010 as a member of the US National Academy of Engineering (NAE) for his leadership in microbial biotechnology and metabolic engineering, including the development of fermentation processes for biodegradable polymers and organic acids. Until 2016, there are only 12 people worldwide who are foreign associates of both NAS and NAE.
He is the first Korean elected to both prestigious academies, the NAS and the NAE in the US. Professor Lee is currently the dean of KAIST Institutes, the world leading institute for multi-and interdisciplinary research. He is also serving as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum.
2017.05.16 View 11146
Distinguished Professor Lee Elected to the NAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was elected as a foreign associate to the US National Academy of Sciences (NAS) on May 2. The National Academy of Sciences elected 84 new members and 21 foreign associates in recognition of their distinguished and continuing achievements in their original research. Election to the Academy is widely regarded as one of the highest honors that a scientist can receive.
Professor Lee was also elected in 2010 as a member of the US National Academy of Engineering (NAE) for his leadership in microbial biotechnology and metabolic engineering, including the development of fermentation processes for biodegradable polymers and organic acids. Until 2016, there are only 12 people worldwide who are foreign associates of both NAS and NAE.
He is the first Korean elected to both prestigious academies, the NAS and the NAE in the US. Professor Lee is currently the dean of KAIST Institutes, the world leading institute for multi-and interdisciplinary research. He is also serving as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum.
2017.05.16 View 11146 -
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 10064
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 10064 -
 13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 19757
13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 19757 -
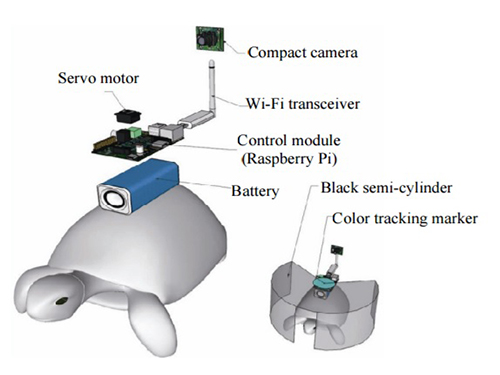 Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 16205
Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 16205 -
 KAIST Undergraduates Win the Innovative Design Contest 2016
A team of KAIST students, consisting of five undergraduates (Do-Hoon Kwon, Tae-Hyun Kim, Hak-Gi Do, Hyun-Joo Lee, and Jong-Ho Jeong) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, won the grand prize at the Innovative Design Contest held at Osaka University in Japan on December 12-13, 2016. The event took place during the 16th Asia Design Engineering Workshop (A-DEWS).
For this year’s contest, a total of ten student teams from such countries as Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Malaysia participated, and Team KAIST earned the highest scores. The five KAIST students, all taking the course entitled “Production of Creative Systems,” developed a manual wheelchair accessory called “Safe Attachable Wheelchair Assistive Device in Capstone Design (SAWADiCap).
SAWADiCap is a detachable auxiliary power device that increases the range and mobility of manual wheelchairs. The device can easily be installed and removed, compared to existing add-on attachments for wheelchairs. Users can also enjoy similar advantages offered by powered wheelchairs at a lower cost. In their presentation on the device, the KAIST students introduced their design to improve the power of manual wheelchairs employing the magnetic reinforcement effect and to include the safety features necessary for users to install or operate the device.
Do-Hoon Kwon said, “Our team had a great experience participating in the contest—we met people with diverse backgrounds and expanded our understanding in the field.”
Professor Seibum B. Choi of the Mechanical Engineering Department, who advises the KAIST team, added, “I hope our technology can help the spread of affordable wheelchairs and increase mobility for the disabled.”
Established in 2000, A-DEWS is held annually by the Asian branch of the Design Engineering Workshop to provide an international forum for researchers and practitioners in the field of design engineering by facilitating the exchange of recent research results and sharing knowledge about design strategies and methods. This year’s theme for the workshop was “Innovation of Life.”
A-DEWS hosts the Innovative Design Contest to encourage young engineers, researchers, and students who are creating innovative products, services, and product-services and to show appreciation for their efforts.
Pictured below from left to right are Hyun-Joo Lee, Do-Hoon Kwon, Jong-Ho Jeong, and Hak-Gi Do.
2017.01.03 View 10725
KAIST Undergraduates Win the Innovative Design Contest 2016
A team of KAIST students, consisting of five undergraduates (Do-Hoon Kwon, Tae-Hyun Kim, Hak-Gi Do, Hyun-Joo Lee, and Jong-Ho Jeong) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, won the grand prize at the Innovative Design Contest held at Osaka University in Japan on December 12-13, 2016. The event took place during the 16th Asia Design Engineering Workshop (A-DEWS).
For this year’s contest, a total of ten student teams from such countries as Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Malaysia participated, and Team KAIST earned the highest scores. The five KAIST students, all taking the course entitled “Production of Creative Systems,” developed a manual wheelchair accessory called “Safe Attachable Wheelchair Assistive Device in Capstone Design (SAWADiCap).
SAWADiCap is a detachable auxiliary power device that increases the range and mobility of manual wheelchairs. The device can easily be installed and removed, compared to existing add-on attachments for wheelchairs. Users can also enjoy similar advantages offered by powered wheelchairs at a lower cost. In their presentation on the device, the KAIST students introduced their design to improve the power of manual wheelchairs employing the magnetic reinforcement effect and to include the safety features necessary for users to install or operate the device.
Do-Hoon Kwon said, “Our team had a great experience participating in the contest—we met people with diverse backgrounds and expanded our understanding in the field.”
Professor Seibum B. Choi of the Mechanical Engineering Department, who advises the KAIST team, added, “I hope our technology can help the spread of affordable wheelchairs and increase mobility for the disabled.”
Established in 2000, A-DEWS is held annually by the Asian branch of the Design Engineering Workshop to provide an international forum for researchers and practitioners in the field of design engineering by facilitating the exchange of recent research results and sharing knowledge about design strategies and methods. This year’s theme for the workshop was “Innovation of Life.”
A-DEWS hosts the Innovative Design Contest to encourage young engineers, researchers, and students who are creating innovative products, services, and product-services and to show appreciation for their efforts.
Pictured below from left to right are Hyun-Joo Lee, Do-Hoon Kwon, Jong-Ho Jeong, and Hak-Gi Do.
2017.01.03 View 10725 -
 KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 12037
KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 12037 -
 Mechanical Engineering Building on Campus Refurbished
KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department has finished the project to remodel its buildings and hosted an opening ceremony on December 12, 2016, which was attended by the university’s senior management and guests including President Steve Kang and Choong-Hwan Ahn, Architecture Policy Officer at the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea (MLIT).
With an investment of approximately USD 10 million, the old buildings (each consisting of seven floors and one basement) were transformed into smart, green buildings. Among the upgrades were the establishment of LED lighting systems, the replacement of the exterior walls with insulated materials, and the installation of double-glazed windows, all resulting in the improvement of the buildings’ energy efficiency. Previously, offices and lecture halls in the buildings had individual cooling and heating systems, which consumed a great deal of energy, but they were replaced with a centralized smart energy control system that monitors the operation status as well as energy consumption in real time.
With these new improvements, the Department was able to slash its energy consumption by 32%, for which it received Green Building Conversion Certification from MLIT. The ministry issues the certification to buildings that reduce their energy consumption by over 20% as a result of infrastructure upgrades. Beginning with the Mechanical Engineering buildings, KAIST will work on obtaining this certification for all of its buildings that are either under renovation or construction.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to offer our students a comfortable environment for study and research and will continue improving outdated facilities and infrastructure to make the campus safer and nicer.”
Picture 1: Ribbon-cutting ceremony for the refurbished Mechanical Engineering buildings on campus
Picture 2: Mechanical engineering buildings
2016.12.09 View 8288
Mechanical Engineering Building on Campus Refurbished
KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department has finished the project to remodel its buildings and hosted an opening ceremony on December 12, 2016, which was attended by the university’s senior management and guests including President Steve Kang and Choong-Hwan Ahn, Architecture Policy Officer at the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea (MLIT).
With an investment of approximately USD 10 million, the old buildings (each consisting of seven floors and one basement) were transformed into smart, green buildings. Among the upgrades were the establishment of LED lighting systems, the replacement of the exterior walls with insulated materials, and the installation of double-glazed windows, all resulting in the improvement of the buildings’ energy efficiency. Previously, offices and lecture halls in the buildings had individual cooling and heating systems, which consumed a great deal of energy, but they were replaced with a centralized smart energy control system that monitors the operation status as well as energy consumption in real time.
With these new improvements, the Department was able to slash its energy consumption by 32%, for which it received Green Building Conversion Certification from MLIT. The ministry issues the certification to buildings that reduce their energy consumption by over 20% as a result of infrastructure upgrades. Beginning with the Mechanical Engineering buildings, KAIST will work on obtaining this certification for all of its buildings that are either under renovation or construction.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to offer our students a comfortable environment for study and research and will continue improving outdated facilities and infrastructure to make the campus safer and nicer.”
Picture 1: Ribbon-cutting ceremony for the refurbished Mechanical Engineering buildings on campus
Picture 2: Mechanical engineering buildings
2016.12.09 View 8288 -
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11453
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11453