AT
-
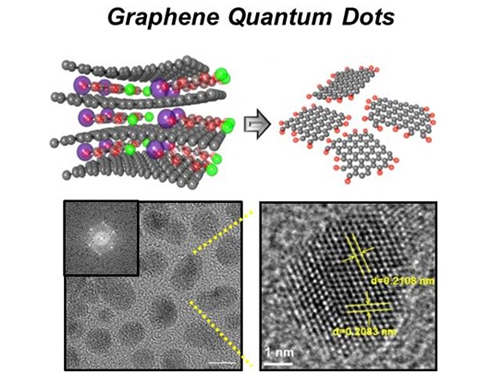 News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 15243
News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 15243 -
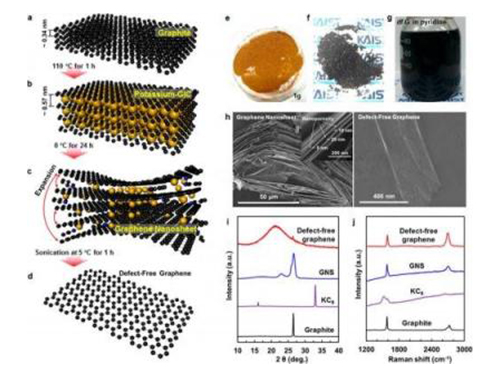 KAIST Researchers Fabricate Defect-free Graphene for Lithium-ion Batteries
Although graphene has been hailed as promising materials for lithium-ion batteries, making it for large-scale production has remained a challenging task for researchers. So far, high-quality graphene has been produced at the expense of large volume. It is possible to fabricate bulk quantities of graphene, but they will likely contain many defects.
Recently, a KAIST research team, headed by Professors Jung-Ki Park and Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a fabrication method to produce a large amount of defect-free graphene (df-G) while preserving the structural integrity of the graphene.
This research result was published online in the July 11, 2014 issue of Nano Letters, entitled "Defect-free, Size-tunable Graphene for High-performance Lithium Ion Battery."
Phys.org, a science, research and technology news website, published an article on this research. To read article, please visit the link below:
Phys.org, August 22, 2014
“Scientists fabricate defect-free graphene, set record reversible capacity for Co3O4 node in Li-ion batteries”
http://phys.org/news/2014-08-scientists-fabricate-defect-free-graphene-reversible.html
2014.09.07 View 10693
KAIST Researchers Fabricate Defect-free Graphene for Lithium-ion Batteries
Although graphene has been hailed as promising materials for lithium-ion batteries, making it for large-scale production has remained a challenging task for researchers. So far, high-quality graphene has been produced at the expense of large volume. It is possible to fabricate bulk quantities of graphene, but they will likely contain many defects.
Recently, a KAIST research team, headed by Professors Jung-Ki Park and Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a fabrication method to produce a large amount of defect-free graphene (df-G) while preserving the structural integrity of the graphene.
This research result was published online in the July 11, 2014 issue of Nano Letters, entitled "Defect-free, Size-tunable Graphene for High-performance Lithium Ion Battery."
Phys.org, a science, research and technology news website, published an article on this research. To read article, please visit the link below:
Phys.org, August 22, 2014
“Scientists fabricate defect-free graphene, set record reversible capacity for Co3O4 node in Li-ion batteries”
http://phys.org/news/2014-08-scientists-fabricate-defect-free-graphene-reversible.html
2014.09.07 View 10693 -
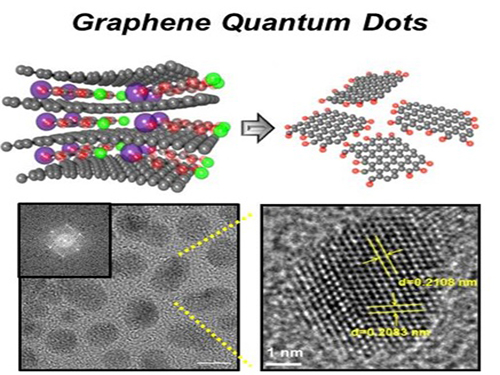 Extracting Light from Graphite: Core Technology of Graphene Quantum Dots Display Developed
Professor Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering announced that they were able to develop topnotch graphene quantum dots from graphite.
Using the method of synthesizing graphite intercalation compound from graphite with salt and water, the research team developed graphene quantum dots in an ecofriendly way.
The quantum dots have a diameter of 5 nanometers with their sizes equal and yield high quantum efficiency. Unlike conventional quantum dots, they are not comprised of toxic materials such as lead or cadmium. As the quantum dots can be developed from materials which can be easily found in the nature, researchers look forward to putting these into mass production at low cost.
The research team also discovered a luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and confirmed the possibility of commercial use by developing quantum dot light-emitting diodes with brightness of 1,000 cd/m2, which is greater than that of cellphone displays.
Professor Seokwoo Jeon said, “Although quantum dot LEDs have a lower luminous efficiency than existing ones, their luminescent property can be further improved” and emphasized that “using quantum dot displays will allow us to develop not only paper-thin displays but also flexible ones.”
Sponsored by Graphene Research Center in KAIST Institute for NanoCentury, the research finding was published online in the April 20th issue of Advanced Optical Materials.
Picture 1: Graphene quantum dots and their synthesis
Picture 2: Luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots
Picture 3: Structure of graphene quantum dots LED and its emission
2014.09.06 View 19759
Extracting Light from Graphite: Core Technology of Graphene Quantum Dots Display Developed
Professor Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering announced that they were able to develop topnotch graphene quantum dots from graphite.
Using the method of synthesizing graphite intercalation compound from graphite with salt and water, the research team developed graphene quantum dots in an ecofriendly way.
The quantum dots have a diameter of 5 nanometers with their sizes equal and yield high quantum efficiency. Unlike conventional quantum dots, they are not comprised of toxic materials such as lead or cadmium. As the quantum dots can be developed from materials which can be easily found in the nature, researchers look forward to putting these into mass production at low cost.
The research team also discovered a luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and confirmed the possibility of commercial use by developing quantum dot light-emitting diodes with brightness of 1,000 cd/m2, which is greater than that of cellphone displays.
Professor Seokwoo Jeon said, “Although quantum dot LEDs have a lower luminous efficiency than existing ones, their luminescent property can be further improved” and emphasized that “using quantum dot displays will allow us to develop not only paper-thin displays but also flexible ones.”
Sponsored by Graphene Research Center in KAIST Institute for NanoCentury, the research finding was published online in the April 20th issue of Advanced Optical Materials.
Picture 1: Graphene quantum dots and their synthesis
Picture 2: Luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots
Picture 3: Structure of graphene quantum dots LED and its emission
2014.09.06 View 19759 -
 IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student
In-Mo Chung, a senior student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, developed a mobile homework book application, IAMSCHOOL, in order to help parents engage, more interactively, in their children’s school activities.
Chung said in an interview with KAIST:
“I came up with creating my company, IAMCOMPANY, when I worked as a volunteer for a student club in 2009 that provides an educational service to high school students living in a less-favored environment. I found out their educational environment very poor, which ultimately led me to build a public interest business model for education.”
Chung created a few mobile applications including IAMSCHOOL and IAMCLASS. The application, IAMSCHOOL, receives school’s notices, homework assignments, or any information related to classes and sends them directly and immediately to parents, allowing real-time communications between parents and teachers. In Korea, parents usually check as many as 50 school notices per month.
Once registered, private educational institutes and public organizations can also receive school information through this application.
In July 2011, the Department of Science Management at KAIST hosted a student competition for startup ideas, and Chung’s idea to build an educational application won the best award. In 2012, he received the grand prize at the KAIST E-5 Startup Competition.
An undergraduate student who is the chief executive officer of a tech startup
Chung established IAMCOMPANY with the seed fund of 13 million Korean won that he had received from the city government of Daejeon. His business idea was selected as one of the 300 College Student Startup Projects, a startup support program operated by Daejeon City to encourage entrepreneurship among college and university students.
Chung talked about the background of his business:
“I think that my idea to offer a “free educational application” helped me win the first prize at the student startup competition. At that time, I was still young, so I considered the winning of the competition as an “exercise” to build my own business in the future. But when I actually started my company, I found out that KAIST’s startup programs helped me a lot throughout the entire process and realized that these programs are good enough for young entrepreneurs to build up their company from a single idea.”
KAIST professors and staff support student startups.
Chung took in-depth mentoring from KAIST professors. Professor Min-Hwa Lee of the Department of Management Science and Professor Lak-Kyoung Song of the Department of Technology Management, who is also the president of the Daejeon Creative Economy Innovation Center, have supported Chung’s endeavors. President Taek-Su Kang of the KAIST Innovation Center gave Chung a lot of advice as he was developing IAMCOMPANY’s initial business model. Chung said that even now, they look for solutions together when his business ran into a brick wall.
Professor Lee said, “IAMCOMPANY does not aim for profit. Instead, by supplying free applications, they improve the environment of education and eventually create public interest. Also, they find out consumers’ hidden demands and satisfied it creatively.”
With 8,000 schools registered to IAMSCHOOL, 750,000 parents are using the application in just two years of its release. Parents and teachers responded enthusiastically.
The application “IAMSCHOOL” provides services for 8,000 schools in Korea. Currently, 750,000 parents are using this application.
The company offers the nation’s largest online education service. The reason behind their rapid growth is that their service solves communications problems between schools and parents in a simple and efficient manner.
Jung-Mi Hwang, a teacher at Galma Elementary School in Dajeon, said:
“After using this application, there are fewer occasions of students forgetting their school materials. We think this is because the parents can check the school notices and newsletters at any time through the application.”
She added, “I hope more and more schools will use this application because it is convenient and also available for free.”
Another teacher from Daedeok Elementary School in Daejeon, Dong-Min Nam, said that “many parents like this application since they are immediately notified with school events.”
KAIST’s Technology Business Incubation Center
“After moving around many places due to expensive rent,” Chung said that “we finally moved into the Technology Business Incubation Center (TBIC) at KAIST. The center helped us not only providing the space, but also mentoring and connecting us with venture investment companies. This was a great help in attracting initial investments.”
Chung added:
“At first, a staff member from TBIC was concerned about the viability of my company. I was then an undergraduate student with zero business experience, and from his standpoint, I was taking a huge risk.”
But in several months after its establishment, IAMCOMPANY has grown to have 16 employees.
An investment of 1.5 billion Korean won from a venture capital company led to a sustainable growth.
In early stage, IAMCOMPANY received 300 million Korean won from a venture capital company, and it recently attracted additional 1.2 billion won from a leading venture capital. With these investments, the company grew further. Moreover, investments from large educational corporations have proved the value and competitiveness of the company in the education market.
Chung plans to expand his service globally, particularly in China and Singapore.
He said that he would not forget how he had started his business, and with such a focused mind, he would strive to provide students and parents with quality educational services while proactively incorporating the advanced information technology (IT) into his products.
A bold movement to Pangyo Techno Valley, a Korean version of Silicon Valley
Although the company started with only two members, as of August 2014, it boasts of having twenty employees, a remarkable leap of growth within just two years.
In April this year, Chung relocated his office from TBIC to Pangyo Techno Valley, the Silicon Valley of Korea, in order to provide a better work environment to his staff.
It was not an easy decision for him to leave the comfortable, well-known place, the KAIST campus, and the colleagues, including TBIC staff and KAIST professors, who had helped his startup efforts in early days. However, in order to recruit better employees and to access additional IT resources and education-related companies, Chung decided to make a bold movement, relocating his business to Pangyo Techno Valley in Seoul.
A reputable American venture capital investor, Timothy C. Draper, invested in IAMCOMPANY
Chung was able to secure solid support from an eminent global investor, Timothy C. Draper, the founder of Draper Fisher Jurvetson, a venture capital based in Menlo Park in California.
Recently, Draper, a legendary investor of the Silicon Valley, invested USD 20,000 in IAMCOMPANY. Draper discovered worldwide venture companies such as Hotmail, Skype, and Baidu. IAMCOMPANY received high marks from him as a company with a competitive edge in the global education market.
Chung met Draper in April 2014 when he participated in a television network’s (Korean Broadcasting System) audition program for startups. Draper was one of the judges for the program, and he was impressed by the robust growth of IAMCOMPANY. He eventually made a decision to chip in USD 20,000 in Chung’s company.
Chung said that he was glad to meet the tycoon of Silicon Valley who recognized the potential of his company.
In last October, IAMSCHOOL was selected for the K-APP Global Hub Program—a global market pioneering program to support the development of mobile applications—which was sponsored by the Small and Medium Business Administration in Korea.
IAMCOMPANY will bring ‘the Korean Wave’ in the area of educational applications.
Chung said, “We plan to sustainably manage the applications and add more functions, so that more educational institutions can adopt our application.”
The company aims to provide its service to over 11,000 schools and 100,000 academies nationally so that more parents are able to receive educational news and information easily.
Chung concluded his interview in an upbeat tone as he predicted the future of his company:
“I am proud that IAMSCHOOL is being recognized by the world’s best investor, and I have gained confidence to advance to the global market. Through global service, I want to make "the Korean Wave" in the field of educational applications and to receive appreciation from students, teachers, and parents worldwide.”
2014.09.04 View 11078
IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student
In-Mo Chung, a senior student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, developed a mobile homework book application, IAMSCHOOL, in order to help parents engage, more interactively, in their children’s school activities.
Chung said in an interview with KAIST:
“I came up with creating my company, IAMCOMPANY, when I worked as a volunteer for a student club in 2009 that provides an educational service to high school students living in a less-favored environment. I found out their educational environment very poor, which ultimately led me to build a public interest business model for education.”
Chung created a few mobile applications including IAMSCHOOL and IAMCLASS. The application, IAMSCHOOL, receives school’s notices, homework assignments, or any information related to classes and sends them directly and immediately to parents, allowing real-time communications between parents and teachers. In Korea, parents usually check as many as 50 school notices per month.
Once registered, private educational institutes and public organizations can also receive school information through this application.
In July 2011, the Department of Science Management at KAIST hosted a student competition for startup ideas, and Chung’s idea to build an educational application won the best award. In 2012, he received the grand prize at the KAIST E-5 Startup Competition.
An undergraduate student who is the chief executive officer of a tech startup
Chung established IAMCOMPANY with the seed fund of 13 million Korean won that he had received from the city government of Daejeon. His business idea was selected as one of the 300 College Student Startup Projects, a startup support program operated by Daejeon City to encourage entrepreneurship among college and university students.
Chung talked about the background of his business:
“I think that my idea to offer a “free educational application” helped me win the first prize at the student startup competition. At that time, I was still young, so I considered the winning of the competition as an “exercise” to build my own business in the future. But when I actually started my company, I found out that KAIST’s startup programs helped me a lot throughout the entire process and realized that these programs are good enough for young entrepreneurs to build up their company from a single idea.”
KAIST professors and staff support student startups.
Chung took in-depth mentoring from KAIST professors. Professor Min-Hwa Lee of the Department of Management Science and Professor Lak-Kyoung Song of the Department of Technology Management, who is also the president of the Daejeon Creative Economy Innovation Center, have supported Chung’s endeavors. President Taek-Su Kang of the KAIST Innovation Center gave Chung a lot of advice as he was developing IAMCOMPANY’s initial business model. Chung said that even now, they look for solutions together when his business ran into a brick wall.
Professor Lee said, “IAMCOMPANY does not aim for profit. Instead, by supplying free applications, they improve the environment of education and eventually create public interest. Also, they find out consumers’ hidden demands and satisfied it creatively.”
With 8,000 schools registered to IAMSCHOOL, 750,000 parents are using the application in just two years of its release. Parents and teachers responded enthusiastically.
The application “IAMSCHOOL” provides services for 8,000 schools in Korea. Currently, 750,000 parents are using this application.
The company offers the nation’s largest online education service. The reason behind their rapid growth is that their service solves communications problems between schools and parents in a simple and efficient manner.
Jung-Mi Hwang, a teacher at Galma Elementary School in Dajeon, said:
“After using this application, there are fewer occasions of students forgetting their school materials. We think this is because the parents can check the school notices and newsletters at any time through the application.”
She added, “I hope more and more schools will use this application because it is convenient and also available for free.”
Another teacher from Daedeok Elementary School in Daejeon, Dong-Min Nam, said that “many parents like this application since they are immediately notified with school events.”
KAIST’s Technology Business Incubation Center
“After moving around many places due to expensive rent,” Chung said that “we finally moved into the Technology Business Incubation Center (TBIC) at KAIST. The center helped us not only providing the space, but also mentoring and connecting us with venture investment companies. This was a great help in attracting initial investments.”
Chung added:
“At first, a staff member from TBIC was concerned about the viability of my company. I was then an undergraduate student with zero business experience, and from his standpoint, I was taking a huge risk.”
But in several months after its establishment, IAMCOMPANY has grown to have 16 employees.
An investment of 1.5 billion Korean won from a venture capital company led to a sustainable growth.
In early stage, IAMCOMPANY received 300 million Korean won from a venture capital company, and it recently attracted additional 1.2 billion won from a leading venture capital. With these investments, the company grew further. Moreover, investments from large educational corporations have proved the value and competitiveness of the company in the education market.
Chung plans to expand his service globally, particularly in China and Singapore.
He said that he would not forget how he had started his business, and with such a focused mind, he would strive to provide students and parents with quality educational services while proactively incorporating the advanced information technology (IT) into his products.
A bold movement to Pangyo Techno Valley, a Korean version of Silicon Valley
Although the company started with only two members, as of August 2014, it boasts of having twenty employees, a remarkable leap of growth within just two years.
In April this year, Chung relocated his office from TBIC to Pangyo Techno Valley, the Silicon Valley of Korea, in order to provide a better work environment to his staff.
It was not an easy decision for him to leave the comfortable, well-known place, the KAIST campus, and the colleagues, including TBIC staff and KAIST professors, who had helped his startup efforts in early days. However, in order to recruit better employees and to access additional IT resources and education-related companies, Chung decided to make a bold movement, relocating his business to Pangyo Techno Valley in Seoul.
A reputable American venture capital investor, Timothy C. Draper, invested in IAMCOMPANY
Chung was able to secure solid support from an eminent global investor, Timothy C. Draper, the founder of Draper Fisher Jurvetson, a venture capital based in Menlo Park in California.
Recently, Draper, a legendary investor of the Silicon Valley, invested USD 20,000 in IAMCOMPANY. Draper discovered worldwide venture companies such as Hotmail, Skype, and Baidu. IAMCOMPANY received high marks from him as a company with a competitive edge in the global education market.
Chung met Draper in April 2014 when he participated in a television network’s (Korean Broadcasting System) audition program for startups. Draper was one of the judges for the program, and he was impressed by the robust growth of IAMCOMPANY. He eventually made a decision to chip in USD 20,000 in Chung’s company.
Chung said that he was glad to meet the tycoon of Silicon Valley who recognized the potential of his company.
In last October, IAMSCHOOL was selected for the K-APP Global Hub Program—a global market pioneering program to support the development of mobile applications—which was sponsored by the Small and Medium Business Administration in Korea.
IAMCOMPANY will bring ‘the Korean Wave’ in the area of educational applications.
Chung said, “We plan to sustainably manage the applications and add more functions, so that more educational institutions can adopt our application.”
The company aims to provide its service to over 11,000 schools and 100,000 academies nationally so that more parents are able to receive educational news and information easily.
Chung concluded his interview in an upbeat tone as he predicted the future of his company:
“I am proud that IAMSCHOOL is being recognized by the world’s best investor, and I have gained confidence to advance to the global market. Through global service, I want to make "the Korean Wave" in the field of educational applications and to receive appreciation from students, teachers, and parents worldwide.”
2014.09.04 View 11078 -
 IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student, featured online in EdSurge
EdSurge is a U.S.-based online news site focused on education and technology innovation, which published an article, dated August 12, 2014, on IAMCOMPANY (http://iamcompany.net), a startup created by a KAIST student, Inmo (Ryan) Chung.
The article introduced one of the company’s most popular and free smartphone applications called “IAMSCHOOL” that “funnels school announcements and class notices to parents’ smartphones using a format similar to Twitter and Google+.”
For more about IAMCOMPANY, please visit the link below:
EdSurge, August 12, 2014
“South Korea’s Biggest Educational Information App Plans Pan-Asian Expansion”
https://www.edsurge.com/n/2014-08-12-south-korea-s-biggest-educational-information-app-plans-pan-asian-expansion
2014.08.19 View 8975
IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student, featured online in EdSurge
EdSurge is a U.S.-based online news site focused on education and technology innovation, which published an article, dated August 12, 2014, on IAMCOMPANY (http://iamcompany.net), a startup created by a KAIST student, Inmo (Ryan) Chung.
The article introduced one of the company’s most popular and free smartphone applications called “IAMSCHOOL” that “funnels school announcements and class notices to parents’ smartphones using a format similar to Twitter and Google+.”
For more about IAMCOMPANY, please visit the link below:
EdSurge, August 12, 2014
“South Korea’s Biggest Educational Information App Plans Pan-Asian Expansion”
https://www.edsurge.com/n/2014-08-12-south-korea-s-biggest-educational-information-app-plans-pan-asian-expansion
2014.08.19 View 8975 -
 EureCar, KAIST's Self-Driving Car, Made It to the Global Student Design Finalists at the 2014 National Instruments Annual Conference in Austin, Texas
The National Instruments Week 2014, an annual conference hosted by the National Instruments Corporation (NI), a global producer of automated test equipment and virtual instrumentation software, was held on August 4-7, 2014 at the Austin Convention Center in Texas. This international conference on graphical system design brought together more than 3,200 leading engineers and scientists across a spectrum of industries, from automotive to telecommunications, to robotics to energy.
On the third day of the keynote sessions at the conference, August 7, 2014, the winner of the Global Student Design Competition (GSDC) was announced.
EureCar, a self-driving car developed by Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, and his students, was one of the three finalists that were invited to the conference to contend for the Global Grand Prize.
The three finalists, each selected from a regional competition, were: EureCar from KAIST, Sepios, a nautical robot from Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zürich (ETH Zürich), and NASA Student Launch Project from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte. A total of 3,250 student research teams from 25 countries entered the 2014 GSDC, and the winner was ETH Zürich.
GSDC is designed to promote a better understanding and application by engineering students of NI’s system design software and hardware in their research and learning. Participating students utilized NI’s LabVIEW (software) and CompactRIO (hardware) to create their own solutions to engineering problems that encompass inexpensive medical devices to complex underwater autonomous vehicles.
For details about the finalists, please go to:
http://www.kaist.ac.kr/Upl/downfile/TS4159_Wahby_Student_Design_Showcase.pdf
2014.08.18 View 9957
EureCar, KAIST's Self-Driving Car, Made It to the Global Student Design Finalists at the 2014 National Instruments Annual Conference in Austin, Texas
The National Instruments Week 2014, an annual conference hosted by the National Instruments Corporation (NI), a global producer of automated test equipment and virtual instrumentation software, was held on August 4-7, 2014 at the Austin Convention Center in Texas. This international conference on graphical system design brought together more than 3,200 leading engineers and scientists across a spectrum of industries, from automotive to telecommunications, to robotics to energy.
On the third day of the keynote sessions at the conference, August 7, 2014, the winner of the Global Student Design Competition (GSDC) was announced.
EureCar, a self-driving car developed by Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, and his students, was one of the three finalists that were invited to the conference to contend for the Global Grand Prize.
The three finalists, each selected from a regional competition, were: EureCar from KAIST, Sepios, a nautical robot from Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zürich (ETH Zürich), and NASA Student Launch Project from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte. A total of 3,250 student research teams from 25 countries entered the 2014 GSDC, and the winner was ETH Zürich.
GSDC is designed to promote a better understanding and application by engineering students of NI’s system design software and hardware in their research and learning. Participating students utilized NI’s LabVIEW (software) and CompactRIO (hardware) to create their own solutions to engineering problems that encompass inexpensive medical devices to complex underwater autonomous vehicles.
For details about the finalists, please go to:
http://www.kaist.ac.kr/Upl/downfile/TS4159_Wahby_Student_Design_Showcase.pdf
2014.08.18 View 9957 -
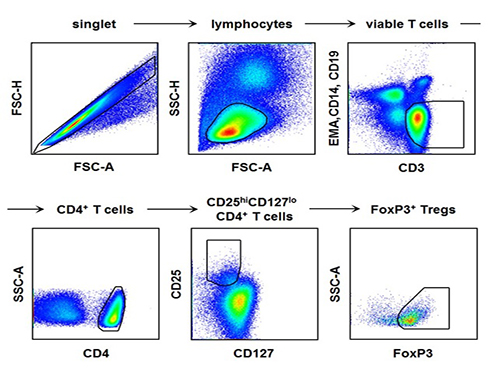 Regulatory T Cells Influence Liver Damage of Hepatitis A Patients
Liver damage becomes more severe with the decrease of regulatory T cells
“This research will aid the development of hepatitis A targeted drug,” said a KAIST researcher.
The KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering’s Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his research team have identified the mechanism, explaining how the regulatory T cells are responsible for the body’s immune system and how they have induced liver damage of hepatitis A patients.
The research results were published online in the July 9th edition of ‘Gut,’ the world’s most prominent journal in the field of gastroenterology.
Hepatitis A is an acute form of hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus spreads through oral contact and enters the body via digestive organs.
Regulatory T cells play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of the body’s immune system by inhibiting the activation of other immune cells. In the case of chronic viral infections, regulatory T cells are known to contribute to the duration of the infection, weakening the immune response to virus infections. However, there has been no information on what roles the regulatory T cells perform in the case of acute viral infections.
The research team used the fluorescence flow cytometry technique to determine the number and characteristics of a variety of immune cells, including regulatory T cells, in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
Consequently, the researchers confirmed that the decrease in the regulatory T cells immune inhibitory ability was consistent with a significant reduction in the number of regulatory T cells in the blood of hepatitis A patients. Furthermore, it was identified that the more noticeable decrease of regulatory T cells led to the occurrence of a more severe liver injury.
The analysis of hepatitis A patient’s blood proved that the cause of the decrease in the number and function of regulatory T cells was the increased expression of cell surface protein ‘Fas,’ which induces cell death.
Professor Shin said, “This study is the first case which proposes the mechanism for clinical aspects in not only hepatitis A, but also acute virus infection.” He added on the future prospect of the research that: “In the future, we can prevent tissue damage by inhibiting cell death of regulatory T cells for severe acute viral infections that do not have an effective treatment for the virus itself.”
[Picture]
The picture shows the process of fluorescence flow cytometry technique to study regulatory T cell in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
2014.08.11 View 11231
Regulatory T Cells Influence Liver Damage of Hepatitis A Patients
Liver damage becomes more severe with the decrease of regulatory T cells
“This research will aid the development of hepatitis A targeted drug,” said a KAIST researcher.
The KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering’s Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his research team have identified the mechanism, explaining how the regulatory T cells are responsible for the body’s immune system and how they have induced liver damage of hepatitis A patients.
The research results were published online in the July 9th edition of ‘Gut,’ the world’s most prominent journal in the field of gastroenterology.
Hepatitis A is an acute form of hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus spreads through oral contact and enters the body via digestive organs.
Regulatory T cells play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of the body’s immune system by inhibiting the activation of other immune cells. In the case of chronic viral infections, regulatory T cells are known to contribute to the duration of the infection, weakening the immune response to virus infections. However, there has been no information on what roles the regulatory T cells perform in the case of acute viral infections.
The research team used the fluorescence flow cytometry technique to determine the number and characteristics of a variety of immune cells, including regulatory T cells, in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
Consequently, the researchers confirmed that the decrease in the regulatory T cells immune inhibitory ability was consistent with a significant reduction in the number of regulatory T cells in the blood of hepatitis A patients. Furthermore, it was identified that the more noticeable decrease of regulatory T cells led to the occurrence of a more severe liver injury.
The analysis of hepatitis A patient’s blood proved that the cause of the decrease in the number and function of regulatory T cells was the increased expression of cell surface protein ‘Fas,’ which induces cell death.
Professor Shin said, “This study is the first case which proposes the mechanism for clinical aspects in not only hepatitis A, but also acute virus infection.” He added on the future prospect of the research that: “In the future, we can prevent tissue damage by inhibiting cell death of regulatory T cells for severe acute viral infections that do not have an effective treatment for the virus itself.”
[Picture]
The picture shows the process of fluorescence flow cytometry technique to study regulatory T cell in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
2014.08.11 View 11231 -
 ASPIRE League 2014: E-Olympics among Five Asian Universities
About 150 undergraduate students from five leading science and technology (S&T) universities in Asia met at the KAIST campus to attend the E-Olympics on August 7-9, 2014.
The E-Olympics began as a student exchange conference held under the Asian Science and Technology Pioneering Institutes of Research and Education (ASPIRE) League, which offers a variety of events, such as workshops, sports matches, lab visits, special lectures, and art performances, to promote academic and research collaborations and cultural sharing between the students of the league member universities.
Founded in 2009, the ASPIRE League is a university consortium consisted of five top S&T universities in Asia: KAIST in Korea, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and Tsinghua University in China, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore, and Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) in Japan. The ASPIRE League aims to provide a knowledge and technology hub for innovation in Asia through the advancement of science and technology and the development of human resources.
Since its start, the ASPIRE League has been holding an annual conference with programs for research collaboration, student exchange, educational cooperation, and satellite laboratories among professors, senior managers, and students of the member universities. This year, however, the consortium decided to dedicate the conference to students by holding the E-Olympics.
Each university sent 30 students to KAIST for the participation of the E-Olympics. For three days, participating students engaged in discussions and presentations at academic workshops; held athletic games including a relay race, basketball, and a rowing race; and toured a few KAIST laboratories, among them: the E-mobility Research Center, the Bio-imaging and Cell Signaling Research Center, the Mechatronics Systems and Control Center, and the Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration and Defense.
The students also attended a music concert performed by a KAIST student club and a lecture entitled “Entrepreneurship through Global Networking” that emphasized the importance of personnel networking in transferring technological innovation into business opportunities.
Chang-Dong Yoo, the Dean of the International Office at KAIST, said, “The E-Olympics will offer students from top science and technology universities in Asia opportunities to interact with each other on a more personal level. I hope that through many of the E-Olympics programs, the students will learn about each other’s culture and academic strength and develop a sense of community to create a “New Asia” by working together.”
2014.08.11 View 14334
ASPIRE League 2014: E-Olympics among Five Asian Universities
About 150 undergraduate students from five leading science and technology (S&T) universities in Asia met at the KAIST campus to attend the E-Olympics on August 7-9, 2014.
The E-Olympics began as a student exchange conference held under the Asian Science and Technology Pioneering Institutes of Research and Education (ASPIRE) League, which offers a variety of events, such as workshops, sports matches, lab visits, special lectures, and art performances, to promote academic and research collaborations and cultural sharing between the students of the league member universities.
Founded in 2009, the ASPIRE League is a university consortium consisted of five top S&T universities in Asia: KAIST in Korea, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and Tsinghua University in China, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore, and Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) in Japan. The ASPIRE League aims to provide a knowledge and technology hub for innovation in Asia through the advancement of science and technology and the development of human resources.
Since its start, the ASPIRE League has been holding an annual conference with programs for research collaboration, student exchange, educational cooperation, and satellite laboratories among professors, senior managers, and students of the member universities. This year, however, the consortium decided to dedicate the conference to students by holding the E-Olympics.
Each university sent 30 students to KAIST for the participation of the E-Olympics. For three days, participating students engaged in discussions and presentations at academic workshops; held athletic games including a relay race, basketball, and a rowing race; and toured a few KAIST laboratories, among them: the E-mobility Research Center, the Bio-imaging and Cell Signaling Research Center, the Mechatronics Systems and Control Center, and the Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration and Defense.
The students also attended a music concert performed by a KAIST student club and a lecture entitled “Entrepreneurship through Global Networking” that emphasized the importance of personnel networking in transferring technological innovation into business opportunities.
Chang-Dong Yoo, the Dean of the International Office at KAIST, said, “The E-Olympics will offer students from top science and technology universities in Asia opportunities to interact with each other on a more personal level. I hope that through many of the E-Olympics programs, the students will learn about each other’s culture and academic strength and develop a sense of community to create a “New Asia” by working together.”
2014.08.11 View 14334 -
 2014 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation: July 31-August 1, 2014, Seoul
The Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST hosted an international conference on nuclear nonproliferation on July 31-August 1, 2014 in Seoul. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Korean Nuclear Safety and Security Commission, and the Korea Nuclear Policy Society (KNPS) sponsored the event.
Over one hundred experts and "thought leaders" in nuclear security and nonproliferation attended the conference and discussed issues related to the nonproliferation of nuclear weapons, the role of scientific community in mitigating nuclear threat and promoting the peaceful use of nuclear power, and nuclear disarmament policy.
Keynote speakers were: Steven E. Miller, Director of International Security Program at Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Harvard University; Scott D. Sagan, Senior Fellow of the Center for International Security and Cooperation, Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies, Stanford University; Mark Fitzpatrick, Director of the Nonproliferation and Disarmament Programme, International Institute for Strategic Studies; Sang-Hyun Lee, Director of Security Strategy, Sejong Institute; and Man-Sung Yim, Professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST.
At the conference, Professor Yim, Director of KAIST NEREC said, “Korea has grown to become a key player in the development of commercial nuclear energy over the past decades. We hope that our conference encourages Korea to be more involved in the efforts of the international community to enhance the global nonproliferation regime.”
2014.08.05 View 15980
2014 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation: July 31-August 1, 2014, Seoul
The Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST hosted an international conference on nuclear nonproliferation on July 31-August 1, 2014 in Seoul. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Korean Nuclear Safety and Security Commission, and the Korea Nuclear Policy Society (KNPS) sponsored the event.
Over one hundred experts and "thought leaders" in nuclear security and nonproliferation attended the conference and discussed issues related to the nonproliferation of nuclear weapons, the role of scientific community in mitigating nuclear threat and promoting the peaceful use of nuclear power, and nuclear disarmament policy.
Keynote speakers were: Steven E. Miller, Director of International Security Program at Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Harvard University; Scott D. Sagan, Senior Fellow of the Center for International Security and Cooperation, Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies, Stanford University; Mark Fitzpatrick, Director of the Nonproliferation and Disarmament Programme, International Institute for Strategic Studies; Sang-Hyun Lee, Director of Security Strategy, Sejong Institute; and Man-Sung Yim, Professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST.
At the conference, Professor Yim, Director of KAIST NEREC said, “Korea has grown to become a key player in the development of commercial nuclear energy over the past decades. We hope that our conference encourages Korea to be more involved in the efforts of the international community to enhance the global nonproliferation regime.”
2014.08.05 View 15980 -
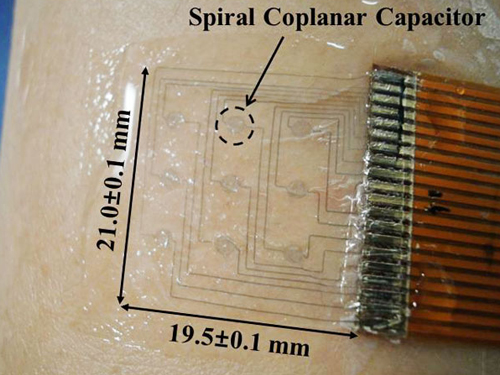 Newsweek: The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel
Newsweek covered the introduction of the goosebump sensor invented by Professor Young-Ho Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST in an article dated July 27, 2014.
The article entitled “The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel” explains how the sensor works and reports on the current research and development trends in emotion-sensing technology.
Professor Cho’s research paper was originally published in the journal Applied Physics Letters on June 24, 2014, titled “A Flexible Skin Piloerection Monitoring Sensor."
Newsweek, July 27, 2014
“The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel”
http://www.newsweek.com/goosebump-sensor-knows-how-you-feel-260689
2014.07.28 View 9247
Newsweek: The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel
Newsweek covered the introduction of the goosebump sensor invented by Professor Young-Ho Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST in an article dated July 27, 2014.
The article entitled “The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel” explains how the sensor works and reports on the current research and development trends in emotion-sensing technology.
Professor Cho’s research paper was originally published in the journal Applied Physics Letters on June 24, 2014, titled “A Flexible Skin Piloerection Monitoring Sensor."
Newsweek, July 27, 2014
“The Goosebump Sensor That Knows How You Feel”
http://www.newsweek.com/goosebump-sensor-knows-how-you-feel-260689
2014.07.28 View 9247 -
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation: Researchers Uncover the Secret Lymphatic Identity of the Schlemm's Canal
The Journal of Clinical Investigation (JCI), a peer-reviewed, top-tier medical journal published by the American Society for Clinical Investigation, carried a commentary entitled “Schlemm’s Canal: More Than Meets the Eye, Lymphatics in Disguise” in the July 25, 2014 issue.
In the commentary, the authors compared a research paper (“Lymphatic regular PROX1 determines Schlemm’s canal integrity and identity”) by Professor Gou-Young Koh of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST with research work from the University of Helsinki (article entitled “The Schlemm’s canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 responsive lymphatic-like vessel”).
The JCI released a press statement dated July 25, 2014 on its commentary. It mentioned that glaucoma, one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide, elevates eye pressure owing to poor drainage of aqueous humor. A specialized structure called “Schlemm’s canal” funnels aqueous humor from the eye back into circulation, which is critical to prevent pressure buildup in the eye. The article discussed the role of Schlemm’s canal in the context of lymphatic vascular characteristics by reviewing two research group’s papers back-to-back.
For the full text of the press release, please visit the link below:
Press Release from the Journal of Clinical Investigation, July 25, 2014
“Researchers uncover the secret lymphatic identity of the Schlemm’s canal”
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2014-07/joci-rut072414.php
2014.07.28 View 9207
The Journal of Clinical Investigation: Researchers Uncover the Secret Lymphatic Identity of the Schlemm's Canal
The Journal of Clinical Investigation (JCI), a peer-reviewed, top-tier medical journal published by the American Society for Clinical Investigation, carried a commentary entitled “Schlemm’s Canal: More Than Meets the Eye, Lymphatics in Disguise” in the July 25, 2014 issue.
In the commentary, the authors compared a research paper (“Lymphatic regular PROX1 determines Schlemm’s canal integrity and identity”) by Professor Gou-Young Koh of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST with research work from the University of Helsinki (article entitled “The Schlemm’s canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 responsive lymphatic-like vessel”).
The JCI released a press statement dated July 25, 2014 on its commentary. It mentioned that glaucoma, one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide, elevates eye pressure owing to poor drainage of aqueous humor. A specialized structure called “Schlemm’s canal” funnels aqueous humor from the eye back into circulation, which is critical to prevent pressure buildup in the eye. The article discussed the role of Schlemm’s canal in the context of lymphatic vascular characteristics by reviewing two research group’s papers back-to-back.
For the full text of the press release, please visit the link below:
Press Release from the Journal of Clinical Investigation, July 25, 2014
“Researchers uncover the secret lymphatic identity of the Schlemm’s canal”
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2014-07/joci-rut072414.php
2014.07.28 View 9207 -
 Cooperation Agreement with Korea's National Information Society Agency on Global Information Education
KAIST and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to launch global information education cooperation. President Steve Kang and President Kwang-Soo Chang of NIA, attended the signing ceremony held at KAIST on July 23, 2014.
Under the MOU, KAIST and NIA will jointly develop contents for global information education; plan and operate educational programs; provide consulting services to train experts in information; and implement exchange programs for faculty and students.
In addition, the two organizations plan to cooperate in the establishment of a network, consisting of alumni and students from the Global Information and Telecommunications Technology Program at KAIST (KAIST ITTP), to deliver a Korean model of electronic government (e-government) to other nations worldwide.
President Kang said, “Korea is one of the most wired nations in the world. By working with the NIA, we hope to have an opportunity to export our knowledge and experiences in the construction of e-governments to less technologically advanced nations by becoming a good precedent for them.”
Since 2006, KAIST has invited 20-30 government officials from underdeveloped or developing countries each year, offering them enrollment in graduate programs at KAIST ITTP.
2014.07.25 View 8221
Cooperation Agreement with Korea's National Information Society Agency on Global Information Education
KAIST and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to launch global information education cooperation. President Steve Kang and President Kwang-Soo Chang of NIA, attended the signing ceremony held at KAIST on July 23, 2014.
Under the MOU, KAIST and NIA will jointly develop contents for global information education; plan and operate educational programs; provide consulting services to train experts in information; and implement exchange programs for faculty and students.
In addition, the two organizations plan to cooperate in the establishment of a network, consisting of alumni and students from the Global Information and Telecommunications Technology Program at KAIST (KAIST ITTP), to deliver a Korean model of electronic government (e-government) to other nations worldwide.
President Kang said, “Korea is one of the most wired nations in the world. By working with the NIA, we hope to have an opportunity to export our knowledge and experiences in the construction of e-governments to less technologically advanced nations by becoming a good precedent for them.”
Since 2006, KAIST has invited 20-30 government officials from underdeveloped or developing countries each year, offering them enrollment in graduate programs at KAIST ITTP.
2014.07.25 View 8221