research
-
 Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
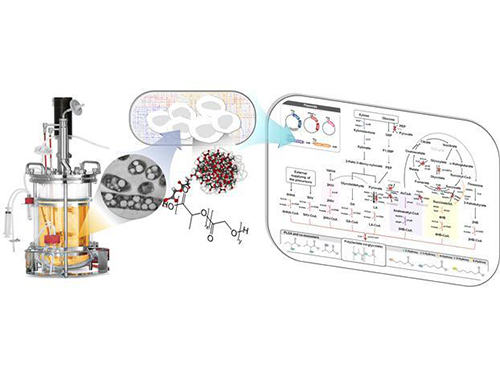
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11444
Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11444 -
 HUBO to Present at the 2016 World Economic Forum
KAIST researchers will lead an IdeasLab on biotechnology for an aging society while HUBO, the winner of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge, will interact with the forum participants, offering an experience of state-of-the-art robotics technology.
Representatives from KAIST will attend the 2016 Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum to run an IdeasLab and showcase its humanoid robot.
With over 2,500 leaders from business, government, international organizations, civil society, academia, media, and the arts expected to participate, the 2016 Annual Meeting will take place on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland. Under the theme of “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution,” global leaders will discuss the period of digital transformation that will have profound effects on economies, societies, and human behavior.
President Sung-Mo Kang will join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a high-level academic meeting to foster collaboration among experts on issues of global concern for the future of higher education and the role of science in society. He will discuss how the emerging revolution in technology will affect the way universities operate and serve society. KAIST is the only Korean university participating in GULF, which is composed of prestigious universities invited from around the world.
Four KAIST professors, including Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department, will lead an IdeasLab on “Biotechnology for an Aging Society.”
Professor Lee said, “In recent decades, much attention has been paid to the potential effect of the growth of an aging population and problems posed by it. At our IdeasLab, we will introduce some of our research breakthroughs in biotechnology to address the challenges of an aging society.”
In particular, he will present his latest research in systems biotechnology and metabolic engineering. His research has explained the mechanisms of how traditional Oriental medicine works in our bodies by identifying structural similarities between effective compounds in traditional medicine and human metabolites, and has proposed more effective treatments by employing such compounds.
KAIST will also display its networked mobile medical service system, “Dr. M.” Built upon a ubiquitous and mobile Internet, such as the Internet of Things, wearable electronics, and smart homes and vehicles, Dr. M will provide patients with a more affordable and accessible healthcare service.
In addition, Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department will showcase his humanoid robot, “HUBO,” during the Annual Meeting. His research team won the International Humanoid Robotics Challenge hosted by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which was held in Pomona, California, on June 5-6, 2015. With 24 international teams participating in the finals, HUBO completed all eight tasks in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, 6 minutes earlier than the runner-up, and almost 11 minutes earlier than the third-place team. Team KAIST walked away with the grand prize of USD 2 million.
Professor Oh said, “Robotics technology will grow exponentially in this century, becoming a real driving force to expedite the Fourth Industrial Revolution. I hope HUBO will offer an opportunity to learn about the current advances in robotics technology.”
President Kang pointed out, “KAIST has participated in the Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum since 2011 and has engaged with a broad spectrum of global leaders through numerous presentations and demonstrations of our excellence in education and research. Next year, we will choreograph our first robotics exhibition on HUBO and present high-tech research results in biotechnology, which, I believe, epitomizes how science and technology breakthroughs in the Fourth Industrial Revolution will shape our future in an unprecedented way.”
2015.11.18 View 12961
HUBO to Present at the 2016 World Economic Forum
KAIST researchers will lead an IdeasLab on biotechnology for an aging society while HUBO, the winner of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge, will interact with the forum participants, offering an experience of state-of-the-art robotics technology.
Representatives from KAIST will attend the 2016 Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum to run an IdeasLab and showcase its humanoid robot.
With over 2,500 leaders from business, government, international organizations, civil society, academia, media, and the arts expected to participate, the 2016 Annual Meeting will take place on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland. Under the theme of “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution,” global leaders will discuss the period of digital transformation that will have profound effects on economies, societies, and human behavior.
President Sung-Mo Kang will join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a high-level academic meeting to foster collaboration among experts on issues of global concern for the future of higher education and the role of science in society. He will discuss how the emerging revolution in technology will affect the way universities operate and serve society. KAIST is the only Korean university participating in GULF, which is composed of prestigious universities invited from around the world.
Four KAIST professors, including Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department, will lead an IdeasLab on “Biotechnology for an Aging Society.”
Professor Lee said, “In recent decades, much attention has been paid to the potential effect of the growth of an aging population and problems posed by it. At our IdeasLab, we will introduce some of our research breakthroughs in biotechnology to address the challenges of an aging society.”
In particular, he will present his latest research in systems biotechnology and metabolic engineering. His research has explained the mechanisms of how traditional Oriental medicine works in our bodies by identifying structural similarities between effective compounds in traditional medicine and human metabolites, and has proposed more effective treatments by employing such compounds.
KAIST will also display its networked mobile medical service system, “Dr. M.” Built upon a ubiquitous and mobile Internet, such as the Internet of Things, wearable electronics, and smart homes and vehicles, Dr. M will provide patients with a more affordable and accessible healthcare service.
In addition, Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department will showcase his humanoid robot, “HUBO,” during the Annual Meeting. His research team won the International Humanoid Robotics Challenge hosted by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which was held in Pomona, California, on June 5-6, 2015. With 24 international teams participating in the finals, HUBO completed all eight tasks in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, 6 minutes earlier than the runner-up, and almost 11 minutes earlier than the third-place team. Team KAIST walked away with the grand prize of USD 2 million.
Professor Oh said, “Robotics technology will grow exponentially in this century, becoming a real driving force to expedite the Fourth Industrial Revolution. I hope HUBO will offer an opportunity to learn about the current advances in robotics technology.”
President Kang pointed out, “KAIST has participated in the Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum since 2011 and has engaged with a broad spectrum of global leaders through numerous presentations and demonstrations of our excellence in education and research. Next year, we will choreograph our first robotics exhibition on HUBO and present high-tech research results in biotechnology, which, I believe, epitomizes how science and technology breakthroughs in the Fourth Industrial Revolution will shape our future in an unprecedented way.”
2015.11.18 View 12961 -
 Using Light to Treat Alzheimer's Disease
Medical application of photoactive chemicals offers a promising therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases.
A research team jointly led by Professor Chan Beum Park of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Kwon Yu from the Bionano Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) conducted research to suppress an abnormal assembly of beta-amyloids, a protein commonly found in the brain, by using photo-excited porphyrins.
Beta-amyloid plaques are known to cause Alzheimer's disease. This research finding suggests new ways to treat neurodegenerative illnesses including Alzheimer's disease. It was published online as the lead article in the September 21th issue of Angewandte Chemie. The title of the article is “Photo-excited Porphyrins as a Strong Suppressor of ß-Amyloid Aggregation and Synaptic Toxicity.”
Light-induced treatments using organic photosensitizers have advantages to managing the treatment in time and area. In the case of cancer treatments, doctors use photodynamic therapies where a patient is injected with an organic photosensitizer, and a light is shed on the patient’s lesion. However, such therapies had never been employed to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Alzheimer's starts when a protein called beta-amyloid is created and deposited in a patient’s brain. The abnormally folded protein created this way harms the brain cells by inducing the degradation of brain functions, for example, dementia. If beta-amyloid creation can be suppressed at an early stage, the formation of amyloid deposits will stop. This could prevent Alzheimer’s disease or halt its progress.
The research team effectively prevented the buildup of beta-amyloids by using blue LED lights and a porphyrin inducer, which is a biocompatible organic compound. By absorbing light energy, a photosensitizer such as porphyrin reaches the excitation state. Active oxygen is created as the porphyrin returns to its ground state. The active oxygen oxidizes a beta-amyloid monomer, and by combining with it, disturbs its assembly.
The technique was tested on drosophilae or fruit flies, which were produced to model Alzheimer on invertebrates. The research showed that symptoms of Alzheimer's disease in the fruit flies such as damage on synapse and muscle, neuronal apoptosis, degradation in motility, and decreased longevity were alleviated. Treatments with light provide additional benefits: less medication is needed than other drug treatments, and there are fewer side effects. When developed, photodynamic therapy will be used widely for this reason.
Professor Park said, “This work has significance as it was the first case to use light and photosensitizers to stop deposits of beta-amyloids. We plan to carry the research further by testing compatibility with other organic and inorganic photosensitizers and by changing the subject of photodynamic therapy to vertebrate such as mice.”
Picture 1 – Deposits of Beta-Amyloid in Fruit Flies Stopped by Using Porphyrin and Blue LED Lights
Picture 2 – The Research Finding Published as the Lead Article in Angewandte Chemie (September 2015)
2015.11.11 View 11596
Using Light to Treat Alzheimer's Disease
Medical application of photoactive chemicals offers a promising therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases.
A research team jointly led by Professor Chan Beum Park of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Kwon Yu from the Bionano Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) conducted research to suppress an abnormal assembly of beta-amyloids, a protein commonly found in the brain, by using photo-excited porphyrins.
Beta-amyloid plaques are known to cause Alzheimer's disease. This research finding suggests new ways to treat neurodegenerative illnesses including Alzheimer's disease. It was published online as the lead article in the September 21th issue of Angewandte Chemie. The title of the article is “Photo-excited Porphyrins as a Strong Suppressor of ß-Amyloid Aggregation and Synaptic Toxicity.”
Light-induced treatments using organic photosensitizers have advantages to managing the treatment in time and area. In the case of cancer treatments, doctors use photodynamic therapies where a patient is injected with an organic photosensitizer, and a light is shed on the patient’s lesion. However, such therapies had never been employed to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Alzheimer's starts when a protein called beta-amyloid is created and deposited in a patient’s brain. The abnormally folded protein created this way harms the brain cells by inducing the degradation of brain functions, for example, dementia. If beta-amyloid creation can be suppressed at an early stage, the formation of amyloid deposits will stop. This could prevent Alzheimer’s disease or halt its progress.
The research team effectively prevented the buildup of beta-amyloids by using blue LED lights and a porphyrin inducer, which is a biocompatible organic compound. By absorbing light energy, a photosensitizer such as porphyrin reaches the excitation state. Active oxygen is created as the porphyrin returns to its ground state. The active oxygen oxidizes a beta-amyloid monomer, and by combining with it, disturbs its assembly.
The technique was tested on drosophilae or fruit flies, which were produced to model Alzheimer on invertebrates. The research showed that symptoms of Alzheimer's disease in the fruit flies such as damage on synapse and muscle, neuronal apoptosis, degradation in motility, and decreased longevity were alleviated. Treatments with light provide additional benefits: less medication is needed than other drug treatments, and there are fewer side effects. When developed, photodynamic therapy will be used widely for this reason.
Professor Park said, “This work has significance as it was the first case to use light and photosensitizers to stop deposits of beta-amyloids. We plan to carry the research further by testing compatibility with other organic and inorganic photosensitizers and by changing the subject of photodynamic therapy to vertebrate such as mice.”
Picture 1 – Deposits of Beta-Amyloid in Fruit Flies Stopped by Using Porphyrin and Blue LED Lights
Picture 2 – The Research Finding Published as the Lead Article in Angewandte Chemie (September 2015)
2015.11.11 View 11596 -
 Professor Key-Sun Choi Receives the Order of Service Merit Green Stripes from the Korean Government
The award recognizes Professor Choi’s life-long research effort to make Korean language digitally available, both nationally and internationally.
Professor Key-Sun Choi of the School of Computing at KAIST received the Order of Service Merit Green Stripes from the Korean government at the 569th Korean Language Day, held annually to commemorate the invention of the Korean language, Hangeul. The ceremony took place on October 9, 2015, at the Sejong Center in Seoul.
Professor Choi has distinguished himself in the field of natural language processing (NLP), including Korean language. He developed a Korean NLP parser that enabled information processing and data analysis of Korean language, as well as a digital Korean dictionary, contributing to the advancement of Korean language-based information technology.
Professor Choi also led the way to widespread use of Korean natural language in computing by developing and commercializing open source software to process the Korean language.
He has served leading roles in many of the international academic societies and standardization organizations, among others, as the vice president of Infoterm (the International Information Center for Terminology), president of the Asia Federation of Natural Language Processing, vice chair of ISO/TC 37, a technical committee in the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and a council member for the International Association of Machine Translation.
2015.10.08 View 9254
Professor Key-Sun Choi Receives the Order of Service Merit Green Stripes from the Korean Government
The award recognizes Professor Choi’s life-long research effort to make Korean language digitally available, both nationally and internationally.
Professor Key-Sun Choi of the School of Computing at KAIST received the Order of Service Merit Green Stripes from the Korean government at the 569th Korean Language Day, held annually to commemorate the invention of the Korean language, Hangeul. The ceremony took place on October 9, 2015, at the Sejong Center in Seoul.
Professor Choi has distinguished himself in the field of natural language processing (NLP), including Korean language. He developed a Korean NLP parser that enabled information processing and data analysis of Korean language, as well as a digital Korean dictionary, contributing to the advancement of Korean language-based information technology.
Professor Choi also led the way to widespread use of Korean natural language in computing by developing and commercializing open source software to process the Korean language.
He has served leading roles in many of the international academic societies and standardization organizations, among others, as the vice president of Infoterm (the International Information Center for Terminology), president of the Asia Federation of Natural Language Processing, vice chair of ISO/TC 37, a technical committee in the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and a council member for the International Association of Machine Translation.
2015.10.08 View 9254 -
 KAIST's DRC-HUBO Wins the DARPA Robotics Challenge 2015
DRC-HUBO finished all eight assignments in less than 45 minutes, taking first place among 24 international teams and claiming the USD 2 million prize offered by a US defense research agency.
The Robotics Challenge Finals 2015 hosted by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) took place on June 5-6, 2015 at the Fairplex in Pomona, California.
Team KAIST of the Republic of Korea led by Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Professor In-So Kweon of the Electrical Engineering Department, and researchers from Rainbow Co., the university’s spin-off company that builds the robots, won the DARPA Finals. The team received USD 2 million as a prize.
The DARPA’s Robotics Challenge (DRC) promotes a competition of robot systems and software teams which seek to develop robots capable of assisting humans in responding to natural and man-made disasters such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear incident in 2011. The DRC consists of three competitions: a software-based Virtual Robotics Challenge which took place in June 2013; the Robotics Challenge Trials in Homestead, Florida, in December 2013; and the Finals in June 2015.
A total of 24 teams from universities and private and public research institutes from Korea, the US, Hong Kong, Germany, Japan, and Italy participated in the Finals. The participating teams had to finish eight assignments in 60 minutes, during which their robots were untethered and operated wirelessly without communication from their engineers.
Each team was assigned a series of tasks: they included driving a vehicle, getting out of a vehicle, opening a door, turning a valve, drilling a hole in a wall, a surprise task such as pushing a button or turning on a switch, walking over rubble or debris, and climbing stairs. Robots scored a point each time they completed their missions. To win, a team had to complete all the tasks successfully in the shortest amount of time possible.
Team KAIST completed the entire course in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, followed by the Institute of Human and Machine Cognition (IHMC) Robotics in Pensacola, Florida in 50:26, and Team TARTAN Rescue of the National Robotics Engineering Center at Carnegie Mellon University in 55:15.
For details, see an article below from the New York Times:
New York Times, June 6, 2015
“Korean Robot Makers Walk Off With $2 Million Prize”
http://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/07/science/korean-robot-makers-walk-off-with-2-million-prize.html?_r=1
DRC-HUBO sticks a plug into an outlet for the surprise task at the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge on June 5-6, 2015, in Pomona, California.
DRC-HUBO turns a valve in a clockwise direction.
DRC-HUBO drills to cut a circle into the wall.
Members of Team KAIST pose together after the award ceremony on June 6, 2015.
2015.06.07 View 24543
KAIST's DRC-HUBO Wins the DARPA Robotics Challenge 2015
DRC-HUBO finished all eight assignments in less than 45 minutes, taking first place among 24 international teams and claiming the USD 2 million prize offered by a US defense research agency.
The Robotics Challenge Finals 2015 hosted by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) took place on June 5-6, 2015 at the Fairplex in Pomona, California.
Team KAIST of the Republic of Korea led by Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Professor In-So Kweon of the Electrical Engineering Department, and researchers from Rainbow Co., the university’s spin-off company that builds the robots, won the DARPA Finals. The team received USD 2 million as a prize.
The DARPA’s Robotics Challenge (DRC) promotes a competition of robot systems and software teams which seek to develop robots capable of assisting humans in responding to natural and man-made disasters such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear incident in 2011. The DRC consists of three competitions: a software-based Virtual Robotics Challenge which took place in June 2013; the Robotics Challenge Trials in Homestead, Florida, in December 2013; and the Finals in June 2015.
A total of 24 teams from universities and private and public research institutes from Korea, the US, Hong Kong, Germany, Japan, and Italy participated in the Finals. The participating teams had to finish eight assignments in 60 minutes, during which their robots were untethered and operated wirelessly without communication from their engineers.
Each team was assigned a series of tasks: they included driving a vehicle, getting out of a vehicle, opening a door, turning a valve, drilling a hole in a wall, a surprise task such as pushing a button or turning on a switch, walking over rubble or debris, and climbing stairs. Robots scored a point each time they completed their missions. To win, a team had to complete all the tasks successfully in the shortest amount of time possible.
Team KAIST completed the entire course in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, followed by the Institute of Human and Machine Cognition (IHMC) Robotics in Pensacola, Florida in 50:26, and Team TARTAN Rescue of the National Robotics Engineering Center at Carnegie Mellon University in 55:15.
For details, see an article below from the New York Times:
New York Times, June 6, 2015
“Korean Robot Makers Walk Off With $2 Million Prize”
http://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/07/science/korean-robot-makers-walk-off-with-2-million-prize.html?_r=1
DRC-HUBO sticks a plug into an outlet for the surprise task at the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge on June 5-6, 2015, in Pomona, California.
DRC-HUBO turns a valve in a clockwise direction.
DRC-HUBO drills to cut a circle into the wall.
Members of Team KAIST pose together after the award ceremony on June 6, 2015.
2015.06.07 View 24543 -
 Professor Shim Featured with His Drone System in IEEE Spectrum
The IEEE Spectrum, a technology and science magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), featured an article of KAIST’s autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) entitled “South Korea Prepares for Drone vs. Drone Combat,” posted on April 1, 2015.
The article introduces the anti-drone defense system being developed by Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST. With the goal of developing guard drones that can detect and capture unknown UAVs, the anti-drone defense system consists of reconnaissance drones, agile multi-rotor UAVs equipped with nets which are dropped to snare enemy drones, and transport UAVs to carry smaller drones.
Professor Shim currently leads KAIST’s Unmanned System Research Group (USRG, http://unmanned.kaist.ac.kr/) and Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration, aNd Defense (C-FRIEND).
For the article, please go to http://spectrum.ieee.org/automaton/robotics/aerial-robots/south-korea-drone-vs-drone.
2015.04.02 View 13717
Professor Shim Featured with His Drone System in IEEE Spectrum
The IEEE Spectrum, a technology and science magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), featured an article of KAIST’s autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) entitled “South Korea Prepares for Drone vs. Drone Combat,” posted on April 1, 2015.
The article introduces the anti-drone defense system being developed by Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST. With the goal of developing guard drones that can detect and capture unknown UAVs, the anti-drone defense system consists of reconnaissance drones, agile multi-rotor UAVs equipped with nets which are dropped to snare enemy drones, and transport UAVs to carry smaller drones.
Professor Shim currently leads KAIST’s Unmanned System Research Group (USRG, http://unmanned.kaist.ac.kr/) and Center of Field Robotics for Innovation, Exploration, aNd Defense (C-FRIEND).
For the article, please go to http://spectrum.ieee.org/automaton/robotics/aerial-robots/south-korea-drone-vs-drone.
2015.04.02 View 13717 -
 Mutations Occurring Only in Brain Responsible for Intractable Epilepsy Identified
KAIST researchers have discovered that brain somatic mutations in MTOR gene induce intractable epilepsy and suggest a precision medicine to treat epileptic seizures.
Epilepsy is a brain disorder which afflicts more than 50 million people worldwide. Many epilepsy patients can control their symptoms through medication, but about 30% suffer from intractable epilepsy and are unable to manage the disease with drugs. Intractable epilepsy causes multiple seizures, permanent mental, physical, and developmental disabilities, and even death. Therefore, surgical removal of the affected area from the brain has been practiced as a treatment for patients with medically refractory seizures, but this too fails to provide a complete solution because only 60% of the patients who undergo surgery are rendered free of seizures.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Professor Dong-Seok Kim of Epilepsy Research Center at Yonsei University College of Medicine has recently identified brain somatic mutations in the gene of mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) as the cause of focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII), one of the most important and common inducers to intractable epilepsy, particularly in children. They propose a targeted therapy to lessen epileptic seizures by suppressing the activation of mTOR kinase, a signaling protein in the brain. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on March 23, 2015.
FCDII contributes to the abnormal developments of the cerebral cortex, ranging from cortical disruption to severe forms of cortical dyslamination, balloon cells, and dysplastic neurons. The research team studied 77 FCDII patients with intractable epilepsy who had received a surgery to remove the affected regions from the brain. The researchers used various deep sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis of the samples obtained from the patients’ brain and blood, or saliva. They reported that about 16% of the studied patients had somatic mutations in their brain. Such mutations, however, did not take place in their blood or saliva DNA.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee of KAIST said, “This is an important finding. Unlike our previous belief that genetic mutations causing intractable epilepsy exist anywhere in the human body including blood, specific gene mutations incurred only in the brain can lead to intractable epilepsy. From our animal models, we could see how a small fraction of mutations carrying neurons in the brain could affect its entire function.”
The research team recapitulated the pathogenesis of intractable epilepsy by inducing the focal cortical expression of mutated mTOR in the mouse brain via electroporation method and observed as the mouse develop epileptic symptoms. They then treated these mice with the drug called “rapamycin” to inhibit the activity of mTOR protein and observed that it suppressed the development of epileptic seizures with cytomegalic neurons.
“Our study offers the first evidence that brain-somatic activating mutations in MTOR cause FCDII and identifies mTOR as a treatment target for intractable epilepsy,” said co-author Dr. Dong-Seok Kim, a neurosurgeon at Yonsei Medical Center with the country’s largest surgical experiences in treating patients with this condition.
The research paper is titled “Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1038/nm.3824)
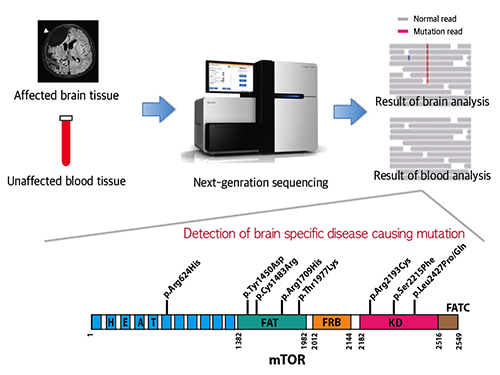
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how to detect brain specific mutation using next-generation sequencing technology with blood-brain paired sample. Simple comparison of non-overlapping mutations between affected and unaffected tissues is able to detect brain specific mutations.
Picture 2: A schematic image to show how to generate focal cortical dysplasia mouse model. This mouse model open the new window of drug screening for seizure patients.
Picture 3: Targeted medicine can rescue the focal cortical dysplasia symptoms including cytomegalic neuron & intractable epilepsy.
2015.03.25 View 14541
Mutations Occurring Only in Brain Responsible for Intractable Epilepsy Identified
KAIST researchers have discovered that brain somatic mutations in MTOR gene induce intractable epilepsy and suggest a precision medicine to treat epileptic seizures.
Epilepsy is a brain disorder which afflicts more than 50 million people worldwide. Many epilepsy patients can control their symptoms through medication, but about 30% suffer from intractable epilepsy and are unable to manage the disease with drugs. Intractable epilepsy causes multiple seizures, permanent mental, physical, and developmental disabilities, and even death. Therefore, surgical removal of the affected area from the brain has been practiced as a treatment for patients with medically refractory seizures, but this too fails to provide a complete solution because only 60% of the patients who undergo surgery are rendered free of seizures.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Professor Dong-Seok Kim of Epilepsy Research Center at Yonsei University College of Medicine has recently identified brain somatic mutations in the gene of mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) as the cause of focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII), one of the most important and common inducers to intractable epilepsy, particularly in children. They propose a targeted therapy to lessen epileptic seizures by suppressing the activation of mTOR kinase, a signaling protein in the brain. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on March 23, 2015.
FCDII contributes to the abnormal developments of the cerebral cortex, ranging from cortical disruption to severe forms of cortical dyslamination, balloon cells, and dysplastic neurons. The research team studied 77 FCDII patients with intractable epilepsy who had received a surgery to remove the affected regions from the brain. The researchers used various deep sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis of the samples obtained from the patients’ brain and blood, or saliva. They reported that about 16% of the studied patients had somatic mutations in their brain. Such mutations, however, did not take place in their blood or saliva DNA.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee of KAIST said, “This is an important finding. Unlike our previous belief that genetic mutations causing intractable epilepsy exist anywhere in the human body including blood, specific gene mutations incurred only in the brain can lead to intractable epilepsy. From our animal models, we could see how a small fraction of mutations carrying neurons in the brain could affect its entire function.”
The research team recapitulated the pathogenesis of intractable epilepsy by inducing the focal cortical expression of mutated mTOR in the mouse brain via electroporation method and observed as the mouse develop epileptic symptoms. They then treated these mice with the drug called “rapamycin” to inhibit the activity of mTOR protein and observed that it suppressed the development of epileptic seizures with cytomegalic neurons.
“Our study offers the first evidence that brain-somatic activating mutations in MTOR cause FCDII and identifies mTOR as a treatment target for intractable epilepsy,” said co-author Dr. Dong-Seok Kim, a neurosurgeon at Yonsei Medical Center with the country’s largest surgical experiences in treating patients with this condition.
The research paper is titled “Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1038/nm.3824)
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how to detect brain specific mutation using next-generation sequencing technology with blood-brain paired sample. Simple comparison of non-overlapping mutations between affected and unaffected tissues is able to detect brain specific mutations.
Picture 2: A schematic image to show how to generate focal cortical dysplasia mouse model. This mouse model open the new window of drug screening for seizure patients.
Picture 3: Targeted medicine can rescue the focal cortical dysplasia symptoms including cytomegalic neuron & intractable epilepsy.
2015.03.25 View 14541 -
 KAIST Develops a Credit-Card-Thick Flexible Lithium Ion Battery
Since the battery can be charged wirelessly, useful applications are expected including medical patches and smart cards.
Professor Jang Wook Choi at KAIST’s Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) and Dr. Jae Yong Song at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science jointly led research to invent a flexible lithium ion battery that is thinner than a credit card and can be charged wirelessly.
Their research findings were published online in Nano Letters on March 6, 2015. Lithium ion batteries are widely used today in various electronics including mobile devices and electronic cars. Researchers said that their work could help accelerate the development of flexible and wearable electronics.
Conventional lithium ion batteries are manufactured based on a layering technology, stacking up anodes, separating films, and cathodes like a sandwich, which makes it difficult to reduce their thickness. In addition, friction arises between layers, making the batteries impossible to bend. The coating films of electrodes easily come off, which contributes to the batteries’ poor performance.
The research team abandoned the existing production technology. Instead, they removed the separating films, layered the cathodes and anodes collinearly on a plane, and created a partition between electrodes to eliminate potential problems, such as short circuits and voltage dips, commonly present in lithium ion batteries.
After more than five thousand consecutive flexing experiments, the research team confirmed the possibility of a more flexible electrode structure while maintaining the battery performance comparable to the level of current lithium ion batteries.
Flexible batteries can be applied to integrated smart cards, cosmetic and medical patches, and skin adhesive sensors that can control a computer with voice commands or gesture as seen in the movie “Iron Man.”
Moreover, the team has successfully developed wireless-charging technology using electromagnetic induction and solar batteries.
They are currently developing a mass production process to combine this planar battery technology and printing, to ultimately create a new paradigm to print semiconductors and batteries using 3D printers.
Professor Choi said, “This new technology will contribute to diversifying patch functions as it is applicable to power various adhesive medical patches.”
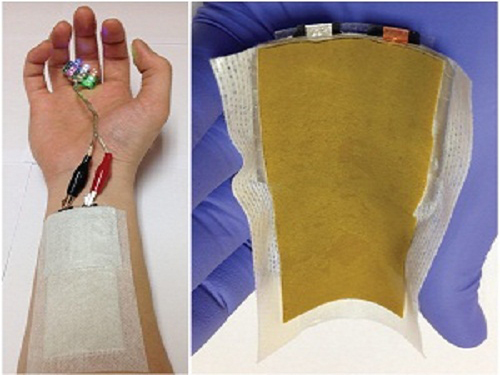
Picture 1: Medical patch (left) and flexible secondary battery (right)
Picture 2: Diagram of flexible battery
Picture 3: Smart card embedding flexible battery
2015.03.24 View 12879
KAIST Develops a Credit-Card-Thick Flexible Lithium Ion Battery
Since the battery can be charged wirelessly, useful applications are expected including medical patches and smart cards.
Professor Jang Wook Choi at KAIST’s Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) and Dr. Jae Yong Song at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science jointly led research to invent a flexible lithium ion battery that is thinner than a credit card and can be charged wirelessly.
Their research findings were published online in Nano Letters on March 6, 2015. Lithium ion batteries are widely used today in various electronics including mobile devices and electronic cars. Researchers said that their work could help accelerate the development of flexible and wearable electronics.
Conventional lithium ion batteries are manufactured based on a layering technology, stacking up anodes, separating films, and cathodes like a sandwich, which makes it difficult to reduce their thickness. In addition, friction arises between layers, making the batteries impossible to bend. The coating films of electrodes easily come off, which contributes to the batteries’ poor performance.
The research team abandoned the existing production technology. Instead, they removed the separating films, layered the cathodes and anodes collinearly on a plane, and created a partition between electrodes to eliminate potential problems, such as short circuits and voltage dips, commonly present in lithium ion batteries.
After more than five thousand consecutive flexing experiments, the research team confirmed the possibility of a more flexible electrode structure while maintaining the battery performance comparable to the level of current lithium ion batteries.
Flexible batteries can be applied to integrated smart cards, cosmetic and medical patches, and skin adhesive sensors that can control a computer with voice commands or gesture as seen in the movie “Iron Man.”
Moreover, the team has successfully developed wireless-charging technology using electromagnetic induction and solar batteries.
They are currently developing a mass production process to combine this planar battery technology and printing, to ultimately create a new paradigm to print semiconductors and batteries using 3D printers.
Professor Choi said, “This new technology will contribute to diversifying patch functions as it is applicable to power various adhesive medical patches.”
Picture 1: Medical patch (left) and flexible secondary battery (right)
Picture 2: Diagram of flexible battery
Picture 3: Smart card embedding flexible battery
2015.03.24 View 12879 -
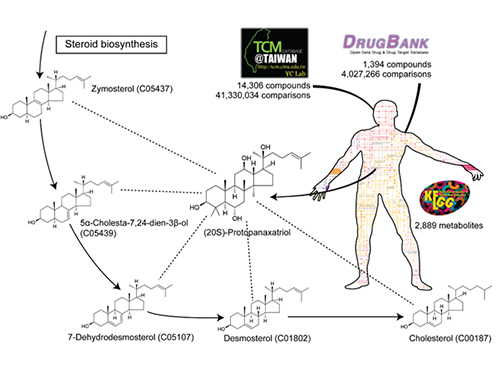 System Approach Using Metabolite Structural Similarity Toward TOM Suggested
A Korean research team at KAIST suggests that a system approach using metabolite structural similarity helps to elucidate the mechanisms of action of traditional oriental medicine.
Traditional oriental medicine (TOM) has been practiced in Asian countries for centuries, and is gaining increasing popularity around the world. Despite its efficacy in various symptoms, TOM has been practiced without precise knowledge of its mechanisms of action. Use of TOM largely comes from empirical knowledge practiced over a long period of time. The fact that some of the compounds found in TOM have led to successful modern drugs such as artemisinin for malaria and taxol (Paclitaxel) for cancer has spurred modernization of TOM.
A research team led by Sang-Yup Lee at KAIST has focused on structural similarities between compounds in TOM and human metabolites to help explain TOM’s mechanisms of action. This systems approach using structural similarities assumes that compounds which are structurally similar to metabolites could affect relevant metabolic pathways and reactions by biosynthesizing structurally similar metabolites.
Structural similarity analysis has helped to identify mechanisms of action of TOM. This is described in a recent study entitled “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine,” published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 6, 2015. In this study, the research team conducted structural comparisons of all the structurally known compounds in TOM and human metabolites on a large-scale. As a control, structures of all available approved drugs were also compared against human metabolites. This structural analysis provides two important results. First, the identification of metabolites structurally similar to TOM compounds helped to narrow down the candidate target pathways and reactions for the effects from TOM compounds. Second, it suggested that a greater fraction of all the structurally known TOM compounds appeared to be more similar to human metabolites than the approved drugs. This second finding indicates that TOM has a great potential to interact with diverse metabolic pathways with strong efficacy. This finding, in fact, shows that TOM compounds might be advantageous for the multitargeting required to cure complex diseases. “Once we have narrowed down candidate target pathways and reactions using this structural similarity approach, additional in silico tools will be necessary to characterize the mechanisms of action of many TOM compounds at a molecular level,” said Hyun Uk Kim, a research professor at KAIST.
TOM’s multicomponent, multitarget approach wherein multiple components show synergistic effects to treat symptoms is highly distinctive. The researchers investigated previously observed effects recorded since 2000 of a set of TOM compounds with known mechanisms of action. TOM compounds’ synergistic combinations largely consist of a major compound providing the intended efficacy to the target site and supporting compounds which maximize the efficacy of the major compound. In fact, such combination designs appear to mirror the Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa design principle of TOM.
That principle, Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa (君臣佐使 or Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi in Chinese) literally means “king-minister-assistant-ambassador.” In ancient East Asian medicine, treating human diseases and taking good care of the human body are analogous to the politics of governing a nation. Just as good governance requires that a king be supported by ministers, assistants and/or ambassadors, treating diseases or good care of the body required the combined use of herbal medicines designed based on the concept of Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa. Here, the Kun (king or the major component) indicates the major medicine (or herb) conveying the major drug efficacy, and is supported by three different types of medicines: the Shin (minister or the complementary component) for enhancing and/or complementing the efficacy of the Kun, Choa (assistant or the neutralizing component) for reducing any side effects caused by the Kun and reducing the minor symptoms accompanying major symptom, and Sa (ambassador or the delivery/retaining component) which facilitated the delivery of the Kun to the target site, and retaining the Kun for prolonged availability in the cells.
The synergistic combinations of TOM compounds reported in the literature showed four different types of synergisms: complementary action (similar to Kun-Shin), neutralizing action (similar to Kun-Choa), facilitating action or pharmacokinetic potentiation (both similar to Kun-Choa or Kun-Sa). Additional structural analyses for these compounds with synergism show that they appeared to affect metabolism of amino acids, co-factors and vitamins as major targets.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarks, “This study lays a foundation for the integration of traditional oriental medicine with modern drug discovery and development. The systems approach taken in this analysis will be used to elucidate mechanisms of action of unknown TOM compounds which will then be subjected to rigorous validation through clinical and in silico experiments.”
Sources: Kim, H.U. et al. “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine.” Nature Biotechnology. 33: 264-268 (2015).
This work was supported by the Bio-Synergy Research Project (2012M3A9C4048759) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
The picture below presents the structural similarity analysis of comparing compounds in traditional oriental medicine and those in all available approved drugs against the structures of human metabolites.
2015.03.09 View 10901
System Approach Using Metabolite Structural Similarity Toward TOM Suggested
A Korean research team at KAIST suggests that a system approach using metabolite structural similarity helps to elucidate the mechanisms of action of traditional oriental medicine.
Traditional oriental medicine (TOM) has been practiced in Asian countries for centuries, and is gaining increasing popularity around the world. Despite its efficacy in various symptoms, TOM has been practiced without precise knowledge of its mechanisms of action. Use of TOM largely comes from empirical knowledge practiced over a long period of time. The fact that some of the compounds found in TOM have led to successful modern drugs such as artemisinin for malaria and taxol (Paclitaxel) for cancer has spurred modernization of TOM.
A research team led by Sang-Yup Lee at KAIST has focused on structural similarities between compounds in TOM and human metabolites to help explain TOM’s mechanisms of action. This systems approach using structural similarities assumes that compounds which are structurally similar to metabolites could affect relevant metabolic pathways and reactions by biosynthesizing structurally similar metabolites.
Structural similarity analysis has helped to identify mechanisms of action of TOM. This is described in a recent study entitled “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine,” published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 6, 2015. In this study, the research team conducted structural comparisons of all the structurally known compounds in TOM and human metabolites on a large-scale. As a control, structures of all available approved drugs were also compared against human metabolites. This structural analysis provides two important results. First, the identification of metabolites structurally similar to TOM compounds helped to narrow down the candidate target pathways and reactions for the effects from TOM compounds. Second, it suggested that a greater fraction of all the structurally known TOM compounds appeared to be more similar to human metabolites than the approved drugs. This second finding indicates that TOM has a great potential to interact with diverse metabolic pathways with strong efficacy. This finding, in fact, shows that TOM compounds might be advantageous for the multitargeting required to cure complex diseases. “Once we have narrowed down candidate target pathways and reactions using this structural similarity approach, additional in silico tools will be necessary to characterize the mechanisms of action of many TOM compounds at a molecular level,” said Hyun Uk Kim, a research professor at KAIST.
TOM’s multicomponent, multitarget approach wherein multiple components show synergistic effects to treat symptoms is highly distinctive. The researchers investigated previously observed effects recorded since 2000 of a set of TOM compounds with known mechanisms of action. TOM compounds’ synergistic combinations largely consist of a major compound providing the intended efficacy to the target site and supporting compounds which maximize the efficacy of the major compound. In fact, such combination designs appear to mirror the Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa design principle of TOM.
That principle, Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa (君臣佐使 or Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi in Chinese) literally means “king-minister-assistant-ambassador.” In ancient East Asian medicine, treating human diseases and taking good care of the human body are analogous to the politics of governing a nation. Just as good governance requires that a king be supported by ministers, assistants and/or ambassadors, treating diseases or good care of the body required the combined use of herbal medicines designed based on the concept of Kun-Shin-Choa-Sa. Here, the Kun (king or the major component) indicates the major medicine (or herb) conveying the major drug efficacy, and is supported by three different types of medicines: the Shin (minister or the complementary component) for enhancing and/or complementing the efficacy of the Kun, Choa (assistant or the neutralizing component) for reducing any side effects caused by the Kun and reducing the minor symptoms accompanying major symptom, and Sa (ambassador or the delivery/retaining component) which facilitated the delivery of the Kun to the target site, and retaining the Kun for prolonged availability in the cells.
The synergistic combinations of TOM compounds reported in the literature showed four different types of synergisms: complementary action (similar to Kun-Shin), neutralizing action (similar to Kun-Choa), facilitating action or pharmacokinetic potentiation (both similar to Kun-Choa or Kun-Sa). Additional structural analyses for these compounds with synergism show that they appeared to affect metabolism of amino acids, co-factors and vitamins as major targets.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarks, “This study lays a foundation for the integration of traditional oriental medicine with modern drug discovery and development. The systems approach taken in this analysis will be used to elucidate mechanisms of action of unknown TOM compounds which will then be subjected to rigorous validation through clinical and in silico experiments.”
Sources: Kim, H.U. et al. “A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine.” Nature Biotechnology. 33: 264-268 (2015).
This work was supported by the Bio-Synergy Research Project (2012M3A9C4048759) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
The picture below presents the structural similarity analysis of comparing compounds in traditional oriental medicine and those in all available approved drugs against the structures of human metabolites.
2015.03.09 View 10901 -
 President Kang to Present at the World Economic Forum
President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST will attend the World Economic Forum (WEF) as a member of the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to represent KAIST. GULF is attended by the world leaders of education and research. Its members represent 26 universities drawn from around the world including Harvard University. KAIST is the only Korean university to be invited.
WEF will be held in Davos, Switzerland, for four days, starting on 21 January 2015. He will discuss the future of higher education, the issues and solutions of science and society at GULF.
By attending GULF, KAIST expects to strengthen its network with top universities around the world and raise KAIST’s profile on an international basis. President Kang said, “The invitation for KAIST to attend the GULF is an evidence of its raised global status.” He continued, “I will show the innovative and challenging achievements KAIST has made to the leaders of the world.”
The theme of the 2015 World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2015 is “The New Global Context” to discuss the integration of economic growth and society, employment and work force, environment and resource scarcity, the future of the Internet, and international crime and anti-corruption.
The World Economic Forum was established in 1971 by Klaus Schwab who is also its Executive Chairman. More than 2,500 people including German Chancellor Angela Merkel, French President François Hollande, Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, Google President Eric Schmidt, and Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella will attend this year's forum.
2015.01.22 View 9018
President Kang to Present at the World Economic Forum
President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST will attend the World Economic Forum (WEF) as a member of the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to represent KAIST. GULF is attended by the world leaders of education and research. Its members represent 26 universities drawn from around the world including Harvard University. KAIST is the only Korean university to be invited.
WEF will be held in Davos, Switzerland, for four days, starting on 21 January 2015. He will discuss the future of higher education, the issues and solutions of science and society at GULF.
By attending GULF, KAIST expects to strengthen its network with top universities around the world and raise KAIST’s profile on an international basis. President Kang said, “The invitation for KAIST to attend the GULF is an evidence of its raised global status.” He continued, “I will show the innovative and challenging achievements KAIST has made to the leaders of the world.”
The theme of the 2015 World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2015 is “The New Global Context” to discuss the integration of economic growth and society, employment and work force, environment and resource scarcity, the future of the Internet, and international crime and anti-corruption.
The World Economic Forum was established in 1971 by Klaus Schwab who is also its Executive Chairman. More than 2,500 people including German Chancellor Angela Merkel, French President François Hollande, Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, Google President Eric Schmidt, and Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella will attend this year's forum.
2015.01.22 View 9018 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 12203
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 12203 -
 KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 10298
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 10298