RNA
-
 Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10368
Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10368 -
 International Students Start a New Semester at KAIST
(International students during a campus tour)
The 2017 fall semester began on August 28 and new and returning students are filling the campus. Our international students are one of the reasons the campus is becoming more dynamic and energetic.
It was easy to see groups of smiling international students walking around the campus. Every semester, KAIST welcomes hundreds of students from around the world to give them the opportunity to study at a world-leading university in science and technology.
This semester, approximately 150 students in degree-seeking programs and 220 exchange students from a total of 74 countries, including Germany, the United States, and France entered KAIST.
(Frederik Hansen, a student from DTU)
Frederik Hansen is an exchange student who came to KAIST this semester from Copenhagen, Denmark. He completed the undergraduate program at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) and is now pursuing a master’s degree.
He decided to join KAIST because he felt the university is up-to-date with subjects in his field of interest.
Frederik, who majored in mechanical engineering, looks forward taking classes related to robotics and solid mechanics. Noting that it’s his first time visiting Asia, he hopes to experience and learn about Korean culture.
In an effort to help foreign students’ soft landing in KAIST, the International Office held a series of orientation programs over three days. The buddy program provides international freshmen with an opportunity to make Korean friends for a more successful life at KAIST, while giving domestic students a chance to learn about different cultures and perhaps build on the global capacity required for becoming a global leader. Information sessions also provided educational information that can support international students living in KAIST. Finally, the counseling program gives information about the KAIST counseling center and ISSS (International Scholar and Student Service). It provides a psychometric test service to those who wish to take it.
If you are interested in pursuing academic programs at KAIST, please visit the International Office via http://io.kaist.ac.kr/index.do .
2017.08.30 View 7315
International Students Start a New Semester at KAIST
(International students during a campus tour)
The 2017 fall semester began on August 28 and new and returning students are filling the campus. Our international students are one of the reasons the campus is becoming more dynamic and energetic.
It was easy to see groups of smiling international students walking around the campus. Every semester, KAIST welcomes hundreds of students from around the world to give them the opportunity to study at a world-leading university in science and technology.
This semester, approximately 150 students in degree-seeking programs and 220 exchange students from a total of 74 countries, including Germany, the United States, and France entered KAIST.
(Frederik Hansen, a student from DTU)
Frederik Hansen is an exchange student who came to KAIST this semester from Copenhagen, Denmark. He completed the undergraduate program at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) and is now pursuing a master’s degree.
He decided to join KAIST because he felt the university is up-to-date with subjects in his field of interest.
Frederik, who majored in mechanical engineering, looks forward taking classes related to robotics and solid mechanics. Noting that it’s his first time visiting Asia, he hopes to experience and learn about Korean culture.
In an effort to help foreign students’ soft landing in KAIST, the International Office held a series of orientation programs over three days. The buddy program provides international freshmen with an opportunity to make Korean friends for a more successful life at KAIST, while giving domestic students a chance to learn about different cultures and perhaps build on the global capacity required for becoming a global leader. Information sessions also provided educational information that can support international students living in KAIST. Finally, the counseling program gives information about the KAIST counseling center and ISSS (International Scholar and Student Service). It provides a psychometric test service to those who wish to take it.
If you are interested in pursuing academic programs at KAIST, please visit the International Office via http://io.kaist.ac.kr/index.do .
2017.08.30 View 7315 -
 Students from Science Academies Shed a Light on KAIST
Recent KAIST statistics show that graduates from science academies distinguish themselves not only by their academic performance at KAIST but also in various professional careers after graduation.
Every year, approximately 20% of newly-enrolled students of KAIST are from science academies. In the case of the class of 2017, 170 students from science academies accounted for 22% of the newly-enrolled students. Moreover, they are forming a top-tier student group on campus. As shown in the table below, the ratio of students graduating early for either enrolling in graduate programs or landing a job indicates their excellent performance at KAIST.
There are eight science academies in Korea: Korea Science Academy of KAIST located in Busan, Seoul Science High School, Gyeonggi Science High School, Gwangju Science High School, Daejeon Science High School, Sejong Academy of Science and Arts, and Incheon Arts and Sciences Academy.
Recently, KAIST analyzed 532 university graduates from the class of 2012. It was found that 23 out of 63 graduates with the alma mater of science academies finished their degree early; as a result, the early graduation ratio of the class of 2012 stood at 36.5%. This percentage was significantly higher than that of students from other high schools.
Among the notable graduates, there was a student who made headlines with donation of 30 million KRW to KAIST. His donation was the largest donation from an enrolled student on record. His story goes back when Android smartphones were about to be distributed. Seung-Gyu Oh, then a student in the School of Electrical Engineering felt that existing subway apps were inconvenient, so he invented his own subway app that navigated the nearest subway lines in 2015. His app hit the market and ranked second in the subway app category. It had approximately five million users, which led to it generating advertising revenue. After the successful launch of the app, Oh accepted the takeover offered by Daum Kakao. He then donated 30 million KRW to his alma mater. “Since high school, I’ve always been thinking that I have received many benefits from my country and felt heavily responsible for it,” the alumnus of Korea Science of Academy and KAIST said. “I decided to make a donation to my alma mater, KAIST because I wanted to return what I had received from my country.” After graduation, Oh is now working for the web firm, Daum Kakao.
In May 24, 2017, the 41st International Collegiate Programming Contest, hosted by Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and sponsored by IBM, was held in Rapid City, South Dakota in the US. It is a prestigious contest that has been held annually since 1977. College students from around the world participate in this contest; and in 2017, a total of 50,000 students from 2,900 universities in 104 countries participated in regional competitions, and approximately 400 students made it to the final round, entering into a fierce competition. KAIST students also participated in this contest. The team was comprised of Ji-Hoon Ko, Jong-Won Lee, and Han-Pil Kang from the School of Computing. They are also alumni of Gyeonggi Science High School. They received the ‘First Problem Solver’ award and a bronze medal which came with a 3,000 USD cash prize.
Sung-Jin Oh, who also graduated from Korea Science Academy of KAIST, is a research professor at the Korea Institute of Advanced Study (KIAS). He is the youngest recipient of the ‘Young Scientist Award’, which he received by proving a hypothesis from Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity mathematically at the age of 27. After graduating from KAIST, Oh earned his master’s and doctorate degrees from Princeton University, completed his post-doctoral fellow at UC Berkeley, and is now immersing himself in research at KIAS.
Heui-Kwang Noh from the Department of Chemistry and Kang-Min Ahn from the School of Computing, who were selected to receive the presidential scholarship for science in 2014, both graduated from Gyeonggi Science High School. Noh was recognized for his outstanding academic capacity and was also chosen for the ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’ in 2015. The ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’, established in 1992 by the GE Foundation, aims at fostering talented students. This program is for post-secondary students who have both creativity and leadership. It selects five outstanding students and provides 3 million KRW per annum for a maximum of three years.
The grantees of this program have become influential people in various fields, including professors, executives, staff members of national/international firms, and researchers. And they are making a huge contribution to the development of engineering and science. Noh continues doing various activities, including the completion of his internship at ‘Harvard-MIT Biomedical Optics’ and the publication of a paper (3rd author) for the ACS Omega of American Chemical Society (ACS).
Ahn, a member of the Young Engineers Honor Society (YEHS) of the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, had an interest in startup businesses. In 2015, he founded DataStorm, a firm specializing in developing data solution, and merged with a cloud back-office, Jobis & Villains, in 2016. Ahn is continuing his business activities and this year he founded, and is successfully running, cocKorea.
“KAIST students whose alma mater are science academies form a top-tier group on campus and produce excellent performance,” said Associate Vice President for Admissions, Hayong Shin. “KAIST is making every effort to assist these students so that they can perform to the best of their ability.”
(Clockwise from top left: Seung-Gyu Oh, Sung-Jin Oh, Heui-Kwang Noh and Kang-Min Ahn)
2017.08.09 View 10407
Students from Science Academies Shed a Light on KAIST
Recent KAIST statistics show that graduates from science academies distinguish themselves not only by their academic performance at KAIST but also in various professional careers after graduation.
Every year, approximately 20% of newly-enrolled students of KAIST are from science academies. In the case of the class of 2017, 170 students from science academies accounted for 22% of the newly-enrolled students. Moreover, they are forming a top-tier student group on campus. As shown in the table below, the ratio of students graduating early for either enrolling in graduate programs or landing a job indicates their excellent performance at KAIST.
There are eight science academies in Korea: Korea Science Academy of KAIST located in Busan, Seoul Science High School, Gyeonggi Science High School, Gwangju Science High School, Daejeon Science High School, Sejong Academy of Science and Arts, and Incheon Arts and Sciences Academy.
Recently, KAIST analyzed 532 university graduates from the class of 2012. It was found that 23 out of 63 graduates with the alma mater of science academies finished their degree early; as a result, the early graduation ratio of the class of 2012 stood at 36.5%. This percentage was significantly higher than that of students from other high schools.
Among the notable graduates, there was a student who made headlines with donation of 30 million KRW to KAIST. His donation was the largest donation from an enrolled student on record. His story goes back when Android smartphones were about to be distributed. Seung-Gyu Oh, then a student in the School of Electrical Engineering felt that existing subway apps were inconvenient, so he invented his own subway app that navigated the nearest subway lines in 2015. His app hit the market and ranked second in the subway app category. It had approximately five million users, which led to it generating advertising revenue. After the successful launch of the app, Oh accepted the takeover offered by Daum Kakao. He then donated 30 million KRW to his alma mater. “Since high school, I’ve always been thinking that I have received many benefits from my country and felt heavily responsible for it,” the alumnus of Korea Science of Academy and KAIST said. “I decided to make a donation to my alma mater, KAIST because I wanted to return what I had received from my country.” After graduation, Oh is now working for the web firm, Daum Kakao.
In May 24, 2017, the 41st International Collegiate Programming Contest, hosted by Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and sponsored by IBM, was held in Rapid City, South Dakota in the US. It is a prestigious contest that has been held annually since 1977. College students from around the world participate in this contest; and in 2017, a total of 50,000 students from 2,900 universities in 104 countries participated in regional competitions, and approximately 400 students made it to the final round, entering into a fierce competition. KAIST students also participated in this contest. The team was comprised of Ji-Hoon Ko, Jong-Won Lee, and Han-Pil Kang from the School of Computing. They are also alumni of Gyeonggi Science High School. They received the ‘First Problem Solver’ award and a bronze medal which came with a 3,000 USD cash prize.
Sung-Jin Oh, who also graduated from Korea Science Academy of KAIST, is a research professor at the Korea Institute of Advanced Study (KIAS). He is the youngest recipient of the ‘Young Scientist Award’, which he received by proving a hypothesis from Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity mathematically at the age of 27. After graduating from KAIST, Oh earned his master’s and doctorate degrees from Princeton University, completed his post-doctoral fellow at UC Berkeley, and is now immersing himself in research at KIAS.
Heui-Kwang Noh from the Department of Chemistry and Kang-Min Ahn from the School of Computing, who were selected to receive the presidential scholarship for science in 2014, both graduated from Gyeonggi Science High School. Noh was recognized for his outstanding academic capacity and was also chosen for the ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’ in 2015. The ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’, established in 1992 by the GE Foundation, aims at fostering talented students. This program is for post-secondary students who have both creativity and leadership. It selects five outstanding students and provides 3 million KRW per annum for a maximum of three years.
The grantees of this program have become influential people in various fields, including professors, executives, staff members of national/international firms, and researchers. And they are making a huge contribution to the development of engineering and science. Noh continues doing various activities, including the completion of his internship at ‘Harvard-MIT Biomedical Optics’ and the publication of a paper (3rd author) for the ACS Omega of American Chemical Society (ACS).
Ahn, a member of the Young Engineers Honor Society (YEHS) of the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, had an interest in startup businesses. In 2015, he founded DataStorm, a firm specializing in developing data solution, and merged with a cloud back-office, Jobis & Villains, in 2016. Ahn is continuing his business activities and this year he founded, and is successfully running, cocKorea.
“KAIST students whose alma mater are science academies form a top-tier group on campus and produce excellent performance,” said Associate Vice President for Admissions, Hayong Shin. “KAIST is making every effort to assist these students so that they can perform to the best of their ability.”
(Clockwise from top left: Seung-Gyu Oh, Sung-Jin Oh, Heui-Kwang Noh and Kang-Min Ahn)
2017.08.09 View 10407 -
 KAIST Team Wins Bronze Medal at Int'l Programming Contest
A KAIST Team consisting of undergraduate students from the School of Computing and Department of Mathematical Science received a bronze medal and First Problem Solver award at an international undergraduate programming competition, The Association for Computing Machinery-International Collegiate Programming Contest (ACM-ICPC) World Finals.
The 41st ACM-ICPC hosted by ACM and funded by IBM was held in South Dakota in the US on May 25. The competition, first held in 1977, is aimed at undergraduate students from around the world. A total of 50,000 students from 2900 universities and 103 countries participated in the regional competition and 400 students competed in the finals.
The competition required teams of three to solve 12 problems. The KAIST team was coached by Emeritus Professor Sung-Yong Shin and Professor Taisook Han. The student contestants were Jihoon Ko and Hanpil Kang from the School of Computing and Jongwoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Science. The team finished ranked 9th, receiving a bronze medal and a $3000 prize. Additionally, the team was the first to solve all the problems and received the First Problem Solver award. Detailed score information can be found on. https://icpc.baylor.edu/scoreboard/
(Photo caption: Professor Taisook Han and his students)
2017.06.12 View 11352
KAIST Team Wins Bronze Medal at Int'l Programming Contest
A KAIST Team consisting of undergraduate students from the School of Computing and Department of Mathematical Science received a bronze medal and First Problem Solver award at an international undergraduate programming competition, The Association for Computing Machinery-International Collegiate Programming Contest (ACM-ICPC) World Finals.
The 41st ACM-ICPC hosted by ACM and funded by IBM was held in South Dakota in the US on May 25. The competition, first held in 1977, is aimed at undergraduate students from around the world. A total of 50,000 students from 2900 universities and 103 countries participated in the regional competition and 400 students competed in the finals.
The competition required teams of three to solve 12 problems. The KAIST team was coached by Emeritus Professor Sung-Yong Shin and Professor Taisook Han. The student contestants were Jihoon Ko and Hanpil Kang from the School of Computing and Jongwoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Science. The team finished ranked 9th, receiving a bronze medal and a $3000 prize. Additionally, the team was the first to solve all the problems and received the First Problem Solver award. Detailed score information can be found on. https://icpc.baylor.edu/scoreboard/
(Photo caption: Professor Taisook Han and his students)
2017.06.12 View 11352 -
 The 2017 International Food Festival
The savory smell of exotic dishes filled the main plaza of the KAIST campus on May 26. Exotic music reverberated throughout the campus. The KAIST community took a break together on a breezy early summer Friday afternoon sharing food with their friends and family. KAIST international student body, KISA (KAIST International Students Association), installed white food tents and prepared their country’s favorite dishes at their 13th annual International Food Festival.
The festival was co-organized with Chungnam National University and the University of Science & Technology (UST). At the festival, students from 18 nations cooked about 60 dishes and sold them to the public. Foreign students’ performances of traditional dance and music on the stage livened the atmosphere.
KISA President Sanzhar Kerimbek of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering said, “We are so glad to show the diversity of KAIST and its rich culture. This is a big opportunity to get together with neighboring universities, CNU and UST and say thank you for their participation and support." Valentin Porcellini, an exchange students from France in the School of Computing, said, “We are so excited to have people taste our crepes, ratatouille, and other dishes.”
Associate Vice President of the International Office Jay Hyung Lee also said he was glad to see so many people joining this festival. While congratulating the students on the success of the festival, he said the festival will serve as an opportunity to better understand each other by sharing the food and culture.
(Photo caption: Paricipants stop by the Indonesian booth to purchase the food at the International Food Festival on May 26.)
2017.05.29 View 6679
The 2017 International Food Festival
The savory smell of exotic dishes filled the main plaza of the KAIST campus on May 26. Exotic music reverberated throughout the campus. The KAIST community took a break together on a breezy early summer Friday afternoon sharing food with their friends and family. KAIST international student body, KISA (KAIST International Students Association), installed white food tents and prepared their country’s favorite dishes at their 13th annual International Food Festival.
The festival was co-organized with Chungnam National University and the University of Science & Technology (UST). At the festival, students from 18 nations cooked about 60 dishes and sold them to the public. Foreign students’ performances of traditional dance and music on the stage livened the atmosphere.
KISA President Sanzhar Kerimbek of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering said, “We are so glad to show the diversity of KAIST and its rich culture. This is a big opportunity to get together with neighboring universities, CNU and UST and say thank you for their participation and support." Valentin Porcellini, an exchange students from France in the School of Computing, said, “We are so excited to have people taste our crepes, ratatouille, and other dishes.”
Associate Vice President of the International Office Jay Hyung Lee also said he was glad to see so many people joining this festival. While congratulating the students on the success of the festival, he said the festival will serve as an opportunity to better understand each other by sharing the food and culture.
(Photo caption: Paricipants stop by the Indonesian booth to purchase the food at the International Food Festival on May 26.)
2017.05.29 View 6679 -
 Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 10788
Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 10788 -
 Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9682
Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9682 -
 Quantum Dot Film Can Withstand High Temperatures and Humidity
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Doh Chang Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was able to fabricate a siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot film, which exhibits stable emission intensity over one month even at high temperatures and humidity.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on November 29, 2016. The research article is entitled “Quantum Dot/Siloxane Composite Film Exceptionally Stable against Oxidation under Heat and Moisture.” (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b10681)
Quantum dots (QDs), light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for next-generation displays, are tiny particles or nanocrystals of semiconducting materials. Their emission wavelength can easily be adjusted by changing their sizes, which are just a few nanometers. A wide spectrum of their colors can also achieve ultra-high definition displays.
Due to these characteristics, QDs are coated on a film as a polymer resin in dispersed form, or they are spread on an LED light source. They are thus considered to be crucial for next generation displays.
Despite their exceptional optical properties, however, QDs are easily oxidized in a high temperature and high humidity environment, and, as a result, this greatly deteriorates their luminescence quality (quantum efficiency). Therefore, they are encapsulated in an extra thin layer to block oxygen and moisture.
QD displays in the current market have a film inserted to separate them from LEDs, which create heat. The high unit cost of this protective layer, however, increases the overall cost of displays, lowering their price competitiveness in the market.
For a solution, the research team applied the sol-gel condensation reaction of silane precursors with QDs. This technology uses the reactions of chemical substances to synthesize ceramics or glass at a low temperature.
The team applied QDs in a heat resistant siloxane polymer by employing this technology. The siloxane resin acted as a cup holding the QDs and also blocked heat and moisture. Thus, their performance can be maintained without an extra protective film.
QDs are evenly dispersed into the resin from a chemical process to fabricate a QD embedded film and retained the high quality luminescence not only at a high temperature of 85°C and in a high humidity of 85%, but also in a high acid and high base environment. Remarkably though, the luminescence actually increased in the high humidity environment.
If this technology is used, the overall price of displays will decrease by producing a stable QD film without an extra protective barrier. In the future, the QD film can be directly applied to a blue LED light source. As a result, it will be possible to develop a QD display that can reduce the amount of QDs needed and improve its performance.
Professor Bae said, “We have proposed a way to make quantum dots overcome their limitations and have wide applications as they are being developed for next-generation displays. Our technology will make significant contributions to the display industry in the country.”
He also added, “In the future, we plan to cooperate with companies both in and out of the country to improve the performance of quantum dots and concentrate on their commercialization.”
The research team is currently applying for related patents both in and out of the country. The team is also plan ning to transfer the patents to Sol Ip Technology Inc., a company founded at KAIST, to start the commercialization.
Picture 1:
Siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot (QD) films showing performance stability in boiling water
Picture 2 and 3:
So-gel condensation reaction in silane precursors between Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTS) and diphenylsilanediol (DPSD). The inset shows photographs of a QD-oligosiloxane resin under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
Free radical addition reactions among carbon double bonds of methacryl functional groups and oleic acids. The inset shows photographs of a QD-silox film under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
2017.02.24 View 11057
Quantum Dot Film Can Withstand High Temperatures and Humidity
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Doh Chang Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was able to fabricate a siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot film, which exhibits stable emission intensity over one month even at high temperatures and humidity.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on November 29, 2016. The research article is entitled “Quantum Dot/Siloxane Composite Film Exceptionally Stable against Oxidation under Heat and Moisture.” (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b10681)
Quantum dots (QDs), light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for next-generation displays, are tiny particles or nanocrystals of semiconducting materials. Their emission wavelength can easily be adjusted by changing their sizes, which are just a few nanometers. A wide spectrum of their colors can also achieve ultra-high definition displays.
Due to these characteristics, QDs are coated on a film as a polymer resin in dispersed form, or they are spread on an LED light source. They are thus considered to be crucial for next generation displays.
Despite their exceptional optical properties, however, QDs are easily oxidized in a high temperature and high humidity environment, and, as a result, this greatly deteriorates their luminescence quality (quantum efficiency). Therefore, they are encapsulated in an extra thin layer to block oxygen and moisture.
QD displays in the current market have a film inserted to separate them from LEDs, which create heat. The high unit cost of this protective layer, however, increases the overall cost of displays, lowering their price competitiveness in the market.
For a solution, the research team applied the sol-gel condensation reaction of silane precursors with QDs. This technology uses the reactions of chemical substances to synthesize ceramics or glass at a low temperature.
The team applied QDs in a heat resistant siloxane polymer by employing this technology. The siloxane resin acted as a cup holding the QDs and also blocked heat and moisture. Thus, their performance can be maintained without an extra protective film.
QDs are evenly dispersed into the resin from a chemical process to fabricate a QD embedded film and retained the high quality luminescence not only at a high temperature of 85°C and in a high humidity of 85%, but also in a high acid and high base environment. Remarkably though, the luminescence actually increased in the high humidity environment.
If this technology is used, the overall price of displays will decrease by producing a stable QD film without an extra protective barrier. In the future, the QD film can be directly applied to a blue LED light source. As a result, it will be possible to develop a QD display that can reduce the amount of QDs needed and improve its performance.
Professor Bae said, “We have proposed a way to make quantum dots overcome their limitations and have wide applications as they are being developed for next-generation displays. Our technology will make significant contributions to the display industry in the country.”
He also added, “In the future, we plan to cooperate with companies both in and out of the country to improve the performance of quantum dots and concentrate on their commercialization.”
The research team is currently applying for related patents both in and out of the country. The team is also plan ning to transfer the patents to Sol Ip Technology Inc., a company founded at KAIST, to start the commercialization.
Picture 1:
Siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot (QD) films showing performance stability in boiling water
Picture 2 and 3:
So-gel condensation reaction in silane precursors between Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTS) and diphenylsilanediol (DPSD). The inset shows photographs of a QD-oligosiloxane resin under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
Free radical addition reactions among carbon double bonds of methacryl functional groups and oleic acids. The inset shows photographs of a QD-silox film under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
2017.02.24 View 11057 -
 Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
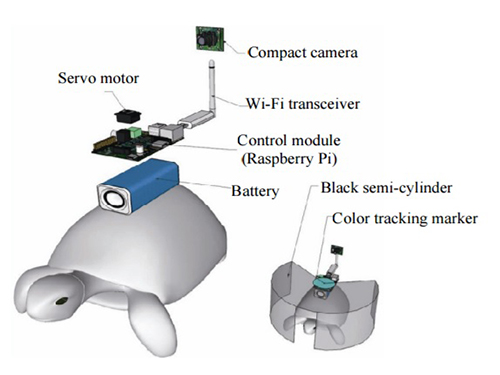
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 16171
Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 16171 -
 Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 9671
Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 9671 -
 Professor Ih Reappointed as Vice President of the ICA
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been re-elected as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA). His second term of office is from October 16, 2016 to September 30, 2019.
Professor Ih, the first Korean who was selected to a senior position on the ICA management board, took over his current post in 2015 when the vice president at the time passed away in the middle of his term.
During his stint, Professor Ih played a key role in planning the ICA’s triennial gathering, the International Congress on Acoustics, in Gyeongju, Korea, scheduled for October 24-28, 2022. He will also serve as the general chair for the conference.
The International Congress on Acoustics is the largest professional meeting in the field of acoustics. It provides a venue to meet, discuss, and exchange ideas covering all aspects of acoustics including an extensive technical exhibition that highlights the latest advances in acoustical products such as materials, systems, and equipment.
Acoustics has grown to become an important element in the Information Age in the areas of automation, machine learning, and virtual reality. Hosting the Congress will support Korea’s goal to lead acoustic research and development on the global stage.
Professor Ih said, “Serving international academic organizations offers great opportunities to learn global trends and to collaborate with various research institutions, universities, and industries worldwide. I hope my service will inspire many young Korean researchers to pursue their careers in this field.”
Professor Ih is also a member of eight eminent international academic societies such as the Audio Engineering Society, the International Congress on Ultrasonics, and the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering.
The ICA was founded in 1951 as a subcommittee of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP), and it consists of 46 member states and four observer nations. It promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, development, education, and standardization.
2016.12.16 View 8277
Professor Ih Reappointed as Vice President of the ICA
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been re-elected as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA). His second term of office is from October 16, 2016 to September 30, 2019.
Professor Ih, the first Korean who was selected to a senior position on the ICA management board, took over his current post in 2015 when the vice president at the time passed away in the middle of his term.
During his stint, Professor Ih played a key role in planning the ICA’s triennial gathering, the International Congress on Acoustics, in Gyeongju, Korea, scheduled for October 24-28, 2022. He will also serve as the general chair for the conference.
The International Congress on Acoustics is the largest professional meeting in the field of acoustics. It provides a venue to meet, discuss, and exchange ideas covering all aspects of acoustics including an extensive technical exhibition that highlights the latest advances in acoustical products such as materials, systems, and equipment.
Acoustics has grown to become an important element in the Information Age in the areas of automation, machine learning, and virtual reality. Hosting the Congress will support Korea’s goal to lead acoustic research and development on the global stage.
Professor Ih said, “Serving international academic organizations offers great opportunities to learn global trends and to collaborate with various research institutions, universities, and industries worldwide. I hope my service will inspire many young Korean researchers to pursue their careers in this field.”
Professor Ih is also a member of eight eminent international academic societies such as the Audio Engineering Society, the International Congress on Ultrasonics, and the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering.
The ICA was founded in 1951 as a subcommittee of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP), and it consists of 46 member states and four observer nations. It promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, development, education, and standardization.
2016.12.16 View 8277 -
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11402
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11402