Engineering
-
 First Korean Member of OceanObs' Organizing Committee
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering became the first Korean to be elected as an organizing committee member of the international conference OceanObs’19’, specializing in the ocean observing field.
Professor Kim has been actively engaged in advisory panels, technical committees, and working groups for the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES). Through numerous activities, he was recognized for his professionalism and academic achievements, which led him to be appointed as a member of the organizing committee.
The organizing committee is comprised of leading scholars and researchers from 20 countries, and Professor Kim will be the first Korean scientist to participate on the committee.
Since 1999, the conference has been held every decade. Global experts specializing in oceanic observation gather to discuss research directions for the next ten years by monitoring physical, biological, and chemical variables in regional, national, and global oceans and applying marine engineering.
This year, approximately 20 institutes including NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Science Foundation, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the European Space Agency will support funds as well as high-tech equipment to the conference.
This year’s conference theme is the governance of global ocean observing systems such as underwater gliders, unmanned vehicles, remote sensing, and observatories. The conference will hold discussions on monitoring technology and information systems to ensure human safety as well as to develop and preserve food resources. Additionally, participants will explore ways to expand observational infrastructures and carry out multidisciplinary approaches.
There will also be collaborations with the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS) and the Partnership for Observation of the Global Oceans (POGO) to organize ocean observing programs and discuss priorities.
Finally, they will set a long-term plan for solving major scientific issues, such as climate change, ocean acidification, energy, and marine pollution.
Professor Kim said, “Based on the outcomes drawn from the conference, I will carry out research on natural disasters and climate change monitoring by using unmanned observing systems. I will also encourage more multidisciplinary research in this field.”
2019.01.25 View 11601
First Korean Member of OceanObs' Organizing Committee
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering became the first Korean to be elected as an organizing committee member of the international conference OceanObs’19’, specializing in the ocean observing field.
Professor Kim has been actively engaged in advisory panels, technical committees, and working groups for the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES). Through numerous activities, he was recognized for his professionalism and academic achievements, which led him to be appointed as a member of the organizing committee.
The organizing committee is comprised of leading scholars and researchers from 20 countries, and Professor Kim will be the first Korean scientist to participate on the committee.
Since 1999, the conference has been held every decade. Global experts specializing in oceanic observation gather to discuss research directions for the next ten years by monitoring physical, biological, and chemical variables in regional, national, and global oceans and applying marine engineering.
This year, approximately 20 institutes including NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Science Foundation, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the European Space Agency will support funds as well as high-tech equipment to the conference.
This year’s conference theme is the governance of global ocean observing systems such as underwater gliders, unmanned vehicles, remote sensing, and observatories. The conference will hold discussions on monitoring technology and information systems to ensure human safety as well as to develop and preserve food resources. Additionally, participants will explore ways to expand observational infrastructures and carry out multidisciplinary approaches.
There will also be collaborations with the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS) and the Partnership for Observation of the Global Oceans (POGO) to organize ocean observing programs and discuss priorities.
Finally, they will set a long-term plan for solving major scientific issues, such as climate change, ocean acidification, energy, and marine pollution.
Professor Kim said, “Based on the outcomes drawn from the conference, I will carry out research on natural disasters and climate change monitoring by using unmanned observing systems. I will also encourage more multidisciplinary research in this field.”
2019.01.25 View 11601 -
 KAIST Seals the Deal for Kenya KAIST Project
KAIST will participate in Kenya’s strategic economic development plan under the provision of a turnkey-based science and technology education consultancy for the establishment of the Kenya Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (Kenya KAIST).KAIST signed the contract on November 30 with the Konza Technopolis Development Authority to establish Kenya KAIST. Korea Eximbank will offer a 95 million USD loan to the Kenyan government for this project. The project will include the educational and architectural design and construction of Kenya KAIST. The campus will be constructed in the Konza Techno City nearby Nairobi by 2021, with the first batch of 200 graduate students starting classes in 2022. KAIST, in consortium with Samwoo and Sunjin architecture and engineering companies, will take the lead of the three-year project, with the kick-off ceremony planned at the end of next January in Nairobi. The Kenyan government plans to transform Kenya into a middle-income country under Vision 2030 through promoting science, technology, and innovation for national economic growth. Nicknamed Africa’s Silicon Savannah, Konza Techno City is a strategic science and technology hub to realize this vision. To this end, the medium-term plan set a goal to provide specialized research and training in various leading-edge engineering and advanced science fields.In the two-phase evaluation of the consultancy bidding, KAIST won preferred bidder status in the technical proposal evaluation, outbidding three other Korean consortia. Invited to the financial proposal bidding, the KAIST consortium successfully completed month-long contract negotiations with Kenya last week.KAIST will develop academic curricula for six initial departments (Mechanical Engineering, Electrical/Electronic Engineering, ICT Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Agricultural Biotechnology), which will lay the ground work for engineering research and education in Kenya to meet emerging socioeconomic demands. In addition, KAIST will provide the education of basic sciences of math, physics, chemistry, and biology for students.It is also notable that the Kenyan government asked to develop an industry-academy cooperation program in Konza Techno City. It reflects the growing industrial needs of Kenya KAIST, which will be located in the center of the Konza Technopolis. It is anticipated that the technopolis will create 16,675 jobs in the medium term and over 200,000 after completion, positioning Kenya as an ICT hub within the region.KAIST also shares a similar history of establishment with Kenya KAIST, as it will be built with a foreign loan. KAIST, created by the Korean government in 1971 to drive the economic engine through advancement of science and technology with a six-million USD loan from USAID, has now become a donor institution that hands down science and technology education systems including the construction of campuses to underdeveloped countries.The successful case of KAIST has been benchmarked by many countries for years. For instance, KAIST set up the curriculum of the nuclear engineering program at the Khalifa University of Science and Technology in UAE in 2010. In China, Chongqing University of Technology is running its electrical engineering and computer science programs based on the educational systems and curricula offered by KAIST from 2015. In October, KAIST also signed an MOU with the Prince Mohammad Bin Salman College of Cyber Security, AI, and Advanced Technologies in Saudi Arabia to provide the undergraduate program for robotics.Among all these programs benchmarking KAIST, Kenya KAIST clearly stands out, for it is carrying out a turnkey-based project that encompasses every aspect of institution building ranging from educational curriculum development to campus construction and supervision.President Sung-Chul Shin is extremely excited about finalizing the deal, remarking, “It is of great significance that KAIST’s successful development model has carved out a unique path to becoming a global leading university that will benefit other countries. In only a half century, we have transitioned from a receiver to a donor institution, as the country itself has done.”“KAIST will spare no effort for Kenya KAIST to become a successful science and technology university that will play a crucial role in Kenya’s national development. I believe Kenya KAIST will be an exemplary case of an ODA (Official Development Assistance) project based on the development of science and technology to benefit underdeveloped countries,” he added.
2018.12.03 View 10350
KAIST Seals the Deal for Kenya KAIST Project
KAIST will participate in Kenya’s strategic economic development plan under the provision of a turnkey-based science and technology education consultancy for the establishment of the Kenya Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (Kenya KAIST).KAIST signed the contract on November 30 with the Konza Technopolis Development Authority to establish Kenya KAIST. Korea Eximbank will offer a 95 million USD loan to the Kenyan government for this project. The project will include the educational and architectural design and construction of Kenya KAIST. The campus will be constructed in the Konza Techno City nearby Nairobi by 2021, with the first batch of 200 graduate students starting classes in 2022. KAIST, in consortium with Samwoo and Sunjin architecture and engineering companies, will take the lead of the three-year project, with the kick-off ceremony planned at the end of next January in Nairobi. The Kenyan government plans to transform Kenya into a middle-income country under Vision 2030 through promoting science, technology, and innovation for national economic growth. Nicknamed Africa’s Silicon Savannah, Konza Techno City is a strategic science and technology hub to realize this vision. To this end, the medium-term plan set a goal to provide specialized research and training in various leading-edge engineering and advanced science fields.In the two-phase evaluation of the consultancy bidding, KAIST won preferred bidder status in the technical proposal evaluation, outbidding three other Korean consortia. Invited to the financial proposal bidding, the KAIST consortium successfully completed month-long contract negotiations with Kenya last week.KAIST will develop academic curricula for six initial departments (Mechanical Engineering, Electrical/Electronic Engineering, ICT Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Agricultural Biotechnology), which will lay the ground work for engineering research and education in Kenya to meet emerging socioeconomic demands. In addition, KAIST will provide the education of basic sciences of math, physics, chemistry, and biology for students.It is also notable that the Kenyan government asked to develop an industry-academy cooperation program in Konza Techno City. It reflects the growing industrial needs of Kenya KAIST, which will be located in the center of the Konza Technopolis. It is anticipated that the technopolis will create 16,675 jobs in the medium term and over 200,000 after completion, positioning Kenya as an ICT hub within the region.KAIST also shares a similar history of establishment with Kenya KAIST, as it will be built with a foreign loan. KAIST, created by the Korean government in 1971 to drive the economic engine through advancement of science and technology with a six-million USD loan from USAID, has now become a donor institution that hands down science and technology education systems including the construction of campuses to underdeveloped countries.The successful case of KAIST has been benchmarked by many countries for years. For instance, KAIST set up the curriculum of the nuclear engineering program at the Khalifa University of Science and Technology in UAE in 2010. In China, Chongqing University of Technology is running its electrical engineering and computer science programs based on the educational systems and curricula offered by KAIST from 2015. In October, KAIST also signed an MOU with the Prince Mohammad Bin Salman College of Cyber Security, AI, and Advanced Technologies in Saudi Arabia to provide the undergraduate program for robotics.Among all these programs benchmarking KAIST, Kenya KAIST clearly stands out, for it is carrying out a turnkey-based project that encompasses every aspect of institution building ranging from educational curriculum development to campus construction and supervision.President Sung-Chul Shin is extremely excited about finalizing the deal, remarking, “It is of great significance that KAIST’s successful development model has carved out a unique path to becoming a global leading university that will benefit other countries. In only a half century, we have transitioned from a receiver to a donor institution, as the country itself has done.”“KAIST will spare no effort for Kenya KAIST to become a successful science and technology university that will play a crucial role in Kenya’s national development. I believe Kenya KAIST will be an exemplary case of an ODA (Official Development Assistance) project based on the development of science and technology to benefit underdeveloped countries,” he added.
2018.12.03 View 10350 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 7999
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 7999 -
 Visualizing Chemical Reaction on Bimetal Surfaces
Catalysts are the result of many chemists searching to unravel the beauty of molecules and the mystery of chemical reactions. Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, whose research focuses on catalytic chemical reactions, is no exception. His research team recently made breakthroughs in addressing long-standing questions for understanding reaction mechanisms on bimetal catalysts.
During the studies reported in Science Advances, following a publication in Nature Communications this month, Professor Park’s research team identified that the formation of metal–oxide interfaces is the key factor responsible for the synergistic catalytic effect in bimetal catalysts. The team confirmed this fundamental reaction mechanism through in situ imaging of reaction conditions. This is the first visualization of bimetal surfaces under reaction conditions, signifying the role of metal–oxide interfaces in heterogeneous catalysis.
Bimetallic materials have outstanding catalytic performance, which opens a new pathway for controlling electronic structures and binding energy in catalysts. Despite considerable research on various catalytic reaction efficiencies, there are yet unanswered questions on the underlying principles behind the improved performance. Even more, it was very hard to figure out what led to the efficiency because the structure, chemical composition, and oxidation state of bimetallic materials change according to reaction conditions.
Recently, some research groups suggested that oxide–metal interfacial sites formed by the surface segregation of bimetallic nanoparticles might be responsible for the increased catalytic performance. However, they failed to present any definitive evidence illustrating the physical nature or the fundamental role of the oxide–metal interfaces leading to the improved performance.
To specifically address this challenge, the research team carried out in situ observations of structural modulation on platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts under carbon monoxide oxidation conditions with ambient pressure scanning tunneling microscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
The team observed that platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts exhibited a variety of different structures depending on the gas conditions. Under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, the surface exhibited a platinum skin layer on the platinum–nickel alloyed surface, selective nickel segregation followed by the formation of nickel oxide clusters using oxygen gas, and finally the coexistence of nickel oxide clusters on the platinum skin during carbon monoxide oxidation. The research team found that the formation of interfacial platinum–nickel oxide nanostructures is responsible for a highly efficient step in the carbon monoxide oxidation reaction.
These findings illustrate that the enhancement of the catalytic activity on the bimetallic catalyst surface originates from the thermodynamically efficient reaction pathways at the metal–metal oxide interface, which demonstrates a straightforward process for the strong metal–support interaction effect. The formation of these interfacial metal–metal oxide nanostructures increases catalytic activity while providing a thermodynamically efficient reaction pathway by lowering the heat of the reactions on the surface. [J. Kim et al. Adsorbate-driven reactive interfacial Pt-NiO1-x nanostructure formation on the Pt3Ni(111) alloy surface, Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aat3151 ]
Professor Park said that one way to monitor catalysts is to detect hot electrons associated with energy dissipation and conversion processes during surface reactions. His team led the real-time detection of hot electrons generated on bimetallic PtCo nanoparticles during exothermic hydrogen oxidation. The team successfully clarified the origin of the synergistic catalytic activity of PtCo nanoparticles with corresponding chemicurrent values.
By estimating the chemicurrent yield, the research team conclude that the catalytic properties of the bimetallic nanoparticles are strongly governed by the oxide–metal interface, which facilitates hot electron transfer. [H. Lee et al. Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles, Nature Comm, 9, 2235 (2018)].
Professor Park explained, “We feel that the precise measurement of hot electrons on catalysts gives insight into the mechanism for heterogeneous catalysis, which can help with the smart design of highly reactive materials. The control of catalytic activity via electronic engineering of catalysts is a promising prospect that may open the door to the new field of combining catalysis with electronics, called “catalytronics.” He added that the study also establishes a strategy for improving catalytic activity for catalytic reactions in industrial chemical reactors.
Professors Park and Yousung Jung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Graduate School of EEWS conducted this research in collaboration with Professor Bongjin Mun from the Department of Physics at GIST.
Figure 1. Evolution of surface structures of PtNi bimetal surfaces under various ambient conditions.
Figure 2. Formation of Pt-CoO interface leads to the catalytic enhancement of PtCo bimetal catalysts.
2018.07.25 View 10218
Visualizing Chemical Reaction on Bimetal Surfaces
Catalysts are the result of many chemists searching to unravel the beauty of molecules and the mystery of chemical reactions. Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, whose research focuses on catalytic chemical reactions, is no exception. His research team recently made breakthroughs in addressing long-standing questions for understanding reaction mechanisms on bimetal catalysts.
During the studies reported in Science Advances, following a publication in Nature Communications this month, Professor Park’s research team identified that the formation of metal–oxide interfaces is the key factor responsible for the synergistic catalytic effect in bimetal catalysts. The team confirmed this fundamental reaction mechanism through in situ imaging of reaction conditions. This is the first visualization of bimetal surfaces under reaction conditions, signifying the role of metal–oxide interfaces in heterogeneous catalysis.
Bimetallic materials have outstanding catalytic performance, which opens a new pathway for controlling electronic structures and binding energy in catalysts. Despite considerable research on various catalytic reaction efficiencies, there are yet unanswered questions on the underlying principles behind the improved performance. Even more, it was very hard to figure out what led to the efficiency because the structure, chemical composition, and oxidation state of bimetallic materials change according to reaction conditions.
Recently, some research groups suggested that oxide–metal interfacial sites formed by the surface segregation of bimetallic nanoparticles might be responsible for the increased catalytic performance. However, they failed to present any definitive evidence illustrating the physical nature or the fundamental role of the oxide–metal interfaces leading to the improved performance.
To specifically address this challenge, the research team carried out in situ observations of structural modulation on platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts under carbon monoxide oxidation conditions with ambient pressure scanning tunneling microscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
The team observed that platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts exhibited a variety of different structures depending on the gas conditions. Under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, the surface exhibited a platinum skin layer on the platinum–nickel alloyed surface, selective nickel segregation followed by the formation of nickel oxide clusters using oxygen gas, and finally the coexistence of nickel oxide clusters on the platinum skin during carbon monoxide oxidation. The research team found that the formation of interfacial platinum–nickel oxide nanostructures is responsible for a highly efficient step in the carbon monoxide oxidation reaction.
These findings illustrate that the enhancement of the catalytic activity on the bimetallic catalyst surface originates from the thermodynamically efficient reaction pathways at the metal–metal oxide interface, which demonstrates a straightforward process for the strong metal–support interaction effect. The formation of these interfacial metal–metal oxide nanostructures increases catalytic activity while providing a thermodynamically efficient reaction pathway by lowering the heat of the reactions on the surface. [J. Kim et al. Adsorbate-driven reactive interfacial Pt-NiO1-x nanostructure formation on the Pt3Ni(111) alloy surface, Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aat3151 ]
Professor Park said that one way to monitor catalysts is to detect hot electrons associated with energy dissipation and conversion processes during surface reactions. His team led the real-time detection of hot electrons generated on bimetallic PtCo nanoparticles during exothermic hydrogen oxidation. The team successfully clarified the origin of the synergistic catalytic activity of PtCo nanoparticles with corresponding chemicurrent values.
By estimating the chemicurrent yield, the research team conclude that the catalytic properties of the bimetallic nanoparticles are strongly governed by the oxide–metal interface, which facilitates hot electron transfer. [H. Lee et al. Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles, Nature Comm, 9, 2235 (2018)].
Professor Park explained, “We feel that the precise measurement of hot electrons on catalysts gives insight into the mechanism for heterogeneous catalysis, which can help with the smart design of highly reactive materials. The control of catalytic activity via electronic engineering of catalysts is a promising prospect that may open the door to the new field of combining catalysis with electronics, called “catalytronics.” He added that the study also establishes a strategy for improving catalytic activity for catalytic reactions in industrial chemical reactors.
Professors Park and Yousung Jung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Graduate School of EEWS conducted this research in collaboration with Professor Bongjin Mun from the Department of Physics at GIST.
Figure 1. Evolution of surface structures of PtNi bimetal surfaces under various ambient conditions.
Figure 2. Formation of Pt-CoO interface leads to the catalytic enhancement of PtCo bimetal catalysts.
2018.07.25 View 10218 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Receives 2018 George Washington Carver Award
(Distinguished Professor Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will become the 11th recipient of the George Washington Carver Award. The award ceremony will be held during the 2018 Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO) World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology from July 16 through 19 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia.
The annual Carver award recognizes an individual who has made a significant contribution to building the bio-based economy by applying industrial biotechnology to create environmentally sustainable products. It serves as a lasting memorial to the original vision of George Washington Carver who, over a century ago, pioneered bio-based products, materials, and energy derived from renewable agricultural feedstock. Previous recipients include the founder and CEO of POET Jeff Broin, the CEO of DuPont Ellen Kullman, and Professor Gregory Stephanopoulos at MIT.
Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of systems metabolic engineering, leveraging technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environment-friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass. He also serves as the dean of the multi-and interdisciplinary research center hub, KAIST Institute.Through his work, Professor Lee has garnered countless achievements, including being one of only 13 people in the world elected as a foreign member of both the National Academy of Sciences USA and the National Academy of Engineering USA.
He has actively promoted the importance of industrial biotechnology through engagement with the public, policymakers, and decision makers around the world. He currently serves as the co-chairman of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology for the World Economic Forum and served as the Chairman of the Emerging Technologies Council and Biotechnology Council for the World Economic Forum.
Upon the award announcement, Dr. Brent Erickson, executive vice president of BIO’s Industrial & Environmental Section lauded Professor Lee’s achievement, saying “Dr. Lee has advanced the bio-based economy by developing innovative products and processes that are sustainable and environmentally friendly. In doing so, he has become a leader in advocating on the importance of industrial biotechnology. His contributions to the advancement of the industry are a continuation of the legacy left behind by George Washington Carver.”
Professor Lee thanked his research team who has worked together for the past few decades, adding, “Industrial biotechnology is becoming increasingly important to help achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. We should continue to work together to advance the field and establish a solid foundation for the sustainable future.”
The George Washington Carver Award is sponsored by the Iowa Biotechnology Association. Joe Hrdlicka, executive director of the Iowa Biotechnology Association, said, “Dr. Sang Yup Lee’s significant contributions to the advancement of industrial biotechnology make him the perfect recipient for the George Washington Carver Award. Having published more than 575 peer-reviewed papers, contributed to 82 books, and holding 636 patents, the culmination of Dr. Lee’s work has led to the establishment of sustainable systems for bio-based production of chemicals, fuels, and materials, thus reducing environmental impact and improving quality of life for all.”
2018.07.12 View 12196
Distinguished Professor Lee Receives 2018 George Washington Carver Award
(Distinguished Professor Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will become the 11th recipient of the George Washington Carver Award. The award ceremony will be held during the 2018 Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO) World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology from July 16 through 19 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia.
The annual Carver award recognizes an individual who has made a significant contribution to building the bio-based economy by applying industrial biotechnology to create environmentally sustainable products. It serves as a lasting memorial to the original vision of George Washington Carver who, over a century ago, pioneered bio-based products, materials, and energy derived from renewable agricultural feedstock. Previous recipients include the founder and CEO of POET Jeff Broin, the CEO of DuPont Ellen Kullman, and Professor Gregory Stephanopoulos at MIT.
Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of systems metabolic engineering, leveraging technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environment-friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass. He also serves as the dean of the multi-and interdisciplinary research center hub, KAIST Institute.Through his work, Professor Lee has garnered countless achievements, including being one of only 13 people in the world elected as a foreign member of both the National Academy of Sciences USA and the National Academy of Engineering USA.
He has actively promoted the importance of industrial biotechnology through engagement with the public, policymakers, and decision makers around the world. He currently serves as the co-chairman of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology for the World Economic Forum and served as the Chairman of the Emerging Technologies Council and Biotechnology Council for the World Economic Forum.
Upon the award announcement, Dr. Brent Erickson, executive vice president of BIO’s Industrial & Environmental Section lauded Professor Lee’s achievement, saying “Dr. Lee has advanced the bio-based economy by developing innovative products and processes that are sustainable and environmentally friendly. In doing so, he has become a leader in advocating on the importance of industrial biotechnology. His contributions to the advancement of the industry are a continuation of the legacy left behind by George Washington Carver.”
Professor Lee thanked his research team who has worked together for the past few decades, adding, “Industrial biotechnology is becoming increasingly important to help achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. We should continue to work together to advance the field and establish a solid foundation for the sustainable future.”
The George Washington Carver Award is sponsored by the Iowa Biotechnology Association. Joe Hrdlicka, executive director of the Iowa Biotechnology Association, said, “Dr. Sang Yup Lee’s significant contributions to the advancement of industrial biotechnology make him the perfect recipient for the George Washington Carver Award. Having published more than 575 peer-reviewed papers, contributed to 82 books, and holding 636 patents, the culmination of Dr. Lee’s work has led to the establishment of sustainable systems for bio-based production of chemicals, fuels, and materials, thus reducing environmental impact and improving quality of life for all.”
2018.07.12 View 12196 -
 KAISTians Receive Future Ocean Science and Technology Awards
(From left: PhD candidates Minseok Kang and Junkeon Ahn)
PhD candidates Minseok Kang and Junkeon Ahn from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received Future Ocean Science and Technology Awards from the Korean Association of Ocean Science and Technology Societies (KAOSTS).
Since 2017, KAOSTS has conferred this award upon graduate students who have published outstanding papers on ocean science and technology in order to encourage young researchers in this area.
Kang published ‘Ship block assembly sequence planning considering productivity and welding deformation’ in Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering in which he proposed an assembly sequence planning method for block assemblies that considers the geometric characteristics of blocks to determine feasible assembly sequences as well as assembly process and productivity factors.
Ahn published ‘Fuzzy-based FMEA of hybrid MCFC and gas turbine system for marine propulsion’ in Power Sources. In this research, he conducted a study proposing a fuzzy-based failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) for a hybrid molten carbonate fuel cell and gas turbine system for liquefied hydrogen tankers.
2018.06.15 View 8198
KAISTians Receive Future Ocean Science and Technology Awards
(From left: PhD candidates Minseok Kang and Junkeon Ahn)
PhD candidates Minseok Kang and Junkeon Ahn from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received Future Ocean Science and Technology Awards from the Korean Association of Ocean Science and Technology Societies (KAOSTS).
Since 2017, KAOSTS has conferred this award upon graduate students who have published outstanding papers on ocean science and technology in order to encourage young researchers in this area.
Kang published ‘Ship block assembly sequence planning considering productivity and welding deformation’ in Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering in which he proposed an assembly sequence planning method for block assemblies that considers the geometric characteristics of blocks to determine feasible assembly sequences as well as assembly process and productivity factors.
Ahn published ‘Fuzzy-based FMEA of hybrid MCFC and gas turbine system for marine propulsion’ in Power Sources. In this research, he conducted a study proposing a fuzzy-based failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) for a hybrid molten carbonate fuel cell and gas turbine system for liquefied hydrogen tankers.
2018.06.15 View 8198 -
 The Center for Anthropocene Studies (CAS) Opens
KAIST will start Anthropocene research, a convergence field of study, to address issues related to the commencement of human activities that have had scientific, industrial, and economic impacts on the Earth’s ecosystem. The National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea endorsed the KAIST Center for Anthropocene Studies as its Convergence Research Center project.
Anthropocene refers to a new geological age in which various polluting materials that humans have made during the post-industrial revolution era have made a significant impact on the Earth and the lives of humankind. The studies expand the diverse socio-economic and environmental sectors for responding to climate change, natural disasters, ecological destruction, the polarization of the inequality and wealth, and many others.
The KAIST research group at the center, in collaboration with the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, the Graduate School of Culture Technology, the School of Humanities & Social Sciences, the Department of Industrial Design, the School of Electrical Engineering, the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaRTec), and the KAIST Initiative for Disaster Studies will conduct multidisciplinary research to address intriguing challenges with complex but creative approaches incorporating the fields of engineering, socioeconomics, and art.
The group will investigate topics such as▲ surface and marine changes to the Earth by applying satellite data ▲disaster prediction and governance system building through AI modeling ▲sustainable housing, transportation, and lifestyles ▲ engineering and artistic approaches for envisioning a new future for humankind and the Earth.
Professor Buhm Soon Park, who is in charge of the center, said, “This pioneering research work will inspire the re-creation of a new paradigm of convergence studies in science, engineering, humanities, and social science. We will contribute to making the world better by designing new technologies and social policies.
2018.06.05 View 12394
The Center for Anthropocene Studies (CAS) Opens
KAIST will start Anthropocene research, a convergence field of study, to address issues related to the commencement of human activities that have had scientific, industrial, and economic impacts on the Earth’s ecosystem. The National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea endorsed the KAIST Center for Anthropocene Studies as its Convergence Research Center project.
Anthropocene refers to a new geological age in which various polluting materials that humans have made during the post-industrial revolution era have made a significant impact on the Earth and the lives of humankind. The studies expand the diverse socio-economic and environmental sectors for responding to climate change, natural disasters, ecological destruction, the polarization of the inequality and wealth, and many others.
The KAIST research group at the center, in collaboration with the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, the Graduate School of Culture Technology, the School of Humanities & Social Sciences, the Department of Industrial Design, the School of Electrical Engineering, the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaRTec), and the KAIST Initiative for Disaster Studies will conduct multidisciplinary research to address intriguing challenges with complex but creative approaches incorporating the fields of engineering, socioeconomics, and art.
The group will investigate topics such as▲ surface and marine changes to the Earth by applying satellite data ▲disaster prediction and governance system building through AI modeling ▲sustainable housing, transportation, and lifestyles ▲ engineering and artistic approaches for envisioning a new future for humankind and the Earth.
Professor Buhm Soon Park, who is in charge of the center, said, “This pioneering research work will inspire the re-creation of a new paradigm of convergence studies in science, engineering, humanities, and social science. We will contribute to making the world better by designing new technologies and social policies.
2018.06.05 View 12394 -
 Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 10188
Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 10188 -
 Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs Open
KAIST opened two cross-generation collaborative labs last month. This novel approach will pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires.
This is one of the Vision 2031 innovation initiatives established to extend the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness. The selected labs will be funded for five years and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
A five-member selection committee including the Nobel Laureates Professor Klaus Von Klitzing at the Max-Planck Institute for Solid State Research and Dr. Kurt Wüthrich from ETH Zürich selected the first two labs with senior-junior pairs in March.
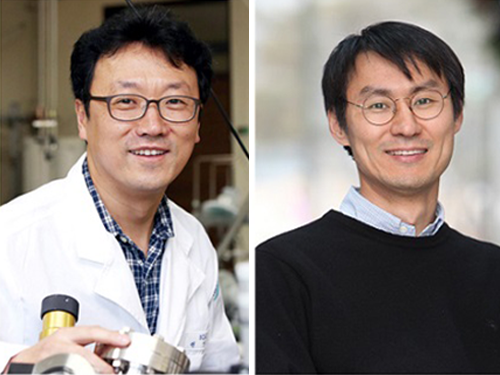
(Two renowned scholars' Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs which opened last month.
Distinguished Professor Lee's lab (above) andChair Professor Sung's lab)
Both labs are run by world-renowned scholars: the Systems Metabolic Engineering and Systems Healthcare Laboratory headed by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare led by Chair Professor Hyung Jin Sung in the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Distinguished Professor Lee will be teamed up with Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and their lab aims to mass produce new eco-friendly chemical materials as well as higher-value-added materials which will be used for medicine. The new platform technologies created in the lab are expected to provide information which will benefit human healthcare.
Meanwhile, the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare will team up with Professors Hyoungsoo Kim and Yeunwoo Cho under Chair Professor Sung. The lab will conduct research on controlling fluids and objects exquisitely on a micro-nano scale by using high-frequency acoustic waves. The lab plans to develop a next-generation healthcare platform for customized diagnoses as well as disease treatment.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who introduced this novel idea in his research innovation initiative, said that he hopes the Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs will contribute to honoring senior scholars’ research legacies and passing knowledge down to junior researchers in order to further develop their academic achievements. He said, “I sincerely hope the labs will make numerous research breakthroughs in the very near future.”
2018.05.03 View 12228
Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs Open
KAIST opened two cross-generation collaborative labs last month. This novel approach will pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires.
This is one of the Vision 2031 innovation initiatives established to extend the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness. The selected labs will be funded for five years and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
A five-member selection committee including the Nobel Laureates Professor Klaus Von Klitzing at the Max-Planck Institute for Solid State Research and Dr. Kurt Wüthrich from ETH Zürich selected the first two labs with senior-junior pairs in March.
(Two renowned scholars' Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs which opened last month.
Distinguished Professor Lee's lab (above) andChair Professor Sung's lab)
Both labs are run by world-renowned scholars: the Systems Metabolic Engineering and Systems Healthcare Laboratory headed by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare led by Chair Professor Hyung Jin Sung in the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Distinguished Professor Lee will be teamed up with Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and their lab aims to mass produce new eco-friendly chemical materials as well as higher-value-added materials which will be used for medicine. The new platform technologies created in the lab are expected to provide information which will benefit human healthcare.
Meanwhile, the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare will team up with Professors Hyoungsoo Kim and Yeunwoo Cho under Chair Professor Sung. The lab will conduct research on controlling fluids and objects exquisitely on a micro-nano scale by using high-frequency acoustic waves. The lab plans to develop a next-generation healthcare platform for customized diagnoses as well as disease treatment.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who introduced this novel idea in his research innovation initiative, said that he hopes the Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs will contribute to honoring senior scholars’ research legacies and passing knowledge down to junior researchers in order to further develop their academic achievements. He said, “I sincerely hope the labs will make numerous research breakthroughs in the very near future.”
2018.05.03 View 12228 -
 Animal Cyborg: Behavioral Control by 'Toy' Craving Circuit
Children love to get toys from parents for their birthday present. This craving toward items also involves object hoarding disorders and shopping addiction. However, the biological meaning of why the brain pursues objects or items has remained unknown. Part of the answer may lie with a neural circuit in the hypothalamus associated with “object craving,” says neuroscientist Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
His research team found that some neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during playing with toys in mice. Thanks to optogenetics, they proved that these neurons in the hypothalamus actually governs obsessive behavior toward non-food objects in mice.
“When we stimulate a neuron in the hypothalamus of mice, they anxiously chased target objects. We found evidence that the neural circuits in the medial preoptic area (MPA) modulate “object craving,” the appetite for possessing objects” said Professor Kim.
Researchers also proved that the MPA circuit facilitate hunting behavior in response to crickets, a natural prey to mice, showing the role of this circuit for catching prey. Further, the MPA nerves send excitatory signals to the periaqueductal gray (PAG), located around the cerebral aqueduct, to create such behavior. The team named this circuit the ‘MPA-PAG’ circuit.
The team showed that they could control mammalian behavior for the first time with this scheme of MPA-Induced Drive Assisted Steering (MIDAS), in which a mouse chase the target objects in the front of head during stimulation of the MPA-PAG circuit. MIDAS allows mice to overcome obstacles to move in a desired path using optogenetics.
(Professor Daesoo Kim)
Professor Kim, who teamed up with Professor Phill Seung Lee in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, explained the significance of the research, “This study provides evidence to treat brain disorders such as compulsive hoarding and kleptomania. It also contributes to the development of technology to control the behavior of animals and humans using strong innate motivation, and thus could impact neuro-economics, defense, and disaster relief.”
He said the team would like to complete the neural circuit map governing behaviors of possession and hunting in the near future by exploring correlations with other neural behaviors controlling possessing and hunting activities.
This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and published in Nature Neuroscience in March 2018.
(Figure 1: Schematics showing possessive behavior induced by the MPA neural circuit)
(Figure 2: Schematics of the MIDAS system that controls mammals behavior using the desire to possess. A MIDAS mouse is following the bait object controlled wirelessly.)
2018.04.23 View 9895
Animal Cyborg: Behavioral Control by 'Toy' Craving Circuit
Children love to get toys from parents for their birthday present. This craving toward items also involves object hoarding disorders and shopping addiction. However, the biological meaning of why the brain pursues objects or items has remained unknown. Part of the answer may lie with a neural circuit in the hypothalamus associated with “object craving,” says neuroscientist Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
His research team found that some neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during playing with toys in mice. Thanks to optogenetics, they proved that these neurons in the hypothalamus actually governs obsessive behavior toward non-food objects in mice.
“When we stimulate a neuron in the hypothalamus of mice, they anxiously chased target objects. We found evidence that the neural circuits in the medial preoptic area (MPA) modulate “object craving,” the appetite for possessing objects” said Professor Kim.
Researchers also proved that the MPA circuit facilitate hunting behavior in response to crickets, a natural prey to mice, showing the role of this circuit for catching prey. Further, the MPA nerves send excitatory signals to the periaqueductal gray (PAG), located around the cerebral aqueduct, to create such behavior. The team named this circuit the ‘MPA-PAG’ circuit.
The team showed that they could control mammalian behavior for the first time with this scheme of MPA-Induced Drive Assisted Steering (MIDAS), in which a mouse chase the target objects in the front of head during stimulation of the MPA-PAG circuit. MIDAS allows mice to overcome obstacles to move in a desired path using optogenetics.
(Professor Daesoo Kim)
Professor Kim, who teamed up with Professor Phill Seung Lee in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, explained the significance of the research, “This study provides evidence to treat brain disorders such as compulsive hoarding and kleptomania. It also contributes to the development of technology to control the behavior of animals and humans using strong innate motivation, and thus could impact neuro-economics, defense, and disaster relief.”
He said the team would like to complete the neural circuit map governing behaviors of possession and hunting in the near future by exploring correlations with other neural behaviors controlling possessing and hunting activities.
This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and published in Nature Neuroscience in March 2018.
(Figure 1: Schematics showing possessive behavior induced by the MPA neural circuit)
(Figure 2: Schematics of the MIDAS system that controls mammals behavior using the desire to possess. A MIDAS mouse is following the bait object controlled wirelessly.)
2018.04.23 View 9895 -
 KAIST to Host FinTech Conference 2018
KAIST will be hosting a FinTech Conference with Princeton University (USA), Tsinghua University (China), and EDHEC Business School (France) in Seoul from April 12 to 13 titled State of the Art in Robo-Advising Systems: Financial Technologies for Enhanced Social Security.
The Bendhein Center for Finance and Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering from Princeton University, Fintech Lab from Tsinghua University, and the Risk Institute from EDHEC will participate as co-hosting organizations in this conference organized by the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering and the KAIST Center for Wealth Management Technologies.
The conference will discuss issues required for providing customized asset management to the public in terms of theory, technology, and industry.
During the conference, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Chairman and CEO of the National Pension Service Sung Joo Kim will deliver welcoming addresses.
Professor John Mulvey from Princeton University, Professor Michael Dempster from Cambridge University, Professors Wei Xu and Changle Lin from Tsinghua University, Professor Lionel Martellini from EDHEC, and Professor Woo Chang Kim from KAIST are some of the invited speakers at the event.
Moreover, renowned experts in related fields will also participate in the conference, including Founder of Vanguard Group John Bogle, Jin Lee from Ant Financial, Youngsuh Cho from Shinhan Financial Group, Jung-Hwan Lee from Samsung Asset Management, and Hye Young Sung from the National Pension Service Research Institute.
Professor Kim said, “Only a small number of wealthy people can receive life-cycle customized asset management services due to the high cost structure; however, new technology derived from the Fourth Industrial Revolution can reduce the service price in an innovative manner, ultimately leading it to be popularized.”
“In an era with the poverty rate of older people reaching almost 50%.Fintech can enable individuals to manage their assets in an active manner, reinforcing social security without additional social costs in the period,” he added.
These four universities have been hosting the FinTech Conference since 2017. China will host the conference this fall, followed by France next year.
Samsung Asset Management, Alibaba Group, and Ant Financial will sponsor the conference. Anyone interested in this event can find more details at http://wmt.kaist.ac.kr/conference.html.
2018.04.02 View 8600
KAIST to Host FinTech Conference 2018
KAIST will be hosting a FinTech Conference with Princeton University (USA), Tsinghua University (China), and EDHEC Business School (France) in Seoul from April 12 to 13 titled State of the Art in Robo-Advising Systems: Financial Technologies for Enhanced Social Security.
The Bendhein Center for Finance and Department of Operations Research and Financial Engineering from Princeton University, Fintech Lab from Tsinghua University, and the Risk Institute from EDHEC will participate as co-hosting organizations in this conference organized by the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering and the KAIST Center for Wealth Management Technologies.
The conference will discuss issues required for providing customized asset management to the public in terms of theory, technology, and industry.
During the conference, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Chairman and CEO of the National Pension Service Sung Joo Kim will deliver welcoming addresses.
Professor John Mulvey from Princeton University, Professor Michael Dempster from Cambridge University, Professors Wei Xu and Changle Lin from Tsinghua University, Professor Lionel Martellini from EDHEC, and Professor Woo Chang Kim from KAIST are some of the invited speakers at the event.
Moreover, renowned experts in related fields will also participate in the conference, including Founder of Vanguard Group John Bogle, Jin Lee from Ant Financial, Youngsuh Cho from Shinhan Financial Group, Jung-Hwan Lee from Samsung Asset Management, and Hye Young Sung from the National Pension Service Research Institute.
Professor Kim said, “Only a small number of wealthy people can receive life-cycle customized asset management services due to the high cost structure; however, new technology derived from the Fourth Industrial Revolution can reduce the service price in an innovative manner, ultimately leading it to be popularized.”
“In an era with the poverty rate of older people reaching almost 50%.Fintech can enable individuals to manage their assets in an active manner, reinforcing social security without additional social costs in the period,” he added.
These four universities have been hosting the FinTech Conference since 2017. China will host the conference this fall, followed by France next year.
Samsung Asset Management, Alibaba Group, and Ant Financial will sponsor the conference. Anyone interested in this event can find more details at http://wmt.kaist.ac.kr/conference.html.
2018.04.02 View 8600 -
 The 8th KINC Fusion Research Awardees
The KAIST Institute for NanoCentury held the 8th KINC Fusion Research Award in order to encourage professors’ convergence studies and instill students’ willingness to research. The award ceremony took place in the KI Building at KAIST on March 13.
The KINC Fusion Research Award selects the most outstanding convergence studies among research undertaken last year, and awards researchers who participated in that research.
The 8th KINC Fusion Research Award went to Professor Yoon Sung Nam from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering. Their research reported the spontaneous self-biomineralization of palladium (Pd) ions on a filamentous virus to form ligand-free Pd nanowires without reducing reagents or using additional surface stabilizers (Title: Virus-Templated Self-Mineralization of Ligand-Free Colloidal Palladium Nanostructures for High Surface Activity and Stability, Advanced Functional Materials (2017)).
Professor Hee-Tae Jung, the Director of KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury and the host of the KINC Fusion Research Award said, “Convergence will be the crucial keyword that will lead to revolutionary change. Hence, the importance of convergence study should be improved. We will put every effort into creating a research environment for increasing convergence study.
The KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury was established in June 2006 under the KAIST Institute with a mission of creating convergence study by tearing down boarders among departments and carrying out interdisciplinary joint research. Currently, approximately 90 professors from 14 departments participate the institute. It aims to become a hub of university institutes for nano-fusion research.
2018.03.19 View 12770
The 8th KINC Fusion Research Awardees
The KAIST Institute for NanoCentury held the 8th KINC Fusion Research Award in order to encourage professors’ convergence studies and instill students’ willingness to research. The award ceremony took place in the KI Building at KAIST on March 13.
The KINC Fusion Research Award selects the most outstanding convergence studies among research undertaken last year, and awards researchers who participated in that research.
The 8th KINC Fusion Research Award went to Professor Yoon Sung Nam from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering. Their research reported the spontaneous self-biomineralization of palladium (Pd) ions on a filamentous virus to form ligand-free Pd nanowires without reducing reagents or using additional surface stabilizers (Title: Virus-Templated Self-Mineralization of Ligand-Free Colloidal Palladium Nanostructures for High Surface Activity and Stability, Advanced Functional Materials (2017)).
Professor Hee-Tae Jung, the Director of KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury and the host of the KINC Fusion Research Award said, “Convergence will be the crucial keyword that will lead to revolutionary change. Hence, the importance of convergence study should be improved. We will put every effort into creating a research environment for increasing convergence study.
The KAIST Institute for the NanoCentury was established in June 2006 under the KAIST Institute with a mission of creating convergence study by tearing down boarders among departments and carrying out interdisciplinary joint research. Currently, approximately 90 professors from 14 departments participate the institute. It aims to become a hub of university institutes for nano-fusion research.
2018.03.19 View 12770