ANG
-
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 9838
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 9838 -
 Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 8728
Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 8728 -
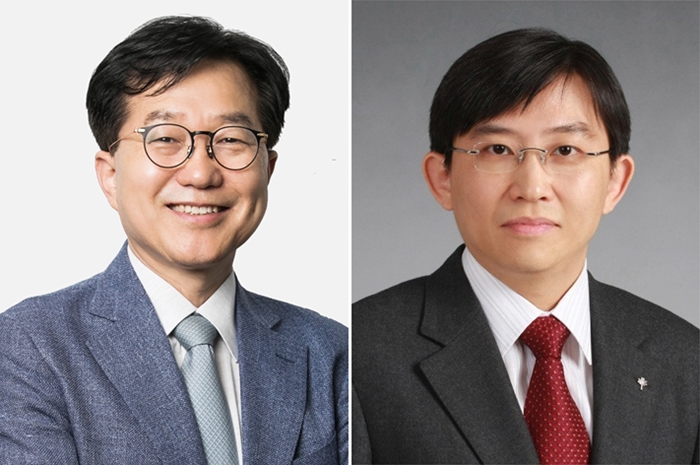 New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 12533
New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 12533 -
 Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 21044
Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 21044 -
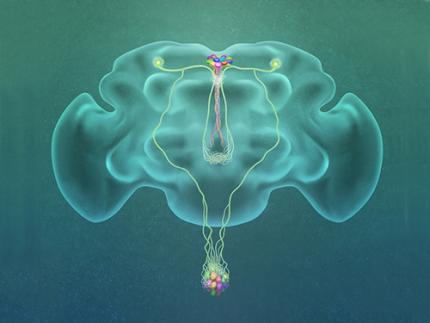 A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 17607
A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 17607 -
 Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 25403
Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 25403 -
 Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 8825
Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 8825 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 10541
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 10541 -
 Enhanced Natural Gas Storage to Help Reduce Global Warming
< Professor Atilhan (left) and Professor Yavuz (right) >
Researchers have designed plastic-based materials that can store natural gas more effectively. These new materials can not only make large-scale, cost-effective, and safe natural gas storage possible, but further hold a strong promise for combating global warming.
Natural gas (predominantly methane) is a clean energy alternative. It is stored by compression, liquefaction, or adsorption. Among these, adsorbed natural gas (ANG) storage is a more efficient, cheaper, and safer alternative to conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage approaches that have drawbacks such as low storage efficiency, high costs, and safety concerns. However, developing adsorptive materials that can more fully exploit the advantages of ANG storage has remained a challenging task.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Cafer T. Yavuz from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS), in collaboration with Professor Mert Atilhan’s group from Texas A&M University, synthesized 29 unique porous polymeric structures with inherent flexibility, and tested their methane gas uptake capacity at high pressures. These porous polymers had varying synthetic complexities, porosities, and morphologies, and the researchers subjected each porous polymer to pure methane gas under various conditions to study the ANG performances.
Of these 29 distinct chemical structures, COP-150 was particularly noteworthy as it achieved a high deliverable gravimetric methane working capacity when cycled between 5 and 100 bar at 273 K, which is 98% of the total uptake capacity. This result surpassed the target set by the United States Department of Energy (US DOE).
COP-150 is the first ever structure to fulfil both the gravimetric and volumetric requirements of the US DOE for successful vehicular use, and the total cost to produce the COP-150 adsorbent was only 1 USD per kilogram.
COP-150 can be produced using freely available and easily accessible plastic materials, and moreover, its synthesis takes place at room temperature, open to the air, and no previous purification of the chemicals is required. The pressure-triggered flexible structure of COP-150 is also advantageous in terms of the total working capacity of deliverable methane for real applications.
The research team believed that the increased pressure flexes the network structure of COP-150 showing “swelling” behavior, and suggested that the flexibility provides rapid desorption and thermal management, while the hydrophobicity and the nature of the covalently bonded framework allow these promising materials to tolerate harsh conditions.
This swelling mechanism of expansion-contraction solves two other major issues, the team noted. Firstly, when using adsorbents based on such a mechanism, unsafe pressure spikes that may occur due to temperature swings can be eliminated. In addition, contamination can also be minimized, since the adsorbent remains contracted when no gas is stored.
Professor Yavuz said, “We envision a whole host of new designs and mechanisms to be developed based on our concept. Since natural gas is a much cleaner fuel than coal and petroleum, new developments in this realm will help switching to the use of less polluting fuels.”
Professor Atilhan agreed the most important impact of their research is on the environment. “Using natural gas more than coal and petroleum will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We believe, one day, we might see vehicles equipped with our materials that are run by a cleaner natural gas fuel,” he added.
This study, reported in Nature Energy on July 8, was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants ( NRF-2016R1A2B4011027, NRF-2017M3A7B4042140, and NRF-2017M3A7B4042235).
< Suggested chemical structure of COP-150 >
< Initial ingredients (left) and final product (right) of COP-150 synthesis >
< Comparison of highest reported volumetric working capacities >
(END)
2019.08.09 View 27018
Enhanced Natural Gas Storage to Help Reduce Global Warming
< Professor Atilhan (left) and Professor Yavuz (right) >
Researchers have designed plastic-based materials that can store natural gas more effectively. These new materials can not only make large-scale, cost-effective, and safe natural gas storage possible, but further hold a strong promise for combating global warming.
Natural gas (predominantly methane) is a clean energy alternative. It is stored by compression, liquefaction, or adsorption. Among these, adsorbed natural gas (ANG) storage is a more efficient, cheaper, and safer alternative to conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage approaches that have drawbacks such as low storage efficiency, high costs, and safety concerns. However, developing adsorptive materials that can more fully exploit the advantages of ANG storage has remained a challenging task.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Cafer T. Yavuz from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS), in collaboration with Professor Mert Atilhan’s group from Texas A&M University, synthesized 29 unique porous polymeric structures with inherent flexibility, and tested their methane gas uptake capacity at high pressures. These porous polymers had varying synthetic complexities, porosities, and morphologies, and the researchers subjected each porous polymer to pure methane gas under various conditions to study the ANG performances.
Of these 29 distinct chemical structures, COP-150 was particularly noteworthy as it achieved a high deliverable gravimetric methane working capacity when cycled between 5 and 100 bar at 273 K, which is 98% of the total uptake capacity. This result surpassed the target set by the United States Department of Energy (US DOE).
COP-150 is the first ever structure to fulfil both the gravimetric and volumetric requirements of the US DOE for successful vehicular use, and the total cost to produce the COP-150 adsorbent was only 1 USD per kilogram.
COP-150 can be produced using freely available and easily accessible plastic materials, and moreover, its synthesis takes place at room temperature, open to the air, and no previous purification of the chemicals is required. The pressure-triggered flexible structure of COP-150 is also advantageous in terms of the total working capacity of deliverable methane for real applications.
The research team believed that the increased pressure flexes the network structure of COP-150 showing “swelling” behavior, and suggested that the flexibility provides rapid desorption and thermal management, while the hydrophobicity and the nature of the covalently bonded framework allow these promising materials to tolerate harsh conditions.
This swelling mechanism of expansion-contraction solves two other major issues, the team noted. Firstly, when using adsorbents based on such a mechanism, unsafe pressure spikes that may occur due to temperature swings can be eliminated. In addition, contamination can also be minimized, since the adsorbent remains contracted when no gas is stored.
Professor Yavuz said, “We envision a whole host of new designs and mechanisms to be developed based on our concept. Since natural gas is a much cleaner fuel than coal and petroleum, new developments in this realm will help switching to the use of less polluting fuels.”
Professor Atilhan agreed the most important impact of their research is on the environment. “Using natural gas more than coal and petroleum will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We believe, one day, we might see vehicles equipped with our materials that are run by a cleaner natural gas fuel,” he added.
This study, reported in Nature Energy on July 8, was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants ( NRF-2016R1A2B4011027, NRF-2017M3A7B4042140, and NRF-2017M3A7B4042235).
< Suggested chemical structure of COP-150 >
< Initial ingredients (left) and final product (right) of COP-150 synthesis >
< Comparison of highest reported volumetric working capacities >
(END)
2019.08.09 View 27018 -
 Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 37305
Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 37305 -
 Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 40668
Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 40668 -
 Efficiently Producing Fatty Acids and Biofuels from Glucose
Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.
The newly developed strain, created by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team, showed the highest efficiency in producing fatty acids and biodiesels ever reported. It will be expected to serve as a new platform to sustainably produce a wide array of fatty acid-based products from glucose and other carbon substrates.
Fossil fuels, which have long been energy resources for our daily lives, are now facing serious challenges: depletion of their reserves and their role in global warming. The production of sustainable bio-based renewable energy has emerged as an essential alternative and many studies to replace fossil fuels are underway. One of the representative examples is biodiesel. Currently, it is mainly being produced through the transesterification of vegetable oils or animal fats.
The research team engineered oleaginous microorganisms, Rhodococcus opacus, to produce fatty acids and their derivatives that can be used as biodiesel from glucose, one of the most abundant and cheap sugars derived from non-edible biomass.
Professor Lee’s team has already engineered Escherichia coli to produce short-chain hydrocarbons, which can be used as gasoline (published in Nature as the cover paper in 2013). However, the production efficiency of the short-chain hydrocarbons using E. coli (0.58 g/L) fell short of the levels required for commercialization.
To overcome these issues, the team employed oil-accumulating Rhodococcus opacus as a host strain in this study. First, the team optimized the cultivation conditions of Rhodococcus opacus to maximize the accumulation of oil (triacylglycerol), which serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and their derivatives. Then, they systematically analyzed the metabolism of the strain and redesigned it to enable higher levels of fatty acids and two kinds of fatty acid-derived biodiesels (fatty acid ethyl esters and long-chain hydrocarbons) to be produced.
They found that the resulting strains produced 50.2, 21.3, and 5.2 g/L of fatty acids, fatty acid ethyl esters, and long-chain hydrocarbons, respectively. These are all the highest concentrations ever reported by microbial fermentations. It is expected that these strains can contribute to the future industrialization of microbial-based biodiesel production.
“This technology creates fatty acids and biodiesel with high efficiency by utilizing lignocellulose, one of the most abundant resources on the Earth, without depending on fossil fuels and vegetable or animal oils. This will provide new opportunities for oil and petroleum industries, which have long relied on fossil fuels, to turn to sustainable and eco-friendly biotechnologies,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels” was published in Nature Chemical Biology on June 17.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557).
(Figure: Metabolic engineering for the production of free fatty acids (FFAs), fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs), and long-chain hydrocarbons (LCHCs) in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.)
# # #
Source:
Hye Mi Kim, Tong Un Chae, So Young Choi, Won Jun Kim and Sang Yup Lee. Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels. Nature Chemical Biology ( https://www.nature.com/nchembio/ ) DOI: 10.1038/s41589-019-0295-5
Profile
Dr. Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Distinguished Professor at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2019.06.19 View 49135
Efficiently Producing Fatty Acids and Biofuels from Glucose
Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.
The newly developed strain, created by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team, showed the highest efficiency in producing fatty acids and biodiesels ever reported. It will be expected to serve as a new platform to sustainably produce a wide array of fatty acid-based products from glucose and other carbon substrates.
Fossil fuels, which have long been energy resources for our daily lives, are now facing serious challenges: depletion of their reserves and their role in global warming. The production of sustainable bio-based renewable energy has emerged as an essential alternative and many studies to replace fossil fuels are underway. One of the representative examples is biodiesel. Currently, it is mainly being produced through the transesterification of vegetable oils or animal fats.
The research team engineered oleaginous microorganisms, Rhodococcus opacus, to produce fatty acids and their derivatives that can be used as biodiesel from glucose, one of the most abundant and cheap sugars derived from non-edible biomass.
Professor Lee’s team has already engineered Escherichia coli to produce short-chain hydrocarbons, which can be used as gasoline (published in Nature as the cover paper in 2013). However, the production efficiency of the short-chain hydrocarbons using E. coli (0.58 g/L) fell short of the levels required for commercialization.
To overcome these issues, the team employed oil-accumulating Rhodococcus opacus as a host strain in this study. First, the team optimized the cultivation conditions of Rhodococcus opacus to maximize the accumulation of oil (triacylglycerol), which serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and their derivatives. Then, they systematically analyzed the metabolism of the strain and redesigned it to enable higher levels of fatty acids and two kinds of fatty acid-derived biodiesels (fatty acid ethyl esters and long-chain hydrocarbons) to be produced.
They found that the resulting strains produced 50.2, 21.3, and 5.2 g/L of fatty acids, fatty acid ethyl esters, and long-chain hydrocarbons, respectively. These are all the highest concentrations ever reported by microbial fermentations. It is expected that these strains can contribute to the future industrialization of microbial-based biodiesel production.
“This technology creates fatty acids and biodiesel with high efficiency by utilizing lignocellulose, one of the most abundant resources on the Earth, without depending on fossil fuels and vegetable or animal oils. This will provide new opportunities for oil and petroleum industries, which have long relied on fossil fuels, to turn to sustainable and eco-friendly biotechnologies,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels” was published in Nature Chemical Biology on June 17.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557).
(Figure: Metabolic engineering for the production of free fatty acids (FFAs), fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs), and long-chain hydrocarbons (LCHCs) in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.)
# # #
Source:
Hye Mi Kim, Tong Un Chae, So Young Choi, Won Jun Kim and Sang Yup Lee. Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels. Nature Chemical Biology ( https://www.nature.com/nchembio/ ) DOI: 10.1038/s41589-019-0295-5
Profile
Dr. Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Distinguished Professor at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2019.06.19 View 49135