research
-
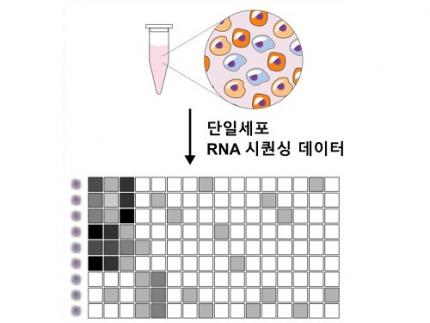 Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 4955
Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 4955 -
 KAIST Develops Sodium Battery Capable of Rapid Charging in Just a Few Seconds
Sodium (Na), which is over 500 times more abundant than lithium (Li), has recently garnered significant attention for its potential in sodium-ion battery technologies. However, existing sodium-ion batteries face fundamental limitations, including lower power output, constrained storage properties, and longer charging times, necessitating the development of next-generation energy storage materials.
On the 11th of April, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery capable of rapid charging.
The innovative hybrid energy storage system integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors. This combination allows the device to achieve both high storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates, positioning it as a viable next-generation alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
However, the development of a hybrid battery with high energy and high power density requires an improvement to the slow energy storage rate of battery-type anodes as well as the enhancement of the relatively low capacity of supercapacitor-type cathode materials.
< Figure 1. Schematic synthetic procedures of high-capacity/high-rate anode and cathode materials for a sodium-ion hybrid energy storages (SIHES) and their proposed energy storage mechanisms. Synthetic procedures for (a) ultrafine iron sulfide-embedded S-doped carbon/graphene (FS/C/G) anode and (b) zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived porous carbon (ZDPC) cathode materials. (c) Proposed energy storage mechanisms of Na+ ions in FS/C/G anode and ClO-4 ions in ZDPC cathode for an SIHES. >
To account for this, Professor Kang's team utilized two distinct metal-organic frameworks for the optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries. This approach led to the development of an anode material with improved kinetics through the inclusion of fine active materials in porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. Additionally, a high-capacity cathode material was synthesized, and the combination of the cathode and anode materials allowed for the development of a sodium-ion storage system optimizing the balance and minimizing the disparities in energy storage rates between the electrodes.
The assembled full cell, comprising the newly developed anode and cathode, forms a high-performance hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device. This device surpasses the energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries and exhibits the characteristics of supercapacitors' power density. It is expected to be suitable for rapid charging applications ranging from electric vehicles to smart electronic devices and aerospace technologies.
< Figure 2. Electrochemical characterizations of FS/C/G-20//ZDPC SIHES full cells (left). Ragone plots for FS/C/G-20//ZDPC (this work) and other previously reported sodium-ion electrochemical energy storage devices (right). >
Professor Kang noted that the hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device, capable of rapid charging and achieving an energy density of 247 Wh/kg and a power density of 34,748 W/kg, represents a breakthrough in overcoming the current limitations of energy storage systems. He anticipates broader applications across various electronic devices, including electric vehicles.
This research, co-authored by KAIST doctoral candidates Jong Hui Choi and Dong Won Kim, was published in the international journal Energy Storage Materials on March 29 with the title "Low-crystallinity conductive multivalence iron sulfide-embedded S-doped anode and high-surface-area O-doped cathode of 3D porous N-rich graphitic carbon frameworks for high-performance sodium-ion hybrid energy storages."
The study was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project.
2024.04.18 View 16645
KAIST Develops Sodium Battery Capable of Rapid Charging in Just a Few Seconds
Sodium (Na), which is over 500 times more abundant than lithium (Li), has recently garnered significant attention for its potential in sodium-ion battery technologies. However, existing sodium-ion batteries face fundamental limitations, including lower power output, constrained storage properties, and longer charging times, necessitating the development of next-generation energy storage materials.
On the 11th of April, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery capable of rapid charging.
The innovative hybrid energy storage system integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors. This combination allows the device to achieve both high storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates, positioning it as a viable next-generation alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
However, the development of a hybrid battery with high energy and high power density requires an improvement to the slow energy storage rate of battery-type anodes as well as the enhancement of the relatively low capacity of supercapacitor-type cathode materials.
< Figure 1. Schematic synthetic procedures of high-capacity/high-rate anode and cathode materials for a sodium-ion hybrid energy storages (SIHES) and their proposed energy storage mechanisms. Synthetic procedures for (a) ultrafine iron sulfide-embedded S-doped carbon/graphene (FS/C/G) anode and (b) zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived porous carbon (ZDPC) cathode materials. (c) Proposed energy storage mechanisms of Na+ ions in FS/C/G anode and ClO-4 ions in ZDPC cathode for an SIHES. >
To account for this, Professor Kang's team utilized two distinct metal-organic frameworks for the optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries. This approach led to the development of an anode material with improved kinetics through the inclusion of fine active materials in porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. Additionally, a high-capacity cathode material was synthesized, and the combination of the cathode and anode materials allowed for the development of a sodium-ion storage system optimizing the balance and minimizing the disparities in energy storage rates between the electrodes.
The assembled full cell, comprising the newly developed anode and cathode, forms a high-performance hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device. This device surpasses the energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries and exhibits the characteristics of supercapacitors' power density. It is expected to be suitable for rapid charging applications ranging from electric vehicles to smart electronic devices and aerospace technologies.
< Figure 2. Electrochemical characterizations of FS/C/G-20//ZDPC SIHES full cells (left). Ragone plots for FS/C/G-20//ZDPC (this work) and other previously reported sodium-ion electrochemical energy storage devices (right). >
Professor Kang noted that the hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device, capable of rapid charging and achieving an energy density of 247 Wh/kg and a power density of 34,748 W/kg, represents a breakthrough in overcoming the current limitations of energy storage systems. He anticipates broader applications across various electronic devices, including electric vehicles.
This research, co-authored by KAIST doctoral candidates Jong Hui Choi and Dong Won Kim, was published in the international journal Energy Storage Materials on March 29 with the title "Low-crystallinity conductive multivalence iron sulfide-embedded S-doped anode and high-surface-area O-doped cathode of 3D porous N-rich graphitic carbon frameworks for high-performance sodium-ion hybrid energy storages."
The study was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project.
2024.04.18 View 16645 -
 KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 6377
KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 6377 -
 KAIST researchers developed a novel ultra-low power memory for neuromorphic computing
A team of Korean researchers is making headlines by developing a new memory device that can be used to replace existing memory or used in implementing neuromorphic computing for next-generation artificial intelligence hardware for its low processing costs and its ultra-low power consumption.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 4th that Professor Shinhyun Choi's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation phase change memory* device featuring ultra-low-power consumption that can replace DRAM and NAND flash memory.
☞ Phase change memory: A memory device that stores and/or processes information by changing the crystalline states of materials to be amorphous or crystalline using heat, thereby changing its resistance state.
Existing phase change memory has the problems such as expensive fabrication process for making highly scaled device and requiring substantial amount of power for operation. To solve these problems, Professor Choi’s research team developed an ultra-low power phase change memory device by electrically forming a very small nanometer (nm) scale phase changeable filament without expensive fabrication processes. This new development has the groundbreaking advantage of not only having a very low processing cost but also of enabling operating with ultra-low power consumption.
DRAM, one of the most popularly used memory, is very fast, but has volatile characteristics in which data disappears when the power is turned off. NAND flash memory, a storage device, has relatively slow read/write speeds, but it has non-volatile characteristic that enables it to preserve the data even when the power is cut off.
Phase change memory, on the other hand, combines the advantages of both DRAM and NAND flash memory, offering high speed and non-volatile characteristics. For this reason, phase change memory is being highlighted as the next-generation memory that can replace existing memory, and is being actively researched as a memory technology or neuromorphic computing technology that mimics the human brain.
However, conventional phase change memory devices require a substantial amount of power to operate, making it difficult to make practical large-capacity memory products or realize a neuromorphic computing system. In order to maximize the thermal efficiency for memory device operation, previous research efforts focused on reducing the power consumption by shrinking the physical size of the device through the use of the state-of-the-art lithography technologies, but they were met with limitations in terms of practicality as the degree of improvement in power consumption was minimal whereas the cost and the difficulty of fabrication increased with each improvement.
In order to solve the power consumption problem of phase change memory, Professor Shinhyun Choi’s research team created a method to electrically form phase change materials in extremely small area, successfully implementing an ultra-low-power phase change memory device that consumes 15 times less power than a conventional phase change memory device fabricated with the expensive lithography tool.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of the ultra-low power phase change memory device developed through this study and the comparison of power consumption by the newly developed phase change memory device compared to conventional phase change memory devices. >
Professor Shinhyun Choi expressed strong confidence in how this research will span out in the future in the new field of research saying, "The phase change memory device we have developed is significant as it offers a novel approach to solve the lingering problems in producing a memory device at a greatly improved manufacturing cost and energy efficiency. We expect the results of our study to become the foundation of future electronic engineering, enabling various applications including high-density three-dimensional vertical memory and neuromorphic computing systems as it opened up the possibilities to choose from a variety of materials.” He went on to add, “I would like to thank the National Research Foundation of Korea and the National NanoFab Center for supporting this research.”
This study, in which See-On Park, a student of MS-PhD Integrated Program, and Seokman Hong, a doctoral student of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, participated as first authors, was published on April 4 in the April issue of the renowned international academic journal Nature. (Paper title: Phase-Change Memory via a Phase-Changeable Self-Confined Nano-Filament)
This research was conducted with support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development (Device) Project, Excellent Emerging Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Semiconductor Process-based Nanomedical Devices Development Project of the National NanoFab Center.
2024.04.04 View 7073
KAIST researchers developed a novel ultra-low power memory for neuromorphic computing
A team of Korean researchers is making headlines by developing a new memory device that can be used to replace existing memory or used in implementing neuromorphic computing for next-generation artificial intelligence hardware for its low processing costs and its ultra-low power consumption.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 4th that Professor Shinhyun Choi's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation phase change memory* device featuring ultra-low-power consumption that can replace DRAM and NAND flash memory.
☞ Phase change memory: A memory device that stores and/or processes information by changing the crystalline states of materials to be amorphous or crystalline using heat, thereby changing its resistance state.
Existing phase change memory has the problems such as expensive fabrication process for making highly scaled device and requiring substantial amount of power for operation. To solve these problems, Professor Choi’s research team developed an ultra-low power phase change memory device by electrically forming a very small nanometer (nm) scale phase changeable filament without expensive fabrication processes. This new development has the groundbreaking advantage of not only having a very low processing cost but also of enabling operating with ultra-low power consumption.
DRAM, one of the most popularly used memory, is very fast, but has volatile characteristics in which data disappears when the power is turned off. NAND flash memory, a storage device, has relatively slow read/write speeds, but it has non-volatile characteristic that enables it to preserve the data even when the power is cut off.
Phase change memory, on the other hand, combines the advantages of both DRAM and NAND flash memory, offering high speed and non-volatile characteristics. For this reason, phase change memory is being highlighted as the next-generation memory that can replace existing memory, and is being actively researched as a memory technology or neuromorphic computing technology that mimics the human brain.
However, conventional phase change memory devices require a substantial amount of power to operate, making it difficult to make practical large-capacity memory products or realize a neuromorphic computing system. In order to maximize the thermal efficiency for memory device operation, previous research efforts focused on reducing the power consumption by shrinking the physical size of the device through the use of the state-of-the-art lithography technologies, but they were met with limitations in terms of practicality as the degree of improvement in power consumption was minimal whereas the cost and the difficulty of fabrication increased with each improvement.
In order to solve the power consumption problem of phase change memory, Professor Shinhyun Choi’s research team created a method to electrically form phase change materials in extremely small area, successfully implementing an ultra-low-power phase change memory device that consumes 15 times less power than a conventional phase change memory device fabricated with the expensive lithography tool.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of the ultra-low power phase change memory device developed through this study and the comparison of power consumption by the newly developed phase change memory device compared to conventional phase change memory devices. >
Professor Shinhyun Choi expressed strong confidence in how this research will span out in the future in the new field of research saying, "The phase change memory device we have developed is significant as it offers a novel approach to solve the lingering problems in producing a memory device at a greatly improved manufacturing cost and energy efficiency. We expect the results of our study to become the foundation of future electronic engineering, enabling various applications including high-density three-dimensional vertical memory and neuromorphic computing systems as it opened up the possibilities to choose from a variety of materials.” He went on to add, “I would like to thank the National Research Foundation of Korea and the National NanoFab Center for supporting this research.”
This study, in which See-On Park, a student of MS-PhD Integrated Program, and Seokman Hong, a doctoral student of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, participated as first authors, was published on April 4 in the April issue of the renowned international academic journal Nature. (Paper title: Phase-Change Memory via a Phase-Changeable Self-Confined Nano-Filament)
This research was conducted with support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development (Device) Project, Excellent Emerging Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Semiconductor Process-based Nanomedical Devices Development Project of the National NanoFab Center.
2024.04.04 View 7073 -
 A KAIST-SNUH Team Devises a Way to Make Mathematical Predictions to find Metabolites Related to Somatic Mutations in Cancers
Cancer is characterized by abnormal metabolic processes different from those of normal cells. Therefore, cancer metabolism has been extensively studied to develop effective diagnosis and treatment strategies. Notable achievements of cancer metabolism studies include the discovery of oncometabolites* and the approval of anticancer drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that target enzymes associated with oncometabolites. Approved anticancer drugs such as ‘Tibsovo (active ingredient: ivosidenib)’ and ‘Idhifa (active ingredient: enasidenib)’ are both used for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Despite such achievements, studying cancer metabolism, especially oncometabolites, remains challenging due to time-consuming and expensive methodologies such as metabolomics. Thus, the number of confirmed oncometabolites is very small although a relatively large number of cancer-associated gene mutations have been well studied.
*Oncometabolite: A metabolite that shows pro-oncogenic function when abnormally accumulated in cancer cells. An oncometabolite is often generated as a result of gene mutations, and this accumulation promotes the growth and survival of cancer cells. Representative oncometabolites include 2-hydroxyglutarate, succinate, and fumarate.
On March 18th, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hyun Uk Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a computational workflow that systematically predicts metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with somatic mutations in cancer through collaboration with research teams under Prof Youngil Koh, Prof. Hongseok Yun, and Prof. Chang Wook Jeong from Seoul National University Hospital.
The research teams have successfully reconstructed patient-specific genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs)* for 1,043 cancer patients across 24 cancer types by integrating publicly available cancer patients’ transcriptome data (i.e., from international cancer genome consortiums such as PCAWG and TCGA) into a generic human GEM. The resulting patient-specific GEMs make it possible to predict each patient’s metabolic phenotypes.
*Genome-scale metabolic model (GEM): A computational model that mathematically describes all of the biochemical reactions that take place inside a cell. It allows for the prediction of the cell’s metabolic phenotypes under various genetic and/or environmental conditions.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a computational methodology for predicting metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with cancer somatic mutations. of a computational methodology for predicting metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with cancer somatic mutations. >
The team developed a four-step computational workflow using the patient-specific GEMs from 1,043 cancer patients and somatic mutation data obtained from the corresponding cancer patients. This workflow begins with the calculation of the flux-sum value of each metabolite by simulating the patient-specific GEMs. The flux-sum value quantifies the intracellular importance of a metabolite. Next, the workflow identifies metabolites that appear to be significantly associated with specific gene mutations through a statistical analysis of the predicted flux-sum data and the mutation data. Finally, the workflow selects altered metabolic pathways that significantly contribute to the biosynthesis of the predicted oncometabolite candidates, ultimately generating metabolite-gene-pathway sets as an output.
The two co-first authors, Dr. GaRyoung Lee (currently a postdoctoral fellow at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School) and Dr. Sang Mi Lee (currently a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard Medical School) said, “The computational workflow developed can systematically predict how genetic mutations affect cellular metabolism through metabolic pathways. Importantly, it can easily be applied to different types of cancer based on the mutation and transcriptome data of cancer patient cohorts.”
Prof. Kim said, “The computational workflow and its resulting prediction outcomes will serve as the groundwork for identifying novel oncometabolites and for facilitating the development of various treatment and diagnosis strategies”.
This study, which was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, has been published online in Genome Biology, a representative journal in the field of biotechnology and genetics, under the title "Prediction of metabolites associated with somatic mutations in cancers by using genome‑scale metabolic models and mutation data".
2024.03.18 View 5656
A KAIST-SNUH Team Devises a Way to Make Mathematical Predictions to find Metabolites Related to Somatic Mutations in Cancers
Cancer is characterized by abnormal metabolic processes different from those of normal cells. Therefore, cancer metabolism has been extensively studied to develop effective diagnosis and treatment strategies. Notable achievements of cancer metabolism studies include the discovery of oncometabolites* and the approval of anticancer drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that target enzymes associated with oncometabolites. Approved anticancer drugs such as ‘Tibsovo (active ingredient: ivosidenib)’ and ‘Idhifa (active ingredient: enasidenib)’ are both used for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Despite such achievements, studying cancer metabolism, especially oncometabolites, remains challenging due to time-consuming and expensive methodologies such as metabolomics. Thus, the number of confirmed oncometabolites is very small although a relatively large number of cancer-associated gene mutations have been well studied.
*Oncometabolite: A metabolite that shows pro-oncogenic function when abnormally accumulated in cancer cells. An oncometabolite is often generated as a result of gene mutations, and this accumulation promotes the growth and survival of cancer cells. Representative oncometabolites include 2-hydroxyglutarate, succinate, and fumarate.
On March 18th, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hyun Uk Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a computational workflow that systematically predicts metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with somatic mutations in cancer through collaboration with research teams under Prof Youngil Koh, Prof. Hongseok Yun, and Prof. Chang Wook Jeong from Seoul National University Hospital.
The research teams have successfully reconstructed patient-specific genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs)* for 1,043 cancer patients across 24 cancer types by integrating publicly available cancer patients’ transcriptome data (i.e., from international cancer genome consortiums such as PCAWG and TCGA) into a generic human GEM. The resulting patient-specific GEMs make it possible to predict each patient’s metabolic phenotypes.
*Genome-scale metabolic model (GEM): A computational model that mathematically describes all of the biochemical reactions that take place inside a cell. It allows for the prediction of the cell’s metabolic phenotypes under various genetic and/or environmental conditions.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a computational methodology for predicting metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with cancer somatic mutations. of a computational methodology for predicting metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with cancer somatic mutations. >
The team developed a four-step computational workflow using the patient-specific GEMs from 1,043 cancer patients and somatic mutation data obtained from the corresponding cancer patients. This workflow begins with the calculation of the flux-sum value of each metabolite by simulating the patient-specific GEMs. The flux-sum value quantifies the intracellular importance of a metabolite. Next, the workflow identifies metabolites that appear to be significantly associated with specific gene mutations through a statistical analysis of the predicted flux-sum data and the mutation data. Finally, the workflow selects altered metabolic pathways that significantly contribute to the biosynthesis of the predicted oncometabolite candidates, ultimately generating metabolite-gene-pathway sets as an output.
The two co-first authors, Dr. GaRyoung Lee (currently a postdoctoral fellow at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School) and Dr. Sang Mi Lee (currently a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard Medical School) said, “The computational workflow developed can systematically predict how genetic mutations affect cellular metabolism through metabolic pathways. Importantly, it can easily be applied to different types of cancer based on the mutation and transcriptome data of cancer patient cohorts.”
Prof. Kim said, “The computational workflow and its resulting prediction outcomes will serve as the groundwork for identifying novel oncometabolites and for facilitating the development of various treatment and diagnosis strategies”.
This study, which was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, has been published online in Genome Biology, a representative journal in the field of biotechnology and genetics, under the title "Prediction of metabolites associated with somatic mutations in cancers by using genome‑scale metabolic models and mutation data".
2024.03.18 View 5656 -
 KAIST Develops Healthcare Device Tracking Chronic Diabetic Wounds
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds.
On the 5th of March, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digital healthcare technology that tracks the wound healing process in real time, which allows appropriate treatments to be administered.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustrations and diagrams of real-time wound monitoring systems. >
The skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from harmful substances, therefore damage to the skin may cause severe health risks to patients in need of intensive care. Especially in the case of diabetic patients, chronic wounds are easily formed due to complications in normal blood circulation and the wound healing process. In the United States alone, hundreds of billions of dollars of medical costs stem from regenerating the skin from such wounds. While various methods exist to promote wound healing, personalized management is essential depending on the condition of each patient's wounds.
Accordingly, the research team tracked the heating response within the wound by utilizing the differences in temperature between the damaged area and the surrounding healthy skin. They then measured heat transfer characteristics to observe moisture changes near the skin surface, ultimately establishing a basis for understanding the formation process of scar tissue. The team conducted experiments using diabetic mice models regarding the delay in wound healing under pathological conditions, and it was demonstrated that the collected data accurately tracks the wound healing process and the formation of scar tissue.
To minimize the tissue damage that may occur in the process of removing the tracking device after healing, the system integrates biodegradable sensor modules capable of natural decomposition within the body. These biodegradable modules disintegrate within the body after use, thus reducing the risk of additional discomfort or tissue damage upon device removal. Furthermore, the device could one day be used for monitoring inside the wound area as there is no need for removal.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon, who led the research, anticipates that continuous monitoring of wound temperature and heat transfer characteristics will enable medical professionals to more accurately assess the status of diabetic patients' wounds and provide appropriate treatment. He further predicted that the implementation of biodegradable sensors allows for the safe decomposition of the device after wound healing without the need for removal, making live monitoring possible not only in hospitals but also at home.
The research team plans to integrate antimicrobial materials into this device, aiming to expand its technological capabilities to enable the observation and prevention of inflammatory responses, bacterial infections, and other complications. The goal is to provide a multi-purpose wound monitoring platform capable of real-time antimicrobial monitoring in hospitals or homes by detecting changes in temperature and heat transfer characteristics indicative of infection levels.
< Image 1. Image of the bioresorbable temperature sensor >
The results of this study were published on February 19th in the international journal Advanced Healthcare Materials and selected as the inside back cover article, titled "Materials and Device Designs for Wireless Monitoring of Temperature and Thermal Transport Properties of Wound Beds during Healing."
This research was conducted with support from the Basic Research Program, the Regional Innovation Center Program, and the BK21 Program.
2024.03.11 View 6000
KAIST Develops Healthcare Device Tracking Chronic Diabetic Wounds
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds.
On the 5th of March, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digital healthcare technology that tracks the wound healing process in real time, which allows appropriate treatments to be administered.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustrations and diagrams of real-time wound monitoring systems. >
The skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from harmful substances, therefore damage to the skin may cause severe health risks to patients in need of intensive care. Especially in the case of diabetic patients, chronic wounds are easily formed due to complications in normal blood circulation and the wound healing process. In the United States alone, hundreds of billions of dollars of medical costs stem from regenerating the skin from such wounds. While various methods exist to promote wound healing, personalized management is essential depending on the condition of each patient's wounds.
Accordingly, the research team tracked the heating response within the wound by utilizing the differences in temperature between the damaged area and the surrounding healthy skin. They then measured heat transfer characteristics to observe moisture changes near the skin surface, ultimately establishing a basis for understanding the formation process of scar tissue. The team conducted experiments using diabetic mice models regarding the delay in wound healing under pathological conditions, and it was demonstrated that the collected data accurately tracks the wound healing process and the formation of scar tissue.
To minimize the tissue damage that may occur in the process of removing the tracking device after healing, the system integrates biodegradable sensor modules capable of natural decomposition within the body. These biodegradable modules disintegrate within the body after use, thus reducing the risk of additional discomfort or tissue damage upon device removal. Furthermore, the device could one day be used for monitoring inside the wound area as there is no need for removal.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon, who led the research, anticipates that continuous monitoring of wound temperature and heat transfer characteristics will enable medical professionals to more accurately assess the status of diabetic patients' wounds and provide appropriate treatment. He further predicted that the implementation of biodegradable sensors allows for the safe decomposition of the device after wound healing without the need for removal, making live monitoring possible not only in hospitals but also at home.
The research team plans to integrate antimicrobial materials into this device, aiming to expand its technological capabilities to enable the observation and prevention of inflammatory responses, bacterial infections, and other complications. The goal is to provide a multi-purpose wound monitoring platform capable of real-time antimicrobial monitoring in hospitals or homes by detecting changes in temperature and heat transfer characteristics indicative of infection levels.
< Image 1. Image of the bioresorbable temperature sensor >
The results of this study were published on February 19th in the international journal Advanced Healthcare Materials and selected as the inside back cover article, titled "Materials and Device Designs for Wireless Monitoring of Temperature and Thermal Transport Properties of Wound Beds during Healing."
This research was conducted with support from the Basic Research Program, the Regional Innovation Center Program, and the BK21 Program.
2024.03.11 View 6000 -
 The World’s First Hacking-preventing Cryptographic Semiconductor Chip
With the dramatic increase in the amount of information exchanged between components or devices in the 5G/6G era, such as for the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous driving, hacking attacks are becoming more sophisticated. Consequently, enhancing security functions is essential for safely transmitting data between and among devices.
On February 29th, a KAIST research team led by Professors Yang-gyu Choi and Seung-tak Ryu from the School of Electrical Engineering announced the successful development of the world's first security cryptographic semiconductor.
The team has developed the Cryptoristor, a cryptographic transistor based on FinFET technology, produced through a 100% silicon-compatible process, for the first time in the world. Cryptoristor is a random number generator (RNG) with unparalleled characteristics, featuring a unique structure comprising a single transistor and a distinctive mechanism.
In all security environments, including artificial intelligence, the most crucial element is the RNG. In the most commonly used security chip, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the RNG is a core component, occupying approximately 75% of the total chip area and more than 85% of its energy consumption. Hence, there is an urgent need for the development of low-power/ultra-small RNGs suitable for mobile or IoT devices.
Existing RNGs come with limitations as they lack compatibility with silicon CMOS processes and circuit-based RNGs occupy a large surface area.
In contrast, the team’s newly developed Cryptoristor, a cryptographic semiconductor based on a single-component structure, consumes and occupies less than .001 of the power and area compared to the current chips being used. Utilizing the inherent randomness of FinFETs, fabricated on a Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) substrate with an insulating layer formed beneath the silicon, the team developed an RNG that unpredictably produces zeroes and ones.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of the security cryptographic transistor device. >
Generally speaking, preventing hackers from predicting the encrypted algorithms during data exchanges through mobile devices is pivotal. Therefore, this method ensures unpredictability by generating random sequences of zeroes and ones that change every time.
Moreover, while the Cryptoristor-based RNG research is the world's first of its kind without any international implementation cases, it shares the same transistor structure as existing logic or memory components. This enables 100% production through rapid mass production processes using existing semiconductor facilities at a low cost.
Seung-il Kim, a PhD student who led the research, explained the significance of the study, stating, "As a cryptographic semiconductor, the ultra-small/low-power random number generator enhances security through its distinctive unpredictability, supporting safe hyperconnectivity with secure transmissions between chips or devices. Particularly, compared to previous research, it offers excellent advantages in terms of energy consumption, integration density, and cost, making it suitable for IoT device environments."
This research, with master’s student Hyung-jin Yoo as the co-author, was officially published in the online edition of Science Advances, a sister journal of Science, in February 2024 (research paper title: Cryptographic transistor for true random number generator with low power consumption).
This research received support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project and the Core Technology Development Project for the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory.
2024.03.07 View 7042
The World’s First Hacking-preventing Cryptographic Semiconductor Chip
With the dramatic increase in the amount of information exchanged between components or devices in the 5G/6G era, such as for the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous driving, hacking attacks are becoming more sophisticated. Consequently, enhancing security functions is essential for safely transmitting data between and among devices.
On February 29th, a KAIST research team led by Professors Yang-gyu Choi and Seung-tak Ryu from the School of Electrical Engineering announced the successful development of the world's first security cryptographic semiconductor.
The team has developed the Cryptoristor, a cryptographic transistor based on FinFET technology, produced through a 100% silicon-compatible process, for the first time in the world. Cryptoristor is a random number generator (RNG) with unparalleled characteristics, featuring a unique structure comprising a single transistor and a distinctive mechanism.
In all security environments, including artificial intelligence, the most crucial element is the RNG. In the most commonly used security chip, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the RNG is a core component, occupying approximately 75% of the total chip area and more than 85% of its energy consumption. Hence, there is an urgent need for the development of low-power/ultra-small RNGs suitable for mobile or IoT devices.
Existing RNGs come with limitations as they lack compatibility with silicon CMOS processes and circuit-based RNGs occupy a large surface area.
In contrast, the team’s newly developed Cryptoristor, a cryptographic semiconductor based on a single-component structure, consumes and occupies less than .001 of the power and area compared to the current chips being used. Utilizing the inherent randomness of FinFETs, fabricated on a Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) substrate with an insulating layer formed beneath the silicon, the team developed an RNG that unpredictably produces zeroes and ones.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of the security cryptographic transistor device. >
Generally speaking, preventing hackers from predicting the encrypted algorithms during data exchanges through mobile devices is pivotal. Therefore, this method ensures unpredictability by generating random sequences of zeroes and ones that change every time.
Moreover, while the Cryptoristor-based RNG research is the world's first of its kind without any international implementation cases, it shares the same transistor structure as existing logic or memory components. This enables 100% production through rapid mass production processes using existing semiconductor facilities at a low cost.
Seung-il Kim, a PhD student who led the research, explained the significance of the study, stating, "As a cryptographic semiconductor, the ultra-small/low-power random number generator enhances security through its distinctive unpredictability, supporting safe hyperconnectivity with secure transmissions between chips or devices. Particularly, compared to previous research, it offers excellent advantages in terms of energy consumption, integration density, and cost, making it suitable for IoT device environments."
This research, with master’s student Hyung-jin Yoo as the co-author, was officially published in the online edition of Science Advances, a sister journal of Science, in February 2024 (research paper title: Cryptographic transistor for true random number generator with low power consumption).
This research received support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project and the Core Technology Development Project for the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory.
2024.03.07 View 7042 -
 KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 5888
KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 5888 -
 KAIST Team Develops an Insect-Mimicking Semiconductor to Detect Motion
The recent development of an “intelligent sensor” semiconductor that mimics the optic nerve of insects while operating at ultra-high speeds and low power offers extensive expandability into various innovative technologies. This technology is expected to be applied to various fields including transportation, safety, and security systems, contributing to both industry and society.
On February 19, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) announced the successful developed an intelligent motion detector by merging various memristor* devices to mimic the visual intelligence** of the optic nerve of insects.
*Memristor: a “memory resistor” whose state of resistance changes depending on the input signal
**Visual intelligence: the ability to interpret visual information and perform calculations within the optic nerve
With the recent advances in AI technology, vision systems are being improved by utilizing AI in various tasks such as image recognition, object detection, and motion analysis. However, existing vision systems typically recognize objects and their behaviour from the received image signals using complex algorithms. This method requires a significant amount of data traffic and higher power consumption, making it difficult to apply in mobile or IoT devices.
Meanwhile, insects are known to be able to effectively process visual information through an optic nerve circuit called the elementary motion detector, allowing them to detect objects and recognize their motion at an advanced level. However, mimicking this pathway using conventional silicon integrated circuit (CMOS) technology requires complex circuits, and its implementation into actual devices has thus been limited.
< Figure 1. Working principle of a biological elementary motion detection system. >
Professor Kyung Min Kim’s research team developed an intelligent motion detecting sensor that operates at a high level of efficiency and ultra-high speeds. The device has a simple structure consisting of only two types of memristors and a resistor developed by the team. The two different memristors each carry out a signal delay function and a signal integration and ignition function, respectively. Through them, the team could directly mimic the optic nerve of insects to analyze object movement.
< Figure 2. (Left) Optical image of the M-EMD device in the left panel (scale bar 200 μm) and SEM image of the device in the right panel (scale bar: 20 μm). (Middle) Responses of the M-EMD in positive direction. (Right) Responses of the M-EMD in negative direction. >
To demonstrate its potential for practical applications, the research team used the newly developed motion detector to design a neuromorphic computing system that can predict the path of a vehicle. The results showed that the device used 92.9% less energy compared to existing technology and predicted motion with more accuracy.
< Figure 3. Neuromorphic computing system configuration based on motion recognition devices >
Professor Kim said, “Insects make use of their very simple visual intelligence systems to detect the motion of objects at a surprising high speed. This research is significant in that we could mimic the functions of a nerve using a memristor device.” He added, “Edge AI devices, such as AI-topped mobile phones, are becoming increasingly important. This research can contribute to the integration of efficient vision systems for motion recognition, so we expect it to be applied to various fields such as autonomous vehicles, vehicle transportation systems, robotics, and machine vision.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Hanchan Song and Min Gu Lee, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST DMSE, was published in the online issue of Advanced Materials on January 29.
This research was supported by the Mid-Sized Research Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, the PIM Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project, the National Nano Fab Center, and the Leap Research Project by KAIST.
2024.02.29 View 6463
KAIST Team Develops an Insect-Mimicking Semiconductor to Detect Motion
The recent development of an “intelligent sensor” semiconductor that mimics the optic nerve of insects while operating at ultra-high speeds and low power offers extensive expandability into various innovative technologies. This technology is expected to be applied to various fields including transportation, safety, and security systems, contributing to both industry and society.
On February 19, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) announced the successful developed an intelligent motion detector by merging various memristor* devices to mimic the visual intelligence** of the optic nerve of insects.
*Memristor: a “memory resistor” whose state of resistance changes depending on the input signal
**Visual intelligence: the ability to interpret visual information and perform calculations within the optic nerve
With the recent advances in AI technology, vision systems are being improved by utilizing AI in various tasks such as image recognition, object detection, and motion analysis. However, existing vision systems typically recognize objects and their behaviour from the received image signals using complex algorithms. This method requires a significant amount of data traffic and higher power consumption, making it difficult to apply in mobile or IoT devices.
Meanwhile, insects are known to be able to effectively process visual information through an optic nerve circuit called the elementary motion detector, allowing them to detect objects and recognize their motion at an advanced level. However, mimicking this pathway using conventional silicon integrated circuit (CMOS) technology requires complex circuits, and its implementation into actual devices has thus been limited.
< Figure 1. Working principle of a biological elementary motion detection system. >
Professor Kyung Min Kim’s research team developed an intelligent motion detecting sensor that operates at a high level of efficiency and ultra-high speeds. The device has a simple structure consisting of only two types of memristors and a resistor developed by the team. The two different memristors each carry out a signal delay function and a signal integration and ignition function, respectively. Through them, the team could directly mimic the optic nerve of insects to analyze object movement.
< Figure 2. (Left) Optical image of the M-EMD device in the left panel (scale bar 200 μm) and SEM image of the device in the right panel (scale bar: 20 μm). (Middle) Responses of the M-EMD in positive direction. (Right) Responses of the M-EMD in negative direction. >
To demonstrate its potential for practical applications, the research team used the newly developed motion detector to design a neuromorphic computing system that can predict the path of a vehicle. The results showed that the device used 92.9% less energy compared to existing technology and predicted motion with more accuracy.
< Figure 3. Neuromorphic computing system configuration based on motion recognition devices >
Professor Kim said, “Insects make use of their very simple visual intelligence systems to detect the motion of objects at a surprising high speed. This research is significant in that we could mimic the functions of a nerve using a memristor device.” He added, “Edge AI devices, such as AI-topped mobile phones, are becoming increasingly important. This research can contribute to the integration of efficient vision systems for motion recognition, so we expect it to be applied to various fields such as autonomous vehicles, vehicle transportation systems, robotics, and machine vision.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Hanchan Song and Min Gu Lee, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST DMSE, was published in the online issue of Advanced Materials on January 29.
This research was supported by the Mid-Sized Research Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, the PIM Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project, the National Nano Fab Center, and the Leap Research Project by KAIST.
2024.02.29 View 6463 -
 A Korean research team develops a new clinical candidate for fatty liver disease
A team of Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a new drug candidate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) acting on peripheral tissues. To date, there has not been an optimal treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and this discovery is expected to set the grounds for the development of new drugs that can safely suppress both liver fat accumulation and liver fibrosis at the same time.
A joint research team led by Professor Jin Hee Ahn from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) and Professor Hail Kim from the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering developed a new chemical that can suppress disease-specific protein (HTR2A) through years of basic research. The team also revealed to have verified its efficacy and safety through preclinical tests (animal tests) at JD Bioscience Inc., a start-up company founded by Professor Ahn.
Although NAFLD has a prevalence rate as high as 20-30%, and about 5% of the global adult population suffers from NASH, there are no commercial drugs targeting them to date. NAFLD is a chronic disease that starts from the fatty liver and progresses into steatohepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The mortality rate of patients increases with accompanied cardiovascular diseases and liver-related complications, and appropriate treatment in the early stage is hence necessary.
< Figure 1. Strategy and history of 5HT2A antagonists. Library and rational design for the development of compound 11c as a potent 5HT2A antagonist. Previous research efforts were discontinued due to limited oral absorption and safety. A therapeutic candidate to overcome this problem was identified and phase 1 clinical trials are currently in progress. >
The new synthetic chemical developed by the joint GIST-KAIST research is an innovative drug candidate that shows therapeutic effects on NASH based on a dual action mechanism that inhibits the accumulation of fat in the liver and liver fibrosis by suppressing the serotonin receptor protein 5HT2A.
The research team confirmed its therapeutic effects in animal models for NAFLD and NASH, in which hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis* caused by fat accumulation in the liver were suppressed simultaneously by 50-70%.
*fibrosis: stiffening of parts of the liver, also used as a major indicator to track the prognosis of steatosis
The research team explained that the material was designed with optimal polarity and lipid affinity to minimize its permeability across the blood-brain barrier. It therefore does not affect the brain, and causes little side effects in the central nervous system (CNS) such as depression and suicidal ideations, while demonstrating excellent inhibition on its target protein present in tissues outside brain (IC50* = 14 nM). The team also demonstrated its superior efficacy in improving liver fibrosis when compared to similar drugs in the phase 3 clinical trial.
*IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration): the concentration at which a chemical suppresses 50% of a particular biological function
< Figure 2. GM-60106 (11c)'s effect on obesity: When GM-60106 was administered to an obese animal model (mice) for 2 months, body weight, body fat mass, and blood sugar were significantly reduced (a-d). In addition, the steatohepatitis level (NAFLD Activity Score) and the expression of genes of the treated mice involved in adipogenesis along with blood/liver fat decreased (e-h) >
Based on the pharmacological data obtained through preclinical trials, the team evaluated the effects of the drug on 88 healthy adults as part of their phase 1 clinical trial, where the side effects and the safe dosage of a drug are tested against healthy adults. Results showed no serious side effects and a good level of drug safety.
In addition, a preliminary efficacy evaluation on eight adults with steatohepatitis is currently underway.
Professor Jin Hee Ahn said, “The aim of this research is to develop a treatment for NASH with little side effects and guaranteed safety by developing a new target. The developed chemical is currently going through phase 1 of the global clinical trial in Australia through JD Bioscience Inc., a bio venture company for innovative drug development.” he added, “The candidate material the research team is currently developing shows not only a high level of safety and preventative effects by suppressing fat accumulation in the liver, but also a direct therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis. This is a strength that distinguishes our material from other competing drugs.”
< Figure 3. Efficacy of GM-60106 (11c) on liver fibrosis: When GM-60106 was administered to a steatohepatitis model (mice) for 3 months, the expression of genes associated with tissue fibrosis was significantly reduced (b-c). As a result of a detailed analysis of the tissues of the animal model, it was confirmed that the rate of tissue fibrosis was reduced and the expression rate of genes related to tissue fibrosis and inflammation was also significantly reduced (e-h). >
Professor Hail Kim from KAIST said, “Until now, this disease did not have a method of treatment other than weight control, and there has been no attempt to develop a drug that can be used for non-obese patients.” He added, “Through this research, we look forward to the development of various treatment techniques targeting a range of metabolic diseases including NASH that do not affect the weight of the patient.”
This study, conducted together by the research teams led by Professor Ahn from GIST and Professor Kim from KAIST, as well as the research team from JD Bioscience Inc., was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National New Drug Development Project. The results of this research were published by Nature Communications on January 20.
The team also presented the results of their clinical study on the candidate material coded GM-60106 targeting metabolic abnormality-related MASH* at NASH-TAG Conference 2024, which was held in Utah for three days starting on January 4, which was selected as an excellent abstract.
*MASH (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis): new replacement term for NASH
2024.02.21 View 7736
A Korean research team develops a new clinical candidate for fatty liver disease
A team of Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a new drug candidate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) acting on peripheral tissues. To date, there has not been an optimal treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and this discovery is expected to set the grounds for the development of new drugs that can safely suppress both liver fat accumulation and liver fibrosis at the same time.
A joint research team led by Professor Jin Hee Ahn from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) and Professor Hail Kim from the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering developed a new chemical that can suppress disease-specific protein (HTR2A) through years of basic research. The team also revealed to have verified its efficacy and safety through preclinical tests (animal tests) at JD Bioscience Inc., a start-up company founded by Professor Ahn.
Although NAFLD has a prevalence rate as high as 20-30%, and about 5% of the global adult population suffers from NASH, there are no commercial drugs targeting them to date. NAFLD is a chronic disease that starts from the fatty liver and progresses into steatohepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The mortality rate of patients increases with accompanied cardiovascular diseases and liver-related complications, and appropriate treatment in the early stage is hence necessary.
< Figure 1. Strategy and history of 5HT2A antagonists. Library and rational design for the development of compound 11c as a potent 5HT2A antagonist. Previous research efforts were discontinued due to limited oral absorption and safety. A therapeutic candidate to overcome this problem was identified and phase 1 clinical trials are currently in progress. >
The new synthetic chemical developed by the joint GIST-KAIST research is an innovative drug candidate that shows therapeutic effects on NASH based on a dual action mechanism that inhibits the accumulation of fat in the liver and liver fibrosis by suppressing the serotonin receptor protein 5HT2A.
The research team confirmed its therapeutic effects in animal models for NAFLD and NASH, in which hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis* caused by fat accumulation in the liver were suppressed simultaneously by 50-70%.
*fibrosis: stiffening of parts of the liver, also used as a major indicator to track the prognosis of steatosis
The research team explained that the material was designed with optimal polarity and lipid affinity to minimize its permeability across the blood-brain barrier. It therefore does not affect the brain, and causes little side effects in the central nervous system (CNS) such as depression and suicidal ideations, while demonstrating excellent inhibition on its target protein present in tissues outside brain (IC50* = 14 nM). The team also demonstrated its superior efficacy in improving liver fibrosis when compared to similar drugs in the phase 3 clinical trial.
*IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration): the concentration at which a chemical suppresses 50% of a particular biological function
< Figure 2. GM-60106 (11c)'s effect on obesity: When GM-60106 was administered to an obese animal model (mice) for 2 months, body weight, body fat mass, and blood sugar were significantly reduced (a-d). In addition, the steatohepatitis level (NAFLD Activity Score) and the expression of genes of the treated mice involved in adipogenesis along with blood/liver fat decreased (e-h) >
Based on the pharmacological data obtained through preclinical trials, the team evaluated the effects of the drug on 88 healthy adults as part of their phase 1 clinical trial, where the side effects and the safe dosage of a drug are tested against healthy adults. Results showed no serious side effects and a good level of drug safety.
In addition, a preliminary efficacy evaluation on eight adults with steatohepatitis is currently underway.
Professor Jin Hee Ahn said, “The aim of this research is to develop a treatment for NASH with little side effects and guaranteed safety by developing a new target. The developed chemical is currently going through phase 1 of the global clinical trial in Australia through JD Bioscience Inc., a bio venture company for innovative drug development.” he added, “The candidate material the research team is currently developing shows not only a high level of safety and preventative effects by suppressing fat accumulation in the liver, but also a direct therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis. This is a strength that distinguishes our material from other competing drugs.”
< Figure 3. Efficacy of GM-60106 (11c) on liver fibrosis: When GM-60106 was administered to a steatohepatitis model (mice) for 3 months, the expression of genes associated with tissue fibrosis was significantly reduced (b-c). As a result of a detailed analysis of the tissues of the animal model, it was confirmed that the rate of tissue fibrosis was reduced and the expression rate of genes related to tissue fibrosis and inflammation was also significantly reduced (e-h). >
Professor Hail Kim from KAIST said, “Until now, this disease did not have a method of treatment other than weight control, and there has been no attempt to develop a drug that can be used for non-obese patients.” He added, “Through this research, we look forward to the development of various treatment techniques targeting a range of metabolic diseases including NASH that do not affect the weight of the patient.”
This study, conducted together by the research teams led by Professor Ahn from GIST and Professor Kim from KAIST, as well as the research team from JD Bioscience Inc., was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National New Drug Development Project. The results of this research were published by Nature Communications on January 20.
The team also presented the results of their clinical study on the candidate material coded GM-60106 targeting metabolic abnormality-related MASH* at NASH-TAG Conference 2024, which was held in Utah for three days starting on January 4, which was selected as an excellent abstract.
*MASH (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis): new replacement term for NASH
2024.02.21 View 7736 -
 Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 7093
Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 7093 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops a Novel “Bone Bandage” Material for Cracked Bones
Bone regeneration is a complex process, and existing methods to aid regeneration including transplants and growth factor transmissions face limitations such as the high cost. But recently, a piezoelectric material that can promote the growth of bone tissue has been developed.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) announced on January 25 the development of a biomimetic scaffold that generates electrical signals upon the application of pressure by utilizing the unique osteogenic ability of hydroxyapatite (HAp). This research was conducted in collaboration with a team led by Professor Jangho Kim from the Department of Convergence Biosystems Engineering at Chonnam National University.
HAp is a basic calcium phosphate material found in bones and teeth. This biocompatible mineral substance is also known to prevent tooth decay and is often used in toothpaste.
Previous studies on piezoelectric scaffolds confirmed the effects of piezoelectricity on promoting bone regeneration and improving bone fusion in various polymer-based materials, but were limited in simulating the complex cellular environment required for optimal bone tissue regeneration. However, this research suggests a new method for utilizing the unique osteogenic abilities of HAp to develop a material that mimics the environment for bone tissue in a living body.
< Figure 1. Design and characterization of piezoelectrically and topographically originated biomimetic scaffolds. (a) Schematic representation of the enhanced bone regeneration mechanism through electrical and topographical cues provided by HAp-incorporated P(VDF-TrFE) scaffolds. (b) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process. >
The research team developed a manufacturing process that fuses HAp with a polymer film. The flexible and free-standing scaffold developed through this process demonstrated its remarkable potential for promoting bone regeneration through in-vitro and in-vivo experiments in rats.
The team also identified the principles of bone regeneration that their scaffold is based on. Using atomic force microscopy (AFM), they analysed the electrical properties of the scaffold and evaluated the detailed surface properties related to cell shape and cell skeletal protein formation. They also investigated the effects of piezoelectricity and surface properties on the expression of growth factors.
Professor Hong from KAIST’s DMSE said, “We have developed a HAp-based piezoelectric composite material that can act like a ‘bone bandage’ through its ability to accelerate bone regeneration.” He added, “This research not only suggests a new direction for designing biomaterials, but is also significant in having explored the effects of piezoelectricity and surface properties on bone regeneration.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Soyun Joo and Soyeon Kim from Professor Hong’s group, was published on ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on January 4 under the title “Piezoelectrically and Topographically Engineered Scaffolds for Accelerating Bone Regeneration”. From Professor Kim’s group, Ph.D. candidate Yonghyun Gwon also participated as co-first author, and Professor Kim himself as a corresponding author.
< Figure 2. Analysis of piezoelectric and surface properties of the biomimetic scaffolds using atomic force microscopy. (a) PFM amplitude and phase images of box-poled composite scaffolds. The white bar represents 2 μm. (b) 3D representations of composite scaffolds paired with typical 2D line sections. (c) In vivo bone regeneration micro-CT analysis, (d) schematic representation of filler-derived electrical origins in bone regeneration. >
This research was supported by the KAIST Research and Development Team, the KUSTAR-KAIST Joint Research Center, the KAIST Global Singularity Project, and the government-funded Basic Research Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.02.01 View 6931
A KAIST Research Team Develops a Novel “Bone Bandage” Material for Cracked Bones
Bone regeneration is a complex process, and existing methods to aid regeneration including transplants and growth factor transmissions face limitations such as the high cost. But recently, a piezoelectric material that can promote the growth of bone tissue has been developed.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) announced on January 25 the development of a biomimetic scaffold that generates electrical signals upon the application of pressure by utilizing the unique osteogenic ability of hydroxyapatite (HAp). This research was conducted in collaboration with a team led by Professor Jangho Kim from the Department of Convergence Biosystems Engineering at Chonnam National University.
HAp is a basic calcium phosphate material found in bones and teeth. This biocompatible mineral substance is also known to prevent tooth decay and is often used in toothpaste.
Previous studies on piezoelectric scaffolds confirmed the effects of piezoelectricity on promoting bone regeneration and improving bone fusion in various polymer-based materials, but were limited in simulating the complex cellular environment required for optimal bone tissue regeneration. However, this research suggests a new method for utilizing the unique osteogenic abilities of HAp to develop a material that mimics the environment for bone tissue in a living body.
< Figure 1. Design and characterization of piezoelectrically and topographically originated biomimetic scaffolds. (a) Schematic representation of the enhanced bone regeneration mechanism through electrical and topographical cues provided by HAp-incorporated P(VDF-TrFE) scaffolds. (b) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process. >
The research team developed a manufacturing process that fuses HAp with a polymer film. The flexible and free-standing scaffold developed through this process demonstrated its remarkable potential for promoting bone regeneration through in-vitro and in-vivo experiments in rats.
The team also identified the principles of bone regeneration that their scaffold is based on. Using atomic force microscopy (AFM), they analysed the electrical properties of the scaffold and evaluated the detailed surface properties related to cell shape and cell skeletal protein formation. They also investigated the effects of piezoelectricity and surface properties on the expression of growth factors.
Professor Hong from KAIST’s DMSE said, “We have developed a HAp-based piezoelectric composite material that can act like a ‘bone bandage’ through its ability to accelerate bone regeneration.” He added, “This research not only suggests a new direction for designing biomaterials, but is also significant in having explored the effects of piezoelectricity and surface properties on bone regeneration.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Soyun Joo and Soyeon Kim from Professor Hong’s group, was published on ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on January 4 under the title “Piezoelectrically and Topographically Engineered Scaffolds for Accelerating Bone Regeneration”. From Professor Kim’s group, Ph.D. candidate Yonghyun Gwon also participated as co-first author, and Professor Kim himself as a corresponding author.
< Figure 2. Analysis of piezoelectric and surface properties of the biomimetic scaffolds using atomic force microscopy. (a) PFM amplitude and phase images of box-poled composite scaffolds. The white bar represents 2 μm. (b) 3D representations of composite scaffolds paired with typical 2D line sections. (c) In vivo bone regeneration micro-CT analysis, (d) schematic representation of filler-derived electrical origins in bone regeneration. >
This research was supported by the KAIST Research and Development Team, the KUSTAR-KAIST Joint Research Center, the KAIST Global Singularity Project, and the government-funded Basic Research Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.02.01 View 6931