IT
-
 The Australian: Asia more than competition, March 30, 2012
The Australian, the largest-selling newspaper in Australia, carried an article titled, “Asia more than competition,” an interview with Dr. Simon Marginson who is Professor of Higher Education in the Center for the Study of Higher Education at the University of Melbourne. Professor Marginson talks about the recent rise of universities in Asia, predicting that the Asian universities will eventually take up as much an equal share of importance as universities in Northwestern Europe in leading the world’s higher education within the next five to ten years. For the article, please follow the link below:
The Australian
Asia more than competition: Simon Marginson
by: John Ross
March 30, 2012 12:00AM
http://www.theaustralian.com.au/higher-education/asia-more-than-competition-marginson/story-e6frgcjx-1226309922402
2012.03.30 View 8237
The Australian: Asia more than competition, March 30, 2012
The Australian, the largest-selling newspaper in Australia, carried an article titled, “Asia more than competition,” an interview with Dr. Simon Marginson who is Professor of Higher Education in the Center for the Study of Higher Education at the University of Melbourne. Professor Marginson talks about the recent rise of universities in Asia, predicting that the Asian universities will eventually take up as much an equal share of importance as universities in Northwestern Europe in leading the world’s higher education within the next five to ten years. For the article, please follow the link below:
The Australian
Asia more than competition: Simon Marginson
by: John Ross
March 30, 2012 12:00AM
http://www.theaustralian.com.au/higher-education/asia-more-than-competition-marginson/story-e6frgcjx-1226309922402
2012.03.30 View 8237 -
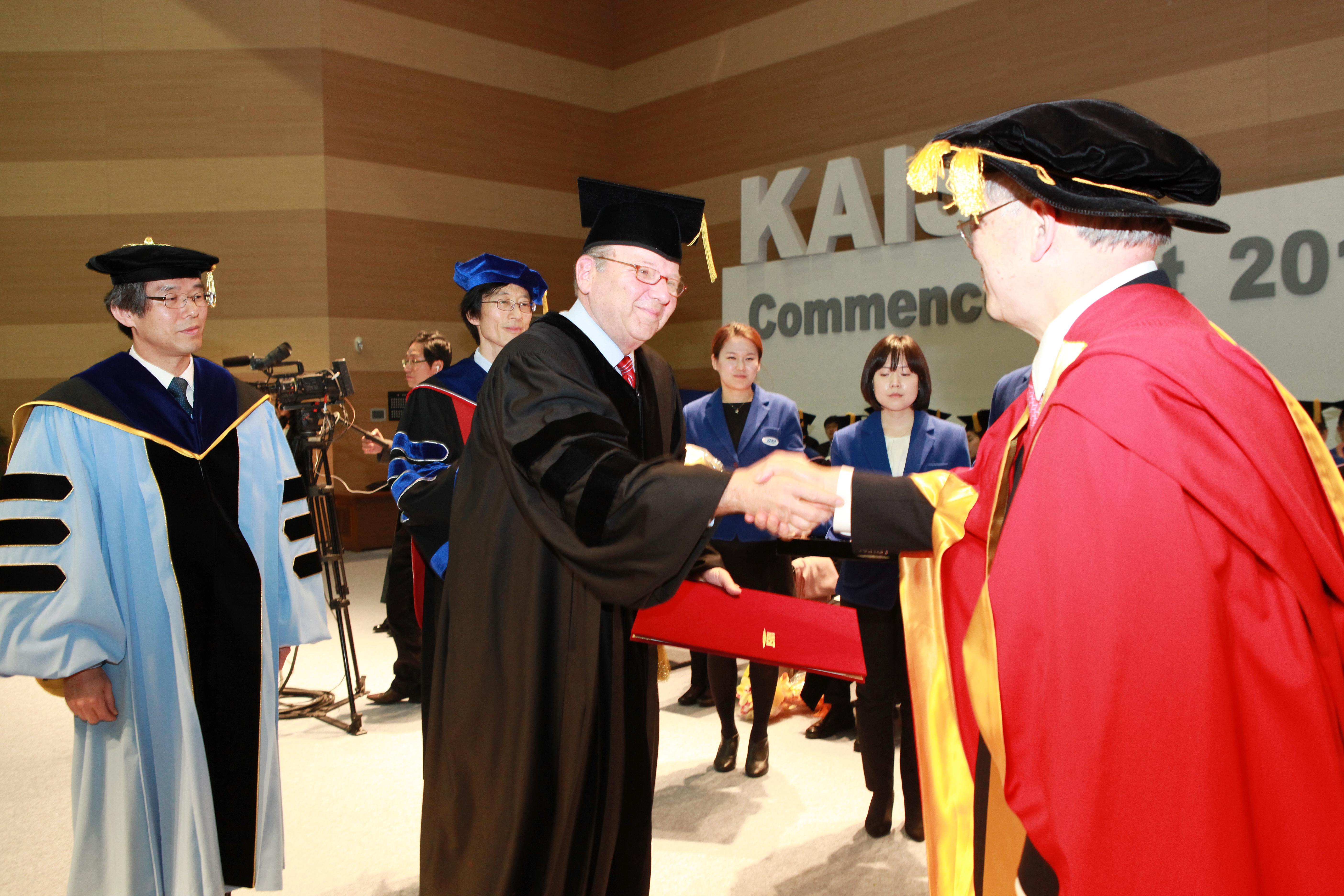 KAIST Confers Honorary Degree to CMU President Cohon
By DongJae Lee
The KAIST Herald Staff Reporter
On February 24, Dr. Jared L. Cohon, President of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), visited KAIST to receive an honorary degree in science and technology and gave a lecture to the university’s students. Dr. Cohon is the eighth president of CMU and has held numerous other public and university positions. During his presidency, CMU has expanded globally and now takes part in joint programs around the world, including those with universities in Korea, Australia, India and Qatar. KAIST and CMU have been collaborating since 2005 in research projects, student and faculty exchange and dual degree programs. Before the 2012 Commencement Ceremony, Dr. Cohon met with The KAIST Herald and other news agencies for an interview.
The interview started with Dr. Cohon giving a brief introduction of CMU. Like KAIST, CMU has a small but special composition and is dedicated to science and technology as well as business and the fine arts. CMU, founded in 1900, is also relatively young by US standards but has nonetheless grown into a world-class university. The power behind this rapid growth can be expressed by four key values: innovation and change, problem-solving, interdisciplinary cooperation, and hard work. The slogan “My heart is in the work” clearly expresses the values of CMU.
One interesting aspect of CMU is its fine arts and business fields. While CMU is dedicated to science and technology, it also has many respected alumni in the aforementioned fields including Andy Warhol, a leading figure in pop art, and Randy Pausch, the author of The Last Lecture. CMU alumni have together won 6 Academy Awards, 22 Emmy Awards, over 100 Tony Awards and 20 Nobel Prizes.
Regarding CMU’s joint projects with KAIST, as well as student and faculty exchanges, Dr. Cohon mentioned joint Ph.D. programs in Civil and Environmental Engineering and Mechanical Engineering and a joint Master’s program in Software Engineering. Currently, the Civil and Environmental Engineering joint Ph.D. program has one participant and the Software Technology Institute joint Master of Software Engineering program has 6 participants.
Dr. Cohon mentioned that receiving an honorary degree in KAIST is a tremendous honor and that he is grateful to be recognized by such a wonderful university like KAIST.
2012.03.23 View 11657
KAIST Confers Honorary Degree to CMU President Cohon
By DongJae Lee
The KAIST Herald Staff Reporter
On February 24, Dr. Jared L. Cohon, President of Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), visited KAIST to receive an honorary degree in science and technology and gave a lecture to the university’s students. Dr. Cohon is the eighth president of CMU and has held numerous other public and university positions. During his presidency, CMU has expanded globally and now takes part in joint programs around the world, including those with universities in Korea, Australia, India and Qatar. KAIST and CMU have been collaborating since 2005 in research projects, student and faculty exchange and dual degree programs. Before the 2012 Commencement Ceremony, Dr. Cohon met with The KAIST Herald and other news agencies for an interview.
The interview started with Dr. Cohon giving a brief introduction of CMU. Like KAIST, CMU has a small but special composition and is dedicated to science and technology as well as business and the fine arts. CMU, founded in 1900, is also relatively young by US standards but has nonetheless grown into a world-class university. The power behind this rapid growth can be expressed by four key values: innovation and change, problem-solving, interdisciplinary cooperation, and hard work. The slogan “My heart is in the work” clearly expresses the values of CMU.
One interesting aspect of CMU is its fine arts and business fields. While CMU is dedicated to science and technology, it also has many respected alumni in the aforementioned fields including Andy Warhol, a leading figure in pop art, and Randy Pausch, the author of The Last Lecture. CMU alumni have together won 6 Academy Awards, 22 Emmy Awards, over 100 Tony Awards and 20 Nobel Prizes.
Regarding CMU’s joint projects with KAIST, as well as student and faculty exchanges, Dr. Cohon mentioned joint Ph.D. programs in Civil and Environmental Engineering and Mechanical Engineering and a joint Master’s program in Software Engineering. Currently, the Civil and Environmental Engineering joint Ph.D. program has one participant and the Software Technology Institute joint Master of Software Engineering program has 6 participants.
Dr. Cohon mentioned that receiving an honorary degree in KAIST is a tremendous honor and that he is grateful to be recognized by such a wonderful university like KAIST.
2012.03.23 View 11657 -
 2012 Reputation Rankings of World Universities by Times Higher Education--KAIST in 81-90
KAIST listed among the world’s most reputable 100 universities
Ranked in the 81st to 90th
The Times Higher Education (THE), a weekly magazine headquartered in London reporting news and issues related to higher education and publishing annually its “World University Rankings,” released on March 15, 2012 the rankings of global universities’ academic reputation, called “2012 World Reputation Rankings.”
KAIST was listed the 81st-90th group, moving up from the 91st to 100th last year. From Korea, only two universities, KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU), were included in the 100 most reputable universities in the world. SNU was in the 51st to 60th band of the list.
The World Reputation Rankings are based on the results of an academic reputation survey carried out by Thompson Reuters. 17,554 respondents from the global academic community from 137 countries participated in the survey of “2012 World Reputation Rankings” that was distributed in April –May 2011.
For the full list of the Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings 2012, please visit the link, http://bit.ly/thewur.
2012.03.20 View 11398
2012 Reputation Rankings of World Universities by Times Higher Education--KAIST in 81-90
KAIST listed among the world’s most reputable 100 universities
Ranked in the 81st to 90th
The Times Higher Education (THE), a weekly magazine headquartered in London reporting news and issues related to higher education and publishing annually its “World University Rankings,” released on March 15, 2012 the rankings of global universities’ academic reputation, called “2012 World Reputation Rankings.”
KAIST was listed the 81st-90th group, moving up from the 91st to 100th last year. From Korea, only two universities, KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU), were included in the 100 most reputable universities in the world. SNU was in the 51st to 60th band of the list.
The World Reputation Rankings are based on the results of an academic reputation survey carried out by Thompson Reuters. 17,554 respondents from the global academic community from 137 countries participated in the survey of “2012 World Reputation Rankings” that was distributed in April –May 2011.
For the full list of the Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings 2012, please visit the link, http://bit.ly/thewur.
2012.03.20 View 11398 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in '2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit'
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in ‘2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit’ held in Chang’an, Beijing
Professor Lee gave a lecture on the vitalization strategy of ‘Bio-Refinery’, which is ‘A bio-based chemical industry to replace fossil fuel-based petro chemistry.
Professor Lee, insisted that for the successful construction of ‘Bio-Refinery’, there should be innovation in all value chain of biomass; biomass producer, bio-refinery business, consumer, government, etc. ▲Securement and distribution of Biomass ▲Development of strain and process for fermentation separation to effectively change biomass into chemical substance and fuel ▲Optimization of transportation and marketing.
During this summit, high-ranking government officials in politics and economics, executives of multicultural and Chinese business participated. From Korea, Do-Young Seung of Manager of technology research of GS and Hang-Deok Roh of laboratory chief of SK Chemical participated as panelist.
World Economy Forum, the gathering of leaders and experts in politics, economics, and policy created a ‘Global Agenda Council’ to find solutions on the issue of ‘sustainable growth of environment of the Earth and humanity’. Professor Lee is the chairperson of ‘Emerging Technologies Global Agenda Council (GAC)’ of Word Economy Forum.
Professor Lee, founder of ‘Systems Metabolic Engineering’, has made remarkable achievements world-wide, including a technology that manipulates metabolic circuit of microorganisms to purify various crude-originated chemical substances into environmentally friendly substances.
Currently, he is working on Systems biology research business in Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Global Frontier Biomass business, Global Frontier Intelligent Bio-system construction and composition, to make progress in metabolic engineering which is essential for the bio-chemical industry.
2012.03.06 View 13804
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in '2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit'
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in ‘2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit’ held in Chang’an, Beijing
Professor Lee gave a lecture on the vitalization strategy of ‘Bio-Refinery’, which is ‘A bio-based chemical industry to replace fossil fuel-based petro chemistry.
Professor Lee, insisted that for the successful construction of ‘Bio-Refinery’, there should be innovation in all value chain of biomass; biomass producer, bio-refinery business, consumer, government, etc. ▲Securement and distribution of Biomass ▲Development of strain and process for fermentation separation to effectively change biomass into chemical substance and fuel ▲Optimization of transportation and marketing.
During this summit, high-ranking government officials in politics and economics, executives of multicultural and Chinese business participated. From Korea, Do-Young Seung of Manager of technology research of GS and Hang-Deok Roh of laboratory chief of SK Chemical participated as panelist.
World Economy Forum, the gathering of leaders and experts in politics, economics, and policy created a ‘Global Agenda Council’ to find solutions on the issue of ‘sustainable growth of environment of the Earth and humanity’. Professor Lee is the chairperson of ‘Emerging Technologies Global Agenda Council (GAC)’ of Word Economy Forum.
Professor Lee, founder of ‘Systems Metabolic Engineering’, has made remarkable achievements world-wide, including a technology that manipulates metabolic circuit of microorganisms to purify various crude-originated chemical substances into environmentally friendly substances.
Currently, he is working on Systems biology research business in Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Global Frontier Biomass business, Global Frontier Intelligent Bio-system construction and composition, to make progress in metabolic engineering which is essential for the bio-chemical industry.
2012.03.06 View 13804 -
 Exhibition of Investment Demonstration on EEWS Research Held
- Five winners of business-planning project exhibition hold exhibition towards thirteen Angel Investors.
Venture capital firm and industry investors are investing for themselves on the Green Growth Project of KAIST, which strives for solutions of global issues, such as; energy depletion, environment pollution and sustainable development.
KAIST awarded the winner of "EEWS business-planning exhibition competition" and held investment demonstration exhibition. The exhibition is opened by the winners of the competition and held towards the firms and inventors encouraging capital on green business project and green technologies.
The venture capital firms that participated in this exhibition were; Coolidge Corner Investment, Dae-Duk Investment Corp, KPM, Locus Capital Partners and Bo-Gwang Investment.
The industry investors that participated were: Samsung C&T Corp, Cheil Industry, Dasan Networks, Hanhwa L&C, thirteen companies in total.
The goal of EEWS Exhibition is to encourage the commercialization of research and development. It was co-hosted by DFJ Athena LLC and Ilshin ventures. The competition was divided into business planning section and business technology section.
Grand prize on green growth went to Professor Joong-Myeon Bae who suggested "Eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cells", runner-up prize went to "Real-time measuring of NOx on Eco-friendly diesels" by Jin-Su Park, the technology director of CIOS.
Grand prize of green technology went to "Highly-refractive, heat resisting hybrimer LED sack’ by Byung-Su Bae, professor of new material engineering, participation award went to ‘ITO-Free touch screen for smart phone’ by Min-yang Yang, professor of the department of Mechanical Engineering.
A representative of KAIST said those of the firms and investors who have gone through commercialization showed interest on the creativity and the high level of the product.
Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of EEWS who supervised the whole exhibition mentioned that, "EEWS Planning Group is consistently going to come up with innovative results” and that “Angel Investors showed enthusiasm. The representatives of Venture capital firm even considered participating as the jury of the competition in the future.”
[Definition]
EEWS stands for Energy depletion, Environment pollution, Water shortages and Sustainability, a project for the solution of such global issues promoted by KAIST.
2012.03.06 View 11511
Exhibition of Investment Demonstration on EEWS Research Held
- Five winners of business-planning project exhibition hold exhibition towards thirteen Angel Investors.
Venture capital firm and industry investors are investing for themselves on the Green Growth Project of KAIST, which strives for solutions of global issues, such as; energy depletion, environment pollution and sustainable development.
KAIST awarded the winner of "EEWS business-planning exhibition competition" and held investment demonstration exhibition. The exhibition is opened by the winners of the competition and held towards the firms and inventors encouraging capital on green business project and green technologies.
The venture capital firms that participated in this exhibition were; Coolidge Corner Investment, Dae-Duk Investment Corp, KPM, Locus Capital Partners and Bo-Gwang Investment.
The industry investors that participated were: Samsung C&T Corp, Cheil Industry, Dasan Networks, Hanhwa L&C, thirteen companies in total.
The goal of EEWS Exhibition is to encourage the commercialization of research and development. It was co-hosted by DFJ Athena LLC and Ilshin ventures. The competition was divided into business planning section and business technology section.
Grand prize on green growth went to Professor Joong-Myeon Bae who suggested "Eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cells", runner-up prize went to "Real-time measuring of NOx on Eco-friendly diesels" by Jin-Su Park, the technology director of CIOS.
Grand prize of green technology went to "Highly-refractive, heat resisting hybrimer LED sack’ by Byung-Su Bae, professor of new material engineering, participation award went to ‘ITO-Free touch screen for smart phone’ by Min-yang Yang, professor of the department of Mechanical Engineering.
A representative of KAIST said those of the firms and investors who have gone through commercialization showed interest on the creativity and the high level of the product.
Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of EEWS who supervised the whole exhibition mentioned that, "EEWS Planning Group is consistently going to come up with innovative results” and that “Angel Investors showed enthusiasm. The representatives of Venture capital firm even considered participating as the jury of the competition in the future.”
[Definition]
EEWS stands for Energy depletion, Environment pollution, Water shortages and Sustainability, a project for the solution of such global issues promoted by KAIST.
2012.03.06 View 11511 -
 Annual Future Knowledge Service International Symposium
Knowledge Service Research preparing for the future knowledge based society has been academically publicized.
The First Annual Future Knowledge Service International Symposium was held in COEX Grand Ball Room Hall by KAIST’s department of Knowledge Service Engineering.
Knowledge Service Engineering is a core component to the future knowledge based society and is the convergent result of decision making, recognition sciences, artificial intelligence, IT, and other knowledge management technologies from each of the industries. Therefore Knowledge Service Engineering will innovate the cooperation and communication between humans and machines thereby forming the center point of the development of knowledge society.
The symposium was attended by 9 important figures from domestic and foreign academia, government representative, and key figures from industries. The symposium was based around debates concerning the role of the Knowledge Service Engineering in the future knowledge based society.
The key note speaker was Chairman of Korea Science and Technology Information Research Institute Park Young Suh and the theme of the speech was ‘Change in Information Environment and Knowledge Service’.
Director of National IT Industry Promotion Agency Kang Hyun Gu gave a lecture on the topic of ‘Important Knowledge Service Policies by National IT Industry Promotion Agency’. And from industry experts, Bradley K. Jensen (Manager of Microsoft Industry-Education Cooperation), Lee Kang Yoon (Research Director at IBM), Choi Yoon Shik (Head of Asia Future Human Resource Institute) proposed a direction for research and gave their account on recent trends of knowledge service from the perspective of onsite experience.
Academic experts like Fred D. Davis (Professor at State University of Arkansas), Jussi Kantola (Professor at KAIST), Kim Young Gul (Professor at KAIST Management University), Yoon Wan Chul (Professor at KAIST Knowledge Service Engineering) gave the recent trends in academic research.
The symposium was held in 3 sessions: ▲Policy of Korean Government ▲Academic Research Trend ▲Recent Trend and Application.
More information can be found at http://kss.kaist.ac.kr
2012.01.31 View 10384
Annual Future Knowledge Service International Symposium
Knowledge Service Research preparing for the future knowledge based society has been academically publicized.
The First Annual Future Knowledge Service International Symposium was held in COEX Grand Ball Room Hall by KAIST’s department of Knowledge Service Engineering.
Knowledge Service Engineering is a core component to the future knowledge based society and is the convergent result of decision making, recognition sciences, artificial intelligence, IT, and other knowledge management technologies from each of the industries. Therefore Knowledge Service Engineering will innovate the cooperation and communication between humans and machines thereby forming the center point of the development of knowledge society.
The symposium was attended by 9 important figures from domestic and foreign academia, government representative, and key figures from industries. The symposium was based around debates concerning the role of the Knowledge Service Engineering in the future knowledge based society.
The key note speaker was Chairman of Korea Science and Technology Information Research Institute Park Young Suh and the theme of the speech was ‘Change in Information Environment and Knowledge Service’.
Director of National IT Industry Promotion Agency Kang Hyun Gu gave a lecture on the topic of ‘Important Knowledge Service Policies by National IT Industry Promotion Agency’. And from industry experts, Bradley K. Jensen (Manager of Microsoft Industry-Education Cooperation), Lee Kang Yoon (Research Director at IBM), Choi Yoon Shik (Head of Asia Future Human Resource Institute) proposed a direction for research and gave their account on recent trends of knowledge service from the perspective of onsite experience.
Academic experts like Fred D. Davis (Professor at State University of Arkansas), Jussi Kantola (Professor at KAIST), Kim Young Gul (Professor at KAIST Management University), Yoon Wan Chul (Professor at KAIST Knowledge Service Engineering) gave the recent trends in academic research.
The symposium was held in 3 sessions: ▲Policy of Korean Government ▲Academic Research Trend ▲Recent Trend and Application.
More information can be found at http://kss.kaist.ac.kr
2012.01.31 View 10384 -
 KAIST Ph.D Mihyun Jang Employed as Professor at Technische Universitat Graz
A Ph.D purely from Korea has been employed as a professor at Technische Universitat Graz.
This is the news of Prof.Mihyun Kang (39) who has graduated from KAIST’s mathematics department. Prof.Kang has transferred on January 2012.
KAIST explained that “it’s the first time for a mathematics Ph.D from Korea has been employed abroad.”
Technische Universitat Graz of Australia is ranked the top third university within the country. It is a global university with 1,700 students from 78 different countries out of its 11,000 students.
Prof. Kang researched mainly theories of combination including random graphing theories, analytical combination theories, and probabilistic combination theories. She has been employed as a lifetime professor through open recruitment where she competed with others through academic debates and interviews.
Technische Universitat Graz valued Prof. Kang’s research highly made her the department head of the ‘Optimization and Discrete Mathematics department’ to create an environment where she could continuously research.
Prof. Kang graduated from Jeju university majoring math educations and did her graduate studies in KAIST. She is a purely ‘Korean’ Ph.D. After her studies, she worked for Germany’s Humboldt University and Freie Universitat Berlin. In 2007, she was able to be employed as a professor in Germany, and in 2008, she was chosen as a Heisenberg fellow.
Prof. Kang who had her research achievements recognized in Germany and Austria was also offered seat as professor in Ludwig Masximilan University of Germany and Alpenadria University in Austria, but chose Technische Universitat Graz.
2012.01.31 View 12486
KAIST Ph.D Mihyun Jang Employed as Professor at Technische Universitat Graz
A Ph.D purely from Korea has been employed as a professor at Technische Universitat Graz.
This is the news of Prof.Mihyun Kang (39) who has graduated from KAIST’s mathematics department. Prof.Kang has transferred on January 2012.
KAIST explained that “it’s the first time for a mathematics Ph.D from Korea has been employed abroad.”
Technische Universitat Graz of Australia is ranked the top third university within the country. It is a global university with 1,700 students from 78 different countries out of its 11,000 students.
Prof. Kang researched mainly theories of combination including random graphing theories, analytical combination theories, and probabilistic combination theories. She has been employed as a lifetime professor through open recruitment where she competed with others through academic debates and interviews.
Technische Universitat Graz valued Prof. Kang’s research highly made her the department head of the ‘Optimization and Discrete Mathematics department’ to create an environment where she could continuously research.
Prof. Kang graduated from Jeju university majoring math educations and did her graduate studies in KAIST. She is a purely ‘Korean’ Ph.D. After her studies, she worked for Germany’s Humboldt University and Freie Universitat Berlin. In 2007, she was able to be employed as a professor in Germany, and in 2008, she was chosen as a Heisenberg fellow.
Prof. Kang who had her research achievements recognized in Germany and Austria was also offered seat as professor in Ludwig Masximilan University of Germany and Alpenadria University in Austria, but chose Technische Universitat Graz.
2012.01.31 View 12486 -
 Quantum Mechanical Calculation Theory Developed
An Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory, based on the widely used quantum mechanical principles and yet accurate and with shortened calculation period, was developed by Korean research team.
*Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory: Theory that proves that it is possible to calculate energy and properties with only simple wave equations and electron densities.
The research was conducted by Professor Jeong Yoo Sung (Graduate School of EEWS) and Professor William Goddard with support from WCU Foster Project initiated by Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and Korea Research Foundation. The result was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Journal.
The research team corrected the error when performing quantum calculations that arises from the length of calculation time and incorrect assumptions and developed a theory and algorithm that is more accurate and faster. The use of wave equations in quantum mechanical calculations results in high accuracy but there is a rapid increase in calculation time and is therefore difficult to implement in large molecules with hundreds, or thousands of atoms. By implementing a low electron density variable with relatively less calculation work, the size of calculable molecule increases but the accuracy decreases.
The team focused on the interaction between electrons with different spins to improve upon the speed of calculation in the conventional accurate calculation. The team used the fact that the interaction between electrons with different spins increases as it comes closer together in accordance with the Pauli’s Exclusion Principle.
In addition the interaction between electrons are local and therefore can ignore the interactions between far away electrons and still get the total energy value. The team also took advantage of this fact and developed the algorithm that decreased calculation time hundredth fold.
Professor Jeong commented that, “So far most of the domestic achievements were made by focusing on integrative researches by calculation science and material design communities but these involved short time frames. In areas that required lengthy time frames like fundamentals and software development, there was no competitive advantage. However this research is significant in that a superior solution was developed domestically”.
2012.01.31 View 12969
Quantum Mechanical Calculation Theory Developed
An Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory, based on the widely used quantum mechanical principles and yet accurate and with shortened calculation period, was developed by Korean research team.
*Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory: Theory that proves that it is possible to calculate energy and properties with only simple wave equations and electron densities.
The research was conducted by Professor Jeong Yoo Sung (Graduate School of EEWS) and Professor William Goddard with support from WCU Foster Project initiated by Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and Korea Research Foundation. The result was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Journal.
The research team corrected the error when performing quantum calculations that arises from the length of calculation time and incorrect assumptions and developed a theory and algorithm that is more accurate and faster. The use of wave equations in quantum mechanical calculations results in high accuracy but there is a rapid increase in calculation time and is therefore difficult to implement in large molecules with hundreds, or thousands of atoms. By implementing a low electron density variable with relatively less calculation work, the size of calculable molecule increases but the accuracy decreases.
The team focused on the interaction between electrons with different spins to improve upon the speed of calculation in the conventional accurate calculation. The team used the fact that the interaction between electrons with different spins increases as it comes closer together in accordance with the Pauli’s Exclusion Principle.
In addition the interaction between electrons are local and therefore can ignore the interactions between far away electrons and still get the total energy value. The team also took advantage of this fact and developed the algorithm that decreased calculation time hundredth fold.
Professor Jeong commented that, “So far most of the domestic achievements were made by focusing on integrative researches by calculation science and material design communities but these involved short time frames. In areas that required lengthy time frames like fundamentals and software development, there was no competitive advantage. However this research is significant in that a superior solution was developed domestically”.
2012.01.31 View 12969 -
 2011 IT Convergence International Workshop
KAIST held the 2011 IT Convergence International Workshop on Future Mobile Service & Service Technology.
The workshop was attended by Kim Byoung Il (Chairman of National Science and Technology Commission), Koichi Asatani (Professor at Kogakuin University), Jay H. Eum (representative of TransLink Capital), among 15 other experts from government, scholar, industry, and IT defense.
The keynote speaker, Chairman Kim Byoung Il, gave a speech on Industry Development Strategy for Software. Professor Koichi Asatani gave a presentation on information communication technology and future trend of future network and service. And Jay H. Eum will be giving a presentation on the technological venture firm strategy that was so successful in Silicon Valley.
There will be presentations and debate on mobile services, IT security and defense, IT convergence technology, software technology and other future IT convergence technologies.
2012.01.31 View 7987
2011 IT Convergence International Workshop
KAIST held the 2011 IT Convergence International Workshop on Future Mobile Service & Service Technology.
The workshop was attended by Kim Byoung Il (Chairman of National Science and Technology Commission), Koichi Asatani (Professor at Kogakuin University), Jay H. Eum (representative of TransLink Capital), among 15 other experts from government, scholar, industry, and IT defense.
The keynote speaker, Chairman Kim Byoung Il, gave a speech on Industry Development Strategy for Software. Professor Koichi Asatani gave a presentation on information communication technology and future trend of future network and service. And Jay H. Eum will be giving a presentation on the technological venture firm strategy that was so successful in Silicon Valley.
There will be presentations and debate on mobile services, IT security and defense, IT convergence technology, software technology and other future IT convergence technologies.
2012.01.31 View 7987 -
 Closer to the Dream: Graphene
A technique that allows easy and larger observation area of graphene’s crystal face was developed by Korean Research Team.
The research team, led by Professor Jeong Hui Tae (KAIST), consists of Doctorate candidate Kim Dae Woo, Dr. Kim Yoon Ho (primary author), Doctorate candidate Jeong Hyun Soo. The research is supported by WCU (World Class Research University) Development Plan, Mid-Aged Researcher Support Business and was published in the online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
(Dissertation: Direct visualization of large0area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency)
Professor Jeong’s team used the optical property of the liquid display used in LCD to visualize the size and shape of the single crystals along a flat surface. The visualization of the single crystal allowed the measurement of a near theoretical value of electrical conductivity of graphene.
Graphene has great electrical conductivity, transparent, mechanically stable, flexible, and is therefore regarded as the next generation electrical material. However the polycrystalinity of graphene meant that the actual electrical, mechanical properties were lower than the theoretical values. The reason was thought to be because of the size of the crystal faces and boundary structures.
Therefore, in order to create graphene that has good properties, observing the domain and boundary of graphene crystal faces is essential.
The new technique developed by the research team is another step towards commercializing transparent electrodes, flexible display, and electric materials like solar cells.
2012.01.31 View 12109
Closer to the Dream: Graphene
A technique that allows easy and larger observation area of graphene’s crystal face was developed by Korean Research Team.
The research team, led by Professor Jeong Hui Tae (KAIST), consists of Doctorate candidate Kim Dae Woo, Dr. Kim Yoon Ho (primary author), Doctorate candidate Jeong Hyun Soo. The research is supported by WCU (World Class Research University) Development Plan, Mid-Aged Researcher Support Business and was published in the online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
(Dissertation: Direct visualization of large0area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency)
Professor Jeong’s team used the optical property of the liquid display used in LCD to visualize the size and shape of the single crystals along a flat surface. The visualization of the single crystal allowed the measurement of a near theoretical value of electrical conductivity of graphene.
Graphene has great electrical conductivity, transparent, mechanically stable, flexible, and is therefore regarded as the next generation electrical material. However the polycrystalinity of graphene meant that the actual electrical, mechanical properties were lower than the theoretical values. The reason was thought to be because of the size of the crystal faces and boundary structures.
Therefore, in order to create graphene that has good properties, observing the domain and boundary of graphene crystal faces is essential.
The new technique developed by the research team is another step towards commercializing transparent electrodes, flexible display, and electric materials like solar cells.
2012.01.31 View 12109 -
 MOU: KAIST-Korea Internet & Security Agency
KAIST signed a MOU with the Korea Internet & Security Agency for the development of IT and International Security.
As a result of the MOU interaction in ▲Exchange of personnel and materials for cooperative research for information protection ▲Information protection policy and technology ▲Education and training for developing information protection personnel, will be increased.
Director of Cyber Security Research Center Joo Dae Joon commented, “Cyber-attack on national infrastructure like DDOS attacks can threaten the nation’s system” and that “the two institutes will establish a response system against cyber-attacks and train experts in information protection”.
2012.01.31 View 8326
MOU: KAIST-Korea Internet & Security Agency
KAIST signed a MOU with the Korea Internet & Security Agency for the development of IT and International Security.
As a result of the MOU interaction in ▲Exchange of personnel and materials for cooperative research for information protection ▲Information protection policy and technology ▲Education and training for developing information protection personnel, will be increased.
Director of Cyber Security Research Center Joo Dae Joon commented, “Cyber-attack on national infrastructure like DDOS attacks can threaten the nation’s system” and that “the two institutes will establish a response system against cyber-attacks and train experts in information protection”.
2012.01.31 View 8326 -
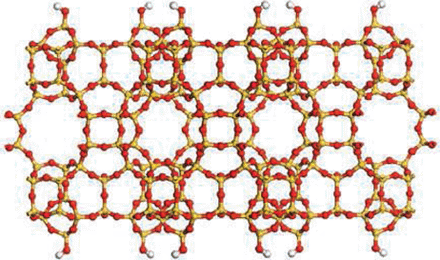 Ten Breakthroughs of the Year 2011 by Science
Porous Zeolite Crytals
Science, an internationally renowned scientific journal based in the US, has recently released a special issue of “Breakthrough of the Year, 2011,” dated December 23, 2011. In the issue, the journal introduces ten most important research breakthroughs made this year, and Professor Ryong Ryoo, Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was one of the scientists behind such notable advancements in 2011. Professor Ryoo has been highly regarded internationally for his research on the development of synthetic version of zeolites, a family of porous minerals that is widely used for products such as laundry detergents, cat litters, etc. Below is the article from Science, stating the zeolite research:
For Science’s “Breakthrough of the Year, 2011”, please go to:
http://www.sciencemag.org/site/special/btoy2011/
[Excerpt from the December 23, 2011 Issue of Science]
Industrial Molecules, Tailor-Made
If you ever doubt that chemistry is still a creative endeavor, just look at zeolites. This family of porous minerals was first discovered in 1756. They"re formed from different arrangements of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen atoms that crystallize into holey structures pocked with a perfect arrangement of pores. Over the past 250 years, 40 natural zeolites have been discovered, and chemists have chipped in roughly 150 more synthetic versions.
View larger version:
In this page
In a new window
Assembly required.
Porous zeolite crystals are widely used as filters and catalysts. This year, researchers found new ways to tailor the size of their pores and create thinner, cheaper membranes.
CREDIT: K. VAROON ET AL., SCIENCE334, 6052 (7 OCTOBER 2001)
This abundance isn"t just for show. Three million tons of zeolites are produced every year for use in laundry detergents, cat litter, and many other products. But zeolites really strut their stuff in two uses: as catalysts and molecular sieves. Oil refineries use zeolite catalysts to break down long hydrocarbon chains in oil into the shorter, volatile hydrocarbons in gasoline. And the minerals" small, regularly arranged pores make them ideal filters for purifying everything from the air on spaceships to the contaminated water around the nuclear reactors destroyed earlier this year in Fukushima, Japan.
Zeolites have their limitations, though. Their pores are almost universally tiny, making it tough to use them as catalysts for large molecules. And they"re difficult to form into ultrathin membranes, which researchers would like to do to enable cheaper separations. But progress by numerous teams on zeolite synthesis this year gave this “mature” area of chemistry new life.
Researchers in South Korea crafted a family of zeolites in which the usual network of small pores is surrounded by walls holed with larger voids. That combination of large and small pores should lead to catalysts for numerous large organic molecules.
Labs in Spain and China produced related large- and small-pore zeolites by using a combination of inorganic and organic materials to guide the structures as they formed.
Meanwhile, researchers in France and Germany discovered that, by carefully controlling growth conditions, they could form a large-pore zeolite without the need for the expensive organic compounds typically used to guide their architecture as they grow. The advance opens the way for cheaper catalysts. In yet another lab, researchers in Minnesota came up with a new route for making ultrathin zeolite membranes, which are likely to be useful as a wide variety of chemically selective filters.
This surge of molecular wizardry provides a vivid reminder that the creativity of chemists keeps their field ever young.
Related References and Web Sites
2011.12.23 View 13563
Ten Breakthroughs of the Year 2011 by Science
Porous Zeolite Crytals
Science, an internationally renowned scientific journal based in the US, has recently released a special issue of “Breakthrough of the Year, 2011,” dated December 23, 2011. In the issue, the journal introduces ten most important research breakthroughs made this year, and Professor Ryong Ryoo, Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was one of the scientists behind such notable advancements in 2011. Professor Ryoo has been highly regarded internationally for his research on the development of synthetic version of zeolites, a family of porous minerals that is widely used for products such as laundry detergents, cat litters, etc. Below is the article from Science, stating the zeolite research:
For Science’s “Breakthrough of the Year, 2011”, please go to:
http://www.sciencemag.org/site/special/btoy2011/
[Excerpt from the December 23, 2011 Issue of Science]
Industrial Molecules, Tailor-Made
If you ever doubt that chemistry is still a creative endeavor, just look at zeolites. This family of porous minerals was first discovered in 1756. They"re formed from different arrangements of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen atoms that crystallize into holey structures pocked with a perfect arrangement of pores. Over the past 250 years, 40 natural zeolites have been discovered, and chemists have chipped in roughly 150 more synthetic versions.
View larger version:
In this page
In a new window
Assembly required.
Porous zeolite crystals are widely used as filters and catalysts. This year, researchers found new ways to tailor the size of their pores and create thinner, cheaper membranes.
CREDIT: K. VAROON ET AL., SCIENCE334, 6052 (7 OCTOBER 2001)
This abundance isn"t just for show. Three million tons of zeolites are produced every year for use in laundry detergents, cat litter, and many other products. But zeolites really strut their stuff in two uses: as catalysts and molecular sieves. Oil refineries use zeolite catalysts to break down long hydrocarbon chains in oil into the shorter, volatile hydrocarbons in gasoline. And the minerals" small, regularly arranged pores make them ideal filters for purifying everything from the air on spaceships to the contaminated water around the nuclear reactors destroyed earlier this year in Fukushima, Japan.
Zeolites have their limitations, though. Their pores are almost universally tiny, making it tough to use them as catalysts for large molecules. And they"re difficult to form into ultrathin membranes, which researchers would like to do to enable cheaper separations. But progress by numerous teams on zeolite synthesis this year gave this “mature” area of chemistry new life.
Researchers in South Korea crafted a family of zeolites in which the usual network of small pores is surrounded by walls holed with larger voids. That combination of large and small pores should lead to catalysts for numerous large organic molecules.
Labs in Spain and China produced related large- and small-pore zeolites by using a combination of inorganic and organic materials to guide the structures as they formed.
Meanwhile, researchers in France and Germany discovered that, by carefully controlling growth conditions, they could form a large-pore zeolite without the need for the expensive organic compounds typically used to guide their architecture as they grow. The advance opens the way for cheaper catalysts. In yet another lab, researchers in Minnesota came up with a new route for making ultrathin zeolite membranes, which are likely to be useful as a wide variety of chemically selective filters.
This surge of molecular wizardry provides a vivid reminder that the creativity of chemists keeps their field ever young.
Related References and Web Sites
2011.12.23 View 13563