-
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 8004
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 8004 -
 Center for Industrial Future Strategy Takes Off at KAIST
(Professor Wonjoon Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management)
Professors from KAIST and major international universities launched a mega-scale research center focusing on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, named the Center for Industrial Future Strategy (CIFS).
This center is funded by the National Research Foundation Korea and will receive 2.25 billion KRW over four years.
Directed by Professor Wonjoon Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management, the center is comprised of ten top-tier researchers and four research associates, including Professor Hawoon Jeong (KAIST), Professor Scott Stern (MIT), Professor Aaron Chatterji (Duke University), Dr. Yong Suk Lee (Stanford University) and Professor Hyejin Youn (Northwestern University).
The center will conduct research on technical, social, and economic changes derived by a new paradigm of technological innovation.
Moreover, they will study policies and strategies in relation to innovation in the corporate and government sectors to achieve economic growth in a sustainable manner. The center will also propose policies and strategies in a variety of economic and industrial settings to establish a sustainable and global innovation ecosystem.
To carry out these studies successfully, CIFS will further expand the AIEA-NBER Conference with the Asia Innovation and Entrepreneurship Association (AIEA) and the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) in which numerous Nobel Laureates in Economics are affiliated. They will also comprise thematic research teams with co-founding universities to build stronger cooperation with one another.
Besides the academic cooperation, the center will also build partnerships with international organizations, including the Asian Development Bank and the Inter-American Development Bank to carry out their missions at multilateral levels.
Their research topics include changes to value chains in a new paradigm of technological innovation, labor market changes in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, sharing economies and social interests, big data, artificial intelligence & privacy policy, and innovation & ethical and institutional countermeasures to AI technology.
Professor Kim said, “The new paradigm of technological innovation is evolving social, economic, and industrial structures, such as R&D, industry, technology, labor, finance, and institutions. The Center will contribute to proposing policies and strategies so that Korea, as well as the international community, can take appropriate measures to these big changes.”
2018.09.11 View 10947
Center for Industrial Future Strategy Takes Off at KAIST
(Professor Wonjoon Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management)
Professors from KAIST and major international universities launched a mega-scale research center focusing on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, named the Center for Industrial Future Strategy (CIFS).
This center is funded by the National Research Foundation Korea and will receive 2.25 billion KRW over four years.
Directed by Professor Wonjoon Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management, the center is comprised of ten top-tier researchers and four research associates, including Professor Hawoon Jeong (KAIST), Professor Scott Stern (MIT), Professor Aaron Chatterji (Duke University), Dr. Yong Suk Lee (Stanford University) and Professor Hyejin Youn (Northwestern University).
The center will conduct research on technical, social, and economic changes derived by a new paradigm of technological innovation.
Moreover, they will study policies and strategies in relation to innovation in the corporate and government sectors to achieve economic growth in a sustainable manner. The center will also propose policies and strategies in a variety of economic and industrial settings to establish a sustainable and global innovation ecosystem.
To carry out these studies successfully, CIFS will further expand the AIEA-NBER Conference with the Asia Innovation and Entrepreneurship Association (AIEA) and the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) in which numerous Nobel Laureates in Economics are affiliated. They will also comprise thematic research teams with co-founding universities to build stronger cooperation with one another.
Besides the academic cooperation, the center will also build partnerships with international organizations, including the Asian Development Bank and the Inter-American Development Bank to carry out their missions at multilateral levels.
Their research topics include changes to value chains in a new paradigm of technological innovation, labor market changes in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, sharing economies and social interests, big data, artificial intelligence & privacy policy, and innovation & ethical and institutional countermeasures to AI technology.
Professor Kim said, “The new paradigm of technological innovation is evolving social, economic, and industrial structures, such as R&D, industry, technology, labor, finance, and institutions. The Center will contribute to proposing policies and strategies so that Korea, as well as the international community, can take appropriate measures to these big changes.”
2018.09.11 View 10947 -
 Electron Heating in Weakly Ionized Collisional Plasmas
(from left: Professor Wonho Choe and Research Professor Sanghoo Park)
A KAIST research team successfully identified the underlying principles behind electron heating, which is one of the most important phenomena in plasmas. As the electric heating determines wide range of physical and chemical properties of plasmas, this outcome will allow relevant industries to extend and effectively customize a range of plasma characteristics for their specific needs.
Plasma, frequently called the fourth state of matter, can be mostly formed by artificially energizing gases in standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atm) range. Among the many types of plasma, atmospheric-pressure plasmas have been gaining a great deal of attention due to their unique features and applicability in various scientific and industrial fields.
Because plasma characteristics strongly depends on gas pressure in the sub-atmospheric to atmospheric pressure range, characterizing the plasma at different pressures is a prerequisite for understanding the fundamental principles of plasmas and for their industrial applications.
In that sense, information on the spatio-temporal evolution in the electron density and temperature is very important because various physical and chemical reactions within a plasma arise from electrons. Hence, electron heating has been an interesting topic in the field of plasma.
Because collisions between free electrons and neutral gases are frequent under atmospheric-pressure conditions, there are physical limits to measuring the electron density and temperature in plasmas using conventional diagnostic tools, thus the principles behind free electron heating could not be experimentally revealed.
Moreover, lacking information on a key parameter of electron heating and its controlling methods is troublesome and limit improving the reactivity and applicability of such plasmas.
To address these issues, Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering employed neutral bremsstrahlung-based electron diagnostics in order to accurately examine the electron density and temperature in target plasmas. In addition, a novel imaging diagnostics for two dimensional distribution of electron information was developed.
Using the diagnostic technique they developed, the team measured the nanosecond-resolved electron temperature in weakly ionized collisional plasmas, and they succeeded in revealing the spatiotemporal distribution and the fundamental principle involved in the electron heating process.
The team successfully revealed the fundamental principle of the electron heating process under atmospheric to sub-atmospheric pressure (0.25-1atm) conditions through conducting the experiment on the spatiotemporal evolution of electron temperature.
Their findings of the underlying research data on free electrons in weakly ionized collisional plasmas will contribute to enhancing the field of plasma science and their commercial applications.
Professor Choe said, “The results of this study provide a clear picture of electron heating in weakly ionized plasmas under conditions where collisions between free electrons and neutral particles are frequent. We hope this study will be informative and helpful in utilizing and commercializing atmospheric-pressure plasma sources in the near future.”
Articles related to this research, led by Research Professor Sanghoo Park, were published in Scientific Reports on May 14 and July 5.
Figure 1. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of the electron heating structure. Spatiotemporal evolution of 514.5-nm continuum radiation,Te, Ar I emission
Figure 2. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of electron heating. Spatiotemporal evolution of neutral bremsstrahlung at 514.5 nm
2018.09.10 View 7112
Electron Heating in Weakly Ionized Collisional Plasmas
(from left: Professor Wonho Choe and Research Professor Sanghoo Park)
A KAIST research team successfully identified the underlying principles behind electron heating, which is one of the most important phenomena in plasmas. As the electric heating determines wide range of physical and chemical properties of plasmas, this outcome will allow relevant industries to extend and effectively customize a range of plasma characteristics for their specific needs.
Plasma, frequently called the fourth state of matter, can be mostly formed by artificially energizing gases in standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atm) range. Among the many types of plasma, atmospheric-pressure plasmas have been gaining a great deal of attention due to their unique features and applicability in various scientific and industrial fields.
Because plasma characteristics strongly depends on gas pressure in the sub-atmospheric to atmospheric pressure range, characterizing the plasma at different pressures is a prerequisite for understanding the fundamental principles of plasmas and for their industrial applications.
In that sense, information on the spatio-temporal evolution in the electron density and temperature is very important because various physical and chemical reactions within a plasma arise from electrons. Hence, electron heating has been an interesting topic in the field of plasma.
Because collisions between free electrons and neutral gases are frequent under atmospheric-pressure conditions, there are physical limits to measuring the electron density and temperature in plasmas using conventional diagnostic tools, thus the principles behind free electron heating could not be experimentally revealed.
Moreover, lacking information on a key parameter of electron heating and its controlling methods is troublesome and limit improving the reactivity and applicability of such plasmas.
To address these issues, Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering employed neutral bremsstrahlung-based electron diagnostics in order to accurately examine the electron density and temperature in target plasmas. In addition, a novel imaging diagnostics for two dimensional distribution of electron information was developed.
Using the diagnostic technique they developed, the team measured the nanosecond-resolved electron temperature in weakly ionized collisional plasmas, and they succeeded in revealing the spatiotemporal distribution and the fundamental principle involved in the electron heating process.
The team successfully revealed the fundamental principle of the electron heating process under atmospheric to sub-atmospheric pressure (0.25-1atm) conditions through conducting the experiment on the spatiotemporal evolution of electron temperature.
Their findings of the underlying research data on free electrons in weakly ionized collisional plasmas will contribute to enhancing the field of plasma science and their commercial applications.
Professor Choe said, “The results of this study provide a clear picture of electron heating in weakly ionized plasmas under conditions where collisions between free electrons and neutral particles are frequent. We hope this study will be informative and helpful in utilizing and commercializing atmospheric-pressure plasma sources in the near future.”
Articles related to this research, led by Research Professor Sanghoo Park, were published in Scientific Reports on May 14 and July 5.
Figure 1. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of the electron heating structure. Spatiotemporal evolution of 514.5-nm continuum radiation,Te, Ar I emission
Figure 2. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of electron heating. Spatiotemporal evolution of neutral bremsstrahlung at 514.5 nm
2018.09.10 View 7112 -
 KAIST Core Technology Fair Accelerates Commercialization
(President Shin makes opening remarks at the KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day in Seoul.)
Technology commercialization is the one of the innovation initiatives KAIST is strongly driving. KAIST showcased six core technologies developed by KAIST research teams during the 2018 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day on September 10 at Coex in Seoul. More than 300 investors, buyers, and venture capitalists showed up for the fair. This is the second fair organized as one of the strategic innovation initiatives that KAIST is promoting.
Developers of key technologies selected in the fields of bio, nano, AI, and semiconductors presented their distinct technological prowess to the attendees. The technologies are highly relevant for the new industrial environment trends in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The 15-member committee comprised of patent attorneys, venture capitalists, and commercialization specialists selected the six core technologies based on their innovativeness, applicability, and marketability. The Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) plans to offer buyers various services for developing business models, business strategy analysis, and marketing at home and abroad. The six core technologies featured at the fair include:
- Novel technology of a nano patterning platform by Professor Hee Tae Chung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Anticancer therapeutic candidate materials strengthening immune function by Professor Byung Sok Choi from the Department of Chemistry
- Biofuel mass production using micro-organisms by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Compact single-shot hyperspectral camera technology by Min Hyuk Kim from the School of Computing
- AI-powered high speed ultra-high definition upscaling technology by Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering - A radiation strong MOSFET device by Hee Chul Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering
President Sung-Chul Shin stressed in his opening remarks that universities should make contributions to economic development through innovation. “Global leading universities are taking an instrumental role in creating new jobs and economic growth with their own technologies. KAIST, as the leading university in Korea, is accelerating the commercialization of technology produced internally to create a meaningful impact for the economy as well as the job market beyond Korea,” he said.
“We are aiming for the global market, not just in Korea. I want KAIST to be a global value creator that can contribute to the betterment of the world through our innovations,” he added.
2018.09.10 View 6672
KAIST Core Technology Fair Accelerates Commercialization
(President Shin makes opening remarks at the KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day in Seoul.)
Technology commercialization is the one of the innovation initiatives KAIST is strongly driving. KAIST showcased six core technologies developed by KAIST research teams during the 2018 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day on September 10 at Coex in Seoul. More than 300 investors, buyers, and venture capitalists showed up for the fair. This is the second fair organized as one of the strategic innovation initiatives that KAIST is promoting.
Developers of key technologies selected in the fields of bio, nano, AI, and semiconductors presented their distinct technological prowess to the attendees. The technologies are highly relevant for the new industrial environment trends in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The 15-member committee comprised of patent attorneys, venture capitalists, and commercialization specialists selected the six core technologies based on their innovativeness, applicability, and marketability. The Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) plans to offer buyers various services for developing business models, business strategy analysis, and marketing at home and abroad. The six core technologies featured at the fair include:
- Novel technology of a nano patterning platform by Professor Hee Tae Chung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Anticancer therapeutic candidate materials strengthening immune function by Professor Byung Sok Choi from the Department of Chemistry
- Biofuel mass production using micro-organisms by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Compact single-shot hyperspectral camera technology by Min Hyuk Kim from the School of Computing
- AI-powered high speed ultra-high definition upscaling technology by Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering - A radiation strong MOSFET device by Hee Chul Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering
President Sung-Chul Shin stressed in his opening remarks that universities should make contributions to economic development through innovation. “Global leading universities are taking an instrumental role in creating new jobs and economic growth with their own technologies. KAIST, as the leading university in Korea, is accelerating the commercialization of technology produced internally to create a meaningful impact for the economy as well as the job market beyond Korea,” he said.
“We are aiming for the global market, not just in Korea. I want KAIST to be a global value creator that can contribute to the betterment of the world through our innovations,” he added.
2018.09.10 View 6672 -
 There Won't Be a Singularity: Professor Jerry Kaplan
(Professor Jerry Kaplan gave a lecture titled, Artificial Intelligence: Think Again at KAIST)
“People are so concerned about super intelligence, but the singularity will not happen,” said Professor Jerry Kaplan at Stanford University, an AI guru and Silicon Valley entrepreneur during a lecture at KAIST. He visited KAIST to give a lecture on Artificial Intelligence: Think Again on September 6.
Professor Kaplan said that some people argue that Korea’s AI research is behind the US and China but he doesn’t agree with that. “Korea is the most digitally connected one and has the world’s best engineers in the field. Korean companies are building products the consumers really like at reasonable prices. Those are attracting global consumers,” he added.
Instead of investing loads of money on AI research, he suggested three tasks for Korea taking a better position in the field of AI: Collecting and saving lots of data; training engineers, not the research talents in AI; and investing in AI infrastructure and relieving regulations by the government.
Referring to AI hype, Professor Kaplan argued that machines are intelligent, but they do not think in the way humans can, and assured the audience that the singularity some futurists predict will not be coming. He said, “Machine learning is a tool extracting useful information, but it does not mean they are so smart that they are taking over the world.”
(Professor Jerry Kaplan gave a lecture titled, Artificial Intelligence: Think Again at KAIST)
But what has made us believing AI myths? He first began pointing out how AI has been mythicized by three major drivers. Those are the entertainment industry, the popular media, and the AI community all wanting to attract more public attention and prestige. The abovementioned drivers are falsely making robots more human and are adding human characteristics.
Instead of being captivated by those AI myths and thinking about how to save the world from robots, he strongly argued, “We need to develop standards for the unintended side effects from AI.” To provide machines socially and ethically mingling with the human world, he believed principles should be set as follows: Define the Safe Operating Envelope (SOE), “safe modes” when out of bounds, study human behavior programmatically, certification and licensing standards, limitations on machine “agency,” and basic computational ethics such as when it is okay to break the law.
Professor Kaplan gave a positive view of AI for humans. “The future will be bright, thanks to AI. They do difficult work and help us and that will drive wealth and quality of life. The rich might get richer, but the benefits will spread throughout the people. It is time to think of innovative ways for using AI for building better world,” he concluded.
2018.09.10 View 5641
There Won't Be a Singularity: Professor Jerry Kaplan
(Professor Jerry Kaplan gave a lecture titled, Artificial Intelligence: Think Again at KAIST)
“People are so concerned about super intelligence, but the singularity will not happen,” said Professor Jerry Kaplan at Stanford University, an AI guru and Silicon Valley entrepreneur during a lecture at KAIST. He visited KAIST to give a lecture on Artificial Intelligence: Think Again on September 6.
Professor Kaplan said that some people argue that Korea’s AI research is behind the US and China but he doesn’t agree with that. “Korea is the most digitally connected one and has the world’s best engineers in the field. Korean companies are building products the consumers really like at reasonable prices. Those are attracting global consumers,” he added.
Instead of investing loads of money on AI research, he suggested three tasks for Korea taking a better position in the field of AI: Collecting and saving lots of data; training engineers, not the research talents in AI; and investing in AI infrastructure and relieving regulations by the government.
Referring to AI hype, Professor Kaplan argued that machines are intelligent, but they do not think in the way humans can, and assured the audience that the singularity some futurists predict will not be coming. He said, “Machine learning is a tool extracting useful information, but it does not mean they are so smart that they are taking over the world.”
(Professor Jerry Kaplan gave a lecture titled, Artificial Intelligence: Think Again at KAIST)
But what has made us believing AI myths? He first began pointing out how AI has been mythicized by three major drivers. Those are the entertainment industry, the popular media, and the AI community all wanting to attract more public attention and prestige. The abovementioned drivers are falsely making robots more human and are adding human characteristics.
Instead of being captivated by those AI myths and thinking about how to save the world from robots, he strongly argued, “We need to develop standards for the unintended side effects from AI.” To provide machines socially and ethically mingling with the human world, he believed principles should be set as follows: Define the Safe Operating Envelope (SOE), “safe modes” when out of bounds, study human behavior programmatically, certification and licensing standards, limitations on machine “agency,” and basic computational ethics such as when it is okay to break the law.
Professor Kaplan gave a positive view of AI for humans. “The future will be bright, thanks to AI. They do difficult work and help us and that will drive wealth and quality of life. The rich might get richer, but the benefits will spread throughout the people. It is time to think of innovative ways for using AI for building better world,” he concluded.
2018.09.10 View 5641 -
 NEREC Summer Program Keeps Fellows Thinking, Engaged in Nuclear Nonproliferation
Nuclear technology is more than just technology. It is the fruit of the most advanced science and technology. It also requires high standards of policymaking and global cooperation for benefiting the technology.
As part of the fifth annual Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) Summer Fellows Program at KAIST, 24 students from 15 countries participated in six-week intensive education and training program. NEREC is the only university-based center dedicated to nuclear nonproliferation education and research established in 2014.
The program, which provides multidisciplinary lectures and seminars on nuclear technology and policy as well as international relations, was designed to nurture global nuclear technology experts well equipped in three areas: in-depth knowledge of technology, applicability gained from sound policy building, and negotiating for international cooperation. It now has grown into the most popular summer program at KAIST.
During the program from July 6 to August 18, participants were able to engage in enriching and stimulating learning experiences in tandem with policies and technology for the utilization and provision of peaceful and safe nuclear technology.
Participating fellows also had to conduct a group research project on a given topic. This year, they explored nuclear nonproliferation issues in relation to nuclear exports and brainstormed some recommendations for current policy. They presented their outcomes at the 2018 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation. After intensive lecture sessions and group research work, the fellows went off to key policy think-tanks, nuclear research institutes, and research power facilities in Korea, Japan, and China.
“NEREC emphasizes nuclear nonproliferation issues related to civilian nuclear power and the associated nuclear fuel cycle development from the point of technology users. I am very glad that the number of participants are increasing year by year,” said the Director of NEREC Man-Sung Yim, a professor in the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering.
Participants’ majors vary from nuclear engineering to international relations to economics. The fellows divided into two groups of graduate and undergraduate courses. They expressed their deep satisfactory in the multidisciplinary lectures by scholars from KAIST, Seoul National University, and Korea National Defense University.
Many participants reported that they learned a lot, not only about policy and international relations but on the research they are conducting and what the key issues will be in dealing for producing meaningful research work.
Moad Aldbissi from the KTH Royal Institute of Technology is one of the students who shared the same view. He said, “Coming from a technical background in nuclear engineering, I managed to learn a lot about nuclear policy and international relations. The importance of integrating the technical and political fields became even clearer.”
Most students concurred that they recognized how important it was to make international collaboration in this powerful field for each country through this program.
“As an engineering student, I just approached this program like an empty glass in policy areas. While working with colleagues during the program, I came to understand how important it is to make cooperation in these fields for the better result of national development and international relations,” said Thanataon Pornphatdetaudom from the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
To Director Yim, this program is becoming well positioned to educate nuclear policy experts in a number of countries of strategic importance. He believes the continuous supply of these experts will contribute to promoting global nuclear nonproliferation and the peaceful use of nuclear energy while the use of nuclear technology continues.
2018.09.04 View 11115
NEREC Summer Program Keeps Fellows Thinking, Engaged in Nuclear Nonproliferation
Nuclear technology is more than just technology. It is the fruit of the most advanced science and technology. It also requires high standards of policymaking and global cooperation for benefiting the technology.
As part of the fifth annual Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) Summer Fellows Program at KAIST, 24 students from 15 countries participated in six-week intensive education and training program. NEREC is the only university-based center dedicated to nuclear nonproliferation education and research established in 2014.
The program, which provides multidisciplinary lectures and seminars on nuclear technology and policy as well as international relations, was designed to nurture global nuclear technology experts well equipped in three areas: in-depth knowledge of technology, applicability gained from sound policy building, and negotiating for international cooperation. It now has grown into the most popular summer program at KAIST.
During the program from July 6 to August 18, participants were able to engage in enriching and stimulating learning experiences in tandem with policies and technology for the utilization and provision of peaceful and safe nuclear technology.
Participating fellows also had to conduct a group research project on a given topic. This year, they explored nuclear nonproliferation issues in relation to nuclear exports and brainstormed some recommendations for current policy. They presented their outcomes at the 2018 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation. After intensive lecture sessions and group research work, the fellows went off to key policy think-tanks, nuclear research institutes, and research power facilities in Korea, Japan, and China.
“NEREC emphasizes nuclear nonproliferation issues related to civilian nuclear power and the associated nuclear fuel cycle development from the point of technology users. I am very glad that the number of participants are increasing year by year,” said the Director of NEREC Man-Sung Yim, a professor in the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering.
Participants’ majors vary from nuclear engineering to international relations to economics. The fellows divided into two groups of graduate and undergraduate courses. They expressed their deep satisfactory in the multidisciplinary lectures by scholars from KAIST, Seoul National University, and Korea National Defense University.
Many participants reported that they learned a lot, not only about policy and international relations but on the research they are conducting and what the key issues will be in dealing for producing meaningful research work.
Moad Aldbissi from the KTH Royal Institute of Technology is one of the students who shared the same view. He said, “Coming from a technical background in nuclear engineering, I managed to learn a lot about nuclear policy and international relations. The importance of integrating the technical and political fields became even clearer.”
Most students concurred that they recognized how important it was to make international collaboration in this powerful field for each country through this program.
“As an engineering student, I just approached this program like an empty glass in policy areas. While working with colleagues during the program, I came to understand how important it is to make cooperation in these fields for the better result of national development and international relations,” said Thanataon Pornphatdetaudom from the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
To Director Yim, this program is becoming well positioned to educate nuclear policy experts in a number of countries of strategic importance. He believes the continuous supply of these experts will contribute to promoting global nuclear nonproliferation and the peaceful use of nuclear energy while the use of nuclear technology continues.
2018.09.04 View 11115 -
 Adding Smart to Science Museum
KAIST and the National Science Museum (NSM) created an Exhibition Research Center for Smart Science to launch exhibitions that integrate emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoTs), and artificial intelligence (AI).
There has been a great demand for a novel technology for better, user-oriented exhibition services. The NSM continuously faces the problem of not having enough professional guides. Additionally, there have been constant complaints about its current mobile application for exhibitions not being very effective.
To tackle these problems, the new center was founded, involving 11 institutes and universities. Sponsored by the National Research Foundation, it will oversee 15 projects in three areas: exhibition-based technology, exhibition operational technology, and exhibition content.
The group first aims to provide a location-based exhibition guide system service, which allows it to incorporate various technological services, such as AR/VR to visitors. An indoor locating system named KAILOS, which was developed by KAIST, will be applied to this service. They will also launch a mobile application service that provides audio-based exhibition guides.
To further cater to visitors’ needs, the group plans to apply a user-centered ecosystem, a living lab concept to create pleasant environment for visitors.
“Every year, hundred thousands of young people visit the National Science Museum. I believe that the exhibition guide system has to be innovative, using cutting-edge IT technology in order to help them cherish their dreams and inspirations through science,” Jeong Heoi Bae, President of Exhibition and Research Bureau of NSM, emphasized.
Professor Dong Soo Han from the School of Computing, who took the position of research head of the group, said, “We will systematically develop exhibition technology and contents for the science museum to create a platform for smart science museums. It will be the first time to provide an exhibition guide system that integrates AR/VR with an indoor location system.”
The center will first apply the new system to the NSM and then expand it to 167 science museums and other regional museums.
2018.09.04 View 9478
Adding Smart to Science Museum
KAIST and the National Science Museum (NSM) created an Exhibition Research Center for Smart Science to launch exhibitions that integrate emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoTs), and artificial intelligence (AI).
There has been a great demand for a novel technology for better, user-oriented exhibition services. The NSM continuously faces the problem of not having enough professional guides. Additionally, there have been constant complaints about its current mobile application for exhibitions not being very effective.
To tackle these problems, the new center was founded, involving 11 institutes and universities. Sponsored by the National Research Foundation, it will oversee 15 projects in three areas: exhibition-based technology, exhibition operational technology, and exhibition content.
The group first aims to provide a location-based exhibition guide system service, which allows it to incorporate various technological services, such as AR/VR to visitors. An indoor locating system named KAILOS, which was developed by KAIST, will be applied to this service. They will also launch a mobile application service that provides audio-based exhibition guides.
To further cater to visitors’ needs, the group plans to apply a user-centered ecosystem, a living lab concept to create pleasant environment for visitors.
“Every year, hundred thousands of young people visit the National Science Museum. I believe that the exhibition guide system has to be innovative, using cutting-edge IT technology in order to help them cherish their dreams and inspirations through science,” Jeong Heoi Bae, President of Exhibition and Research Bureau of NSM, emphasized.
Professor Dong Soo Han from the School of Computing, who took the position of research head of the group, said, “We will systematically develop exhibition technology and contents for the science museum to create a platform for smart science museums. It will be the first time to provide an exhibition guide system that integrates AR/VR with an indoor location system.”
The center will first apply the new system to the NSM and then expand it to 167 science museums and other regional museums.
2018.09.04 View 9478 -
 Potential Drug to Cure Ciliopathies
(from left: Professor Joon Kim and PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim)
Ciliopathies are rare disorders involving functional and structural abnormalities of cilia. Although they are rare, they may reach 1 in 1,000 births. Unfortunately, there are no small-molecule drugs for treating ciliary defects. A KAIST research team conducted successful research that introduces a potential treatment that will be a foundation for developing drugs to treat the disease as well as a platform for developing small-molecule drugs for similar genetic disorders.
It was found that mutations in genes required for the formation or function of primary cilia cause ciliopathies and they result in cerebellar disorders, kidney dysfunction, and retinal degeneration.
Primary cilia are cell organelles playing a crucial role in the human body. They participate in intercellular signal transduction during embryonic development and allow retinal photoreceptor cells to function.
Currently, there are no approved drugs available for treating most ciliopathies. In fact, this is the case for most of the rare genetic disorders involving functional abnormalities through genetic mutation, and gene therapy is usually the only treatment available.
To tackle this issue, a team led by Professor Joon Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Ho Jeong Kwon from Yonsei University constructed a cell that mimics a gene-mutated CEP290, one of the main causes of ciliopathies, through genome editing. They then used cell-based compound library screening to obtain a natural small-molecule compound capable of relieving defects in ciliogenesis, the production of cilia.
The CEP290 protein forms a complex with a ciliopathy protein called NPHP5 to support the function of the ciliary transition zone. In cases where the CEP290 protein is not formed due to a genetic mutation, NPHP5 will not function normally. Here, the compound was confirmed to partially restore the function of the complex by normalizing the function of NPHP5.
The team also identified that the compound is capable of retarding retinal degeneration by injecting the compound into animal models.
As a result, they discovered a lead compound for developing medication to treat ciliopathy patients involving retinal degeneration. Hence, the findings imply that chemical compounds that target other proteins interacting with the disease protein can mitigate shortages of a disease protein in recessive genetic disorders.
PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim stated, “This study shows how genetic disorders caused by genetic mutation can be treated with small-molecule drugs.”
Professor Kim said, “Since the efficacy of the candidate drug has been verified through animal testing, a follow-up study will also be conducted to demonstrate the effect on humans.”
This research was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on July 23.
Figure 1. Identification of compounds that rescue ciliogenesis defects caused by CEP290 knockout
Figure 2. Eupatilin injection ameliorates M-opsin trafficking and electrophysiological response of cone photoreceptors in rd16 mice
2018.08.30 View 8491
Potential Drug to Cure Ciliopathies
(from left: Professor Joon Kim and PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim)
Ciliopathies are rare disorders involving functional and structural abnormalities of cilia. Although they are rare, they may reach 1 in 1,000 births. Unfortunately, there are no small-molecule drugs for treating ciliary defects. A KAIST research team conducted successful research that introduces a potential treatment that will be a foundation for developing drugs to treat the disease as well as a platform for developing small-molecule drugs for similar genetic disorders.
It was found that mutations in genes required for the formation or function of primary cilia cause ciliopathies and they result in cerebellar disorders, kidney dysfunction, and retinal degeneration.
Primary cilia are cell organelles playing a crucial role in the human body. They participate in intercellular signal transduction during embryonic development and allow retinal photoreceptor cells to function.
Currently, there are no approved drugs available for treating most ciliopathies. In fact, this is the case for most of the rare genetic disorders involving functional abnormalities through genetic mutation, and gene therapy is usually the only treatment available.
To tackle this issue, a team led by Professor Joon Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Ho Jeong Kwon from Yonsei University constructed a cell that mimics a gene-mutated CEP290, one of the main causes of ciliopathies, through genome editing. They then used cell-based compound library screening to obtain a natural small-molecule compound capable of relieving defects in ciliogenesis, the production of cilia.
The CEP290 protein forms a complex with a ciliopathy protein called NPHP5 to support the function of the ciliary transition zone. In cases where the CEP290 protein is not formed due to a genetic mutation, NPHP5 will not function normally. Here, the compound was confirmed to partially restore the function of the complex by normalizing the function of NPHP5.
The team also identified that the compound is capable of retarding retinal degeneration by injecting the compound into animal models.
As a result, they discovered a lead compound for developing medication to treat ciliopathy patients involving retinal degeneration. Hence, the findings imply that chemical compounds that target other proteins interacting with the disease protein can mitigate shortages of a disease protein in recessive genetic disorders.
PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim stated, “This study shows how genetic disorders caused by genetic mutation can be treated with small-molecule drugs.”
Professor Kim said, “Since the efficacy of the candidate drug has been verified through animal testing, a follow-up study will also be conducted to demonstrate the effect on humans.”
This research was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on July 23.
Figure 1. Identification of compounds that rescue ciliogenesis defects caused by CEP290 knockout
Figure 2. Eupatilin injection ameliorates M-opsin trafficking and electrophysiological response of cone photoreceptors in rd16 mice
2018.08.30 View 8491 -
 Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 7457
Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 7457 -
 Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 6819
Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 6819 -
 Metabolic Engineering of E. coli for the Secretory Production of Free Haem
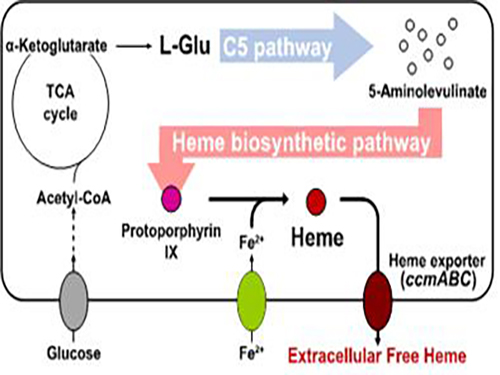
Researchers of KAIST have defined a novel strategy for the secretory production of free haem using engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains. They utilized the C5 pathway, the optimized downstream pathways, and the haem exporter to construct a recombinant micro-organism producing extracellular haem using fed-batch fermentation. This is the first report to extracellularly produce haem using engineered E. coli.
This strategy will expedite the efficient production of free haem to serve as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent and an important prosthetic group of multiple hemoproteins for medical uses. This study, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, was published in Nature Catalysis on Aug. 28.
Haem, an organometallic compound complexed with a ferrous ion, is an essential molecule delivering oxygen in the blood of many animals. It is also a key component of electron transport chains responsible for the respiration of aerobic organisms including diverse bacteria. It is now being widely applied as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent in the healthcare and dietary supplement industries. The demand for haem and the need for the efficient production of this compound continue to grow.
Many previous researchers have attempted to produce free haem using engineered E. coli. However, none of the studies was successful in producing free haem extracellularly, requiring an additional step to extract the accumulated haem from cells for subsequent uses. The secretion of haem in the form of haem peptides or proteins also requires an extraction step to isolate the free haem from the secreted products. Thus, the secretory production of free haem is an important task for the economical production of haem that is suitable for human consumption.
Although some researchers could produce intracellular haem using recombinant E. coli strains, its final titer was extremely low, resulting from the use of sub-optimal metabolic pathways. Furthermore, the addition of the precursors L-glycine and succinate was deemed undesirable for massive industrial production. Thus, it is necessary to construct an optimized haem biosynthetic pathway to enable the efficient production of haem and examine the consequent secretion of free haem.
To address this issue, the KAIST team used multiple strategies to produce extracellular free haem by enhancing its biosynthesis in E. coli. First, the capacities of the C4 and C5 pathways to produce aminolevulinate (ALA) without feeding precursors were examined. After confirming the superior performance of the C5 pathway over the C4 pathway, the metabolic genes of the C5 pathway and downstream pathways for haem biosynthesis were overexpressed. Then, the metabolic pathways were optimized by adjusting the expression levels of the relevant genes and disrupting the putative haem degradation enzyme encoded by the yfeX gene.
Consequently, the resulting engineered strain secreted a significant amount of haem to the medium. Subsequent optimization of the cultivation conditions and the supplementation of nitrogen sources further increased both the titer of the total free haem and the amount of free haem secreted to the medium. Finally, the overexpression of the ccmABC genes encoding the haem exporter further enhanced the production and secretion of haem, producing the highest titer of haem both intracellularly and extracellularly from glucose.
Professor Lee said, “The eco-friendly and sustainable chemical industry is a key global agenda every nation faces. We are conducting research to bio-synthesize high concentrations, high yields, and high productivity in natural products. This novel technology will serve as an opportunity to advance the biochemical industry moving forward.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. Further Contact: Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr+82-42-350-3930).
2018.08.28 View 6072
Metabolic Engineering of E. coli for the Secretory Production of Free Haem
Researchers of KAIST have defined a novel strategy for the secretory production of free haem using engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains. They utilized the C5 pathway, the optimized downstream pathways, and the haem exporter to construct a recombinant micro-organism producing extracellular haem using fed-batch fermentation. This is the first report to extracellularly produce haem using engineered E. coli.
This strategy will expedite the efficient production of free haem to serve as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent and an important prosthetic group of multiple hemoproteins for medical uses. This study, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, was published in Nature Catalysis on Aug. 28.
Haem, an organometallic compound complexed with a ferrous ion, is an essential molecule delivering oxygen in the blood of many animals. It is also a key component of electron transport chains responsible for the respiration of aerobic organisms including diverse bacteria. It is now being widely applied as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent in the healthcare and dietary supplement industries. The demand for haem and the need for the efficient production of this compound continue to grow.
Many previous researchers have attempted to produce free haem using engineered E. coli. However, none of the studies was successful in producing free haem extracellularly, requiring an additional step to extract the accumulated haem from cells for subsequent uses. The secretion of haem in the form of haem peptides or proteins also requires an extraction step to isolate the free haem from the secreted products. Thus, the secretory production of free haem is an important task for the economical production of haem that is suitable for human consumption.
Although some researchers could produce intracellular haem using recombinant E. coli strains, its final titer was extremely low, resulting from the use of sub-optimal metabolic pathways. Furthermore, the addition of the precursors L-glycine and succinate was deemed undesirable for massive industrial production. Thus, it is necessary to construct an optimized haem biosynthetic pathway to enable the efficient production of haem and examine the consequent secretion of free haem.
To address this issue, the KAIST team used multiple strategies to produce extracellular free haem by enhancing its biosynthesis in E. coli. First, the capacities of the C4 and C5 pathways to produce aminolevulinate (ALA) without feeding precursors were examined. After confirming the superior performance of the C5 pathway over the C4 pathway, the metabolic genes of the C5 pathway and downstream pathways for haem biosynthesis were overexpressed. Then, the metabolic pathways were optimized by adjusting the expression levels of the relevant genes and disrupting the putative haem degradation enzyme encoded by the yfeX gene.
Consequently, the resulting engineered strain secreted a significant amount of haem to the medium. Subsequent optimization of the cultivation conditions and the supplementation of nitrogen sources further increased both the titer of the total free haem and the amount of free haem secreted to the medium. Finally, the overexpression of the ccmABC genes encoding the haem exporter further enhanced the production and secretion of haem, producing the highest titer of haem both intracellularly and extracellularly from glucose.
Professor Lee said, “The eco-friendly and sustainable chemical industry is a key global agenda every nation faces. We are conducting research to bio-synthesize high concentrations, high yields, and high productivity in natural products. This novel technology will serve as an opportunity to advance the biochemical industry moving forward.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. Further Contact: Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr+82-42-350-3930).
2018.08.28 View 6072 -
 Improved Efficiency of CQD Solar Cells Using an Organic Thin Film
(from left: Professor Jung-Yong Lee and Dr. Se-Woong Baek)
Recently, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of colloidal quantum dot (CQD)-based solar cells has been enhanced, paving the way for their commercialization in various fields; nevertheless, they are still a long way from being commercialized due to their efficiency not matching their stability. In this research, a KAIST team achieved highly stable and efficient CQD-based solar cells by using an amorphous organic layer to block oxygen and water permeation.
CQD-based solar cells are light-weight, flexible, and they boost light harvesting by absorbing near-infrared lights. Especially, they draw special attention for their optical properties controlled efficiently by changing the quantum dot sizes. However, they are still incompatible with existing solar cells in terms of efficiency, stability, and cost. Therefore, there is great demand for a novel technology that can simultaneously improve both PCE and stability while using an inexpensive electrode material.
Responding to this demand, Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team introduced a technology to improve the efficiency and stability of CQD-based solar cells.
The team found that an amorphous organic thin film has a strong resistance to oxygen and water. Using these properties, they employed this doped organic layer as a top-hole selective layer (HSL) for the PbS CQD solar cells, and confirmed that the hydro/oxo-phobic properties of the layer efficiently protected the PbS layer. According to the molecular dynamics simulations, the layer significantly postponed the oxygen and water permeation into the PbS layer. Moreover, the efficient injection of the holes in the layer reduced interfacial resistance and improved performance.
With this technology, the team finally developed CQD-based solar cells with excellent stability. The PCE of their device stood at 11.7% and maintained over 90% of its initial performance when stored for one year under ambient conditions.
Professor Lee said, “This technology can be also applied to QD LEDs and Perovskite devices. I hope this technology can hasten the commercialization of CQD-based solar cells.”
This research, led by Dr. Se-Woong Baek and a Ph.D. student, Sang-Hoon Lee, was published in Energy & Environmental Science on May 10.
Figure 1. The schematic of the equilibrated structure of the amorphous organic film
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of CQD-based solar cells and graphs showing their performance
2018.08.27 View 8370
Improved Efficiency of CQD Solar Cells Using an Organic Thin Film
(from left: Professor Jung-Yong Lee and Dr. Se-Woong Baek)
Recently, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of colloidal quantum dot (CQD)-based solar cells has been enhanced, paving the way for their commercialization in various fields; nevertheless, they are still a long way from being commercialized due to their efficiency not matching their stability. In this research, a KAIST team achieved highly stable and efficient CQD-based solar cells by using an amorphous organic layer to block oxygen and water permeation.
CQD-based solar cells are light-weight, flexible, and they boost light harvesting by absorbing near-infrared lights. Especially, they draw special attention for their optical properties controlled efficiently by changing the quantum dot sizes. However, they are still incompatible with existing solar cells in terms of efficiency, stability, and cost. Therefore, there is great demand for a novel technology that can simultaneously improve both PCE and stability while using an inexpensive electrode material.
Responding to this demand, Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team introduced a technology to improve the efficiency and stability of CQD-based solar cells.
The team found that an amorphous organic thin film has a strong resistance to oxygen and water. Using these properties, they employed this doped organic layer as a top-hole selective layer (HSL) for the PbS CQD solar cells, and confirmed that the hydro/oxo-phobic properties of the layer efficiently protected the PbS layer. According to the molecular dynamics simulations, the layer significantly postponed the oxygen and water permeation into the PbS layer. Moreover, the efficient injection of the holes in the layer reduced interfacial resistance and improved performance.
With this technology, the team finally developed CQD-based solar cells with excellent stability. The PCE of their device stood at 11.7% and maintained over 90% of its initial performance when stored for one year under ambient conditions.
Professor Lee said, “This technology can be also applied to QD LEDs and Perovskite devices. I hope this technology can hasten the commercialization of CQD-based solar cells.”
This research, led by Dr. Se-Woong Baek and a Ph.D. student, Sang-Hoon Lee, was published in Energy & Environmental Science on May 10.
Figure 1. The schematic of the equilibrated structure of the amorphous organic film
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of CQD-based solar cells and graphs showing their performance
2018.08.27 View 8370