-
 Scientist of October, Professor Haeshin Lee
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry)
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry received the ‘Science and Technology Award of October’ from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea for his contribution to developing an antibleeding injection needle. This novel outcome will fundamentally prevent the problem of secondary infections of AIDS, Ebola and Hepatitis viruses transmitting from patients to medical teams.
This needle’s surface is coated with hemostatic materials. Its concept is simple and the key to this technology is to make materials that are firmly coated on the needle so that they can endure frictional force when being injected into skin and blood vessels. Moreover, the materials should be adhesive to skin and the interior of blood vessels, but harmless to humans.
Professor Lee found a solution from natural polymer ingredients. Catecholamine can be found in mussels. Professor Lee conjugated catechol groups on the chitosan backbone. He applied this mussel-inspired adhesive polymer Chitosan-catechol, which immediately forms an adhesive layer with blood, as a bioadhesion for the antibleeding injection needle.
Professor Lee said, “Chitosan-catechol, which copies the adhesive mechanism of mussels, shows high solubility in physiological saline as well as great mucoadhesion. Hence, it is perfectly suitable for coating the injection needle. Combining it with proteins allows for efficient drug delivery to the heart, which is a challenging injection location, so it will be also useful for treating incurable heart disease.”
2018.10.05 View 10664
Scientist of October, Professor Haeshin Lee
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry)
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry received the ‘Science and Technology Award of October’ from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea for his contribution to developing an antibleeding injection needle. This novel outcome will fundamentally prevent the problem of secondary infections of AIDS, Ebola and Hepatitis viruses transmitting from patients to medical teams.
This needle’s surface is coated with hemostatic materials. Its concept is simple and the key to this technology is to make materials that are firmly coated on the needle so that they can endure frictional force when being injected into skin and blood vessels. Moreover, the materials should be adhesive to skin and the interior of blood vessels, but harmless to humans.
Professor Lee found a solution from natural polymer ingredients. Catecholamine can be found in mussels. Professor Lee conjugated catechol groups on the chitosan backbone. He applied this mussel-inspired adhesive polymer Chitosan-catechol, which immediately forms an adhesive layer with blood, as a bioadhesion for the antibleeding injection needle.
Professor Lee said, “Chitosan-catechol, which copies the adhesive mechanism of mussels, shows high solubility in physiological saline as well as great mucoadhesion. Hence, it is perfectly suitable for coating the injection needle. Combining it with proteins allows for efficient drug delivery to the heart, which is a challenging injection location, so it will be also useful for treating incurable heart disease.”
2018.10.05 View 10664 -
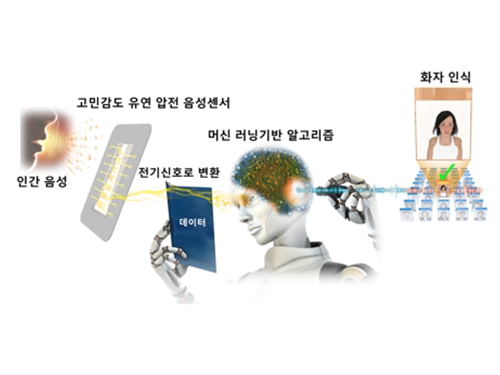 Flexible Piezoelectric Acoustic Sensors for Speaker Recognition
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Material Science and Engineering has developed a machine learning-based acoustic sensor for speaker recognition.
Acoustic sensors were spotlighted as one of the most intuitive bilateral communication devices between humans and machines. However, conventional acoustic sensors use a condenser-type device for measuring capacitance between two conducting layers, resulting in low sensitivity, short recognition distance, and low speaker recognition rates.
The team fabricated a flexible piezoelectric membrane by mimicking the basilar membrane in the human cochlear. Resonant frequencies vibrate corresponding regions of the trapezoidal piezoelectric membrane, which converts voice to electrical signal with a highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensor.
This multi-channel piezoelectric acoustic sensor exhibits sensitivity more than two times higher and allows for more abundant voice information compared to conventional acoustic sensors, which can detect minute sounds from farther distances. In addition, the acoustic sensor can achieve a 97.5% speaker recognition rate using a machine learning algorithm, reducing by 75% error rate than the reference microphone.
AI speaker recognition is the next big thing for future individual customized services. However, conventional technology attempts to improve recognition rates by using software upgrades, resulting in limited speaker recognition rates. The team enhanced the speaker recognition system by replacing the existing hardware with an innovative flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor. Further software improvement of the piezoelectric acoustic sensor will significantly increase the speaker and voice recognition rate in diverse environments.
Professor Lee said, “Highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensors for speaker recognition can be used for personalized voice services such as smart home appliances, AI secretaries, always-on IoT, biometric authentication, and FinTech.”
These research “Basilar Membrane-Inspired Self-Powered Acoustic Sensor” and “Machine Learning-based Acoustic Sensor for Speaker Recognition” were published in the September 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Firgure 1: A flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor mimicking the human cochlear.
Figure 2: Speaker recognition with a machine learning algorithm.
2018.10.04 View 7679
Flexible Piezoelectric Acoustic Sensors for Speaker Recognition
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Material Science and Engineering has developed a machine learning-based acoustic sensor for speaker recognition.
Acoustic sensors were spotlighted as one of the most intuitive bilateral communication devices between humans and machines. However, conventional acoustic sensors use a condenser-type device for measuring capacitance between two conducting layers, resulting in low sensitivity, short recognition distance, and low speaker recognition rates.
The team fabricated a flexible piezoelectric membrane by mimicking the basilar membrane in the human cochlear. Resonant frequencies vibrate corresponding regions of the trapezoidal piezoelectric membrane, which converts voice to electrical signal with a highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensor.
This multi-channel piezoelectric acoustic sensor exhibits sensitivity more than two times higher and allows for more abundant voice information compared to conventional acoustic sensors, which can detect minute sounds from farther distances. In addition, the acoustic sensor can achieve a 97.5% speaker recognition rate using a machine learning algorithm, reducing by 75% error rate than the reference microphone.
AI speaker recognition is the next big thing for future individual customized services. However, conventional technology attempts to improve recognition rates by using software upgrades, resulting in limited speaker recognition rates. The team enhanced the speaker recognition system by replacing the existing hardware with an innovative flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor. Further software improvement of the piezoelectric acoustic sensor will significantly increase the speaker and voice recognition rate in diverse environments.
Professor Lee said, “Highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensors for speaker recognition can be used for personalized voice services such as smart home appliances, AI secretaries, always-on IoT, biometric authentication, and FinTech.”
These research “Basilar Membrane-Inspired Self-Powered Acoustic Sensor” and “Machine Learning-based Acoustic Sensor for Speaker Recognition” were published in the September 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Firgure 1: A flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor mimicking the human cochlear.
Figure 2: Speaker recognition with a machine learning algorithm.
2018.10.04 View 7679 -
 The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 8993
The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 8993 -
 Spray Coated Tactile Sensor on a 3-D Surface for Robotic Skin
Robots will be able to conduct a wide variety of tasks as well as humans if they can be given tactile sensing capabilities.
A KAIST research team has reported a stretchable pressure insensitive strain sensor by using an all solution-based process. The solution-based process is easily scalable to accommodate for large areas and can be coated as a thin-film on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects via spray coating. These conditions make their processing technique unique and highly suitable for robotic electronic skin or wearable electronic applications.
The making of electronic skin to mimic the tactile sensing properties of human skin is an active area of research for various applications such as wearable electronics, robotics, and prosthetics. One of the major challenges in electronic skin research is differentiating various external stimuli, particularly between strain and pressure. Another issue is uniformly depositing electrical skin on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects.
To overcome these issues, the research team led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed electronic skin that can be uniformly coated on 3-dimensional surfaces and distinguish mechanical stimuli. The new electronic skin can also distinguish mechanical stimuli analogous to human skin. The structure of the electronic skin was designed to respond differently under applied pressure and strain. Under applied strain, conducting pathways undergo significant conformational changes, considerably changing the resistance. On the other hand, under applied pressure, negligible conformational change in the conducting pathway occurs; e-skin is therefore non-responsive to pressure. The research team is currently working on strain insensitive pressure sensors to use with the developed strain sensors.
The research team also spatially mapped the local strain without the use of patterned electrode arrays utilizing electrical impedance tomography (EIT). By using EIT, it is possible to minimize the number of electrodes, increase durability, and enable facile fabrication onto 3-dimensional surfaces.
Professor Park said, “Our electronic skin can be mass produced at a low cost and can easily be coated onto complex 3-dimensional surfaces. It is a key technology that can bring us closer to the commercialization of electronic skin for various applications in the near future.”
The result of this work entitled “Pressure Insensitive Strain Sensor with Facile Solution-based Process for Tactile Sensing Applications” was published in the August issue of ACS Nano as a cover article.
(Figure: Detecting mechanical stimuli using electrical impedance tomography.)
2018.09.21 View 8694
Spray Coated Tactile Sensor on a 3-D Surface for Robotic Skin
Robots will be able to conduct a wide variety of tasks as well as humans if they can be given tactile sensing capabilities.
A KAIST research team has reported a stretchable pressure insensitive strain sensor by using an all solution-based process. The solution-based process is easily scalable to accommodate for large areas and can be coated as a thin-film on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects via spray coating. These conditions make their processing technique unique and highly suitable for robotic electronic skin or wearable electronic applications.
The making of electronic skin to mimic the tactile sensing properties of human skin is an active area of research for various applications such as wearable electronics, robotics, and prosthetics. One of the major challenges in electronic skin research is differentiating various external stimuli, particularly between strain and pressure. Another issue is uniformly depositing electrical skin on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects.
To overcome these issues, the research team led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed electronic skin that can be uniformly coated on 3-dimensional surfaces and distinguish mechanical stimuli. The new electronic skin can also distinguish mechanical stimuli analogous to human skin. The structure of the electronic skin was designed to respond differently under applied pressure and strain. Under applied strain, conducting pathways undergo significant conformational changes, considerably changing the resistance. On the other hand, under applied pressure, negligible conformational change in the conducting pathway occurs; e-skin is therefore non-responsive to pressure. The research team is currently working on strain insensitive pressure sensors to use with the developed strain sensors.
The research team also spatially mapped the local strain without the use of patterned electrode arrays utilizing electrical impedance tomography (EIT). By using EIT, it is possible to minimize the number of electrodes, increase durability, and enable facile fabrication onto 3-dimensional surfaces.
Professor Park said, “Our electronic skin can be mass produced at a low cost and can easily be coated onto complex 3-dimensional surfaces. It is a key technology that can bring us closer to the commercialization of electronic skin for various applications in the near future.”
The result of this work entitled “Pressure Insensitive Strain Sensor with Facile Solution-based Process for Tactile Sensing Applications” was published in the August issue of ACS Nano as a cover article.
(Figure: Detecting mechanical stimuli using electrical impedance tomography.)
2018.09.21 View 8694 -
 President Shin Presents Opportunities & Challenges of the 4IR at the Summer Davos Forum
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the 2018 Summer Davos Forum in China on Sept.20.)
KAIST co-hosted the Asia Session with the World Economic Forum during the 2018 Summer Davos Forum in Tianjin, China from September 18 through 20. The session highlighted regional collaboration in Asia to promote inclusive growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
KAIST is working closely with the WEF to take the lead in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Last July, KAIST established the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) at the KAIST Institute and signed an MOU with the Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR) at the WEF in October. The session is a follow-up event KAIST and the C4IR agreed to last year during the Roundtable Session held in Seoul.
Many experts in new emerging industries as well as many project directors, including Director Murat Sonmez of the C4IR, attended the session KAIST hosted. Director Chizuru Suga at the C4IR in Japan, Director Danil Kerimi in China, and Director Shailesh Sharda in India also attended the session and discussed ways to expand collaboration and networks among the countries.
In his keynote speech at the session on September 20, President Sung-Chul Shin presented how the Korean government is trying to drive the economy by strategically investing in focused industries in the new global industrial environment. President Shin introduced the government’s strategic roadmap to build the competitiveness of emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
He also stressed that the three components of innovation, collaboration, and speed should be prioritized in all sectors for the successful realization of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. For instance, innovation in education, research, and technology commercialization, expansive domestic and international collaboration beyond the private and public sectors, speedy deregulation, and efficient governance will all be critical.
He also said that KAIST will launch new pilot collaboration projects along with the WEF soon. “We paved the way for leading the network with major countries including Japan and India for advancing the Fourth Industrial Revolution through this session,” President Shin said.
2018.09.21 View 8563
President Shin Presents Opportunities & Challenges of the 4IR at the Summer Davos Forum
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the 2018 Summer Davos Forum in China on Sept.20.)
KAIST co-hosted the Asia Session with the World Economic Forum during the 2018 Summer Davos Forum in Tianjin, China from September 18 through 20. The session highlighted regional collaboration in Asia to promote inclusive growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
KAIST is working closely with the WEF to take the lead in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Last July, KAIST established the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) at the KAIST Institute and signed an MOU with the Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR) at the WEF in October. The session is a follow-up event KAIST and the C4IR agreed to last year during the Roundtable Session held in Seoul.
Many experts in new emerging industries as well as many project directors, including Director Murat Sonmez of the C4IR, attended the session KAIST hosted. Director Chizuru Suga at the C4IR in Japan, Director Danil Kerimi in China, and Director Shailesh Sharda in India also attended the session and discussed ways to expand collaboration and networks among the countries.
In his keynote speech at the session on September 20, President Sung-Chul Shin presented how the Korean government is trying to drive the economy by strategically investing in focused industries in the new global industrial environment. President Shin introduced the government’s strategic roadmap to build the competitiveness of emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
He also stressed that the three components of innovation, collaboration, and speed should be prioritized in all sectors for the successful realization of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. For instance, innovation in education, research, and technology commercialization, expansive domestic and international collaboration beyond the private and public sectors, speedy deregulation, and efficient governance will all be critical.
He also said that KAIST will launch new pilot collaboration projects along with the WEF soon. “We paved the way for leading the network with major countries including Japan and India for advancing the Fourth Industrial Revolution through this session,” President Shin said.
2018.09.21 View 8563 -
 KAIST Develops VRFB with Longer Durability
(from left: PhD candidate Soohyun Kim, Professor Hee-Tak Kim and PhD candidate Junghoon Choi)
There has been growing demand for large-scale storage for energy produced from renewable energy sources in an efficient and stable way. To meet this demand, a KAIST research team developed a new vanadium redox-flow battery (VRFB) with 15 times greater capacity retention and five times longer durability. This VRFB battery can be an excellent candidate for a large-scale rechargeable battery with no risk of explosion.
The VRFB has received much attention for its high efficiency and reliability with the absence of cross-contamination. However, it has the limitation of having insufficient charge and discharge efficiency and a low capacity retention rate because its perfluorinated membrane is very permeable to any active materials. To minimize energy loss, it needs a membrane that has low vanadium ion permeability and high ion conductivity. Hence, there was an attempt to incorporate a hydrocarbon membrane that has low cost and high ion selectivity but it turned out that the VO₂+ caused chemical degradation, which led to shortening the battery life drastically.
To develop a membrane with pore sizes smaller than the hydrated size of vanadium ions yet larger than that of the protons, a research team co-led by Professor Hee-Tae Jung and Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering implemented a graphene-oxide framework (GOF) membrane by cross-linking graphene oxide nanosheets. They believed that GOF, having strong ion selectivity, would be a good candidate for the membrane component for the VRFB. The interlayer spacing between the GO sheets limited moisture expansion and provided selective ion permeation.
The GOF membrane increased the capacity retention of the VRFB, which showed a 15 times higher rate than that of perfluorinated membranes. Its cycling stability was also enhanced up to five times, compared to conventional hydrocarbon membranes.
These pore-sized-tuned graphene oxide frameworks will allow pore-sized tuning of membranes and will be applicable to electrochemical systems that utilize ions of various sizes, such as rechargeable batteries and sensors.
Professor Kim said, “Developing a membrane that prevents the mixing of positive and negative active materials has been a chronic issue in the field of redox-flow batteries. Through this research, we showed that nanotechnology can prevent this crossover issue and membrane degradation. I believe that this technology can be applied to various rechargeable batteries requiring large-scale storage.”
This research was published in Nano Letters on May 3.
Figure 1. Electrochemical performances of the VRFBs with Nafion 115, SPAES (sulfonated poly), and GOF/SPAES: discharge capacity
Figure 2. Schematic of the selective ion transfer of hydrated vanadium ions and protons in the GOF membrane and the molecular structure of the GOF membrane, showing that the GO nanosheets are cross-linked with EDA (ethylenediamine)
2018.09.20 View 7591
KAIST Develops VRFB with Longer Durability
(from left: PhD candidate Soohyun Kim, Professor Hee-Tak Kim and PhD candidate Junghoon Choi)
There has been growing demand for large-scale storage for energy produced from renewable energy sources in an efficient and stable way. To meet this demand, a KAIST research team developed a new vanadium redox-flow battery (VRFB) with 15 times greater capacity retention and five times longer durability. This VRFB battery can be an excellent candidate for a large-scale rechargeable battery with no risk of explosion.
The VRFB has received much attention for its high efficiency and reliability with the absence of cross-contamination. However, it has the limitation of having insufficient charge and discharge efficiency and a low capacity retention rate because its perfluorinated membrane is very permeable to any active materials. To minimize energy loss, it needs a membrane that has low vanadium ion permeability and high ion conductivity. Hence, there was an attempt to incorporate a hydrocarbon membrane that has low cost and high ion selectivity but it turned out that the VO₂+ caused chemical degradation, which led to shortening the battery life drastically.
To develop a membrane with pore sizes smaller than the hydrated size of vanadium ions yet larger than that of the protons, a research team co-led by Professor Hee-Tae Jung and Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering implemented a graphene-oxide framework (GOF) membrane by cross-linking graphene oxide nanosheets. They believed that GOF, having strong ion selectivity, would be a good candidate for the membrane component for the VRFB. The interlayer spacing between the GO sheets limited moisture expansion and provided selective ion permeation.
The GOF membrane increased the capacity retention of the VRFB, which showed a 15 times higher rate than that of perfluorinated membranes. Its cycling stability was also enhanced up to five times, compared to conventional hydrocarbon membranes.
These pore-sized-tuned graphene oxide frameworks will allow pore-sized tuning of membranes and will be applicable to electrochemical systems that utilize ions of various sizes, such as rechargeable batteries and sensors.
Professor Kim said, “Developing a membrane that prevents the mixing of positive and negative active materials has been a chronic issue in the field of redox-flow batteries. Through this research, we showed that nanotechnology can prevent this crossover issue and membrane degradation. I believe that this technology can be applied to various rechargeable batteries requiring large-scale storage.”
This research was published in Nano Letters on May 3.
Figure 1. Electrochemical performances of the VRFBs with Nafion 115, SPAES (sulfonated poly), and GOF/SPAES: discharge capacity
Figure 2. Schematic of the selective ion transfer of hydrated vanadium ions and protons in the GOF membrane and the molecular structure of the GOF membrane, showing that the GO nanosheets are cross-linked with EDA (ethylenediamine)
2018.09.20 View 7591 -
 Using Donut-shaped Lithium Sulfide for Higher Performing Batteries
(from left: Research Professor Fangmin Ye and Professor Hee-Tak Kim)
A KAIST research team developed a lithium-sulfur battery with a doughnut-shaped active material structure showing a record lifecycle of over 600 cycles. Having higher energy density and lower production cost than a lithium-ion battery (LIB), it can be used in electric vehicles that require a longer battery life.
There has been an intense research conducted for developing lithium-sulfur batteries with high energy density because LIBs only allow for a very short travel distance per charge. However, Li-S batteries are still unable to provide a longer lifecycle due to the poor reversibility of the lithium metal cathode.
To tackle this issue, Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team used lithium sulfide (Li₂S) cathodes and combine them with graphite anodes to enhance energy density and lifecycles for the batteries.
Yet, lithium sulfide is costly and, so far, there has not been an electrode architecture and electrolyte design that enables a longer lifecycle between the graphite anodes and lithium sulfide cathodes.
Hence, the team produced a doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide cathode active material from low-cost lithium sulfide developed from raw materials. They have also developed a lithium sulfide ion battery with a graphite anode and lithium sulfide cathode using a high concentration salt electrolyte.
This doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide showed outstanding charge and discharge reversibility through improving the transfer of lithium ions. Its highly concentrated salt electrolyte formed a stable film on the surface of the graphite electrode, which showed strong durability.
Through this technology, the team achieved 30% higher energy density than that of conventional LIBs and secured a lifecycle of more than 600 cycles. This doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide-based electrode can be manufactured using low-cost raw materials and a single heat treatment process. The electrode can also be applied to existing LIBs.
Professor Kim said, “We have demonstrated that applying low-cost sulfur compounds to LIBs can improve both energy density and the lifecycle simultaneously.”
This research, led by Research Professor Fangmin Ye, was published in Advanced Science on May 7.
Figure 1. Structural characterization of Li₂SO₄/CNT and Li₂S/CNT electrodes and suggested mechanism for the formation of the holey-Li₂S nanoarchitecture
2018.09.19 View 5851
Using Donut-shaped Lithium Sulfide for Higher Performing Batteries
(from left: Research Professor Fangmin Ye and Professor Hee-Tak Kim)
A KAIST research team developed a lithium-sulfur battery with a doughnut-shaped active material structure showing a record lifecycle of over 600 cycles. Having higher energy density and lower production cost than a lithium-ion battery (LIB), it can be used in electric vehicles that require a longer battery life.
There has been an intense research conducted for developing lithium-sulfur batteries with high energy density because LIBs only allow for a very short travel distance per charge. However, Li-S batteries are still unable to provide a longer lifecycle due to the poor reversibility of the lithium metal cathode.
To tackle this issue, Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team used lithium sulfide (Li₂S) cathodes and combine them with graphite anodes to enhance energy density and lifecycles for the batteries.
Yet, lithium sulfide is costly and, so far, there has not been an electrode architecture and electrolyte design that enables a longer lifecycle between the graphite anodes and lithium sulfide cathodes.
Hence, the team produced a doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide cathode active material from low-cost lithium sulfide developed from raw materials. They have also developed a lithium sulfide ion battery with a graphite anode and lithium sulfide cathode using a high concentration salt electrolyte.
This doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide showed outstanding charge and discharge reversibility through improving the transfer of lithium ions. Its highly concentrated salt electrolyte formed a stable film on the surface of the graphite electrode, which showed strong durability.
Through this technology, the team achieved 30% higher energy density than that of conventional LIBs and secured a lifecycle of more than 600 cycles. This doughnut-shaped lithium sulfide-based electrode can be manufactured using low-cost raw materials and a single heat treatment process. The electrode can also be applied to existing LIBs.
Professor Kim said, “We have demonstrated that applying low-cost sulfur compounds to LIBs can improve both energy density and the lifecycle simultaneously.”
This research, led by Research Professor Fangmin Ye, was published in Advanced Science on May 7.
Figure 1. Structural characterization of Li₂SO₄/CNT and Li₂S/CNT electrodes and suggested mechanism for the formation of the holey-Li₂S nanoarchitecture
2018.09.19 View 5851 -
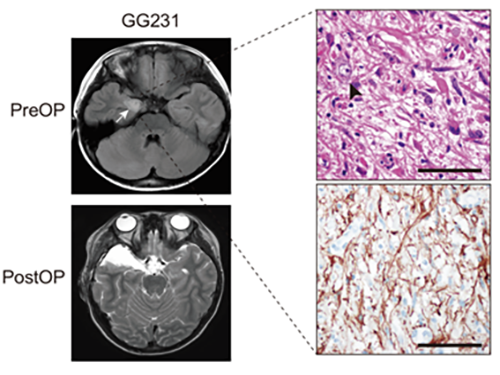 Understanding Epilepsy in Pediatric Tumors; New Therapeutic Target of Intractable Epilepsy Identified
Pediatric brain tumors are characterized by frequent complications due to intractable epilepsy compared to adult brain tumors. However, the genetic cause of refractory epilepsy in pediatric brain tumors has not been elucidated yet, and it is difficult to treat patients because the tumors do not respond to existing antiepileptic drugs and debilitate children’s development.
A research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering has recently identified a neuronal BRAF somatic mutation that causes intrinsic epileptogenicity in pediatric brain tumors. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on September 17.
The research team studied patients’ tissue diagnosed with ganglioglioma (GG), one of the main causes of tumor-associated intractable epilepsy, and found that the BRAF V600E somatic mutation is involved in the development of neural stem cells by using deep DNA sequencing. This mutation was carried out in an animal model to reproduce the pathology of GG and to observe seizures to establish an animal model for the treatment of epileptic seizures caused by pediatric brain tumors.
Using immunohistochemical and transcriptome analysis, they realized that the BRAF V600E mutation that arose in early progenitor cells during embryonic brain formation led to the acquisition of intrinsic epileptogenic properties in neuronal lineage cells, whereas tumorigenic properties were attributed to a high proliferation of glial lineage cells exhibiting the mutation. Notably, researchers found that seizures in mice were significantly alleviated by intraventricular infusion of the BRAF V600E inhibitor, Vemurafenib, a clinical anticancer drug.
The authors said, “Our study offers the first direct evidence that the BRAF somatic mutation arising from neural stem cells plays a key role in epileptogenesis in the brain tumor. This study also showed a new therapeutic target for tumor-associated epileptic disorders.”
In collaboration with the KAIST startup company, SoVarGen, the research team is currently developing innovative therapeutics for epileptic seizures derived from pediatric brain tumors. This study was supported by the Suh Kyungbae Foundation (SUHF) and the Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy.
(Figure: Preoperative and postoperative brain MRI (left panel), tumor H&E (right upper panel) and GFAP immunohistochemical (right lower panel) staining images from a patient with ganglioglioma (GG231) carrying the BRAFV600E mutation. The white arrow and the black arrowhead indicate the brain tumor and a dysplastic neuron, respectively.)
2018.09.19 View 5824
Understanding Epilepsy in Pediatric Tumors; New Therapeutic Target of Intractable Epilepsy Identified
Pediatric brain tumors are characterized by frequent complications due to intractable epilepsy compared to adult brain tumors. However, the genetic cause of refractory epilepsy in pediatric brain tumors has not been elucidated yet, and it is difficult to treat patients because the tumors do not respond to existing antiepileptic drugs and debilitate children’s development.
A research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering has recently identified a neuronal BRAF somatic mutation that causes intrinsic epileptogenicity in pediatric brain tumors. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on September 17.
The research team studied patients’ tissue diagnosed with ganglioglioma (GG), one of the main causes of tumor-associated intractable epilepsy, and found that the BRAF V600E somatic mutation is involved in the development of neural stem cells by using deep DNA sequencing. This mutation was carried out in an animal model to reproduce the pathology of GG and to observe seizures to establish an animal model for the treatment of epileptic seizures caused by pediatric brain tumors.
Using immunohistochemical and transcriptome analysis, they realized that the BRAF V600E mutation that arose in early progenitor cells during embryonic brain formation led to the acquisition of intrinsic epileptogenic properties in neuronal lineage cells, whereas tumorigenic properties were attributed to a high proliferation of glial lineage cells exhibiting the mutation. Notably, researchers found that seizures in mice were significantly alleviated by intraventricular infusion of the BRAF V600E inhibitor, Vemurafenib, a clinical anticancer drug.
The authors said, “Our study offers the first direct evidence that the BRAF somatic mutation arising from neural stem cells plays a key role in epileptogenesis in the brain tumor. This study also showed a new therapeutic target for tumor-associated epileptic disorders.”
In collaboration with the KAIST startup company, SoVarGen, the research team is currently developing innovative therapeutics for epileptic seizures derived from pediatric brain tumors. This study was supported by the Suh Kyungbae Foundation (SUHF) and the Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy.
(Figure: Preoperative and postoperative brain MRI (left panel), tumor H&E (right upper panel) and GFAP immunohistochemical (right lower panel) staining images from a patient with ganglioglioma (GG231) carrying the BRAFV600E mutation. The white arrow and the black arrowhead indicate the brain tumor and a dysplastic neuron, respectively.)
2018.09.19 View 5824 -
 Effective Drug Delivery to Heart with Tannic Acid
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry) Typical methods of drug delivery to the heart require surgical procedures involving incisions in the chest wall and bones. To efficiently treat cardiovascular and related vascular diseases without surgery, a KAIST research team developed a heart-targeting drug delivery technology using tannin acid via intravenous systemic injection. This method can be applied to the development of a variety of new protein-based drugs.
Cardiovascular-circulatory disease is currently the second leading cause of death in Korea. A typical example of this disease is myocardial infarction caused by poor oxygen and nutrient supply due to narrowed coronary arteries and poor blood flow to the heart.
Although there have been numerous research projects to develop chemotherapeutic drugs and therapeutic proteins, clinics still rely on surgical procedures. Drug delivery can be an alternative, but it is quite challenging because ceaseless dynamic cycles of the heart and massive exchanges of blood mean administered therapeutics do not stay inside the heart very long.
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry and his team employed tannic acid (TA), which is known for giving bitter taste to wines. It is one of the most abundant polyphenols and can be easily found in plants, such as fruits, vegetables, cacao, and others. TA has also been used as a multifunctional coating molecule.
Using these properties of TA, the team complexed protein and peptide therapeutics with tannic acid and succeeded in targeting protein and peptide therapeutics to the heart. TA, coated on the surface of a granulated protein complex, helps maintain cardiac function because it adheres to extracellular matrices, elastin, and collagens in heart tissues allowing the protein to stay attached to the heart tissue for a longer period.
The team confirmed that these Tannic-acid-modified proteins stay in blood vessels five days longer than with protein-only injections. Additionally they found that TA-protein complexes do not show any cardiac toxicity and do not cause noticeable pathology.
The team has been continuously developing biomaterials for medical applications by testing various polyphenolic materials that feature adhesive and coating properties, including tannic acid. They have injected a mixture of TA and fibroblast growth factors (FGF) into animal models with myocardial infarctions. After four weeks, they confirmed that the infarction was reduced and the left ventricular pressure and cardiac output were almost normalized.
Professor Lee said, “Although there have been numerous drugs related to heart disease, so far there has not been efficient drug delivery to the heart so this technology will be able to reformulate existing drugs into new and more efficient drugs.”
This research, jointly led by Dr. Ki-Suk Kim from the Predictive Model Research Center, was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on April 30 ( http://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-018-0227-9 ).
Figure 1. Schematic for the heart-targeting mechanism of TANNylated protein nanocomplexes: (1) size-dependent permeation, (2) phenolic (that is, TA), and (3) internalization by internalization by myoblasts
Figure 2. Effect of TA based protein complexes on cardiac cell transport efficiency and viral gene expression efficiency and therapeutic function in animal models with myocardial infarction
2018.09.18 View 5585
Effective Drug Delivery to Heart with Tannic Acid
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry) Typical methods of drug delivery to the heart require surgical procedures involving incisions in the chest wall and bones. To efficiently treat cardiovascular and related vascular diseases without surgery, a KAIST research team developed a heart-targeting drug delivery technology using tannin acid via intravenous systemic injection. This method can be applied to the development of a variety of new protein-based drugs.
Cardiovascular-circulatory disease is currently the second leading cause of death in Korea. A typical example of this disease is myocardial infarction caused by poor oxygen and nutrient supply due to narrowed coronary arteries and poor blood flow to the heart.
Although there have been numerous research projects to develop chemotherapeutic drugs and therapeutic proteins, clinics still rely on surgical procedures. Drug delivery can be an alternative, but it is quite challenging because ceaseless dynamic cycles of the heart and massive exchanges of blood mean administered therapeutics do not stay inside the heart very long.
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry and his team employed tannic acid (TA), which is known for giving bitter taste to wines. It is one of the most abundant polyphenols and can be easily found in plants, such as fruits, vegetables, cacao, and others. TA has also been used as a multifunctional coating molecule.
Using these properties of TA, the team complexed protein and peptide therapeutics with tannic acid and succeeded in targeting protein and peptide therapeutics to the heart. TA, coated on the surface of a granulated protein complex, helps maintain cardiac function because it adheres to extracellular matrices, elastin, and collagens in heart tissues allowing the protein to stay attached to the heart tissue for a longer period.
The team confirmed that these Tannic-acid-modified proteins stay in blood vessels five days longer than with protein-only injections. Additionally they found that TA-protein complexes do not show any cardiac toxicity and do not cause noticeable pathology.
The team has been continuously developing biomaterials for medical applications by testing various polyphenolic materials that feature adhesive and coating properties, including tannic acid. They have injected a mixture of TA and fibroblast growth factors (FGF) into animal models with myocardial infarctions. After four weeks, they confirmed that the infarction was reduced and the left ventricular pressure and cardiac output were almost normalized.
Professor Lee said, “Although there have been numerous drugs related to heart disease, so far there has not been efficient drug delivery to the heart so this technology will be able to reformulate existing drugs into new and more efficient drugs.”
This research, jointly led by Dr. Ki-Suk Kim from the Predictive Model Research Center, was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on April 30 ( http://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-018-0227-9 ).
Figure 1. Schematic for the heart-targeting mechanism of TANNylated protein nanocomplexes: (1) size-dependent permeation, (2) phenolic (that is, TA), and (3) internalization by internalization by myoblasts
Figure 2. Effect of TA based protein complexes on cardiac cell transport efficiency and viral gene expression efficiency and therapeutic function in animal models with myocardial infarction
2018.09.18 View 5585 -
 Engineered E. coli Using Formic Acid and CO2 As a C1-Refinery Platform Strain
(Figure: Formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathways consisting of the reconstructed THF cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. This schematic diagram shows the formic acid and CO2 assimilation procedure through the pathway. Plasmids used in this study and the genetic engineering performed in this study are illustrated.)
A research group at KAIST has developed an engineered E. coli strain that converts formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produces cellular energy from formic acid through reconstructed one-carbon pathways. The strategy described in this study provides a new platform for producing value-added chemicals from one-carbon sources.
Formic acid is a carboxylic acid composed of one carbon. Formic acid was produced from CO2 by the chemical method. Recently, the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center has successfully developed a biological process that produces formic acid from carbon monoxide for the first time. Formic acid is in a liquid state when at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. In addition, it is chemically stable and less toxic, thus, easy to store and transport. Therefore, it can be used as an alternative carbon source in the microbial fermentation process. In order to produce value-added chemicals using formic acid, a metabolic pathway that converts formic acid into cellular molecules composed of multiple carbons is required. However, a metabolic pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid into cellular molecules has not been developed. This acted as an obstacle for the production of value-added chemicals using formic acid
A research group of Ph.D. student Junho Bang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. This study, entitled “Assimilation of Formic Acid and CO2 by Engineered Escherichia coli Equipped with Reconstructed One-Carbon Assimilation Pathways”, has been published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on September 18.
There has been increasing interest in utilizing formic acid as an alternative carbon source for the production of value-added chemicals. This research reports the development of an engineered E. coli strain that can convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produce cellular energy from formic acid through the reconstructed one-carbon pathways.
The metabolic pathway that efficiently converts formic acid and CO2 into pyruvate was constructed by the combined use of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. The tetrahydrofolate cycle was reconstructed by utilizing Methylobacterium extorquens formate-THF ligase, methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase, and methylene-THF dehydrogenase. The glycine cleavage reaction was reversed by knocking out the repressor gene (gcvR) and overexpressing the gcvTHP genes that encode enzymes related with the glycine cleavage reaction. Formic acid and CO2 conversion to pyruvate was increased via metabolic engineering of the E. coli strain equipped with the one-carbon assimilation pathway.
In addition, in order to reduce glucose consumption and increase formic acid consumption, Candida boidnii formate dehydrogenase was additionally introduced to construct a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid. This reduces glucose consumption and increases formic acid consumption.
The reconstructed one-carbon pathways can supply cellular molecules and cellular energies from the formic acid and CO2. Thus, the engineered E. coli strain equipped with the formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathway and cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid showed cell growth from formic acid and CO2 without glucose. Cell growth was monitored and 13C isotope analysis was performed to confirm E. coli growth from the formic acid and CO2. It was found that the engineered E. coli strain sustained cell growth from the formic acid and CO2 without glucose.
Professor Lee said, “To construct the C1-refinery system, a platform strain that can convert one-carbon materials to higher carbon materials needs to be developed. In this report, a one-carbon pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate was developed and a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid was introduced. This resulted in an engineered E. coli strain that can efficiently utilize formic acid as a carbon source while glucose consumption was reduced. The reconstructed one-carbon pathways in this research will be useful for the construction of the C1-refinery system.”
This work was supported by the C1 Gas Refinery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2016M3D3A1A01913250). For further information: Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
2018.09.18 View 7040
Engineered E. coli Using Formic Acid and CO2 As a C1-Refinery Platform Strain
(Figure: Formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathways consisting of the reconstructed THF cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. This schematic diagram shows the formic acid and CO2 assimilation procedure through the pathway. Plasmids used in this study and the genetic engineering performed in this study are illustrated.)
A research group at KAIST has developed an engineered E. coli strain that converts formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produces cellular energy from formic acid through reconstructed one-carbon pathways. The strategy described in this study provides a new platform for producing value-added chemicals from one-carbon sources.
Formic acid is a carboxylic acid composed of one carbon. Formic acid was produced from CO2 by the chemical method. Recently, the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center has successfully developed a biological process that produces formic acid from carbon monoxide for the first time. Formic acid is in a liquid state when at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. In addition, it is chemically stable and less toxic, thus, easy to store and transport. Therefore, it can be used as an alternative carbon source in the microbial fermentation process. In order to produce value-added chemicals using formic acid, a metabolic pathway that converts formic acid into cellular molecules composed of multiple carbons is required. However, a metabolic pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid into cellular molecules has not been developed. This acted as an obstacle for the production of value-added chemicals using formic acid
A research group of Ph.D. student Junho Bang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. This study, entitled “Assimilation of Formic Acid and CO2 by Engineered Escherichia coli Equipped with Reconstructed One-Carbon Assimilation Pathways”, has been published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on September 18.
There has been increasing interest in utilizing formic acid as an alternative carbon source for the production of value-added chemicals. This research reports the development of an engineered E. coli strain that can convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produce cellular energy from formic acid through the reconstructed one-carbon pathways.
The metabolic pathway that efficiently converts formic acid and CO2 into pyruvate was constructed by the combined use of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. The tetrahydrofolate cycle was reconstructed by utilizing Methylobacterium extorquens formate-THF ligase, methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase, and methylene-THF dehydrogenase. The glycine cleavage reaction was reversed by knocking out the repressor gene (gcvR) and overexpressing the gcvTHP genes that encode enzymes related with the glycine cleavage reaction. Formic acid and CO2 conversion to pyruvate was increased via metabolic engineering of the E. coli strain equipped with the one-carbon assimilation pathway.
In addition, in order to reduce glucose consumption and increase formic acid consumption, Candida boidnii formate dehydrogenase was additionally introduced to construct a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid. This reduces glucose consumption and increases formic acid consumption.
The reconstructed one-carbon pathways can supply cellular molecules and cellular energies from the formic acid and CO2. Thus, the engineered E. coli strain equipped with the formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathway and cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid showed cell growth from formic acid and CO2 without glucose. Cell growth was monitored and 13C isotope analysis was performed to confirm E. coli growth from the formic acid and CO2. It was found that the engineered E. coli strain sustained cell growth from the formic acid and CO2 without glucose.
Professor Lee said, “To construct the C1-refinery system, a platform strain that can convert one-carbon materials to higher carbon materials needs to be developed. In this report, a one-carbon pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate was developed and a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid was introduced. This resulted in an engineered E. coli strain that can efficiently utilize formic acid as a carbon source while glucose consumption was reduced. The reconstructed one-carbon pathways in this research will be useful for the construction of the C1-refinery system.”
This work was supported by the C1 Gas Refinery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2016M3D3A1A01913250). For further information: Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
2018.09.18 View 7040 -
 Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 6401
Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 6401 -
 Mathematical Principle behind AI's 'Black Box'
(from left: Professor Jong Chul Ye, PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha)
A KAIST research team identified the geometrical structure of artificial intelligence (AI) and discovered the mathematical principles of highly performing artificial neural networks, which can be applicable in fields such as medical imaging.
Deep neural networks are an exemplary method of implementing deep learning, which is at the core of the AI technology, and have shown explosive growth in recent years. This technique has been used in various fields, such as image and speech recognition as well as image processing.
Despite its excellent performance and usefulness, the exact working principles of deep neural networks has not been well understood, and they often suffer from unexpected results or errors. Hence, there is an increasing social and technical demand for interpretable deep neural network models.
To address these issues, Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering and his team attempted to find the geometric structure in a higher dimensional space where the structure of the deep neural network can be easily understood. They proposed a general deep learning framework, called deep convolutional framelets, to understand the mathematical principle of a deep neural network in terms of the mathematical tools in Harmonic analysis.
As a result, it was found that deep neural networks’ structure appears during the process of decomposition of high dimensionally lifted signal via Hankel matrix, which is a high-dimensional structure formerly studied intensively in the field of signal processing.
In the process of decomposing the lifted signal, two bases categorized as local and non-local basis emerge. The researchers found that non-local and local basis functions play a role in pooling and filtering operation in convolutional neural network, respectively.
Previously, when implementing AI, deep neural networks were usually constructed through empirical trial and errors. The significance of the research lies in the fact that it provides a mathematical understanding on the neural network structure in high dimensional space, which guides users to design an optimized neural network.
They demonstrated improved performance of the deep convolutional framelets’ neural networks in the applications of image denoising, image pixel in painting, and medical image restoration.
Professor Ye said, “Unlike conventional neural networks designed through trial-and-error, our theory shows that neural network structure can be optimized to each desired application and are easily predictable in their effects by exploiting the high dimensional geometry. This technology can be applied to a variety of fields requiring interpretation of the architecture, such as medical imaging.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha, was published in the April 26th issue of the SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences.
Figure 1. The design of deep neural network using mathematical principles
Figure 2. The results of image noise cancelling
Figure 3. The artificial neural network restoration results in the case where 80% of the pixels are lost
2018.09.12 View 6520
Mathematical Principle behind AI's 'Black Box'
(from left: Professor Jong Chul Ye, PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha)
A KAIST research team identified the geometrical structure of artificial intelligence (AI) and discovered the mathematical principles of highly performing artificial neural networks, which can be applicable in fields such as medical imaging.
Deep neural networks are an exemplary method of implementing deep learning, which is at the core of the AI technology, and have shown explosive growth in recent years. This technique has been used in various fields, such as image and speech recognition as well as image processing.
Despite its excellent performance and usefulness, the exact working principles of deep neural networks has not been well understood, and they often suffer from unexpected results or errors. Hence, there is an increasing social and technical demand for interpretable deep neural network models.
To address these issues, Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering and his team attempted to find the geometric structure in a higher dimensional space where the structure of the deep neural network can be easily understood. They proposed a general deep learning framework, called deep convolutional framelets, to understand the mathematical principle of a deep neural network in terms of the mathematical tools in Harmonic analysis.
As a result, it was found that deep neural networks’ structure appears during the process of decomposition of high dimensionally lifted signal via Hankel matrix, which is a high-dimensional structure formerly studied intensively in the field of signal processing.
In the process of decomposing the lifted signal, two bases categorized as local and non-local basis emerge. The researchers found that non-local and local basis functions play a role in pooling and filtering operation in convolutional neural network, respectively.
Previously, when implementing AI, deep neural networks were usually constructed through empirical trial and errors. The significance of the research lies in the fact that it provides a mathematical understanding on the neural network structure in high dimensional space, which guides users to design an optimized neural network.
They demonstrated improved performance of the deep convolutional framelets’ neural networks in the applications of image denoising, image pixel in painting, and medical image restoration.
Professor Ye said, “Unlike conventional neural networks designed through trial-and-error, our theory shows that neural network structure can be optimized to each desired application and are easily predictable in their effects by exploiting the high dimensional geometry. This technology can be applied to a variety of fields requiring interpretation of the architecture, such as medical imaging.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha, was published in the April 26th issue of the SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences.
Figure 1. The design of deep neural network using mathematical principles
Figure 2. The results of image noise cancelling
Figure 3. The artificial neural network restoration results in the case where 80% of the pixels are lost
2018.09.12 View 6520