research
-
 Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13180
Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13180 -
 A Substance with Amazingly Improved Efficiency of Capturing Carbon Dioxides Developed
From left to right: Prof.Ali Coskun, Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Yousung Jung
- Selectivity of CO2 increased by 300 times in comparison to nitrogen, published in Nature Communications-
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s joint research team led by Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, Prof. Ali Coskun, and Prof. Yousung Jung has developed the world"s most efficient CO2 absorbent that has 300 times higher carbon dioxide selectivity in comparison to nitrogen.
Recently, the importance of CCS* technology, which is about capturing, storing and treating carbon dioxides, has begun to emerge world-widely as a practical alternative for the response to climate change.
* CCS : Carbon Capture and sequestration
Current carbon dioxide capturing technologies are wet capturing using liquid absorbent, dry capturing using solid absorbent and separation-membrane capturing using a thin membrane like a film.
For the places like power plant and forge, where the emission of carbon dioxides is huge, the main task is to maintain the capturing efficiency under extremely hot and humid conditions.
The previously studied dry absorbents, such as MOF or zeolite, had the disadvantages of instability in moist conditions and expensive cost for synthesis.
On the other hand, the research team"s newly discovered dry absorbent, named ‘Azo-COP’, can be synthesized without any expensive catalysts so the production cost is very low. It is also stable under hot and humid conditions.
COP is a structure consisting of simple organic molecules combined into porous polymer and is the first dry carbon dioxide capturing material developed by this research team.
The research team introduced an additional functional group called "Azo" to the substance, so that it can selectively capture carbon dioxides among the mixture of gas.
Azo-COP, which includes ‘Azo’ functional group, is manufactured easily by using common synthesis methods, and impurities are removed simply by using cheap solvents like water and acetone instead of expensive catalysts. As a result, the manufacturing cost has lowered drastically.
Especially, Azo-COP is combined with carbon dioxides by weak attraction force rather than chemical attraction so the recycling energy cost for the absorbent can be reduced innovatively, and it is expected to be used for capturing substances other than carbon dioxides in various areas as it is stable under extreme conditions even under 350 degrees Celsius.
This research is supported by Korea Carbon Capture&Sequestration R&D Center(Head: Sangdo Park) and KAIST EEWS planning group.
Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Ali Coskun said that “when Azo-COP is used for separation of CO2 and N2, the capturing efficiency has increased by hundred times.” He continued “This substance does not need any catalysts and has great chemical characteristics like water stability and structure stability so is expected to be used in various fields including carbon dioxides capturing”
Meanwhile, this research is published in ‘Nature’s stablemate ‘Nature Communications’ on 15th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 14099
A Substance with Amazingly Improved Efficiency of Capturing Carbon Dioxides Developed
From left to right: Prof.Ali Coskun, Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Yousung Jung
- Selectivity of CO2 increased by 300 times in comparison to nitrogen, published in Nature Communications-
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s joint research team led by Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, Prof. Ali Coskun, and Prof. Yousung Jung has developed the world"s most efficient CO2 absorbent that has 300 times higher carbon dioxide selectivity in comparison to nitrogen.
Recently, the importance of CCS* technology, which is about capturing, storing and treating carbon dioxides, has begun to emerge world-widely as a practical alternative for the response to climate change.
* CCS : Carbon Capture and sequestration
Current carbon dioxide capturing technologies are wet capturing using liquid absorbent, dry capturing using solid absorbent and separation-membrane capturing using a thin membrane like a film.
For the places like power plant and forge, where the emission of carbon dioxides is huge, the main task is to maintain the capturing efficiency under extremely hot and humid conditions.
The previously studied dry absorbents, such as MOF or zeolite, had the disadvantages of instability in moist conditions and expensive cost for synthesis.
On the other hand, the research team"s newly discovered dry absorbent, named ‘Azo-COP’, can be synthesized without any expensive catalysts so the production cost is very low. It is also stable under hot and humid conditions.
COP is a structure consisting of simple organic molecules combined into porous polymer and is the first dry carbon dioxide capturing material developed by this research team.
The research team introduced an additional functional group called "Azo" to the substance, so that it can selectively capture carbon dioxides among the mixture of gas.
Azo-COP, which includes ‘Azo’ functional group, is manufactured easily by using common synthesis methods, and impurities are removed simply by using cheap solvents like water and acetone instead of expensive catalysts. As a result, the manufacturing cost has lowered drastically.
Especially, Azo-COP is combined with carbon dioxides by weak attraction force rather than chemical attraction so the recycling energy cost for the absorbent can be reduced innovatively, and it is expected to be used for capturing substances other than carbon dioxides in various areas as it is stable under extreme conditions even under 350 degrees Celsius.
This research is supported by Korea Carbon Capture&Sequestration R&D Center(Head: Sangdo Park) and KAIST EEWS planning group.
Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Ali Coskun said that “when Azo-COP is used for separation of CO2 and N2, the capturing efficiency has increased by hundred times.” He continued “This substance does not need any catalysts and has great chemical characteristics like water stability and structure stability so is expected to be used in various fields including carbon dioxides capturing”
Meanwhile, this research is published in ‘Nature’s stablemate ‘Nature Communications’ on 15th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 14099 -
 KAIST Professors win 2012 Korea Engineering Award
Distinguished Professor Hwang Gyu Young (Department of Computer Science) and Professor Yang Dong Yol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) from KAIST received the 2012 ‘Korea Engineering Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korea Research Foundation.
The ‘Korea Engineering Award’ is given biennially to researchers who have accomplished world class research and have contributed greatly to Korea’s development in the field of Science and Technology. The award started in 1994 and a total of 24 recipients were recognized in various fields such as electronics, mechanics, chemistry, construction, etc. The recipients of the award areawarded the Presidential award as well as 50million won as prize money.
Professor Hwang was recognized for his research on DBMS close-coupling architecture as well as other new data base system theories, contributing to the development of the IT software industry in Korea. Professor Yang was praised for his work in precision shape creation and manufacturing, especially for his work in the nano-stereolithography process.
In addition, Professor Oum Sang-il from the Deparment of Mathematical Science received the 2012 ‘Young Scientist Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The ceremony for ‘Korea Engineering Award’ and the ‘Young Scientist Award’ was held in Seoul Press Center Press Club on the 21st of December.
2012.12.26 View 16138
KAIST Professors win 2012 Korea Engineering Award
Distinguished Professor Hwang Gyu Young (Department of Computer Science) and Professor Yang Dong Yol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) from KAIST received the 2012 ‘Korea Engineering Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korea Research Foundation.
The ‘Korea Engineering Award’ is given biennially to researchers who have accomplished world class research and have contributed greatly to Korea’s development in the field of Science and Technology. The award started in 1994 and a total of 24 recipients were recognized in various fields such as electronics, mechanics, chemistry, construction, etc. The recipients of the award areawarded the Presidential award as well as 50million won as prize money.
Professor Hwang was recognized for his research on DBMS close-coupling architecture as well as other new data base system theories, contributing to the development of the IT software industry in Korea. Professor Yang was praised for his work in precision shape creation and manufacturing, especially for his work in the nano-stereolithography process.
In addition, Professor Oum Sang-il from the Deparment of Mathematical Science received the 2012 ‘Young Scientist Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The ceremony for ‘Korea Engineering Award’ and the ‘Young Scientist Award’ was held in Seoul Press Center Press Club on the 21st of December.
2012.12.26 View 16138 -
 High Efficiency Bio-butanol production technology developed
KAIST and Korean Company cooperative research team has developed the technology that increases the productivity of bio-butanol to equal that of bio-ethanol and decreases the cost of production.
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Department of Biological-Chemical Engineering) collaborated with GS Caltex and BioFuelChem Ltd. to develop a bio-butanol production process using the system metabolism engineering method that increased the productivity and decreased the production cost.
Bio-butanol is being widely regarded as the environmentally friendly next generation energy source that surpasses bio-ethanol.
The energy density of bio-butanol is 29.9MJ (mega Joule) per Liter, 48% larger than bio-ethanol (19.6MJ) and comparable to gasoline (32MJ). Bio-butanol is advantageous in that it can be processed from inedible biomass and is therefore unrelated to food crises.
Especially because bio-butanol shows similar characteristics especially in its octane rating, enthalpy of vaporization, and air-fuel ratio, it can be used in a gasoline engine.
However barriers such as difficulty in gene manipulation of producer bacterium and insufficient information prevented the mass production of bio-butanol.
Professor Lee’s team applied the system metabolism engineering method that he had invented to shift the focus to the production pathway of bio-butanol and made a new metabolism model.
In the new model the bio-butanol production pathway is divided into the hot channel and the cold channel.
The research team focused on improving the efficiency of the hot channel and succeeded in improving the product yield of 49% (compared to theoretical yield) to 87%.
The team furthered their research and developed a live bio-butanol collection and removal system with GS Caltex. The collaboration succeeded in producing 585g of butanol using 1.8kg of glucose at a rate of 1.3g per hour, boasting world’s highest concentration, productivity, and rate and improving productivity of fermentation by three fold and decreasing costs by 30%.
The result of the research was published in world renowned ‘mBio’ microbiology journal.
2012.12.21 View 10428
High Efficiency Bio-butanol production technology developed
KAIST and Korean Company cooperative research team has developed the technology that increases the productivity of bio-butanol to equal that of bio-ethanol and decreases the cost of production.
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Department of Biological-Chemical Engineering) collaborated with GS Caltex and BioFuelChem Ltd. to develop a bio-butanol production process using the system metabolism engineering method that increased the productivity and decreased the production cost.
Bio-butanol is being widely regarded as the environmentally friendly next generation energy source that surpasses bio-ethanol.
The energy density of bio-butanol is 29.9MJ (mega Joule) per Liter, 48% larger than bio-ethanol (19.6MJ) and comparable to gasoline (32MJ). Bio-butanol is advantageous in that it can be processed from inedible biomass and is therefore unrelated to food crises.
Especially because bio-butanol shows similar characteristics especially in its octane rating, enthalpy of vaporization, and air-fuel ratio, it can be used in a gasoline engine.
However barriers such as difficulty in gene manipulation of producer bacterium and insufficient information prevented the mass production of bio-butanol.
Professor Lee’s team applied the system metabolism engineering method that he had invented to shift the focus to the production pathway of bio-butanol and made a new metabolism model.
In the new model the bio-butanol production pathway is divided into the hot channel and the cold channel.
The research team focused on improving the efficiency of the hot channel and succeeded in improving the product yield of 49% (compared to theoretical yield) to 87%.
The team furthered their research and developed a live bio-butanol collection and removal system with GS Caltex. The collaboration succeeded in producing 585g of butanol using 1.8kg of glucose at a rate of 1.3g per hour, boasting world’s highest concentration, productivity, and rate and improving productivity of fermentation by three fold and decreasing costs by 30%.
The result of the research was published in world renowned ‘mBio’ microbiology journal.
2012.12.21 View 10428 -
 Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situ
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 10102
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situ
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 10102 -
 Household Scale Indoor Position Tracking Technology Developed
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 9266
Household Scale Indoor Position Tracking Technology Developed
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 9266 -
 Novel material that prevents health decline with age found
Professor Kim Dae Soo (Department of Biological Science), his research team, the Choong Nam University Medicine School, and various companies conducted collaborative research succeeded in developing a novel material that prevents health decline with age. The result was published in PLoS One Journal with the title “Beta-lapachone, a modulator of NAD metabolism, prevents health declines in aged mice”.
Longevity and health can be obtained with reducing consumption of food and aerobic exercise.
Professor Kim’s team focused on the fact that reduced consumption of food and aerobic exercise increase the coenzyme (NAD+) which suppresses the aging of cells. The research team discovered that by activating NQO1 enzyme with Beta-lapachone, the amount of NAD+ in the body increases even without reduction of food consumption or aerobic exercise.
Even consumption of Beta-lapachone by aging mice caused an improved on the brain and exercise ability of the mice. It is expected that commercialization of Beta-lapachone will be possible as it is a chemical that is commonly found in herbs used in both the orient and the oxidant.
2012.12.21 View 8634
Novel material that prevents health decline with age found
Professor Kim Dae Soo (Department of Biological Science), his research team, the Choong Nam University Medicine School, and various companies conducted collaborative research succeeded in developing a novel material that prevents health decline with age. The result was published in PLoS One Journal with the title “Beta-lapachone, a modulator of NAD metabolism, prevents health declines in aged mice”.
Longevity and health can be obtained with reducing consumption of food and aerobic exercise.
Professor Kim’s team focused on the fact that reduced consumption of food and aerobic exercise increase the coenzyme (NAD+) which suppresses the aging of cells. The research team discovered that by activating NQO1 enzyme with Beta-lapachone, the amount of NAD+ in the body increases even without reduction of food consumption or aerobic exercise.
Even consumption of Beta-lapachone by aging mice caused an improved on the brain and exercise ability of the mice. It is expected that commercialization of Beta-lapachone will be possible as it is a chemical that is commonly found in herbs used in both the orient and the oxidant.
2012.12.21 View 8634 -
 Prof. Jang-Uk Choi develops Strong, Long-lasting Lithium-ion Battery
Lithium-ion secondary battery with high power, as well asmuch longer life span, has been developed using nanotechnology. Professor Jang-Uk Choi and his colleagues at KAIST University EEWS graduate school has succeeded in developing a new lithium-ion secondary battery that has more than five times the output and three times the life span of the conventional batteries.
The industry expects the new battery to significantly improve the acceleration performance and solve the drawbacks of slow electric cars, which occurred due to failure of battery performance to keep up with the output of the motors during acceleration.
It is also expected that the new battery could be utilized in various fields that require high power batteries such as Smart Grid, which is the next generation intelligent electrical grid, as well as electric tools and many others.
Currently, the most widely used commercial lithium ion batteries’ lithium-cobalt-based cathode material has the disadvantage of expensive cost, high toxicity, short life expectancy and long-charge/discharge time. Also, it has been difficult to apply in electric cars that require a large current density and are vulnerable to heat generated during charging/discharging.
On the other hand, Professor Choi and his colleagues’ lithium-manganese based cathode material is gaining popularity for having the advantages such as abundant raw materials, cheap prices, eco-friendliness and especially excellent high-temperature stability and high output, which are suitable for use as electrode material in electric cars.
The pure lithium manganese based cathode material has a critical drawback of a very short life expectancy, only lasting about average of 1-2 years, which is due to the elution when the melted manganese flows out into the electrolyte. There have been various studies to solve this problem; however, the unique crystal structure of the material remained as a challenge for many scientists.
Professor Choi’s team analyzed the structure of the crystal at the time shortly before manganese oxides were formed, while controlling the reaction temperature at the step of synthesizing nanomaterial. It has been found that, at 220℃, there are simultaneously existing two crystal faces, one that inhibits the dissolution of manganese ions and the other that enables lithium ions to move smoothly.
Each of these crystal faces improves both the life span and output, increasing the output more than five times and life expectancy over three times. In addition, the existing high temperature life span, that was known to be especially vulnerable, has improved ten-fold.
“By controlling the crystal face of lithium manganese anode material, which has previously existed in the battery as chunks of about 10 micro-meter particles, both output and life span has significantly improved,” said Professor Choi, “Domestic and international patent application for the regarding technology has been finished and we have plans to work with companies in the future for commercialization within 2-3 years.”
Professor Yi Cui of Stanford University, the world’s leading scholar on the secondary battery, has evaluated that “This research exemplifies how nanotechnology can innovatively develop the field of secondary battery.”
Meanwhile, the research led by Professor Jang-Uk Choi and participated by researcher Ju-Seong Kim has been published on the online edition (dated Nov 27th) of Nanoletters, the world’s leading authority on Nanoscience.
2012.12.21 View 10949
Prof. Jang-Uk Choi develops Strong, Long-lasting Lithium-ion Battery
Lithium-ion secondary battery with high power, as well asmuch longer life span, has been developed using nanotechnology. Professor Jang-Uk Choi and his colleagues at KAIST University EEWS graduate school has succeeded in developing a new lithium-ion secondary battery that has more than five times the output and three times the life span of the conventional batteries.
The industry expects the new battery to significantly improve the acceleration performance and solve the drawbacks of slow electric cars, which occurred due to failure of battery performance to keep up with the output of the motors during acceleration.
It is also expected that the new battery could be utilized in various fields that require high power batteries such as Smart Grid, which is the next generation intelligent electrical grid, as well as electric tools and many others.
Currently, the most widely used commercial lithium ion batteries’ lithium-cobalt-based cathode material has the disadvantage of expensive cost, high toxicity, short life expectancy and long-charge/discharge time. Also, it has been difficult to apply in electric cars that require a large current density and are vulnerable to heat generated during charging/discharging.
On the other hand, Professor Choi and his colleagues’ lithium-manganese based cathode material is gaining popularity for having the advantages such as abundant raw materials, cheap prices, eco-friendliness and especially excellent high-temperature stability and high output, which are suitable for use as electrode material in electric cars.
The pure lithium manganese based cathode material has a critical drawback of a very short life expectancy, only lasting about average of 1-2 years, which is due to the elution when the melted manganese flows out into the electrolyte. There have been various studies to solve this problem; however, the unique crystal structure of the material remained as a challenge for many scientists.
Professor Choi’s team analyzed the structure of the crystal at the time shortly before manganese oxides were formed, while controlling the reaction temperature at the step of synthesizing nanomaterial. It has been found that, at 220℃, there are simultaneously existing two crystal faces, one that inhibits the dissolution of manganese ions and the other that enables lithium ions to move smoothly.
Each of these crystal faces improves both the life span and output, increasing the output more than five times and life expectancy over three times. In addition, the existing high temperature life span, that was known to be especially vulnerable, has improved ten-fold.
“By controlling the crystal face of lithium manganese anode material, which has previously existed in the battery as chunks of about 10 micro-meter particles, both output and life span has significantly improved,” said Professor Choi, “Domestic and international patent application for the regarding technology has been finished and we have plans to work with companies in the future for commercialization within 2-3 years.”
Professor Yi Cui of Stanford University, the world’s leading scholar on the secondary battery, has evaluated that “This research exemplifies how nanotechnology can innovatively develop the field of secondary battery.”
Meanwhile, the research led by Professor Jang-Uk Choi and participated by researcher Ju-Seong Kim has been published on the online edition (dated Nov 27th) of Nanoletters, the world’s leading authority on Nanoscience.
2012.12.21 View 10949 -
 Firefly inspired high efficiency LED technology developed
A firefly inspired, high efficiency self-illuminating LED has been developed.
Professor Jeong Gi Hoon (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) mimicked the nanostructure of the external layer of the illumination organ of a firefly and succeeded in fabricating high illumination efficiency LED lenses.
Conventional lenses required expensive anti-reflection coating. The developed lenses utilize the bio-inspired nanostructure on the surface of the lenses themselves to reduce the reflectivity of the lenses thereby decreasing production costs.
The developed antireflection nanostructure is expected to be applied to various digital devices and lighting fixtures.
Antireflective structures have been applied in various fields in order to enhance light efficiency However these structures have been limited to flat surfaces and therefore was difficult to implement to curved surfaces like LED lenses.
Professor Jeong’s team solved this problem by using three dimensional micro molding processes.
The team fabricated the nanostructure by forming a single nanoparticle layer on the silicon oxide and performing dry etching. On this nanostructure PDMS was poured and manipulated to fabricate a lens structure similar to that of a firefly.
The fabricated lens showed similar efficiency as conventional antireflection coating.
2012.11.29 View 9774
Firefly inspired high efficiency LED technology developed
A firefly inspired, high efficiency self-illuminating LED has been developed.
Professor Jeong Gi Hoon (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) mimicked the nanostructure of the external layer of the illumination organ of a firefly and succeeded in fabricating high illumination efficiency LED lenses.
Conventional lenses required expensive anti-reflection coating. The developed lenses utilize the bio-inspired nanostructure on the surface of the lenses themselves to reduce the reflectivity of the lenses thereby decreasing production costs.
The developed antireflection nanostructure is expected to be applied to various digital devices and lighting fixtures.
Antireflective structures have been applied in various fields in order to enhance light efficiency However these structures have been limited to flat surfaces and therefore was difficult to implement to curved surfaces like LED lenses.
Professor Jeong’s team solved this problem by using three dimensional micro molding processes.
The team fabricated the nanostructure by forming a single nanoparticle layer on the silicon oxide and performing dry etching. On this nanostructure PDMS was poured and manipulated to fabricate a lens structure similar to that of a firefly.
The fabricated lens showed similar efficiency as conventional antireflection coating.
2012.11.29 View 9774 -
 Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9950
Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9950 -
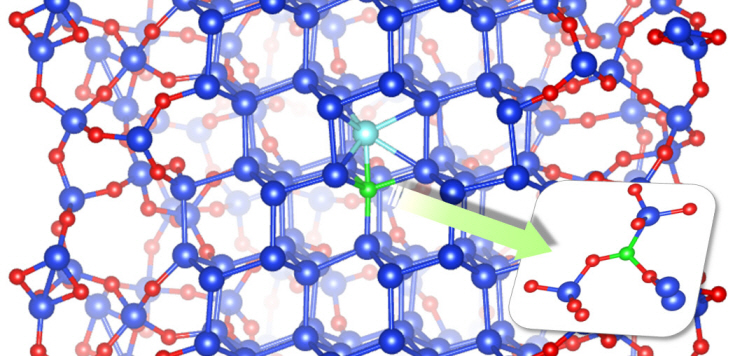 Dopant properties of silicon nanowires investigated
Professor Chang Kee Joo
Professor Kee Joo Chang’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has successfully unearthed the properties of boron and phosphorous dopants in silicon nanowires, a material expected to be used in next generation semiconductors. The research team was the first in the world to investigate the movement of boron and phosphorous (impurities or ‘dopants’ added for electrical flow) in oxidized silicon nanowires and study the mechanism behind its deactivation.
It is nearly impossible to develop a silicon based semiconductor thinner than 10nm, even using the most advanced modern technology. However, the thickness of silicon nanowires are within the nano level and hence, allows a higher degree of integration in semiconductors.
For silicon nanowires to carry electricity, small amounts of boron and phosphorous need to be added (‘doping’ process). Compared to silicon, nanowires are harder to create due to the difficulties in the doping process as well as the control of electrical conduction properties.
Professor Chang’s research team improved upon the existing simple model by applying revolutionary quantum simulation theory to create a realistic core-shell atomic model. This research successfully investigated the cause of the escape of boron dopants from the silicon core during oxidation. It was also found that although phosphorous dopants do not escape as oxides, they form electrically deactivated pairs which decreases the efficiency. These phenomena were attributed to the film shape of the nano-wires, which increases the relative surface area compared to a same volume of silicon.
The research results were published in the online September edition of the world renowned Nano Letters.
Figure: The longitudinal section diagram of the Silicon/oxide core-shell model
2012.11.28 View 9442
Dopant properties of silicon nanowires investigated
Professor Chang Kee Joo
Professor Kee Joo Chang’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has successfully unearthed the properties of boron and phosphorous dopants in silicon nanowires, a material expected to be used in next generation semiconductors. The research team was the first in the world to investigate the movement of boron and phosphorous (impurities or ‘dopants’ added for electrical flow) in oxidized silicon nanowires and study the mechanism behind its deactivation.
It is nearly impossible to develop a silicon based semiconductor thinner than 10nm, even using the most advanced modern technology. However, the thickness of silicon nanowires are within the nano level and hence, allows a higher degree of integration in semiconductors.
For silicon nanowires to carry electricity, small amounts of boron and phosphorous need to be added (‘doping’ process). Compared to silicon, nanowires are harder to create due to the difficulties in the doping process as well as the control of electrical conduction properties.
Professor Chang’s research team improved upon the existing simple model by applying revolutionary quantum simulation theory to create a realistic core-shell atomic model. This research successfully investigated the cause of the escape of boron dopants from the silicon core during oxidation. It was also found that although phosphorous dopants do not escape as oxides, they form electrically deactivated pairs which decreases the efficiency. These phenomena were attributed to the film shape of the nano-wires, which increases the relative surface area compared to a same volume of silicon.
The research results were published in the online September edition of the world renowned Nano Letters.
Figure: The longitudinal section diagram of the Silicon/oxide core-shell model
2012.11.28 View 9442 -
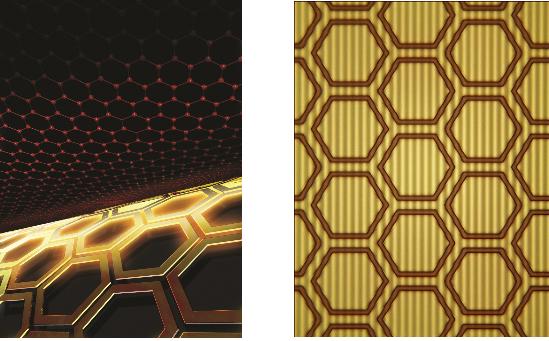 The control of light at the nano-level
Professor Min Bumki
Professor Min Bumki’s research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have successfully gained control of the transmittance of light in optical devices using graphene* and artificial 2-dimensional metamaterials**.
* Graphene : a thin membrane composed of pure carbon, with atoms arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern
** Metamaterials : artificial materials engineered to have properties that may not be found in nature
The research results were published in the recent online edition (September 30th) of Nature Materials, a sister journal of the world renowned Nature journal, under the title ‘Terahertz waves with gate-controlled active graphene metamaterials’
Since the discovery of graphene in 2004 by Professors Novoselov and Geim from the University of Manchester (2010 Nobel Prize winners in Physics), it has been dubbed “the dream material” because of its outstanding physical properties.
Graphene has been especially praised for its ability to absorb approximately 2.3% of near infrared and visible rays due to its characteristic electron structure. This property allows graphene to be used as a transparent electrode, which is a vital electrical component used in touch screens and solar batteries. However, graphene’s optical transmittance was largely ignored by researchers due to its limited control using electrical methods and its small optical modulation in data transfer.
Professor Min’s team combined 0.34 nanometer-thick graphene with metamaterials to allow a more effective control of light transmittance and greater optical modulation. This graphene metamaterial can be integrated in to a thin and flexible macromolecule substrate which allows the control of transmittance using electric signals.
This research experimentally showed that graphene metamaterials can not only effective control optical transmittance, but can also be used in graphene optical memory devices using electrical hysteresis.
Professor Min said that “this research allows the effective control of light at the nanometer level” and that “this research will help in the development of microscopic optical modulators or memory disks”.
figure 1. The working drawing of graphene metamaterials
figure 2. Conceptual diagram (Left) and microscopic photo (right) of graphene metamaterials
2012.11.23 View 12121
The control of light at the nano-level
Professor Min Bumki
Professor Min Bumki’s research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have successfully gained control of the transmittance of light in optical devices using graphene* and artificial 2-dimensional metamaterials**.
* Graphene : a thin membrane composed of pure carbon, with atoms arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern
** Metamaterials : artificial materials engineered to have properties that may not be found in nature
The research results were published in the recent online edition (September 30th) of Nature Materials, a sister journal of the world renowned Nature journal, under the title ‘Terahertz waves with gate-controlled active graphene metamaterials’
Since the discovery of graphene in 2004 by Professors Novoselov and Geim from the University of Manchester (2010 Nobel Prize winners in Physics), it has been dubbed “the dream material” because of its outstanding physical properties.
Graphene has been especially praised for its ability to absorb approximately 2.3% of near infrared and visible rays due to its characteristic electron structure. This property allows graphene to be used as a transparent electrode, which is a vital electrical component used in touch screens and solar batteries. However, graphene’s optical transmittance was largely ignored by researchers due to its limited control using electrical methods and its small optical modulation in data transfer.
Professor Min’s team combined 0.34 nanometer-thick graphene with metamaterials to allow a more effective control of light transmittance and greater optical modulation. This graphene metamaterial can be integrated in to a thin and flexible macromolecule substrate which allows the control of transmittance using electric signals.
This research experimentally showed that graphene metamaterials can not only effective control optical transmittance, but can also be used in graphene optical memory devices using electrical hysteresis.
Professor Min said that “this research allows the effective control of light at the nanometer level” and that “this research will help in the development of microscopic optical modulators or memory disks”.
figure 1. The working drawing of graphene metamaterials
figure 2. Conceptual diagram (Left) and microscopic photo (right) of graphene metamaterials
2012.11.23 View 12121