AT
-
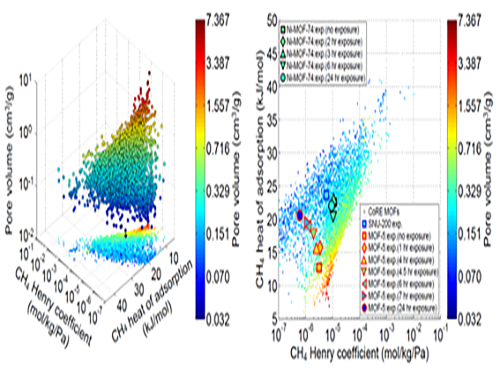 Analysis of Gas Adsorption Properties for Amorphous Porous Materials
Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a method to predict gas adsorption properties of amorphous porous materials.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have large surface area and high density of pores, making them appropriate for various energy and environmental-related applications. And although most MOFs are crystalline, these structures can deform during synthesis and/or industrial processes, leading to loss in long-range order. Unfortunately, without the structural information, existing computer simulation techniques cannot be used to model these materials.
In this research, Professor Kim’s research team demonstrated that one can replace the material properties of structurally deformed MOFs with those of crystalline MOFs to indirectly analyze/model the material properties of amorphous materials. First, the team conducted simulations on methane gas adsorption properties for over 12,000 crystalline MOFs to obtain a large training set data, and created a resulting structure-property map. Upon mapping the experimental data of amorphous MOFs onto the structure-property map, results showed that regardless of crystallinity, the gas adsorption properties of MOFs showed congruence and consistency amongst one another.
Based on these findings, selected crystalline MOFs with the most similar gas adsorption properties as the collapsed structure from the 12,000 candidates. Then, the team verified that the adsorption properties of these similar MOFs can be successfully transferred to the deformed MOFs across different temperatures and even to different gas molecules (e.g. hydrogen), demonstrating transferability of properties.
These findings allow material property prediction in porous materials such as MOFs without structural information, and the techniques here can be used to better predict and understand optimal materials for various applications including, carbon dioxide capture, gas storage and separations.
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Dae-Woon Lim at Kyoto University, Professor Myunghyun Paik at Seoul National University, Professor Minyoung Yoon at Gachon University, and Aadesh Harale at Saudi Arabian Oil Company. The research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online on 10 July and the co-first authors were Ph. D. candidate WooSeok Jeong and Professor Dae-Woon Lim.
This research was funded by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
(Figure 1. Trends in structure - material property map and in collapsed structures)
(Figure 2. Transferability between the experimental results of collapsed MOFs and the simulation results of crystalline MOFs)
2017.07.26 View 10583
Analysis of Gas Adsorption Properties for Amorphous Porous Materials
Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a method to predict gas adsorption properties of amorphous porous materials.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have large surface area and high density of pores, making them appropriate for various energy and environmental-related applications. And although most MOFs are crystalline, these structures can deform during synthesis and/or industrial processes, leading to loss in long-range order. Unfortunately, without the structural information, existing computer simulation techniques cannot be used to model these materials.
In this research, Professor Kim’s research team demonstrated that one can replace the material properties of structurally deformed MOFs with those of crystalline MOFs to indirectly analyze/model the material properties of amorphous materials. First, the team conducted simulations on methane gas adsorption properties for over 12,000 crystalline MOFs to obtain a large training set data, and created a resulting structure-property map. Upon mapping the experimental data of amorphous MOFs onto the structure-property map, results showed that regardless of crystallinity, the gas adsorption properties of MOFs showed congruence and consistency amongst one another.
Based on these findings, selected crystalline MOFs with the most similar gas adsorption properties as the collapsed structure from the 12,000 candidates. Then, the team verified that the adsorption properties of these similar MOFs can be successfully transferred to the deformed MOFs across different temperatures and even to different gas molecules (e.g. hydrogen), demonstrating transferability of properties.
These findings allow material property prediction in porous materials such as MOFs without structural information, and the techniques here can be used to better predict and understand optimal materials for various applications including, carbon dioxide capture, gas storage and separations.
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Dae-Woon Lim at Kyoto University, Professor Myunghyun Paik at Seoul National University, Professor Minyoung Yoon at Gachon University, and Aadesh Harale at Saudi Arabian Oil Company. The research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online on 10 July and the co-first authors were Ph. D. candidate WooSeok Jeong and Professor Dae-Woon Lim.
This research was funded by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
(Figure 1. Trends in structure - material property map and in collapsed structures)
(Figure 2. Transferability between the experimental results of collapsed MOFs and the simulation results of crystalline MOFs)
2017.07.26 View 10583 -
 KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 13076
KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 13076 -
 Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 8485
Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 8485 -
 Cooperative Tumor Cell Membrane-Targeted Phototherapy
A KAIST research team led by Professor Ji-Ho Park in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST developed a technology for the effective treatment of cancer by delivering synthetic receptors throughout tumor tissue. The study, led by Ph.D. candidate Heegon Kim, was published online in Nature Communications on June 19.
Cancer targeted therapy generally refers to therapy targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and generation of cancer. The targeted delivery of therapeutics using targeting agents such as antibodies or nanomaterials has improved the precision and safety of cancer therapy.
However, the paucity and heterogeneity of identified molecular targets within tumors have resulted in poor and uneven distribution of targeted agents, thus compromising treatment outcomes.
To solve this problem, the team constructed a cooperative targeting system in which synthetic and biological nanocomponents participate together in the tumor cell membrane-selective localization of synthetic receptors to amplify the subsequent targeting of therapeutics. Here, synthetic and biological nanocomponents refer to liposomes and extracellular vesicles, respectively.
The synthetic receptors are first delivered selectively to tumor cell membranes in the perivascular region using liposomes. By hitchhiking with extracellular vesicles secreted by the cells, the synthetic receptors are transferred to neighboring cells and further spread throughout the tumor tissues where the molecular targets are limited.
Hitchhiking extracellular vesicles for delivery of synthetic receptors was possible since extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, mediate intercellular communications by transferring various biological components such as lipids, cytosolic proteins, and RNA through a membrane fusion process. They also play a supportive role in promoting tumor progression in that tumor-derived extracellular vesicles deliver oncogenic signals to normal host cells.
The team showed that this tumor cell membrane-targeted delivery of synthetic receptors led to a uniform distribution of synthetic receptors throughout a tumor and subsequently led to enhanced phototherapeutic efficacy of the targeted photosensitizer.
Professor Park said, “The cooperative tumor targeting system is expected to be applied in treating various diseases that are hard to target.”
The research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control funded by the Ministry for Health and Welfare.
(Ph.D. candidates Hee Gon Kim (left) and Chanhee Oh)
Figure 1. A schematic of a cooperative tumor targeting system via delivery of synthetic receptors.
Figure 2. A confocal microscopic image of a tumor section after cooperative targeting by synthetic receptor delivery. Green and magenta represent vessels and therapeutic agents inside a tumor respectively.
2017.07.07 View 12037
Cooperative Tumor Cell Membrane-Targeted Phototherapy
A KAIST research team led by Professor Ji-Ho Park in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST developed a technology for the effective treatment of cancer by delivering synthetic receptors throughout tumor tissue. The study, led by Ph.D. candidate Heegon Kim, was published online in Nature Communications on June 19.
Cancer targeted therapy generally refers to therapy targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and generation of cancer. The targeted delivery of therapeutics using targeting agents such as antibodies or nanomaterials has improved the precision and safety of cancer therapy.
However, the paucity and heterogeneity of identified molecular targets within tumors have resulted in poor and uneven distribution of targeted agents, thus compromising treatment outcomes.
To solve this problem, the team constructed a cooperative targeting system in which synthetic and biological nanocomponents participate together in the tumor cell membrane-selective localization of synthetic receptors to amplify the subsequent targeting of therapeutics. Here, synthetic and biological nanocomponents refer to liposomes and extracellular vesicles, respectively.
The synthetic receptors are first delivered selectively to tumor cell membranes in the perivascular region using liposomes. By hitchhiking with extracellular vesicles secreted by the cells, the synthetic receptors are transferred to neighboring cells and further spread throughout the tumor tissues where the molecular targets are limited.
Hitchhiking extracellular vesicles for delivery of synthetic receptors was possible since extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, mediate intercellular communications by transferring various biological components such as lipids, cytosolic proteins, and RNA through a membrane fusion process. They also play a supportive role in promoting tumor progression in that tumor-derived extracellular vesicles deliver oncogenic signals to normal host cells.
The team showed that this tumor cell membrane-targeted delivery of synthetic receptors led to a uniform distribution of synthetic receptors throughout a tumor and subsequently led to enhanced phototherapeutic efficacy of the targeted photosensitizer.
Professor Park said, “The cooperative tumor targeting system is expected to be applied in treating various diseases that are hard to target.”
The research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control funded by the Ministry for Health and Welfare.
(Ph.D. candidates Hee Gon Kim (left) and Chanhee Oh)
Figure 1. A schematic of a cooperative tumor targeting system via delivery of synthetic receptors.
Figure 2. A confocal microscopic image of a tumor section after cooperative targeting by synthetic receptor delivery. Green and magenta represent vessels and therapeutic agents inside a tumor respectively.
2017.07.07 View 12037 -
 Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 8486
Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 8486 -
 President Shin Shares His Biggest Challenges, Success, and New Mission
President Sung-Chul Shin talks on his biggest challenges, successes, and new mission in an interview with Times Higher Education on June 29. Followings are the full text of the interview.
▶ What are the unique challenges and advantages of being a university in the Asia-Pacific region?
Globalization is definitely the biggest challenge. KAIST has made strenuous institutional efforts to address this issue for decades. Globalization is not just about language issues, especially for an Asian university. There are still lingering cultural barriers. However, we are improving and seeing significant progress. Approximately 85 per cent of our classes are being lectured in English, and my ultimate goal is to make KAIST a bilingual campus for a more globalized environment.
Speaking of advantages, we can recruit top-quality students from neighboring countries.
▶ What role do universities have in creating social equality?
I strongly believe that education is an essential means of empowerment and social mobility. KAIST has diligently promoted policies to help ensure greater diversity, without discriminating against anyone’s talents on the basis of gender, race, or background.
We implement an equal opportunity admission system, with special consideration given to the underprivileged, geographically-excluded groups, North Korean refugees, and many other disadvantaged groups. We recruit five percent of our freshmen from these groups under our admission system annually.
As for the gender gap, our female student population is now over 25 per cent, and we expect in the very near future the ratio will increase up to 30 percent. However, female faculty ratio stands at around 10 per cent, so we will attempt to double the ratio soon.
In addition, we work to emphasize social responsibility to our students. They are a privileged group, so they should be responsible for giving back their knowledge and talents to society in diverse ways. I am very glad that many of our students engage in the social entrepreneurship programs we are running now. That will be fruitful for ensuring social equity as well as making society better.
▶ What is the most important issue affecting your university right now?
KAIST has now emerged as a world-class university and one of the most innovative universities in the Asia-Pacific region. However, building on our new reputation as a "world-leading" university remains a big challenge. As the first and top research university in Korea, KAIST has been the gateway to the advancement of science and technology and innovation.
We are now responsible for taking the lead in creating new knowledge that will make a global impact. This is the momentum we need to make another quantum leap to become the university which creates the most global value.
▶ There is a great pressure in Korea for young people to get into a “top” university. Is this pressure on school students too great?
Traditionally, going to a top school was deemed the ladder to success in life. We went through the economically tough times in which diverse groups of occupations had never existed before. As a result, competition between individuals was incredibly high to get into good school and good company.
It is true that such social pressure occupied thoughts of many young students and their parents. In effect, that was also the driving force for achieving Korea’s economic growth in a relatively short period of time. But things are changing now.
We are living in a complex global economic environment. The number of new occupations creates new knowledge and new types of jobs. Even more, this new era changed the conventional paradigm of jobs and success. Successful careers take collaboration, and one must seek whom to work with, where you fit, and what you will do and how you can reach your potential.
This change of perception has begun to transform the general definition of a successful life. The government and educational institutions are working to reflect new socio-economic trend to maximize students’ creativity and their own uniqueness in many educational institutions.
However, strong competition to get into a top university seems to be a universal problem - as is also the case for the Ivy League in the US and many other regions.
▶ South Korean universities have some of the closest links to industry. Is a lot of your job about building relationships with companies rather than focusing on educational issues?
The relationship with industry is increasingly significant, and collaboration is very important in Korea. It is a crucial source for securing students’ jobs. On top of that, we get research funding from companies and supply the pipeline of new inventions and innovation for them, in many case through collaboration projects. That could also be interpreted as our reputation of institutional performance through diverse evaluation indicators.
From the industry side, we are a very good supplier of high-caliber manpower. Therefore, a solid relationship with industry is key to the creation of added value of knowledge, as well as a critical steppingstone for technology commercialization.
Therefore, scaling up the organic relationship with industry is part of our education and research portfolio as well as part of my job as president.
▶ Do you think the main role of universities is to prepare graduates for the world of work?
The role of higher education is to educate the future generation and create new knowledge though research. The conventional concept of research and development (R&D) has expanded to R&DB, as it now includes business. Thus, the role of a university is also evolving. Universities should provide diverse opportunities for graduates to prepare them to contribute to society. That will be one of the ways to realize the social responsibility of a university.
▶ If someone else was taking over your role tomorrow, what’s the most useful advice you could give them?
When I took the office in March, I made up my mind to serve our students, faculty and staff with all my heart. I would say, inspire your people with leadership that they can emotionally connected with, if possible. In addition, I think only professionalism can make the best professionals.
▶ Who has inspired you during your career?
Dr. Kun-Mo Chung, former vice president of KAIST and former minister for science and technology, is my role model and mentor. He is an internationally renowned nuclear engineer and scholar, and successful technocrat who served as the minister for science and technology twice. He still teaches at KAIST in his eighties.
I admired his visionary leadership and his successful career as administrator as well as accomplished scholar. After graduating from Seoul National University, he went to Michigan State University. In his early thirties, he came back to Korea as a member of the United States Agency for International Development survey team to conduct the feasibility study for founding KAIST. He wrote the proposal in the Terman Report to the USAID that the establishment of KAIST would be necessary and useful for Korea. With $6 million dollar loan from the agency, he founded KAIST. He is the true innovator, I think.
▶ How do you use data to make sure your university is performing well? We are analyzing the diverse data released from international evaluation institutions such as THE data and Clarivate Analytics, as well as domestic institutions. Through the various indicators of data, we are keen to realize the global standard of our institution and advance our innovation competitiveness at a global level.
2017.07.06 View 7493
President Shin Shares His Biggest Challenges, Success, and New Mission
President Sung-Chul Shin talks on his biggest challenges, successes, and new mission in an interview with Times Higher Education on June 29. Followings are the full text of the interview.
▶ What are the unique challenges and advantages of being a university in the Asia-Pacific region?
Globalization is definitely the biggest challenge. KAIST has made strenuous institutional efforts to address this issue for decades. Globalization is not just about language issues, especially for an Asian university. There are still lingering cultural barriers. However, we are improving and seeing significant progress. Approximately 85 per cent of our classes are being lectured in English, and my ultimate goal is to make KAIST a bilingual campus for a more globalized environment.
Speaking of advantages, we can recruit top-quality students from neighboring countries.
▶ What role do universities have in creating social equality?
I strongly believe that education is an essential means of empowerment and social mobility. KAIST has diligently promoted policies to help ensure greater diversity, without discriminating against anyone’s talents on the basis of gender, race, or background.
We implement an equal opportunity admission system, with special consideration given to the underprivileged, geographically-excluded groups, North Korean refugees, and many other disadvantaged groups. We recruit five percent of our freshmen from these groups under our admission system annually.
As for the gender gap, our female student population is now over 25 per cent, and we expect in the very near future the ratio will increase up to 30 percent. However, female faculty ratio stands at around 10 per cent, so we will attempt to double the ratio soon.
In addition, we work to emphasize social responsibility to our students. They are a privileged group, so they should be responsible for giving back their knowledge and talents to society in diverse ways. I am very glad that many of our students engage in the social entrepreneurship programs we are running now. That will be fruitful for ensuring social equity as well as making society better.
▶ What is the most important issue affecting your university right now?
KAIST has now emerged as a world-class university and one of the most innovative universities in the Asia-Pacific region. However, building on our new reputation as a "world-leading" university remains a big challenge. As the first and top research university in Korea, KAIST has been the gateway to the advancement of science and technology and innovation.
We are now responsible for taking the lead in creating new knowledge that will make a global impact. This is the momentum we need to make another quantum leap to become the university which creates the most global value.
▶ There is a great pressure in Korea for young people to get into a “top” university. Is this pressure on school students too great?
Traditionally, going to a top school was deemed the ladder to success in life. We went through the economically tough times in which diverse groups of occupations had never existed before. As a result, competition between individuals was incredibly high to get into good school and good company.
It is true that such social pressure occupied thoughts of many young students and their parents. In effect, that was also the driving force for achieving Korea’s economic growth in a relatively short period of time. But things are changing now.
We are living in a complex global economic environment. The number of new occupations creates new knowledge and new types of jobs. Even more, this new era changed the conventional paradigm of jobs and success. Successful careers take collaboration, and one must seek whom to work with, where you fit, and what you will do and how you can reach your potential.
This change of perception has begun to transform the general definition of a successful life. The government and educational institutions are working to reflect new socio-economic trend to maximize students’ creativity and their own uniqueness in many educational institutions.
However, strong competition to get into a top university seems to be a universal problem - as is also the case for the Ivy League in the US and many other regions.
▶ South Korean universities have some of the closest links to industry. Is a lot of your job about building relationships with companies rather than focusing on educational issues?
The relationship with industry is increasingly significant, and collaboration is very important in Korea. It is a crucial source for securing students’ jobs. On top of that, we get research funding from companies and supply the pipeline of new inventions and innovation for them, in many case through collaboration projects. That could also be interpreted as our reputation of institutional performance through diverse evaluation indicators.
From the industry side, we are a very good supplier of high-caliber manpower. Therefore, a solid relationship with industry is key to the creation of added value of knowledge, as well as a critical steppingstone for technology commercialization.
Therefore, scaling up the organic relationship with industry is part of our education and research portfolio as well as part of my job as president.
▶ Do you think the main role of universities is to prepare graduates for the world of work?
The role of higher education is to educate the future generation and create new knowledge though research. The conventional concept of research and development (R&D) has expanded to R&DB, as it now includes business. Thus, the role of a university is also evolving. Universities should provide diverse opportunities for graduates to prepare them to contribute to society. That will be one of the ways to realize the social responsibility of a university.
▶ If someone else was taking over your role tomorrow, what’s the most useful advice you could give them?
When I took the office in March, I made up my mind to serve our students, faculty and staff with all my heart. I would say, inspire your people with leadership that they can emotionally connected with, if possible. In addition, I think only professionalism can make the best professionals.
▶ Who has inspired you during your career?
Dr. Kun-Mo Chung, former vice president of KAIST and former minister for science and technology, is my role model and mentor. He is an internationally renowned nuclear engineer and scholar, and successful technocrat who served as the minister for science and technology twice. He still teaches at KAIST in his eighties.
I admired his visionary leadership and his successful career as administrator as well as accomplished scholar. After graduating from Seoul National University, he went to Michigan State University. In his early thirties, he came back to Korea as a member of the United States Agency for International Development survey team to conduct the feasibility study for founding KAIST. He wrote the proposal in the Terman Report to the USAID that the establishment of KAIST would be necessary and useful for Korea. With $6 million dollar loan from the agency, he founded KAIST. He is the true innovator, I think.
▶ How do you use data to make sure your university is performing well? We are analyzing the diverse data released from international evaluation institutions such as THE data and Clarivate Analytics, as well as domestic institutions. Through the various indicators of data, we are keen to realize the global standard of our institution and advance our innovation competitiveness at a global level.
2017.07.06 View 7493 -
 KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 12572
KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 12572 -
 2017 World Friends ICT KAIST Sets Off to Ethiopia, Tanzania
KAIST launched the ‘2017 World Friends ICT KAIST’ on 21 June at a ceremony held at the Faculty Club. The event was attended by 40 student volunteers and faculty members including President Sung-Chul Shin and student volunteers.
The ‘2017 World Friends ICT KAIST’ is an oversees volunteer program aimed at providing ICT education for students from developing countries and for cultural exchange. The program was organized by the KAIST Leadership Center and sponsored by the National Information Agency (NIA) since 2015.
President Sung-Chul Shin delivered words of encouragement to start the opening ceremony, followed by an oath-taking by the volunteer group, safety training, and a commemorative photoshoot. This year’s World Friends ICT volunteer group consisted of 32 students and 2 staff members to lead and to support the team.
The group was divided into eight teams including APP-frica, KAI-Tigers, and WITH (4 members per team) to volunteer in Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAIT) and Adama Science and Technology University in Ethiopia (ASTU), as well as Nelson Mandela African Institute of Science and Technology (NM-AIST) in Tanzania. The teams will educate local students on ICT and promote cultural exchanges. The volunteer period is from July 7 to August 5, lasting about a month.
KAIST conducted primary document examinations and interviews from April 27 to May 18 on volunteer candidates who registered to take part, and selected 32 student volunteers. A total of 68 students registered to volunteer, resulting in a 1:2.1 competition rate.
The volunteering program was customized to the local needs of Ethiopia and Tanzania and thus consisted of ICT education, cultural exchanges, volunteering at farms on the weekends, and science experiments. The area with the most focus by the volunteer team is ICT education, which accounts for 70% of the total volunteer activities. The aim is to educate Ethiopian students at AAIT and ASTU on Windows, MS Office, Adobe Photoshop, and using smartphones. In Tanzania, the team is to volunteer with students of NM-AIST to provide ICT application education such as water tank control using appropriate technology and Arduino to local high school students.
The team is also planning to promote cultural exchanges by preparing K-Pop dancing, traditional Korean games such as Korean shuttlecock game (jegichagi) and Korean wrestling (ssireum), traditional cooking such as bibimbab and half-moon-shaped rice cake (songpyeon), and teaching the Korean language, as well as preparing cultural performances with local university students. On the weekends, the team will visit local farms to volunteer, and local elementary schools and orphanages to conduct science experiments for children, as well as physical education and art activities.
(Photo caption: Volunteers poses with faculty and staff members including President Sung-Chul Shin at a ceremony on June 21.)
2017.06.29 View 12542
2017 World Friends ICT KAIST Sets Off to Ethiopia, Tanzania
KAIST launched the ‘2017 World Friends ICT KAIST’ on 21 June at a ceremony held at the Faculty Club. The event was attended by 40 student volunteers and faculty members including President Sung-Chul Shin and student volunteers.
The ‘2017 World Friends ICT KAIST’ is an oversees volunteer program aimed at providing ICT education for students from developing countries and for cultural exchange. The program was organized by the KAIST Leadership Center and sponsored by the National Information Agency (NIA) since 2015.
President Sung-Chul Shin delivered words of encouragement to start the opening ceremony, followed by an oath-taking by the volunteer group, safety training, and a commemorative photoshoot. This year’s World Friends ICT volunteer group consisted of 32 students and 2 staff members to lead and to support the team.
The group was divided into eight teams including APP-frica, KAI-Tigers, and WITH (4 members per team) to volunteer in Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAIT) and Adama Science and Technology University in Ethiopia (ASTU), as well as Nelson Mandela African Institute of Science and Technology (NM-AIST) in Tanzania. The teams will educate local students on ICT and promote cultural exchanges. The volunteer period is from July 7 to August 5, lasting about a month.
KAIST conducted primary document examinations and interviews from April 27 to May 18 on volunteer candidates who registered to take part, and selected 32 student volunteers. A total of 68 students registered to volunteer, resulting in a 1:2.1 competition rate.
The volunteering program was customized to the local needs of Ethiopia and Tanzania and thus consisted of ICT education, cultural exchanges, volunteering at farms on the weekends, and science experiments. The area with the most focus by the volunteer team is ICT education, which accounts for 70% of the total volunteer activities. The aim is to educate Ethiopian students at AAIT and ASTU on Windows, MS Office, Adobe Photoshop, and using smartphones. In Tanzania, the team is to volunteer with students of NM-AIST to provide ICT application education such as water tank control using appropriate technology and Arduino to local high school students.
The team is also planning to promote cultural exchanges by preparing K-Pop dancing, traditional Korean games such as Korean shuttlecock game (jegichagi) and Korean wrestling (ssireum), traditional cooking such as bibimbab and half-moon-shaped rice cake (songpyeon), and teaching the Korean language, as well as preparing cultural performances with local university students. On the weekends, the team will visit local farms to volunteer, and local elementary schools and orphanages to conduct science experiments for children, as well as physical education and art activities.
(Photo caption: Volunteers poses with faculty and staff members including President Sung-Chul Shin at a ceremony on June 21.)
2017.06.29 View 12542 -
 Winning Best in Theme Award in NASA RASC-AL
A students team from the Department of Aerospace Engineering won the Best in Theme Award for moon exploration system design at Revolutionary Aerospace Systems Concepts - Academic Linkage (RASC-AL), an aerospace mission system design competition organized by NASA in the USA.
The KAIST team, consisting of Jaeyoul Ko, Jongeun Suh, Juseong Lee, Sukmin Choi, and Eunkwang Lee, and supervised by Professor Jaemyung Ahn, competed as a joint team with Texas Tech University and the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Australia,
The joint team was selected as one of the 14 finalists after two preliminary rounds. The finals of RASC-AL Forum took place from May 30 to June 3 in Florida. The team received the top prize with their design entitled ‘Earth to Lunar Interchangeable Transportation Environment (ELITE) for Logistics Delivery Systems’, one of the four themes of the competition.
Since 2002, RASC-AL competitions, managed by NASA, have been held with themes on innovative aerospace system and missions, in which world-class undergraduate and graduate students have participated.
This year’s themes were ▲ Lightweight Exercise Suite ▲ Airlock Design ▲ Commercially Enabled LEO/Mars Habitable Module and ▲ Logistics Delivery System.
Moon exploration requires a great deal of time and supplies. The KAIST team has been researching supply delivery systems in space for long-term manned moon exploration with their joint team for the last eight months. In particular, incidents can occur during the initial stages of long-term manned moon exploration missions that are unpredictable during system design and planning. Therefore, to cope with such unpredictability in the mission, the KAIST team deduced a system and an operational concept with increased flexibility to maximize the cost effectiveness of the supply transport.
The spacecraft was divided into propulsion and transport modules based on their functionalities, and can allow the flexibility by switching the transport module according to the demands of the moon base. The operational flexibility and cost effectiveness are further increased by introducing multiple departure orbits from the Earth (e.g. low Earth orbit vs. geosynchronous Earth orbit) enabled by utilization of various launch vehicles.
Professor Ahn, the advisor for the team, said, “I am proud of the students who collaborated with the international joint teams and achieved great result.” He continued, “I believe this to be the result of continuous efforts and initiatives of the department for system design-centered education. We will keep providing high-quality system design and education through various opportunities such as international cooperation in design education.”
(Photo caption: KAIST team of the Department of Aerospace Engineering poses after winning the Best in Theme Award in NASA's RASC-AL)
2017.06.22 View 10219
Winning Best in Theme Award in NASA RASC-AL
A students team from the Department of Aerospace Engineering won the Best in Theme Award for moon exploration system design at Revolutionary Aerospace Systems Concepts - Academic Linkage (RASC-AL), an aerospace mission system design competition organized by NASA in the USA.
The KAIST team, consisting of Jaeyoul Ko, Jongeun Suh, Juseong Lee, Sukmin Choi, and Eunkwang Lee, and supervised by Professor Jaemyung Ahn, competed as a joint team with Texas Tech University and the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Australia,
The joint team was selected as one of the 14 finalists after two preliminary rounds. The finals of RASC-AL Forum took place from May 30 to June 3 in Florida. The team received the top prize with their design entitled ‘Earth to Lunar Interchangeable Transportation Environment (ELITE) for Logistics Delivery Systems’, one of the four themes of the competition.
Since 2002, RASC-AL competitions, managed by NASA, have been held with themes on innovative aerospace system and missions, in which world-class undergraduate and graduate students have participated.
This year’s themes were ▲ Lightweight Exercise Suite ▲ Airlock Design ▲ Commercially Enabled LEO/Mars Habitable Module and ▲ Logistics Delivery System.
Moon exploration requires a great deal of time and supplies. The KAIST team has been researching supply delivery systems in space for long-term manned moon exploration with their joint team for the last eight months. In particular, incidents can occur during the initial stages of long-term manned moon exploration missions that are unpredictable during system design and planning. Therefore, to cope with such unpredictability in the mission, the KAIST team deduced a system and an operational concept with increased flexibility to maximize the cost effectiveness of the supply transport.
The spacecraft was divided into propulsion and transport modules based on their functionalities, and can allow the flexibility by switching the transport module according to the demands of the moon base. The operational flexibility and cost effectiveness are further increased by introducing multiple departure orbits from the Earth (e.g. low Earth orbit vs. geosynchronous Earth orbit) enabled by utilization of various launch vehicles.
Professor Ahn, the advisor for the team, said, “I am proud of the students who collaborated with the international joint teams and achieved great result.” He continued, “I believe this to be the result of continuous efforts and initiatives of the department for system design-centered education. We will keep providing high-quality system design and education through various opportunities such as international cooperation in design education.”
(Photo caption: KAIST team of the Department of Aerospace Engineering poses after winning the Best in Theme Award in NASA's RASC-AL)
2017.06.22 View 10219 -
 KAIST Team Wins Bronze Medal at Int'l Programming Contest
A KAIST Team consisting of undergraduate students from the School of Computing and Department of Mathematical Science received a bronze medal and First Problem Solver award at an international undergraduate programming competition, The Association for Computing Machinery-International Collegiate Programming Contest (ACM-ICPC) World Finals.
The 41st ACM-ICPC hosted by ACM and funded by IBM was held in South Dakota in the US on May 25. The competition, first held in 1977, is aimed at undergraduate students from around the world. A total of 50,000 students from 2900 universities and 103 countries participated in the regional competition and 400 students competed in the finals.
The competition required teams of three to solve 12 problems. The KAIST team was coached by Emeritus Professor Sung-Yong Shin and Professor Taisook Han. The student contestants were Jihoon Ko and Hanpil Kang from the School of Computing and Jongwoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Science. The team finished ranked 9th, receiving a bronze medal and a $3000 prize. Additionally, the team was the first to solve all the problems and received the First Problem Solver award. Detailed score information can be found on. https://icpc.baylor.edu/scoreboard/
(Photo caption: Professor Taisook Han and his students)
2017.06.12 View 11372
KAIST Team Wins Bronze Medal at Int'l Programming Contest
A KAIST Team consisting of undergraduate students from the School of Computing and Department of Mathematical Science received a bronze medal and First Problem Solver award at an international undergraduate programming competition, The Association for Computing Machinery-International Collegiate Programming Contest (ACM-ICPC) World Finals.
The 41st ACM-ICPC hosted by ACM and funded by IBM was held in South Dakota in the US on May 25. The competition, first held in 1977, is aimed at undergraduate students from around the world. A total of 50,000 students from 2900 universities and 103 countries participated in the regional competition and 400 students competed in the finals.
The competition required teams of three to solve 12 problems. The KAIST team was coached by Emeritus Professor Sung-Yong Shin and Professor Taisook Han. The student contestants were Jihoon Ko and Hanpil Kang from the School of Computing and Jongwoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Science. The team finished ranked 9th, receiving a bronze medal and a $3000 prize. Additionally, the team was the first to solve all the problems and received the First Problem Solver award. Detailed score information can be found on. https://icpc.baylor.edu/scoreboard/
(Photo caption: Professor Taisook Han and his students)
2017.06.12 View 11372 -
 KATT Tops at Appropriate Technology Competition
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of KAIST international students received gold and bronze awards at ‘the 9th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90%’. This year’s competition was hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning at Seoul National University’s Global Convention Plaza on May 26. Undergraduate and graduate students nationwide formed 65 teams to participate in the competition.
The aim of the competition is to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance quality of life for those with no or little access to science technology and its products around the world. This year’s competition categorized the designs into IT; water and energy; agriculture, hygiene, safety, and housing; and education. The teams were evaluated on their presentations and prototypes.
KATT produced alarm warning bracelets for people in developing countries and smart hybrid dryers for agricultural products. The alarm warning bracelets were designed for those living in tsunami risk zones; they use wireless communication technology to receive and transmit warning signals and can be produced for less than $4.
The smart hybrid dryers featured solar energy generation, aimed to help those with low income in subtropical, low-altitude regions with unstable climates, since there are currently no drying methods for agricultural products without direct exposure to sunlight. Therefore, the hybrid dryers allowed drying regardless of the weather, and thus increased the storage and distribution efficiency of agricultural products.
Ashar Alam from India who participated in developing the alarm warning bracelet said, “Through the appropriate technology club, I recognized problems in India that also affect neighboring countries such as Indonesia and Bangladesh. I wanted to actively use the science and technology knowledge I have accumulated in KAIST for the less fortunate.” He continued, “It was meaningful to develop the product using the respective talents of students from various countries with the spirit of developing appropriate technology.”
(Photo caption: Alarm warning bracelet team received the gold award)
2017.06.12 View 8991
KATT Tops at Appropriate Technology Competition
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of KAIST international students received gold and bronze awards at ‘the 9th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90%’. This year’s competition was hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning at Seoul National University’s Global Convention Plaza on May 26. Undergraduate and graduate students nationwide formed 65 teams to participate in the competition.
The aim of the competition is to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance quality of life for those with no or little access to science technology and its products around the world. This year’s competition categorized the designs into IT; water and energy; agriculture, hygiene, safety, and housing; and education. The teams were evaluated on their presentations and prototypes.
KATT produced alarm warning bracelets for people in developing countries and smart hybrid dryers for agricultural products. The alarm warning bracelets were designed for those living in tsunami risk zones; they use wireless communication technology to receive and transmit warning signals and can be produced for less than $4.
The smart hybrid dryers featured solar energy generation, aimed to help those with low income in subtropical, low-altitude regions with unstable climates, since there are currently no drying methods for agricultural products without direct exposure to sunlight. Therefore, the hybrid dryers allowed drying regardless of the weather, and thus increased the storage and distribution efficiency of agricultural products.
Ashar Alam from India who participated in developing the alarm warning bracelet said, “Through the appropriate technology club, I recognized problems in India that also affect neighboring countries such as Indonesia and Bangladesh. I wanted to actively use the science and technology knowledge I have accumulated in KAIST for the less fortunate.” He continued, “It was meaningful to develop the product using the respective talents of students from various countries with the spirit of developing appropriate technology.”
(Photo caption: Alarm warning bracelet team received the gold award)
2017.06.12 View 8991 -
 Mutations Unveiled that Predispose Lung Cancer Cells to Refractory Histologic Transformation
Cancer pedigree analysis reveals the mutations in RB1 and TP53 genes play a key role in treatment-resistant, cancer cell-type transformation during EGFR inhibitor therapy for lung cancers.
Research led by Korean medical scientists has discovered that a specific type of drug resistance mechanism to EGFR inhibitor therapy in lung cancer is predisposed by mutations in two canonical cancer-related genes: RB1 and TP53. Published in Journal of Clinical Oncology on May 12, the study also found those mutations can be detectable in patients' tumors at the point of clinical diagnosis. Therefore, it can be used as strong markers in clinic for predicting poor outcome for the targeted treatment for lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer, and about 15% of patients in Western countries and 50% of patients in Asian countries have mutations in the EGFR gene, which is critical for the development of lung cancer. Patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the EGFR mutation show favorable responses to EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib (Tarceva) or gefitinib (Iressa), but ultimately relapse with drug-resistant tumors. Since the initial report in 2006, it has been known that in about 5~15% of patients, the lung adenocarcinoma cells undergo a mysterious transformation into a very different cancer cell type called “small cell lung cancer,” a much more aggressive lung cancer subtype, common in cigarette smokers.
To find out the genetic basis of this process, the researchers compared the genome sequences of multiple cancer tissues acquired during the treatment courses of patients whose tumors underwent small-cell transformation. They reconstructed the cancer cell pedigree by comparing mutations between cancer tissues, and identified that RB1 and TP53 genes are completely inactivated by mutations already in their lung adenocarcinoma tissues.
"We tried to compare the somatic mutational profile of pre-EGFR inhibitor treatment lung adenocarcinomas and post-treatment small cell carcinomas and to reconstruct the pedigrees of the cancer evolution in each patient. Strikingly, both copies of RB1 and TP53 genes were already inactivated at the stage of lung adenocarcinomas in all sequenced cases," said Dr. Jake June-Koo Lee, the first author from KAIST.
They further pursued the clinical implications of RB1 and TP53 inactivation by investigating 75 EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma tissues from patients who received EGFR inhibitor therapy, including patients with small-cell transformation. In this analysis, the lung adenocarcinomas with a complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 genes tended to have a 43-times greater risk of transformation into small cell lung cancer during their EGFR inhibitor treatment courses.
Dr. Young Seok Ju, the co-last author from KAIST, explained, "This study shows the power of entire genome analyses to better understand the mechanisms underlying mysterious phenomenon encountered in clinic. Upon accurate bioinformatics, we are finding cancer-specific somatic mutations from the whole-genomes of patients’ cancer cells. These mutations allow us to track the evolution of cancer cells throughout the extraordinary clinical course of a special set of lung cancers."
The complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 tumor suppressor genes is found in a minor (<10%) subset of lung adenocarcinoma. This study suggests that the clinical course against targeted therapy is endogenously different for the cancers in the subgroup, and specific drug-resistance mechanisms are predisposed by the two genetic mutations. Indeed, RB1 and TP53 double inactivation is a genetic hallmark of primary small cell lung cancer, observed in nearly all cases.
"We are actively investigating patient tumor tissues to develop optimal surveillance plans and treatment options for patients with lung adenocarcinomas more prone to small-cell transformation," said Dr. Tae Min Kim, the co-last author from Seoul National University Hospital.
The researchers are implementing their findings into lung cancer clinics by screening the RB1 and TP53 mutational status in lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving EGFR inhibitor treatment, and following their treatment courses to develop a treatment strategy for those patients.
This research (doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.9096) was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2013H1A2A1032691 to J.-K.L., NRF-2014R1A2A2A05003665 to Y.T.K.); Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (K-16-L03-C02-S02 to J.L.); and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, which was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (HI14C1234 to T.M.K., HI16C2387 to Y.S.J.)
Figure. Phylogeny analysis of serially-acquired tumors
A. Phylogeny trees of sequenced cases (LC1−LC4) are reconstructed from the WGS data. Conceptual illustrations are depicted with grey color. Circles indicate major clones of the tumors. The length of each branch is proportional to the number of mutations that occurred in the branch. Mutations of cancer-related genes in each branch are indicated with arrows. The time points of relevant treatments are summarized below the trees.
B. Mutations of RB1 and TP53 in two early LADCs (LC1b and LC4a) are visualized using Integrative Genomics Viewer (left panel). Allele-specific copy number analysis shows loss of heterozygosity of chromosomes 13 and 17 in both early LADCs and EGFR TKI-resistant SCLCs (right panel).
C. Clonal evolution of LC1 is described with clinical history and tumor volumes. The horizontal axis represents the time from the diagnosis (0), and the vertical axis indicates the volume of tumors calculated from the computed tomography images.
Abbreviations: LADC, lung adenocarcinoma; SCLC, small cell lung cancer
2017.06.07 View 9452
Mutations Unveiled that Predispose Lung Cancer Cells to Refractory Histologic Transformation
Cancer pedigree analysis reveals the mutations in RB1 and TP53 genes play a key role in treatment-resistant, cancer cell-type transformation during EGFR inhibitor therapy for lung cancers.
Research led by Korean medical scientists has discovered that a specific type of drug resistance mechanism to EGFR inhibitor therapy in lung cancer is predisposed by mutations in two canonical cancer-related genes: RB1 and TP53. Published in Journal of Clinical Oncology on May 12, the study also found those mutations can be detectable in patients' tumors at the point of clinical diagnosis. Therefore, it can be used as strong markers in clinic for predicting poor outcome for the targeted treatment for lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer, and about 15% of patients in Western countries and 50% of patients in Asian countries have mutations in the EGFR gene, which is critical for the development of lung cancer. Patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the EGFR mutation show favorable responses to EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib (Tarceva) or gefitinib (Iressa), but ultimately relapse with drug-resistant tumors. Since the initial report in 2006, it has been known that in about 5~15% of patients, the lung adenocarcinoma cells undergo a mysterious transformation into a very different cancer cell type called “small cell lung cancer,” a much more aggressive lung cancer subtype, common in cigarette smokers.
To find out the genetic basis of this process, the researchers compared the genome sequences of multiple cancer tissues acquired during the treatment courses of patients whose tumors underwent small-cell transformation. They reconstructed the cancer cell pedigree by comparing mutations between cancer tissues, and identified that RB1 and TP53 genes are completely inactivated by mutations already in their lung adenocarcinoma tissues.
"We tried to compare the somatic mutational profile of pre-EGFR inhibitor treatment lung adenocarcinomas and post-treatment small cell carcinomas and to reconstruct the pedigrees of the cancer evolution in each patient. Strikingly, both copies of RB1 and TP53 genes were already inactivated at the stage of lung adenocarcinomas in all sequenced cases," said Dr. Jake June-Koo Lee, the first author from KAIST.
They further pursued the clinical implications of RB1 and TP53 inactivation by investigating 75 EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma tissues from patients who received EGFR inhibitor therapy, including patients with small-cell transformation. In this analysis, the lung adenocarcinomas with a complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 genes tended to have a 43-times greater risk of transformation into small cell lung cancer during their EGFR inhibitor treatment courses.
Dr. Young Seok Ju, the co-last author from KAIST, explained, "This study shows the power of entire genome analyses to better understand the mechanisms underlying mysterious phenomenon encountered in clinic. Upon accurate bioinformatics, we are finding cancer-specific somatic mutations from the whole-genomes of patients’ cancer cells. These mutations allow us to track the evolution of cancer cells throughout the extraordinary clinical course of a special set of lung cancers."
The complete inactivation of both RB1 and TP53 tumor suppressor genes is found in a minor (<10%) subset of lung adenocarcinoma. This study suggests that the clinical course against targeted therapy is endogenously different for the cancers in the subgroup, and specific drug-resistance mechanisms are predisposed by the two genetic mutations. Indeed, RB1 and TP53 double inactivation is a genetic hallmark of primary small cell lung cancer, observed in nearly all cases.
"We are actively investigating patient tumor tissues to develop optimal surveillance plans and treatment options for patients with lung adenocarcinomas more prone to small-cell transformation," said Dr. Tae Min Kim, the co-last author from Seoul National University Hospital.
The researchers are implementing their findings into lung cancer clinics by screening the RB1 and TP53 mutational status in lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving EGFR inhibitor treatment, and following their treatment courses to develop a treatment strategy for those patients.
This research (doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.9096) was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2013H1A2A1032691 to J.-K.L., NRF-2014R1A2A2A05003665 to Y.T.K.); Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (K-16-L03-C02-S02 to J.L.); and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, which was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (HI14C1234 to T.M.K., HI16C2387 to Y.S.J.)
Figure. Phylogeny analysis of serially-acquired tumors
A. Phylogeny trees of sequenced cases (LC1−LC4) are reconstructed from the WGS data. Conceptual illustrations are depicted with grey color. Circles indicate major clones of the tumors. The length of each branch is proportional to the number of mutations that occurred in the branch. Mutations of cancer-related genes in each branch are indicated with arrows. The time points of relevant treatments are summarized below the trees.
B. Mutations of RB1 and TP53 in two early LADCs (LC1b and LC4a) are visualized using Integrative Genomics Viewer (left panel). Allele-specific copy number analysis shows loss of heterozygosity of chromosomes 13 and 17 in both early LADCs and EGFR TKI-resistant SCLCs (right panel).
C. Clonal evolution of LC1 is described with clinical history and tumor volumes. The horizontal axis represents the time from the diagnosis (0), and the vertical axis indicates the volume of tumors calculated from the computed tomography images.
Abbreviations: LADC, lung adenocarcinoma; SCLC, small cell lung cancer
2017.06.07 View 9452