ETRI
-
 Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 55287
Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 55287 -
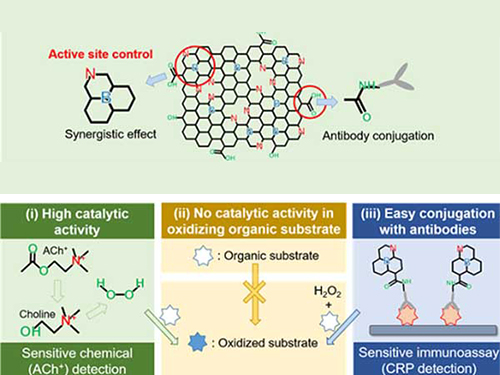 Nanomaterials Mimicking Natural Enzymes with Superior Catalytic Activity and Selectivity for Detecting Acetylcholine
(Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
A KAIST research team doped nitrogen and boron into graphene to selectively increase peroxidase-like activity and succeeded in synthesizing a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with a low cost and superior catalytic activity. These nanomaterials can be applied for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Enzymes are the main catalysts in our body and are widely used in bioassays. In particular, peroxidase, which oxidizes transparent colorimetric substrates to become a colored product in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, is the most common enzyme that is used in colorimetric bioassays.
However, natural enzymes consisting of proteins are unstable against temperature and pH, hard to synthesize, and costly. Nanozymes, on the other hand, do not consist of proteins, meaning the disadvantages of enzymes can be overcome with their robustness and high productivity. In contrast, most nanonzymes do not have selectivity; for example, peroxidase-mimicking nanozymes demonstrate oxidase-like activity that oxidizes colorimetric substrates in the absence of hydrogen peroxide, which keeps them away from precisely detecting the target materials, such as hydrogen peroxide.
Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team were able to synthesize a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with superior catalytic activity and selectivity toward hydrogen peroxide. Co-doping of nitrogen and boron into graphene, which has negligible peroxidase-like activity, selectively increased the peroxidase-like activity without oxidase-like activity to accurately mimic the nature peroxidase and has become a powerful candidate to replace the peroxidase.
The experimental results were also verified with computational chemistry. The nitrogen and boron co-doped graphene was also applied to the colorimetric detection of acetylcholine, which is an important neurotransmitter and successfully detected the acetylcholine even better than the nature peroxidase.
Professor Lee said, “We began to study nanozymes due to their potential for replacing existing enzymes. Through this study, we have secured core technologies to synthesize nanozymes that have high enzyme activity along with selectivity. We believe that they can be applied to effectively detect acetylcholine for quickly diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease.
This research, led by PhD Min Su Kim, was published in ACS Nano (10.1021/acsnano.8b09519) on March 25, 2019.
Figure 1. Comparison of the catalytic activities of various nanozymes and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) toward TMB and H₂O₂
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of NB-rGO Reactions in Bioassays
2019.04.30 View 37780
Nanomaterials Mimicking Natural Enzymes with Superior Catalytic Activity and Selectivity for Detecting Acetylcholine
(Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
A KAIST research team doped nitrogen and boron into graphene to selectively increase peroxidase-like activity and succeeded in synthesizing a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with a low cost and superior catalytic activity. These nanomaterials can be applied for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Enzymes are the main catalysts in our body and are widely used in bioassays. In particular, peroxidase, which oxidizes transparent colorimetric substrates to become a colored product in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, is the most common enzyme that is used in colorimetric bioassays.
However, natural enzymes consisting of proteins are unstable against temperature and pH, hard to synthesize, and costly. Nanozymes, on the other hand, do not consist of proteins, meaning the disadvantages of enzymes can be overcome with their robustness and high productivity. In contrast, most nanonzymes do not have selectivity; for example, peroxidase-mimicking nanozymes demonstrate oxidase-like activity that oxidizes colorimetric substrates in the absence of hydrogen peroxide, which keeps them away from precisely detecting the target materials, such as hydrogen peroxide.
Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team were able to synthesize a peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with superior catalytic activity and selectivity toward hydrogen peroxide. Co-doping of nitrogen and boron into graphene, which has negligible peroxidase-like activity, selectively increased the peroxidase-like activity without oxidase-like activity to accurately mimic the nature peroxidase and has become a powerful candidate to replace the peroxidase.
The experimental results were also verified with computational chemistry. The nitrogen and boron co-doped graphene was also applied to the colorimetric detection of acetylcholine, which is an important neurotransmitter and successfully detected the acetylcholine even better than the nature peroxidase.
Professor Lee said, “We began to study nanozymes due to their potential for replacing existing enzymes. Through this study, we have secured core technologies to synthesize nanozymes that have high enzyme activity along with selectivity. We believe that they can be applied to effectively detect acetylcholine for quickly diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease.
This research, led by PhD Min Su Kim, was published in ACS Nano (10.1021/acsnano.8b09519) on March 25, 2019.
Figure 1. Comparison of the catalytic activities of various nanozymes and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) toward TMB and H₂O₂
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of NB-rGO Reactions in Bioassays
2019.04.30 View 37780 -
 KAIST-THE Innovation & Impact Summit Touts New Roles of Higher Education
Global leaders from 115 institutions across 35 countries reaffirmed that the roles of universities are evolving to become much broader and more diverse, and redefined the impact of higher education last week at KAIST. During the THE Innovation and Impact Summit hosted by KAIST in partnership with the Times Higher Education, global leaders in higher education, industry, and government all agreed that universities should respond better in order to have a lasting and sustainable impact on society.
In an effort to encourage social responsibility and boost the impact of universities, the THE first launched the University Impact Rankings based on the Sustainable Developed Goals declared during the 2015 UN summit. The THE’s University Impact Rankings are the first global attempt to evaluate universities’ impact on society, rather than only focusing on research and teaching performance.
The new metrics include universities’ policies and outcomes based on 11 of the 17 UN SDGs. More than 500 institutions from 75 countries submitted data for the new rankings. The top three scores from ten of the SDGs were combined with SDG 17 to calculate the final score. The University of Auckland placed first in this new ranking while KAIST ranked fourth in the category of SDG 9 on Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
President Shin said, “KAIST has dedicated itself to producing knowledge that could serve as a growth engine for national development over the past half century. Now, taking on the UN’s 17 SDGs as new indicators, we will do our utmost to become a leading university in creating global value and better serving the world.”
(Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer of THE)
Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer at THE said, “I would like to applaud KAIST for being a pioneer, taking a new way of looking at university excellence. KAIST’s performance was strong overall, but especially outstanding in SDG 9. Its data proves that the university is fully engaged in knowledge creation and entrepreneur activities.”
Keynote speakers all shared their views on disruptive knowledge and how to adjust to the new AI technology-driven, socio-economic culture.
(from left: Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President and Sung-Chul Shin, KAIST President)
Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President, argued in his keynote speech that there has been amazing growth in university enrollments, coupled with a substantial mismatch between what universities teach and what society needs. He went on to say that universities should look beyond the classical university model and find a way to train the next generation in a way that ensures society has a role for them.
“The likelihood of each generation having a higher income at the age of 30 than their parents has diminished dramatically,” he said. He provided data that showed that middle-income professions have been declining, and between 2000 and 2010 the number of very high-skilled jobs and very low-skilled jobs doubled, whereas the number of those in the middle increased far more slowly. He expected that this trend will continue, saying that universities should focus on instilling critical thinking, interdisciplinary studies, and ‘productive failure’ to students in the new era.
He also shared the secret recipe for the reduced youth unemployment statistics in Switzerland. He said that the education system in Switzerland was designed so that only 20 percent of an age cohort undertakes a classical university education, while 80 percent do vocational training run by companies. They learn what is really needed by industry and society from the early stages of their careers, so no mismatch exists.
(Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier)
Meanwhile, Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier, claimed in his keynote speech that universities should stop evaluating researchers only on their publication and citation counts. He said that doing so was driving academics to turn out multiple papers based on a single study in a practice called ‘salami publishing.’ Chi said, “It’s a responsibility we bear together, and we certainly, as industry associates, have to work hard to educate the world that publishing isn’t everything, but the impact is. But the impact is not just citations, either.”
Chi said that there is a global ‘tech-lash’ that has arisen due to falling trust in major IT companies. On the other hand, universities are trustworthy. People perceive that universities are not merely seeking profits, and they can take advantage of it for fostering next generation researchers and CEOs, which can stand for ‘Chief Ethics Officers’.
“Universities are collaborative,” said Chi. Universities’ research will flourish with more collaboration at a global scale. Collaborative research shows higher citation and impact rates. Instead of competing against one another, universities and industries should collaborate for advancing research. He argued further saying, “If they can uphold this reputation, universities, not companies, will be the institutions that people trust to influence and educate the next generation. Universities, in contrast to industry, have long-term vision, can facilitate collaborative research, and are trustworthy.”
(President Joseph Aoun, Northeastern University)
In the last day’s keynote speech, President Joseph Aoun of Northeastern University said that higher education risks becoming obsolete if it does not fully embrace lifelong learning. He also talked about preparing learners to succeed in the AI age.
He said that lifelong learners made up 74 percent of learners in the US, and only 34 percent of universities in the country fill their seats, but higher education has not yet incorporated lifelong learning as part of its core mission. He said that lifelong learning is going to require that we listen to the needs of society, of both individuals and organizations.
He also called for institutions to create curricula based on what he termed ‘humanics’ – the integration of technological literacy, data literacy, and human literacy, and said that this should be combined with experiential learning.
(from left: So Young Kim, Guohua Chen, Aqil Jamal, Mooyoung Jung and Max Lu)
(from left: Hubo and Duncan Ross, chief data officer of THE)
2019.04.09 View 5255
KAIST-THE Innovation & Impact Summit Touts New Roles of Higher Education
Global leaders from 115 institutions across 35 countries reaffirmed that the roles of universities are evolving to become much broader and more diverse, and redefined the impact of higher education last week at KAIST. During the THE Innovation and Impact Summit hosted by KAIST in partnership with the Times Higher Education, global leaders in higher education, industry, and government all agreed that universities should respond better in order to have a lasting and sustainable impact on society.
In an effort to encourage social responsibility and boost the impact of universities, the THE first launched the University Impact Rankings based on the Sustainable Developed Goals declared during the 2015 UN summit. The THE’s University Impact Rankings are the first global attempt to evaluate universities’ impact on society, rather than only focusing on research and teaching performance.
The new metrics include universities’ policies and outcomes based on 11 of the 17 UN SDGs. More than 500 institutions from 75 countries submitted data for the new rankings. The top three scores from ten of the SDGs were combined with SDG 17 to calculate the final score. The University of Auckland placed first in this new ranking while KAIST ranked fourth in the category of SDG 9 on Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
President Shin said, “KAIST has dedicated itself to producing knowledge that could serve as a growth engine for national development over the past half century. Now, taking on the UN’s 17 SDGs as new indicators, we will do our utmost to become a leading university in creating global value and better serving the world.”
(Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer of THE)
Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer at THE said, “I would like to applaud KAIST for being a pioneer, taking a new way of looking at university excellence. KAIST’s performance was strong overall, but especially outstanding in SDG 9. Its data proves that the university is fully engaged in knowledge creation and entrepreneur activities.”
Keynote speakers all shared their views on disruptive knowledge and how to adjust to the new AI technology-driven, socio-economic culture.
(from left: Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President and Sung-Chul Shin, KAIST President)
Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President, argued in his keynote speech that there has been amazing growth in university enrollments, coupled with a substantial mismatch between what universities teach and what society needs. He went on to say that universities should look beyond the classical university model and find a way to train the next generation in a way that ensures society has a role for them.
“The likelihood of each generation having a higher income at the age of 30 than their parents has diminished dramatically,” he said. He provided data that showed that middle-income professions have been declining, and between 2000 and 2010 the number of very high-skilled jobs and very low-skilled jobs doubled, whereas the number of those in the middle increased far more slowly. He expected that this trend will continue, saying that universities should focus on instilling critical thinking, interdisciplinary studies, and ‘productive failure’ to students in the new era.
He also shared the secret recipe for the reduced youth unemployment statistics in Switzerland. He said that the education system in Switzerland was designed so that only 20 percent of an age cohort undertakes a classical university education, while 80 percent do vocational training run by companies. They learn what is really needed by industry and society from the early stages of their careers, so no mismatch exists.
(Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier)
Meanwhile, Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier, claimed in his keynote speech that universities should stop evaluating researchers only on their publication and citation counts. He said that doing so was driving academics to turn out multiple papers based on a single study in a practice called ‘salami publishing.’ Chi said, “It’s a responsibility we bear together, and we certainly, as industry associates, have to work hard to educate the world that publishing isn’t everything, but the impact is. But the impact is not just citations, either.”
Chi said that there is a global ‘tech-lash’ that has arisen due to falling trust in major IT companies. On the other hand, universities are trustworthy. People perceive that universities are not merely seeking profits, and they can take advantage of it for fostering next generation researchers and CEOs, which can stand for ‘Chief Ethics Officers’.
“Universities are collaborative,” said Chi. Universities’ research will flourish with more collaboration at a global scale. Collaborative research shows higher citation and impact rates. Instead of competing against one another, universities and industries should collaborate for advancing research. He argued further saying, “If they can uphold this reputation, universities, not companies, will be the institutions that people trust to influence and educate the next generation. Universities, in contrast to industry, have long-term vision, can facilitate collaborative research, and are trustworthy.”
(President Joseph Aoun, Northeastern University)
In the last day’s keynote speech, President Joseph Aoun of Northeastern University said that higher education risks becoming obsolete if it does not fully embrace lifelong learning. He also talked about preparing learners to succeed in the AI age.
He said that lifelong learners made up 74 percent of learners in the US, and only 34 percent of universities in the country fill their seats, but higher education has not yet incorporated lifelong learning as part of its core mission. He said that lifelong learning is going to require that we listen to the needs of society, of both individuals and organizations.
He also called for institutions to create curricula based on what he termed ‘humanics’ – the integration of technological literacy, data literacy, and human literacy, and said that this should be combined with experiential learning.
(from left: So Young Kim, Guohua Chen, Aqil Jamal, Mooyoung Jung and Max Lu)
(from left: Hubo and Duncan Ross, chief data officer of THE)
2019.04.09 View 5255 -
 New Catalyst for Synthesizing Chiral Molecules Selectively
(from left: Dr. Yoonsu Park and Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
Molecules in nature often have “twin” molecules that look identical. In particular, the twin molecules that look like mirror images to each other are called enantiomers. However, even though they have the same type and number of elements, these twin molecules exhibit completely different properties.
Professor Sukbok Chang and Dr. Yoonsu Park from the Department of Chemistry developed a new catalyst capable of selectively synthesizing only one of the two enantiomers. Using this catalyst, the have succeeded in manufacturing the chiral lactam, an essential ingredient in pharmaceuticals, from a hydrocarbon compound.
Enantiomerism or chirality is considered very important for drug development. Biomaterials, such as DNAs and proteins also have chiral properties, but they exhibit different physiological activities depending on the types of drugs. One type of the enantiomer could be useful while the other is toxic. Hence, the technology for selective synthesizing (i.e. asymmetric synthesis) is required, but it is still regarded as a great challenge faced by modern chemistry to date.
The researchers solved this problem by developing a new catalyst. Earlier they presented their research on developing an iridium catalyst that converts hydrocarbons into high value γ-lactam compounds, and published it in Science in March 2018. However, the developed catalyst still had a limitation that both types of enantiomers are obtained without selectivity.
In this study, they found that among dozens of other catalyst candidates, iridium catalysts with chiral diamine scaffolds were able to select the correct enantiomer with a selectivity of 99% or more. This novel catalyst can be used to synthesize the various chiral γ-lactam as required. A left-handed γ-lactam and a right-handed γ-lactam can be produced using a left-handed iridium catalyst and a right-handed iridium catalyst, respectively.
They analyzed the reason for the high selectivity through computational chemistry simulations. They identified that temporal hydrogen bonding occurred between the chiral diamine catalysts and the hydrocarbon compound during the reaction. As a result of the hydrogen bonding, the formation of the left-handed lactam was boosted.
With their new catalyst, they also succeeded in synthesizing chiral lactam compounds with different structures. By using inexpensive and readily available feedstock hydrocarbons, the researchers produced a group of chiral lactams in different shapes. As their chirality and diverse structures enable lactams to function as an active compound in the body for antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, or anti-tumoral functions, this study may facilitate the development of potential drugs in a more efficient and cheaper way.
Professor Chang said, “We hope that our research on selectively producing core units of effective drugs will lead to developing new drugs that demonstrate fewer side-effects and higher efficacy. There are also economic advantages of this research because it uses hydrocarbon compounds, which can be abundantly found in nature, to produce high-value raw materials.
This research was published in Nature Catalysis(10.1038/s41929-019-0230-x) on February 19, 2019.
Figure 1. Asymmetric formation of chiral γ-lactam
Figure 2. Outline of research outcome
2019.03.05 View 7561
New Catalyst for Synthesizing Chiral Molecules Selectively
(from left: Dr. Yoonsu Park and Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
Molecules in nature often have “twin” molecules that look identical. In particular, the twin molecules that look like mirror images to each other are called enantiomers. However, even though they have the same type and number of elements, these twin molecules exhibit completely different properties.
Professor Sukbok Chang and Dr. Yoonsu Park from the Department of Chemistry developed a new catalyst capable of selectively synthesizing only one of the two enantiomers. Using this catalyst, the have succeeded in manufacturing the chiral lactam, an essential ingredient in pharmaceuticals, from a hydrocarbon compound.
Enantiomerism or chirality is considered very important for drug development. Biomaterials, such as DNAs and proteins also have chiral properties, but they exhibit different physiological activities depending on the types of drugs. One type of the enantiomer could be useful while the other is toxic. Hence, the technology for selective synthesizing (i.e. asymmetric synthesis) is required, but it is still regarded as a great challenge faced by modern chemistry to date.
The researchers solved this problem by developing a new catalyst. Earlier they presented their research on developing an iridium catalyst that converts hydrocarbons into high value γ-lactam compounds, and published it in Science in March 2018. However, the developed catalyst still had a limitation that both types of enantiomers are obtained without selectivity.
In this study, they found that among dozens of other catalyst candidates, iridium catalysts with chiral diamine scaffolds were able to select the correct enantiomer with a selectivity of 99% or more. This novel catalyst can be used to synthesize the various chiral γ-lactam as required. A left-handed γ-lactam and a right-handed γ-lactam can be produced using a left-handed iridium catalyst and a right-handed iridium catalyst, respectively.
They analyzed the reason for the high selectivity through computational chemistry simulations. They identified that temporal hydrogen bonding occurred between the chiral diamine catalysts and the hydrocarbon compound during the reaction. As a result of the hydrogen bonding, the formation of the left-handed lactam was boosted.
With their new catalyst, they also succeeded in synthesizing chiral lactam compounds with different structures. By using inexpensive and readily available feedstock hydrocarbons, the researchers produced a group of chiral lactams in different shapes. As their chirality and diverse structures enable lactams to function as an active compound in the body for antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, or anti-tumoral functions, this study may facilitate the development of potential drugs in a more efficient and cheaper way.
Professor Chang said, “We hope that our research on selectively producing core units of effective drugs will lead to developing new drugs that demonstrate fewer side-effects and higher efficacy. There are also economic advantages of this research because it uses hydrocarbon compounds, which can be abundantly found in nature, to produce high-value raw materials.
This research was published in Nature Catalysis(10.1038/s41929-019-0230-x) on February 19, 2019.
Figure 1. Asymmetric formation of chiral γ-lactam
Figure 2. Outline of research outcome
2019.03.05 View 7561 -
 Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence in Robots
(from left: PhD candidate Su Jin An, Dr. Jee Hang Lee and Professor Sang Wan Lee)
Research groups in KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology, and Google DeepMind argue that our understanding of how humans make intelligent decisions has now reached a critical point in which robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses when we make decisions in our everyday lives.
In our rapidly changing world, both humans and autonomous robots constantly need to learn and adapt to new environments. But the difference is that humans are capable of making decisions according to the unique situations, whereas robots still rely on predetermined data to make decisions.
Despite the rapid progress being made in strengthening the physical capability of robots, their central control systems, which govern how robots decide what to do at any one time, are still inferior to those of humans. In particular, they often rely on pre-programmed instructions to direct their behavior, and lack the hallmark of human behavior, that is, the flexibility and capacity to quickly learn and adapt.
Applying neuroscience in robotics, Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST and Professor Ben Seymour from the University of Cambridge and Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology proposed a case in which robots should be designed based on the principles of the human brain. They argue that robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses during decision-making processes in everyday life.
The problem with importing human-like intelligence into robots has always been a difficult task without knowing the computational principles for how the human brain makes decisions –in other words, how to translate brain activity into computer code for the robots’ ‘brains’.
However, researchers now argue that, following a series of recent discoveries in the field of computational neuroscience, there is enough of this code to effectively write it into robots. One of the examples discovered is the human brain’s ‘meta-controller’, a mechanism by which the brain decides how to switch between different subsystems to carry out complex tasks. Another example is the human pain system, which allows them to protect themselves in potentially hazardous environments. “Copying the brain’s code for these could greatly enhance the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robots,” Professor Lee said.
The team argued that this inter-disciplinary approach will provide just as many benefits to neuroscience as to robotics. The recent explosion of interest in what lies behind psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression, and addiction has given rise to a set of sophisticated theories that are complex and difficult to test without some sort of advanced situation platform.
Professor Seymour explained, “We need a way of modelling the human brain to find how it interacts with the world in real-life to test whether and how different abnormalities in these models give rise to certain disorders. For instance, if we could reproduce anxiety behavior or obsessive-compulsive disorder in a robot, we could then predict what we need to do to treat it in humans.”
The team expects that producing robot models of different psychiatric disorders, in a similar way to how researchers use animal models now, will become a key future technology in clinical research.
The team also stated that there may also be other benefits to humans and intelligent robots learning, acting, and behaving in the same way. In future societies in which humans and robots live and work amongst each other, the ability to cooperate and empathize with robots might be much greater if we feel they think like us.
Professor Seymour said, “We might think that having robots with the human traits of being a bit impulsive or overcautious would be a detriment, but these traits are an unavoidable by-product of human-like intelligence. And it turns out that this is helping us to understand human behavior as human.”
The framework for achieving this brain-inspired artificial intelligence was published in two journals, Science Robotics (10.1126/scirobotics.aav2975) on January 16 and Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences (10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.12.012) on February 6, 2019.
Figure 1. Overview of neuroscience - robotics approach for decision-making. The figure details key areas for interdisciplinary study (Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences)
Figure 2. Brain-inspired solutions to robot learning. Neuroscientific views on various aspects of learning and cognition converge and create a new idea called prefrontal metacontrol, which can inspire researchers to design learning agents that can address various key challenges in robotics such as performance-efficiency-speed, cooperation-competition, and exploration-exploitation trade-offs (Science Robotics)
2019.02.20 View 6209
Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence in Robots
(from left: PhD candidate Su Jin An, Dr. Jee Hang Lee and Professor Sang Wan Lee)
Research groups in KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology, and Google DeepMind argue that our understanding of how humans make intelligent decisions has now reached a critical point in which robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses when we make decisions in our everyday lives.
In our rapidly changing world, both humans and autonomous robots constantly need to learn and adapt to new environments. But the difference is that humans are capable of making decisions according to the unique situations, whereas robots still rely on predetermined data to make decisions.
Despite the rapid progress being made in strengthening the physical capability of robots, their central control systems, which govern how robots decide what to do at any one time, are still inferior to those of humans. In particular, they often rely on pre-programmed instructions to direct their behavior, and lack the hallmark of human behavior, that is, the flexibility and capacity to quickly learn and adapt.
Applying neuroscience in robotics, Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST and Professor Ben Seymour from the University of Cambridge and Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology proposed a case in which robots should be designed based on the principles of the human brain. They argue that robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses during decision-making processes in everyday life.
The problem with importing human-like intelligence into robots has always been a difficult task without knowing the computational principles for how the human brain makes decisions –in other words, how to translate brain activity into computer code for the robots’ ‘brains’.
However, researchers now argue that, following a series of recent discoveries in the field of computational neuroscience, there is enough of this code to effectively write it into robots. One of the examples discovered is the human brain’s ‘meta-controller’, a mechanism by which the brain decides how to switch between different subsystems to carry out complex tasks. Another example is the human pain system, which allows them to protect themselves in potentially hazardous environments. “Copying the brain’s code for these could greatly enhance the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robots,” Professor Lee said.
The team argued that this inter-disciplinary approach will provide just as many benefits to neuroscience as to robotics. The recent explosion of interest in what lies behind psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression, and addiction has given rise to a set of sophisticated theories that are complex and difficult to test without some sort of advanced situation platform.
Professor Seymour explained, “We need a way of modelling the human brain to find how it interacts with the world in real-life to test whether and how different abnormalities in these models give rise to certain disorders. For instance, if we could reproduce anxiety behavior or obsessive-compulsive disorder in a robot, we could then predict what we need to do to treat it in humans.”
The team expects that producing robot models of different psychiatric disorders, in a similar way to how researchers use animal models now, will become a key future technology in clinical research.
The team also stated that there may also be other benefits to humans and intelligent robots learning, acting, and behaving in the same way. In future societies in which humans and robots live and work amongst each other, the ability to cooperate and empathize with robots might be much greater if we feel they think like us.
Professor Seymour said, “We might think that having robots with the human traits of being a bit impulsive or overcautious would be a detriment, but these traits are an unavoidable by-product of human-like intelligence. And it turns out that this is helping us to understand human behavior as human.”
The framework for achieving this brain-inspired artificial intelligence was published in two journals, Science Robotics (10.1126/scirobotics.aav2975) on January 16 and Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences (10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.12.012) on February 6, 2019.
Figure 1. Overview of neuroscience - robotics approach for decision-making. The figure details key areas for interdisciplinary study (Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences)
Figure 2. Brain-inspired solutions to robot learning. Neuroscientific views on various aspects of learning and cognition converge and create a new idea called prefrontal metacontrol, which can inspire researchers to design learning agents that can address various key challenges in robotics such as performance-efficiency-speed, cooperation-competition, and exploration-exploitation trade-offs (Science Robotics)
2019.02.20 View 6209 -
 Ultrathin Digital Camera Inspired by Xenos Peckii Eyes
(Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The visual system of Xenos peckii, an endoparasite of paper wasps, demonstrates distinct benefits for high sensitivity and high resolution, differing from the compound eyes of most insects. Taking their unique features, a KAIST team developed an ultrathin digital camera that emulates the unique eyes of Xenos peckii.
The ultrathin digital camera offers a wide field of view and high resolution in a slimmer body compared to existing imaging systems. It is expected to support various applications, such as monitoring equipment, medical imaging devices, and mobile imaging systems.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team are known for mimicking biological visual organs. The team’s past research includes an LED lens based on the abdominal segments of fireflies and biologically inspired anti-reflective structures.
Recently, the demand for ultrathin digital cameras has increased, due to the miniaturization of electronic and optical devices. However, most camera modules use multiple lenses along the optical axis to compensate for optical aberrations, resulting in a larger volume as well as a thicker total track length of digital cameras. Resolution and sensitivity would be compromised if these modules were to be simply reduced in size and thickness.
To address this issue, the team have developed micro-optical components, inspired from the visual system of Xenos peckii, and combined them with a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensor to achieve an ultrathin digital camera.
This new camera, measuring less than 2mm in thickness, emulates the eyes of Xenos peckii by using dozens of microprism arrays and microlens arrays. A microprism and microlens pair form a channel and the light-absorbing medium between the channels reduces optical crosstalk. Each channel captures the partial image at slightly different orientation, and the retrieved partial images are combined into a single image, thereby ensuring a wide field of view and high resolution.
Professor Jeong said, “We have proposed a novel method of fabricating an ultrathin camera. As the first insect-inspired, ultrathin camera that integrates a microcamera on a conventional CMOS image sensor array, our study will have a significant impact in optics and related fields.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Dongmin Keum and Kyung-Won Jang, was published in Light: Science & Applications on October 24, 2018.
Figure 1. Natural Xenos peckii eye and the biological inspiration for the ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
Figure 2. Optical images captured by the bioinspired ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
2018.12.31 View 8715
Ultrathin Digital Camera Inspired by Xenos Peckii Eyes
(Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The visual system of Xenos peckii, an endoparasite of paper wasps, demonstrates distinct benefits for high sensitivity and high resolution, differing from the compound eyes of most insects. Taking their unique features, a KAIST team developed an ultrathin digital camera that emulates the unique eyes of Xenos peckii.
The ultrathin digital camera offers a wide field of view and high resolution in a slimmer body compared to existing imaging systems. It is expected to support various applications, such as monitoring equipment, medical imaging devices, and mobile imaging systems.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team are known for mimicking biological visual organs. The team’s past research includes an LED lens based on the abdominal segments of fireflies and biologically inspired anti-reflective structures.
Recently, the demand for ultrathin digital cameras has increased, due to the miniaturization of electronic and optical devices. However, most camera modules use multiple lenses along the optical axis to compensate for optical aberrations, resulting in a larger volume as well as a thicker total track length of digital cameras. Resolution and sensitivity would be compromised if these modules were to be simply reduced in size and thickness.
To address this issue, the team have developed micro-optical components, inspired from the visual system of Xenos peckii, and combined them with a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensor to achieve an ultrathin digital camera.
This new camera, measuring less than 2mm in thickness, emulates the eyes of Xenos peckii by using dozens of microprism arrays and microlens arrays. A microprism and microlens pair form a channel and the light-absorbing medium between the channels reduces optical crosstalk. Each channel captures the partial image at slightly different orientation, and the retrieved partial images are combined into a single image, thereby ensuring a wide field of view and high resolution.
Professor Jeong said, “We have proposed a novel method of fabricating an ultrathin camera. As the first insect-inspired, ultrathin camera that integrates a microcamera on a conventional CMOS image sensor array, our study will have a significant impact in optics and related fields.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Dongmin Keum and Kyung-Won Jang, was published in Light: Science & Applications on October 24, 2018.
Figure 1. Natural Xenos peckii eye and the biological inspiration for the ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
Figure 2. Optical images captured by the bioinspired ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
2018.12.31 View 8715 -
 OUIC Presents the Six Most Promising Techs Transferrable to Local SMEs
KAIST will showcase the six most promising technologies for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) on November 14 in the Academic Cultural Complex. To strengthen the competitive edge of local SMEs in Daejeon, the Office of University-Industry made a survey of their technological needs and came up with the six most promising technologies. Developers will introduce their technologies during the session.Besides the introduction of the promising technologies, the session will also provide a program named University to Business (U2B) to match up technologies according to the SMEs’ needs. SMEs who wish to engage in technology transfers can receive counseling and other support programs during the session.First, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae from the Department of Industrial Design will present a technology for controlling cooperation robots. Professor Bae inserted flexible materials between the controllers to allow robots to use both hands stably and operate more accurately and swiftly. It can be applied to automatic robots, industrial robots, and service robots.Professor Hyun Myung from the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering will demonstrate a robot navigation system in a dynamic indoor and outdoor environment, which can be applied to robotics in logistics, smart factories, and autonomous vehicles. Providing robust simultaneous localization and mapping systems, this technology shows high-performing navigation with low-cost sensors.Meanwhile, Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will introduce a technology for forming stable adhesive emulsions. An emulsion is a stable mixture of water and oil. Conventionally, a small amount of surfactant is added to stabilize an emulsion. Here, Professor Choi developed a stable emulsion system without using any chemical substances. This technology can be applied to various fields, including the cosmetics, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and painting industries. The session will also present smart IoTs platform technology developed by Professor Jinhong Yang from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence. His technology minimizes errors occurring when multiple IoT devices are connected simultaneously. Professor Yong Keun Park from the Department of Physics will introduce a technology for measuring glycated hemoglobin by using the optical properties of red blood cells. This technology can be applied to make low-cost, small-sized measuring equipment. It can also be used for vitro diagnoses including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, tumors, kidney disease, and infectious diseases. Professor Yong Man Ro from the School of Electrical Engineering will show technology for biometric access control. Conventional technologies for face recognition fall behind other biometrics. Professor Ro and his team developed a facial dynamics interpreting network which allows very accurate facial recognition by interpreting the relationships between facial local dynamics and estimating facial traits. This technology can be applied to security and communication in finance, computers, and information system.KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “KAIST will continue to support SMEs to have stronger competitiveness in the market. Through technology transfer, we will drive innovation in technological commercialization where a university’s research and development creates economic value.”
2018.11.13 View 9149
OUIC Presents the Six Most Promising Techs Transferrable to Local SMEs
KAIST will showcase the six most promising technologies for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) on November 14 in the Academic Cultural Complex. To strengthen the competitive edge of local SMEs in Daejeon, the Office of University-Industry made a survey of their technological needs and came up with the six most promising technologies. Developers will introduce their technologies during the session.Besides the introduction of the promising technologies, the session will also provide a program named University to Business (U2B) to match up technologies according to the SMEs’ needs. SMEs who wish to engage in technology transfers can receive counseling and other support programs during the session.First, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae from the Department of Industrial Design will present a technology for controlling cooperation robots. Professor Bae inserted flexible materials between the controllers to allow robots to use both hands stably and operate more accurately and swiftly. It can be applied to automatic robots, industrial robots, and service robots.Professor Hyun Myung from the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering will demonstrate a robot navigation system in a dynamic indoor and outdoor environment, which can be applied to robotics in logistics, smart factories, and autonomous vehicles. Providing robust simultaneous localization and mapping systems, this technology shows high-performing navigation with low-cost sensors.Meanwhile, Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will introduce a technology for forming stable adhesive emulsions. An emulsion is a stable mixture of water and oil. Conventionally, a small amount of surfactant is added to stabilize an emulsion. Here, Professor Choi developed a stable emulsion system without using any chemical substances. This technology can be applied to various fields, including the cosmetics, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and painting industries. The session will also present smart IoTs platform technology developed by Professor Jinhong Yang from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence. His technology minimizes errors occurring when multiple IoT devices are connected simultaneously. Professor Yong Keun Park from the Department of Physics will introduce a technology for measuring glycated hemoglobin by using the optical properties of red blood cells. This technology can be applied to make low-cost, small-sized measuring equipment. It can also be used for vitro diagnoses including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, tumors, kidney disease, and infectious diseases. Professor Yong Man Ro from the School of Electrical Engineering will show technology for biometric access control. Conventional technologies for face recognition fall behind other biometrics. Professor Ro and his team developed a facial dynamics interpreting network which allows very accurate facial recognition by interpreting the relationships between facial local dynamics and estimating facial traits. This technology can be applied to security and communication in finance, computers, and information system.KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “KAIST will continue to support SMEs to have stronger competitiveness in the market. Through technology transfer, we will drive innovation in technological commercialization where a university’s research and development creates economic value.”
2018.11.13 View 9149 -
 Professor Baik Awarded Sangsan Young Mathematician Prize
(Professor Hyungryul Baik)
Professor Hyungryul Baik from the Department of Mathematical Sciences was honored as the recipient of the 2018 Sangsan Prize for Young Mathematicians by the Korean Mathematical Society (KMS).
The Sangsan Prize recognizes young mathematicians who finished their degree within the previous five years and have begun an outstanding research career. Professor Baik was recognized for his studies in the fields of low-dimensional topology, geophysical mathematics, and geometric theory. In particular, his Ph.D. dissertation presented a new criterion that completely identifies the hyperbolic surface group, making an inference about the nature of the hyperbolic manifold group.
Recently, Professor Baik co-published a paper entitled Spaces of Invariant Circular Orders of Groups with Professor Eric Samperton at the University of California Santa Barbara in the renowned academic journal Groups, Geometry, and Dynamics in 2018.
Professor Baik earned his BS at KAIST and finished his MS and Ph.D. in mathematics in 2014 at Cornell University. He joined KAIST as a faculty member last year.
2018.10.30 View 6711
Professor Baik Awarded Sangsan Young Mathematician Prize
(Professor Hyungryul Baik)
Professor Hyungryul Baik from the Department of Mathematical Sciences was honored as the recipient of the 2018 Sangsan Prize for Young Mathematicians by the Korean Mathematical Society (KMS).
The Sangsan Prize recognizes young mathematicians who finished their degree within the previous five years and have begun an outstanding research career. Professor Baik was recognized for his studies in the fields of low-dimensional topology, geophysical mathematics, and geometric theory. In particular, his Ph.D. dissertation presented a new criterion that completely identifies the hyperbolic surface group, making an inference about the nature of the hyperbolic manifold group.
Recently, Professor Baik co-published a paper entitled Spaces of Invariant Circular Orders of Groups with Professor Eric Samperton at the University of California Santa Barbara in the renowned academic journal Groups, Geometry, and Dynamics in 2018.
Professor Baik earned his BS at KAIST and finished his MS and Ph.D. in mathematics in 2014 at Cornell University. He joined KAIST as a faculty member last year.
2018.10.30 View 6711 -
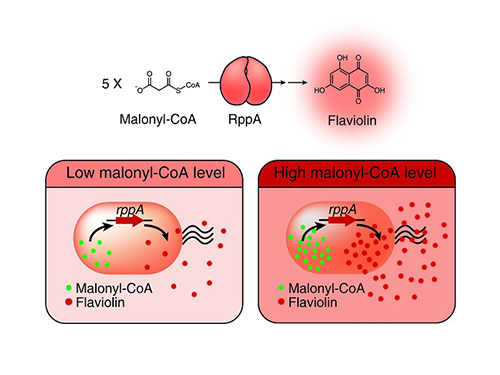 A Novel Biosensor to Advance Diverse High-Level Production of Microbial Cell Factories
A research group at KAIST presented a novel biosensor which can produce diverse, high-level microbial cell factories. The biosensor monitors the concentration of products and even intermediates when new strains are being developed. This strategy provides a new platform for manufacturing diverse natural products from renewable resources. The team succeeded in creating four natural products of high-level pharmaceutical importance with this strategy.
Malonyl-CoA is a major building block for many value-added chemicals including diverse natural products with pharmaceutical importance. However, due to the low availability of malonyl-CoA in bacteria, many malonyl-CoA-derived natural products have been produced by chemical synthesis or extraction from natural resources that are harmful to the environment and are unsustainable. For the sustainable biological production of malonyl-CoA-derived natural products, increasing the intracellular malonyl-CoA pool is necessary. To this end, the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor was required to monitor the concentration of intracellular malonyl-CoA abundance as new strains are developed.
Metabolic engineering researchers at KAIST addressed this issue. This research reports the development of a simple and robust malonyl-CoA biosensor by repurposing a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA), which produces flaviolin, a colorimetric indicator of malonyl-CoA. Subsequently, the RppA biosensor was used for the rapid and efficient colorimetric screening of gene manipulation targets enabling enhanced malonyl-CoA abundance. The screened beneficial gene targets were employed for the high-level production of four representative natural products derived from malonyl-CoA. Compared with the previous strategies, which were expensive and time-consuming, the new biosensor could be easily applied to industrially relevant bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and Corynebacterium glutamicum to enable a one-step process.
The study employs synthetic small regulatory RNA (sRNA) technology to rapidly and efficiently reduce endogenous target gene expression for improved malonyl-CoA production. The researchers constructed an E. coli genome-scale synthetic sRNA library targeting 1,858 genes covering all major metabolic genes in E. coli. This library was employed with the RppA biosensor to screen for gene targets which are believed to be beneficial for enhancing malonyl-CoA accumulation upon their expression knockdown.
From this colorimetric screening, 14 gene targets were selected, all of which were successful at significantly increasing the production of four natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin). Although specific examples are demonstrated in E. coli as a host, the researchers showed that the biosensor is also functional in P. putida and C. glutamicum, industrially important representative gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The malonyl-CoA biosensor developed in this research will serve as an efficient platform for the rapid development of strains capable of producing natural products crucial for the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics, and food industries.
An important aspect of this work is that the high-performance strains constructed in this research were developed rapidly and easily by utilizing the simple approach of colorimetric screening, without involving extensive metabolic engineering approaches. 6-Methylsalicylic acid (an antibiotic) could be produced to the highest titer reported for E. coli, and the microbial production of aloesone (a precursor of aloesin, an anti-inflammatory agent/whitening agent) was achieved for the first time.
“A sustainable process for producing diverse natural products using renewable resources is of great interest. This study represents the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor generally applicable to a wide range of industrially important bacteria. The capability of this biosensor for screening a large library was demonstrated to show that the rapid and efficient construction of high-performance strains is feasible. This research will be useful for further accelerating the development process of strains capable of producing valuable chemicals to industrially relevant levels,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, who led the research.
This study entitled “Repurposing type III polyketide synthase as a malonyl-CoA biosensor for metabolic engineering in bacteria,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on October 02.
PhD students Dongsoo Yang and Won Jun Kim, MS student Shin Hee Ha, research staff Mun Hee Lee, Research Professor Seung Min Yoo, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Dr. Jong Hyun Choi of the Applied Microbiology Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) participated in this research.
Figure: Type III polyketide synthase (RppA) as a malonyl-CoA biosensor. RppA converts five molecules of malonyl-CoA into one molecule of red-colored flaviolin. This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of the malonyl-CoA biosensor by indicating that higher malonyl-CoA abundance leads to higher production and secretion of flaviolin, resulting in a deeper red color of the culture. This system was employed for the enhanced production of four representative natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin) from engineered E. coli strains.
2018.10.11 View 9839
A Novel Biosensor to Advance Diverse High-Level Production of Microbial Cell Factories
A research group at KAIST presented a novel biosensor which can produce diverse, high-level microbial cell factories. The biosensor monitors the concentration of products and even intermediates when new strains are being developed. This strategy provides a new platform for manufacturing diverse natural products from renewable resources. The team succeeded in creating four natural products of high-level pharmaceutical importance with this strategy.
Malonyl-CoA is a major building block for many value-added chemicals including diverse natural products with pharmaceutical importance. However, due to the low availability of malonyl-CoA in bacteria, many malonyl-CoA-derived natural products have been produced by chemical synthesis or extraction from natural resources that are harmful to the environment and are unsustainable. For the sustainable biological production of malonyl-CoA-derived natural products, increasing the intracellular malonyl-CoA pool is necessary. To this end, the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor was required to monitor the concentration of intracellular malonyl-CoA abundance as new strains are developed.
Metabolic engineering researchers at KAIST addressed this issue. This research reports the development of a simple and robust malonyl-CoA biosensor by repurposing a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA), which produces flaviolin, a colorimetric indicator of malonyl-CoA. Subsequently, the RppA biosensor was used for the rapid and efficient colorimetric screening of gene manipulation targets enabling enhanced malonyl-CoA abundance. The screened beneficial gene targets were employed for the high-level production of four representative natural products derived from malonyl-CoA. Compared with the previous strategies, which were expensive and time-consuming, the new biosensor could be easily applied to industrially relevant bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and Corynebacterium glutamicum to enable a one-step process.
The study employs synthetic small regulatory RNA (sRNA) technology to rapidly and efficiently reduce endogenous target gene expression for improved malonyl-CoA production. The researchers constructed an E. coli genome-scale synthetic sRNA library targeting 1,858 genes covering all major metabolic genes in E. coli. This library was employed with the RppA biosensor to screen for gene targets which are believed to be beneficial for enhancing malonyl-CoA accumulation upon their expression knockdown.
From this colorimetric screening, 14 gene targets were selected, all of which were successful at significantly increasing the production of four natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin). Although specific examples are demonstrated in E. coli as a host, the researchers showed that the biosensor is also functional in P. putida and C. glutamicum, industrially important representative gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The malonyl-CoA biosensor developed in this research will serve as an efficient platform for the rapid development of strains capable of producing natural products crucial for the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics, and food industries.
An important aspect of this work is that the high-performance strains constructed in this research were developed rapidly and easily by utilizing the simple approach of colorimetric screening, without involving extensive metabolic engineering approaches. 6-Methylsalicylic acid (an antibiotic) could be produced to the highest titer reported for E. coli, and the microbial production of aloesone (a precursor of aloesin, an anti-inflammatory agent/whitening agent) was achieved for the first time.
“A sustainable process for producing diverse natural products using renewable resources is of great interest. This study represents the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor generally applicable to a wide range of industrially important bacteria. The capability of this biosensor for screening a large library was demonstrated to show that the rapid and efficient construction of high-performance strains is feasible. This research will be useful for further accelerating the development process of strains capable of producing valuable chemicals to industrially relevant levels,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, who led the research.
This study entitled “Repurposing type III polyketide synthase as a malonyl-CoA biosensor for metabolic engineering in bacteria,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on October 02.
PhD students Dongsoo Yang and Won Jun Kim, MS student Shin Hee Ha, research staff Mun Hee Lee, Research Professor Seung Min Yoo, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Dr. Jong Hyun Choi of the Applied Microbiology Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) participated in this research.
Figure: Type III polyketide synthase (RppA) as a malonyl-CoA biosensor. RppA converts five molecules of malonyl-CoA into one molecule of red-colored flaviolin. This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of the malonyl-CoA biosensor by indicating that higher malonyl-CoA abundance leads to higher production and secretion of flaviolin, resulting in a deeper red color of the culture. This system was employed for the enhanced production of four representative natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin) from engineered E. coli strains.
2018.10.11 View 9839 -
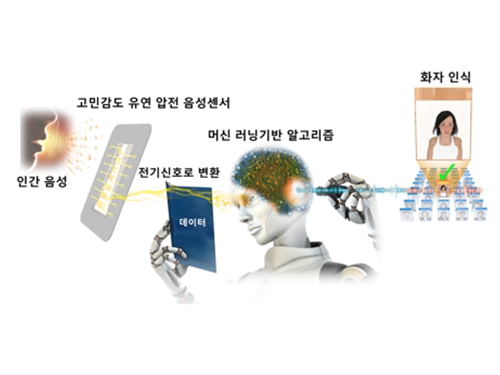 Flexible Piezoelectric Acoustic Sensors for Speaker Recognition
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Material Science and Engineering has developed a machine learning-based acoustic sensor for speaker recognition.
Acoustic sensors were spotlighted as one of the most intuitive bilateral communication devices between humans and machines. However, conventional acoustic sensors use a condenser-type device for measuring capacitance between two conducting layers, resulting in low sensitivity, short recognition distance, and low speaker recognition rates.
The team fabricated a flexible piezoelectric membrane by mimicking the basilar membrane in the human cochlear. Resonant frequencies vibrate corresponding regions of the trapezoidal piezoelectric membrane, which converts voice to electrical signal with a highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensor.
This multi-channel piezoelectric acoustic sensor exhibits sensitivity more than two times higher and allows for more abundant voice information compared to conventional acoustic sensors, which can detect minute sounds from farther distances. In addition, the acoustic sensor can achieve a 97.5% speaker recognition rate using a machine learning algorithm, reducing by 75% error rate than the reference microphone.
AI speaker recognition is the next big thing for future individual customized services. However, conventional technology attempts to improve recognition rates by using software upgrades, resulting in limited speaker recognition rates. The team enhanced the speaker recognition system by replacing the existing hardware with an innovative flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor. Further software improvement of the piezoelectric acoustic sensor will significantly increase the speaker and voice recognition rate in diverse environments.
Professor Lee said, “Highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensors for speaker recognition can be used for personalized voice services such as smart home appliances, AI secretaries, always-on IoT, biometric authentication, and FinTech.”
These research “Basilar Membrane-Inspired Self-Powered Acoustic Sensor” and “Machine Learning-based Acoustic Sensor for Speaker Recognition” were published in the September 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Firgure 1: A flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor mimicking the human cochlear.
Figure 2: Speaker recognition with a machine learning algorithm.
2018.10.04 View 7562
Flexible Piezoelectric Acoustic Sensors for Speaker Recognition
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Material Science and Engineering has developed a machine learning-based acoustic sensor for speaker recognition.
Acoustic sensors were spotlighted as one of the most intuitive bilateral communication devices between humans and machines. However, conventional acoustic sensors use a condenser-type device for measuring capacitance between two conducting layers, resulting in low sensitivity, short recognition distance, and low speaker recognition rates.
The team fabricated a flexible piezoelectric membrane by mimicking the basilar membrane in the human cochlear. Resonant frequencies vibrate corresponding regions of the trapezoidal piezoelectric membrane, which converts voice to electrical signal with a highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensor.
This multi-channel piezoelectric acoustic sensor exhibits sensitivity more than two times higher and allows for more abundant voice information compared to conventional acoustic sensors, which can detect minute sounds from farther distances. In addition, the acoustic sensor can achieve a 97.5% speaker recognition rate using a machine learning algorithm, reducing by 75% error rate than the reference microphone.
AI speaker recognition is the next big thing for future individual customized services. However, conventional technology attempts to improve recognition rates by using software upgrades, resulting in limited speaker recognition rates. The team enhanced the speaker recognition system by replacing the existing hardware with an innovative flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor. Further software improvement of the piezoelectric acoustic sensor will significantly increase the speaker and voice recognition rate in diverse environments.
Professor Lee said, “Highly sensitive self-powered acoustic sensors for speaker recognition can be used for personalized voice services such as smart home appliances, AI secretaries, always-on IoT, biometric authentication, and FinTech.”
These research “Basilar Membrane-Inspired Self-Powered Acoustic Sensor” and “Machine Learning-based Acoustic Sensor for Speaker Recognition” were published in the September 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Firgure 1: A flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor mimicking the human cochlear.
Figure 2: Speaker recognition with a machine learning algorithm.
2018.10.04 View 7562 -
 Mathematical Principle behind AI's 'Black Box'
(from left: Professor Jong Chul Ye, PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha)
A KAIST research team identified the geometrical structure of artificial intelligence (AI) and discovered the mathematical principles of highly performing artificial neural networks, which can be applicable in fields such as medical imaging.
Deep neural networks are an exemplary method of implementing deep learning, which is at the core of the AI technology, and have shown explosive growth in recent years. This technique has been used in various fields, such as image and speech recognition as well as image processing.
Despite its excellent performance and usefulness, the exact working principles of deep neural networks has not been well understood, and they often suffer from unexpected results or errors. Hence, there is an increasing social and technical demand for interpretable deep neural network models.
To address these issues, Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering and his team attempted to find the geometric structure in a higher dimensional space where the structure of the deep neural network can be easily understood. They proposed a general deep learning framework, called deep convolutional framelets, to understand the mathematical principle of a deep neural network in terms of the mathematical tools in Harmonic analysis.
As a result, it was found that deep neural networks’ structure appears during the process of decomposition of high dimensionally lifted signal via Hankel matrix, which is a high-dimensional structure formerly studied intensively in the field of signal processing.
In the process of decomposing the lifted signal, two bases categorized as local and non-local basis emerge. The researchers found that non-local and local basis functions play a role in pooling and filtering operation in convolutional neural network, respectively.
Previously, when implementing AI, deep neural networks were usually constructed through empirical trial and errors. The significance of the research lies in the fact that it provides a mathematical understanding on the neural network structure in high dimensional space, which guides users to design an optimized neural network.
They demonstrated improved performance of the deep convolutional framelets’ neural networks in the applications of image denoising, image pixel in painting, and medical image restoration.
Professor Ye said, “Unlike conventional neural networks designed through trial-and-error, our theory shows that neural network structure can be optimized to each desired application and are easily predictable in their effects by exploiting the high dimensional geometry. This technology can be applied to a variety of fields requiring interpretation of the architecture, such as medical imaging.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha, was published in the April 26th issue of the SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences.
Figure 1. The design of deep neural network using mathematical principles
Figure 2. The results of image noise cancelling
Figure 3. The artificial neural network restoration results in the case where 80% of the pixels are lost
2018.09.12 View 6411
Mathematical Principle behind AI's 'Black Box'
(from left: Professor Jong Chul Ye, PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha)
A KAIST research team identified the geometrical structure of artificial intelligence (AI) and discovered the mathematical principles of highly performing artificial neural networks, which can be applicable in fields such as medical imaging.
Deep neural networks are an exemplary method of implementing deep learning, which is at the core of the AI technology, and have shown explosive growth in recent years. This technique has been used in various fields, such as image and speech recognition as well as image processing.
Despite its excellent performance and usefulness, the exact working principles of deep neural networks has not been well understood, and they often suffer from unexpected results or errors. Hence, there is an increasing social and technical demand for interpretable deep neural network models.
To address these issues, Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering and his team attempted to find the geometric structure in a higher dimensional space where the structure of the deep neural network can be easily understood. They proposed a general deep learning framework, called deep convolutional framelets, to understand the mathematical principle of a deep neural network in terms of the mathematical tools in Harmonic analysis.
As a result, it was found that deep neural networks’ structure appears during the process of decomposition of high dimensionally lifted signal via Hankel matrix, which is a high-dimensional structure formerly studied intensively in the field of signal processing.
In the process of decomposing the lifted signal, two bases categorized as local and non-local basis emerge. The researchers found that non-local and local basis functions play a role in pooling and filtering operation in convolutional neural network, respectively.
Previously, when implementing AI, deep neural networks were usually constructed through empirical trial and errors. The significance of the research lies in the fact that it provides a mathematical understanding on the neural network structure in high dimensional space, which guides users to design an optimized neural network.
They demonstrated improved performance of the deep convolutional framelets’ neural networks in the applications of image denoising, image pixel in painting, and medical image restoration.
Professor Ye said, “Unlike conventional neural networks designed through trial-and-error, our theory shows that neural network structure can be optimized to each desired application and are easily predictable in their effects by exploiting the high dimensional geometry. This technology can be applied to a variety of fields requiring interpretation of the architecture, such as medical imaging.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Yoseob Han and Eunju Cha, was published in the April 26th issue of the SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences.
Figure 1. The design of deep neural network using mathematical principles
Figure 2. The results of image noise cancelling
Figure 3. The artificial neural network restoration results in the case where 80% of the pixels are lost
2018.09.12 View 6411 -
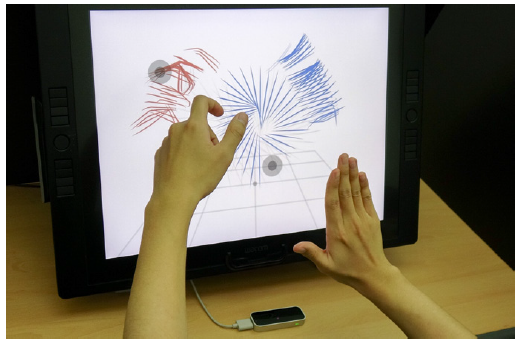 It's Time to 3D Sketch with Air Scaffolding
People often use their hands when describing an object, while pens are great tools for describing objects in detail. Taking this idea, a KAIST team introduced a new 3D sketching workflow, combining the strengths of hand and pen input. This technique will ease the way for ideation in three dimensions, leading to efficient product design in terms of time and cost.
For a designer's drawing to become a product in reality, one has to transform a designer's 2D drawing into a 3D shape; however, it is difficult to infer accurate 3D shapes that match the original intention from an inaccurate 2D drawing made by hand. When creating a 3D shape from a planar 2D drawing, unobtainable information is required. On the other hand, loss of depth information occurs when a 3D shape is expressed as a 2D drawing using perspective drawing techniques.
To fill in these “missing links” during the conversion, "3D sketching" techniques have been actively studied. Their main purpose is to help designers naturally provide missing 3D shape information in a 2D drawing. For example, if a designer draws two symmetric curves from a single point of view or draws the same curves from different points of view, the geometric clues that are left in this process are collected and mathematically interpreted to define the proper 3D curve. As a result, designers can use 3D sketching to directly draw a 3D shape as if using pen and paper.
Among 3D sketching tools, sketching with hand motions, in VR environments in particular, has drawn attention because it is easy and quick. But the biggest limitation is that they cannot articulate the design solely using rough hand motions, hence they are difficult to be applied to product designs. Moreover, users may feel tired after raising their hands in the air during the entire drawing process.
Using hand motions but to elaborate designs, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design integrated hand motions and pen-based sketching, allocating roles according to their strengths. This new technique is called Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding. Designers use their hand motions in the air to create rough 3D shapes which will be used as scaffolds, and then they can add details with pen-based 3D sketching on a tablet (Figure 1).
Figure 1. In the agile 3D sketching workflow with air scaffolding, the user (a) makes unconstrained hand movements in the air to quickly generate rough shapes to be used as scaffolds, (b) uses the scaffolds as references and draws finer details with them, (c) produces a high-fidelity 3D concept sketch of a steering wheel in an iterative and progressive manner.
The team came up with an algorithm to identify descriptive hand motions from transitory hand motions and extract only the intended shapes from unconstrained hand motions, based on air scaffolds from the identified motions.
Through user tests, the team identified that this technique is easy to learn and use, and demonstrates good applicability. Most importantly, the users can reduce time, yet enhance the accuracy of defining the proportion and scale of products.
Eventually, this tool will be able to be applied to various fields including the automobile industry, home appliances, animations and the movie making industry, and robotics. It also can be linked to smart production technology, such as 3D printing, to make manufacturing process faster and more flexible.
PhD candidate Yongkwan Kim, who led the research project, said, “I believe the system will enhance product quality and work efficiency because designers can express their 3D ideas quickly yet accurately without using complex 3D CAD modeling software. I will make it into a product that every designer wants to use in various fields.”
“There have been many attempts to encourage creative activities in various fields by using advanced computer technology. Based on in-depth understanding of designers, we will take the lead in innovating the design process by applying cutting-edge technology,” Professor Bae added.
Professor Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design has been delving into developing better 3D sketching tools. They started with a 3D curve sketching system for professional designers called ILoveSketch and moved on to SketchingWithHands for designing a handheld product with first-person hand postures captured by a hand-tracking sensor. They then took their project to the next level and introduced Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding, a new 3D sketching workflow combining hand motion and pen drawing which was chosen as one of the CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2018 Best Papers by the Association for Computing Machinery.
- Click the link to watch video clip of SketchingWithHands
2018.07.25 View 9755
It's Time to 3D Sketch with Air Scaffolding
People often use their hands when describing an object, while pens are great tools for describing objects in detail. Taking this idea, a KAIST team introduced a new 3D sketching workflow, combining the strengths of hand and pen input. This technique will ease the way for ideation in three dimensions, leading to efficient product design in terms of time and cost.
For a designer's drawing to become a product in reality, one has to transform a designer's 2D drawing into a 3D shape; however, it is difficult to infer accurate 3D shapes that match the original intention from an inaccurate 2D drawing made by hand. When creating a 3D shape from a planar 2D drawing, unobtainable information is required. On the other hand, loss of depth information occurs when a 3D shape is expressed as a 2D drawing using perspective drawing techniques.
To fill in these “missing links” during the conversion, "3D sketching" techniques have been actively studied. Their main purpose is to help designers naturally provide missing 3D shape information in a 2D drawing. For example, if a designer draws two symmetric curves from a single point of view or draws the same curves from different points of view, the geometric clues that are left in this process are collected and mathematically interpreted to define the proper 3D curve. As a result, designers can use 3D sketching to directly draw a 3D shape as if using pen and paper.
Among 3D sketching tools, sketching with hand motions, in VR environments in particular, has drawn attention because it is easy and quick. But the biggest limitation is that they cannot articulate the design solely using rough hand motions, hence they are difficult to be applied to product designs. Moreover, users may feel tired after raising their hands in the air during the entire drawing process.
Using hand motions but to elaborate designs, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design integrated hand motions and pen-based sketching, allocating roles according to their strengths. This new technique is called Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding. Designers use their hand motions in the air to create rough 3D shapes which will be used as scaffolds, and then they can add details with pen-based 3D sketching on a tablet (Figure 1).
Figure 1. In the agile 3D sketching workflow with air scaffolding, the user (a) makes unconstrained hand movements in the air to quickly generate rough shapes to be used as scaffolds, (b) uses the scaffolds as references and draws finer details with them, (c) produces a high-fidelity 3D concept sketch of a steering wheel in an iterative and progressive manner.
The team came up with an algorithm to identify descriptive hand motions from transitory hand motions and extract only the intended shapes from unconstrained hand motions, based on air scaffolds from the identified motions.
Through user tests, the team identified that this technique is easy to learn and use, and demonstrates good applicability. Most importantly, the users can reduce time, yet enhance the accuracy of defining the proportion and scale of products.
Eventually, this tool will be able to be applied to various fields including the automobile industry, home appliances, animations and the movie making industry, and robotics. It also can be linked to smart production technology, such as 3D printing, to make manufacturing process faster and more flexible.
PhD candidate Yongkwan Kim, who led the research project, said, “I believe the system will enhance product quality and work efficiency because designers can express their 3D ideas quickly yet accurately without using complex 3D CAD modeling software. I will make it into a product that every designer wants to use in various fields.”
“There have been many attempts to encourage creative activities in various fields by using advanced computer technology. Based on in-depth understanding of designers, we will take the lead in innovating the design process by applying cutting-edge technology,” Professor Bae added.
Professor Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design has been delving into developing better 3D sketching tools. They started with a 3D curve sketching system for professional designers called ILoveSketch and moved on to SketchingWithHands for designing a handheld product with first-person hand postures captured by a hand-tracking sensor. They then took their project to the next level and introduced Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding, a new 3D sketching workflow combining hand motion and pen drawing which was chosen as one of the CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2018 Best Papers by the Association for Computing Machinery.
- Click the link to watch video clip of SketchingWithHands
2018.07.25 View 9755