society
-
 Non-Adiabatic Reaction Mechanism Identified at Conical Intersection
(Professor Kim(center) and Ph.D. candidates Kyung Chul Woo (left) and Kang Do Hyung)
Research team led by Professor Sang Kyu Kim at KAIST Department of Chemistry observed two distinct reaction pathways that occur at conical intersection where two different adiabatic potential energy surfaces cross at the same nuclear configuration.
Professor Kim previously identified the existence and molecular structure of conical intersection in 2010. In this following study, the team accurately measured reaction rates of two totally different reaction pathways activated only at conical intersection where the seminal Born-Oppenheimer approximation breaks down.
This study led by Kyung Chul Woo (1st author) and Do Hyung Kang, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST, was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society in November 7th, 2017.
Chemical reaction induced by light occurs in excited electronic states where the reaction outcome is often destined by coupling among different electronic states mediated by nuclear motions during chemical reaction. Such a coupling is most critical and important at the conical intersection as nonadiabtic surface-hopping is most probable at situation where the Born-Oppenheimer approximation fails.
Professor Kim used spectroscopic methods in 2010 to experimentally observe conical intersection of polyatomic molecule. And yet, it was not possible to disentangle complex dynamic processes with frequency-domain study only.
The research team used pico-second time-resolution kinetic energy resolved mass spectrometry to identify two possible distinct reaction pathways in both energy and time domains.,.
The research team demonstrated that the reactive flux prepared at the conical intersection is bifurcated into adiabatic or non-adiabatic reaction pathways. These two pathways are quite distinct in terms of reaction rates, energy releases, and product branching ratios.
This is the first study to capture the moment of bifurcation dynamics at the conical intersection for complex polyatomic molecular system. The study could contribute to conceptual improvement in understanding complicated nonadiabatic dynamics in general.
Professor Kim said, “Basic science research is essential in understanding and wisely using the nature. New technological advances cannot be made without the advancement in basic science.” He continued, “I hope this study could lead to growth in many young academic talents in basic sciences.”
(Figure 1. Reaction graph starting from reaction intersection that divides into adiabatic reaction pathway (red) and non-adiabatic pathway (blue))
2017.12.19 View 6856
Non-Adiabatic Reaction Mechanism Identified at Conical Intersection
(Professor Kim(center) and Ph.D. candidates Kyung Chul Woo (left) and Kang Do Hyung)
Research team led by Professor Sang Kyu Kim at KAIST Department of Chemistry observed two distinct reaction pathways that occur at conical intersection where two different adiabatic potential energy surfaces cross at the same nuclear configuration.
Professor Kim previously identified the existence and molecular structure of conical intersection in 2010. In this following study, the team accurately measured reaction rates of two totally different reaction pathways activated only at conical intersection where the seminal Born-Oppenheimer approximation breaks down.
This study led by Kyung Chul Woo (1st author) and Do Hyung Kang, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST, was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society in November 7th, 2017.
Chemical reaction induced by light occurs in excited electronic states where the reaction outcome is often destined by coupling among different electronic states mediated by nuclear motions during chemical reaction. Such a coupling is most critical and important at the conical intersection as nonadiabtic surface-hopping is most probable at situation where the Born-Oppenheimer approximation fails.
Professor Kim used spectroscopic methods in 2010 to experimentally observe conical intersection of polyatomic molecule. And yet, it was not possible to disentangle complex dynamic processes with frequency-domain study only.
The research team used pico-second time-resolution kinetic energy resolved mass spectrometry to identify two possible distinct reaction pathways in both energy and time domains.,.
The research team demonstrated that the reactive flux prepared at the conical intersection is bifurcated into adiabatic or non-adiabatic reaction pathways. These two pathways are quite distinct in terms of reaction rates, energy releases, and product branching ratios.
This is the first study to capture the moment of bifurcation dynamics at the conical intersection for complex polyatomic molecular system. The study could contribute to conceptual improvement in understanding complicated nonadiabatic dynamics in general.
Professor Kim said, “Basic science research is essential in understanding and wisely using the nature. New technological advances cannot be made without the advancement in basic science.” He continued, “I hope this study could lead to growth in many young academic talents in basic sciences.”
(Figure 1. Reaction graph starting from reaction intersection that divides into adiabatic reaction pathway (red) and non-adiabatic pathway (blue))
2017.12.19 View 6856 -
 Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 7352
Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 7352 -
 Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 9690
Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 9690 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 13933
Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 13933 -
 Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Sensitive Hydrogen Sensor
(From left: Professor Kim, Ph.D. candidate Koo, and Professor Penner)
A KAIST team made an ultra-fast hydrogen sensor that can detect hydrogen gas levels under 1% in less than seven seconds. The sensor also can detect hundreds of parts per million levels of hydrogen gas within 60 seconds at room temperature.
A research group under Professor Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, in collaboration with Professor Reginald M. Penner of the University of California-Irvine, has developed an ultra-fast hydrogen gas detection system based on a palladium (Pd) nanowire array coated with a metal-organic framework (MOF).
Hydrogen has been regarded as an eco-friendly next-generation energy source. However, it is a flammable gas that can explode even with a small spark. For safety, the lower explosion limit for hydrogen gas is 4 vol% so sensors should be able to detect the colorless and odorless hydrogen molecule quickly. The importance of sensors capable of rapidly detecting colorless and odorless hydrogen gas has been emphasized in recent guidelines issued by the U.S. Department of Energy. According to the guidelines, hydrogen sensors should detect 1 vol% of hydrogen in air in less than 60 seconds for adequate response and recovery times.
To overcome the limitations of Pd-based hydrogen sensors, the research team introduced a MOF layer on top of a Pd nanowire array. Lithographically patterned Pd nanowires were simply overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer composed of Zn ions and organic ligands. ZIF-8 film is easily coated on Pd nanowires by simple dipping (for 2–6 hours) in a methanol solution including Zn (NO3)2·6H2O and 2-methylimidazole.
(This cover image depicts lithographically-patterned Pd nanowires overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer.)
As synthesized ZIF-8 is a highly porous material composed of a number of micro-pores of 0.34 nm and 1.16 nm, hydrogen gas with a kinetic diameter of 0.289 nm can easily penetrate inside the ZIF-8 membrane, while large molecules (> 0.34 nm) are effectively screened by the MOF filter. Thus, the ZIF-8 filter on the Pd nanowires allows the predominant penetration of hydrogen molecules, leading to the acceleration of Pd-based H2 sensors with a 20-fold faster recovery and response speed compared to pristine Pd nanowires at room temperature.
Professor Kim expects that the ultra-fast hydrogen sensor can be useful for the prevention of explosion accidents caused by the leakage of hydrogen gas. In addition, he expects that other harmful gases in the air can be accurately detected through effective nano-filtration by using of a variety of MOF layers.
This study was carried out by Ph.D. candidate Won-Tae Koo (first author), Professor Kim (co-corresponding author), and Professor Penner (co-corresponding author). The study has been published in the online edition of ACS Nano, as the cover-featured image for the September issue.
Figure 1. Representative image for this paper published in ACS Nano, August, 18.
Figure 2. Images of Pd nanowire array-based hydrogen sensors, scanning electron microscopy image of a Pd nanowire covered by a metal-organic framework layer, and the hydrogen sensing properties of the sensors.
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of a metal-organic framework (MOF). The MOF, consisting of metal ions and organic ligands, is a highly porous material with an ultrahigh surface area. The various structures of MOFs can be synthesized depending on the kinds of metal ions and organic ligands.
2017.09.28 View 11609
Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Sensitive Hydrogen Sensor
(From left: Professor Kim, Ph.D. candidate Koo, and Professor Penner)
A KAIST team made an ultra-fast hydrogen sensor that can detect hydrogen gas levels under 1% in less than seven seconds. The sensor also can detect hundreds of parts per million levels of hydrogen gas within 60 seconds at room temperature.
A research group under Professor Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, in collaboration with Professor Reginald M. Penner of the University of California-Irvine, has developed an ultra-fast hydrogen gas detection system based on a palladium (Pd) nanowire array coated with a metal-organic framework (MOF).
Hydrogen has been regarded as an eco-friendly next-generation energy source. However, it is a flammable gas that can explode even with a small spark. For safety, the lower explosion limit for hydrogen gas is 4 vol% so sensors should be able to detect the colorless and odorless hydrogen molecule quickly. The importance of sensors capable of rapidly detecting colorless and odorless hydrogen gas has been emphasized in recent guidelines issued by the U.S. Department of Energy. According to the guidelines, hydrogen sensors should detect 1 vol% of hydrogen in air in less than 60 seconds for adequate response and recovery times.
To overcome the limitations of Pd-based hydrogen sensors, the research team introduced a MOF layer on top of a Pd nanowire array. Lithographically patterned Pd nanowires were simply overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer composed of Zn ions and organic ligands. ZIF-8 film is easily coated on Pd nanowires by simple dipping (for 2–6 hours) in a methanol solution including Zn (NO3)2·6H2O and 2-methylimidazole.
(This cover image depicts lithographically-patterned Pd nanowires overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer.)
As synthesized ZIF-8 is a highly porous material composed of a number of micro-pores of 0.34 nm and 1.16 nm, hydrogen gas with a kinetic diameter of 0.289 nm can easily penetrate inside the ZIF-8 membrane, while large molecules (> 0.34 nm) are effectively screened by the MOF filter. Thus, the ZIF-8 filter on the Pd nanowires allows the predominant penetration of hydrogen molecules, leading to the acceleration of Pd-based H2 sensors with a 20-fold faster recovery and response speed compared to pristine Pd nanowires at room temperature.
Professor Kim expects that the ultra-fast hydrogen sensor can be useful for the prevention of explosion accidents caused by the leakage of hydrogen gas. In addition, he expects that other harmful gases in the air can be accurately detected through effective nano-filtration by using of a variety of MOF layers.
This study was carried out by Ph.D. candidate Won-Tae Koo (first author), Professor Kim (co-corresponding author), and Professor Penner (co-corresponding author). The study has been published in the online edition of ACS Nano, as the cover-featured image for the September issue.
Figure 1. Representative image for this paper published in ACS Nano, August, 18.
Figure 2. Images of Pd nanowire array-based hydrogen sensors, scanning electron microscopy image of a Pd nanowire covered by a metal-organic framework layer, and the hydrogen sensing properties of the sensors.
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of a metal-organic framework (MOF). The MOF, consisting of metal ions and organic ligands, is a highly porous material with an ultrahigh surface area. The various structures of MOFs can be synthesized depending on the kinds of metal ions and organic ligands.
2017.09.28 View 11609 -
 Draining Eyes Clogged with Glaucoma
Professor Gou Young Koh in the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and his team have identified a new mechanism involved in the development and progression of glaucoma, and found a potential therapeutic option to treat it. Glaucoma is the second cause of irreversible blindness, after cataracts. It affects about 3.5% of the world population aged 40 to 80.
Professor Koh also serves as the director of the Center for Vascular Research at the Institute for Basic Science. The IBS said the study, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, is expected to help the development of therapies to treat primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), which counts for three quarters of all glaucoma patients.
One of the most important risk factors for glaucoma is the increased pressure inside the eye. A liquid called aqueous humor is constantly produced and drained out from the eye. It transports nutrients and inflates the eye giving it a roughly spherical shape. However, if this fluid cannot flow out of the eye chambers freely, an increase in intraocular pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss. The precise mechanism of elevated resistance to aqueous humor outflow remains unclear, and although the current treatments for glaucoma tackle the production and outflow of aqueous humor, their outcomes are still poor.
A component of the eye that plays a fundamental role in draining out the aqueous humor is Schlemm's canal. It collects the aqueous humor and mediates its transfer from the eye chambers to blood circulation. The cells on the walls of the canal, endothelial cells, ship the liquid from the inner to the outer side in “packages”, called vacuoles. As the shape and number of the vacuoles reflects the outflow performance, several giant vacuoles are expected in the normal outflow process.
The team explained how imbalances in Schlemm's canal significantly increase the risk of glaucoma. They showed that an important regulator for canal functionality is the angiopoietin-Tie2 system. Angiopoietins, such as Ang1 and Ang2, are proteins important for the growth of new blood vessels and Tie2 is the receptor that binds them. It is known that the angiopoietin-Tie2 system plays a role in Schlemm’s canal formation, as Tie2 mutations or angiopoietin absence result in congenital glaucoma. However, this study clarified that it is also critically important during adulthood.
The researchers reported that adult mice deficient in Tie2 suffer from an elevated intraocular pressure, retinal neuronal damage and partial visual impairment. Moreover, they had a markedly decreased number of giant vacuoles inside Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells, which indicate a poor aqueous humor drainage.
The scientists also investigated if and how this process changes in older mice, as aging is a major risk factor for glaucoma, and showed that aged mice experience reduced levels of giant vacuoles, Tie2, Ang1, and Ang2, as well as other proteins connected with the angiopoietin-Tie2 pathway, like Prox1.
To test whether Tie2 activation could shift the situation, the researchers tested the antibody ABTAA (Ang2-binding and Tie2-activating antibody). They injected it in one eye of mice, while the other eye of the same mice functioned as the negative control. After one week, levels of Tie2 and Prox1, number and diameter of giant vacuoles in Schlemm’s canals increased in the ABTAA-treated eyes compared to control eyes. The researchers observed a similar outcome with decreased intraocular pressure when ABTAA was injected to the eyes of mice suffering from POAG with regressed Schlemm’s canals, indicating that this antibody might be considered as a therapeutic option.
"Slow development of glaucoma treatments is partly due to the poor understanding of the underlying pathogenesis," said Professor Koh, the corresponding author of the study. "We hope that identifying the critical role of the angiopoietin-Tie2 system in adult Schlemm’s canals will bring a significant boost in the development of therapeutics."
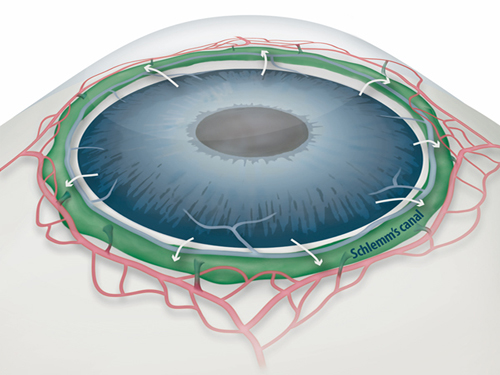
Figure 1: Schlemm's canal position inside the eye.
Schlemm's canal (green) plays a fundamental role in draining the aqueous humor (white arrows) from the anterior chamber of the eye to blood circulation. If the aqueous humor is not able to flow out freely, elevated intraocular pressure damages the optical nerve causing glaucoma and eventually blindness.
Figure 2: Electron microscope images reveal how the aqueous humor is packaged in vacuoles (arrowheads) inside the cells forming the walls of Schlemm's canal.
Aging and glaucoma cause the number and size of giant vacuoles to decrease, meaning that the aqueous humor outflow is compromised. The images compare the giant vacuoles in Schlemm's canals of a healthy mouse (top) and a mouse lacking Tie2 (bottom)
Figure 3: The Ang2-binding and Tie2-activating antibody (ABTAA) rejuvenates the eye of aged mice and rescues them from glaucoma.
Aging causes a reduction of the protein Tie2, a risk factor for increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma. In this experiment, one eye of mice lacking Ang1 and Ang2 was injected with the premixed ABTAA and Ang2, while the other eye was used as negative control. The researchers observed an increase in the area of Schlemm’s canal, together with higher levels of Tie2 (red) and lower intraocular pressure, suggesting that ABTAA restores the canal's functionality. The image includes the transcription factor Prox1 (green) and CD144 (blue), a protein present at the junctions between cells that form the wall of the canal. The angiopoietin-Tie2 system and Prox1 are linked by a vicious circle: the less Tie2 and Ang2, the less Prox1, leading to Schlemm's canal damage, increase in intraocular pressure, and acceleration of glaucoma progression.
2017.09.19 View 7885
Draining Eyes Clogged with Glaucoma
Professor Gou Young Koh in the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and his team have identified a new mechanism involved in the development and progression of glaucoma, and found a potential therapeutic option to treat it. Glaucoma is the second cause of irreversible blindness, after cataracts. It affects about 3.5% of the world population aged 40 to 80.
Professor Koh also serves as the director of the Center for Vascular Research at the Institute for Basic Science. The IBS said the study, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, is expected to help the development of therapies to treat primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), which counts for three quarters of all glaucoma patients.
One of the most important risk factors for glaucoma is the increased pressure inside the eye. A liquid called aqueous humor is constantly produced and drained out from the eye. It transports nutrients and inflates the eye giving it a roughly spherical shape. However, if this fluid cannot flow out of the eye chambers freely, an increase in intraocular pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss. The precise mechanism of elevated resistance to aqueous humor outflow remains unclear, and although the current treatments for glaucoma tackle the production and outflow of aqueous humor, their outcomes are still poor.
A component of the eye that plays a fundamental role in draining out the aqueous humor is Schlemm's canal. It collects the aqueous humor and mediates its transfer from the eye chambers to blood circulation. The cells on the walls of the canal, endothelial cells, ship the liquid from the inner to the outer side in “packages”, called vacuoles. As the shape and number of the vacuoles reflects the outflow performance, several giant vacuoles are expected in the normal outflow process.
The team explained how imbalances in Schlemm's canal significantly increase the risk of glaucoma. They showed that an important regulator for canal functionality is the angiopoietin-Tie2 system. Angiopoietins, such as Ang1 and Ang2, are proteins important for the growth of new blood vessels and Tie2 is the receptor that binds them. It is known that the angiopoietin-Tie2 system plays a role in Schlemm’s canal formation, as Tie2 mutations or angiopoietin absence result in congenital glaucoma. However, this study clarified that it is also critically important during adulthood.
The researchers reported that adult mice deficient in Tie2 suffer from an elevated intraocular pressure, retinal neuronal damage and partial visual impairment. Moreover, they had a markedly decreased number of giant vacuoles inside Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells, which indicate a poor aqueous humor drainage.
The scientists also investigated if and how this process changes in older mice, as aging is a major risk factor for glaucoma, and showed that aged mice experience reduced levels of giant vacuoles, Tie2, Ang1, and Ang2, as well as other proteins connected with the angiopoietin-Tie2 pathway, like Prox1.
To test whether Tie2 activation could shift the situation, the researchers tested the antibody ABTAA (Ang2-binding and Tie2-activating antibody). They injected it in one eye of mice, while the other eye of the same mice functioned as the negative control. After one week, levels of Tie2 and Prox1, number and diameter of giant vacuoles in Schlemm’s canals increased in the ABTAA-treated eyes compared to control eyes. The researchers observed a similar outcome with decreased intraocular pressure when ABTAA was injected to the eyes of mice suffering from POAG with regressed Schlemm’s canals, indicating that this antibody might be considered as a therapeutic option.
"Slow development of glaucoma treatments is partly due to the poor understanding of the underlying pathogenesis," said Professor Koh, the corresponding author of the study. "We hope that identifying the critical role of the angiopoietin-Tie2 system in adult Schlemm’s canals will bring a significant boost in the development of therapeutics."
Figure 1: Schlemm's canal position inside the eye.
Schlemm's canal (green) plays a fundamental role in draining the aqueous humor (white arrows) from the anterior chamber of the eye to blood circulation. If the aqueous humor is not able to flow out freely, elevated intraocular pressure damages the optical nerve causing glaucoma and eventually blindness.
Figure 2: Electron microscope images reveal how the aqueous humor is packaged in vacuoles (arrowheads) inside the cells forming the walls of Schlemm's canal.
Aging and glaucoma cause the number and size of giant vacuoles to decrease, meaning that the aqueous humor outflow is compromised. The images compare the giant vacuoles in Schlemm's canals of a healthy mouse (top) and a mouse lacking Tie2 (bottom)
Figure 3: The Ang2-binding and Tie2-activating antibody (ABTAA) rejuvenates the eye of aged mice and rescues them from glaucoma.
Aging causes a reduction of the protein Tie2, a risk factor for increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma. In this experiment, one eye of mice lacking Ang1 and Ang2 was injected with the premixed ABTAA and Ang2, while the other eye was used as negative control. The researchers observed an increase in the area of Schlemm’s canal, together with higher levels of Tie2 (red) and lower intraocular pressure, suggesting that ABTAA restores the canal's functionality. The image includes the transcription factor Prox1 (green) and CD144 (blue), a protein present at the junctions between cells that form the wall of the canal. The angiopoietin-Tie2 system and Prox1 are linked by a vicious circle: the less Tie2 and Ang2, the less Prox1, leading to Schlemm's canal damage, increase in intraocular pressure, and acceleration of glaucoma progression.
2017.09.19 View 7885 -
 Humicotta Wins the Silver Prize at the 2017 IDEA
The 3D-printed ceramic humidifier made by the research team led by Professor Sang-Min Bae won the silver prize at the 2017 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Professor Bae’s ID+IM team was also listed as winners of three more appropriate technology designs at the IDEA. The awards, sponsored by the Industrial Designers Society of America, are one of the three prestigious design awards including the Red Dot Design Award and the iF Design Award in Germany.
The silver prize winner in the category of home and bath, Humicotta is an energy-efficient, bacteria free, and easy to clean humidifier. It includes a base module and filter. The base is a cylindrical pedestal with a built-in fan on which the filter is placed. The filter is a 3D-printed honeycomb structure made of diatomite. When water is added, the honeycomb structure and porous terracotta maximize natural humidification. It also offers an open platform service that customizes the filters or provides files that users can use their own 3D printer.
Professor Bae’s team has worked on philanthropy design using appropriate technology as their main topic for years. Their designs have been recognized at prestigious global design awards events, winning more than 50 prizes with innovative designs made for addressing various global and social problems.
The Light Funnel is a novel type of lighting device designed for off-grid areas of Africa. It helps to maximize the natural light effect in the daytime without any drastic home renovations. It consists of a transparent acrylic sphere and a reflective pathway. After filling the acrylic sphere with water and placing it on a rooftop, sunlight passes into the house through the water inside the sphere. It provides a lighted environment nine times brighter than without it. Also, once installed, it can be used almost permanently.
The Maasai Smart Cane is made using wood sticks purchased through fair trade with the Maasai tribe. GPS is installed into the grip of the birch-tree cane, so that cane users can send a signal when in an emergency situation. All of the proceeds of this product go to the tribe.
S.Cone is a first aid kit made in collaboration with Samsung Fire and Marine Insurance. The traffic cone-shaped kit is designed to help users handle an emergency situation intact and safe. The S.Cone has unique versions for fires, car accidents, and marine accidents. For example, the S.Cone for fires is equipped with a small fire extinguisher, smoke mask, and fire blanket. The cap of the S.Cone also functions as an IoT station connecting the fire and gas detector with smart phones.
Professor Bae said of his team’s winning design products, “By making the data public, any person can design their own humidifier if they have access to a 3D-printer. We want it to be a very accessible product for the public. The Light Funnel and Maasai Smart Cane are designed for economically-marginalized populations and the elderly. We will continue to make the best designed products serving the marginalized 90% of the population around the world.”
2017.09.14 View 28694
Humicotta Wins the Silver Prize at the 2017 IDEA
The 3D-printed ceramic humidifier made by the research team led by Professor Sang-Min Bae won the silver prize at the 2017 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Professor Bae’s ID+IM team was also listed as winners of three more appropriate technology designs at the IDEA. The awards, sponsored by the Industrial Designers Society of America, are one of the three prestigious design awards including the Red Dot Design Award and the iF Design Award in Germany.
The silver prize winner in the category of home and bath, Humicotta is an energy-efficient, bacteria free, and easy to clean humidifier. It includes a base module and filter. The base is a cylindrical pedestal with a built-in fan on which the filter is placed. The filter is a 3D-printed honeycomb structure made of diatomite. When water is added, the honeycomb structure and porous terracotta maximize natural humidification. It also offers an open platform service that customizes the filters or provides files that users can use their own 3D printer.
Professor Bae’s team has worked on philanthropy design using appropriate technology as their main topic for years. Their designs have been recognized at prestigious global design awards events, winning more than 50 prizes with innovative designs made for addressing various global and social problems.
The Light Funnel is a novel type of lighting device designed for off-grid areas of Africa. It helps to maximize the natural light effect in the daytime without any drastic home renovations. It consists of a transparent acrylic sphere and a reflective pathway. After filling the acrylic sphere with water and placing it on a rooftop, sunlight passes into the house through the water inside the sphere. It provides a lighted environment nine times brighter than without it. Also, once installed, it can be used almost permanently.
The Maasai Smart Cane is made using wood sticks purchased through fair trade with the Maasai tribe. GPS is installed into the grip of the birch-tree cane, so that cane users can send a signal when in an emergency situation. All of the proceeds of this product go to the tribe.
S.Cone is a first aid kit made in collaboration with Samsung Fire and Marine Insurance. The traffic cone-shaped kit is designed to help users handle an emergency situation intact and safe. The S.Cone has unique versions for fires, car accidents, and marine accidents. For example, the S.Cone for fires is equipped with a small fire extinguisher, smoke mask, and fire blanket. The cap of the S.Cone also functions as an IoT station connecting the fire and gas detector with smart phones.
Professor Bae said of his team’s winning design products, “By making the data public, any person can design their own humidifier if they have access to a 3D-printer. We want it to be a very accessible product for the public. The Light Funnel and Maasai Smart Cane are designed for economically-marginalized populations and the elderly. We will continue to make the best designed products serving the marginalized 90% of the population around the world.”
2017.09.14 View 28694 -
 Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10447
Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10447 -
 A Novel and Practical Fab-route for Superomniphobic Liquid-free Surfaces
(clockwise from left: Jaeho Choi, Hee Tak Kim, Shin-Hyun Kim)
A joint research team led by Professor Hee Tak Kim and Shin-Hyun Kim in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a fabrication technology that can inexpensively produce surfaces capable of repelling liquids, including water and oil.
The team used the photofluidization of azobenzene molecule-containing polymers to generate a superomniphobic surface which can be applied for developing stain-free fabrics, non-biofouling medical tubing, and corrosion-free surfaces.
Mushroom-shaped surface textures, also called doubly re-entrant structures, are known to be the most effective surface structure that enhances resistance against liquid invasion, thereby exhibiting superior superomniphobic property.
However, the existing procedures for their fabrication are highly delicate, time-consuming, and costly. Moreover, the materials required for the fabrication are restricted to an inflexible and expensive silicon wafer, which limits the practical use of the surface.
To overcome such limitations, the research team used a different approach to fabricate the re-entrant structures called localized photofludization by using the peculiar optical phenomenon of azobenzene molecule-containing polymers (referred to as azopolymers). It is a phenomenon where an azopolymer becomes fluidized under irradiation, and the fluidization takes place locally within the thin surface layer of the azopolymer.
With this novel approach, the team facilitated the localized photofluidization in the top surface layer of azopolymer cylindrical posts, successfully reconfiguring the cylindrical posts to doubly re-entrant geometry while the fluidized thin top surface of an azopolymer is flowing down.
The structure developed by the team exhibits a superior superomniphobic property even for liquids infiltrating the surface immediately.
Moreover, the superomniphobic property can be maintained on a curved target surface because its surficial materials are based on high molecules.
Furthermore, the fabrication procedure of the structure is highly reproducible and scalable, providing a practical route to creating robust omniphobic surfaces.
Professor Hee Tak Kim said, “Not only does the novel photo-fluidization technology in this study produce superior superomniphobic surfaces, but it also possesses many practical advantages in terms of fab-procedures and material flexibility; therefore, it could greatly contribute to real uses in diverse applications.”
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim added, “The designed doubly re-entrant geometry in this study was inspired by the skin structure of springtails, insects dwelling in soil that breathe through their skin. As I carried out this research, I once again realized that humans can learn from nature to create new engineering designs.”
The paper (Jaeho Choi as a first author) was published in ACS Nano, an international journal for Nano-technology, in August.
(Schematic diagram of mushroom-shaped structure fabrication)
(SEM image of mushroom-shaped structure)
(Image of superomniphobic property of different types of liquid)
2017.09.08 View 8240
A Novel and Practical Fab-route for Superomniphobic Liquid-free Surfaces
(clockwise from left: Jaeho Choi, Hee Tak Kim, Shin-Hyun Kim)
A joint research team led by Professor Hee Tak Kim and Shin-Hyun Kim in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a fabrication technology that can inexpensively produce surfaces capable of repelling liquids, including water and oil.
The team used the photofluidization of azobenzene molecule-containing polymers to generate a superomniphobic surface which can be applied for developing stain-free fabrics, non-biofouling medical tubing, and corrosion-free surfaces.
Mushroom-shaped surface textures, also called doubly re-entrant structures, are known to be the most effective surface structure that enhances resistance against liquid invasion, thereby exhibiting superior superomniphobic property.
However, the existing procedures for their fabrication are highly delicate, time-consuming, and costly. Moreover, the materials required for the fabrication are restricted to an inflexible and expensive silicon wafer, which limits the practical use of the surface.
To overcome such limitations, the research team used a different approach to fabricate the re-entrant structures called localized photofludization by using the peculiar optical phenomenon of azobenzene molecule-containing polymers (referred to as azopolymers). It is a phenomenon where an azopolymer becomes fluidized under irradiation, and the fluidization takes place locally within the thin surface layer of the azopolymer.
With this novel approach, the team facilitated the localized photofluidization in the top surface layer of azopolymer cylindrical posts, successfully reconfiguring the cylindrical posts to doubly re-entrant geometry while the fluidized thin top surface of an azopolymer is flowing down.
The structure developed by the team exhibits a superior superomniphobic property even for liquids infiltrating the surface immediately.
Moreover, the superomniphobic property can be maintained on a curved target surface because its surficial materials are based on high molecules.
Furthermore, the fabrication procedure of the structure is highly reproducible and scalable, providing a practical route to creating robust omniphobic surfaces.
Professor Hee Tak Kim said, “Not only does the novel photo-fluidization technology in this study produce superior superomniphobic surfaces, but it also possesses many practical advantages in terms of fab-procedures and material flexibility; therefore, it could greatly contribute to real uses in diverse applications.”
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim added, “The designed doubly re-entrant geometry in this study was inspired by the skin structure of springtails, insects dwelling in soil that breathe through their skin. As I carried out this research, I once again realized that humans can learn from nature to create new engineering designs.”
The paper (Jaeho Choi as a first author) was published in ACS Nano, an international journal for Nano-technology, in August.
(Schematic diagram of mushroom-shaped structure fabrication)
(SEM image of mushroom-shaped structure)
(Image of superomniphobic property of different types of liquid)
2017.09.08 View 8240 -
 Innovative Nanosensor for Disease Diagnosis
(Figure 1. Sensing Device)
(Figure 2. Protein templating route)
Breath pattern recognition is a futuristic diagnostic platform. Simple characterizing target gas concentrations of human exhaled breath will lead to diagnose of the disease as well as physical condition.
A research group under Prof. Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science has developed diagnostic sensors using protein-encapsulated nanocatalysts, which can diagnose certain diseases by analyzing human exhaled breath. This technology enables early monitoring of various diseases through pattern recognition of biomarker gases related to diseases in human exhalation.
The protein-templated catalyst synthesis route is very simple and versatile for producing not only a single component of catalytic nanoparticles, but also diverse heterogeneous intermetallic catalysts with sizes less than 3 nm. The research team has developed ever more sensitive and selective chemiresistive sensors that can potentially diagnose specific diseases by analyzing exhaled breath gases.
The results of this study, which were contributed by Dr. Sang-Joon Kim and Dr. Seon-Jin Choi as first authors were selected as the cover-featured article in the July issue of 'Accounts of Chemical Research,' an international journal of the American Chemical Society.
In human breath, diverse components are found including water vapor, hydrogen, acetone, toluene, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon monoxide, which are more excessively exhaled from patients. Some of these components are closely related to diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and halitosis.
Breath analysis for disease diagnosis started from capturing exhaled breaths in a Tedlar bag and subsequently the captured breath gases were injected into a miniaturized sensor system, similar to an alcohol detector. It is possible to analyze exhaled breath very rapidly with a simple analyzing process. The breath analysis can detect trace changes in exhaled breath components, which contribute to early diagnosis of diseases.
However, technological advances are needed to accurately analyze gases in the breath, which occur at very low levels, from 1 ppb to 1 ppm. In particular, it has been a critical challenge for chemiresistive type chemical sensors to selectively detect specific biomarkers in thousands of interfering gases including humid vapor.
Conventionally, noble metallic catalysts such as platinum and palladium have been functionalized onto metal oxide sensing layers. However, the gas sensitivity was not enough to detect ppb-levels of biomarker species in exhaled breath.
To overcome the current limitations, the research team utilized nanoscale protein (apoferritin) in animals as sacrificial templates. The protein templates possess hollow nanocages at the core site and various alloy catalytic nanoparticles can be encapsulated inside the protein nanocages.
The protein nanocages are advantageous because a nearly unlimited number of material compositions in the periodic table can be assembled for the synthesis of heterogeneous catalytic nanoparticles. In addition, intermetallic nanocatalysts with a controlled atomic ratio of two different elements can be achieved using the protein nanocages, which is an innovative strategy for finding new types of catalysts. For example, highly efficient platinum-based catalysts can be synthesized, such as platinum-palladium (PtPd), platinum-nickel (PtNi), platinum-ruthenium (PtRu), and platinum-yttrium (PtY).
The research team developed outstanding sensing layers consisting of metal oxide nanofibers functionalized by the heterogeneous catalysts with large and highly-porous surface areas, which are especially optimized for selective detection of specific biomarkers. The biomarker sensing performance was improved approximately 3~4-fold as compared to the conventional single component of platinum and palladium catalysts-loaded nanofiber sensors. In particular, 100-fold resistance transitions toward acetone (1 ppm) and hydrogen sulfide (1 ppm) were observed in exhaled breath sensors using the heterogeneous nanocatalysts, which is the best performance ever reported in literature.
The research team developed a disease diagnosis platform that recognizes individual breathing patterns by using a multiple sensor array system with diverse sensing layers and heterogeneous catalysts, so that the people can easily identify health abnormalities. Using a 16-sensor array system, physical conditions can be continuously monitored by analyzing concentration changes of biomarkers in exhaled breath gases.
Prof. Kim said, “New types of heterogeneous nanocatalysts were synthesized using protein templates with sizes around 2 nm and functionalized on various metal oxide nanofiber sensing layers. The established sensing libraries can detect biomarker species with high sensitivity and selectivity.” He added, “the new and innovative breath gas analysis platform will be very helpful for reducing medical expenditures and continuous monitoring of physical conditions”
Patents related to this technology were licensed to two companies in March and June this year.
2017.07.19 View 11485
Innovative Nanosensor for Disease Diagnosis
(Figure 1. Sensing Device)
(Figure 2. Protein templating route)
Breath pattern recognition is a futuristic diagnostic platform. Simple characterizing target gas concentrations of human exhaled breath will lead to diagnose of the disease as well as physical condition.
A research group under Prof. Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science has developed diagnostic sensors using protein-encapsulated nanocatalysts, which can diagnose certain diseases by analyzing human exhaled breath. This technology enables early monitoring of various diseases through pattern recognition of biomarker gases related to diseases in human exhalation.
The protein-templated catalyst synthesis route is very simple and versatile for producing not only a single component of catalytic nanoparticles, but also diverse heterogeneous intermetallic catalysts with sizes less than 3 nm. The research team has developed ever more sensitive and selective chemiresistive sensors that can potentially diagnose specific diseases by analyzing exhaled breath gases.
The results of this study, which were contributed by Dr. Sang-Joon Kim and Dr. Seon-Jin Choi as first authors were selected as the cover-featured article in the July issue of 'Accounts of Chemical Research,' an international journal of the American Chemical Society.
In human breath, diverse components are found including water vapor, hydrogen, acetone, toluene, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon monoxide, which are more excessively exhaled from patients. Some of these components are closely related to diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and halitosis.
Breath analysis for disease diagnosis started from capturing exhaled breaths in a Tedlar bag and subsequently the captured breath gases were injected into a miniaturized sensor system, similar to an alcohol detector. It is possible to analyze exhaled breath very rapidly with a simple analyzing process. The breath analysis can detect trace changes in exhaled breath components, which contribute to early diagnosis of diseases.
However, technological advances are needed to accurately analyze gases in the breath, which occur at very low levels, from 1 ppb to 1 ppm. In particular, it has been a critical challenge for chemiresistive type chemical sensors to selectively detect specific biomarkers in thousands of interfering gases including humid vapor.
Conventionally, noble metallic catalysts such as platinum and palladium have been functionalized onto metal oxide sensing layers. However, the gas sensitivity was not enough to detect ppb-levels of biomarker species in exhaled breath.
To overcome the current limitations, the research team utilized nanoscale protein (apoferritin) in animals as sacrificial templates. The protein templates possess hollow nanocages at the core site and various alloy catalytic nanoparticles can be encapsulated inside the protein nanocages.
The protein nanocages are advantageous because a nearly unlimited number of material compositions in the periodic table can be assembled for the synthesis of heterogeneous catalytic nanoparticles. In addition, intermetallic nanocatalysts with a controlled atomic ratio of two different elements can be achieved using the protein nanocages, which is an innovative strategy for finding new types of catalysts. For example, highly efficient platinum-based catalysts can be synthesized, such as platinum-palladium (PtPd), platinum-nickel (PtNi), platinum-ruthenium (PtRu), and platinum-yttrium (PtY).
The research team developed outstanding sensing layers consisting of metal oxide nanofibers functionalized by the heterogeneous catalysts with large and highly-porous surface areas, which are especially optimized for selective detection of specific biomarkers. The biomarker sensing performance was improved approximately 3~4-fold as compared to the conventional single component of platinum and palladium catalysts-loaded nanofiber sensors. In particular, 100-fold resistance transitions toward acetone (1 ppm) and hydrogen sulfide (1 ppm) were observed in exhaled breath sensors using the heterogeneous nanocatalysts, which is the best performance ever reported in literature.
The research team developed a disease diagnosis platform that recognizes individual breathing patterns by using a multiple sensor array system with diverse sensing layers and heterogeneous catalysts, so that the people can easily identify health abnormalities. Using a 16-sensor array system, physical conditions can be continuously monitored by analyzing concentration changes of biomarkers in exhaled breath gases.
Prof. Kim said, “New types of heterogeneous nanocatalysts were synthesized using protein templates with sizes around 2 nm and functionalized on various metal oxide nanofiber sensing layers. The established sensing libraries can detect biomarker species with high sensitivity and selectivity.” He added, “the new and innovative breath gas analysis platform will be very helpful for reducing medical expenditures and continuous monitoring of physical conditions”
Patents related to this technology were licensed to two companies in March and June this year.
2017.07.19 View 11485 -
 Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 8523
Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 8523 -
 Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 8988
Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 8988