Science
-
 Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 13517
Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 13517 -
 Mystery Solved with Math: Cytoplasmic Traffic Jam Disrupts Sleep-Wake Cycles
KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators at Florida State University have identified the principle of how aging and diseases like dementia and obesity cause sleep disorders. A combination of mathematical modelling and experiments demonstrated that the cytoplasmic congestion caused by aging, dementia, and/or obesity disrupts the circadian rhythms in the human body and leads to irregular sleep-wake cycles. This finding suggests new treatment strategies for addressing unstable sleep-wake cycles.
Human bodies adjust sleep schedules in accordance with the ‘circadian rhythms’, which are regulated by our time keeping system, the ‘circadian clock’. This clock tells our body when to rest by generating the 24-hour rhythms of a protein called PERIOD (PER) (See Figure 1).
The amount of the PER protein increases for half of the day and then decreases for the remaining half. The principle is that the PER protein accumulating in the cytoplasm for several hours enters the cell nucleus all at once, hindering the transcription of PER genes and thereby reducing the amount of PER.
However, it has remained a mystery how thousands of PER molecules can simultaneously enter into the nucleus in a complex cell environment where a variety of materials co-exist and can interfere with the motion of PER. This would be like finding a way for thousands of employees from all over New York City to enter an office building at the same time every day.
A group of researchers led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences solved the mystery by developing a spatiotemporal and probabilistic model that describes the motion of PER molecules in a cell environment.
This study was conducted in collaboration with Professor Choogon Lee’s group from Florida State University, where the experiments were carried out, and the results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) last month.
The joint research team’s spatial stochastic model (See Figure 2) described the motion of PER molecules in cells and demonstrated that the PER molecule should be sufficiently condensed around the cell nucleus to be phosphorylated simultaneously and enter the nucleus together (See Figure 3 Left). Thanks to this phosphorylation synchronization switch, thousands of PER molecules can enter the nucleus at the same time every day and maintain stable circadian rhythms.
However, when aging and/or diseases including dementia and obesity cause the cytoplasm to become congested with increased cytoplasmic obstacles such as protein aggregates and fat vacuoles, it hinders the timely condensation of PER molecules around the cell nucleus (See Figure 3 Right). As a result, the phosphorylation synchronization switch does not work and PER proteins enter into the nucleus at irregular times, making the circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles unstable, the study revealed.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of new treatment strategies that can improve the lives of so many patients who suffer from irregular sleep-wake cycles. Taking these findings as an opportunity, I hope to see more active interchanges of ideas and collaboration between mathematical and biological sciences.”
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation in the US, and the International Human Frontiers Science Program Organization and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Beesley, S. and Kim, D. W, et al. (2020) Wake-sleep cycles are severely disrupted by diseases affecting cytoplasmic homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 45, 28402-28411. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003524117
Profile:
Jae Kyoung Kim, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
@umichkim on Twitter
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Choogon Lee, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
clee@neuro.fsu.edu
https://med.fsu.edu/biosci/lee-lab
Department of Biomedical Sciences
Florida State University
Florida, USA
(END)
2020.12.11 View 10633
Mystery Solved with Math: Cytoplasmic Traffic Jam Disrupts Sleep-Wake Cycles
KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators at Florida State University have identified the principle of how aging and diseases like dementia and obesity cause sleep disorders. A combination of mathematical modelling and experiments demonstrated that the cytoplasmic congestion caused by aging, dementia, and/or obesity disrupts the circadian rhythms in the human body and leads to irregular sleep-wake cycles. This finding suggests new treatment strategies for addressing unstable sleep-wake cycles.
Human bodies adjust sleep schedules in accordance with the ‘circadian rhythms’, which are regulated by our time keeping system, the ‘circadian clock’. This clock tells our body when to rest by generating the 24-hour rhythms of a protein called PERIOD (PER) (See Figure 1).
The amount of the PER protein increases for half of the day and then decreases for the remaining half. The principle is that the PER protein accumulating in the cytoplasm for several hours enters the cell nucleus all at once, hindering the transcription of PER genes and thereby reducing the amount of PER.
However, it has remained a mystery how thousands of PER molecules can simultaneously enter into the nucleus in a complex cell environment where a variety of materials co-exist and can interfere with the motion of PER. This would be like finding a way for thousands of employees from all over New York City to enter an office building at the same time every day.
A group of researchers led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences solved the mystery by developing a spatiotemporal and probabilistic model that describes the motion of PER molecules in a cell environment.
This study was conducted in collaboration with Professor Choogon Lee’s group from Florida State University, where the experiments were carried out, and the results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) last month.
The joint research team’s spatial stochastic model (See Figure 2) described the motion of PER molecules in cells and demonstrated that the PER molecule should be sufficiently condensed around the cell nucleus to be phosphorylated simultaneously and enter the nucleus together (See Figure 3 Left). Thanks to this phosphorylation synchronization switch, thousands of PER molecules can enter the nucleus at the same time every day and maintain stable circadian rhythms.
However, when aging and/or diseases including dementia and obesity cause the cytoplasm to become congested with increased cytoplasmic obstacles such as protein aggregates and fat vacuoles, it hinders the timely condensation of PER molecules around the cell nucleus (See Figure 3 Right). As a result, the phosphorylation synchronization switch does not work and PER proteins enter into the nucleus at irregular times, making the circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles unstable, the study revealed.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of new treatment strategies that can improve the lives of so many patients who suffer from irregular sleep-wake cycles. Taking these findings as an opportunity, I hope to see more active interchanges of ideas and collaboration between mathematical and biological sciences.”
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation in the US, and the International Human Frontiers Science Program Organization and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Beesley, S. and Kim, D. W, et al. (2020) Wake-sleep cycles are severely disrupted by diseases affecting cytoplasmic homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 45, 28402-28411. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003524117
Profile:
Jae Kyoung Kim, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
@umichkim on Twitter
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Choogon Lee, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
clee@neuro.fsu.edu
https://med.fsu.edu/biosci/lee-lab
Department of Biomedical Sciences
Florida State University
Florida, USA
(END)
2020.12.11 View 10633 -
 Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 11612
Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 11612 -
 'Mini-Lungs' Reveal Early Stages of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Researchers in Korea and the UK have successfully grown miniature models of critical lung structures called alveoli, and used them to study how the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 infects the lungs.
To date, there have been more than 40 million cases of COVID-19 and almost 1.13 million deaths worldwide. The main target tissues of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, especially in patients that develop pneumonia, appear to be alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that take up the oxygen we breathe and exchange it with carbon dioxide to exhale.
To better understand how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease, a team of Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST in collaboration with the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge turned to organoids – ‘mini-organs’ grown in three dimensions to mimic the behaviour of tissue and organs.
The team used tissue donated to tissue banks at the Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge University NHS Foundations Trust, UK, and Seoul National University Hospital to extract a type of lung cell known as human lung alveolar type 2 cells. By reprogramming these cells back to their earlier ‘stem cell’ stage, they were able to grow self-organizing alveolar-like 3D structures that mimic the behaviour of key lung tissue.
“The research community now has a powerful new platform to study precisely how the virus infects the lungs, as well as explore possible treatments,” said Professor Ju, co-senior author of the research.
Dr. Joo-Hyeon Lee, another co-senior author at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, said: “We still know surprisingly little about how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease. Our approach has allowed us to grow 3D models of key lung tissue – in a sense, ‘mini-lungs’ – in the lab and study what happens when they become infected.”
The team infected the organoids with a strain of SARS-CoV-2 taken from a patient in Korea who was diagnosed with COVID-19 on January 26 after traveling to Wuhan, China. Using a combination of fluorescence imaging and single cell genetic analysis, they were able to study how the cells responded to the virus.
When the 3D models were exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus began to replicate rapidly, reaching full cellular infection just six hours after infection. Replication enables the virus to spread throughout the body, infecting other cells and tissue.
Around the same time, the cells began to produce interferons – proteins that act as warning signals to neighbouring cells, telling them to activate their antiviral defences. After 48 hours, the interferons triggered the innate immune response – its first line of defence – and the cells started fighting back against infection.
Sixty hours after infection, a subset of alveolar cells began to disintegrate, leading to cell death and damage to the lung tissue.
Although the researchers observed changes to the lung cells within three days of infection, clinical symptoms of COVID-19 rarely occur so quickly and can sometimes take more than ten days after exposure to appear. The team say there are several possible reasons for this. It may take several days from the virus first infiltrating the upper respiratory tract to it reaching the alveoli. It may also require a substantial proportion of alveolar cells to be infected or for further interactions with immune cells resulting in inflammation before a patient displays symptoms.
“Based on our model we can tackle many unanswered key questions, such as understanding genetic susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, assessing relative infectivity of viral mutants, and revealing the damage processes of the virus in human alveolar cells,” said Professor Ju. “Most importantly, it provides the opportunity to develop and screen potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
“We hope to use our technique to grow these 3D models from cells of patients who are particularly vulnerable to infection, such as the elderly or people with diseased lungs, and find out what happens to their tissue,” added Dr. Lee.
The research was a collaboration involving scientists from KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Korea National Institute of Health, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul National University Hospital and Genome Insight in Korea.
- ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLaboratory of Cancer Genomics https://julab.kaist.ac.kr the Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.26 View 11900
'Mini-Lungs' Reveal Early Stages of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Researchers in Korea and the UK have successfully grown miniature models of critical lung structures called alveoli, and used them to study how the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 infects the lungs.
To date, there have been more than 40 million cases of COVID-19 and almost 1.13 million deaths worldwide. The main target tissues of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, especially in patients that develop pneumonia, appear to be alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that take up the oxygen we breathe and exchange it with carbon dioxide to exhale.
To better understand how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease, a team of Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST in collaboration with the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge turned to organoids – ‘mini-organs’ grown in three dimensions to mimic the behaviour of tissue and organs.
The team used tissue donated to tissue banks at the Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge University NHS Foundations Trust, UK, and Seoul National University Hospital to extract a type of lung cell known as human lung alveolar type 2 cells. By reprogramming these cells back to their earlier ‘stem cell’ stage, they were able to grow self-organizing alveolar-like 3D structures that mimic the behaviour of key lung tissue.
“The research community now has a powerful new platform to study precisely how the virus infects the lungs, as well as explore possible treatments,” said Professor Ju, co-senior author of the research.
Dr. Joo-Hyeon Lee, another co-senior author at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, said: “We still know surprisingly little about how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease. Our approach has allowed us to grow 3D models of key lung tissue – in a sense, ‘mini-lungs’ – in the lab and study what happens when they become infected.”
The team infected the organoids with a strain of SARS-CoV-2 taken from a patient in Korea who was diagnosed with COVID-19 on January 26 after traveling to Wuhan, China. Using a combination of fluorescence imaging and single cell genetic analysis, they were able to study how the cells responded to the virus.
When the 3D models were exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus began to replicate rapidly, reaching full cellular infection just six hours after infection. Replication enables the virus to spread throughout the body, infecting other cells and tissue.
Around the same time, the cells began to produce interferons – proteins that act as warning signals to neighbouring cells, telling them to activate their antiviral defences. After 48 hours, the interferons triggered the innate immune response – its first line of defence – and the cells started fighting back against infection.
Sixty hours after infection, a subset of alveolar cells began to disintegrate, leading to cell death and damage to the lung tissue.
Although the researchers observed changes to the lung cells within three days of infection, clinical symptoms of COVID-19 rarely occur so quickly and can sometimes take more than ten days after exposure to appear. The team say there are several possible reasons for this. It may take several days from the virus first infiltrating the upper respiratory tract to it reaching the alveoli. It may also require a substantial proportion of alveolar cells to be infected or for further interactions with immune cells resulting in inflammation before a patient displays symptoms.
“Based on our model we can tackle many unanswered key questions, such as understanding genetic susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, assessing relative infectivity of viral mutants, and revealing the damage processes of the virus in human alveolar cells,” said Professor Ju. “Most importantly, it provides the opportunity to develop and screen potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
“We hope to use our technique to grow these 3D models from cells of patients who are particularly vulnerable to infection, such as the elderly or people with diseased lungs, and find out what happens to their tissue,” added Dr. Lee.
The research was a collaboration involving scientists from KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Korea National Institute of Health, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul National University Hospital and Genome Insight in Korea.
- ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLaboratory of Cancer Genomics https://julab.kaist.ac.kr the Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.26 View 11900 -
 Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11742
Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11742 -
 Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 12095
Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 12095 -
 Professor Won-Ki Cho Selected as the 2020 SUHF Young Investigator
Professor Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of three recipients of the 2020 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Award.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 67 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the three recipients.
Professor Cho proposed research on how to observe the interactions between nuclear structures and constantly-changing chromatin monomers in four dimensions through ultra-high-resolution imaging of single living cells. This proposal was recognized as one that could help us better understand the process of transcription regulation, which remains a long-standing question in biology.
The other awards were given to Professor Soung-hun Roh of Seoul National University and Professor Joo-Hyeon Lee of the University of Cambridge.
With these three new awardees, a total of 17 scientists have been named SUHF Young Investigators to date, and the funding to support these scientists now totals 42.5 billion KRW.
Professor Inkyung Jung and Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences, and Professor Young Seok Ju and Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering are the four previous winners from KAIST in the years 2017 through 2019.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13539
Professor Won-Ki Cho Selected as the 2020 SUHF Young Investigator
Professor Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of three recipients of the 2020 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Award.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 67 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the three recipients.
Professor Cho proposed research on how to observe the interactions between nuclear structures and constantly-changing chromatin monomers in four dimensions through ultra-high-resolution imaging of single living cells. This proposal was recognized as one that could help us better understand the process of transcription regulation, which remains a long-standing question in biology.
The other awards were given to Professor Soung-hun Roh of Seoul National University and Professor Joo-Hyeon Lee of the University of Cambridge.
With these three new awardees, a total of 17 scientists have been named SUHF Young Investigators to date, and the funding to support these scientists now totals 42.5 billion KRW.
Professor Inkyung Jung and Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences, and Professor Young Seok Ju and Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering are the four previous winners from KAIST in the years 2017 through 2019.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13539 -
 Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 15463
Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 15463 -
 Before Eyes Open, They Get Ready to See
- Spontaneous retinal waves can generate long-range horizontal connectivity in visual cortex. -
A KAIST research team’s computational simulations demonstrated that the waves of spontaneous neural activity in the retinas of still-closed eyes in mammals develop long-range horizontal connections in the visual cortex during early developmental stages.
This new finding featured in the August 19 edition of Journal of Neuroscience as a cover article has resolved a long-standing puzzle for understanding visual neuroscience regarding the early organization of functional architectures in the mammalian visual cortex before eye-opening, especially the long-range horizontal connectivity known as “feature-specific” circuitry.
To prepare the animal to see when its eyes open, neural circuits in the brain’s visual system must begin developing earlier. However, the proper development of many brain regions involved in vision generally requires sensory input through the eyes.
In the primary visual cortex of the higher mammalian taxa, cortical neurons of similar functional tuning to a visual feature are linked together by long-range horizontal circuits that play a crucial role in visual information processing.
Surprisingly, these long-range horizontal connections in the primary visual cortex of higher mammals emerge before the onset of sensory experience, and the mechanism underlying this phenomenon has remained elusive.
To investigate this mechanism, a group of researchers led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST implemented computational simulations of early visual pathways using data obtained from the retinal circuits in young animals before eye-opening, including cats, monkeys, and mice.
From these simulations, the researchers found that spontaneous waves propagating in ON and OFF retinal mosaics can initialize the wiring of long-range horizontal connections by selectively co-activating cortical neurons of similar functional tuning, whereas equivalent random activities cannot induce such organizations.
The simulations also showed that emerged long-range horizontal connections can induce the patterned cortical activities, matching the topography of underlying functional maps even in salt-and-pepper type organizations observed in rodents. This result implies that the model developed by Professor Paik and his group can provide a universal principle for the developmental mechanism of long-range horizontal connections in both higher mammals as well as rodents.
Professor Paik said, “Our model provides a deeper understanding of how the functional architectures in the visual cortex can originate from the spatial organization of the periphery, without sensory experience during early developmental periods.”
He continued, “We believe that our findings will be of great interest to scientists working in a wide range of fields such as neuroscience, vision science, and developmental biology.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). Undergraduate student Jinwoo Kim participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
Figures and image credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Jinwoo Kim, Min Song, and Se-Bum Paik. (2020). Spontaneous retinal waves generate long-range horizontal connectivity in visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, Available online athttps://www.jneurosci.org/content/early/2020/07/17/JNEUROSCI.0649-20.2020
Profile: Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Jinwoo Kim
Undergraduate Student
bugkjw@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST
Profile: Min Song
Ph.D. Candidate
night@kaist.ac.kr
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering, KAIST
(END)
2020.08.25 View 13144
Before Eyes Open, They Get Ready to See
- Spontaneous retinal waves can generate long-range horizontal connectivity in visual cortex. -
A KAIST research team’s computational simulations demonstrated that the waves of spontaneous neural activity in the retinas of still-closed eyes in mammals develop long-range horizontal connections in the visual cortex during early developmental stages.
This new finding featured in the August 19 edition of Journal of Neuroscience as a cover article has resolved a long-standing puzzle for understanding visual neuroscience regarding the early organization of functional architectures in the mammalian visual cortex before eye-opening, especially the long-range horizontal connectivity known as “feature-specific” circuitry.
To prepare the animal to see when its eyes open, neural circuits in the brain’s visual system must begin developing earlier. However, the proper development of many brain regions involved in vision generally requires sensory input through the eyes.
In the primary visual cortex of the higher mammalian taxa, cortical neurons of similar functional tuning to a visual feature are linked together by long-range horizontal circuits that play a crucial role in visual information processing.
Surprisingly, these long-range horizontal connections in the primary visual cortex of higher mammals emerge before the onset of sensory experience, and the mechanism underlying this phenomenon has remained elusive.
To investigate this mechanism, a group of researchers led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST implemented computational simulations of early visual pathways using data obtained from the retinal circuits in young animals before eye-opening, including cats, monkeys, and mice.
From these simulations, the researchers found that spontaneous waves propagating in ON and OFF retinal mosaics can initialize the wiring of long-range horizontal connections by selectively co-activating cortical neurons of similar functional tuning, whereas equivalent random activities cannot induce such organizations.
The simulations also showed that emerged long-range horizontal connections can induce the patterned cortical activities, matching the topography of underlying functional maps even in salt-and-pepper type organizations observed in rodents. This result implies that the model developed by Professor Paik and his group can provide a universal principle for the developmental mechanism of long-range horizontal connections in both higher mammals as well as rodents.
Professor Paik said, “Our model provides a deeper understanding of how the functional architectures in the visual cortex can originate from the spatial organization of the periphery, without sensory experience during early developmental periods.”
He continued, “We believe that our findings will be of great interest to scientists working in a wide range of fields such as neuroscience, vision science, and developmental biology.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). Undergraduate student Jinwoo Kim participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
Figures and image credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Jinwoo Kim, Min Song, and Se-Bum Paik. (2020). Spontaneous retinal waves generate long-range horizontal connectivity in visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, Available online athttps://www.jneurosci.org/content/early/2020/07/17/JNEUROSCI.0649-20.2020
Profile: Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Jinwoo Kim
Undergraduate Student
bugkjw@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST
Profile: Min Song
Ph.D. Candidate
night@kaist.ac.kr
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering, KAIST
(END)
2020.08.25 View 13144 -
 Professor Jaehyouk Choi, IT Young Engineer of the Year
Professor Jaehyouk Choi from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the ‘IT Young Engineer Award’ for 2020. The award was co-presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and sponsored by the Haedong Science and Culture Foundation.
The ‘IT Young Engineer Award’ selects only one mid-career scientist or engineer 40 years old or younger every year, who has made a great contribution to academic or technological advancements in the field of IT.
Professor Choi’s research topics include high-performance semiconductor circuit design for ultrahigh-speed communication systems including 5G communication. In particular, he is widely known for his field of the ‘ultra-low-noise, high-frequency signal generation circuit,’ key technology for next-generation wired and wireless communications, as well as for memory systems. He has published 64 papers in SCI journals and at international conferences, and applied for and registered 25 domestic and international patents.
Professor Choi is also an active member of the Technical Program Committee of international symposiums in the field of semiconductor circuits including the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) and the European Solid-State Circuit Conference (ESSCIRC). Beginning this year, he also serves as a distinguished lecturer at the IEEE Solid-State Circuit Society (SSCS).
(END)
2020.08.20 View 11535
Professor Jaehyouk Choi, IT Young Engineer of the Year
Professor Jaehyouk Choi from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the ‘IT Young Engineer Award’ for 2020. The award was co-presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and sponsored by the Haedong Science and Culture Foundation.
The ‘IT Young Engineer Award’ selects only one mid-career scientist or engineer 40 years old or younger every year, who has made a great contribution to academic or technological advancements in the field of IT.
Professor Choi’s research topics include high-performance semiconductor circuit design for ultrahigh-speed communication systems including 5G communication. In particular, he is widely known for his field of the ‘ultra-low-noise, high-frequency signal generation circuit,’ key technology for next-generation wired and wireless communications, as well as for memory systems. He has published 64 papers in SCI journals and at international conferences, and applied for and registered 25 domestic and international patents.
Professor Choi is also an active member of the Technical Program Committee of international symposiums in the field of semiconductor circuits including the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) and the European Solid-State Circuit Conference (ESSCIRC). Beginning this year, he also serves as a distinguished lecturer at the IEEE Solid-State Circuit Society (SSCS).
(END)
2020.08.20 View 11535 -
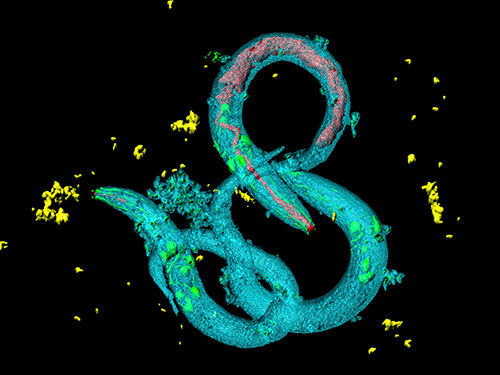 Tinkering with Roundworm Proteins Offers Hope for Anti-aging Drugs
- The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for developing longevity-promoting drugs. These new findings were published on July 1 in Science Advances.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a millimeter-long nematode commonly used in lab testing, enjoyed a boost in its lifespan when researchers tinkered with a couple of proteins involved in monitoring the energy use by its cells.
The proteins VRK-1 and AMPK work in tandem in roundworm cells, with the former telling the latter to get to work by sticking a phosphate molecule, composed of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms, on it. In turn, AMPK’s role is to monitor energy levels in cells, when cellular energy is running low. In essence, VRK-1 regulates AMPK, and AMPK regulates the cellular energy status.
Using a range of different biological research tools, including introducing foreign genes into the worm, a group of researchers led by Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST were able to dial up and down the activity of the gene that tells cells to produce the VRK-1 protein. This gene has remained pretty much unchanged throughout evolution. Most complex organisms have this same gene, including humans.
Lead author of the study Sangsoon Park and his colleagues confirmed that the overexpression, or increased production, of the VRK-1 protein boosted the lifespan of the C. elegans, which normally lives just two to three weeks, and the inhibition of VRK-1 production reduced its lifespan.
The research team found that the activity of the VRK-1-to-AMPK cellular-energy monitoring process is increased in low cellular energy status by reduced mitochondrial respiration, the set of metabolic chemical reactions that make use of the oxygen the worm breathes to convert macronutrients from food into the energy “currency” that cells spend to do everything they need to do.
It is already known that mitochondria, the energy-producing engine rooms in cells, play a crucial role in aging, and declines in the functioning of mitochondria are associated with age-related diseases. At the same time, the mild inhibition of mitochondrial respiration has been shown to promote longevity in a range of species, including flies and mammals.
When the research team performed similar tinkering with cultured human cells, they found they could also replicate this ramping up and down of the VRK-1-to-AMPK process that occurs in roundworms.
“This raises the intriguing possibility that VRK-1 also functions as a factor in governing human longevity, and so perhaps we can start developing longevity-promoting drugs that alter the activity of VRK-1,” explained Professor Lee.
At the very least, the research points us in an interesting direction for investigating new therapeutic strategies to combat metabolic disorders by targeting the modulation of VRK-1. Metabolic disorders involve the disruption of chemical reactions in the body, including diseases of the mitochondria.
But before metabolic disorder therapeutics or longevity drugs can be contemplated by scientists, further research still needs to be carried out to better understand how VRK-1 works to activate AMPK, as well as figure out the precise mechanics of how AMPK controls cellular energy.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea.
Image credit: Seung-Jae V. LEE, KAIST.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Park, S., et al. (2020) ‘VRK-1 extends life span by activation of AMPK via phosphorylation’. Science Advances, Volume 6. No. 27, eaaw7824. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw7824
Profile: Seung-Jae V. Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
seungjaevlee@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/view/mgakaist
Molecular Genetics of Aging Laboratory
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.31 View 12551
Tinkering with Roundworm Proteins Offers Hope for Anti-aging Drugs
- The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for developing longevity-promoting drugs. These new findings were published on July 1 in Science Advances.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a millimeter-long nematode commonly used in lab testing, enjoyed a boost in its lifespan when researchers tinkered with a couple of proteins involved in monitoring the energy use by its cells.
The proteins VRK-1 and AMPK work in tandem in roundworm cells, with the former telling the latter to get to work by sticking a phosphate molecule, composed of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms, on it. In turn, AMPK’s role is to monitor energy levels in cells, when cellular energy is running low. In essence, VRK-1 regulates AMPK, and AMPK regulates the cellular energy status.
Using a range of different biological research tools, including introducing foreign genes into the worm, a group of researchers led by Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST were able to dial up and down the activity of the gene that tells cells to produce the VRK-1 protein. This gene has remained pretty much unchanged throughout evolution. Most complex organisms have this same gene, including humans.
Lead author of the study Sangsoon Park and his colleagues confirmed that the overexpression, or increased production, of the VRK-1 protein boosted the lifespan of the C. elegans, which normally lives just two to three weeks, and the inhibition of VRK-1 production reduced its lifespan.
The research team found that the activity of the VRK-1-to-AMPK cellular-energy monitoring process is increased in low cellular energy status by reduced mitochondrial respiration, the set of metabolic chemical reactions that make use of the oxygen the worm breathes to convert macronutrients from food into the energy “currency” that cells spend to do everything they need to do.
It is already known that mitochondria, the energy-producing engine rooms in cells, play a crucial role in aging, and declines in the functioning of mitochondria are associated with age-related diseases. At the same time, the mild inhibition of mitochondrial respiration has been shown to promote longevity in a range of species, including flies and mammals.
When the research team performed similar tinkering with cultured human cells, they found they could also replicate this ramping up and down of the VRK-1-to-AMPK process that occurs in roundworms.
“This raises the intriguing possibility that VRK-1 also functions as a factor in governing human longevity, and so perhaps we can start developing longevity-promoting drugs that alter the activity of VRK-1,” explained Professor Lee.
At the very least, the research points us in an interesting direction for investigating new therapeutic strategies to combat metabolic disorders by targeting the modulation of VRK-1. Metabolic disorders involve the disruption of chemical reactions in the body, including diseases of the mitochondria.
But before metabolic disorder therapeutics or longevity drugs can be contemplated by scientists, further research still needs to be carried out to better understand how VRK-1 works to activate AMPK, as well as figure out the precise mechanics of how AMPK controls cellular energy.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea.
Image credit: Seung-Jae V. LEE, KAIST.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Park, S., et al. (2020) ‘VRK-1 extends life span by activation of AMPK via phosphorylation’. Science Advances, Volume 6. No. 27, eaaw7824. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw7824
Profile: Seung-Jae V. Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
seungjaevlee@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/view/mgakaist
Molecular Genetics of Aging Laboratory
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.31 View 12551 -
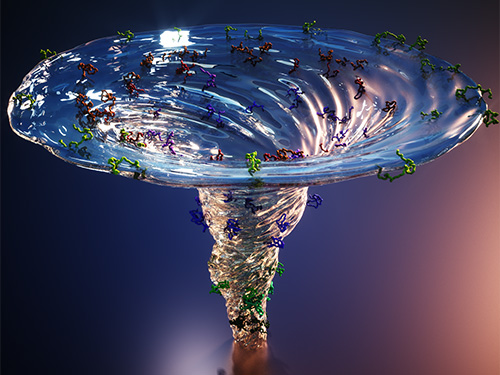 X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 15365
X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 15365