Energy
-
 Press Release on Piezoelectric Nanogenerators of ZnO with Aluminium Nitride Stacked Layers by the American Institute of Physics
The
American Institute of Physics (AIP) released a news article entitled “Zinc
Oxide Materials Tapped for Tiny Energy Harvesting Devices” on January 13, 2015.
The
article described the research led by Professor Giwan Yoon of the
Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST. It was published in the January
12, 2015 issue of Applied Physics Letters.
AIP publishes the journal. For the news release, please visit the
link below:
The American
Institute of Physics, January 13, 2015
“Zinc
Oxide Materials Tapped for Tiny Energy Harvesting Devices”
New research helps
pave the way toward highly energy-efficient zinc oxide-based micro energy
harvesting devices with applications in portable communications, healthcare and
environmental monitoring, and more
http://www.aip.org/publishing/journal-highlights/zinc-oxide-materials-tapped-tiny-energy-harvesting-devices
2015.02.04 View 33338
Press Release on Piezoelectric Nanogenerators of ZnO with Aluminium Nitride Stacked Layers by the American Institute of Physics
The
American Institute of Physics (AIP) released a news article entitled “Zinc
Oxide Materials Tapped for Tiny Energy Harvesting Devices” on January 13, 2015.
The
article described the research led by Professor Giwan Yoon of the
Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST. It was published in the January
12, 2015 issue of Applied Physics Letters.
AIP publishes the journal. For the news release, please visit the
link below:
The American
Institute of Physics, January 13, 2015
“Zinc
Oxide Materials Tapped for Tiny Energy Harvesting Devices”
New research helps
pave the way toward highly energy-efficient zinc oxide-based micro energy
harvesting devices with applications in portable communications, healthcare and
environmental monitoring, and more
http://www.aip.org/publishing/journal-highlights/zinc-oxide-materials-tapped-tiny-energy-harvesting-devices
2015.02.04 View 33338 -
 Elsevier Selects a KAIST Graduate's Paper as the Top Cited Papers in 2011-2012
Dr. Myung-Won Seo, a graduate from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST, published a paper in January 2011 in Chemical Engineering Journal, which was entitled “Solid Circulation and Loop-seal Characteristics of a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed: Experiments and CFD Simulation.” His paper was selected by Elsevier as the Top Cited Papers of 2011-2012. The Chemical Engineering Journal is a renowned peer-reviewed journal issued by Elsevier.
Dr. Seo published another paper, “CFD Simulation with Experiments in a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasifier,” in January 2012 in Computers & Chemical Engineering, which was also selected as the Most Downloaded Papers in 2012-2013.
Dr. Seo graduated with a doctoral degree from KAIST in 2011. He is currently working at the Clean Fuel Laboratory, the Korea Institute of Energy Research, Daejeon, as a researcher. His research areas are coal gasification, upgrading, and liquefaction, as well as energy and chemical production from low-grade fuels such as biomass and wastes.
2014.11.24 View 10203
Elsevier Selects a KAIST Graduate's Paper as the Top Cited Papers in 2011-2012
Dr. Myung-Won Seo, a graduate from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST, published a paper in January 2011 in Chemical Engineering Journal, which was entitled “Solid Circulation and Loop-seal Characteristics of a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed: Experiments and CFD Simulation.” His paper was selected by Elsevier as the Top Cited Papers of 2011-2012. The Chemical Engineering Journal is a renowned peer-reviewed journal issued by Elsevier.
Dr. Seo published another paper, “CFD Simulation with Experiments in a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasifier,” in January 2012 in Computers & Chemical Engineering, which was also selected as the Most Downloaded Papers in 2012-2013.
Dr. Seo graduated with a doctoral degree from KAIST in 2011. He is currently working at the Clean Fuel Laboratory, the Korea Institute of Energy Research, Daejeon, as a researcher. His research areas are coal gasification, upgrading, and liquefaction, as well as energy and chemical production from low-grade fuels such as biomass and wastes.
2014.11.24 View 10203 -
 KAIST and the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis Agree to Cooperate
KAIST signed a cooperation agreement with the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) on October 29, 2014 at the president’s office.
Established in 1972 and based in Austria as a non-governmental research organization, IIASA is an international scientific institute that conducts policy-oriented research into global problems such as climate change, energy security, or population aging. IIASA examines such issues and devises strategies for cooperative action unconstrained by political and national self-interest.
Dr. Pavel Kabat, the Director General and CEO of IIASA, headed a delegation that visited KAIST to attend the signing ceremony of the agreement. He said, “KAIST has been known as a leading research university, and its strength in the development of green technology and environmental policy will benefit our institution. In particular, we expect to see vibrant exchanges of knowledge and researchers with the Graduate School of Green Growth (GSGG) and the Graduate School of EEWS (energy, environment, water, and sustainability) at KAIST.”
The two organizations will implement joint research projects in the diffusion analysis of green technology, the development and improvement of evaluation models to integrate economy, energy, and environment, the development of an analysis system for water resources, and the establishment of academic workshops and conferences.
The Dean of GSGG, Professor Jae-Kyu Lee said, “IIASA is a well-respected international organization with accumulated knowledge about analysis and prediction techniques. With this agreement, we hope that KAIST will intensify its research capacity in environmental science and lead education and research in green growth and environmental technology.”
The picture below shows Dr. Pavel Kabat, the Director General and CEO of IIASA, on the left and President Steve Kang of KAIST on the right holding the signed agreement with professors from GSGG and EEWS Graduate School including Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, to the right of President Kang.
2014.11.05 View 10958
KAIST and the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis Agree to Cooperate
KAIST signed a cooperation agreement with the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) on October 29, 2014 at the president’s office.
Established in 1972 and based in Austria as a non-governmental research organization, IIASA is an international scientific institute that conducts policy-oriented research into global problems such as climate change, energy security, or population aging. IIASA examines such issues and devises strategies for cooperative action unconstrained by political and national self-interest.
Dr. Pavel Kabat, the Director General and CEO of IIASA, headed a delegation that visited KAIST to attend the signing ceremony of the agreement. He said, “KAIST has been known as a leading research university, and its strength in the development of green technology and environmental policy will benefit our institution. In particular, we expect to see vibrant exchanges of knowledge and researchers with the Graduate School of Green Growth (GSGG) and the Graduate School of EEWS (energy, environment, water, and sustainability) at KAIST.”
The two organizations will implement joint research projects in the diffusion analysis of green technology, the development and improvement of evaluation models to integrate economy, energy, and environment, the development of an analysis system for water resources, and the establishment of academic workshops and conferences.
The Dean of GSGG, Professor Jae-Kyu Lee said, “IIASA is a well-respected international organization with accumulated knowledge about analysis and prediction techniques. With this agreement, we hope that KAIST will intensify its research capacity in environmental science and lead education and research in green growth and environmental technology.”
The picture below shows Dr. Pavel Kabat, the Director General and CEO of IIASA, on the left and President Steve Kang of KAIST on the right holding the signed agreement with professors from GSGG and EEWS Graduate School including Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, to the right of President Kang.
2014.11.05 View 10958 -
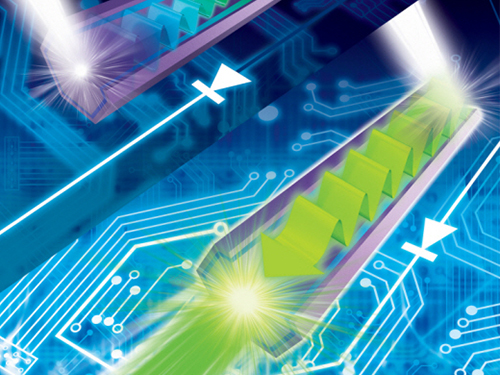 Development of a Photonic Diode with Light Speed, Single-Direction Transfer
A photonic diode using a nitride semiconductor rod can increase the possibility of developing all-optical integrated circuits, an alternative to conventional integrated circuits.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team from the Department of Physics, KAIST, developed a photonic diode which can selectively transfer light in one way, using semiconductor rods.
The photonic diode has a diameter of hundreds of nanometers (nm) and a length of few micrometers. This size enables its use in large-scale integration (LSI). The diode’s less sensitivity towards polarized light angle makes it more useful.
In an integrated circuit, a diode controls the flow of electrons. If this diode controls light rather than electrons, data can be transferred at high speed, and its loss is minimized to a greater extent. Since these implementations conserve more energy, this is a very promising future technology.
However, conventional electronic diodes, made up of asymmetric meta-materials or photonic crystalline structures, are large, which makes them difficult to be used in LSI. These diodes could only be implemented under limited conditions due to its sensitivity towards polarized light angle.
The research team used nitride semiconductor rods to develop a highly efficient photonic diode with distinct light intensities from opposite ends.
The semiconductor rod yields different amount of energy horizontally. According to the research team, this is because the width of the quantum well and its indium quantity is continuously controlled.
Professor Cho said, "A large energy difference in a horizontal direction causes asymmetrical light propagation, enabling it to be operated as a photonic diode." He added that “If light, instead of electrons, were adopted in integrated circuits, the transfer speed would be expected as great as that of light.”
The research findings were published in the September 10th issue of Nano Letters as the cover paper.
Under the guidance of Professor Cho, two Ph.D. candidates, Suk-Min Ko and Su-Hyun Gong, conducted this research. This research project was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST’s EEWS (energy, environment, water, and sustainability) Research Center.
Figure Description: Computer simulated image of photonic diode made of semiconductor rod implemented in an all-optical integrated circuit
2014.09.23 View 11824
Development of a Photonic Diode with Light Speed, Single-Direction Transfer
A photonic diode using a nitride semiconductor rod can increase the possibility of developing all-optical integrated circuits, an alternative to conventional integrated circuits.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team from the Department of Physics, KAIST, developed a photonic diode which can selectively transfer light in one way, using semiconductor rods.
The photonic diode has a diameter of hundreds of nanometers (nm) and a length of few micrometers. This size enables its use in large-scale integration (LSI). The diode’s less sensitivity towards polarized light angle makes it more useful.
In an integrated circuit, a diode controls the flow of electrons. If this diode controls light rather than electrons, data can be transferred at high speed, and its loss is minimized to a greater extent. Since these implementations conserve more energy, this is a very promising future technology.
However, conventional electronic diodes, made up of asymmetric meta-materials or photonic crystalline structures, are large, which makes them difficult to be used in LSI. These diodes could only be implemented under limited conditions due to its sensitivity towards polarized light angle.
The research team used nitride semiconductor rods to develop a highly efficient photonic diode with distinct light intensities from opposite ends.
The semiconductor rod yields different amount of energy horizontally. According to the research team, this is because the width of the quantum well and its indium quantity is continuously controlled.
Professor Cho said, "A large energy difference in a horizontal direction causes asymmetrical light propagation, enabling it to be operated as a photonic diode." He added that “If light, instead of electrons, were adopted in integrated circuits, the transfer speed would be expected as great as that of light.”
The research findings were published in the September 10th issue of Nano Letters as the cover paper.
Under the guidance of Professor Cho, two Ph.D. candidates, Suk-Min Ko and Su-Hyun Gong, conducted this research. This research project was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST’s EEWS (energy, environment, water, and sustainability) Research Center.
Figure Description: Computer simulated image of photonic diode made of semiconductor rod implemented in an all-optical integrated circuit
2014.09.23 View 11824 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 12520
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 12520 -
 Professor Ilkwon Oh Receives the Energy Technology Innovation Award
Professor Ilkwon Oh from the Division of Ocean Systems Engineering at the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, received the Energy Technology Innovation Award at the Energy Tech Insight 2014 Conference, which was held on August 28, 2014 at COEX in Seoul. The conference was co-hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea, and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Oh has been recognized for his distinguished research on a synthetic technology to develop 3-dimensional carbon nanostructures based on defect engineering and for his efforts to apply this technology to produce cathode materials for high performance, high density lithium-ion secondary batteries.
In 2010, the Ministry of Education, the Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea included Professor Oh's research in the 100 Best Research in Basic Sciences of the Year, and the 50 Best Research in Basic Sciences in 2012 and 2014, respectively.
2014.09.07 View 9231
Professor Ilkwon Oh Receives the Energy Technology Innovation Award
Professor Ilkwon Oh from the Division of Ocean Systems Engineering at the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, received the Energy Technology Innovation Award at the Energy Tech Insight 2014 Conference, which was held on August 28, 2014 at COEX in Seoul. The conference was co-hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea, and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Oh has been recognized for his distinguished research on a synthetic technology to develop 3-dimensional carbon nanostructures based on defect engineering and for his efforts to apply this technology to produce cathode materials for high performance, high density lithium-ion secondary batteries.
In 2010, the Ministry of Education, the Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea included Professor Oh's research in the 100 Best Research in Basic Sciences of the Year, and the 50 Best Research in Basic Sciences in 2012 and 2014, respectively.
2014.09.07 View 9231 -
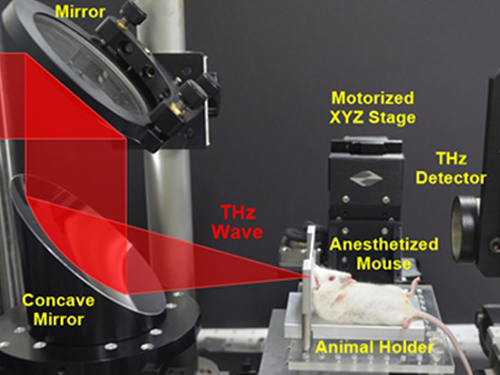 First Instance of Negative Effects from Terahertz-Range Electromagnetic Waves
Professor Philhan Kim
Electromagnetic waves (EM-wave) in the terahertz range were widely regarded as the “dream wavelength” due to its perceived neutrality. Its application was also wider than X-rays. However, KAIST scientists have discovered negative effects from terahertz EM-waves.
Professor Philhan Kim of KAIST’s Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology and Dr. Young-wook Jeong of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) observed inflammation of animal skin tissue when exposed to terahertz EM-waves.
The results were published in the online edition of Optics Express (May 19, 20104).
Terahertz waves range from 0.1 to 10 terahertz and have a longer wavelength than visible or infrared light. Commonly used to see through objects like the X-ray, it was believed that the low energy of terahertz waves did not inflict any harm on the human body.
Despite being applied for security checks, next-generation wireless communications, and medical imaging technology, little research has been conducted in proving its safety and impact. Conventional research failed to predict the exact impact of terahertz waves on organic tissues as only artificially cultured cells were used.
The research team at KAERI developed a high power terahertz EM-wave generator that can be used on live organisms. A high power generator was necessary in applications such as biosensors and required up to 10 times greater power than currently used telecommunications EM-wave. Simultaneously, a KAIST research team developed a high speed, high resolution video-laser microscope that can distinguish cells within the organism.
The experiment exposed 30 minutes of terahertz EM-wave on genetically modified mice and found six times the normal number of inflammation cells in the skin tissue after six hours. It was the first instance where negative side effects of terahertz EM-wave were observed.
Professor Kim commented that “the research has set a standard for how we can use the terahertz EM-wave safely” and that “we will use this research to analyze and understand the effects of other EM-waves on organisms.”
2014.06.20 View 10048
First Instance of Negative Effects from Terahertz-Range Electromagnetic Waves
Professor Philhan Kim
Electromagnetic waves (EM-wave) in the terahertz range were widely regarded as the “dream wavelength” due to its perceived neutrality. Its application was also wider than X-rays. However, KAIST scientists have discovered negative effects from terahertz EM-waves.
Professor Philhan Kim of KAIST’s Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology and Dr. Young-wook Jeong of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) observed inflammation of animal skin tissue when exposed to terahertz EM-waves.
The results were published in the online edition of Optics Express (May 19, 20104).
Terahertz waves range from 0.1 to 10 terahertz and have a longer wavelength than visible or infrared light. Commonly used to see through objects like the X-ray, it was believed that the low energy of terahertz waves did not inflict any harm on the human body.
Despite being applied for security checks, next-generation wireless communications, and medical imaging technology, little research has been conducted in proving its safety and impact. Conventional research failed to predict the exact impact of terahertz waves on organic tissues as only artificially cultured cells were used.
The research team at KAERI developed a high power terahertz EM-wave generator that can be used on live organisms. A high power generator was necessary in applications such as biosensors and required up to 10 times greater power than currently used telecommunications EM-wave. Simultaneously, a KAIST research team developed a high speed, high resolution video-laser microscope that can distinguish cells within the organism.
The experiment exposed 30 minutes of terahertz EM-wave on genetically modified mice and found six times the normal number of inflammation cells in the skin tissue after six hours. It was the first instance where negative side effects of terahertz EM-wave were observed.
Professor Kim commented that “the research has set a standard for how we can use the terahertz EM-wave safely” and that “we will use this research to analyze and understand the effects of other EM-waves on organisms.”
2014.06.20 View 10048 -
 Thermoelectric generator on glass fabric for wearable electronic devices
Wearable computers or devices have been hailed as the next generation of mobile electronic gadgets, from smart watches to smart glasses to smart pacemakers. For electronics to be worn by a user, they must be light, flexible, and equipped with a power source, which could be a portable, long-lasting battery or no battery at all but a generator. How to supply power in a stable and reliable manner is one of the most critical issues to commercialize wearable devices.
A team of KAIST researchers headed by Byung Jin Cho, a professor of electrical engineering, proposed a solution to this problem by developing a glass fabric-based thermoelectric (TE) generator that is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. In fact, it is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles.
To date, two types of TE generators have been developed based either on organic or inorganic materials. The organic-based TE generators use polymers that are highly flexible and compatible with human skin, ideal for wearable electronics. The polymers, however, have a low power output. Inorganic-based TE generators produce a high electrical energy, but they are heavy, rigid, and bulky.
Professor Cho came up with a new concept and design technique to build a flexible TE generator that minimizes thermal energy loss but maximizes power output. His team synthesized liquid-like pastes of n-type (Bi2Te3) and p-type (Sb2Te3) TE materials and printed them onto a glass fabric by applying a screen printing technique. The pastes permeated through the meshes of the fabric and formed films of TE materials in a range of thickness of several hundreds of microns. As a result, hundreds of TE material dots (in combination of n and p types) were printed and well arranged on a specific area of the glass fabric.
Professor Cho explained that his TE generator has a self-sustaining structure, eliminating thick external substrates (usually made of ceramic or alumina) that hold inorganic TE materials. These substrates have taken away a great portion of thermal energy, a serious setback which causes low output power.
He also commented,
"For our case, the glass fabric itself serves as the upper and lower substrates of a TE generator, keeping the inorganic TE materials in between. This is quite a revolutionary approach to design a generator. In so doing, we were able to significantly reduce the weight of our generator (~0.13g/cm2), which is an essential element for wearable electronics."
When using KAIST's TE generator (with a size of 10 cm x 10 cm) for a wearable wristband device, it will produce around 40 mW electric power based on the temperature difference of 31 °F between human skin and the surrounding air.
Professor Cho further described about the merits of the new generator:
"Our technology presents an easy and simple way of fabricating an extremely flexible, light, and high-performance TE generator. We expect that this technology will find further applications in scale-up systems such as automobiles, factories, aircrafts, and vessels where we see abundant thermal energy being wasted."
This research result was published online in the March 14th issue of Energy & Environmental Science and was entitled "Wearable Thermoelectric Generator Fabricated on Glass Fabric."
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlN9lvEzCuw&feature=youtu.be
[Picture Captions]
Caption 1: The picture shows a high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Caption 2: A thermoelectric generator developed as a wristband. The generator can be easily curved along with the shape of human body.
Caption 3: KAIST’s thermoelectric generator can be bent as many as 120 times, but it still shows the same high performance.
2014.04.21 View 20926
Thermoelectric generator on glass fabric for wearable electronic devices
Wearable computers or devices have been hailed as the next generation of mobile electronic gadgets, from smart watches to smart glasses to smart pacemakers. For electronics to be worn by a user, they must be light, flexible, and equipped with a power source, which could be a portable, long-lasting battery or no battery at all but a generator. How to supply power in a stable and reliable manner is one of the most critical issues to commercialize wearable devices.
A team of KAIST researchers headed by Byung Jin Cho, a professor of electrical engineering, proposed a solution to this problem by developing a glass fabric-based thermoelectric (TE) generator that is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. In fact, it is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles.
To date, two types of TE generators have been developed based either on organic or inorganic materials. The organic-based TE generators use polymers that are highly flexible and compatible with human skin, ideal for wearable electronics. The polymers, however, have a low power output. Inorganic-based TE generators produce a high electrical energy, but they are heavy, rigid, and bulky.
Professor Cho came up with a new concept and design technique to build a flexible TE generator that minimizes thermal energy loss but maximizes power output. His team synthesized liquid-like pastes of n-type (Bi2Te3) and p-type (Sb2Te3) TE materials and printed them onto a glass fabric by applying a screen printing technique. The pastes permeated through the meshes of the fabric and formed films of TE materials in a range of thickness of several hundreds of microns. As a result, hundreds of TE material dots (in combination of n and p types) were printed and well arranged on a specific area of the glass fabric.
Professor Cho explained that his TE generator has a self-sustaining structure, eliminating thick external substrates (usually made of ceramic or alumina) that hold inorganic TE materials. These substrates have taken away a great portion of thermal energy, a serious setback which causes low output power.
He also commented,
"For our case, the glass fabric itself serves as the upper and lower substrates of a TE generator, keeping the inorganic TE materials in between. This is quite a revolutionary approach to design a generator. In so doing, we were able to significantly reduce the weight of our generator (~0.13g/cm2), which is an essential element for wearable electronics."
When using KAIST's TE generator (with a size of 10 cm x 10 cm) for a wearable wristband device, it will produce around 40 mW electric power based on the temperature difference of 31 °F between human skin and the surrounding air.
Professor Cho further described about the merits of the new generator:
"Our technology presents an easy and simple way of fabricating an extremely flexible, light, and high-performance TE generator. We expect that this technology will find further applications in scale-up systems such as automobiles, factories, aircrafts, and vessels where we see abundant thermal energy being wasted."
This research result was published online in the March 14th issue of Energy & Environmental Science and was entitled "Wearable Thermoelectric Generator Fabricated on Glass Fabric."
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlN9lvEzCuw&feature=youtu.be
[Picture Captions]
Caption 1: The picture shows a high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Caption 2: A thermoelectric generator developed as a wristband. The generator can be easily curved along with the shape of human body.
Caption 3: KAIST’s thermoelectric generator can be bent as many as 120 times, but it still shows the same high performance.
2014.04.21 View 20926 -
 Seung-Han Lee, a doctoral student in electrical engineering, receives the best paper award from ISQED 2014
Seung-Han
Lee, a doctoral candidate in the department of electrical engineering at KAIST,
received a Best Paper Award from the International Symposium on Quality
Electronic Design (ISQED), a high-profile international conference started in 2000 to promote innovation and quality in electronic and
engineering designs through inter- and multidisciplinary approaches. The
award ceremony will take place at the 2014 ISQED on March 3-5, 2014 at the Convention
Center in Santa Clara, CA, USA.
Professor
Chong-Min Kyung, an advisor to Seung-Han, expressed his excitement about his student's achievement.
“This is
the first time a Korean has ever received the best paper award at this academic
conference. It’s great news to our student as well as to KAIST.”
The topic
of Lee’s research paper was dynamic cache data management for minimizing the
energy consumption of three-dimensional multi-processor semiconductor chips.
2014.03.03 View 11014
Seung-Han Lee, a doctoral student in electrical engineering, receives the best paper award from ISQED 2014
Seung-Han
Lee, a doctoral candidate in the department of electrical engineering at KAIST,
received a Best Paper Award from the International Symposium on Quality
Electronic Design (ISQED), a high-profile international conference started in 2000 to promote innovation and quality in electronic and
engineering designs through inter- and multidisciplinary approaches. The
award ceremony will take place at the 2014 ISQED on March 3-5, 2014 at the Convention
Center in Santa Clara, CA, USA.
Professor
Chong-Min Kyung, an advisor to Seung-Han, expressed his excitement about his student's achievement.
“This is
the first time a Korean has ever received the best paper award at this academic
conference. It’s great news to our student as well as to KAIST.”
The topic
of Lee’s research paper was dynamic cache data management for minimizing the
energy consumption of three-dimensional multi-processor semiconductor chips.
2014.03.03 View 11014 -
 KAIST Student Awarded Prize from Energy Saving Contest
Jun-Min Kwon, an undergraduate student in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was awarded a prize from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea, at the 35th Energy Saving Contest which was held on November 20.
The student club he has been leading was also selected as one of the best groups by the Save Energy Save Earth (SESE), a volunteer organization supported by the Korea Energy Management Corporation and the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Kwon began promoting energy conservation through a blog and participated in related meetings and workshops as a high school student to improve the understanding on the importance of energy saving and recycling.He also received awards from the Second National Assembly Forum on Climate Change, the Korean National Science Fair, as well as the Samsung Human Tech Paper Award.
2013.12.24 View 13267
KAIST Student Awarded Prize from Energy Saving Contest
Jun-Min Kwon, an undergraduate student in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was awarded a prize from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea, at the 35th Energy Saving Contest which was held on November 20.
The student club he has been leading was also selected as one of the best groups by the Save Energy Save Earth (SESE), a volunteer organization supported by the Korea Energy Management Corporation and the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Kwon began promoting energy conservation through a blog and participated in related meetings and workshops as a high school student to improve the understanding on the importance of energy saving and recycling.He also received awards from the Second National Assembly Forum on Climate Change, the Korean National Science Fair, as well as the Samsung Human Tech Paper Award.
2013.12.24 View 13267 -
 Graduate Student at KAIST Awarded Best Prize at the 9th Inside Edge
Sun-Jin Choi, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, under the guidance of Professor Il-Doo Kim, won the best prize at the 9th Inside Edge Contest hosted by Samsung Electro-Mechanics.
Choi was awarded prize money totaling fifteen million won at the award ceremony held on November 22 at the Mirae Hall at the headquarters of Samsung Electro-Mechanics in Suwon.
Choi’s research, titled “Exhaled Breath Sensor Arrays for the Non-invasive and Real-time Diagnosis of Diabetes by Detection of Acetone,” was recognized for its creativity and uniqueness.The Inside Edge is an international thesis competition which was started in 2005 to encourage and support creative research and potential technological development among young scientists and engineers.
Sun-Jin Choi (left) and Professor Il-Doo Kim (right).
2013.12.11 View 10186
Graduate Student at KAIST Awarded Best Prize at the 9th Inside Edge
Sun-Jin Choi, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, under the guidance of Professor Il-Doo Kim, won the best prize at the 9th Inside Edge Contest hosted by Samsung Electro-Mechanics.
Choi was awarded prize money totaling fifteen million won at the award ceremony held on November 22 at the Mirae Hall at the headquarters of Samsung Electro-Mechanics in Suwon.
Choi’s research, titled “Exhaled Breath Sensor Arrays for the Non-invasive and Real-time Diagnosis of Diabetes by Detection of Acetone,” was recognized for its creativity and uniqueness.The Inside Edge is an international thesis competition which was started in 2005 to encourage and support creative research and potential technological development among young scientists and engineers.
Sun-Jin Choi (left) and Professor Il-Doo Kim (right).
2013.12.11 View 10186 -
 KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9321
KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9321