TE
-
 Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11482
Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11482 -
 Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
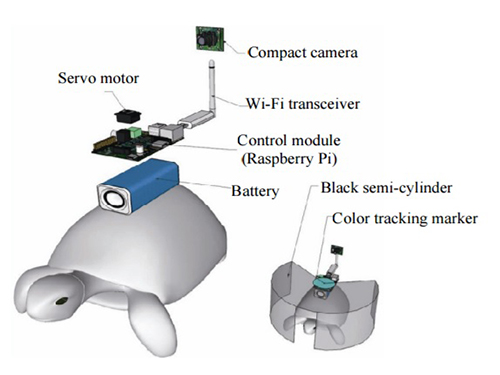
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 15152
Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 15152 -
 KAIST Celebrates the 2017 Commencement
KAIST hosted its 2017 Commencement, awarding diplomas to 2,767 members of the Class of 2017 during a ceremony on February 17. President Sung-Mo Kang, Minister Yang-hee Choi of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Jang-Moo Lee joined the ceremony along with the graduates and their family and friends at the Ryu Keun Chul Sports Complex.
The graduating class included 638 Ph.D. degrees, 1,335 Master’s degrees, and 794 Bachelor’s degrees being conferred. Among them, Young-Ki Song from the Department of Electric Engineering was honored to win the Minister’s Award, the highest award bestowed to an undergraduate. The KAIST Presidential Award went to Min-Jae Park of the Department of Mathematical Sciences and the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairman’s Award was presented to Jae-Hyung Cho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Including this year’s graduating class, KAIST has turned out more than 59,000 highly educated science and technology talents including 11,731 Ph.D.s since its foundation in 1971. This year, 24-year-old Seo-Hee Oh earned her Ph.D. in chemistry as the youngest Ph.D. of the year after completing her Master’s and Ph.D. combined course in three years.
President Sung-Mo Kang praised the creativity of this graduating class and their excellent ability in his charge, saying, “As future leaders of our society, you are expected to develop a sense of compassion and outstanding professionalism to contribute to the advancement of not only Korea but also the whole world.’
For full text of President Kang’s charge to the graduates, please click.
2017.02.17 View 9195
KAIST Celebrates the 2017 Commencement
KAIST hosted its 2017 Commencement, awarding diplomas to 2,767 members of the Class of 2017 during a ceremony on February 17. President Sung-Mo Kang, Minister Yang-hee Choi of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Jang-Moo Lee joined the ceremony along with the graduates and their family and friends at the Ryu Keun Chul Sports Complex.
The graduating class included 638 Ph.D. degrees, 1,335 Master’s degrees, and 794 Bachelor’s degrees being conferred. Among them, Young-Ki Song from the Department of Electric Engineering was honored to win the Minister’s Award, the highest award bestowed to an undergraduate. The KAIST Presidential Award went to Min-Jae Park of the Department of Mathematical Sciences and the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairman’s Award was presented to Jae-Hyung Cho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Including this year’s graduating class, KAIST has turned out more than 59,000 highly educated science and technology talents including 11,731 Ph.D.s since its foundation in 1971. This year, 24-year-old Seo-Hee Oh earned her Ph.D. in chemistry as the youngest Ph.D. of the year after completing her Master’s and Ph.D. combined course in three years.
President Sung-Mo Kang praised the creativity of this graduating class and their excellent ability in his charge, saying, “As future leaders of our society, you are expected to develop a sense of compassion and outstanding professionalism to contribute to the advancement of not only Korea but also the whole world.’
For full text of President Kang’s charge to the graduates, please click.
2017.02.17 View 9195 -
 Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6777
Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6777 -
 EWB-KAIST Wraps up Five-Year Project in Nepal
‘Engineers Without Borders-KAIST (EWB-KAIST)’ led by Professor Tae-ho Song from the Department of Mechanical Engineering returned to Korea on January 10 after a two-week project in Nangi, Nepal.
EWB-KAIST was established in 2012 by KAIST students and professors. Since then, the team visited Nangi, in the Annapurna region of Nepal, to engage in Appropriate Technology (AT) development projects. The projects included building passive houses and small hydroelectric power, and teaching science education. In particular, passive houses that use straw as an insulator received great a reception from the locals.
This was their last visit to Nepal, since the five-year project has now come to an end. Future projects in Mongolia will be led by Professor Buhm Soon Park from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy.
Professor Song commented, “I am glad that the Nepal project was successfully conducted over the last five years. To make sure the support does not end here, I will personally continue to visit the Himalayas to assist the villagers.”
EWB-KAIST is a non-profit organization that conducts activities with the aim of AT development and providing support for less-developed countries in need of the benefits of technology.
( Passive house made of straws by EWB-KAIST team in Nangi, Nepal.)
2017.02.01 View 7499
EWB-KAIST Wraps up Five-Year Project in Nepal
‘Engineers Without Borders-KAIST (EWB-KAIST)’ led by Professor Tae-ho Song from the Department of Mechanical Engineering returned to Korea on January 10 after a two-week project in Nangi, Nepal.
EWB-KAIST was established in 2012 by KAIST students and professors. Since then, the team visited Nangi, in the Annapurna region of Nepal, to engage in Appropriate Technology (AT) development projects. The projects included building passive houses and small hydroelectric power, and teaching science education. In particular, passive houses that use straw as an insulator received great a reception from the locals.
This was their last visit to Nepal, since the five-year project has now come to an end. Future projects in Mongolia will be led by Professor Buhm Soon Park from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy.
Professor Song commented, “I am glad that the Nepal project was successfully conducted over the last five years. To make sure the support does not end here, I will personally continue to visit the Himalayas to assist the villagers.”
EWB-KAIST is a non-profit organization that conducts activities with the aim of AT development and providing support for less-developed countries in need of the benefits of technology.
( Passive house made of straws by EWB-KAIST team in Nangi, Nepal.)
2017.02.01 View 7499 -
 KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8413
KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8413 -
 Educating for Sustainability: KAIST's Graduate Schools of EEWS and Green Growth
At the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Annual Meeting (Davos Forum) January 17-20, 2017 in Davos, Switzerland, the International Sustainable Campus Network (ISCN) and the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) shared exemplary case studies for teaching “sustainability” on campuses, which were implemented by 30 leading universities around the world.
KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang participated in the meeting and introduced two of the university’s graduate schools and their main activities in 2016: The Graduate School of EEWS (energy, environment, water and sustainability) and The Graduate School of Green Growth.
President Kang explained that the EEWS Graduate School, created in 2009, represents KAIST’s commitment to interdisciplinary education and research, addressing key issues of today’s global challenges including energy, environment, and water for a sustainable society. The graduate school hosted its first international forum last October, “The EEWS 2016: Progress and Perspective of Energy Science and Technology.” Over 200 participants from Korea and across the world discussed and learned about recent advances, challenges, and future opportunities in energy science and technology, such as the development of sustainable energy harvesting and storage, catalytic energy conversion technology, green chemical materials, and photocatalytic systems for sustainable water treatment.
He also presented the Green Growth Graduate School as KAIST’s initiative to a build global alliance for sustainable growth. Established in 2013 in the College of Business, the graduate school provides world-class education and research on green business, finance, and policy. Among many international conferences and workshops it hosts, the school has held the Seoul Climate Energy Conference annually since 2014. Last year alone, over 400 international participants including climate and energy policy makers and scholars gathered at the conference and strengthened partnerships with the global community. The school has been an active member of international organizations that advocate for green economies and sustainable development, the Global Green Growth Institute and the United Nations Environment Programme, for example.
President Kang noted that KAIST has been at the forefront of formulating and implementing holistic and cross-disciplinary approaches to foster learning and research environments in which university members can take on global issues, which are critical to humanity and our ecosystem, and work toward a more sustainable future.
Founded in 2007, the ISCN is a non-profit association of globally-leading colleges and universities representing over 30 countries and working together to holistically integrate sustainability into campus operations, research, and teaching.
Created in 2006, the GULF is one of the WEF’s expert communities, which consists of top leaders from 26 global universities, including the University of Cambridge, Peking University, Stanford University, and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. The GULF offers in-depth discussions and exchange of ideas on the future of higher education and the role of science in society. Since 2012, KAIST has been a member of GULF, the only university from Korea.
The ISCN and GULF have held a meeting each year at the Davos Forum since 2011 to share information, insights, and best practices for achieving sustainable campus operations and integrating sustainability into research and teaching.
To see the full report on the 2017 WEF ISCN-GULF case studies, please go to
http://www.international-sustainable-campus-network.org/downloads/general/462-educating-for-sustainability/file.
2017.01.25 View 9593
Educating for Sustainability: KAIST's Graduate Schools of EEWS and Green Growth
At the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Annual Meeting (Davos Forum) January 17-20, 2017 in Davos, Switzerland, the International Sustainable Campus Network (ISCN) and the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) shared exemplary case studies for teaching “sustainability” on campuses, which were implemented by 30 leading universities around the world.
KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang participated in the meeting and introduced two of the university’s graduate schools and their main activities in 2016: The Graduate School of EEWS (energy, environment, water and sustainability) and The Graduate School of Green Growth.
President Kang explained that the EEWS Graduate School, created in 2009, represents KAIST’s commitment to interdisciplinary education and research, addressing key issues of today’s global challenges including energy, environment, and water for a sustainable society. The graduate school hosted its first international forum last October, “The EEWS 2016: Progress and Perspective of Energy Science and Technology.” Over 200 participants from Korea and across the world discussed and learned about recent advances, challenges, and future opportunities in energy science and technology, such as the development of sustainable energy harvesting and storage, catalytic energy conversion technology, green chemical materials, and photocatalytic systems for sustainable water treatment.
He also presented the Green Growth Graduate School as KAIST’s initiative to a build global alliance for sustainable growth. Established in 2013 in the College of Business, the graduate school provides world-class education and research on green business, finance, and policy. Among many international conferences and workshops it hosts, the school has held the Seoul Climate Energy Conference annually since 2014. Last year alone, over 400 international participants including climate and energy policy makers and scholars gathered at the conference and strengthened partnerships with the global community. The school has been an active member of international organizations that advocate for green economies and sustainable development, the Global Green Growth Institute and the United Nations Environment Programme, for example.
President Kang noted that KAIST has been at the forefront of formulating and implementing holistic and cross-disciplinary approaches to foster learning and research environments in which university members can take on global issues, which are critical to humanity and our ecosystem, and work toward a more sustainable future.
Founded in 2007, the ISCN is a non-profit association of globally-leading colleges and universities representing over 30 countries and working together to holistically integrate sustainability into campus operations, research, and teaching.
Created in 2006, the GULF is one of the WEF’s expert communities, which consists of top leaders from 26 global universities, including the University of Cambridge, Peking University, Stanford University, and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. The GULF offers in-depth discussions and exchange of ideas on the future of higher education and the role of science in society. Since 2012, KAIST has been a member of GULF, the only university from Korea.
The ISCN and GULF have held a meeting each year at the Davos Forum since 2011 to share information, insights, and best practices for achieving sustainable campus operations and integrating sustainability into research and teaching.
To see the full report on the 2017 WEF ISCN-GULF case studies, please go to
http://www.international-sustainable-campus-network.org/downloads/general/462-educating-for-sustainability/file.
2017.01.25 View 9593 -
 JETS Conference 2017
KAIST and four science and technology research universities in Korea co-hosted a technology start-up fair, the 2017 JETS (Job, Exhibition, Tech Forum, and Startup) Conference January 19 ~20 in the Ryu Geun-chul Sports Complex at KAIST.
Korea’s major science and technology research universities, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Pohang University of Science and Technology (Postech), and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), held the event in a collaborative effort to educate, inspire, and connect young entrepreneurs, especially those who will launch technology start-ups.
The conference brought entrepreneurs and innovators together who seek ways of working with and supporting start-ups and for their sustainable growth. It also drew aspiring young students and researchers from universities and the government-funded research institutions who are in the process of commercializing their technology. Students from each university’s industry-academia cooperation program who incubated their technology and ideas were key contributors.
At the Tech Forum, entrepreneurship and technology consultation specialists including Joe Jasin, managing director at DNA Investment Partners in the US, the founder of Cyworld Dong-Hyung Lee, and Professor Hawoong Jeong, a complex bio-network specialist from the Department of Physics of KAIST lectured on the ecosystem of start-ups and its trends and development.
The Dean of University-Industry Cooperation at KAIST Joongmyeon Bae said, "We organized this event in collaboration with four major research universities to further encourage technology start-ups from young students and help their ideas and technology bear fruit. We will continue to strive to create an ecosystem of start-ups which works efficiently.”
(Above photo: Founder of the Cyworld, Dong-Hyung Lee gives a lecture at the Tech Forum. Below photo: Students visit exhibition booth of each participating institution.)
2017.01.20 View 12141
JETS Conference 2017
KAIST and four science and technology research universities in Korea co-hosted a technology start-up fair, the 2017 JETS (Job, Exhibition, Tech Forum, and Startup) Conference January 19 ~20 in the Ryu Geun-chul Sports Complex at KAIST.
Korea’s major science and technology research universities, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Pohang University of Science and Technology (Postech), and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), held the event in a collaborative effort to educate, inspire, and connect young entrepreneurs, especially those who will launch technology start-ups.
The conference brought entrepreneurs and innovators together who seek ways of working with and supporting start-ups and for their sustainable growth. It also drew aspiring young students and researchers from universities and the government-funded research institutions who are in the process of commercializing their technology. Students from each university’s industry-academia cooperation program who incubated their technology and ideas were key contributors.
At the Tech Forum, entrepreneurship and technology consultation specialists including Joe Jasin, managing director at DNA Investment Partners in the US, the founder of Cyworld Dong-Hyung Lee, and Professor Hawoong Jeong, a complex bio-network specialist from the Department of Physics of KAIST lectured on the ecosystem of start-ups and its trends and development.
The Dean of University-Industry Cooperation at KAIST Joongmyeon Bae said, "We organized this event in collaboration with four major research universities to further encourage technology start-ups from young students and help their ideas and technology bear fruit. We will continue to strive to create an ecosystem of start-ups which works efficiently.”
(Above photo: Founder of the Cyworld, Dong-Hyung Lee gives a lecture at the Tech Forum. Below photo: Students visit exhibition booth of each participating institution.)
2017.01.20 View 12141 -
 Science, IT & Culture Volunteering Team at Cambodia
The Science, IT and Culture Volunteering Team, which is composed of 17 undergraduates, is visiting Cambodia January 1 to 16. Based at Hosanna High School in Phnom Penh, the KAIST volunteering team will participate in diverse science and IT classes as well as cultural events for Cambodian high school students.
The KAIST volunteering service is designed to improve Cambodian students’ science education including the areas of physics, chemistry, biology, earth science, as well as an increased exposure to IT technologies. For this service, the volunteering team has prepared for three months, making syllabi for the science classes in addition to planning Arduino IT classes and cultural performances, including K-pop dances and Korean traditional games.
The team will present various science experiments including smart electric fan and mini vehicles using Arduino. Before departing, the students made great efforts to ensure this service would be a success by taking a basic Khmer language class and studying safety education.
Se-Woong Oh, the head of the team said, "All our members are very excited to have the chance to share our knowledge with Cambodian students and help them learn science and IT technology. We hope this service will serve as an opportunity to understand a different culture as well. We made every effort to prepare for an activity we believe in."
(KAIST volunteer team with Hosanna High School students in Phnom Penh, Cambodia.)
2017.01.10 View 4999
Science, IT & Culture Volunteering Team at Cambodia
The Science, IT and Culture Volunteering Team, which is composed of 17 undergraduates, is visiting Cambodia January 1 to 16. Based at Hosanna High School in Phnom Penh, the KAIST volunteering team will participate in diverse science and IT classes as well as cultural events for Cambodian high school students.
The KAIST volunteering service is designed to improve Cambodian students’ science education including the areas of physics, chemistry, biology, earth science, as well as an increased exposure to IT technologies. For this service, the volunteering team has prepared for three months, making syllabi for the science classes in addition to planning Arduino IT classes and cultural performances, including K-pop dances and Korean traditional games.
The team will present various science experiments including smart electric fan and mini vehicles using Arduino. Before departing, the students made great efforts to ensure this service would be a success by taking a basic Khmer language class and studying safety education.
Se-Woong Oh, the head of the team said, "All our members are very excited to have the chance to share our knowledge with Cambodian students and help them learn science and IT technology. We hope this service will serve as an opportunity to understand a different culture as well. We made every effort to prepare for an activity we believe in."
(KAIST volunteer team with Hosanna High School students in Phnom Penh, Cambodia.)
2017.01.10 View 4999 -
 KAIST Undergraduates Win the Innovative Design Contest 2016
A team of KAIST students, consisting of five undergraduates (Do-Hoon Kwon, Tae-Hyun Kim, Hak-Gi Do, Hyun-Joo Lee, and Jong-Ho Jeong) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, won the grand prize at the Innovative Design Contest held at Osaka University in Japan on December 12-13, 2016. The event took place during the 16th Asia Design Engineering Workshop (A-DEWS).
For this year’s contest, a total of ten student teams from such countries as Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Malaysia participated, and Team KAIST earned the highest scores. The five KAIST students, all taking the course entitled “Production of Creative Systems,” developed a manual wheelchair accessory called “Safe Attachable Wheelchair Assistive Device in Capstone Design (SAWADiCap).
SAWADiCap is a detachable auxiliary power device that increases the range and mobility of manual wheelchairs. The device can easily be installed and removed, compared to existing add-on attachments for wheelchairs. Users can also enjoy similar advantages offered by powered wheelchairs at a lower cost. In their presentation on the device, the KAIST students introduced their design to improve the power of manual wheelchairs employing the magnetic reinforcement effect and to include the safety features necessary for users to install or operate the device.
Do-Hoon Kwon said, “Our team had a great experience participating in the contest—we met people with diverse backgrounds and expanded our understanding in the field.”
Professor Seibum B. Choi of the Mechanical Engineering Department, who advises the KAIST team, added, “I hope our technology can help the spread of affordable wheelchairs and increase mobility for the disabled.”
Established in 2000, A-DEWS is held annually by the Asian branch of the Design Engineering Workshop to provide an international forum for researchers and practitioners in the field of design engineering by facilitating the exchange of recent research results and sharing knowledge about design strategies and methods. This year’s theme for the workshop was “Innovation of Life.”
A-DEWS hosts the Innovative Design Contest to encourage young engineers, researchers, and students who are creating innovative products, services, and product-services and to show appreciation for their efforts.
Pictured below from left to right are Hyun-Joo Lee, Do-Hoon Kwon, Jong-Ho Jeong, and Hak-Gi Do.
2017.01.03 View 9744
KAIST Undergraduates Win the Innovative Design Contest 2016
A team of KAIST students, consisting of five undergraduates (Do-Hoon Kwon, Tae-Hyun Kim, Hak-Gi Do, Hyun-Joo Lee, and Jong-Ho Jeong) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, won the grand prize at the Innovative Design Contest held at Osaka University in Japan on December 12-13, 2016. The event took place during the 16th Asia Design Engineering Workshop (A-DEWS).
For this year’s contest, a total of ten student teams from such countries as Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and Malaysia participated, and Team KAIST earned the highest scores. The five KAIST students, all taking the course entitled “Production of Creative Systems,” developed a manual wheelchair accessory called “Safe Attachable Wheelchair Assistive Device in Capstone Design (SAWADiCap).
SAWADiCap is a detachable auxiliary power device that increases the range and mobility of manual wheelchairs. The device can easily be installed and removed, compared to existing add-on attachments for wheelchairs. Users can also enjoy similar advantages offered by powered wheelchairs at a lower cost. In their presentation on the device, the KAIST students introduced their design to improve the power of manual wheelchairs employing the magnetic reinforcement effect and to include the safety features necessary for users to install or operate the device.
Do-Hoon Kwon said, “Our team had a great experience participating in the contest—we met people with diverse backgrounds and expanded our understanding in the field.”
Professor Seibum B. Choi of the Mechanical Engineering Department, who advises the KAIST team, added, “I hope our technology can help the spread of affordable wheelchairs and increase mobility for the disabled.”
Established in 2000, A-DEWS is held annually by the Asian branch of the Design Engineering Workshop to provide an international forum for researchers and practitioners in the field of design engineering by facilitating the exchange of recent research results and sharing knowledge about design strategies and methods. This year’s theme for the workshop was “Innovation of Life.”
A-DEWS hosts the Innovative Design Contest to encourage young engineers, researchers, and students who are creating innovative products, services, and product-services and to show appreciation for their efforts.
Pictured below from left to right are Hyun-Joo Lee, Do-Hoon Kwon, Jong-Ho Jeong, and Hak-Gi Do.
2017.01.03 View 9744 -
 KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 10691
KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 10691 -
 EEWS Graduate School Team Receives the S-Oil Best Paper Award
Professor Hyungjun Kim and Dr. He-Young Shin from the EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School at KAIST received the Best Paper Award in Chemistry from S-Oil, a Korean petroleum and refinery company, on November 29, 2016.
Established in 2011, the S-Oil Best Paper Awards are bestowed annually upon ten young scientists in the fields of five basic sciences: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and earth science. The scientists are selected at the recommendation of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the Association of Korean Universities. The awards grant a total of USD 230,000 for research funding.
Dr. Shin, the lead author of the awarded research paper, said, “My research interest has been catalyst studies based on theoretical chemistry. I am pleased to accept this award that will support my studies, and will continue to research catalyst design that can predict parameters and integrate them into catalytic systems.”
Professor Hyungjun Kim (left) and Dr. He-Young Shin (right)
2016.12.23 View 10377
EEWS Graduate School Team Receives the S-Oil Best Paper Award
Professor Hyungjun Kim and Dr. He-Young Shin from the EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School at KAIST received the Best Paper Award in Chemistry from S-Oil, a Korean petroleum and refinery company, on November 29, 2016.
Established in 2011, the S-Oil Best Paper Awards are bestowed annually upon ten young scientists in the fields of five basic sciences: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and earth science. The scientists are selected at the recommendation of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the Association of Korean Universities. The awards grant a total of USD 230,000 for research funding.
Dr. Shin, the lead author of the awarded research paper, said, “My research interest has been catalyst studies based on theoretical chemistry. I am pleased to accept this award that will support my studies, and will continue to research catalyst design that can predict parameters and integrate them into catalytic systems.”
Professor Hyungjun Kim (left) and Dr. He-Young Shin (right)
2016.12.23 View 10377