TE
-
 KAIST-WEF Roundtable on Inclusive Growth and Job Creation
The World Economic Forum (WEF) will join KAIST in an effort to address sweeping global problems in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The two will co-host a roundtable on ‘Shaping Korea’s Priorities for Inclusive Growth and Job Creation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ on October 13 at Lotte Hotel in Seoul.
The roundtable will bring together leaders from government, industry, universities, and non-profit civic organizations to have an in-depth discussion on a thought-provoking agenda of inclusive growth and job creation which scientific and technological changes will bring about. The event will provide a platform to explore practical collaboration and innovative strategies for better job creation and innovation ecosystems.
The two will also sign an MOU for collaboration between the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) of KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
President Sung-Chul Shin of KAIST and the Head of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, will lead the panel discussion titled ‘Inclusive Growth and the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ which will be attended by leaders from government, industry, and non-profit civic organizations.
At the breakout sessions, the topics will be “Future Jobs” and the “Creation of Innovation Ecosystems”. Additionally, a discussion on the “SME 4.0 Initiative”, which is a program pushed forward by KAIST in collaboration with local governments, will talk about job creation through innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The WEF will introduce their two-year activities and research on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which have great potential and a high possibility of successfully undergoing the revolution, to Korea.
Since WEF Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab brought up the topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the WEF has been leading agenda topics and discussions on high-profile matters, including ‘technology-driven but human-centered inclusive growth’ in predicting the future of jobs.
The WEF is a nonprofit organization committed to addressing the world’s weightiest problems. It is best known for its annual meetings in Davos, Switzerland, which attracts leaders from around the world. KAIST has been participating in this summit since 2009. President Shin will also attend the upcoming Davos summit next January. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee who heads the KAIST Institute and the FIRIC is the co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the WEF.
Moreover, President Shin and Mr. Sonmez will explain the background of the roundtable and share the results of the sessions at a joint news conference.
2017.09.28 View 11393
KAIST-WEF Roundtable on Inclusive Growth and Job Creation
The World Economic Forum (WEF) will join KAIST in an effort to address sweeping global problems in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The two will co-host a roundtable on ‘Shaping Korea’s Priorities for Inclusive Growth and Job Creation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ on October 13 at Lotte Hotel in Seoul.
The roundtable will bring together leaders from government, industry, universities, and non-profit civic organizations to have an in-depth discussion on a thought-provoking agenda of inclusive growth and job creation which scientific and technological changes will bring about. The event will provide a platform to explore practical collaboration and innovative strategies for better job creation and innovation ecosystems.
The two will also sign an MOU for collaboration between the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) of KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
President Sung-Chul Shin of KAIST and the Head of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, will lead the panel discussion titled ‘Inclusive Growth and the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ which will be attended by leaders from government, industry, and non-profit civic organizations.
At the breakout sessions, the topics will be “Future Jobs” and the “Creation of Innovation Ecosystems”. Additionally, a discussion on the “SME 4.0 Initiative”, which is a program pushed forward by KAIST in collaboration with local governments, will talk about job creation through innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The WEF will introduce their two-year activities and research on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which have great potential and a high possibility of successfully undergoing the revolution, to Korea.
Since WEF Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab brought up the topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the WEF has been leading agenda topics and discussions on high-profile matters, including ‘technology-driven but human-centered inclusive growth’ in predicting the future of jobs.
The WEF is a nonprofit organization committed to addressing the world’s weightiest problems. It is best known for its annual meetings in Davos, Switzerland, which attracts leaders from around the world. KAIST has been participating in this summit since 2009. President Shin will also attend the upcoming Davos summit next January. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee who heads the KAIST Institute and the FIRIC is the co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the WEF.
Moreover, President Shin and Mr. Sonmez will explain the background of the roundtable and share the results of the sessions at a joint news conference.
2017.09.28 View 11393 -
 Sangeun Oh Recognized as a 2017 Google Fellow
Sangeun Oh, a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Computing was selected as a Google PhD Fellow in 2017. He is one of 47 awardees of the Google PhD Fellowship in the world.
The Google PhD Fellowship awards students showing outstanding performance in the field of computer science and related research. Since being established in 2009, the program has provided various benefits, including scholarships worth $10,000 USD and one-to-one research discussion with mentors from Google.
His research work on a mobile system that allows interactions among various kinds of smart devices was recognized in the field of mobile computing. He developed a mobile platform that allows smart devices to share diverse functions, including logins, payments, and sensors. This technology provides numerous user experiences that existing mobile platforms could not offer. Through cross-device functionality sharing, users can utilize multiple smart devices in a more convenient manner. The research was presented at The Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys) of the Association for Computing Machinery in July, 2017.
Oh said, “I would like to express my gratitude to my advisor, the professors in the School of Computing, and my lab colleagues. I will devote myself to carrying out more research in order to contribute to society.”
His advisor, Insik Shin, a professor in the School of Computing said, “Being recognized as a Google PhD Fellow is an honor to both the student as well as KAIST. I strongly anticipate and believe that Oh will make the next step by carrying out good quality research.”
2017.09.27 View 14245
Sangeun Oh Recognized as a 2017 Google Fellow
Sangeun Oh, a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Computing was selected as a Google PhD Fellow in 2017. He is one of 47 awardees of the Google PhD Fellowship in the world.
The Google PhD Fellowship awards students showing outstanding performance in the field of computer science and related research. Since being established in 2009, the program has provided various benefits, including scholarships worth $10,000 USD and one-to-one research discussion with mentors from Google.
His research work on a mobile system that allows interactions among various kinds of smart devices was recognized in the field of mobile computing. He developed a mobile platform that allows smart devices to share diverse functions, including logins, payments, and sensors. This technology provides numerous user experiences that existing mobile platforms could not offer. Through cross-device functionality sharing, users can utilize multiple smart devices in a more convenient manner. The research was presented at The Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys) of the Association for Computing Machinery in July, 2017.
Oh said, “I would like to express my gratitude to my advisor, the professors in the School of Computing, and my lab colleagues. I will devote myself to carrying out more research in order to contribute to society.”
His advisor, Insik Shin, a professor in the School of Computing said, “Being recognized as a Google PhD Fellow is an honor to both the student as well as KAIST. I strongly anticipate and believe that Oh will make the next step by carrying out good quality research.”
2017.09.27 View 14245 -
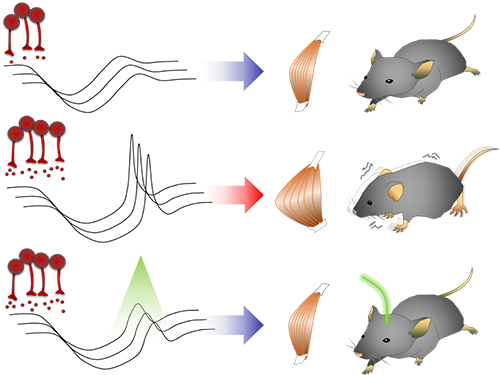 Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11415
Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11415 -
 Humicotta Wins the Silver Prize at the 2017 IDEA
The 3D-printed ceramic humidifier made by the research team led by Professor Sang-Min Bae won the silver prize at the 2017 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Professor Bae’s ID+IM team was also listed as winners of three more appropriate technology designs at the IDEA. The awards, sponsored by the Industrial Designers Society of America, are one of the three prestigious design awards including the Red Dot Design Award and the iF Design Award in Germany.
The silver prize winner in the category of home and bath, Humicotta is an energy-efficient, bacteria free, and easy to clean humidifier. It includes a base module and filter. The base is a cylindrical pedestal with a built-in fan on which the filter is placed. The filter is a 3D-printed honeycomb structure made of diatomite. When water is added, the honeycomb structure and porous terracotta maximize natural humidification. It also offers an open platform service that customizes the filters or provides files that users can use their own 3D printer.
Professor Bae’s team has worked on philanthropy design using appropriate technology as their main topic for years. Their designs have been recognized at prestigious global design awards events, winning more than 50 prizes with innovative designs made for addressing various global and social problems.
The Light Funnel is a novel type of lighting device designed for off-grid areas of Africa. It helps to maximize the natural light effect in the daytime without any drastic home renovations. It consists of a transparent acrylic sphere and a reflective pathway. After filling the acrylic sphere with water and placing it on a rooftop, sunlight passes into the house through the water inside the sphere. It provides a lighted environment nine times brighter than without it. Also, once installed, it can be used almost permanently.
The Maasai Smart Cane is made using wood sticks purchased through fair trade with the Maasai tribe. GPS is installed into the grip of the birch-tree cane, so that cane users can send a signal when in an emergency situation. All of the proceeds of this product go to the tribe.
S.Cone is a first aid kit made in collaboration with Samsung Fire and Marine Insurance. The traffic cone-shaped kit is designed to help users handle an emergency situation intact and safe. The S.Cone has unique versions for fires, car accidents, and marine accidents. For example, the S.Cone for fires is equipped with a small fire extinguisher, smoke mask, and fire blanket. The cap of the S.Cone also functions as an IoT station connecting the fire and gas detector with smart phones.
Professor Bae said of his team’s winning design products, “By making the data public, any person can design their own humidifier if they have access to a 3D-printer. We want it to be a very accessible product for the public. The Light Funnel and Maasai Smart Cane are designed for economically-marginalized populations and the elderly. We will continue to make the best designed products serving the marginalized 90% of the population around the world.”
2017.09.14 View 28992
Humicotta Wins the Silver Prize at the 2017 IDEA
The 3D-printed ceramic humidifier made by the research team led by Professor Sang-Min Bae won the silver prize at the 2017 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). Professor Bae’s ID+IM team was also listed as winners of three more appropriate technology designs at the IDEA. The awards, sponsored by the Industrial Designers Society of America, are one of the three prestigious design awards including the Red Dot Design Award and the iF Design Award in Germany.
The silver prize winner in the category of home and bath, Humicotta is an energy-efficient, bacteria free, and easy to clean humidifier. It includes a base module and filter. The base is a cylindrical pedestal with a built-in fan on which the filter is placed. The filter is a 3D-printed honeycomb structure made of diatomite. When water is added, the honeycomb structure and porous terracotta maximize natural humidification. It also offers an open platform service that customizes the filters or provides files that users can use their own 3D printer.
Professor Bae’s team has worked on philanthropy design using appropriate technology as their main topic for years. Their designs have been recognized at prestigious global design awards events, winning more than 50 prizes with innovative designs made for addressing various global and social problems.
The Light Funnel is a novel type of lighting device designed for off-grid areas of Africa. It helps to maximize the natural light effect in the daytime without any drastic home renovations. It consists of a transparent acrylic sphere and a reflective pathway. After filling the acrylic sphere with water and placing it on a rooftop, sunlight passes into the house through the water inside the sphere. It provides a lighted environment nine times brighter than without it. Also, once installed, it can be used almost permanently.
The Maasai Smart Cane is made using wood sticks purchased through fair trade with the Maasai tribe. GPS is installed into the grip of the birch-tree cane, so that cane users can send a signal when in an emergency situation. All of the proceeds of this product go to the tribe.
S.Cone is a first aid kit made in collaboration with Samsung Fire and Marine Insurance. The traffic cone-shaped kit is designed to help users handle an emergency situation intact and safe. The S.Cone has unique versions for fires, car accidents, and marine accidents. For example, the S.Cone for fires is equipped with a small fire extinguisher, smoke mask, and fire blanket. The cap of the S.Cone also functions as an IoT station connecting the fire and gas detector with smart phones.
Professor Bae said of his team’s winning design products, “By making the data public, any person can design their own humidifier if they have access to a 3D-printer. We want it to be a very accessible product for the public. The Light Funnel and Maasai Smart Cane are designed for economically-marginalized populations and the elderly. We will continue to make the best designed products serving the marginalized 90% of the population around the world.”
2017.09.14 View 28992 -
 Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10650
Professor Jin Woo Kim Wins the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award
Professor Jin Woo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST received the 14th Macrogen Scientist Award at the 2017 KSMCB International Conference held in COEX on September 12, 2017.
The award is given by the Korean Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology (KSMCB) and sponsored by Macrogen, a service provider of genome research. The award was established in 2004 to recognize biological scientists who have accomplished excellent performance in the field of basic life sciences.
Professor Kim has achieved outstanding research performances on nerve development, such as identifying the cause of senile retinal degenerative disease and finding retinal nerve cells that distinguish light and darkness in dark conditions.
Recently, he discovered intercellular communication, which controls the development of retinal neurons. His findings have contributed to addressing the principles of maintenance and regeneration of retinal neurons.
Since joining KAIST, he has presented approximately 20 papers and published in numerous international journals including Cell Reports, Genes and Development, and EMBO Journal. Moreover, he delivered special lectures at international conferences, universities, and institutes around the world.
2017.09.14 View 10650 -
 Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems Opens
(Distinguished guests including President Shin (fourth from the right) and Director Lee (third from left) at the opening ceremony)
The Research Center for a Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems was recently established at KAIST with the purpose of taking the lead in developing fundamental and applicable technology for submerged floating tunnels as well as fostering creative and talented people. Haeng-Ki Lee, a professor in the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering at KAIST is heading the center.
KAIST held its opening ceremony on September 7, 2017 in the Applied Engineering Building located on the main campus.
Distinguished guests, including KAIST president Sung-Chul Shin, the President of the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology Gi-Hoon Hong, the President of the Korean Society of Civil Engineering Young-Seok Park, and the Director in the Division of Engineering at the National Research Foundation of Korea Joong-Kon Park attended the ceremony.
The National Research Foundation of Korea provides Engineering Research Center (ERC) projects which find and foster groups with outstanding research performance in a field of engineering. The projects support these groups so that they can strengthen their global competitiveness while enhancing national competence in basic research.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ was selected as one of the ERC projects in 2017. For the next seven years, the research center will work to develop a submerged floating tunnel system resistant depths greater than 100 meters.
To achieve its goal, the center has defined crucial research topics including: i) a structural analysis program and integrated design technology specific for submerged floating tunnel systems, ii) high-durability marine construction materials and submerged construction integrated systems, and iii) safety and maintenance integrated technology for smart submerged floating tunnel systems.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ will devote itself to developing a variety of fundamental and applicable technology that will be leading global maritime construction. Moreover, it will concentrate on fostering professional research manpower in related areas.
The Director of the Center Lee said, “The center will cooperate with KAIST researchers who are experts in various fields, including structures, materials, construction, and maritime research. Based on this collaboration, the center will contribute to achieving autonomous technologies by developing fundamental and applicable technology related with submerged floating tunnel systems. It will also take the role of a leading global research hub in the field of submerged floating tunnels as well as construction technologies.”
2017.09.07 View 11152
Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems Opens
(Distinguished guests including President Shin (fourth from the right) and Director Lee (third from left) at the opening ceremony)
The Research Center for a Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems was recently established at KAIST with the purpose of taking the lead in developing fundamental and applicable technology for submerged floating tunnels as well as fostering creative and talented people. Haeng-Ki Lee, a professor in the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering at KAIST is heading the center.
KAIST held its opening ceremony on September 7, 2017 in the Applied Engineering Building located on the main campus.
Distinguished guests, including KAIST president Sung-Chul Shin, the President of the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology Gi-Hoon Hong, the President of the Korean Society of Civil Engineering Young-Seok Park, and the Director in the Division of Engineering at the National Research Foundation of Korea Joong-Kon Park attended the ceremony.
The National Research Foundation of Korea provides Engineering Research Center (ERC) projects which find and foster groups with outstanding research performance in a field of engineering. The projects support these groups so that they can strengthen their global competitiveness while enhancing national competence in basic research.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ was selected as one of the ERC projects in 2017. For the next seven years, the research center will work to develop a submerged floating tunnel system resistant depths greater than 100 meters.
To achieve its goal, the center has defined crucial research topics including: i) a structural analysis program and integrated design technology specific for submerged floating tunnel systems, ii) high-durability marine construction materials and submerged construction integrated systems, and iii) safety and maintenance integrated technology for smart submerged floating tunnel systems.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ will devote itself to developing a variety of fundamental and applicable technology that will be leading global maritime construction. Moreover, it will concentrate on fostering professional research manpower in related areas.
The Director of the Center Lee said, “The center will cooperate with KAIST researchers who are experts in various fields, including structures, materials, construction, and maritime research. Based on this collaboration, the center will contribute to achieving autonomous technologies by developing fundamental and applicable technology related with submerged floating tunnel systems. It will also take the role of a leading global research hub in the field of submerged floating tunnels as well as construction technologies.”
2017.09.07 View 11152 -
 Hyosung R&DB Labs to Teach Special Class on High Molecule Chemistry for the Fall Semester
The Department of Chemistry in collaboration with the Hyosung Group’s R&DB Labs will open a ‘special class on high molecule chemistry’ for Masters and Ph.D. candidates. The class, led by researchers at Hyosung’s R&D think tank, will provide the latest market and technology trends in the molecule chemical industry during the fall semester.
Hyosung joined this special industry program in an effort to enhance students’ hands-on understanding of new technologies that will emerge in the global market. During the semester, Hyosung plans to present the technology portfolios on their brand new materials of TAC film, membrane, and carbon fiber as well as the existing products leading the world in market share such as spandex, tire cords.
Hyosung plans to recruit students who previously took courses led by Hyosung researchers. President Tu-Won Chang of Hyosung R&DB said, “This program is designed to foster highly qualified R&D personnel especially catering to our company’s needs and market demands. We will continue to share our company’s market analysis and R&D know-how with outstanding universities.
2017.09.07 View 5966
Hyosung R&DB Labs to Teach Special Class on High Molecule Chemistry for the Fall Semester
The Department of Chemistry in collaboration with the Hyosung Group’s R&DB Labs will open a ‘special class on high molecule chemistry’ for Masters and Ph.D. candidates. The class, led by researchers at Hyosung’s R&D think tank, will provide the latest market and technology trends in the molecule chemical industry during the fall semester.
Hyosung joined this special industry program in an effort to enhance students’ hands-on understanding of new technologies that will emerge in the global market. During the semester, Hyosung plans to present the technology portfolios on their brand new materials of TAC film, membrane, and carbon fiber as well as the existing products leading the world in market share such as spandex, tire cords.
Hyosung plans to recruit students who previously took courses led by Hyosung researchers. President Tu-Won Chang of Hyosung R&DB said, “This program is designed to foster highly qualified R&D personnel especially catering to our company’s needs and market demands. We will continue to share our company’s market analysis and R&D know-how with outstanding universities.
2017.09.07 View 5966 -
 KAIST Partners with Technion and Hyundai Motors for Future Mobility Technology Development
(KAIST Associate Vice President of Research Joung-Ho Kim(third from left) poses with Technion President Pereta Lavie and CTO Tae Won Im of Hyundai Motors)
KAIST has partnered with the Israel Institute of Technology, Technion, and Hyundai Motors to take the lead in the field of future mobility technologies. The three parties signed a consortium of global alliance for future mobility partnership at Technion on Sept. 5. KAIST Associate Vice President of Research Kim Joung-Ho, Hyundai Motor’s Central Advanced Research and Engineering CTO Tae Won Lim, and Technion President Peretz Lavie signed the MOU.
The three parties agreed to conduct joint research on hi-tech mobility areas including self-driving systems, cyber security, and AI in mobility. With the signing of the consortium, KAIST's technology in AI, semiconductors, and autonomous cars will produce synergy with Technion’s connected car solutions, advancing Hyundai Motor's competitiveness in the future mobility market.
In addition to the consortium, the three parties will set-up a startup consulting committee, which will provide consulting services for nurturing venture startups with creative ideas and outstanding technological prowess in their host countries.
2017.09.07 View 7357
KAIST Partners with Technion and Hyundai Motors for Future Mobility Technology Development
(KAIST Associate Vice President of Research Joung-Ho Kim(third from left) poses with Technion President Pereta Lavie and CTO Tae Won Im of Hyundai Motors)
KAIST has partnered with the Israel Institute of Technology, Technion, and Hyundai Motors to take the lead in the field of future mobility technologies. The three parties signed a consortium of global alliance for future mobility partnership at Technion on Sept. 5. KAIST Associate Vice President of Research Kim Joung-Ho, Hyundai Motor’s Central Advanced Research and Engineering CTO Tae Won Lim, and Technion President Peretz Lavie signed the MOU.
The three parties agreed to conduct joint research on hi-tech mobility areas including self-driving systems, cyber security, and AI in mobility. With the signing of the consortium, KAIST's technology in AI, semiconductors, and autonomous cars will produce synergy with Technion’s connected car solutions, advancing Hyundai Motor's competitiveness in the future mobility market.
In addition to the consortium, the three parties will set-up a startup consulting committee, which will provide consulting services for nurturing venture startups with creative ideas and outstanding technological prowess in their host countries.
2017.09.07 View 7357 -
 KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 8393
KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 8393 -
 Professor Dae-Sik Im to Head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office at the Ministry of Science & ICT
(Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences)
Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences, a renowned molecular cell biologist, was named to head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office in the Ministry of Science and ICT on August 31. He will be responsible for the oversight of national R&D projects as well as budget deliberation. Joining the KAIST faculty in 2002, he led the Creative Research Center of Cell Division and Differentiation at KAIST.
Announcing the nomination of Professor Im, Cheong Wa Dae spokesman Park Soo-Hyun said, “Professor Im will be the best person to lead the innovation of the research infrastructure system for basic research studies. We believe that his expertise and leadership will make a significant impact in enhancing the nation’s science and technology competitiveness. This vice minister position in the Ministry of Science and ICT was newly created in an effort to enhance national science and technology initiatives by President Moon Jae-In.
Professor Im said at the news conference, “I would like to make a sustainable, as well as credible, system ensuring the ingenuity of scientists in Korean labs. To this end, I will make every effort to enhance Korea’s innovative research environment in a way to maximize research achievements.”
2017.09.03 View 10576
Professor Dae-Sik Im to Head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office at the Ministry of Science & ICT
(Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences)
Professor Dae-Sik Im of the Department of Biological Sciences, a renowned molecular cell biologist, was named to head the Science, Technology and Innovation Office in the Ministry of Science and ICT on August 31. He will be responsible for the oversight of national R&D projects as well as budget deliberation. Joining the KAIST faculty in 2002, he led the Creative Research Center of Cell Division and Differentiation at KAIST.
Announcing the nomination of Professor Im, Cheong Wa Dae spokesman Park Soo-Hyun said, “Professor Im will be the best person to lead the innovation of the research infrastructure system for basic research studies. We believe that his expertise and leadership will make a significant impact in enhancing the nation’s science and technology competitiveness. This vice minister position in the Ministry of Science and ICT was newly created in an effort to enhance national science and technology initiatives by President Moon Jae-In.
Professor Im said at the news conference, “I would like to make a sustainable, as well as credible, system ensuring the ingenuity of scientists in Korean labs. To this end, I will make every effort to enhance Korea’s innovative research environment in a way to maximize research achievements.”
2017.09.03 View 10576 -
 International Students Start a New Semester at KAIST
(International students during a campus tour)
The 2017 fall semester began on August 28 and new and returning students are filling the campus. Our international students are one of the reasons the campus is becoming more dynamic and energetic.
It was easy to see groups of smiling international students walking around the campus. Every semester, KAIST welcomes hundreds of students from around the world to give them the opportunity to study at a world-leading university in science and technology.
This semester, approximately 150 students in degree-seeking programs and 220 exchange students from a total of 74 countries, including Germany, the United States, and France entered KAIST.
(Frederik Hansen, a student from DTU)
Frederik Hansen is an exchange student who came to KAIST this semester from Copenhagen, Denmark. He completed the undergraduate program at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) and is now pursuing a master’s degree.
He decided to join KAIST because he felt the university is up-to-date with subjects in his field of interest.
Frederik, who majored in mechanical engineering, looks forward taking classes related to robotics and solid mechanics. Noting that it’s his first time visiting Asia, he hopes to experience and learn about Korean culture.
In an effort to help foreign students’ soft landing in KAIST, the International Office held a series of orientation programs over three days. The buddy program provides international freshmen with an opportunity to make Korean friends for a more successful life at KAIST, while giving domestic students a chance to learn about different cultures and perhaps build on the global capacity required for becoming a global leader. Information sessions also provided educational information that can support international students living in KAIST. Finally, the counseling program gives information about the KAIST counseling center and ISSS (International Scholar and Student Service). It provides a psychometric test service to those who wish to take it.
If you are interested in pursuing academic programs at KAIST, please visit the International Office via http://io.kaist.ac.kr/index.do .
2017.08.30 View 7442
International Students Start a New Semester at KAIST
(International students during a campus tour)
The 2017 fall semester began on August 28 and new and returning students are filling the campus. Our international students are one of the reasons the campus is becoming more dynamic and energetic.
It was easy to see groups of smiling international students walking around the campus. Every semester, KAIST welcomes hundreds of students from around the world to give them the opportunity to study at a world-leading university in science and technology.
This semester, approximately 150 students in degree-seeking programs and 220 exchange students from a total of 74 countries, including Germany, the United States, and France entered KAIST.
(Frederik Hansen, a student from DTU)
Frederik Hansen is an exchange student who came to KAIST this semester from Copenhagen, Denmark. He completed the undergraduate program at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) and is now pursuing a master’s degree.
He decided to join KAIST because he felt the university is up-to-date with subjects in his field of interest.
Frederik, who majored in mechanical engineering, looks forward taking classes related to robotics and solid mechanics. Noting that it’s his first time visiting Asia, he hopes to experience and learn about Korean culture.
In an effort to help foreign students’ soft landing in KAIST, the International Office held a series of orientation programs over three days. The buddy program provides international freshmen with an opportunity to make Korean friends for a more successful life at KAIST, while giving domestic students a chance to learn about different cultures and perhaps build on the global capacity required for becoming a global leader. Information sessions also provided educational information that can support international students living in KAIST. Finally, the counseling program gives information about the KAIST counseling center and ISSS (International Scholar and Student Service). It provides a psychometric test service to those who wish to take it.
If you are interested in pursuing academic programs at KAIST, please visit the International Office via http://io.kaist.ac.kr/index.do .
2017.08.30 View 7442 -
 Professor Dan Keun Sung Endows Scholarship in Honor of His Retirement
Professor Dan Keun Sung in the School of Electrical Engineering contributed a 100 million KRW scholarship fund this month to KAIST to mark his retirement after more than three decades of work.
“As my retirement date comes closer, I have been thinking about what I could do for the school. I wanted to leave something behind, even though it’s small, for my lifelong school and students. I am hoping that this scholarship fund will benefit the members of KAIST.”
This isn’t his first time making a donation to KAIST. In 2013, Professor Sung donated ten million KRW, which was his cash prize from the 9th Haedong Academic Award of The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS). At that time, Professor Sung had the chance to create a scholarship fund in his name; however, he wanted to highlight that the scholarship fund was for ‘someone,’ not created by ‘someone.’ In that sense, his scholarship fund was created with no name to benefit students in the School of Electrical Engineering. His colleagues and students supported his idea. Professor Seonghwan Cho, students, and alumni also participated in fund raising efforts, which reached 55 million KRW in total.
Professor Sung emphasized, “Donations should always be remembered, no matter how small they are.” He then explained his purpose for creating the scholarship fund by saying, “Fundraising can be truly meaningful to contributors, knowing that their money is going to supporting the school and students.”
Professor Sung, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Communication Society, started his post at KAIST in 1986. For the past 30 years, he has devoted himself to fostering young scholars and studying in the area of information and communication. He also participated in developing technologies for the resource management of various future cellular components, such as satellites, switchboards, and signaling networks.
2017.08.11 View 10702
Professor Dan Keun Sung Endows Scholarship in Honor of His Retirement
Professor Dan Keun Sung in the School of Electrical Engineering contributed a 100 million KRW scholarship fund this month to KAIST to mark his retirement after more than three decades of work.
“As my retirement date comes closer, I have been thinking about what I could do for the school. I wanted to leave something behind, even though it’s small, for my lifelong school and students. I am hoping that this scholarship fund will benefit the members of KAIST.”
This isn’t his first time making a donation to KAIST. In 2013, Professor Sung donated ten million KRW, which was his cash prize from the 9th Haedong Academic Award of The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS). At that time, Professor Sung had the chance to create a scholarship fund in his name; however, he wanted to highlight that the scholarship fund was for ‘someone,’ not created by ‘someone.’ In that sense, his scholarship fund was created with no name to benefit students in the School of Electrical Engineering. His colleagues and students supported his idea. Professor Seonghwan Cho, students, and alumni also participated in fund raising efforts, which reached 55 million KRW in total.
Professor Sung emphasized, “Donations should always be remembered, no matter how small they are.” He then explained his purpose for creating the scholarship fund by saying, “Fundraising can be truly meaningful to contributors, knowing that their money is going to supporting the school and students.”
Professor Sung, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Communication Society, started his post at KAIST in 1986. For the past 30 years, he has devoted himself to fostering young scholars and studying in the area of information and communication. He also participated in developing technologies for the resource management of various future cellular components, such as satellites, switchboards, and signaling networks.
2017.08.11 View 10702