Sang+Yup+Lee
-
 A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 11338
A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 11338 -
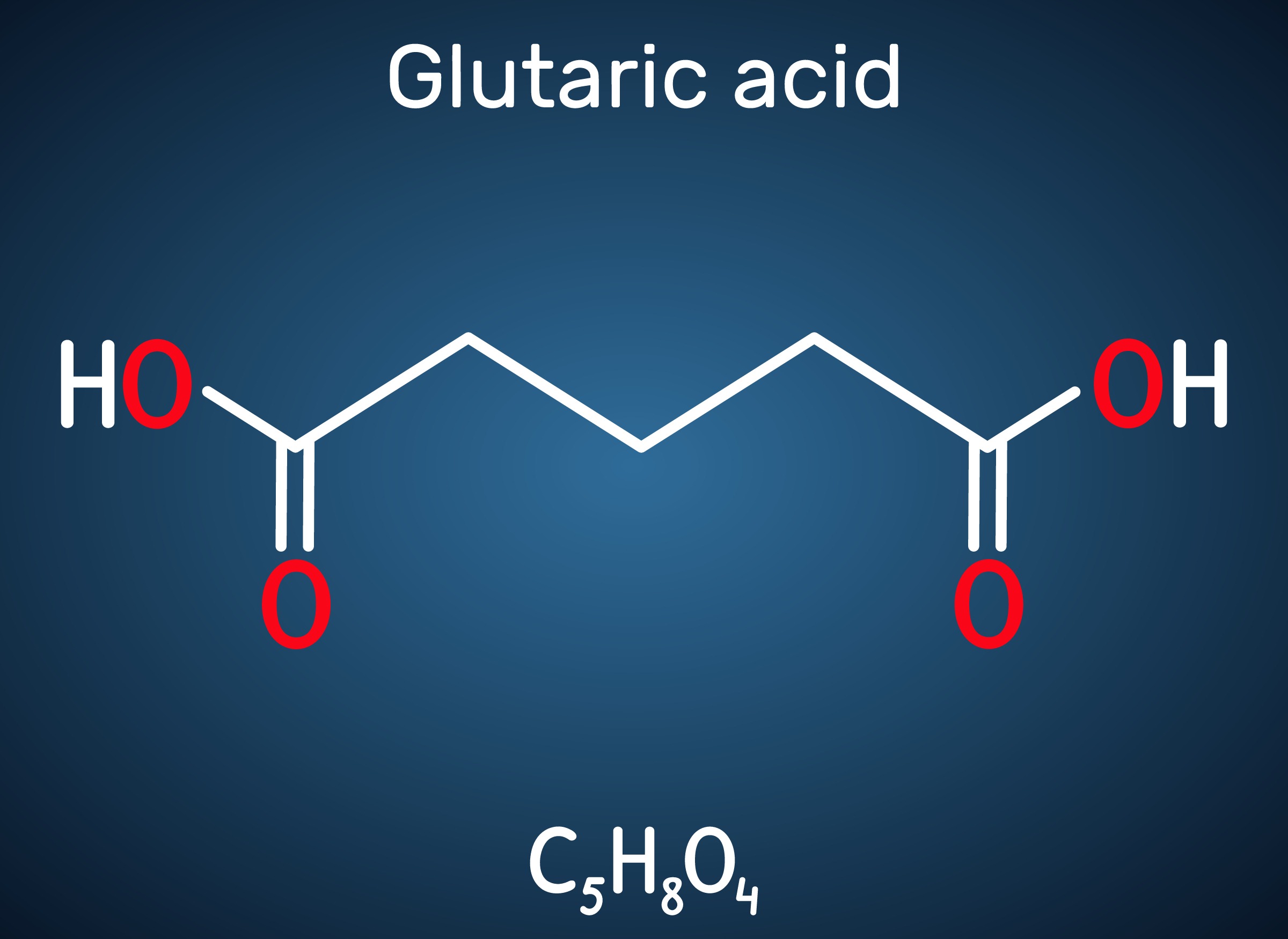 Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 7645
Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 7645 -
 Experts to Help Asia Navigate the Post-COVID-19 and 4IR Eras
Risk Quotient 2020, an international conference co-hosted by KAIST and the National University of Singapore (NUS), will bring together world-leading experts from academia and industry to help Asia navigate the post-COVID-19 and Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) eras.
The online conference will be held on October 29 from 10 a.m. Korean time under the theme “COVID-19 Pandemic and A Brave New World”. It will be streamed live on YouTube at https://www.youtube.com/c/KAISTofficial and https://www.youtube.com/user/NUScast.
The Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) at KAIST organized this conference in collaboration with the Lloyd's Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk (IPUR) at NUS.
During the conference, global leaders will examine the socioeconomic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on areas including digital innovation, education, the workforce, and the economy. They will then highlight digital and 4IR technologies that could be utilized to effectively mitigate the risks and challenges associated with the pandemic, while harnessing the opportunities that these socioeconomic effects may present. Their discussions will mainly focus on the Asian region.
In his opening remarks, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin will express his appreciation for the Asian populations’ greater trust in and compliance with their governments, which have given the continent a leg up against the coronavirus. He will then emphasize that by working together through the exchange of ideas and global collaboration, we will be able to shape ‘a brave new world’ to better humanity. Welcoming remarks by Prof. Sang Yup Lee (Dean, KAIST Institutes) and Prof. Tze Yun Leong (Director, AI Technology at AI Singapore) will follow.
For the keynote speech, Prof. Lan Xue (Dean, Schwarzman College, Tsinghua University) will share China’s response to COVID-19 and lessons for crisis management. Prof. Danny Quah (Dean, Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, NUS) will present possible ways to overcome these difficult times. Dr. Kak-Soo Shin (Senior Advisor, Shin & Kim LLC, Former Ambassador to the State of Israel and Japan, and Former First and Second Vice Minister of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Korea) will stress the importance of the international community’s solidarity to ensure peace, prosperity, and safety in this new era.
Panel Session I will address the impact of COVID-19 on digital innovation. Dr. Carol Soon (Senior Research Fellow, Institute of Policy Studies, NUS) will present her interpretation of recent technological developments as both opportunities for our society as a whole and challenges for vulnerable groups such as low-income families. Dr. Christopher SungWook Chang (Managing Director, Kakao Mobility) will show how changes in mobility usage patterns can be captured by Kakao Mobility’s big data analysis. He will illustrate how the data can be used to interpret citizen’s behaviors and how risks can be transformed into opportunities by utilizing technology. Mr. Steve Ledzian’s (Vice President, Chief Technology Officer, FireEye) talk will discuss the dangers caused by threat actors and other cyber risk implications of COVID-19. Dr. June Sung Park (Chairman, Korea Software Technology Association (KOSTA)) will share how COVID-19 has accelerated digital transformations across all industries and why software education should be reformed to improve Korea’s competitiveness.
Panel Session II will examine the impact on education and the workforce. Dr. Sang-Jin Ban (President, Korean Educational Development Institute (KEDI)) will explain Korea’s educational response to the pandemic and the concept of “blended learning” as a new paradigm, and present both positive and negative impacts of online education on students’ learning experiences. Prof. Reuben Ng (Professor, Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, NUS) will present on graduate underemployment, which seems to have worsened during COVID-19. Dr. Michael Fung’s presentation (Deputy Chief Executive (Industry), SkillsFuture SG) will introduce the promotion of lifelong learning in Singapore through a new national initiative known as the ‘SkillsFuture Movement’. This movement serves as an example of a national response to disruptions in the job market and the pace of skills obsolescence triggered by AI and COVID-19.
Panel Session III will touch on technology leadership and Asia’s digital economy and society. Prof. Naubahar Sharif (Professor, Division of Social Science and Division of Public Policy, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)) will share his views on the potential of China in taking over global technological leadership based on its massive domestic market, its government support, and the globalization process. Prof. Yee Kuang Heng (Professor, Graduate School of Public Policy, University of Tokyo) will illustrate how different legal and political needs in China and Japan have shaped the ways technologies have been deployed in responding to COVID-19. Dr. Hayun Kang (Head, International Cooperation Research Division, Korea Information Society Development Institute (KISDI)) will explain Korea’s relative success containing the pandemic compared to other countries, and how policy leaders and institutions that embrace digital technologies in the pursuit of public welfare objectives can produce positive outcomes while minimizing the side effects.
Prof. Kyung Ryul Park (Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, KAIST) will be hosting the entire conference, whereas Prof. Alice Hae Yun Oh (Director, MARS Artificial Intelligence Research Center, KAIST), Prof. Wonjoon Kim (Dean, Graduate School of Innovation and Technology Management, College of Business, KAIST), Prof. Youngsun Kwon (Dean, KAIST Academy), and Prof. Taejun Lee (Korea Development Institute (KDI) School of Public Policy and Management) are to chair discussions with the keynote speakers and panelists.
Closing remarks will be delivered by Prof. Chan Ghee Koh (Director, NUS IPUR), Prof. So Young Kim (Director, KAIST KPC4IR), and Prof. Joungho Kim (Director, KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI)).
“This conference is expected to serve as a springboard to help Asian countries recover from global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic through active cooperation and joint engagement among scholars, experts, and policymakers,” according to Director So Young Kim.
(END)
2020.10.22 View 15201
Experts to Help Asia Navigate the Post-COVID-19 and 4IR Eras
Risk Quotient 2020, an international conference co-hosted by KAIST and the National University of Singapore (NUS), will bring together world-leading experts from academia and industry to help Asia navigate the post-COVID-19 and Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) eras.
The online conference will be held on October 29 from 10 a.m. Korean time under the theme “COVID-19 Pandemic and A Brave New World”. It will be streamed live on YouTube at https://www.youtube.com/c/KAISTofficial and https://www.youtube.com/user/NUScast.
The Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) at KAIST organized this conference in collaboration with the Lloyd's Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk (IPUR) at NUS.
During the conference, global leaders will examine the socioeconomic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on areas including digital innovation, education, the workforce, and the economy. They will then highlight digital and 4IR technologies that could be utilized to effectively mitigate the risks and challenges associated with the pandemic, while harnessing the opportunities that these socioeconomic effects may present. Their discussions will mainly focus on the Asian region.
In his opening remarks, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin will express his appreciation for the Asian populations’ greater trust in and compliance with their governments, which have given the continent a leg up against the coronavirus. He will then emphasize that by working together through the exchange of ideas and global collaboration, we will be able to shape ‘a brave new world’ to better humanity. Welcoming remarks by Prof. Sang Yup Lee (Dean, KAIST Institutes) and Prof. Tze Yun Leong (Director, AI Technology at AI Singapore) will follow.
For the keynote speech, Prof. Lan Xue (Dean, Schwarzman College, Tsinghua University) will share China’s response to COVID-19 and lessons for crisis management. Prof. Danny Quah (Dean, Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, NUS) will present possible ways to overcome these difficult times. Dr. Kak-Soo Shin (Senior Advisor, Shin & Kim LLC, Former Ambassador to the State of Israel and Japan, and Former First and Second Vice Minister of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Korea) will stress the importance of the international community’s solidarity to ensure peace, prosperity, and safety in this new era.
Panel Session I will address the impact of COVID-19 on digital innovation. Dr. Carol Soon (Senior Research Fellow, Institute of Policy Studies, NUS) will present her interpretation of recent technological developments as both opportunities for our society as a whole and challenges for vulnerable groups such as low-income families. Dr. Christopher SungWook Chang (Managing Director, Kakao Mobility) will show how changes in mobility usage patterns can be captured by Kakao Mobility’s big data analysis. He will illustrate how the data can be used to interpret citizen’s behaviors and how risks can be transformed into opportunities by utilizing technology. Mr. Steve Ledzian’s (Vice President, Chief Technology Officer, FireEye) talk will discuss the dangers caused by threat actors and other cyber risk implications of COVID-19. Dr. June Sung Park (Chairman, Korea Software Technology Association (KOSTA)) will share how COVID-19 has accelerated digital transformations across all industries and why software education should be reformed to improve Korea’s competitiveness.
Panel Session II will examine the impact on education and the workforce. Dr. Sang-Jin Ban (President, Korean Educational Development Institute (KEDI)) will explain Korea’s educational response to the pandemic and the concept of “blended learning” as a new paradigm, and present both positive and negative impacts of online education on students’ learning experiences. Prof. Reuben Ng (Professor, Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, NUS) will present on graduate underemployment, which seems to have worsened during COVID-19. Dr. Michael Fung’s presentation (Deputy Chief Executive (Industry), SkillsFuture SG) will introduce the promotion of lifelong learning in Singapore through a new national initiative known as the ‘SkillsFuture Movement’. This movement serves as an example of a national response to disruptions in the job market and the pace of skills obsolescence triggered by AI and COVID-19.
Panel Session III will touch on technology leadership and Asia’s digital economy and society. Prof. Naubahar Sharif (Professor, Division of Social Science and Division of Public Policy, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)) will share his views on the potential of China in taking over global technological leadership based on its massive domestic market, its government support, and the globalization process. Prof. Yee Kuang Heng (Professor, Graduate School of Public Policy, University of Tokyo) will illustrate how different legal and political needs in China and Japan have shaped the ways technologies have been deployed in responding to COVID-19. Dr. Hayun Kang (Head, International Cooperation Research Division, Korea Information Society Development Institute (KISDI)) will explain Korea’s relative success containing the pandemic compared to other countries, and how policy leaders and institutions that embrace digital technologies in the pursuit of public welfare objectives can produce positive outcomes while minimizing the side effects.
Prof. Kyung Ryul Park (Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, KAIST) will be hosting the entire conference, whereas Prof. Alice Hae Yun Oh (Director, MARS Artificial Intelligence Research Center, KAIST), Prof. Wonjoon Kim (Dean, Graduate School of Innovation and Technology Management, College of Business, KAIST), Prof. Youngsun Kwon (Dean, KAIST Academy), and Prof. Taejun Lee (Korea Development Institute (KDI) School of Public Policy and Management) are to chair discussions with the keynote speakers and panelists.
Closing remarks will be delivered by Prof. Chan Ghee Koh (Director, NUS IPUR), Prof. So Young Kim (Director, KAIST KPC4IR), and Prof. Joungho Kim (Director, KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI)).
“This conference is expected to serve as a springboard to help Asian countries recover from global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic through active cooperation and joint engagement among scholars, experts, and policymakers,” according to Director So Young Kim.
(END)
2020.10.22 View 15201 -
 E. coli Engineered to Grow on CO₂ and Formic Acid as Sole Carbon Sources
- An E. coli strain that can grow to a relatively high cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid was developed by employing metabolic engineering. -
Most biorefinery processes have relied on the use of biomass as a raw material for the production of chemicals and materials. Even though the use of CO₂ as a carbon source in biorefineries is desirable, it has not been possible to make common microbial strains such as E. coli grow on CO₂.
Now, a metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed a strategy to grow an E. coli strain to higher cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid. Formic acid is a one carbon carboxylic acid, and can be easily produced from CO₂ using a variety of methods. Since it is easier to store and transport than CO₂, formic acid can be considered a good liquid-form alternative of CO₂.
With support from the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stepped up their work to develop an engineered E. coli strain capable of growing up to 11-fold higher cell density than those previously reported, using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources. This work was published in Nature Microbiology on September 28.
Despite the recent reports by several research groups on the development of E. coli strains capable of growing on CO₂ and formic acid, the maximum cell growth remained too low (optical density of around 1) and thus the production of chemicals from CO₂ and formic acid has been far from realized.
The team previously reported the reconstruction of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage pathway to construct an engineered E. coli strain that can sustain growth on CO₂ and formic acid. To further enhance the growth, the research team introduced the previously designed synthetic CO₂ and formic acid assimilation pathway, and two formate dehydrogenases.
Metabolic fluxes were also fine-tuned, the gluconeogenic flux enhanced, and the levels of cytochrome bo3 and bd-I ubiquinol oxidase for ATP generation were optimized. This engineered E. coli strain was able to grow to a relatively high OD600 of 7~11, showing promise as a platform strain growing solely on CO₂ and formic acid.
Professor Lee said, “We engineered E. coli that can grow to a higher cell density only using CO₂ and formic acid. We think that this is an important step forward, but this is not the end. The engineered strain we developed still needs further engineering so that it can grow faster to a much higher density.”
Professor Lee’s team is continuing to develop such a strain. “In the future, we would be delighted to see the production of chemicals from an engineered E. coli strain using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources,” he added.
-Profile:Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Leehttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.09.29 View 11723
E. coli Engineered to Grow on CO₂ and Formic Acid as Sole Carbon Sources
- An E. coli strain that can grow to a relatively high cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid was developed by employing metabolic engineering. -
Most biorefinery processes have relied on the use of biomass as a raw material for the production of chemicals and materials. Even though the use of CO₂ as a carbon source in biorefineries is desirable, it has not been possible to make common microbial strains such as E. coli grow on CO₂.
Now, a metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed a strategy to grow an E. coli strain to higher cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid. Formic acid is a one carbon carboxylic acid, and can be easily produced from CO₂ using a variety of methods. Since it is easier to store and transport than CO₂, formic acid can be considered a good liquid-form alternative of CO₂.
With support from the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stepped up their work to develop an engineered E. coli strain capable of growing up to 11-fold higher cell density than those previously reported, using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources. This work was published in Nature Microbiology on September 28.
Despite the recent reports by several research groups on the development of E. coli strains capable of growing on CO₂ and formic acid, the maximum cell growth remained too low (optical density of around 1) and thus the production of chemicals from CO₂ and formic acid has been far from realized.
The team previously reported the reconstruction of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage pathway to construct an engineered E. coli strain that can sustain growth on CO₂ and formic acid. To further enhance the growth, the research team introduced the previously designed synthetic CO₂ and formic acid assimilation pathway, and two formate dehydrogenases.
Metabolic fluxes were also fine-tuned, the gluconeogenic flux enhanced, and the levels of cytochrome bo3 and bd-I ubiquinol oxidase for ATP generation were optimized. This engineered E. coli strain was able to grow to a relatively high OD600 of 7~11, showing promise as a platform strain growing solely on CO₂ and formic acid.
Professor Lee said, “We engineered E. coli that can grow to a higher cell density only using CO₂ and formic acid. We think that this is an important step forward, but this is not the end. The engineered strain we developed still needs further engineering so that it can grow faster to a much higher density.”
Professor Lee’s team is continuing to develop such a strain. “In the future, we would be delighted to see the production of chemicals from an engineered E. coli strain using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources,” he added.
-Profile:Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Leehttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.09.29 View 11723 -
 Researchers Present a Microbial Strain Capable of Massive Succinic Acid Production
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee reported the production of a microbial strain capable of the massive production of succinic acid with the highest production efficiency to date. This strategy of integrating systems metabolic engineering with enzyme engineering will be useful for the production of industrially competitive bio-based chemicals. Their strategy was described in Nature Communications on April 23.
The bio-based production of industrial chemicals from renewable non-food biomass has become increasingly important as a sustainable substitute for conventional petroleum-based production processes relying on fossil resources. Here, systems metabolic engineering, which is the key component for biorefinery technology, is utilized to effectively engineer the complex metabolic pathways of microorganisms to enable the efficient production of industrial chemicals.
Succinic acid, a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid, is one of the most promising platform chemicals serving as a precursor for industrially important chemicals. Among microorganisms producing succinic acid, Mannheimia succiniciproducens has been proven to be one of the best strains for succinic acid production.
The research team has developed a bio-based succinic acid production technology using the M. succiniciproducens strain isolated from the rumen of Korean cow for over 20 years and succeeded in developing a strain capable of producing succinic acid with the highest production efficiency.
They carried out systems metabolic engineering to optimize the succinic acid production pathway of the M. succiniciproducens strain by determining the crystal structure of key enzymes important for succinic acid production and performing protein engineering to develop enzymes with better catalytic performance.
As a result, 134 g per liter of succinic acid was produced from the fermentation of an engineered strain using glucose, glycerol, and carbon dioxide. They were able to achieve 21 g per liter per hour of succinic acid production, which is one of the key factors determining the economic feasibility of the overall production process. This is the world’s best succinic acid production efficiency reported to date. Previous production methods averaged 1~3 g per liter per hour.
Distinguished professor Sang Yup Lee explained that his team’s work will significantly contribute to transforming the current petrochemical-based industry into an eco-friendly bio-based one.
“Our research on the highly efficient bio-based production of succinic acid from renewable non-food resources and carbon dioxide has provided a basis for reducing our strong dependence on fossil resources, which is the main cause of the environmental crisis,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes via Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries and the C1 Gas Refinery Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2020.05.06 View 9989
Researchers Present a Microbial Strain Capable of Massive Succinic Acid Production
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee reported the production of a microbial strain capable of the massive production of succinic acid with the highest production efficiency to date. This strategy of integrating systems metabolic engineering with enzyme engineering will be useful for the production of industrially competitive bio-based chemicals. Their strategy was described in Nature Communications on April 23.
The bio-based production of industrial chemicals from renewable non-food biomass has become increasingly important as a sustainable substitute for conventional petroleum-based production processes relying on fossil resources. Here, systems metabolic engineering, which is the key component for biorefinery technology, is utilized to effectively engineer the complex metabolic pathways of microorganisms to enable the efficient production of industrial chemicals.
Succinic acid, a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid, is one of the most promising platform chemicals serving as a precursor for industrially important chemicals. Among microorganisms producing succinic acid, Mannheimia succiniciproducens has been proven to be one of the best strains for succinic acid production.
The research team has developed a bio-based succinic acid production technology using the M. succiniciproducens strain isolated from the rumen of Korean cow for over 20 years and succeeded in developing a strain capable of producing succinic acid with the highest production efficiency.
They carried out systems metabolic engineering to optimize the succinic acid production pathway of the M. succiniciproducens strain by determining the crystal structure of key enzymes important for succinic acid production and performing protein engineering to develop enzymes with better catalytic performance.
As a result, 134 g per liter of succinic acid was produced from the fermentation of an engineered strain using glucose, glycerol, and carbon dioxide. They were able to achieve 21 g per liter per hour of succinic acid production, which is one of the key factors determining the economic feasibility of the overall production process. This is the world’s best succinic acid production efficiency reported to date. Previous production methods averaged 1~3 g per liter per hour.
Distinguished professor Sang Yup Lee explained that his team’s work will significantly contribute to transforming the current petrochemical-based industry into an eco-friendly bio-based one.
“Our research on the highly efficient bio-based production of succinic acid from renewable non-food resources and carbon dioxide has provided a basis for reducing our strong dependence on fossil resources, which is the main cause of the environmental crisis,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes via Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries and the C1 Gas Refinery Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2020.05.06 View 9989 -
 Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 9094
Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Opens
The World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution opened its Korean affiliate center at KAIST on December 10. The Korea Policy Center for the 4th Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will develop policy norms and frameworks for accelerating the benefits of emerging technologies.
Many dignitaries including KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, National Assemblyman Sang-Min Lee, Daejeon City Mayor Her Tae-Jeong, and Managing Director of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Murat Sonmez attended the opening ceremony.
The center will play a vital role in helping to shape the development of national Fourth Industrial Revolution strategies and public-private initiatives. The Center will actively engage with the government on policy design and piloting activities.
The Center is the result of KAIST’s close partnership with the WEF and its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in San Francisco. KAIST signed an MOU with the WEF in 2017 for this collaboration. Dr. Klaus Schwab expressed his high hopes many times regarding Korea’s potential in responding to the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In addition, he said that KAIST and the City of Daejeon would play a significant role in helping the Fourth Industrial Revolution move forward.
During a meeting with President Moon Jae-In last June, Dr. Schwab expressed his strong desire to collaborate with Korea, and the Korean government designated KAIST as an affiliate center of the WEF.
The KPC4IR had already begun conducting policy research in the areas of block chain and precision medicine even before making a partnership with the WEF. The director of the Center, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, said, “We have focused on the development of technology but rarely talk about governance. Technology should come with policy. We will conduct policy development on how to ensure inclusive growth capitalizing on emerging technologies. We will also make policy guidelines for technological applications after considering all the ethical perspectives.
President Shin also said in his opening remarks, “Korea has been a fast follower over the past decades in making economic development and innovations. I believe that the Fourth Industrial Revolution gives us the best opportunity to play the role of ‘first mover.’ I look forward to the KPC4IR serving as a ‘Think and Do’ tank, not limiting itself to the role of ‘think tank.’ We will continue to work closely with the WEF in the fields of AI, blockchain, and precision medicine.
2019.12.10 View 9094 -
 Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 38027
Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 38027 -
 Efficiently Producing Fatty Acids and Biofuels from Glucose
Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.
The newly developed strain, created by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team, showed the highest efficiency in producing fatty acids and biodiesels ever reported. It will be expected to serve as a new platform to sustainably produce a wide array of fatty acid-based products from glucose and other carbon substrates.
Fossil fuels, which have long been energy resources for our daily lives, are now facing serious challenges: depletion of their reserves and their role in global warming. The production of sustainable bio-based renewable energy has emerged as an essential alternative and many studies to replace fossil fuels are underway. One of the representative examples is biodiesel. Currently, it is mainly being produced through the transesterification of vegetable oils or animal fats.
The research team engineered oleaginous microorganisms, Rhodococcus opacus, to produce fatty acids and their derivatives that can be used as biodiesel from glucose, one of the most abundant and cheap sugars derived from non-edible biomass.
Professor Lee’s team has already engineered Escherichia coli to produce short-chain hydrocarbons, which can be used as gasoline (published in Nature as the cover paper in 2013). However, the production efficiency of the short-chain hydrocarbons using E. coli (0.58 g/L) fell short of the levels required for commercialization.
To overcome these issues, the team employed oil-accumulating Rhodococcus opacus as a host strain in this study. First, the team optimized the cultivation conditions of Rhodococcus opacus to maximize the accumulation of oil (triacylglycerol), which serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and their derivatives. Then, they systematically analyzed the metabolism of the strain and redesigned it to enable higher levels of fatty acids and two kinds of fatty acid-derived biodiesels (fatty acid ethyl esters and long-chain hydrocarbons) to be produced.
They found that the resulting strains produced 50.2, 21.3, and 5.2 g/L of fatty acids, fatty acid ethyl esters, and long-chain hydrocarbons, respectively. These are all the highest concentrations ever reported by microbial fermentations. It is expected that these strains can contribute to the future industrialization of microbial-based biodiesel production.
“This technology creates fatty acids and biodiesel with high efficiency by utilizing lignocellulose, one of the most abundant resources on the Earth, without depending on fossil fuels and vegetable or animal oils. This will provide new opportunities for oil and petroleum industries, which have long relied on fossil fuels, to turn to sustainable and eco-friendly biotechnologies,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels” was published in Nature Chemical Biology on June 17.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557).
(Figure: Metabolic engineering for the production of free fatty acids (FFAs), fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs), and long-chain hydrocarbons (LCHCs) in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.)
# # #
Source:
Hye Mi Kim, Tong Un Chae, So Young Choi, Won Jun Kim and Sang Yup Lee. Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels. Nature Chemical Biology ( https://www.nature.com/nchembio/ ) DOI: 10.1038/s41589-019-0295-5
Profile
Dr. Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Distinguished Professor at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2019.06.19 View 49877
Efficiently Producing Fatty Acids and Biofuels from Glucose
Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.
The newly developed strain, created by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team, showed the highest efficiency in producing fatty acids and biodiesels ever reported. It will be expected to serve as a new platform to sustainably produce a wide array of fatty acid-based products from glucose and other carbon substrates.
Fossil fuels, which have long been energy resources for our daily lives, are now facing serious challenges: depletion of their reserves and their role in global warming. The production of sustainable bio-based renewable energy has emerged as an essential alternative and many studies to replace fossil fuels are underway. One of the representative examples is biodiesel. Currently, it is mainly being produced through the transesterification of vegetable oils or animal fats.
The research team engineered oleaginous microorganisms, Rhodococcus opacus, to produce fatty acids and their derivatives that can be used as biodiesel from glucose, one of the most abundant and cheap sugars derived from non-edible biomass.
Professor Lee’s team has already engineered Escherichia coli to produce short-chain hydrocarbons, which can be used as gasoline (published in Nature as the cover paper in 2013). However, the production efficiency of the short-chain hydrocarbons using E. coli (0.58 g/L) fell short of the levels required for commercialization.
To overcome these issues, the team employed oil-accumulating Rhodococcus opacus as a host strain in this study. First, the team optimized the cultivation conditions of Rhodococcus opacus to maximize the accumulation of oil (triacylglycerol), which serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and their derivatives. Then, they systematically analyzed the metabolism of the strain and redesigned it to enable higher levels of fatty acids and two kinds of fatty acid-derived biodiesels (fatty acid ethyl esters and long-chain hydrocarbons) to be produced.
They found that the resulting strains produced 50.2, 21.3, and 5.2 g/L of fatty acids, fatty acid ethyl esters, and long-chain hydrocarbons, respectively. These are all the highest concentrations ever reported by microbial fermentations. It is expected that these strains can contribute to the future industrialization of microbial-based biodiesel production.
“This technology creates fatty acids and biodiesel with high efficiency by utilizing lignocellulose, one of the most abundant resources on the Earth, without depending on fossil fuels and vegetable or animal oils. This will provide new opportunities for oil and petroleum industries, which have long relied on fossil fuels, to turn to sustainable and eco-friendly biotechnologies,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels” was published in Nature Chemical Biology on June 17.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557).
(Figure: Metabolic engineering for the production of free fatty acids (FFAs), fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs), and long-chain hydrocarbons (LCHCs) in Rhodococcus opacus PD630. Researchers have presented a new strategy for efficiently producing fatty acids and biofuels that can transform glucose and oleaginous microorganisms into microbial diesel fuel, with one-step direct fermentative production.)
# # #
Source:
Hye Mi Kim, Tong Un Chae, So Young Choi, Won Jun Kim and Sang Yup Lee. Engineering of an oleaginous bacterium for the production of fatty acids and fuels. Nature Chemical Biology ( https://www.nature.com/nchembio/ ) DOI: 10.1038/s41589-019-0295-5
Profile
Dr. Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Distinguished Professor at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2019.06.19 View 49877 -
 Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 55861
Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 55861 -
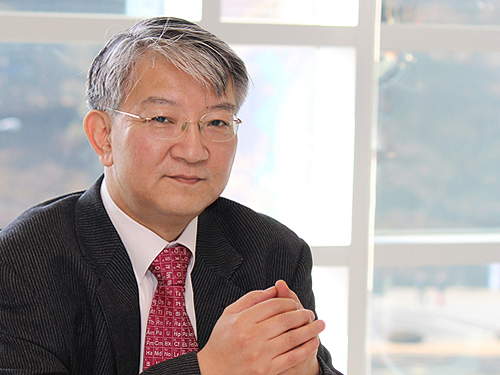 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 8909
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 8909 -
 KAIST and LG Electronics Team up for 6G Wireless Communications
(LG Electronics CTO Il-Pyung Park (left) and Dean of KAIST Institute Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST and LG Electronics are working together to take the lead in next-generation wireless communications and launched the LG-KAIST 6G Research Center on January 28, 2019.
KAIST Institute has been focusing on developing a new growth engine for the national economy through interdisciplinary research. In particular, its research work in the field of next-generation wireless communication was listed in the National Research and Development Excellence 100 in 2016 and 2017.
LG Electronics has been a global leader in this field for many years. According to TechIPM, the company had the most 4G LTE/LTE-A patents from 2012 to 2016. Also, it first standardized the Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything, which is the core technology for autonomous vehicles.
The new head of the research center, Professor Dong Ho Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering said, “We will work on developing source technology for sixth generation mobile communications, which will enhance national competence and prepare for the future industries.”
CTO of LG Electronics Il-Pyung Park said, “We are hoping to take the lead in the global standardization of sixth generation wireless communications and secure new business opportunities.”
2019.01.29 View 2805
KAIST and LG Electronics Team up for 6G Wireless Communications
(LG Electronics CTO Il-Pyung Park (left) and Dean of KAIST Institute Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST and LG Electronics are working together to take the lead in next-generation wireless communications and launched the LG-KAIST 6G Research Center on January 28, 2019.
KAIST Institute has been focusing on developing a new growth engine for the national economy through interdisciplinary research. In particular, its research work in the field of next-generation wireless communication was listed in the National Research and Development Excellence 100 in 2016 and 2017.
LG Electronics has been a global leader in this field for many years. According to TechIPM, the company had the most 4G LTE/LTE-A patents from 2012 to 2016. Also, it first standardized the Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything, which is the core technology for autonomous vehicles.
The new head of the research center, Professor Dong Ho Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering said, “We will work on developing source technology for sixth generation mobile communications, which will enhance national competence and prepare for the future industries.”
CTO of LG Electronics Il-Pyung Park said, “We are hoping to take the lead in the global standardization of sixth generation wireless communications and secure new business opportunities.”
2019.01.29 View 2805 -
 President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 7413
President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 7413