research
-
 Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 13029
Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 13029 -
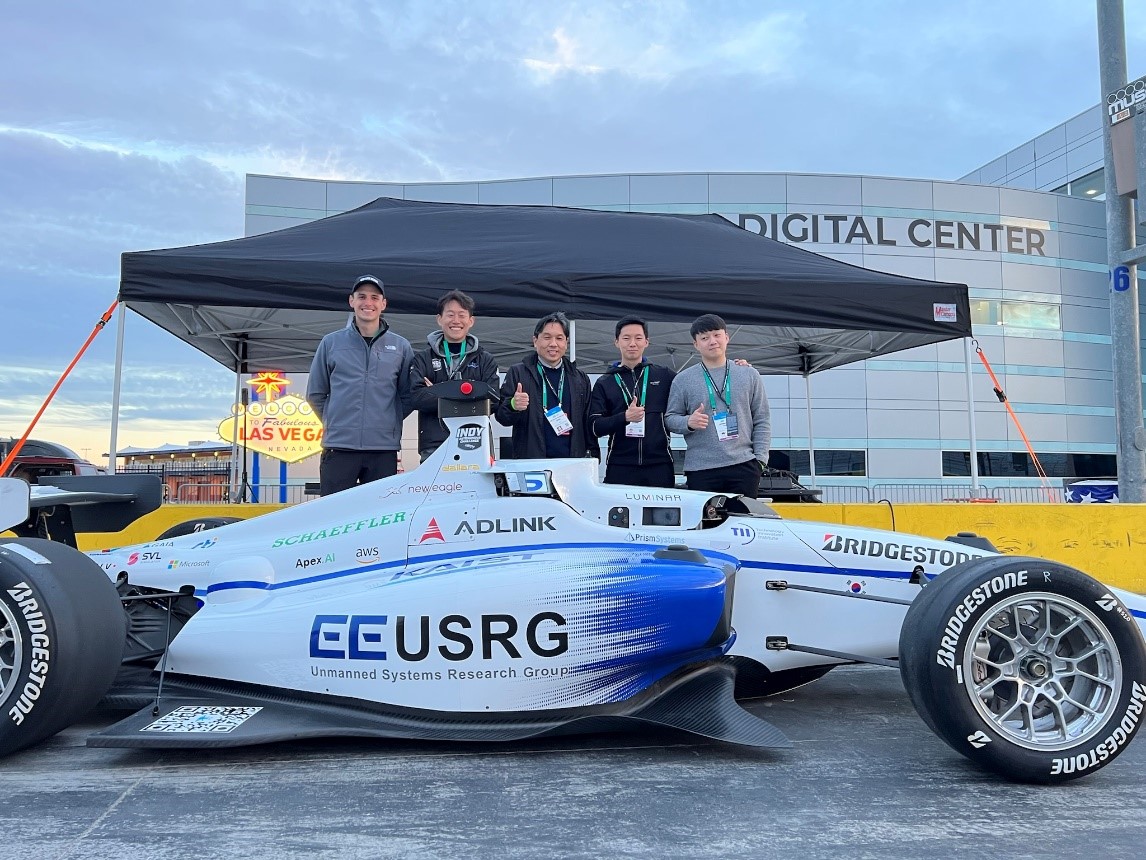 Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 10733
Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 10733 -
 AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 6344
AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 6344 -
 Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 11063
Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 11063 -
 Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 14036
Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 14036 -
 Natural Rainbow Colorants Microbially Produced
Integrated strategies of systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering led to the production of natural rainbow colorants comprising seven natural colorants from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered bacterial strains capable of producing three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives, completing the seven colors in the rainbow spectrum. The research team integrated systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering strategies for the production of seven natural rainbow colorants in engineered Escherichia coli strains. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Colorants are widely used in our lives and are directly related to human health when we eat food additives and wear cosmetics. However, most of these colorants are made from petroleum, causing unexpected side effects and health problems. Furthermore, they raise environmental concerns such as water pollution from dyeing fabric in the textiles industry. For these reasons, the demand for the production of natural colorants using microorganisms has increased, but could not be readily realized due to the high cost and low yield of the bioprocesses.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST including researchers Dr. Dongsoo Yang and Dr. Seon Young Park, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team reported the study entitled “Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” in Advanced Science online on May 5. It was selected as the journal cover of the July 7 issue.
This research reports for the first time the production of rainbow colorants comprising three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives from glucose or glycerol via systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering. The research group focused on the production of hydrophobic natural colorants useful for lipophilic food and dyeing garments. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, three carotenoids comprising astaxanthin (red), -carotene (orange), and zeaxanthin (yellow), and four violacein derivatives comprising proviolacein (green), prodeoxyviolacein (blue), violacein (navy), and deoxyviolacein (purple) could be produced. Thus, the production of natural colorants covering the complete rainbow spectrum was achieved.
When hydrophobic colorants are produced from microorganisms, the colorants are accumulated inside the cell. As the accumulation capacity is limited, the hydrophobic colorants could not be produced with concentrations higher than the limit. In this regard, the researchers engineered the cell morphology and generated inner-membrane vesicles (spherical membranous structures) to increase the intracellular capacity for accumulating the natural colorants. To further promote production, the researchers generated outer-membrane vesicles to secrete the natural colorants, thus succeeding in efficiently producing all of seven rainbow colorants. It was even more impressive that the production of natural green and navy colorants was achieved for the first time.
“The production of the seven natural rainbow colorants that can replace the current petroleum-based synthetic colorants was achieved for the first time,” said Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals. “As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Lee.
This work was supported by the "Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01550602)" Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
-Publication:Dongsoo Yang, Seon Young Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Advanced Science, 2100743.
-Profile Distinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.09 View 11197
Natural Rainbow Colorants Microbially Produced
Integrated strategies of systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering led to the production of natural rainbow colorants comprising seven natural colorants from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered bacterial strains capable of producing three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives, completing the seven colors in the rainbow spectrum. The research team integrated systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering strategies for the production of seven natural rainbow colorants in engineered Escherichia coli strains. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Colorants are widely used in our lives and are directly related to human health when we eat food additives and wear cosmetics. However, most of these colorants are made from petroleum, causing unexpected side effects and health problems. Furthermore, they raise environmental concerns such as water pollution from dyeing fabric in the textiles industry. For these reasons, the demand for the production of natural colorants using microorganisms has increased, but could not be readily realized due to the high cost and low yield of the bioprocesses.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST including researchers Dr. Dongsoo Yang and Dr. Seon Young Park, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team reported the study entitled “Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” in Advanced Science online on May 5. It was selected as the journal cover of the July 7 issue.
This research reports for the first time the production of rainbow colorants comprising three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives from glucose or glycerol via systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering. The research group focused on the production of hydrophobic natural colorants useful for lipophilic food and dyeing garments. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, three carotenoids comprising astaxanthin (red), -carotene (orange), and zeaxanthin (yellow), and four violacein derivatives comprising proviolacein (green), prodeoxyviolacein (blue), violacein (navy), and deoxyviolacein (purple) could be produced. Thus, the production of natural colorants covering the complete rainbow spectrum was achieved.
When hydrophobic colorants are produced from microorganisms, the colorants are accumulated inside the cell. As the accumulation capacity is limited, the hydrophobic colorants could not be produced with concentrations higher than the limit. In this regard, the researchers engineered the cell morphology and generated inner-membrane vesicles (spherical membranous structures) to increase the intracellular capacity for accumulating the natural colorants. To further promote production, the researchers generated outer-membrane vesicles to secrete the natural colorants, thus succeeding in efficiently producing all of seven rainbow colorants. It was even more impressive that the production of natural green and navy colorants was achieved for the first time.
“The production of the seven natural rainbow colorants that can replace the current petroleum-based synthetic colorants was achieved for the first time,” said Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals. “As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Lee.
This work was supported by the "Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01550602)" Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
-Publication:Dongsoo Yang, Seon Young Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Advanced Science, 2100743.
-Profile Distinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.09 View 11197 -
 Microbial Production of a Natural Red Colorant Carminic Acid
Metabolic engineering and computer-simulated enzyme engineering led to the production of carminic acid, a natural red colorant, from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced by farming cochineals, a scale insect which only grows in the region around Peru and Canary Islands, followed by complicated multi-step purification processes. Moreover, carminic acid often contains protein contaminants that cause allergies so many people are unwilling to consume products made of insect-driven colorants. On that account, manufacturers around the world are using alternative red colorants despite the fact that carminic acid is one of the most stable natural red colorants.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineering research group at KAIST to address this issue. Its members include postdoctoral researchers Dongsoo Yang and Woo Dae Jang, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. This study entitled “Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on April 2.
This research reports for the first time the development of a bacterial strain capable of producing carminic acid from glucose via metabolic engineering and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering. The research group optimized the type II polyketide synthase machinery to efficiently produce the precursor of carminic acid, flavokermesic acid.
Since the enzymes responsible for the remaining two reactions were neither discovered nor functional, biochemical reaction analysis was performed to identify enzymes that can convert flavokermesic acid into carminic acid. Then, homology modeling and docking simulations were performed to enhance the activities of the two identified enzymes. The team could confirm that the final engineered strain could produce carminic acid directly from glucose. The C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study was found to be generally applicable for other natural products as showcased by the successful production of an additional product, aloesin, which is found in aloe leaves.
“The most important part of this research is that unknown enzymes for the production of target natural products were identified and improved by biochemical reaction analyses and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering,” says Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained the development of a generally applicable C-glucosyltransferase is also useful since C-glucosylation is a relatively unexplored reaction in bacteria including Escherichia coli. Using the C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study, both carminic acid and aloesin were successfully produced from glucose.
“A sustainable and insect-free method of producing carminic acid was achieved for the first time in this study. Unknown or inefficient enzymes have always been a major problem in natural product biosynthesis, and here we suggest one effective solution for solving this problem. As maintaining good health in the aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab project; Sang Yup Lee and Dongsoo Yang were also supported by Novo Nordisk Foundation in Denmark.
Publication:
Dongsoo Yang, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. https://doi.org.10.1021/jacs.0c12406
Profile:
Sang Yup Lee, PhD
Distinguished Professor
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.04.06 View 12582
Microbial Production of a Natural Red Colorant Carminic Acid
Metabolic engineering and computer-simulated enzyme engineering led to the production of carminic acid, a natural red colorant, from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced by farming cochineals, a scale insect which only grows in the region around Peru and Canary Islands, followed by complicated multi-step purification processes. Moreover, carminic acid often contains protein contaminants that cause allergies so many people are unwilling to consume products made of insect-driven colorants. On that account, manufacturers around the world are using alternative red colorants despite the fact that carminic acid is one of the most stable natural red colorants.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineering research group at KAIST to address this issue. Its members include postdoctoral researchers Dongsoo Yang and Woo Dae Jang, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. This study entitled “Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on April 2.
This research reports for the first time the development of a bacterial strain capable of producing carminic acid from glucose via metabolic engineering and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering. The research group optimized the type II polyketide synthase machinery to efficiently produce the precursor of carminic acid, flavokermesic acid.
Since the enzymes responsible for the remaining two reactions were neither discovered nor functional, biochemical reaction analysis was performed to identify enzymes that can convert flavokermesic acid into carminic acid. Then, homology modeling and docking simulations were performed to enhance the activities of the two identified enzymes. The team could confirm that the final engineered strain could produce carminic acid directly from glucose. The C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study was found to be generally applicable for other natural products as showcased by the successful production of an additional product, aloesin, which is found in aloe leaves.
“The most important part of this research is that unknown enzymes for the production of target natural products were identified and improved by biochemical reaction analyses and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering,” says Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained the development of a generally applicable C-glucosyltransferase is also useful since C-glucosylation is a relatively unexplored reaction in bacteria including Escherichia coli. Using the C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study, both carminic acid and aloesin were successfully produced from glucose.
“A sustainable and insect-free method of producing carminic acid was achieved for the first time in this study. Unknown or inefficient enzymes have always been a major problem in natural product biosynthesis, and here we suggest one effective solution for solving this problem. As maintaining good health in the aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab project; Sang Yup Lee and Dongsoo Yang were also supported by Novo Nordisk Foundation in Denmark.
Publication:
Dongsoo Yang, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. https://doi.org.10.1021/jacs.0c12406
Profile:
Sang Yup Lee, PhD
Distinguished Professor
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.04.06 View 12582 -
 Acoustic Graphene Plasmons Study Paves Way for Optoelectronic Applications
- The first images of mid-infrared optical waves compressed 1,000 times captured using a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. -
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that ‘graphene plasmons’ – collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light – can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric layer separating graphene from a metallic sheet. In such a configuration, graphene’s conduction electrons are “reflected” in the metal, so when the light waves “push” the electrons in graphene, their image charges in metal also start to oscillate. This new type of collective electronic oscillation mode is called ‘acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP)’.
The existence of AGP could previously be observed only via indirect methods such as far-field infrared spectroscopy and photocurrent mapping. This indirect observation was the price that researchers had to pay for the strong compression of optical waves inside nanometer-thin structures. It was believed that the intensity of electromagnetic fields outside the device was insufficient for direct near-field optical imaging of AGP.
Challenged by these limitations, three research groups combined their efforts to bring together a unique experimental technique using advanced nanofabrication methods. Their findings were published in Nature Communications on February 19.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide, visualizing thousand-fold compression of mid-infrared light for the first time.
Professor Jang and a post-doc researcher in his group, Sergey G. Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of AGP waves by taking advantage of their rapidly decaying yet always present electric field above graphene. They showed that AGPs are detectable even when most of their energy is flowing inside the dielectric below the graphene.
This became possible due to the ultra-smooth surfaces inside the nano-waveguides where plasmonic waves can propagate at longer distances. The AGP mode probed by the researchers was up to 2.3 times more confined and exhibited a 1.4 times higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length compared to the graphene surface plasmon under similar conditions.
These ultra-smooth nanostructures of the waveguides used in the experiment were created using a template-stripping method by Professor Sang-Hyun Oh and a post-doc researcher, In-Ho Lee, from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Minnesota.
Professor Young Hee Lee and his researchers at the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics (CINAP) of the Institute of Basic Science (IBS) at Sungkyunkwan University synthesized the graphene with a monocrystalline structure, and this high-quality, large-area graphene enabled low-loss plasmonic propagation.
The chemical and physical properties of many important organic molecules can be detected and evaluated by their absorption signatures in the mid-infrared spectrum. However, conventional detection methods require a large number of molecules for successful detection, whereas the ultra-compressed AGP fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection sensitivity down to a single molecule.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated that the mid-infrared AGPs are inherently less sensitive to losses in graphene due to their fields being mostly confined within the dielectric. The research team’s reported results suggest that AGPs could become a promising platform for electrically tunable graphene-based optoelectronic devices that typically suffer from higher absorption rates in graphene such as metasurfaces, optical switches, photovoltaics, and other optoelectronic applications operating at infrared frequencies.
Professor Jang said, “Our research revealed that the ultra-compressed electromagnetic fields of acoustic graphene plasmons can be directly accessed through near-field optical microscopy methods. I hope this realization will motivate other researchers to apply AGPs to various problems where strong light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss are needed.”
This research was primarily funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics. The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), Samsung Global Research Outreach (GRO) Program, and Institute for Basic Science of Korea (IBS) also supported the work.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2021) Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition. Nature Communications 12, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21193-5
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professorjang.minseok@kaist.ac.krhttp://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Min Seok Jang Research GroupSchool of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.16 View 14840
Acoustic Graphene Plasmons Study Paves Way for Optoelectronic Applications
- The first images of mid-infrared optical waves compressed 1,000 times captured using a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. -
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that ‘graphene plasmons’ – collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light – can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric layer separating graphene from a metallic sheet. In such a configuration, graphene’s conduction electrons are “reflected” in the metal, so when the light waves “push” the electrons in graphene, their image charges in metal also start to oscillate. This new type of collective electronic oscillation mode is called ‘acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP)’.
The existence of AGP could previously be observed only via indirect methods such as far-field infrared spectroscopy and photocurrent mapping. This indirect observation was the price that researchers had to pay for the strong compression of optical waves inside nanometer-thin structures. It was believed that the intensity of electromagnetic fields outside the device was insufficient for direct near-field optical imaging of AGP.
Challenged by these limitations, three research groups combined their efforts to bring together a unique experimental technique using advanced nanofabrication methods. Their findings were published in Nature Communications on February 19.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide, visualizing thousand-fold compression of mid-infrared light for the first time.
Professor Jang and a post-doc researcher in his group, Sergey G. Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of AGP waves by taking advantage of their rapidly decaying yet always present electric field above graphene. They showed that AGPs are detectable even when most of their energy is flowing inside the dielectric below the graphene.
This became possible due to the ultra-smooth surfaces inside the nano-waveguides where plasmonic waves can propagate at longer distances. The AGP mode probed by the researchers was up to 2.3 times more confined and exhibited a 1.4 times higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length compared to the graphene surface plasmon under similar conditions.
These ultra-smooth nanostructures of the waveguides used in the experiment were created using a template-stripping method by Professor Sang-Hyun Oh and a post-doc researcher, In-Ho Lee, from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Minnesota.
Professor Young Hee Lee and his researchers at the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics (CINAP) of the Institute of Basic Science (IBS) at Sungkyunkwan University synthesized the graphene with a monocrystalline structure, and this high-quality, large-area graphene enabled low-loss plasmonic propagation.
The chemical and physical properties of many important organic molecules can be detected and evaluated by their absorption signatures in the mid-infrared spectrum. However, conventional detection methods require a large number of molecules for successful detection, whereas the ultra-compressed AGP fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection sensitivity down to a single molecule.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated that the mid-infrared AGPs are inherently less sensitive to losses in graphene due to their fields being mostly confined within the dielectric. The research team’s reported results suggest that AGPs could become a promising platform for electrically tunable graphene-based optoelectronic devices that typically suffer from higher absorption rates in graphene such as metasurfaces, optical switches, photovoltaics, and other optoelectronic applications operating at infrared frequencies.
Professor Jang said, “Our research revealed that the ultra-compressed electromagnetic fields of acoustic graphene plasmons can be directly accessed through near-field optical microscopy methods. I hope this realization will motivate other researchers to apply AGPs to various problems where strong light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss are needed.”
This research was primarily funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics. The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), Samsung Global Research Outreach (GRO) Program, and Institute for Basic Science of Korea (IBS) also supported the work.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2021) Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition. Nature Communications 12, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21193-5
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professorjang.minseok@kaist.ac.krhttp://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Min Seok Jang Research GroupSchool of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.16 View 14840 -
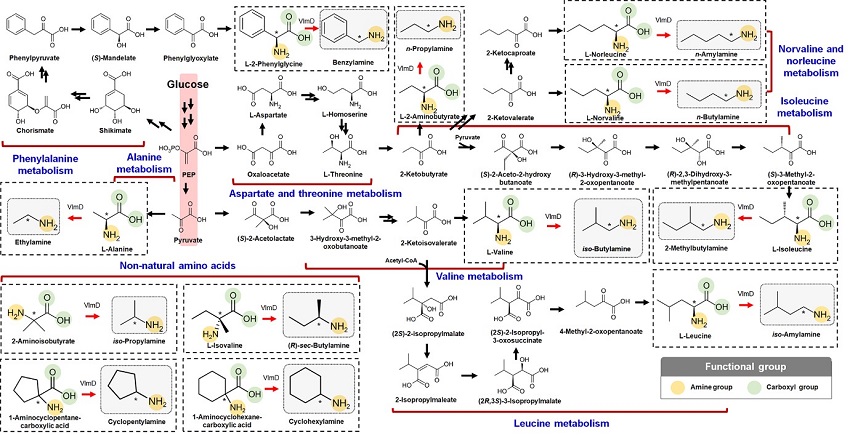 Expanding the Biosynthetic Pathway via Retrobiosynthesis
- Researchers reports a new strategy for the microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. -
KAIST metabolic engineers presented the bio-based production of multiple short-chain primary amines that have a wide range of applications in chemical industries for the first time. The research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering designed the novel biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step.
The research team verified the newly designed pathways by confirming the in vivo production of 10 short-chain primary amines by supplying the precursors. Furthermore, the platform Escherichia coli strains were metabolically engineered to produce three proof-of-concept short-chain primary amines from glucose, demonstrating the possibility of the bio-based production of diverse short-chain primary amines from renewable resources. The research team said this study expands the strategy of systematically designing biosynthetic pathways for the production of a group of related chemicals as demonstrated by multiple short-chain primary amines as examples.
Currently, most of the industrial chemicals used in our daily lives are produced with petroleum-based products. However, there are several serious issues with the petroleum industry such as the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and environmental problems including global warming. To solve these problems, the sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials is being explored with microorganisms as cell factories and renewable non-food biomass as raw materials for alternative to petroleum-based products. The engineering of these microorganisms has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of systems metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering the metabolism of a living organism toward the production of a desired metabolite. In this regard, the number of chemicals produced using biomass as a raw material has substantially increased.
Although the scope of chemicals that are producible using microorganisms continues to expand through advances in systems metabolic engineering, the biological production of short-chain primary amines has not yet been reported despite their industrial importance. Short-chain primary amines are the chemicals that have an alkyl or aryl group in the place of a hydrogen atom in ammonia with carbon chain lengths ranging from C1 to C7. Short-chain primary amines have a wide range of applications in chemical industries, for example, as a precursor for pharmaceuticals (e.g., antidiabetic and antihypertensive drugs), agrochemicals (e.g., herbicides, fungicides and insecticides), solvents, and vulcanization accelerators for rubber and plasticizers. The market size of short-chain primary amines was estimated to be more than 4 billion US dollars in 2014.
The main reason why the bio-based production of short-chain primary amines was not yet possible was due to their unknown biosynthetic pathways. Therefore, the team designed synthetic biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step. The retrobiosynthesis allowed the systematic design of a biosynthetic pathway for short-chain primary amines by using a set of biochemical reaction rules that describe chemical transformation patterns between a substrate and product molecules at an atomic level.
These multiple precursors predicted for the possible biosynthesis of each short-chain primary amine were sequentially narrowed down by using the precursor selection step for efficient metabolic engineering experiments.
“Our research demonstrates the possibility of the renewable production of short-chain primary amines for the first time. We are planning to increase production efficiencies of short-chain primary amines. We believe that our study will play an important role in the development of sustainable and eco-friendly bio-based industries and the reorganization of the chemical industry, which is mandatory for solving the environmental problems threating the survival of mankind,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis” was published in Nature Communications. This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
-Publication
Dong In Kim, Tong Un Chae, Hyun Uk Kim, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. Nature Communications ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20423-6)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.14 View 12445
Expanding the Biosynthetic Pathway via Retrobiosynthesis
- Researchers reports a new strategy for the microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. -
KAIST metabolic engineers presented the bio-based production of multiple short-chain primary amines that have a wide range of applications in chemical industries for the first time. The research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering designed the novel biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step.
The research team verified the newly designed pathways by confirming the in vivo production of 10 short-chain primary amines by supplying the precursors. Furthermore, the platform Escherichia coli strains were metabolically engineered to produce three proof-of-concept short-chain primary amines from glucose, demonstrating the possibility of the bio-based production of diverse short-chain primary amines from renewable resources. The research team said this study expands the strategy of systematically designing biosynthetic pathways for the production of a group of related chemicals as demonstrated by multiple short-chain primary amines as examples.
Currently, most of the industrial chemicals used in our daily lives are produced with petroleum-based products. However, there are several serious issues with the petroleum industry such as the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and environmental problems including global warming. To solve these problems, the sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials is being explored with microorganisms as cell factories and renewable non-food biomass as raw materials for alternative to petroleum-based products. The engineering of these microorganisms has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of systems metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering the metabolism of a living organism toward the production of a desired metabolite. In this regard, the number of chemicals produced using biomass as a raw material has substantially increased.
Although the scope of chemicals that are producible using microorganisms continues to expand through advances in systems metabolic engineering, the biological production of short-chain primary amines has not yet been reported despite their industrial importance. Short-chain primary amines are the chemicals that have an alkyl or aryl group in the place of a hydrogen atom in ammonia with carbon chain lengths ranging from C1 to C7. Short-chain primary amines have a wide range of applications in chemical industries, for example, as a precursor for pharmaceuticals (e.g., antidiabetic and antihypertensive drugs), agrochemicals (e.g., herbicides, fungicides and insecticides), solvents, and vulcanization accelerators for rubber and plasticizers. The market size of short-chain primary amines was estimated to be more than 4 billion US dollars in 2014.
The main reason why the bio-based production of short-chain primary amines was not yet possible was due to their unknown biosynthetic pathways. Therefore, the team designed synthetic biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step. The retrobiosynthesis allowed the systematic design of a biosynthetic pathway for short-chain primary amines by using a set of biochemical reaction rules that describe chemical transformation patterns between a substrate and product molecules at an atomic level.
These multiple precursors predicted for the possible biosynthesis of each short-chain primary amine were sequentially narrowed down by using the precursor selection step for efficient metabolic engineering experiments.
“Our research demonstrates the possibility of the renewable production of short-chain primary amines for the first time. We are planning to increase production efficiencies of short-chain primary amines. We believe that our study will play an important role in the development of sustainable and eco-friendly bio-based industries and the reorganization of the chemical industry, which is mandatory for solving the environmental problems threating the survival of mankind,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis” was published in Nature Communications. This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
-Publication
Dong In Kim, Tong Un Chae, Hyun Uk Kim, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. Nature Communications ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20423-6)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.14 View 12445 -
 DeepTFactor Predicts Transcription Factors
A deep learning-based tool predicts transcription factors using protein sequences as inputs
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis of the transcriptional regulatory system of an organism.
Previously, transcription factors have been predicted by analyzing sequence homology with already characterized transcription factors or by data-driven approaches such as machine learning. Conventional machine learning models require a rigorous feature selection process that relies on domain expertise such as calculating the physicochemical properties of molecules or analyzing the homology of biological sequences. Meanwhile, deep learning can inherently learn latent features for the specific task.
A joint research team comprised of Ph.D. candidate Gi Bae Kim and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Ye Gao and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Biochemical Engineering at UCSD reported a deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. Their research paper “DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors” was published online in PNAS.
Their article reports the development of DeepTFactor, a deep learning-based tool that predicts whether a given protein sequence is a transcription factor using three parallel convolutional neural networks. The joint research team predicted 332 transcription factors of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 using DeepTFactor and the performance of DeepTFactor by experimentally confirming the genome-wide binding sites of three predicted transcription factors (YqhC, YiaU, and YahB).
The joint research team further used a saliency method to understand the reasoning process of DeepTFactor. The researchers confirmed that even though information on the DNA binding domains of the transcription factor was not explicitly given the training process, DeepTFactor implicitly learned and used them for prediction. Unlike previous transcription factor prediction tools that were developed only for protein sequences of specific organisms, DeepTFactor is expected to be used in the analysis of the transcription systems of all organisms at a high level of performance.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “DeepTFactor can be used to discover unknown transcription factors from numerous protein sequences that have not yet been characterized. It is expected that DeepTFactor will serve as an important tool for analyzing the regulatory systems of organisms of interest.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication
Gi Bae Kim, Ye Gao, Bernhard O. Palsson, and Sang Yup Lee. DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas202117118)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.05 View 9875
DeepTFactor Predicts Transcription Factors
A deep learning-based tool predicts transcription factors using protein sequences as inputs
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis of the transcriptional regulatory system of an organism.
Previously, transcription factors have been predicted by analyzing sequence homology with already characterized transcription factors or by data-driven approaches such as machine learning. Conventional machine learning models require a rigorous feature selection process that relies on domain expertise such as calculating the physicochemical properties of molecules or analyzing the homology of biological sequences. Meanwhile, deep learning can inherently learn latent features for the specific task.
A joint research team comprised of Ph.D. candidate Gi Bae Kim and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Ye Gao and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Biochemical Engineering at UCSD reported a deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. Their research paper “DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors” was published online in PNAS.
Their article reports the development of DeepTFactor, a deep learning-based tool that predicts whether a given protein sequence is a transcription factor using three parallel convolutional neural networks. The joint research team predicted 332 transcription factors of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 using DeepTFactor and the performance of DeepTFactor by experimentally confirming the genome-wide binding sites of three predicted transcription factors (YqhC, YiaU, and YahB).
The joint research team further used a saliency method to understand the reasoning process of DeepTFactor. The researchers confirmed that even though information on the DNA binding domains of the transcription factor was not explicitly given the training process, DeepTFactor implicitly learned and used them for prediction. Unlike previous transcription factor prediction tools that were developed only for protein sequences of specific organisms, DeepTFactor is expected to be used in the analysis of the transcription systems of all organisms at a high level of performance.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “DeepTFactor can be used to discover unknown transcription factors from numerous protein sequences that have not yet been characterized. It is expected that DeepTFactor will serve as an important tool for analyzing the regulatory systems of organisms of interest.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication
Gi Bae Kim, Ye Gao, Bernhard O. Palsson, and Sang Yup Lee. DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas202117118)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.05 View 9875 -
 A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 11168
A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 11168 -
 KAIST Joins IBM Q Network to Accelerate Quantum Computing Research and Foster Quantum Industry
KAIST has joined the IBM Q Network, a community of Fortune 500 companies, academic institutions, startups, and research labs working with IBM to advance quantum computing for business and science.
As the IBM Q Network’s first academic partner in Korea, KAIST will use IBM's advanced quantum computing systems to carry out research projects that advance quantum information science and explore early applications. KAIST will also utilize IBM Quantum resources for talent training and education in preparation for building a quantum workforce for the quantum computing era that will bring huge changes to science and business. By joining the network, KAIST will take a leading role in fostering the ecosystem of quantum computing in Korea, which is expected to be a necessary enabler to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Professor June-Koo Rhee who also serves as Director of the KAIST Information Technology Research Center (ITRC) of Quantum Computing for AI has led the agreement on KAIST’s joining the IBM Q Network. Director Rhee described quantum computing as "a new technology that can calculate mathematical challenges at very high speed and low power” and also as “one that will change the future.”
Director Rhee said, “Korea started investment in quantum computing relatively late, and thus requires to take bold steps with innovative R&D strategies to pave the roadmap for the next technological leap in the field”. With KAIST joining the IBM Q Network, “Korea will be better equipped to establish a quantum industry, an important foundation for securing national competitiveness,” he added.
The KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI has been using the publicly available IBM Quantum Experience delivered over the IBM Cloud for research, development and training of quantum algorithms such as quantum artificial intelligence, quantum chemical calculation, and quantum computing education.
KAIST will have access to the most advanced IBM Quantum systems to explore practical research and experiments such as diagnosis of diseases based on quantum artificial intelligence, quantum computational chemistry, and quantum machine learning technology. In addition, knowledge exchanges and sharing with overseas universities and companies under the IBM Q Network will help KAIST strengthen the global presence of Korean technology in quantum computing.
About IBM Quantum
IBM Quantum is an industry-first initiative to build quantum systems for business and science applications. For more information about IBM's quantum computing efforts, please visit www.ibm.com/ibmq.
For more information about the IBM Q Network, as well as a full list of all partners, members, and hubs, visit https://www.research.ibm.com/ibm-q/network/
©Thumbnail Image: IBM.
(END)
2020.09.29 View 9169
KAIST Joins IBM Q Network to Accelerate Quantum Computing Research and Foster Quantum Industry
KAIST has joined the IBM Q Network, a community of Fortune 500 companies, academic institutions, startups, and research labs working with IBM to advance quantum computing for business and science.
As the IBM Q Network’s first academic partner in Korea, KAIST will use IBM's advanced quantum computing systems to carry out research projects that advance quantum information science and explore early applications. KAIST will also utilize IBM Quantum resources for talent training and education in preparation for building a quantum workforce for the quantum computing era that will bring huge changes to science and business. By joining the network, KAIST will take a leading role in fostering the ecosystem of quantum computing in Korea, which is expected to be a necessary enabler to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Professor June-Koo Rhee who also serves as Director of the KAIST Information Technology Research Center (ITRC) of Quantum Computing for AI has led the agreement on KAIST’s joining the IBM Q Network. Director Rhee described quantum computing as "a new technology that can calculate mathematical challenges at very high speed and low power” and also as “one that will change the future.”
Director Rhee said, “Korea started investment in quantum computing relatively late, and thus requires to take bold steps with innovative R&D strategies to pave the roadmap for the next technological leap in the field”. With KAIST joining the IBM Q Network, “Korea will be better equipped to establish a quantum industry, an important foundation for securing national competitiveness,” he added.
The KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI has been using the publicly available IBM Quantum Experience delivered over the IBM Cloud for research, development and training of quantum algorithms such as quantum artificial intelligence, quantum chemical calculation, and quantum computing education.
KAIST will have access to the most advanced IBM Quantum systems to explore practical research and experiments such as diagnosis of diseases based on quantum artificial intelligence, quantum computational chemistry, and quantum machine learning technology. In addition, knowledge exchanges and sharing with overseas universities and companies under the IBM Q Network will help KAIST strengthen the global presence of Korean technology in quantum computing.
About IBM Quantum
IBM Quantum is an industry-first initiative to build quantum systems for business and science applications. For more information about IBM's quantum computing efforts, please visit www.ibm.com/ibmq.
For more information about the IBM Q Network, as well as a full list of all partners, members, and hubs, visit https://www.research.ibm.com/ibm-q/network/
©Thumbnail Image: IBM.
(END)
2020.09.29 View 9169