NT
-
 KAIST Captures Protein Reaction in Just Six Milliseconds
Understanding biomolecular processes - such as protein-protein interactions and enzyme-substrate reactions that occur on the microseconds to millisecond time scale is essential for comprehending life processes and advancing drug development. KAIST researchers have developed a method for freezing and analyzing biochemical reaction dynamics within a span of just a few milliseconds, marking a significant step forward in better understanding complex biological reactions.
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jin Young Kang and Haerang Hwang of the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program of the Department of Chemistry, along with Professor Wonhee Lee of the Department of Physics >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th of March that a joint research team led by Professor Jin Young Kang from the Department of Chemistry and Professor Wonhee Lee from the Department of Physics has developed a parylene-based thin-film microfluidic mixing-and-spraying device for ultra-fast biochemical reaction studies.
*Parylene: A key material for microfluidic devices used to observe protein dynamics at ultra-high speeds. It can be fabricated into a few micrometer-thick films, which can be used in making a spray nozzle for microfluidic devices.
This research overcomes the limitations of the existing time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy (TRCEM) method by reducing sample consumption to one-third of the conventional amount while improving the minimum time resolution—down to just six milliseconds (6 ms).
TRCEM is a technique that rapidly freezes protein complexes during intermediate reaction stages under cryogenic conditions, which allows researchers to analyze their structures. This approach has gained significant attention recently for its ability to capture transient biochemical events.
< Figure 1. Time-resolved cryo-EM (TRCEM) technique using microfluidic channels. In order to capture the intermediate structure of biomolecules during a biochemical reaction over time, biomolecules and reaction substrates are mixed in a microfluidic channel, and then sprayed on a grid after a certain reaction time and frozen in liquid ethane to prepare a cryo-EM sample. This can then be analyzed by cryo-EM to observe the structural changes of proteins over time. >
Transient intermediate structures of protein complexes could not be captured by traditional cryo-electron microscopy due to their extremely short lifespans. Although several TRCEM techniques have been developed to address this issue, previous methods were hindered by large sample consumption and limited time resolution. To overcome these challenges, the KAIST team developed a new mixing-and-spraying device using ultra-thin parylene films. The integrated design of the device further enhanced the precision and reproducibility of experiments.
< Figure 2. TRCEM grid fabrication setup using a parylene-based thin-film microfluidic device and actual appearance of the device. You can see that a thin-film parylene channel is inserted into the injection nozzle. The integration of the reaction channel and the injection nozzle allowed the residence time in the device to be reduced to at least 0.5 ms. >
“This research makes TRCEM more practical and paves the way for diverse applications of the parylene thin-film device in structural biology, drug development, enzyme reaction studies, and biosensor research.” Professor Jin Young Kang explained, emphasizing the significance of the study.
Professor Wonhee Lee added, “The team aims to continue this research, focusing on improvement of the technique to achieve higher time resolution with minimal sample consumption.”
< Figure 3. Comparison of the spraying patterns of the parylene mixing-jet device and the conventional mixing-jet device and the filament length in the resulting RecA-ssDNA filament formation reaction. It was shown that the thin film spray nozzle structure affects the uniformity and accuracy of the final reaction time. >
The research findings, with Haerang Hwang (a graduate student in the integrated master's and Ph.D. program in the Department of Chemistry) as the first author, were published online on January 28, 2025, in the international journal Advanced Functional Materials. (Paper Title: “Integrated Parylene-Based Thin-Film Microfluidic Device for Time-Resolved Cryo-Electron Microscopy”, DOI: doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202418224)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Samsung Future Technology Development Program, and the CELINE consortium.
2025.03.24 View 3604
KAIST Captures Protein Reaction in Just Six Milliseconds
Understanding biomolecular processes - such as protein-protein interactions and enzyme-substrate reactions that occur on the microseconds to millisecond time scale is essential for comprehending life processes and advancing drug development. KAIST researchers have developed a method for freezing and analyzing biochemical reaction dynamics within a span of just a few milliseconds, marking a significant step forward in better understanding complex biological reactions.
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jin Young Kang and Haerang Hwang of the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program of the Department of Chemistry, along with Professor Wonhee Lee of the Department of Physics >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th of March that a joint research team led by Professor Jin Young Kang from the Department of Chemistry and Professor Wonhee Lee from the Department of Physics has developed a parylene-based thin-film microfluidic mixing-and-spraying device for ultra-fast biochemical reaction studies.
*Parylene: A key material for microfluidic devices used to observe protein dynamics at ultra-high speeds. It can be fabricated into a few micrometer-thick films, which can be used in making a spray nozzle for microfluidic devices.
This research overcomes the limitations of the existing time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy (TRCEM) method by reducing sample consumption to one-third of the conventional amount while improving the minimum time resolution—down to just six milliseconds (6 ms).
TRCEM is a technique that rapidly freezes protein complexes during intermediate reaction stages under cryogenic conditions, which allows researchers to analyze their structures. This approach has gained significant attention recently for its ability to capture transient biochemical events.
< Figure 1. Time-resolved cryo-EM (TRCEM) technique using microfluidic channels. In order to capture the intermediate structure of biomolecules during a biochemical reaction over time, biomolecules and reaction substrates are mixed in a microfluidic channel, and then sprayed on a grid after a certain reaction time and frozen in liquid ethane to prepare a cryo-EM sample. This can then be analyzed by cryo-EM to observe the structural changes of proteins over time. >
Transient intermediate structures of protein complexes could not be captured by traditional cryo-electron microscopy due to their extremely short lifespans. Although several TRCEM techniques have been developed to address this issue, previous methods were hindered by large sample consumption and limited time resolution. To overcome these challenges, the KAIST team developed a new mixing-and-spraying device using ultra-thin parylene films. The integrated design of the device further enhanced the precision and reproducibility of experiments.
< Figure 2. TRCEM grid fabrication setup using a parylene-based thin-film microfluidic device and actual appearance of the device. You can see that a thin-film parylene channel is inserted into the injection nozzle. The integration of the reaction channel and the injection nozzle allowed the residence time in the device to be reduced to at least 0.5 ms. >
“This research makes TRCEM more practical and paves the way for diverse applications of the parylene thin-film device in structural biology, drug development, enzyme reaction studies, and biosensor research.” Professor Jin Young Kang explained, emphasizing the significance of the study.
Professor Wonhee Lee added, “The team aims to continue this research, focusing on improvement of the technique to achieve higher time resolution with minimal sample consumption.”
< Figure 3. Comparison of the spraying patterns of the parylene mixing-jet device and the conventional mixing-jet device and the filament length in the resulting RecA-ssDNA filament formation reaction. It was shown that the thin film spray nozzle structure affects the uniformity and accuracy of the final reaction time. >
The research findings, with Haerang Hwang (a graduate student in the integrated master's and Ph.D. program in the Department of Chemistry) as the first author, were published online on January 28, 2025, in the international journal Advanced Functional Materials. (Paper Title: “Integrated Parylene-Based Thin-Film Microfluidic Device for Time-Resolved Cryo-Electron Microscopy”, DOI: doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202418224)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Samsung Future Technology Development Program, and the CELINE consortium.
2025.03.24 View 3604 -
 KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3851
KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3851 -
 KAIST perfectly reproduces Joseon-era Irworobongdo without pigments
Typically, chemical pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum are required to produce colors. However, KAIST researchers have successfully reproduced the Joseon-era Irworobongdo [일월오봉도] painting using ultra-precise color graphics without any chemical pigments, allowing for the permanent and eco-friendly preservation of color graphics without fading or discoloration.
< (From left) Chaerim Son, a graduate of the Department of Biochemical Engineering (lead author), Seong Kyeong Nam, a graduate of the PhD program, Jiwoo Lee, a PhD student, and Professor Shin-Hyun Kim >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th of February that a research team led by Professor Shinhyun Kim from the Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering had developed a technology that enables high-resolution color graphics without using any chemical pigments by employing hemisphere-shaped microstructures.
Morpho butterflies that are brilliant blue in color or Panther chameleons that change skin color exhibit coloration without chemical pigments, as ordered nanostructures within a material reflect visible light through optical interference. Since structural colors arise from physical structures rather than chemical substances, a single material can produce a wide range of colors.
However, the artificial implementation of structural coloration is highly challenging due to the complexity of creating ordered nanostructures. Additionally, it is difficult to produce a variety of colors and to pattern them precisely into complex designs.
< Figure 1. Principle of structural color expression using micro-hemispheres (left) and method of forming micro-hemisphere patterns based on photolithography (right) >
Professor Kim’s team overcame these challenges by using smooth-surfaced hemispherical microstructures instead of ordered nanostructures, enabling the high-precision patterning of diverse structural colors.
When light enters the inverted hemispherical microstructures, the portion of light entering from the sides undergoes total internal reflection along the curved surface, creating retroreflection. When the hemisphere diameter is approximately 10 micrometers (about one-tenth the thickness of a human hair), light traveling along different reflection paths interferes within the visible spectrum, producing structural coloration.
< Figure 2. “Irworobongdo”, the Painting of the Sun, Moon, and the Five Peaks, reproduced in fingernail size without pigment using approximately 200,000 micro-hemispheres >
The structural color can be tuned by adjusting the size of the hemispheres. By arranging hemispheres of varying sizes, much like mixing paints on a palette, an infinite range of colors can be generated.
To precisely pattern microscale hemispheres of different sizes, the research team employed photolithography* using positive photoresists** commonly used in semiconductor processing. They first patterned photoresists into micropillar structures, then induced reflow*** by heating the material, forming hemispherical microstructures.
*Photolithography: A technique used in semiconductor fabrication to pattern microscale structures.
**Positive photoresist: A photosensitive polymer that dissolves more easily in a developer solution after exposure to ultraviolet light.
***Reflow: A process in which a polymer material softens and reshapes into a curved structure when heated.
This method enables the formation of hemisphere-shaped microstructures with the desired sizes and colors in a single-step fabrication process. It also allows for the reproduction of arbitrary color graphics using a single material without any pigments.
The ultra-precise color graphics created with this technique can exhibit color variations depending on the angle of incident light or the viewing perspective. The pattern appears colored from one direction while remaining transparent from the opposite side, exhibiting a Janus effect. These structural color graphics achieve resolution comparable to cutting-edge LED displays, allowing complex color images to be captured within a fingernail-sized area and projected onto large screens.
< Figure 3. “Irworobongdo” that displays different shades depending on the angle of light and viewing direction >
Professor Shinhyun Kim, who led the research, stated, “Our newly developed pigment-free color graphics technology can serve as an innovative method for artistic expression, merging art with advanced materials. Additionally, it holds broad application potential in optical devices and sensors, anti-counterfeiting materials, aesthetic photocard printing, and many other fields.”
This research, with KAIST researcher Chaerim Son as the first author, was published in the prestigious materials science journal Advanced Materials on February 5.
(Paper title: “Retroreflective Multichrome Microdome Arrays Created by Single-Step Reflow”, DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413143 )
< Figure 4. Famous paintings reproduced without pigment: “Impression, Sunrise” (left), “Girl with a Pearl Earring” (right) >
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Pioneer Converging Technology R&D Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program.
2025.02.26 View 4275
KAIST perfectly reproduces Joseon-era Irworobongdo without pigments
Typically, chemical pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum are required to produce colors. However, KAIST researchers have successfully reproduced the Joseon-era Irworobongdo [일월오봉도] painting using ultra-precise color graphics without any chemical pigments, allowing for the permanent and eco-friendly preservation of color graphics without fading or discoloration.
< (From left) Chaerim Son, a graduate of the Department of Biochemical Engineering (lead author), Seong Kyeong Nam, a graduate of the PhD program, Jiwoo Lee, a PhD student, and Professor Shin-Hyun Kim >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th of February that a research team led by Professor Shinhyun Kim from the Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering had developed a technology that enables high-resolution color graphics without using any chemical pigments by employing hemisphere-shaped microstructures.
Morpho butterflies that are brilliant blue in color or Panther chameleons that change skin color exhibit coloration without chemical pigments, as ordered nanostructures within a material reflect visible light through optical interference. Since structural colors arise from physical structures rather than chemical substances, a single material can produce a wide range of colors.
However, the artificial implementation of structural coloration is highly challenging due to the complexity of creating ordered nanostructures. Additionally, it is difficult to produce a variety of colors and to pattern them precisely into complex designs.
< Figure 1. Principle of structural color expression using micro-hemispheres (left) and method of forming micro-hemisphere patterns based on photolithography (right) >
Professor Kim’s team overcame these challenges by using smooth-surfaced hemispherical microstructures instead of ordered nanostructures, enabling the high-precision patterning of diverse structural colors.
When light enters the inverted hemispherical microstructures, the portion of light entering from the sides undergoes total internal reflection along the curved surface, creating retroreflection. When the hemisphere diameter is approximately 10 micrometers (about one-tenth the thickness of a human hair), light traveling along different reflection paths interferes within the visible spectrum, producing structural coloration.
< Figure 2. “Irworobongdo”, the Painting of the Sun, Moon, and the Five Peaks, reproduced in fingernail size without pigment using approximately 200,000 micro-hemispheres >
The structural color can be tuned by adjusting the size of the hemispheres. By arranging hemispheres of varying sizes, much like mixing paints on a palette, an infinite range of colors can be generated.
To precisely pattern microscale hemispheres of different sizes, the research team employed photolithography* using positive photoresists** commonly used in semiconductor processing. They first patterned photoresists into micropillar structures, then induced reflow*** by heating the material, forming hemispherical microstructures.
*Photolithography: A technique used in semiconductor fabrication to pattern microscale structures.
**Positive photoresist: A photosensitive polymer that dissolves more easily in a developer solution after exposure to ultraviolet light.
***Reflow: A process in which a polymer material softens and reshapes into a curved structure when heated.
This method enables the formation of hemisphere-shaped microstructures with the desired sizes and colors in a single-step fabrication process. It also allows for the reproduction of arbitrary color graphics using a single material without any pigments.
The ultra-precise color graphics created with this technique can exhibit color variations depending on the angle of incident light or the viewing perspective. The pattern appears colored from one direction while remaining transparent from the opposite side, exhibiting a Janus effect. These structural color graphics achieve resolution comparable to cutting-edge LED displays, allowing complex color images to be captured within a fingernail-sized area and projected onto large screens.
< Figure 3. “Irworobongdo” that displays different shades depending on the angle of light and viewing direction >
Professor Shinhyun Kim, who led the research, stated, “Our newly developed pigment-free color graphics technology can serve as an innovative method for artistic expression, merging art with advanced materials. Additionally, it holds broad application potential in optical devices and sensors, anti-counterfeiting materials, aesthetic photocard printing, and many other fields.”
This research, with KAIST researcher Chaerim Son as the first author, was published in the prestigious materials science journal Advanced Materials on February 5.
(Paper title: “Retroreflective Multichrome Microdome Arrays Created by Single-Step Reflow”, DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413143 )
< Figure 4. Famous paintings reproduced without pigment: “Impression, Sunrise” (left), “Girl with a Pearl Earring” (right) >
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Pioneer Converging Technology R&D Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program.
2025.02.26 View 4275 -
 KAIST achieves quantum entanglement essential for quantum error correction
Quantum computing is a technology capable of solving complex problems that classical computers struggle with. To perform accurate computations, quantum computers must correct errors that arise during operations. However, generating the quantum entanglement necessary for quantum error correction has long been considered a major challenge.
< Photo 1. (From left) Students Young-Do Yoon and Chan Roh of the Master's and Doctoral Integrated Program of the Department of Physics poses with Professor Young-Sik Ra and Student Geunhee Gwak of the same program >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of February that a research team led by Professor Young-Sik Ra from the Department of Physics has successfully implemented a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, a key component for quantum error correction, through experimental demonstration.
Measurement-based quantum computing is an emerging paradigm that implements quantum computations by measuring specially entangled cluster states. The core of this approach lies in the generation of these cluster quantum entangled states, with two-dimensional cluster states commonly used for universal quantum computing.
However, to advance towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, which can correct quantum errors occurring during computations, a more complex three-dimensional cluster state is required. While previous studies have reported the generation of two-dimensional cluster states, experimental implementation of the three-dimensional cluster states necessary for fault-tolerant quantum computing had remained elusive due to the extreme complexity of their entanglement structure.
< Figure 1. (a) Experimental schematic. A pulse laser with a wavelength of 800 nm is converted into a pulse laser with a wavelength of 400 nm through second harmonic generation, and this is incident on a nonlinear crystal (PPKTP) to generate multiple quantum entanglement sources. (b) Generation of a 3D cluster state through optical mode basis change >
The research team overcame this challenge by developing a technique to control femtosecond time-frequency modes, successfully generating a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state for the first time.
The team directed a femtosecond laser into a nonlinear crystal, simultaneously generating quantum light sources across multiple frequency modes. (A femtosecond laser is a device that emits ultrashort, high-intensity light pulses.) Using this approach, they successfully created a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state.
Professor Young-Sik Ra noted, “This study marks the first successful demonstration of a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, which was previously difficult to achieve with existing technology. This breakthrough is expected to serve as a crucial stepping stone for future research in measurement-based and fault-tolerant quantum computing.”
< Figure 2. Results of 3D cluster state generation. (a) Nullifier measurement of the cluster state. (b) 3D cluster state reconstructed using quantum state tomography. (c) Confirmation of quantum entanglement characteristics of the 3D cluster state >
The study was published online in Nature Photonics on February 24, 2025. The first author is Chan Roh, a Ph.D. candidate in KAIST’s integrated master’s and doctoral program, with Geunhee Gwak and Youngdo Yoon contributing as co-authors. (Paper title: “Generation of Three-Dimensional Cluster Entangled State”, DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01631-2)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Quantum Computing Technology Development Program, Mid-Career Researcher Support Program, and Quantum Simulator for Materials Innovation Program), the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (Quantum Internet Core Technology Program, University ICT Research Center Support Program), and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory.
2025.02.25 View 3238
KAIST achieves quantum entanglement essential for quantum error correction
Quantum computing is a technology capable of solving complex problems that classical computers struggle with. To perform accurate computations, quantum computers must correct errors that arise during operations. However, generating the quantum entanglement necessary for quantum error correction has long been considered a major challenge.
< Photo 1. (From left) Students Young-Do Yoon and Chan Roh of the Master's and Doctoral Integrated Program of the Department of Physics poses with Professor Young-Sik Ra and Student Geunhee Gwak of the same program >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of February that a research team led by Professor Young-Sik Ra from the Department of Physics has successfully implemented a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, a key component for quantum error correction, through experimental demonstration.
Measurement-based quantum computing is an emerging paradigm that implements quantum computations by measuring specially entangled cluster states. The core of this approach lies in the generation of these cluster quantum entangled states, with two-dimensional cluster states commonly used for universal quantum computing.
However, to advance towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, which can correct quantum errors occurring during computations, a more complex three-dimensional cluster state is required. While previous studies have reported the generation of two-dimensional cluster states, experimental implementation of the three-dimensional cluster states necessary for fault-tolerant quantum computing had remained elusive due to the extreme complexity of their entanglement structure.
< Figure 1. (a) Experimental schematic. A pulse laser with a wavelength of 800 nm is converted into a pulse laser with a wavelength of 400 nm through second harmonic generation, and this is incident on a nonlinear crystal (PPKTP) to generate multiple quantum entanglement sources. (b) Generation of a 3D cluster state through optical mode basis change >
The research team overcame this challenge by developing a technique to control femtosecond time-frequency modes, successfully generating a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state for the first time.
The team directed a femtosecond laser into a nonlinear crystal, simultaneously generating quantum light sources across multiple frequency modes. (A femtosecond laser is a device that emits ultrashort, high-intensity light pulses.) Using this approach, they successfully created a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state.
Professor Young-Sik Ra noted, “This study marks the first successful demonstration of a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, which was previously difficult to achieve with existing technology. This breakthrough is expected to serve as a crucial stepping stone for future research in measurement-based and fault-tolerant quantum computing.”
< Figure 2. Results of 3D cluster state generation. (a) Nullifier measurement of the cluster state. (b) 3D cluster state reconstructed using quantum state tomography. (c) Confirmation of quantum entanglement characteristics of the 3D cluster state >
The study was published online in Nature Photonics on February 24, 2025. The first author is Chan Roh, a Ph.D. candidate in KAIST’s integrated master’s and doctoral program, with Geunhee Gwak and Youngdo Yoon contributing as co-authors. (Paper title: “Generation of Three-Dimensional Cluster Entangled State”, DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01631-2)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Quantum Computing Technology Development Program, Mid-Career Researcher Support Program, and Quantum Simulator for Materials Innovation Program), the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (Quantum Internet Core Technology Program, University ICT Research Center Support Program), and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory.
2025.02.25 View 3238 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 5142
KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 5142 -
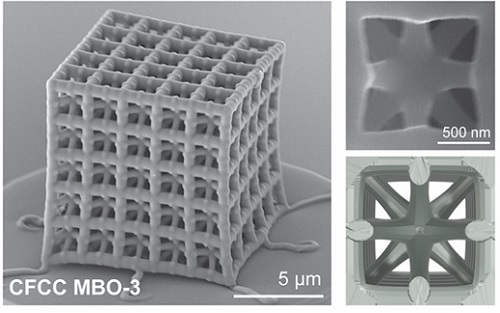 Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4977
Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4977 -
 Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 3971
Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 3971 -
 KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 6047
KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 6047 -
 KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 6869
KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 6869 -
 KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 4383
KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 4383 -
 KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 26668
KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 26668 -
 A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 7465
A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 7465