ICA
-
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6311
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6311 -
 KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 4037
KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 4037 -
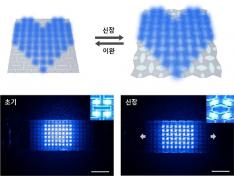 KAIST Develops Stretchable Displays Featuring 25% Expansion Without Image Distortion
Stretchable displays, praised for their spatial efficiency, design flexibility, and human-like flexibility, are seen as the next generation of display technology. A team of Korean researchers has developed a stretchable display that can expand by 25% while maintaining clear image quality without distortion. It can also stretch and contract up to 5,000 times at 15% expansion without any performance degradation, making it the first deformation-free stretchable display with a negative Poisson's ratio* developed in Korea.
*Poisson’s ratio of -1: A ratio where both width and length stretch equally, expressed as a negative value. A positive Poisson's ratio represents the ratio where horizontal stretching leads to vertical contraction, which is the case for most materials.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of August that a research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (Director of the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center) , in collaboration with the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials (President Seoghyeon Ryu), successfully developed a stretchable display substrate that suppresses image distortion through omnidirectional stretchability.
Currently, most stretchable displays are made with highly elastic elastomer* materials, but these materials possess a positive Poisson's ratio, causing unavoidable image distortion when the display is stretched.
*Elastomer: A polymer with elasticity similar to rubber.
To address this, the introduction of auxetic* meta-structures has been gaining attention. Unlike conventional materials, auxetic structures have a unique 'negative Poisson's ratio,' expanding in all directions when stretched in just one direction. However, traditional auxetic structures contain many empty spaces, limiting their stability and usability in display substrates.
*Auxetic structure: A special geometric structure that exhibits a negative Poisson's ratio.
To tackle the issue of image distortion, Professor Bae's research team developed a method to create a seamless surface for the auxetic meta-structure, achieving the ideal negative Poisson's ratio of -1 and overcoming the biggest challenge in auxetic meta-structures.
To overcome the second issue of elastic modulus*, the team inserted a textile made of glass fiber bundles with a diameter of just 25 micrometers (a quarter of the thickness of human hair) into the elastomer material. They then filled the empty spaces with the same elastomer, creating a flat and stable integrated film without gaps.
*Elastic Modulus: The ratio that indicates the extent of deformation when force is applied to a material. A higher elastic modulus means that the material is less likely to deform under force.
The research team theoretically identified that the difference in elasticity between the auxetic structure and the elastomer material directly influences the negative Poisson's ratio and successfully achieved an elasticity difference of over 230,000 times, producing a film with a Poisson's ratio of -1, the theoretical limit.
< Figure 2. Deformation of S-AUX film. a) Configurations and visualized principal strain distribution of the optimized S-AUX film at various strain rates. b) Biaxial stretching image. While pristine elastomer shrinks in the directions that were not stretched, S-AUX film developed in this study expands in all directions simultaneously while maintaining its original shape. >
Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, who led the study, explained, "Preventing image distortion using auxetic structures in stretchable displays is a core technology, but it has faced challenges due to the many empty spaces in the surface, making it difficult to use as a substrate. This research outcome is expected to significantly accelerate commercialization through high-resolution, distortion-free stretchable display applications that utilize the entire surface."
This study, co-authored by Dr. Yung Lee from KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Dr. Bongkyun Jang from the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, was published on August 20th in the international journal Nature Communications under the title "A seamless auxetic substrate with a negative Poisson's ratio of –1".
The research was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center at KAIST, the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, and LG Display.
< Figure 3. Structural configuration of the distortion-free display components on the S-AUX film and a contour image of a micro-LED chip transferred onto the S-AUX film. >
< Figure 4. Schematic illustrations and photographic images of the S-AUX film-based image: distortion-free display in its stretched state and released state. >
2024.09.20 View 5861
KAIST Develops Stretchable Displays Featuring 25% Expansion Without Image Distortion
Stretchable displays, praised for their spatial efficiency, design flexibility, and human-like flexibility, are seen as the next generation of display technology. A team of Korean researchers has developed a stretchable display that can expand by 25% while maintaining clear image quality without distortion. It can also stretch and contract up to 5,000 times at 15% expansion without any performance degradation, making it the first deformation-free stretchable display with a negative Poisson's ratio* developed in Korea.
*Poisson’s ratio of -1: A ratio where both width and length stretch equally, expressed as a negative value. A positive Poisson's ratio represents the ratio where horizontal stretching leads to vertical contraction, which is the case for most materials.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of August that a research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (Director of the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center) , in collaboration with the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials (President Seoghyeon Ryu), successfully developed a stretchable display substrate that suppresses image distortion through omnidirectional stretchability.
Currently, most stretchable displays are made with highly elastic elastomer* materials, but these materials possess a positive Poisson's ratio, causing unavoidable image distortion when the display is stretched.
*Elastomer: A polymer with elasticity similar to rubber.
To address this, the introduction of auxetic* meta-structures has been gaining attention. Unlike conventional materials, auxetic structures have a unique 'negative Poisson's ratio,' expanding in all directions when stretched in just one direction. However, traditional auxetic structures contain many empty spaces, limiting their stability and usability in display substrates.
*Auxetic structure: A special geometric structure that exhibits a negative Poisson's ratio.
To tackle the issue of image distortion, Professor Bae's research team developed a method to create a seamless surface for the auxetic meta-structure, achieving the ideal negative Poisson's ratio of -1 and overcoming the biggest challenge in auxetic meta-structures.
To overcome the second issue of elastic modulus*, the team inserted a textile made of glass fiber bundles with a diameter of just 25 micrometers (a quarter of the thickness of human hair) into the elastomer material. They then filled the empty spaces with the same elastomer, creating a flat and stable integrated film without gaps.
*Elastic Modulus: The ratio that indicates the extent of deformation when force is applied to a material. A higher elastic modulus means that the material is less likely to deform under force.
The research team theoretically identified that the difference in elasticity between the auxetic structure and the elastomer material directly influences the negative Poisson's ratio and successfully achieved an elasticity difference of over 230,000 times, producing a film with a Poisson's ratio of -1, the theoretical limit.
< Figure 2. Deformation of S-AUX film. a) Configurations and visualized principal strain distribution of the optimized S-AUX film at various strain rates. b) Biaxial stretching image. While pristine elastomer shrinks in the directions that were not stretched, S-AUX film developed in this study expands in all directions simultaneously while maintaining its original shape. >
Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, who led the study, explained, "Preventing image distortion using auxetic structures in stretchable displays is a core technology, but it has faced challenges due to the many empty spaces in the surface, making it difficult to use as a substrate. This research outcome is expected to significantly accelerate commercialization through high-resolution, distortion-free stretchable display applications that utilize the entire surface."
This study, co-authored by Dr. Yung Lee from KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Dr. Bongkyun Jang from the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, was published on August 20th in the international journal Nature Communications under the title "A seamless auxetic substrate with a negative Poisson's ratio of –1".
The research was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center at KAIST, the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, and LG Display.
< Figure 3. Structural configuration of the distortion-free display components on the S-AUX film and a contour image of a micro-LED chip transferred onto the S-AUX film. >
< Figure 4. Schematic illustrations and photographic images of the S-AUX film-based image: distortion-free display in its stretched state and released state. >
2024.09.20 View 5861 -
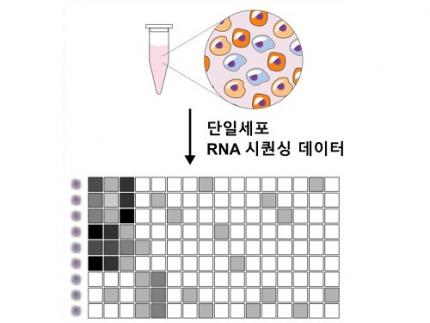 Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 6099
Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 6099 -
 KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 7233
KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 7233 -
 Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 8822
Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 8822 -
 KAIST Professor Jiyun Lee becomes the first Korean to receive the Thurlow Award from the American Institute of Navigation
< Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on January 27th that Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering had won the Colonel Thomas L. Thurlow Award from the American Institute of Navigation (ION) for her achievements in the field of satellite navigation.
The American Institute of Navigation (ION) announced Distinguished Professor Lee as the winner of the Thurlow Award at its annual awards ceremony held in conjunction with its international conference in Long Beach, California on January 25th. This is the first time a person of Korean descent has received the award.
The Thurlow Award was established in 1945 to honor Colonel Thomas L. Thurlow, who made significant contributions to the development of navigation equipment and the training of navigators. This award aims to recognize an individual who has made an outstanding contribution to the development of navigation and it is awarded to one person each year. Past recipients include MIT professor Charles Stark Draper, who is well-known as the father of inertial navigation and who developed the guidance computer for the Apollo moon landing project.
Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee was recognized for her significant contributions to technological advancements that ensure the safety of satellite-based navigation systems for aviation. In particular, she was recognized as a world authority in the field of navigation integrity architecture design, which is essential for ensuring the stability of intelligent transportation systems and autonomous unmanned systems. Distinguished Professor Lee made a groundbreaking contribution to help ensure the safety of satellite-based navigation systems from ionospheric disturbances, including those affected by sudden changes in external factors such as the solar and space environment.
She has achieved numerous scientific discoveries in the field of ionospheric research, while developing new ionospheric threat modeling methods, ionospheric anomaly monitoring and mitigation techniques, and integrity and availability assessment techniques for next-generation augmented navigation systems. She also contributed to the international standardization of technology through the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
Distinguished Professor Lee and her research group have pioneered innovative navigation technologies for the safe and autonomous operation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and urban air mobility (UAM). She was the first to propose and develop a low-cost navigation satellite system (GNSS) augmented architecture for UAVs with a near-field network operation concept that ensures high integrity, and a networked ground station-based augmented navigation system for UAM. She also contributed to integrity design techniques, including failure monitoring and integrity risk assessment for multi-sensor integrated navigation systems.
< Professor Jiyoon Lee upon receiving the Thurlow Award >
Bradford Parkinson, professor emeritus at Stanford University and winner of the 1986 Thurlow Award, who is known as the father of GPS, congratulated Distinguished Professor Lee upon hearing that she was receiving the Thurlow Award and commented that her innovative research has addressed many important topics in the field of navigation and her solutions are highly innovative and highly regarded.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “I am very honored and delighted to receive this award with its deep history and tradition in the field of navigation.” She added, “I will strive to help develop the future mobility industry by securing safe and sustainable navigation technology.”
2024.01.26 View 7566
KAIST Professor Jiyun Lee becomes the first Korean to receive the Thurlow Award from the American Institute of Navigation
< Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on January 27th that Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering had won the Colonel Thomas L. Thurlow Award from the American Institute of Navigation (ION) for her achievements in the field of satellite navigation.
The American Institute of Navigation (ION) announced Distinguished Professor Lee as the winner of the Thurlow Award at its annual awards ceremony held in conjunction with its international conference in Long Beach, California on January 25th. This is the first time a person of Korean descent has received the award.
The Thurlow Award was established in 1945 to honor Colonel Thomas L. Thurlow, who made significant contributions to the development of navigation equipment and the training of navigators. This award aims to recognize an individual who has made an outstanding contribution to the development of navigation and it is awarded to one person each year. Past recipients include MIT professor Charles Stark Draper, who is well-known as the father of inertial navigation and who developed the guidance computer for the Apollo moon landing project.
Distinguished Professor Jiyun Lee was recognized for her significant contributions to technological advancements that ensure the safety of satellite-based navigation systems for aviation. In particular, she was recognized as a world authority in the field of navigation integrity architecture design, which is essential for ensuring the stability of intelligent transportation systems and autonomous unmanned systems. Distinguished Professor Lee made a groundbreaking contribution to help ensure the safety of satellite-based navigation systems from ionospheric disturbances, including those affected by sudden changes in external factors such as the solar and space environment.
She has achieved numerous scientific discoveries in the field of ionospheric research, while developing new ionospheric threat modeling methods, ionospheric anomaly monitoring and mitigation techniques, and integrity and availability assessment techniques for next-generation augmented navigation systems. She also contributed to the international standardization of technology through the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
Distinguished Professor Lee and her research group have pioneered innovative navigation technologies for the safe and autonomous operation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and urban air mobility (UAM). She was the first to propose and develop a low-cost navigation satellite system (GNSS) augmented architecture for UAVs with a near-field network operation concept that ensures high integrity, and a networked ground station-based augmented navigation system for UAM. She also contributed to integrity design techniques, including failure monitoring and integrity risk assessment for multi-sensor integrated navigation systems.
< Professor Jiyoon Lee upon receiving the Thurlow Award >
Bradford Parkinson, professor emeritus at Stanford University and winner of the 1986 Thurlow Award, who is known as the father of GPS, congratulated Distinguished Professor Lee upon hearing that she was receiving the Thurlow Award and commented that her innovative research has addressed many important topics in the field of navigation and her solutions are highly innovative and highly regarded.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “I am very honored and delighted to receive this award with its deep history and tradition in the field of navigation.” She added, “I will strive to help develop the future mobility industry by securing safe and sustainable navigation technology.”
2024.01.26 View 7566 -
 KAIST Research Team Breaks Down Musical Instincts with AI
Music, often referred to as the universal language, is known to be a common component in all cultures. Then, could ‘musical instinct’ be something that is shared to some degree despite the extensive environmental differences amongst cultures?
On January 16, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hawoong Jung from the Department of Physics announced to have identified the principle by which musical instincts emerge from the human brain without special learning using an artificial neural network model.
Previously, many researchers have attempted to identify the similarities and differences between the music that exist in various different cultures, and tried to understand the origin of the universality. A paper published in Science in 2019 had revealed that music is produced in all ethnographically distinct cultures, and that similar forms of beats and tunes are used. Neuroscientist have also previously found out that a specific part of the human brain, namely the auditory cortex, is responsible for processing musical information.
Professor Jung’s team used an artificial neural network model to show that cognitive functions for music forms spontaneously as a result of processing auditory information received from nature, without being taught music. The research team utilized AudioSet, a large-scale collection of sound data provided by Google, and taught the artificial neural network to learn the various sounds. Interestingly, the research team discovered that certain neurons within the network model would respond selectively to music. In other words, they observed the spontaneous generation of neurons that reacted minimally to various other sounds like those of animals, nature, or machines, but showed high levels of response to various forms of music including both instrumental and vocal.
The neurons in the artificial neural network model showed similar reactive behaviours to those in the auditory cortex of a real brain. For example, artificial neurons responded less to the sound of music that was cropped into short intervals and were rearranged. This indicates that the spontaneously-generated music-selective neurons encode the temporal structure of music. This property was not limited to a specific genre of music, but emerged across 25 different genres including classic, pop, rock, jazz, and electronic.
< Figure 1. Illustration of the musicality of the brain and artificial neural network (created with DALL·E3 AI based on the paper content) >
Furthermore, suppressing the activity of the music-selective neurons was found to greatly impede the cognitive accuracy for other natural sounds. That is to say, the neural function that processes musical information helps process other sounds, and that ‘musical ability’ may be an instinct formed as a result of an evolutionary adaptation acquired to better process sounds from nature.
Professor Hawoong Jung, who advised the research, said, “The results of our study imply that evolutionary pressure has contributed to forming the universal basis for processing musical information in various cultures.” As for the significance of the research, he explained, “We look forward for this artificially built model with human-like musicality to become an original model for various applications including AI music generation, musical therapy, and for research in musical cognition.” He also commented on its limitations, adding, “This research however does not take into consideration the developmental process that follows the learning of music, and it must be noted that this is a study on the foundation of processing musical information in early development.”
< Figure 2. The artificial neural network that learned to recognize non-musical natural sounds in the cyber space distinguishes between music and non-music. >
This research, conducted by first author Dr. Gwangsu Kim of the KAIST Department of Physics (current affiliation: MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences) and Dr. Dong-Kyum Kim (current affiliation: IBS) was published in Nature Communications under the title, “Spontaneous emergence of rudimentary music detectors in deep neural networks”.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.01.23 View 7801
KAIST Research Team Breaks Down Musical Instincts with AI
Music, often referred to as the universal language, is known to be a common component in all cultures. Then, could ‘musical instinct’ be something that is shared to some degree despite the extensive environmental differences amongst cultures?
On January 16, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hawoong Jung from the Department of Physics announced to have identified the principle by which musical instincts emerge from the human brain without special learning using an artificial neural network model.
Previously, many researchers have attempted to identify the similarities and differences between the music that exist in various different cultures, and tried to understand the origin of the universality. A paper published in Science in 2019 had revealed that music is produced in all ethnographically distinct cultures, and that similar forms of beats and tunes are used. Neuroscientist have also previously found out that a specific part of the human brain, namely the auditory cortex, is responsible for processing musical information.
Professor Jung’s team used an artificial neural network model to show that cognitive functions for music forms spontaneously as a result of processing auditory information received from nature, without being taught music. The research team utilized AudioSet, a large-scale collection of sound data provided by Google, and taught the artificial neural network to learn the various sounds. Interestingly, the research team discovered that certain neurons within the network model would respond selectively to music. In other words, they observed the spontaneous generation of neurons that reacted minimally to various other sounds like those of animals, nature, or machines, but showed high levels of response to various forms of music including both instrumental and vocal.
The neurons in the artificial neural network model showed similar reactive behaviours to those in the auditory cortex of a real brain. For example, artificial neurons responded less to the sound of music that was cropped into short intervals and were rearranged. This indicates that the spontaneously-generated music-selective neurons encode the temporal structure of music. This property was not limited to a specific genre of music, but emerged across 25 different genres including classic, pop, rock, jazz, and electronic.
< Figure 1. Illustration of the musicality of the brain and artificial neural network (created with DALL·E3 AI based on the paper content) >
Furthermore, suppressing the activity of the music-selective neurons was found to greatly impede the cognitive accuracy for other natural sounds. That is to say, the neural function that processes musical information helps process other sounds, and that ‘musical ability’ may be an instinct formed as a result of an evolutionary adaptation acquired to better process sounds from nature.
Professor Hawoong Jung, who advised the research, said, “The results of our study imply that evolutionary pressure has contributed to forming the universal basis for processing musical information in various cultures.” As for the significance of the research, he explained, “We look forward for this artificially built model with human-like musicality to become an original model for various applications including AI music generation, musical therapy, and for research in musical cognition.” He also commented on its limitations, adding, “This research however does not take into consideration the developmental process that follows the learning of music, and it must be noted that this is a study on the foundation of processing musical information in early development.”
< Figure 2. The artificial neural network that learned to recognize non-musical natural sounds in the cyber space distinguishes between music and non-music. >
This research, conducted by first author Dr. Gwangsu Kim of the KAIST Department of Physics (current affiliation: MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences) and Dr. Dong-Kyum Kim (current affiliation: IBS) was published in Nature Communications under the title, “Spontaneous emergence of rudimentary music detectors in deep neural networks”.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.01.23 View 7801 -
 KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 11019
KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 11019 -
 North Korea and Beyond: AI-Powered Satellite Analysis Reveals the Unseen Economic Landscape of Underdeveloped Nations
- A joint research team in computer science, economics, and geography has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) technology to measure grid-level economic development within six-square-kilometer regions.
- This AI technology is applicable in regions with limited statistical data (e.g., North Korea), supporting international efforts to propose policies for economic growth and poverty reduction in underdeveloped countries.
- The research team plans to make this technology freely available for use to contribute to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The United Nations reports that more than 700 million people are in extreme poverty, earning less than two dollars a day. However, an accurate assessment of poverty remains a global challenge. For example, 53 countries have not conducted agricultural surveys in the past 15 years, and 17 countries have not published a population census. To fill this data gap, new technologies are being explored to estimate poverty using alternative sources such as street views, aerial photos, and satellite images.
The paper published in Nature Communications demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can help analyze economic conditions from daytime satellite imagery. This new technology can even apply to the least developed countries - such as North Korea - that do not have reliable statistical data for typical machine learning training.
The researchers used Sentinel-2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA) that are publicly available. They split these images into small six-square-kilometer grids. At this zoom level, visual information such as buildings, roads, and greenery can be used to quantify economic indicators. As a result, the team obtained the first ever fine-grained economic map of regions like North Korea. The same algorithm was applied to other underdeveloped countries in Asia: North Korea, Nepal, Laos, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Cambodia (see Image 1).
The key feature of their research model is the "human-machine collaborative approach," which lets researchers combine human input with AI predictions for areas with scarce data. In this research, ten human experts compared satellite images and judged the economic conditions in the area, with the AI learning from this human data and giving economic scores to each image. The results showed that the Human-AI collaborative approach outperformed machine-only learning algorithms.
< Image 1. Nightlight satellite images of North Korea (Top-left: Background photo provided by NASA's Earth Observatory). South Korea appears brightly lit compared to North Korea, which is mostly dark except for Pyongyang. In contrast, the model developed by the research team uses daytime satellite imagery to predict more detailed economic predictions for North Korea (top-right) and five Asian countries (Bottom: Background photo from Google Earth). >
The research was led by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, economists, and a geographer from KAIST & IBS (Donghyun Ahn, Meeyoung Cha, Jihee Kim), Sogang University (Hyunjoo Yang), HKUST (Sangyoon Park), and NUS (Jeasurk Yang). Dr Charles Axelsson, Associate Editor at Nature Communications, handled this paper during the peer review process at the journal.
The research team found that the scores showed a strong correlation with traditional socio-economic metrics such as population density, employment, and number of businesses. This demonstrates the wide applicability and scalability of the approach, particularly in data-scarce countries. Furthermore, the model's strength lies in its ability to detect annual changes in economic conditions at a more detailed geospatial level without using any survey data (see Image 2).
< Image 2. Differences in satellite imagery and economic scores in North Korea between 2016 and 2019. Significant development was found in the Wonsan Kalma area (top), one of the tourist development zones, but no changes were observed in the Wiwon Industrial Development Zone (bottom). (Background photo: Sentinel-2 satellite imagery provided by the European Space Agency (ESA)). >
This model would be especially valuable for rapidly monitoring the progress of Sustainable Development Goals such as reducing poverty and promoting more equitable and sustainable growth on an international scale. The model can also be adapted to measure various social and environmental indicators. For example, it can be trained to identify regions with high vulnerability to climate change and disasters to provide timely guidance on disaster relief efforts.
As an example, the researchers explored how North Korea changed before and after the United Nations sanctions against the country. By applying the model to satellite images of North Korea both in 2016 and in 2019, the researchers discovered three key trends in the country's economic development between 2016 and 2019. First, economic growth in North Korea became more concentrated in Pyongyang and major cities, exacerbating the urban-rural divide. Second, satellite imagery revealed significant changes in areas designated for tourism and economic development, such as new building construction and other meaningful alterations. Third, traditional industrial and export development zones showed relatively minor changes.
Meeyoung Cha, a data scientist in the team explained, "This is an important interdisciplinary effort to address global challenges like poverty. We plan to apply our AI algorithm to other international issues, such as monitoring carbon emissions, disaster damage detection, and the impact of climate change."
An economist on the research team, Jihee Kim, commented that this approach would enable detailed examinations of economic conditions in the developing world at a low cost, reducing data disparities between developed and developing nations. She further emphasized that this is most essential because many public policies require economic measurements to achieve their goals, whether they are for growth, equality, or sustainability.
The research team has made the source code publicly available via GitHub and plans to continue improving the technology, applying it to new satellite images updated annually. The results of this study, with Ph.D. candidate Donghyun Ahn at KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Jeasurk Yang at NUS as joint first authors, were published in Nature Communications under the title "A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery."
< Photos of the main authors. 1. Donghyun Ahn, PhD candidate at KAIST School of Computing 2. Jeasurk Yang, PhD candidate at the Department of Geography of National University of Singapore 3. Meeyoung Cha, Professor of KAIST School of Computing and CI at IBS 4. Jihee Kim, Professor of KAIST School of Business and Technology Management 5. Sangyoon Park, Professor of the Division of Social Science at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 6. Hyunjoo Yang, Professor of the Department of Economics at Sogang University >
2023.12.07 View 9027
North Korea and Beyond: AI-Powered Satellite Analysis Reveals the Unseen Economic Landscape of Underdeveloped Nations
- A joint research team in computer science, economics, and geography has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) technology to measure grid-level economic development within six-square-kilometer regions.
- This AI technology is applicable in regions with limited statistical data (e.g., North Korea), supporting international efforts to propose policies for economic growth and poverty reduction in underdeveloped countries.
- The research team plans to make this technology freely available for use to contribute to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The United Nations reports that more than 700 million people are in extreme poverty, earning less than two dollars a day. However, an accurate assessment of poverty remains a global challenge. For example, 53 countries have not conducted agricultural surveys in the past 15 years, and 17 countries have not published a population census. To fill this data gap, new technologies are being explored to estimate poverty using alternative sources such as street views, aerial photos, and satellite images.
The paper published in Nature Communications demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can help analyze economic conditions from daytime satellite imagery. This new technology can even apply to the least developed countries - such as North Korea - that do not have reliable statistical data for typical machine learning training.
The researchers used Sentinel-2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA) that are publicly available. They split these images into small six-square-kilometer grids. At this zoom level, visual information such as buildings, roads, and greenery can be used to quantify economic indicators. As a result, the team obtained the first ever fine-grained economic map of regions like North Korea. The same algorithm was applied to other underdeveloped countries in Asia: North Korea, Nepal, Laos, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Cambodia (see Image 1).
The key feature of their research model is the "human-machine collaborative approach," which lets researchers combine human input with AI predictions for areas with scarce data. In this research, ten human experts compared satellite images and judged the economic conditions in the area, with the AI learning from this human data and giving economic scores to each image. The results showed that the Human-AI collaborative approach outperformed machine-only learning algorithms.
< Image 1. Nightlight satellite images of North Korea (Top-left: Background photo provided by NASA's Earth Observatory). South Korea appears brightly lit compared to North Korea, which is mostly dark except for Pyongyang. In contrast, the model developed by the research team uses daytime satellite imagery to predict more detailed economic predictions for North Korea (top-right) and five Asian countries (Bottom: Background photo from Google Earth). >
The research was led by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, economists, and a geographer from KAIST & IBS (Donghyun Ahn, Meeyoung Cha, Jihee Kim), Sogang University (Hyunjoo Yang), HKUST (Sangyoon Park), and NUS (Jeasurk Yang). Dr Charles Axelsson, Associate Editor at Nature Communications, handled this paper during the peer review process at the journal.
The research team found that the scores showed a strong correlation with traditional socio-economic metrics such as population density, employment, and number of businesses. This demonstrates the wide applicability and scalability of the approach, particularly in data-scarce countries. Furthermore, the model's strength lies in its ability to detect annual changes in economic conditions at a more detailed geospatial level without using any survey data (see Image 2).
< Image 2. Differences in satellite imagery and economic scores in North Korea between 2016 and 2019. Significant development was found in the Wonsan Kalma area (top), one of the tourist development zones, but no changes were observed in the Wiwon Industrial Development Zone (bottom). (Background photo: Sentinel-2 satellite imagery provided by the European Space Agency (ESA)). >
This model would be especially valuable for rapidly monitoring the progress of Sustainable Development Goals such as reducing poverty and promoting more equitable and sustainable growth on an international scale. The model can also be adapted to measure various social and environmental indicators. For example, it can be trained to identify regions with high vulnerability to climate change and disasters to provide timely guidance on disaster relief efforts.
As an example, the researchers explored how North Korea changed before and after the United Nations sanctions against the country. By applying the model to satellite images of North Korea both in 2016 and in 2019, the researchers discovered three key trends in the country's economic development between 2016 and 2019. First, economic growth in North Korea became more concentrated in Pyongyang and major cities, exacerbating the urban-rural divide. Second, satellite imagery revealed significant changes in areas designated for tourism and economic development, such as new building construction and other meaningful alterations. Third, traditional industrial and export development zones showed relatively minor changes.
Meeyoung Cha, a data scientist in the team explained, "This is an important interdisciplinary effort to address global challenges like poverty. We plan to apply our AI algorithm to other international issues, such as monitoring carbon emissions, disaster damage detection, and the impact of climate change."
An economist on the research team, Jihee Kim, commented that this approach would enable detailed examinations of economic conditions in the developing world at a low cost, reducing data disparities between developed and developing nations. She further emphasized that this is most essential because many public policies require economic measurements to achieve their goals, whether they are for growth, equality, or sustainability.
The research team has made the source code publicly available via GitHub and plans to continue improving the technology, applying it to new satellite images updated annually. The results of this study, with Ph.D. candidate Donghyun Ahn at KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Jeasurk Yang at NUS as joint first authors, were published in Nature Communications under the title "A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery."
< Photos of the main authors. 1. Donghyun Ahn, PhD candidate at KAIST School of Computing 2. Jeasurk Yang, PhD candidate at the Department of Geography of National University of Singapore 3. Meeyoung Cha, Professor of KAIST School of Computing and CI at IBS 4. Jihee Kim, Professor of KAIST School of Business and Technology Management 5. Sangyoon Park, Professor of the Division of Social Science at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 6. Hyunjoo Yang, Professor of the Department of Economics at Sogang University >
2023.12.07 View 9027 -
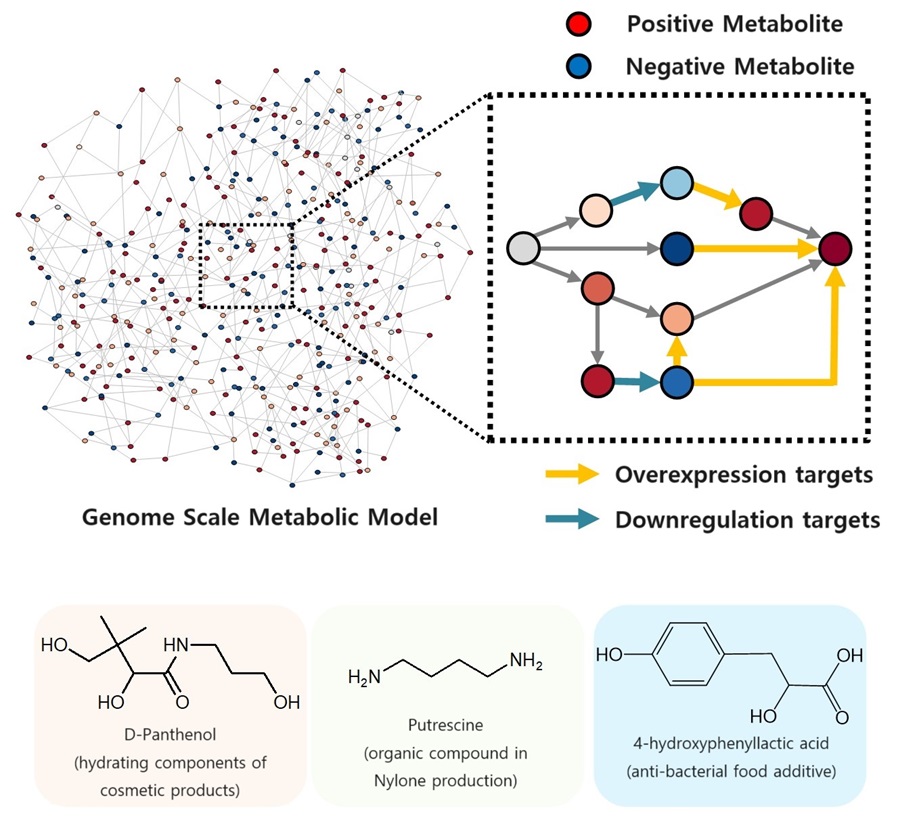 KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8684
KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8684 -
 KAIST holds its first ‘KAIST Tech Fair’ in New York, USA
< Photo 1. 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 11th that it will hold the ‘2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York’ at the Kimmel Center at New York University in Manhattan, USA, on the 22nd of this month. It is an event designed to be the starting point for KAIST to expand its startup ecosystem into the global stage, and it is to attract investments and secure global customers in New York by demonstrating the technological value of KAIST startup companies directly at location.
< Photo 2. President Kwang Hyung Lee at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST has been holding briefing sessions for technology transfer in Korea every year since 2018, and this year is the first time to hold a tech fair overseas for global companies.
KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (Director Sung-Yool Choi) has prepared for this event over the past six months with the Korea International Trade Association (hereinafter KITA, CEO Christopher Koo) to survey customer base and investment companies to conduct market analysis.
Among the companies founded with the technologies developed by the faculty and students of KAIST and their partners, 7 companies were selected to be matched with companies overseas that expressed interests in these technologies. Global multinational companies in the fields of IT, artificial intelligence, environment, logistics, distribution, and retail are participating as demand agencies and are testing the marketability of the start-up's technology as of September.
Daim Research, founded by Professor Young Jae Jang of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, is a company specializing in smart factory automation solutions and is knocking on the door of the global market with a platform technology optimized for automated logistics systems.
< Photo 3. Presentation by Professor Young Jae Jang for DAIM Research >
It is a ‘collaborative intelligence’ solution that maximizes work productivity by having a number of robots used in industrial settings collaborate with one another. The strength of their solution is that logistics robots equipped with AI reinforced learning technology can respond to processes and environmental changes on their own, minimizing maintenance costs and the system can achieve excellent performance even with a small amount of data when it is combined with the digital twin technology the company has developed on its own.
A student startup, ‘Aniai’, is entering the US market, the home of hamburgers, with hamburger patty automation equipments and solutions. This is a robot kitchen startup founded by its CEO Gunpil Hwang, a graduate of KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering which gathered together the experts in the fields of robot control, design, and artificial intelligence and cognitive technology to develop technology to automatically cook hamburger patties.
At the touch of a button, both sides of the patty are cooked simultaneously for consistent taste and quality according to the set condition. Since it can cook about 200 dishes in an hour, it is attracting attention as a technology that can not only solve manpower shortages but also accelerate the digital transformation of the restaurant industry.
Also, at the tech fair to be held at the Kimmel Center of New York University on the 22nd, the following startups who are currently under market verification in the U.S. will be participating: ▴'TheWaveTalk', which developed a water quality management system that can measure external substances and metal ions by transferring original technology from KAIST; ▴‘VIRNECT’, which helps workers improve their skills by remotely managing industrial sites using XR*; ▴‘Datumo’, a solution that helps process and analyze artificial intelligence big data, ▴‘VESSL AI’, the provider of a solution to eliminate the overhead** of machine learning systems; and ▴ ‘DolbomDream’, which developed an inflatable vest that helps the psychological stability of people with developmental disabilities.
* XR (eXtended Reality): Ultra-realistic technology that enhances immersion by utilizing augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies
** Overhead: Additional time required for stable processing of the program
In addition, two companies (Plasmapp and NotaAI) that are participating in the D-Unicorn program with the support of the Daejeon City and two companies (Enget and ILIAS Biologics) that are receiving support from the Scale Up Tips of the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, three companies (WiPowerOne, IDK Lab, and Artificial Photosynthesis Lab) that are continuing to realize the sustainable development goals for a total of 14 KAIST startups, will hold a corporate information session with about 100 invited guests from global companies and venture capital.
< Photo 4. Presentation for AP Lab >
Prior to this event, participating startups will be visiting the New York Economic Development Corporation and large law firms to receive advice on U.S. government support programs and on their attemps to enter the U.S. market. In addition, the participating companies plan to visit a startup support investment institution pursuing sustainable development goals and the Leslie eLab, New York University's one-stop startup support space, to lay the foundation for KAIST's leap forward in global technology commercialization.
< Photo 5. Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (left) at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York with the key participants >
Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “KAIST prepared this event to realize its vision of being a leading university in creating global value.” He added, “We hope that our startups founded with KAIST technology would successfully completed market verification to be successful in securing global demands and in attracting investments for their endeavors.”
2023.09.11 View 18556
KAIST holds its first ‘KAIST Tech Fair’ in New York, USA
< Photo 1. 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 11th that it will hold the ‘2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York’ at the Kimmel Center at New York University in Manhattan, USA, on the 22nd of this month. It is an event designed to be the starting point for KAIST to expand its startup ecosystem into the global stage, and it is to attract investments and secure global customers in New York by demonstrating the technological value of KAIST startup companies directly at location.
< Photo 2. President Kwang Hyung Lee at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST has been holding briefing sessions for technology transfer in Korea every year since 2018, and this year is the first time to hold a tech fair overseas for global companies.
KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (Director Sung-Yool Choi) has prepared for this event over the past six months with the Korea International Trade Association (hereinafter KITA, CEO Christopher Koo) to survey customer base and investment companies to conduct market analysis.
Among the companies founded with the technologies developed by the faculty and students of KAIST and their partners, 7 companies were selected to be matched with companies overseas that expressed interests in these technologies. Global multinational companies in the fields of IT, artificial intelligence, environment, logistics, distribution, and retail are participating as demand agencies and are testing the marketability of the start-up's technology as of September.
Daim Research, founded by Professor Young Jae Jang of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, is a company specializing in smart factory automation solutions and is knocking on the door of the global market with a platform technology optimized for automated logistics systems.
< Photo 3. Presentation by Professor Young Jae Jang for DAIM Research >
It is a ‘collaborative intelligence’ solution that maximizes work productivity by having a number of robots used in industrial settings collaborate with one another. The strength of their solution is that logistics robots equipped with AI reinforced learning technology can respond to processes and environmental changes on their own, minimizing maintenance costs and the system can achieve excellent performance even with a small amount of data when it is combined with the digital twin technology the company has developed on its own.
A student startup, ‘Aniai’, is entering the US market, the home of hamburgers, with hamburger patty automation equipments and solutions. This is a robot kitchen startup founded by its CEO Gunpil Hwang, a graduate of KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering which gathered together the experts in the fields of robot control, design, and artificial intelligence and cognitive technology to develop technology to automatically cook hamburger patties.
At the touch of a button, both sides of the patty are cooked simultaneously for consistent taste and quality according to the set condition. Since it can cook about 200 dishes in an hour, it is attracting attention as a technology that can not only solve manpower shortages but also accelerate the digital transformation of the restaurant industry.
Also, at the tech fair to be held at the Kimmel Center of New York University on the 22nd, the following startups who are currently under market verification in the U.S. will be participating: ▴'TheWaveTalk', which developed a water quality management system that can measure external substances and metal ions by transferring original technology from KAIST; ▴‘VIRNECT’, which helps workers improve their skills by remotely managing industrial sites using XR*; ▴‘Datumo’, a solution that helps process and analyze artificial intelligence big data, ▴‘VESSL AI’, the provider of a solution to eliminate the overhead** of machine learning systems; and ▴ ‘DolbomDream’, which developed an inflatable vest that helps the psychological stability of people with developmental disabilities.
* XR (eXtended Reality): Ultra-realistic technology that enhances immersion by utilizing augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies
** Overhead: Additional time required for stable processing of the program
In addition, two companies (Plasmapp and NotaAI) that are participating in the D-Unicorn program with the support of the Daejeon City and two companies (Enget and ILIAS Biologics) that are receiving support from the Scale Up Tips of the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, three companies (WiPowerOne, IDK Lab, and Artificial Photosynthesis Lab) that are continuing to realize the sustainable development goals for a total of 14 KAIST startups, will hold a corporate information session with about 100 invited guests from global companies and venture capital.
< Photo 4. Presentation for AP Lab >
Prior to this event, participating startups will be visiting the New York Economic Development Corporation and large law firms to receive advice on U.S. government support programs and on their attemps to enter the U.S. market. In addition, the participating companies plan to visit a startup support investment institution pursuing sustainable development goals and the Leslie eLab, New York University's one-stop startup support space, to lay the foundation for KAIST's leap forward in global technology commercialization.
< Photo 5. Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (left) at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York with the key participants >
Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “KAIST prepared this event to realize its vision of being a leading university in creating global value.” He added, “We hope that our startups founded with KAIST technology would successfully completed market verification to be successful in securing global demands and in attracting investments for their endeavors.”
2023.09.11 View 18556