ES
-
 Soul-Searching & Odds-Defying Determination: A Commencement Story of Dr. Tae-Hyun Oh
(Dr. Tae-Hyun Oh, one of the 2736 graduates of the 2018)
Each and every one of the 2,736 graduates has come a long way to the 2018 Commencement. Tae-Hyun Oh, who just started his new research career at MIT after completing his Ph.D. at KAIST, is no exception.
Unlike the most KAIST freshmen straight out of the ingenious science academies of Korea, he is among the many who endured very challenging and turbulent adolescent years. Buffeted by family instability and struggling during his time at school, he saw himself trapped by seemingly impenetrable barriers. His mother, who hated to see his struggling, advised him to take a break to reflect on who he is and what he wanted to do.
After dropping out of high school in his first year, ways to make money and support his family occupied his thoughts. He took on odd jobs from a car body shop to a gas station, but the real world was very tough and sometimes even cruel to the high school dropout.
Bias and prejudice stigmatizing dropouts hurt him so much. He often overheard a parent who dropped by the body shop that he worked in saying, “If you do not study hard, you will end up like this guy.” Hearing such things terrified him and awoke his sense of purpose. So he decided to do something meaningful and be a better man than he was.
“I didn’t like the person I was growing up to become. I needed to find myself and get away from the place I was growing up. It was my adventure and it was the best decision I ever made,” says Oh.
After completing his high school diploma national certificate, he planned to apply to an engineering college. On his second try, he gained admission into the Department of Electrical Engineering at Kwang Woon University with a full scholarship. He was so thrilled for this opportunity and hoped he could do well at college. Signal processing and image processing became the interest of his research and he finished his undergraduate degree summa cum laude.
Gaining confidence in his studies, he searched around graduate school department websites in Korea to select the path he was interested in. Among others, the Robotics and Computer Vision Lab of Professor In-So Kweon at the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST was attractive to him.
Professor Kweon’s lab is globally renowned for robot vision technology. Their technologies were applied into HUBO, the KAIST-developed bimodal humanoid robot that won the 2015 DARPA Challenges.
“I am so appreciate of Professor Kweon, who accepted and guided me,” he said. Under Professor Kweon’s advising, he could finish his Master’s and Ph.D. courses in seven years. The mathematical modeling on fundamental computer algorithms became his main research topic.
While at KAIST, his academic research has blossomed. He won a total of 13 research prizes sponsored by corporations at home and abroad such as Kolon, Samsung, Hyundai Motors, and Qualcomm.
In 2015, he won the Microsoft Research Asia Fellowship as the sole Korean among 13 Ph.D. candidates in the Asian region. With the MSRA fellowship, he could intern at the MS Research Beijing Office for half a year and then in Redmond, Washington in the US.
“Professor Kweon’s lab filled me up with knowledge. Whenever I presented our team’s paper at an international conference, I was amazed by the strong interest shown by foreign experts, researchers, and professors. Their strong support and interest encouraged me a lot. I was fully charged with the belief that I could go abroad and explore more opportunities,” he said.
Dr. Oh, who completed his dissertation last fall, now works at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT under Professor Wojciech Matusik.
“I think the research environment at KAIST is on par with MIT. I have very rich resources for my studies and research at both schools, but at MIT the working culture is a little different and it remains a big challenge for me. I am still not familiar with collaborative work with colleagues from very diverse backgrounds and countries, and to persuade them and communicate with them is very tough. But I think I am getting better and better,” he said.
Oh, who is an avid computer game player as well, said life seems to be a game. The level of the game will be upgraded to the next level after something is accomplished. He feels great joy when he is moving up and he believes such diverse experiences have helped him become a better person day by day. Once he identified what gave him a strong sense of purpose, he wasn’t stressed out by his studies any more. He was so excited to be able to follow his passion and is ready for the next challenge.
2018.02.23 View 11133
Soul-Searching & Odds-Defying Determination: A Commencement Story of Dr. Tae-Hyun Oh
(Dr. Tae-Hyun Oh, one of the 2736 graduates of the 2018)
Each and every one of the 2,736 graduates has come a long way to the 2018 Commencement. Tae-Hyun Oh, who just started his new research career at MIT after completing his Ph.D. at KAIST, is no exception.
Unlike the most KAIST freshmen straight out of the ingenious science academies of Korea, he is among the many who endured very challenging and turbulent adolescent years. Buffeted by family instability and struggling during his time at school, he saw himself trapped by seemingly impenetrable barriers. His mother, who hated to see his struggling, advised him to take a break to reflect on who he is and what he wanted to do.
After dropping out of high school in his first year, ways to make money and support his family occupied his thoughts. He took on odd jobs from a car body shop to a gas station, but the real world was very tough and sometimes even cruel to the high school dropout.
Bias and prejudice stigmatizing dropouts hurt him so much. He often overheard a parent who dropped by the body shop that he worked in saying, “If you do not study hard, you will end up like this guy.” Hearing such things terrified him and awoke his sense of purpose. So he decided to do something meaningful and be a better man than he was.
“I didn’t like the person I was growing up to become. I needed to find myself and get away from the place I was growing up. It was my adventure and it was the best decision I ever made,” says Oh.
After completing his high school diploma national certificate, he planned to apply to an engineering college. On his second try, he gained admission into the Department of Electrical Engineering at Kwang Woon University with a full scholarship. He was so thrilled for this opportunity and hoped he could do well at college. Signal processing and image processing became the interest of his research and he finished his undergraduate degree summa cum laude.
Gaining confidence in his studies, he searched around graduate school department websites in Korea to select the path he was interested in. Among others, the Robotics and Computer Vision Lab of Professor In-So Kweon at the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST was attractive to him.
Professor Kweon’s lab is globally renowned for robot vision technology. Their technologies were applied into HUBO, the KAIST-developed bimodal humanoid robot that won the 2015 DARPA Challenges.
“I am so appreciate of Professor Kweon, who accepted and guided me,” he said. Under Professor Kweon’s advising, he could finish his Master’s and Ph.D. courses in seven years. The mathematical modeling on fundamental computer algorithms became his main research topic.
While at KAIST, his academic research has blossomed. He won a total of 13 research prizes sponsored by corporations at home and abroad such as Kolon, Samsung, Hyundai Motors, and Qualcomm.
In 2015, he won the Microsoft Research Asia Fellowship as the sole Korean among 13 Ph.D. candidates in the Asian region. With the MSRA fellowship, he could intern at the MS Research Beijing Office for half a year and then in Redmond, Washington in the US.
“Professor Kweon’s lab filled me up with knowledge. Whenever I presented our team’s paper at an international conference, I was amazed by the strong interest shown by foreign experts, researchers, and professors. Their strong support and interest encouraged me a lot. I was fully charged with the belief that I could go abroad and explore more opportunities,” he said.
Dr. Oh, who completed his dissertation last fall, now works at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT under Professor Wojciech Matusik.
“I think the research environment at KAIST is on par with MIT. I have very rich resources for my studies and research at both schools, but at MIT the working culture is a little different and it remains a big challenge for me. I am still not familiar with collaborative work with colleagues from very diverse backgrounds and countries, and to persuade them and communicate with them is very tough. But I think I am getting better and better,” he said.
Oh, who is an avid computer game player as well, said life seems to be a game. The level of the game will be upgraded to the next level after something is accomplished. He feels great joy when he is moving up and he believes such diverse experiences have helped him become a better person day by day. Once he identified what gave him a strong sense of purpose, he wasn’t stressed out by his studies any more. He was so excited to be able to follow his passion and is ready for the next challenge.
2018.02.23 View 11133 -
 First Female Grand Prize Awardee of Samsung Humantech
Yeunhee Huh, PhD candidate (Professor Gyu-Hyeong Cho) from the School of Electrical Engineering received the grand prize of the 24th Humantech Paper Award. She is the first female recipient of this prize since its establishment in 1994. The Humantech Paper Award is hosted by Samsung Electronics and sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT with JoongAng Daily Newspaper. Her paper is titled, ‘A Hybrid Structure Dual-Path Step-Down Converter with 96.2% Peak Efficiency using 250mΩ Large-DCR Inductor’. Electronic devices require numerous chips and have a power converter to supply energy adequately. She proposed a new structure to enhance energy efficiency by combining inductors and capacitors. Enhancing energy efficiency can reduce energy loss, which prolongs battery hours and solves overheating of devices; for instance, energy loss leads to the overheating issue affecting phone chargers. This technology can be applied to various electronic devices, such as cell phones, laptops, and drones. Huh said, “Power has to go up in order to meet customers’ needs; however the overheating problem emerges during this process. This problem affects surrounding circuits and causes other issues, such as malfunctions of electronic devices. This technology may vary according to the conditions, but it can enhance energy efficiency up to 4%.”During the ceremony, about eight hundred million KRW worth cash prizes was conferred to 119 papers. KAIST (44 papers) and Gyeonggi Science High School (6 papers) received special awards given to the schools.
2018.02.12 View 9597
First Female Grand Prize Awardee of Samsung Humantech
Yeunhee Huh, PhD candidate (Professor Gyu-Hyeong Cho) from the School of Electrical Engineering received the grand prize of the 24th Humantech Paper Award. She is the first female recipient of this prize since its establishment in 1994. The Humantech Paper Award is hosted by Samsung Electronics and sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT with JoongAng Daily Newspaper. Her paper is titled, ‘A Hybrid Structure Dual-Path Step-Down Converter with 96.2% Peak Efficiency using 250mΩ Large-DCR Inductor’. Electronic devices require numerous chips and have a power converter to supply energy adequately. She proposed a new structure to enhance energy efficiency by combining inductors and capacitors. Enhancing energy efficiency can reduce energy loss, which prolongs battery hours and solves overheating of devices; for instance, energy loss leads to the overheating issue affecting phone chargers. This technology can be applied to various electronic devices, such as cell phones, laptops, and drones. Huh said, “Power has to go up in order to meet customers’ needs; however the overheating problem emerges during this process. This problem affects surrounding circuits and causes other issues, such as malfunctions of electronic devices. This technology may vary according to the conditions, but it can enhance energy efficiency up to 4%.”During the ceremony, about eight hundred million KRW worth cash prizes was conferred to 119 papers. KAIST (44 papers) and Gyeonggi Science High School (6 papers) received special awards given to the schools.
2018.02.12 View 9597 -
 Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 8424
Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 8424 -
 Finding Human Thermal Comfort with a Watch-type Sweat Rate Sensor
(from left: Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher SungHyun Yoon)
KAIST developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor. This subminiature device can detect human thermal comfort accurately and steadily by measuring an individual’s sweat rate.
It is natural to sweat more in the summer and less in the winter; however, an individual’s sweat rate may vary in a given environment. Therefore, sweat can be an excellent proxy for sensing core body temperature.
Conventional sweat rate sensors using natural ventilation require bulky external devices, such as pumps and ice condensers. They are usually for physiological experiments, hence they need a manual ventilation process or high power, bulky thermos-pneumatic actuators to lift sweat rate detection chambers above skin for continuous measurement. There is also a small sweat rate sensor, but it needs a long recovery period.
To overcome these problems, Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed a lightweight, watch-type sweat sensor. The team integrated miniaturized thermos-pneumatic actuators for automatic natural ventilation, which allows sweat to be measured continuously.
This watch-type sensor measures sweat rate with the humidity rising rate when the chamber is closed during skin contact. Since the team integrated thermos-pneumatic actuators, the chamber no longer needs to be separated manually from skin after each measurement in order for the chamber to ventilate the collected humidity.
Moreover, this sensor is wind-resistant enough to be used for portable and wearable devices. The team identified that the sensor operates steadily with air velocity ranging up to 1.5m/s, equivalent to the average human walking speed.
Although this subminiature sensor (35mm x 25mm) only weighs 30 grams, it operates continuously for more than four hours using the conventional wrist watch batteries.
The team plans to utilize this technology for developing a new concept of cognitive air-conditioning systems recognizing Human thermal status directly; while the conventional air-conditioning systems measuring air temperature and humidity.
Professor Cho said, “Our sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring can be applied to customized or smart air conditioners. Furthermore, there will be more demands for both physical and mental healthcare, hence this technology will serve as a new platform for personalized emotional communion between humans and devices.”
This research, led by researchers Jai Kyoung Sim and SungHyun Yoon, was published in Scientific Reports on January 19, 2018.
Figure1. The fabricated watch-type sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring
Figure 2. Views of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
Figure 3. Operation of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
2018.02.08 View 8760
Finding Human Thermal Comfort with a Watch-type Sweat Rate Sensor
(from left: Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher SungHyun Yoon)
KAIST developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor. This subminiature device can detect human thermal comfort accurately and steadily by measuring an individual’s sweat rate.
It is natural to sweat more in the summer and less in the winter; however, an individual’s sweat rate may vary in a given environment. Therefore, sweat can be an excellent proxy for sensing core body temperature.
Conventional sweat rate sensors using natural ventilation require bulky external devices, such as pumps and ice condensers. They are usually for physiological experiments, hence they need a manual ventilation process or high power, bulky thermos-pneumatic actuators to lift sweat rate detection chambers above skin for continuous measurement. There is also a small sweat rate sensor, but it needs a long recovery period.
To overcome these problems, Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed a lightweight, watch-type sweat sensor. The team integrated miniaturized thermos-pneumatic actuators for automatic natural ventilation, which allows sweat to be measured continuously.
This watch-type sensor measures sweat rate with the humidity rising rate when the chamber is closed during skin contact. Since the team integrated thermos-pneumatic actuators, the chamber no longer needs to be separated manually from skin after each measurement in order for the chamber to ventilate the collected humidity.
Moreover, this sensor is wind-resistant enough to be used for portable and wearable devices. The team identified that the sensor operates steadily with air velocity ranging up to 1.5m/s, equivalent to the average human walking speed.
Although this subminiature sensor (35mm x 25mm) only weighs 30 grams, it operates continuously for more than four hours using the conventional wrist watch batteries.
The team plans to utilize this technology for developing a new concept of cognitive air-conditioning systems recognizing Human thermal status directly; while the conventional air-conditioning systems measuring air temperature and humidity.
Professor Cho said, “Our sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring can be applied to customized or smart air conditioners. Furthermore, there will be more demands for both physical and mental healthcare, hence this technology will serve as a new platform for personalized emotional communion between humans and devices.”
This research, led by researchers Jai Kyoung Sim and SungHyun Yoon, was published in Scientific Reports on January 19, 2018.
Figure1. The fabricated watch-type sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring
Figure 2. Views of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
Figure 3. Operation of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
2018.02.08 View 8760 -
 KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 9361
KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 9361 -
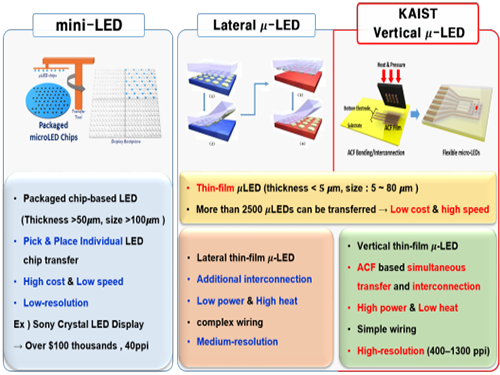 Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 13509
Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 13509 -
 Three Professors Named KAST Fellows
(Professor Dan Keun Sung at the center)
(Professor Y.H. Cho at the center)
(Professor K.H. Cho at the center)
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) inducted three KAIST professors as fellows at the New Year’s ceremony held at KAST on January 12. They were among the 24 newly elected fellows of the most distinguished academy in Korea. The new fellows are Professor Dan Keun Sung of the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics.
Professor Sung was recognized for his lifetime academic achievements in fields related with network protocols and energy ICT. He also played a crucial role in launching the Korean satellites KITSAT-1,2,3 and the establishment of the Satellite Technology Research Center at KAIST.
Professor Y.H.Cho has been a pioneer in the field of low-dimensional semiconductor-powered quantum photonics that enables quantum optical research in solid state. He has been recognized as a renowned scholar in this field internationally.
Professor K.H.Cho has conducted original research that combines IT and BT in systems biology and has applied novel technologies of electronic modeling and computer simulation analysis for investigating complex life sciences. Professor Cho, who is in his 40s, is the youngest fellow among the newly inducted fellows.
2018.01.16 View 14530
Three Professors Named KAST Fellows
(Professor Dan Keun Sung at the center)
(Professor Y.H. Cho at the center)
(Professor K.H. Cho at the center)
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) inducted three KAIST professors as fellows at the New Year’s ceremony held at KAST on January 12. They were among the 24 newly elected fellows of the most distinguished academy in Korea. The new fellows are Professor Dan Keun Sung of the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics.
Professor Sung was recognized for his lifetime academic achievements in fields related with network protocols and energy ICT. He also played a crucial role in launching the Korean satellites KITSAT-1,2,3 and the establishment of the Satellite Technology Research Center at KAIST.
Professor Y.H.Cho has been a pioneer in the field of low-dimensional semiconductor-powered quantum photonics that enables quantum optical research in solid state. He has been recognized as a renowned scholar in this field internationally.
Professor K.H.Cho has conducted original research that combines IT and BT in systems biology and has applied novel technologies of electronic modeling and computer simulation analysis for investigating complex life sciences. Professor Cho, who is in his 40s, is the youngest fellow among the newly inducted fellows.
2018.01.16 View 14530 -
 Harnessing the Strength of KAIST Alumni: New Head of KAA Inaugurated
KAIST alumni gathered in Seoul on January 13 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAIST Alumni Association (KAA). More than 300 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, joined the gala event held at the Lotte Hotel.
Photo: Ki-Chul Cha(left) and Jung Sik Koh(right)
The KAA inaugurated its new president, Ki-Chul Cha, who was preceded by Jung Sik Koh, the former CEO at the Korea Resources Corporation. His term starts from January 2018 to December 2020.
Cha is the CEO of Inbody Co Ltd., a global company specializing in developing and selling medical instruments, such as a body composition analyzers, and medical solutions. He is also an adjunct professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University. Cha obtained a master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering at KAIST in 1980, and a Ph.D. in Bioengineering at the University of Utah, before finishing his post-doc fellowship at Harvard Medical School.
Cha plans to explore the idea that alumni engagement, saying, “KAIST stays as a home in the memories of 60,000 alumni. I will dedicate myself to stimulating the alumni association to make KAISTians proud.”
At the gala event, the KAA awarded the Alumni of the Year honor to six alumni who distinguished themselves in the areas of professional achievement, humanitarianism, and public service. They are the Director of Startup KAIST Professor Byoung Yoon Kim; President of LG Chem Ltd and Head of Battery Research and Development Myung Hwan Kim; Director of INNOX Advanced Materials Co., Ltd Kyung Ho Chang; Vice President of the Korea International Trade Association Jung-Kwan Kim; CEO of Samsung Electro-Mechanics Yun-Tae Lee; and CEO of ENF Technology Jinbae Jung.
Photo: President Shin(far right) poses with six awardees of the Distinguished Alumni Award and the former President of KAA, Koh(far left)
2018.01.16 View 11017
Harnessing the Strength of KAIST Alumni: New Head of KAA Inaugurated
KAIST alumni gathered in Seoul on January 13 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAIST Alumni Association (KAA). More than 300 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, joined the gala event held at the Lotte Hotel.
Photo: Ki-Chul Cha(left) and Jung Sik Koh(right)
The KAA inaugurated its new president, Ki-Chul Cha, who was preceded by Jung Sik Koh, the former CEO at the Korea Resources Corporation. His term starts from January 2018 to December 2020.
Cha is the CEO of Inbody Co Ltd., a global company specializing in developing and selling medical instruments, such as a body composition analyzers, and medical solutions. He is also an adjunct professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University. Cha obtained a master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering at KAIST in 1980, and a Ph.D. in Bioengineering at the University of Utah, before finishing his post-doc fellowship at Harvard Medical School.
Cha plans to explore the idea that alumni engagement, saying, “KAIST stays as a home in the memories of 60,000 alumni. I will dedicate myself to stimulating the alumni association to make KAISTians proud.”
At the gala event, the KAA awarded the Alumni of the Year honor to six alumni who distinguished themselves in the areas of professional achievement, humanitarianism, and public service. They are the Director of Startup KAIST Professor Byoung Yoon Kim; President of LG Chem Ltd and Head of Battery Research and Development Myung Hwan Kim; Director of INNOX Advanced Materials Co., Ltd Kyung Ho Chang; Vice President of the Korea International Trade Association Jung-Kwan Kim; CEO of Samsung Electro-Mechanics Yun-Tae Lee; and CEO of ENF Technology Jinbae Jung.
Photo: President Shin(far right) poses with six awardees of the Distinguished Alumni Award and the former President of KAA, Koh(far left)
2018.01.16 View 11017 -
 KAIST Students Invited to the BNL
Siheon Ryee and Taek Jung Kim, combined Masters and PhD students from the Department of Physics, have been invited to be visiting researchers at the Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL).
The BNL, located in Long Island, New York, is one of the most esteemed institutes in the United States. Ryee and Kim received the invitation from the Center for Computational Design of Functional Strongly Correlated Materials and Theoretical Spectroscopy. This center was established by scholars who have been leading this field in the United States.
The two students will be participating in developing a methodology and code for calculating strongly correlated electronic materials, and a grant of 40,000 USD will be provided to each student. This amount of support is not often awarded to researchers outside of postdoctoral programs.
Moreover, they are guaranteed to continue their combined Masters and PhD program and write their dissertations under the supervision of their advisor, Professor Myung Joon Han from the Department of Physics.
Professor Han said, “I was impressed by how well-known scholars established the center in order to cooperate with each other to solve challenging problems. Also, I was surprised and happy that my students were invited to this outstanding institute.”
“I believe that doing research with leaders in their field will give valuable experience to the students. At the same time, my students will be a great help to the scholars of the institute,” he added.
2018.01.11 View 8295
KAIST Students Invited to the BNL
Siheon Ryee and Taek Jung Kim, combined Masters and PhD students from the Department of Physics, have been invited to be visiting researchers at the Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL).
The BNL, located in Long Island, New York, is one of the most esteemed institutes in the United States. Ryee and Kim received the invitation from the Center for Computational Design of Functional Strongly Correlated Materials and Theoretical Spectroscopy. This center was established by scholars who have been leading this field in the United States.
The two students will be participating in developing a methodology and code for calculating strongly correlated electronic materials, and a grant of 40,000 USD will be provided to each student. This amount of support is not often awarded to researchers outside of postdoctoral programs.
Moreover, they are guaranteed to continue their combined Masters and PhD program and write their dissertations under the supervision of their advisor, Professor Myung Joon Han from the Department of Physics.
Professor Han said, “I was impressed by how well-known scholars established the center in order to cooperate with each other to solve challenging problems. Also, I was surprised and happy that my students were invited to this outstanding institute.”
“I believe that doing research with leaders in their field will give valuable experience to the students. At the same time, my students will be a great help to the scholars of the institute,” he added.
2018.01.11 View 8295 -
 A Glance at the 2017 KAIST Literary Awards Ceremony
Since KAIST is a university specializing in science and engineering, people may think that the students rarely engage in literary activities. But KAIST students also excel in writing literature.
The 23rd KAIST Literary Award Ceremony was held on December 14 on the KAIST main campus. The award was established in 1995 to encourage students’ creative activities and to promote literary attainment. It is open to all KAIST students from undergraduate to masters and PhD students. This year, 43 students submitted a total of 68 literary works in the genres of poetry, novel, critique, and scenario.
KAIST professors Dong Ju Kim, Bong Gwan Jun, and Yunjeong Jo from the School of Humanities & Social Sciences participated as judges for the awards and they were joined by writers from the 8th Endless Road Program who served as invited judges for the novels and scenarios.
The Endless Road Program is a KAIST project for supporting artists who are engaged in literary works including scenarios, novels, webtoons, and movies by providing residences and funds. Novelists Jin Young Choi and Hak Chan Kim participated as judges for the novels and a drama scriptwriter, Joo Kim, as a judge of the scenarios.
After thorough evaluation, four submissions were chosen as awardees.
Section
Award
Name
Poetry
Winner
Sung Gil Moon (PhD candidate from the College of Business)
Runner-up
Jong Ik Jeon (Undergraduate student)
Novel
Winner
Joo Hwan Kim
(Undergraduate from the Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Runner-up
-
Essay & Critique
Winner
-
Runner-up
Jung Joon Park
(PhD candidate from the Dept. of Bio and Brain Engineering)
Scenario
Winner
-
Runner-up
-
The literary works as well as a review of the awards will be published in the KAIST Times in 2018.
2017.12.15 View 8122
A Glance at the 2017 KAIST Literary Awards Ceremony
Since KAIST is a university specializing in science and engineering, people may think that the students rarely engage in literary activities. But KAIST students also excel in writing literature.
The 23rd KAIST Literary Award Ceremony was held on December 14 on the KAIST main campus. The award was established in 1995 to encourage students’ creative activities and to promote literary attainment. It is open to all KAIST students from undergraduate to masters and PhD students. This year, 43 students submitted a total of 68 literary works in the genres of poetry, novel, critique, and scenario.
KAIST professors Dong Ju Kim, Bong Gwan Jun, and Yunjeong Jo from the School of Humanities & Social Sciences participated as judges for the awards and they were joined by writers from the 8th Endless Road Program who served as invited judges for the novels and scenarios.
The Endless Road Program is a KAIST project for supporting artists who are engaged in literary works including scenarios, novels, webtoons, and movies by providing residences and funds. Novelists Jin Young Choi and Hak Chan Kim participated as judges for the novels and a drama scriptwriter, Joo Kim, as a judge of the scenarios.
After thorough evaluation, four submissions were chosen as awardees.
Section
Award
Name
Poetry
Winner
Sung Gil Moon (PhD candidate from the College of Business)
Runner-up
Jong Ik Jeon (Undergraduate student)
Novel
Winner
Joo Hwan Kim
(Undergraduate from the Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Runner-up
-
Essay & Critique
Winner
-
Runner-up
Jung Joon Park
(PhD candidate from the Dept. of Bio and Brain Engineering)
Scenario
Winner
-
Runner-up
-
The literary works as well as a review of the awards will be published in the KAIST Times in 2018.
2017.12.15 View 8122 -
 MoU by KAIST-Seoul-Seocho-gu for the 4th Industrial Revolution
The opening ceremony of the Yangjae R&CD Innovation Hub was held in Seoul on December 5. More than 400 guests came to the ceremony from major institutes and companies that are based in the hub. KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the Mayor of Seoul, Won-soon Park, and the Mayor of Seocho-gu, Eun Hee Cho, signed an MoU for Seoul to be the leading city for successfully realizing the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The three organizations aim to cooperate with one another in various areas, including an economic boost for local job creation, technology development, and the promotion of projects through an industry-academia-institute network and fostering manpower.
Yangjae R&CD is the first facility specializing in and dedicated for Artificial Intelligence, which is the major topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The hub is comprised of enterprises specializing in AI, open co-work spaces, conference rooms, an open networking lounge, and spaces for fostering professional manpower. The hub will recruit additional enterprises and individuals who wish to move in. KAIST, an institute containing professors and researchers in the field of AI, and Modulabs, an organization becoming distinguished in AI research, will be in charge of operating the facility together.
The Yangjae R&CD Innovation Hub will operate a professional training program with participation from KAIST professors, which aims to produce 500 professionals in AI research and development by 2020. It will also provide inexpensive space as well as consultations and venture capital to startup and venture companies. It plans to find and foster 50 innovation companies by 2020.
In particular, the hub will operate a course for new AI business models 24 times over three years.
The hub also offers job consultations, academic conferences, public space for companies residing in the hub, a free GPU cluster server, technical training, seminars, forums, investment attraction, overseas expansion, and one-to-one technical consultations.
The Yangjae R&CD Zone is the place established for the Fourth Industrial Revolution by Seoul. R&CD is a concept combining Research and Development, Connection, Companies, Community, and Culture.
Seoul aims to create the Yangjae Zone as an urban innovation hub for facilitating industry-academia linkage as well as establishing a startup-settlement-growth technical ecosystem.
2017.12.11 View 9931
MoU by KAIST-Seoul-Seocho-gu for the 4th Industrial Revolution
The opening ceremony of the Yangjae R&CD Innovation Hub was held in Seoul on December 5. More than 400 guests came to the ceremony from major institutes and companies that are based in the hub. KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the Mayor of Seoul, Won-soon Park, and the Mayor of Seocho-gu, Eun Hee Cho, signed an MoU for Seoul to be the leading city for successfully realizing the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The three organizations aim to cooperate with one another in various areas, including an economic boost for local job creation, technology development, and the promotion of projects through an industry-academia-institute network and fostering manpower.
Yangjae R&CD is the first facility specializing in and dedicated for Artificial Intelligence, which is the major topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The hub is comprised of enterprises specializing in AI, open co-work spaces, conference rooms, an open networking lounge, and spaces for fostering professional manpower. The hub will recruit additional enterprises and individuals who wish to move in. KAIST, an institute containing professors and researchers in the field of AI, and Modulabs, an organization becoming distinguished in AI research, will be in charge of operating the facility together.
The Yangjae R&CD Innovation Hub will operate a professional training program with participation from KAIST professors, which aims to produce 500 professionals in AI research and development by 2020. It will also provide inexpensive space as well as consultations and venture capital to startup and venture companies. It plans to find and foster 50 innovation companies by 2020.
In particular, the hub will operate a course for new AI business models 24 times over three years.
The hub also offers job consultations, academic conferences, public space for companies residing in the hub, a free GPU cluster server, technical training, seminars, forums, investment attraction, overseas expansion, and one-to-one technical consultations.
The Yangjae R&CD Zone is the place established for the Fourth Industrial Revolution by Seoul. R&CD is a concept combining Research and Development, Connection, Companies, Community, and Culture.
Seoul aims to create the Yangjae Zone as an urban innovation hub for facilitating industry-academia linkage as well as establishing a startup-settlement-growth technical ecosystem.
2017.12.11 View 9931 -
 Professor Dong Ho Cho Awarded at the Haedong Conference 2017
Professor Dong Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST received an award at the 13th Haedong Conference 2017 in Seoul on the first of December.
The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences recognized Professor Cho for his significant contributions in the field of mobile communication networks. He has carried out groundbreaking research on mobile systems, including architecture, protocols, algorithms, optimization, and efficiency analysis.
As a result, he has produced 73 papers in renowned international journals, 138 papers at international conferences, and filed 52 international patents and 121 domestic patents. In addition, he transferred 14 of the patents he filed to Korean and international companies.
2017.12.07 View 6857
Professor Dong Ho Cho Awarded at the Haedong Conference 2017
Professor Dong Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST received an award at the 13th Haedong Conference 2017 in Seoul on the first of December.
The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences recognized Professor Cho for his significant contributions in the field of mobile communication networks. He has carried out groundbreaking research on mobile systems, including architecture, protocols, algorithms, optimization, and efficiency analysis.
As a result, he has produced 73 papers in renowned international journals, 138 papers at international conferences, and filed 52 international patents and 121 domestic patents. In addition, he transferred 14 of the patents he filed to Korean and international companies.
2017.12.07 View 6857