AT
-
 KAIST Alumnus NYU Professor Supports Female AI Researchers
A KAIST alumnus and an associate professor at New York University (NYU), Dr. Kyunghyun Cho donated 3,000 USD to the KAIST Graduate School of AI to support female AI researchers.
Professor Cho spoke as a guest lecturer at the 2019 Samsung AI Forum on November 4 and received 3,000 USD as an honorarium. He donated this honorarium to the KAIST Graduate School of AI with a special request to support the school’s female PhD students attending the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), where he serves as a program co-chair.
Professor Cho received his BS degree from KAIST’s School of Computing in 2009 and is now serving as an associate professor at NYU’s Computer Science Department and Center for Data Science. His research mainly covers machine learning and natural language processing.
Professor Cho said that he decided to make this donation because “In Korea and even in the US, women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) lack opportunities and environments that allow them to excel.”
Professor Song Chong, the Head of the KAIST Graduate School of AI, responded, “We are so grateful for Professor Kyunghyun Cho’s contribution and we will also use funds from the school in addition to the donation to support our female PhD students who will attend the ICLR.”
(END)
2019.11.15 View 10373
KAIST Alumnus NYU Professor Supports Female AI Researchers
A KAIST alumnus and an associate professor at New York University (NYU), Dr. Kyunghyun Cho donated 3,000 USD to the KAIST Graduate School of AI to support female AI researchers.
Professor Cho spoke as a guest lecturer at the 2019 Samsung AI Forum on November 4 and received 3,000 USD as an honorarium. He donated this honorarium to the KAIST Graduate School of AI with a special request to support the school’s female PhD students attending the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), where he serves as a program co-chair.
Professor Cho received his BS degree from KAIST’s School of Computing in 2009 and is now serving as an associate professor at NYU’s Computer Science Department and Center for Data Science. His research mainly covers machine learning and natural language processing.
Professor Cho said that he decided to make this donation because “In Korea and even in the US, women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) lack opportunities and environments that allow them to excel.”
Professor Song Chong, the Head of the KAIST Graduate School of AI, responded, “We are so grateful for Professor Kyunghyun Cho’s contribution and we will also use funds from the school in addition to the donation to support our female PhD students who will attend the ICLR.”
(END)
2019.11.15 View 10373 -
 AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 19575
AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 19575 -
 Ultrafast Quantum Motion in a Nanoscale Trap Detected
< Professor Heung-Sun Sim (left) and Co-author Dr. Sungguen Ryu (right) >
KAIST researchers have reported the detection of a picosecond electron motion in a silicon transistor. This study has presented a new protocol for measuring ultrafast electronic dynamics in an effective time-resolved fashion of picosecond resolution. The detection was made in collaboration with Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) in Japan and National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK and is the first report to the best of our knowledge.
When an electron is captured in a nanoscale trap in solids, its quantum mechanical wave function can exhibit spatial oscillation at sub-terahertz frequencies. Time-resolved detection of such picosecond dynamics of quantum waves is important, as the detection provides a way of understanding the quantum behavior of electrons in nano-electronics. It also applies to quantum information technologies such as the ultrafast quantum-bit operation of quantum computing and high-sensitivity electromagnetic-field sensing. However, detecting picosecond dynamics has been a challenge since the sub-terahertz scale is far beyond the latest bandwidth measurement tools.
A KAIST team led by Professor Heung-Sun Sim developed a theory of ultrafast electron dynamics in a nanoscale trap, and proposed a scheme for detecting the dynamics, which utilizes a quantum-mechanical resonant state formed beside the trap. The coupling between the electron dynamics and the resonant state is switched on and off at a picosecond so that information on the dynamics is read out on the electric current being generated when the coupling is switched on.
NTT realized, together with NPL, the detection scheme and applied it to electron motions in a nanoscale trap formed in a silicon transistor. A single electron was captured in the trap by controlling electrostatic gates, and a resonant state was formed in the potential barrier of the trap.
The switching on and off of the coupling between the electron and the resonant state was achieved by aligning the resonance energy with the energy of the electron within a picosecond. An electric current from the trap through the resonant state to an electrode was measured at only a few Kelvin degrees, unveiling the spatial quantum-coherent oscillation of the electron with 250 GHz frequency inside the trap.
Professor Sim said, “This work suggests a scheme of detecting picosecond electron motions in submicron scales by utilizing quantum resonance. It will be useful in dynamical control of quantum mechanical electron waves for various purposes in nano-electronics, quantum sensing, and quantum information”.
This work was published online at Nature Nanotechnology on November 4. It was partly supported by the Korea National Research Foundation through the SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matter. For more on the NTT news release this article, please visit https://www.ntt.co.jp/news2019/1911e/191105a.html
-ProfileProfessor Heung-Sun Sim
Department of PhysicsDirector, SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matterhttps://qet.kaist.ac.kr KAIST
-Publication:Gento Yamahata, Sungguen Ryu, Nathan Johnson, H.-S. Sim, Akira Fujiwara, and Masaya Kataoka. 2019. Picosecond coherent electron motion in a silicon single-electron source. Nature Nanotechnology (Online Publication). 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0563-2
2019.11.05 View 19701
Ultrafast Quantum Motion in a Nanoscale Trap Detected
< Professor Heung-Sun Sim (left) and Co-author Dr. Sungguen Ryu (right) >
KAIST researchers have reported the detection of a picosecond electron motion in a silicon transistor. This study has presented a new protocol for measuring ultrafast electronic dynamics in an effective time-resolved fashion of picosecond resolution. The detection was made in collaboration with Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) in Japan and National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK and is the first report to the best of our knowledge.
When an electron is captured in a nanoscale trap in solids, its quantum mechanical wave function can exhibit spatial oscillation at sub-terahertz frequencies. Time-resolved detection of such picosecond dynamics of quantum waves is important, as the detection provides a way of understanding the quantum behavior of electrons in nano-electronics. It also applies to quantum information technologies such as the ultrafast quantum-bit operation of quantum computing and high-sensitivity electromagnetic-field sensing. However, detecting picosecond dynamics has been a challenge since the sub-terahertz scale is far beyond the latest bandwidth measurement tools.
A KAIST team led by Professor Heung-Sun Sim developed a theory of ultrafast electron dynamics in a nanoscale trap, and proposed a scheme for detecting the dynamics, which utilizes a quantum-mechanical resonant state formed beside the trap. The coupling between the electron dynamics and the resonant state is switched on and off at a picosecond so that information on the dynamics is read out on the electric current being generated when the coupling is switched on.
NTT realized, together with NPL, the detection scheme and applied it to electron motions in a nanoscale trap formed in a silicon transistor. A single electron was captured in the trap by controlling electrostatic gates, and a resonant state was formed in the potential barrier of the trap.
The switching on and off of the coupling between the electron and the resonant state was achieved by aligning the resonance energy with the energy of the electron within a picosecond. An electric current from the trap through the resonant state to an electrode was measured at only a few Kelvin degrees, unveiling the spatial quantum-coherent oscillation of the electron with 250 GHz frequency inside the trap.
Professor Sim said, “This work suggests a scheme of detecting picosecond electron motions in submicron scales by utilizing quantum resonance. It will be useful in dynamical control of quantum mechanical electron waves for various purposes in nano-electronics, quantum sensing, and quantum information”.
This work was published online at Nature Nanotechnology on November 4. It was partly supported by the Korea National Research Foundation through the SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matter. For more on the NTT news release this article, please visit https://www.ntt.co.jp/news2019/1911e/191105a.html
-ProfileProfessor Heung-Sun Sim
Department of PhysicsDirector, SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matterhttps://qet.kaist.ac.kr KAIST
-Publication:Gento Yamahata, Sungguen Ryu, Nathan Johnson, H.-S. Sim, Akira Fujiwara, and Masaya Kataoka. 2019. Picosecond coherent electron motion in a silicon single-electron source. Nature Nanotechnology (Online Publication). 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0563-2
2019.11.05 View 19701 -
 SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
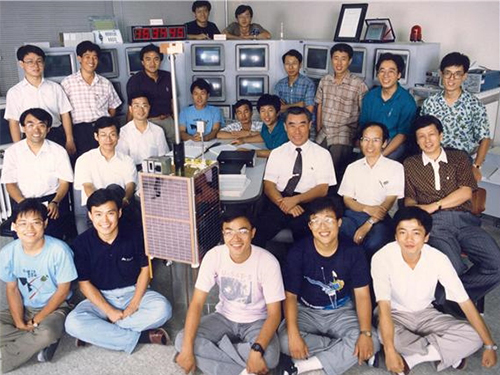
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 7612
SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 7612 -
 Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 22930
Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 22930 -
 A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
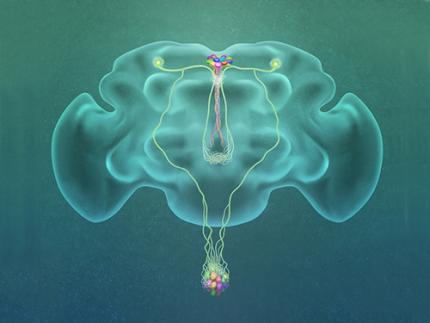
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 18735
A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 18735 -
 Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 27703
Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 27703 -
 A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 29596
A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 29596 -
 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 13719
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 13719 -
 Professor Byong-Guk Park Named Scientist of October
< Professor Byong-Guk Park >
Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2019 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of spin-orbit torque (SOT)-based magnetic random access memory (MRAM) technology. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
A next-generation, non-volatile memory device MRAM consists of thin magnetic films. It can be applied in “logic-in-memory” devices, in which logic and memory functionalities coexist, thus drastically improving the performance of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processors. Conventional MRAM technology is limited in its ability to increase the operation speed of a memory device while maintaining a high density.
Professor Park tackled this challenge by introducing a new material, antiferromagnet (IrMn), that generates a sizable amount of SOT as well as an exchange-bias field, which makes successful data writing possible without an external magnetic field. This research outcome paved the way for the development of MRAM, which has a simple device structure but features high speeds and density.
Professor Park said, “I feel rewarded to have forwarded the feasibility and applicability of MRAM. I will continue devoting myself to studying further on the development of new materials that can help enhance the performance of memory devices."
(END)
2019.10.10 View 11569
Professor Byong-Guk Park Named Scientist of October
< Professor Byong-Guk Park >
Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2019 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of spin-orbit torque (SOT)-based magnetic random access memory (MRAM) technology. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
A next-generation, non-volatile memory device MRAM consists of thin magnetic films. It can be applied in “logic-in-memory” devices, in which logic and memory functionalities coexist, thus drastically improving the performance of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processors. Conventional MRAM technology is limited in its ability to increase the operation speed of a memory device while maintaining a high density.
Professor Park tackled this challenge by introducing a new material, antiferromagnet (IrMn), that generates a sizable amount of SOT as well as an exchange-bias field, which makes successful data writing possible without an external magnetic field. This research outcome paved the way for the development of MRAM, which has a simple device structure but features high speeds and density.
Professor Park said, “I feel rewarded to have forwarded the feasibility and applicability of MRAM. I will continue devoting myself to studying further on the development of new materials that can help enhance the performance of memory devices."
(END)
2019.10.10 View 11569 -
 Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 29931
Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 29931 -
 Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 8708
Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 8708