ion
-
 Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 29889
Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 29889 -
 Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 10213
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 10213 -
 KAIST to Transfer Core Tech to Domestic Companies amid Japan's Export Curbs
< Associate Vice President Kyung-Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST >
KAIST will transfer four core technologies related to materials, parts, and equipment to domestic companies to help them combat the latest export curbs triggered by Korea’s removal from Japan’s ‘white list’ of preferential trade partners. In addition, KAIST’s five patented technologies in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and materials and parts will also be transferred to the companies in order to reduce the reliance on Japan and achieve technological independence through the ‘localization’ of key technologies.
KAIST announced these university-industry cooperation promotion plans at the ‘2019 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day Conference’ held in Seoul on September 17. More than 200 entrepreneurs and investors attended the briefing and on-site consulting sessions delivered by nine KAIST professors who led the development of the technologies.
The four technologies were presented at the conference as those that can replace Japanese technologies subject to the export curbs. They include:
1. ‘Transparent fluorinated polyimide with low thermal expansion’ developed by Professor Sang-Youl Kim of the Department of Chemistry
2. ‘A non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system’ developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
3. ‘A nanotechnology-based electrode material for use in advanced secondary batteries’ developed by Professor Do-Kyung Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
4. ‘A high-resolution photoresist’ developed by Professor Emeritus Jin-Baek Kim of the Department of Chemistry.
Of particular interest is the non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system technology developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee. This new cost-effective technology enables tests that were impossible to carry out using conventional technologies and yields a cost reduction of more than 50 percent compared to foreign technologies.
By introducing Professor Do-Kyung Kim’s new electrode material technology, the efficiency of electric vehicles can be increased. As this technology uses relatively low-cost sodium ion batteries, industries can prepare for the possible jump from the more expensive lithium batteries currently being used.
Another five patented AI and materials and parts technologies disclosed at the conference include:
1. ‘Enhanced HTTP adaptive streaming with CNN-based super-resolution’ developed by Professor Dong-soo Han of the School of Electrical Engineering
2. ‘Method and apparatus of brain-computer interface design for estimating choice behavior and decision strategy’ developed by Professor Sang-Wan Lee of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
3. ‘Eco-friendly fabrication of metal oxide nanoparticles and fabrication of non-toxic polymer sunscreen ingredients by electron irradiation’ developed by Professor Sung-Oh Cho of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
4. ‘High-density nanofiber yarn-based coloricmetric gas sensors’ developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
5. ‘Silicon-pocket energy storage electrode with high energy density and its manufacturing technology’ developed by Professor Jeung-Ku Kang of the Graduate school of EEWS.
The patented nanofiber-based coloricmetric gas sensor technology developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim allows for the diagnosis of diseases by only using the patient’s respiration. Due to its high productivity and processability, it is expected to be applied to various fields in the fast-growing disease diagnosis sensor market, which includes mobile devices and wearable sensors.
Moreover, Professor Dong-soo Han’s patented adaptive streaming technology attracted attention along with the ever-growing Over The Top (OTT) and Video On Demand (VOD) service markets, since it has significant potential for improving the streaming quality of videos and reducing costs for video providers.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, the Associate Vice President of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST, said, “KAIST OUIC and KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP) have been working tirelessly to help Korean companies cope with the recent Japanese export restrictions. KAIST’s efforts will enhance the competitiveness and growth of the Korean industry and economy, turning this national crisis into opportunity.”
(END)
2019.09.20 View 7859
KAIST to Transfer Core Tech to Domestic Companies amid Japan's Export Curbs
< Associate Vice President Kyung-Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST >
KAIST will transfer four core technologies related to materials, parts, and equipment to domestic companies to help them combat the latest export curbs triggered by Korea’s removal from Japan’s ‘white list’ of preferential trade partners. In addition, KAIST’s five patented technologies in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and materials and parts will also be transferred to the companies in order to reduce the reliance on Japan and achieve technological independence through the ‘localization’ of key technologies.
KAIST announced these university-industry cooperation promotion plans at the ‘2019 KAIST Core Tech Transfer Day Conference’ held in Seoul on September 17. More than 200 entrepreneurs and investors attended the briefing and on-site consulting sessions delivered by nine KAIST professors who led the development of the technologies.
The four technologies were presented at the conference as those that can replace Japanese technologies subject to the export curbs. They include:
1. ‘Transparent fluorinated polyimide with low thermal expansion’ developed by Professor Sang-Youl Kim of the Department of Chemistry
2. ‘A non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system’ developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
3. ‘A nanotechnology-based electrode material for use in advanced secondary batteries’ developed by Professor Do-Kyung Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
4. ‘A high-resolution photoresist’ developed by Professor Emeritus Jin-Baek Kim of the Department of Chemistry.
Of particular interest is the non-destructive electromagnetic performance testing system technology developed by Professor Jung-Ryul Lee. This new cost-effective technology enables tests that were impossible to carry out using conventional technologies and yields a cost reduction of more than 50 percent compared to foreign technologies.
By introducing Professor Do-Kyung Kim’s new electrode material technology, the efficiency of electric vehicles can be increased. As this technology uses relatively low-cost sodium ion batteries, industries can prepare for the possible jump from the more expensive lithium batteries currently being used.
Another five patented AI and materials and parts technologies disclosed at the conference include:
1. ‘Enhanced HTTP adaptive streaming with CNN-based super-resolution’ developed by Professor Dong-soo Han of the School of Electrical Engineering
2. ‘Method and apparatus of brain-computer interface design for estimating choice behavior and decision strategy’ developed by Professor Sang-Wan Lee of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
3. ‘Eco-friendly fabrication of metal oxide nanoparticles and fabrication of non-toxic polymer sunscreen ingredients by electron irradiation’ developed by Professor Sung-Oh Cho of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
4. ‘High-density nanofiber yarn-based coloricmetric gas sensors’ developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
5. ‘Silicon-pocket energy storage electrode with high energy density and its manufacturing technology’ developed by Professor Jeung-Ku Kang of the Graduate school of EEWS.
The patented nanofiber-based coloricmetric gas sensor technology developed by Professor Il-Doo Kim allows for the diagnosis of diseases by only using the patient’s respiration. Due to its high productivity and processability, it is expected to be applied to various fields in the fast-growing disease diagnosis sensor market, which includes mobile devices and wearable sensors.
Moreover, Professor Dong-soo Han’s patented adaptive streaming technology attracted attention along with the ever-growing Over The Top (OTT) and Video On Demand (VOD) service markets, since it has significant potential for improving the streaming quality of videos and reducing costs for video providers.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, the Associate Vice President of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) at KAIST, said, “KAIST OUIC and KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP) have been working tirelessly to help Korean companies cope with the recent Japanese export restrictions. KAIST’s efforts will enhance the competitiveness and growth of the Korean industry and economy, turning this national crisis into opportunity.”
(END)
2019.09.20 View 7859 -
 Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10308
Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10308 -
 Algorithm Identifies Optimal Pairs for Composing Metal-Organic Frameworks
The integration of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and other metal nanoparticles has increasingly led to the creation of new multifunctional materials. Many researchers have integrated MOFs with other classes of materials to produce new structures with synergetic properties.
Despite there being over 70,000 collections of synthesized MOFs that can be used as building blocks, the precise nature of the interaction and the bonding at the interface between the two materials still remains unknown. The question is how to sort out the right matching pairs out of 70,000 MOFs.
An algorithmic study published in Nature Communications by a KAIST research team presents a clue for finding the perfect pairs. The team, led by Professor Ji-Han Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a joint computational and experimental approach to rationally design MOF@MOFs, a composite of MOFs where an MOF is grown on a different MOF.
Professor Kim’s team, in collaboration with UNIST, noted that the metal node of one MOF can coordinately bond with the linker of a different MOF and the precisely matched interface configurations at atomic and molecular levels can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs.
They screened thousands of MOFs and identified optimal MOF pairs that can seamlessly connect to one another by taking advantage of the fact that the metal node of one MOF can form coordination bonds with the linkers of the second MOF. Six pairs predicted from the computational algorithm successfully grew into single crystals.
This computational workflow can readily extend into other classes of materials and can lead to the rapid exploration of the composite MOFs arena for accelerated materials development. Even more, the workflow can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs in the form of large single crystals, and thereby demonstrated the utility of rationally designing the MOF@MOFs.
This study is the first algorithm for predicting the synthesis of composite MOFs, to the best of their knowledge. Professor Kim said, “The number of predicted pairs can increase even more with the more general 2D lattice matching, and it is worth investigating in the future.”
This study was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
(Figure: An example of a rationally synthesized MOF@MOFs (cubic HKUST-1@MOF-5 ))
2019.08.30 View 17929
Algorithm Identifies Optimal Pairs for Composing Metal-Organic Frameworks
The integration of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and other metal nanoparticles has increasingly led to the creation of new multifunctional materials. Many researchers have integrated MOFs with other classes of materials to produce new structures with synergetic properties.
Despite there being over 70,000 collections of synthesized MOFs that can be used as building blocks, the precise nature of the interaction and the bonding at the interface between the two materials still remains unknown. The question is how to sort out the right matching pairs out of 70,000 MOFs.
An algorithmic study published in Nature Communications by a KAIST research team presents a clue for finding the perfect pairs. The team, led by Professor Ji-Han Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a joint computational and experimental approach to rationally design MOF@MOFs, a composite of MOFs where an MOF is grown on a different MOF.
Professor Kim’s team, in collaboration with UNIST, noted that the metal node of one MOF can coordinately bond with the linker of a different MOF and the precisely matched interface configurations at atomic and molecular levels can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs.
They screened thousands of MOFs and identified optimal MOF pairs that can seamlessly connect to one another by taking advantage of the fact that the metal node of one MOF can form coordination bonds with the linkers of the second MOF. Six pairs predicted from the computational algorithm successfully grew into single crystals.
This computational workflow can readily extend into other classes of materials and can lead to the rapid exploration of the composite MOFs arena for accelerated materials development. Even more, the workflow can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs in the form of large single crystals, and thereby demonstrated the utility of rationally designing the MOF@MOFs.
This study is the first algorithm for predicting the synthesis of composite MOFs, to the best of their knowledge. Professor Kim said, “The number of predicted pairs can increase even more with the more general 2D lattice matching, and it is worth investigating in the future.”
This study was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
(Figure: An example of a rationally synthesized MOF@MOFs (cubic HKUST-1@MOF-5 ))
2019.08.30 View 17929 -
 Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 21844
Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 21844 -
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Donates His Prize Money
The honoree of the 2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Award, Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang donated his prize money of one hundred million KRW to the Chemistry Department Scholarship Fund and the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex Management Fund during a donation ceremony last week.
Professor Chang won the award last month in recognition of his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. Professor Chang, a world renowned chemist, has been recognized for his highly selective catalytic systems, allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals.
“All my achievements are the results of my students’ hard work and dedication. I feel very fortunate to have such talented team members. I want to express my sincere gratitude for such a great research environment that we have worked together in so far,” said Professor Chang at the ceremony.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “Not only will Professor Chang’s donation make a significant contribution to the Department of Chemistry, but also to the improvement of the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex’s management, which directly links to the health and welfare of the KAIST community.”
Professor Chang currently holds the position of distinguished professor at KAIST and director of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations in the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). He previously received the Kyung-Ahm Academic Award in 2013 and the Korea Toray Science Award in 2018. All these prize money also went to the school.
(END)
2019.08.26 View 9324
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Donates His Prize Money
The honoree of the 2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Award, Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang donated his prize money of one hundred million KRW to the Chemistry Department Scholarship Fund and the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex Management Fund during a donation ceremony last week.
Professor Chang won the award last month in recognition of his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. Professor Chang, a world renowned chemist, has been recognized for his highly selective catalytic systems, allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals.
“All my achievements are the results of my students’ hard work and dedication. I feel very fortunate to have such talented team members. I want to express my sincere gratitude for such a great research environment that we have worked together in so far,” said Professor Chang at the ceremony.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “Not only will Professor Chang’s donation make a significant contribution to the Department of Chemistry, but also to the improvement of the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex’s management, which directly links to the health and welfare of the KAIST community.”
Professor Chang currently holds the position of distinguished professor at KAIST and director of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations in the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). He previously received the Kyung-Ahm Academic Award in 2013 and the Korea Toray Science Award in 2018. All these prize money also went to the school.
(END)
2019.08.26 View 9324 -
 Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 29428
Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 29428 -
 Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 30233
Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 30233 -
 Professor Sang Gyu Kim Receives Yeochon Award for Ecology
Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the winner of the 12th Yeochon Award for Ecology presented by the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research.
The award was conferred on August 13 in Jeju at the annual conference co-hosted by the Ecological Society of Korea and the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research. Professor Kim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his achievements and contributions in studying herbivorous insects ‘rice weevils’ and their host plant ‘wild tobacco’, especially for having explored the known facts in traditional ecology at the molecular level. His findings are presented in his paper titled ‘Trichobaris weevils distinguish amongst toxic host plants by sensing volatiles that do not affect larval performance’ published in Molecular Ecology in July 2016.
Furthermore, Professor Kim’s research team is continuing their work to identify the ecological functions of plant metabolites as well as interactions between flowers and insect vectors at the molecular level. In doing so, the team edits genes in various plant species using the latest gene editing technology.
The Yeochon Award for Ecology was first established in 2005 with funds donated by a senior ecologist, the late Honorary Professor Joon-Ho Kim of Seoul National University. The award is named after the professor’s pen name “Yeochon” and is intended to encourage promising next-generation ecologists to produce outstanding research achievements in the field of basic ecology.
Professor Kim said, “I will take this award as encouragement to continue taking challenging risks to observe ecological phenomenon from a new perspective. I will continue my research with my students with joy and enthusiasm.”
2019.08.14 View 7752
Professor Sang Gyu Kim Receives Yeochon Award for Ecology
Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the winner of the 12th Yeochon Award for Ecology presented by the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research.
The award was conferred on August 13 in Jeju at the annual conference co-hosted by the Ecological Society of Korea and the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research. Professor Kim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his achievements and contributions in studying herbivorous insects ‘rice weevils’ and their host plant ‘wild tobacco’, especially for having explored the known facts in traditional ecology at the molecular level. His findings are presented in his paper titled ‘Trichobaris weevils distinguish amongst toxic host plants by sensing volatiles that do not affect larval performance’ published in Molecular Ecology in July 2016.
Furthermore, Professor Kim’s research team is continuing their work to identify the ecological functions of plant metabolites as well as interactions between flowers and insect vectors at the molecular level. In doing so, the team edits genes in various plant species using the latest gene editing technology.
The Yeochon Award for Ecology was first established in 2005 with funds donated by a senior ecologist, the late Honorary Professor Joon-Ho Kim of Seoul National University. The award is named after the professor’s pen name “Yeochon” and is intended to encourage promising next-generation ecologists to produce outstanding research achievements in the field of basic ecology.
Professor Kim said, “I will take this award as encouragement to continue taking challenging risks to observe ecological phenomenon from a new perspective. I will continue my research with my students with joy and enthusiasm.”
2019.08.14 View 7752 -
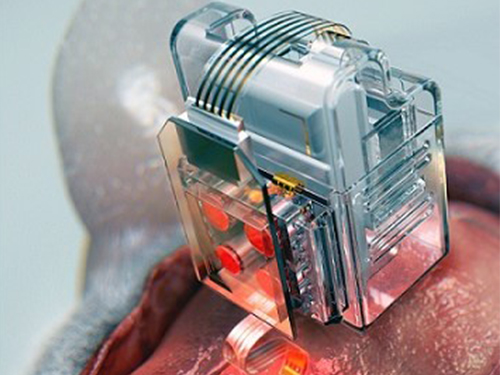 Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 33986
Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 33986 -
 Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 7414
Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 7414