initiative
-
 Professor Jae-Woong Jeong Receives Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected for the Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, funded by the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation (Chairman Soo-il Kwak, honorary professor at Seoul National University Business School).
The Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, presented for the first time in 2021, is an award newly founded by the donations of Chairman Soo-il Kwak of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation, who aims to reward excellent KAIST scholars who have made outstanding academic achievements.
Every year, through the strict evaluations of the selection committee of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation and the faculty reward recommendation board, KAIST will choose one faculty member that may represent the school with their excellent academic achievement, and reward them with a plaque and 100 million won.
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, the winner of this year’s award, developed the first IoT-based wireless remote brain neural network control system to overcome brain diseases, and has been leading the field. The research was published in 2021 in Nature Biomedical Engineering, one of world’s best scientific journals, and has been recognized as a novel technology that suggested a new vision for the automation of brain research and disease treatment. This study, led by Professor Jeong’s research team, was part of the KAIST College of Engineering Global Initiative Interdisciplinary Research Project, and was jointly studied by Washington University School of Medicine through an international research collaboration. The technology was introduced more than 60 times through both domestic and international media, including Medical Xpress, MBC News, and Maeil Business News.
Professor Jeong has also developed a wirelessly chargeable soft machine for brain transplants, and the results were published in Nature Communications. He thereby opened a new paradigm for implantable semi-permanent devices for transplants, and is making unprecedented research achievements.
2022.06.13 View 9091
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong Receives Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected for the Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, funded by the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation (Chairman Soo-il Kwak, honorary professor at Seoul National University Business School).
The Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, presented for the first time in 2021, is an award newly founded by the donations of Chairman Soo-il Kwak of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation, who aims to reward excellent KAIST scholars who have made outstanding academic achievements.
Every year, through the strict evaluations of the selection committee of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation and the faculty reward recommendation board, KAIST will choose one faculty member that may represent the school with their excellent academic achievement, and reward them with a plaque and 100 million won.
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, the winner of this year’s award, developed the first IoT-based wireless remote brain neural network control system to overcome brain diseases, and has been leading the field. The research was published in 2021 in Nature Biomedical Engineering, one of world’s best scientific journals, and has been recognized as a novel technology that suggested a new vision for the automation of brain research and disease treatment. This study, led by Professor Jeong’s research team, was part of the KAIST College of Engineering Global Initiative Interdisciplinary Research Project, and was jointly studied by Washington University School of Medicine through an international research collaboration. The technology was introduced more than 60 times through both domestic and international media, including Medical Xpress, MBC News, and Maeil Business News.
Professor Jeong has also developed a wirelessly chargeable soft machine for brain transplants, and the results were published in Nature Communications. He thereby opened a new paradigm for implantable semi-permanent devices for transplants, and is making unprecedented research achievements.
2022.06.13 View 9091 -
 Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center Launches Scientific Rocket
Undergraduate startup Perigree Aerospace develops suborbital rocket called Blue Whale 0.1
On December 29, Perigee Aerospace, an undergraduate startup, launched a test rocket with a length of 3.2 m, a diameter of 19 cm, and a weight of 51 kg, using ethanol and liquid oxygen as fuel. The launch took place off Jeju Island. It was aimed at building experience and checking the combustion of a liquid propulsion engine and the performance of pre-set flight and trajectory, communication, and navigation devices. It was also one of the projects marking the 50th anniversary of KAIST in 2021.
However, after flying for several seconds, the rocket lost its track due to a gust of wind that activated the rocket’s automatic flight suspension system. "At the moment the rocket took off, there was a much stronger gust than expected," Dong-Yoon Shin, CEO of Perigee said. "The wind sent it flying off course and the automatic flight suspension system stopped its engine." However, Shin was not disappointed, saying the launch, which was conducted in collaboration with Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center provided a good experience.
"Some people say that Blue Whale 0.1 is like a toy because of its small size. Of course, it's much smaller than the rockets I’ve dreamed of, but like other rockets, it has all the technology needed for launch," said Shin, who established his company in 2018 as a KAIST aerospace engineering student to develop small liquid-propellant orbital rockets. Perigee Aerospace aims to develop the world’s lightest launch vehicle using high-powered engines, with a goal of leading the global market for small launch vehicles in the new space generation.
Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center was founded in 2019 for the research and development of rocket propellants and has been testing the combustion of rocket engines of various sizes in their liquid propellant rocket combustion lab located on the KAIST Munji Campus.
The research center initiated the 50th anniversary rocket launch project in late April of last year, finished the examination of their preliminary design in late May, and secured a tentative launching site through the KAIST-Jejudo agreement in early July.
The ethanol engine combustion was tested in late July, and an examination meeting regarding the detailed design that took place in late August was followed by two months of static firing tests of the assembled rocket in October and November.
This was a very meaningful trial in which a domestic private enterprise founded by a college student collaborated with a university to successfully develop and launch a technically challenging liquid propellant rocket.
Shin's near-term goal is to launch a two-stage orbital rocket that uses liquid methane as fuel and weighs 1.8 tons. To secure competitiveness in the small projectile market, KAIST and Perigee Aerospace have set up a joint research center to test various rocket engine sizes and develop the world's lightest projectile using a high-performance engine.
Professor Jae-Hung Han, head of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, said, “The scientific rocket system secured through the launch of the celebratory rocket will be utilized for design and system-oriented education, and for carrying out various scientific missions.” He added, “It is very rare both domestically and globally that a scientific rocket designed by the initiatives of a department should be incorporated as part of a regular aerospace system design curriculum. This will be an exemplary case we can boast about to the rest of the world.”
Perigee Aerospace will improve the technology they have developed through the course of this project to develop subminiature vehicles they may use to launch small satellites into the low Earth orbit.
Shin said, “I am happy just with the fact that we have participated in a rocket project to celebrate the 50th anniversary of KAIST, and I would like to thank the engineers at my company and members of the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering.” He added, “I’m looking forward to the day that we develop a space launch vehicle that can deliver satellites even higher.”
2022.01.14 View 9853
Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center Launches Scientific Rocket
Undergraduate startup Perigree Aerospace develops suborbital rocket called Blue Whale 0.1
On December 29, Perigee Aerospace, an undergraduate startup, launched a test rocket with a length of 3.2 m, a diameter of 19 cm, and a weight of 51 kg, using ethanol and liquid oxygen as fuel. The launch took place off Jeju Island. It was aimed at building experience and checking the combustion of a liquid propulsion engine and the performance of pre-set flight and trajectory, communication, and navigation devices. It was also one of the projects marking the 50th anniversary of KAIST in 2021.
However, after flying for several seconds, the rocket lost its track due to a gust of wind that activated the rocket’s automatic flight suspension system. "At the moment the rocket took off, there was a much stronger gust than expected," Dong-Yoon Shin, CEO of Perigee said. "The wind sent it flying off course and the automatic flight suspension system stopped its engine." However, Shin was not disappointed, saying the launch, which was conducted in collaboration with Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center provided a good experience.
"Some people say that Blue Whale 0.1 is like a toy because of its small size. Of course, it's much smaller than the rockets I’ve dreamed of, but like other rockets, it has all the technology needed for launch," said Shin, who established his company in 2018 as a KAIST aerospace engineering student to develop small liquid-propellant orbital rockets. Perigee Aerospace aims to develop the world’s lightest launch vehicle using high-powered engines, with a goal of leading the global market for small launch vehicles in the new space generation.
Perigee-KAIST Rocket Research Center was founded in 2019 for the research and development of rocket propellants and has been testing the combustion of rocket engines of various sizes in their liquid propellant rocket combustion lab located on the KAIST Munji Campus.
The research center initiated the 50th anniversary rocket launch project in late April of last year, finished the examination of their preliminary design in late May, and secured a tentative launching site through the KAIST-Jejudo agreement in early July.
The ethanol engine combustion was tested in late July, and an examination meeting regarding the detailed design that took place in late August was followed by two months of static firing tests of the assembled rocket in October and November.
This was a very meaningful trial in which a domestic private enterprise founded by a college student collaborated with a university to successfully develop and launch a technically challenging liquid propellant rocket.
Shin's near-term goal is to launch a two-stage orbital rocket that uses liquid methane as fuel and weighs 1.8 tons. To secure competitiveness in the small projectile market, KAIST and Perigee Aerospace have set up a joint research center to test various rocket engine sizes and develop the world's lightest projectile using a high-performance engine.
Professor Jae-Hung Han, head of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, said, “The scientific rocket system secured through the launch of the celebratory rocket will be utilized for design and system-oriented education, and for carrying out various scientific missions.” He added, “It is very rare both domestically and globally that a scientific rocket designed by the initiatives of a department should be incorporated as part of a regular aerospace system design curriculum. This will be an exemplary case we can boast about to the rest of the world.”
Perigee Aerospace will improve the technology they have developed through the course of this project to develop subminiature vehicles they may use to launch small satellites into the low Earth orbit.
Shin said, “I am happy just with the fact that we have participated in a rocket project to celebrate the 50th anniversary of KAIST, and I would like to thank the engineers at my company and members of the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering.” He added, “I’m looking forward to the day that we develop a space launch vehicle that can deliver satellites even higher.”
2022.01.14 View 9853 -
 KPC4IR Publishes Global Standards Mapping Initiative 2.0
The report highlights South Korea as an early adopter of blockchain in policy and business
The KAIST Policy Center for the 4IR (KPC4IR), one of the nine working groups of the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), published the Global Standards Mapping Initiative (GSMI) 2.0, highlighting Korea as an early adopter of blockchain. The report also offers an overview of how blockchain was adopted through an analysis of policy and business cases of South Korea.
In partnership with 131 institutions, GSMI 2.0 maps, catalogues, and analyzes data from 187 jurisdictions, 479 industry consortia, 38 technical standards, and 389 university courses and degree programs to provide a holistic view of the industry’s global activity.
Among the nine working groups, KAIST is the sole investigator for researching South Korea’s adoption of blockchain for policy and business. It says that in terms of policy and regulations for blockchain as a virtual asset, South Korea amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specific Financial Transaction Information to comply with the Financial Action Task Force’s recommendations.
The report also reviewed South Korea’s blockchain R&D. Seventeen ministries have funded 417 projects to cultivate blockchain inventions since 2015. Significantly, the Ministry of Science and ICT’s Blockchain Convergence Technology Development Program supported 50 projects between 2018 and 2021. Their R&D focused on virtual assets during the initial stage in 2015 and soon shifted its application to various domains, including identification and logistics.
The report noted that the Korea Customs Service was one of the first agencies in the world to introduce blockchain into customs clearance. Through collaborations with the private sector, the Korean government has also created the world’s first blockchain-based vaccination certification services and extended it to a globally integrated decentralized identity system.
Finally, the report states that these South Korean cases highlight three ambiguities in blockchain policies. First, blockchain involves both financial and industrial features. Thus, it needs a new regulatory framework that embraces the two features together.
Second, integrating services on a blockchain platform will bring forth seamless automation of industries across the manufacturing, financial, and public sectors. South Korea, which already has well-proven manufacturing capabilities, is in need of a comprehensive strategy to encompass multiple services on one platform.
Third, the two cases of the government’s adoption of blockchain suggest that innovations in blockchain can be facilitated through effective cooperation among government ministries and agencies regarding particular businesses in the private sector. Consequently, the government’s policy is not simply to invest in virtual assets but also to develop a virtual-physical world woven by blockchain. The new environment demands that South Korea transform its policy stances on blockchain, from specialization to comprehensiveness and cooperation.
Professor So Young Kim who heads the center said, “This report shows the main lessons from South Korea for other countries adopting blockchain. We will continue to work closely with our partners including the World Economic Forum to investigate many other global issues.”
2021.12.21 View 7789
KPC4IR Publishes Global Standards Mapping Initiative 2.0
The report highlights South Korea as an early adopter of blockchain in policy and business
The KAIST Policy Center for the 4IR (KPC4IR), one of the nine working groups of the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), published the Global Standards Mapping Initiative (GSMI) 2.0, highlighting Korea as an early adopter of blockchain. The report also offers an overview of how blockchain was adopted through an analysis of policy and business cases of South Korea.
In partnership with 131 institutions, GSMI 2.0 maps, catalogues, and analyzes data from 187 jurisdictions, 479 industry consortia, 38 technical standards, and 389 university courses and degree programs to provide a holistic view of the industry’s global activity.
Among the nine working groups, KAIST is the sole investigator for researching South Korea’s adoption of blockchain for policy and business. It says that in terms of policy and regulations for blockchain as a virtual asset, South Korea amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specific Financial Transaction Information to comply with the Financial Action Task Force’s recommendations.
The report also reviewed South Korea’s blockchain R&D. Seventeen ministries have funded 417 projects to cultivate blockchain inventions since 2015. Significantly, the Ministry of Science and ICT’s Blockchain Convergence Technology Development Program supported 50 projects between 2018 and 2021. Their R&D focused on virtual assets during the initial stage in 2015 and soon shifted its application to various domains, including identification and logistics.
The report noted that the Korea Customs Service was one of the first agencies in the world to introduce blockchain into customs clearance. Through collaborations with the private sector, the Korean government has also created the world’s first blockchain-based vaccination certification services and extended it to a globally integrated decentralized identity system.
Finally, the report states that these South Korean cases highlight three ambiguities in blockchain policies. First, blockchain involves both financial and industrial features. Thus, it needs a new regulatory framework that embraces the two features together.
Second, integrating services on a blockchain platform will bring forth seamless automation of industries across the manufacturing, financial, and public sectors. South Korea, which already has well-proven manufacturing capabilities, is in need of a comprehensive strategy to encompass multiple services on one platform.
Third, the two cases of the government’s adoption of blockchain suggest that innovations in blockchain can be facilitated through effective cooperation among government ministries and agencies regarding particular businesses in the private sector. Consequently, the government’s policy is not simply to invest in virtual assets but also to develop a virtual-physical world woven by blockchain. The new environment demands that South Korea transform its policy stances on blockchain, from specialization to comprehensiveness and cooperation.
Professor So Young Kim who heads the center said, “This report shows the main lessons from South Korea for other countries adopting blockchain. We will continue to work closely with our partners including the World Economic Forum to investigate many other global issues.”
2021.12.21 View 7789 -
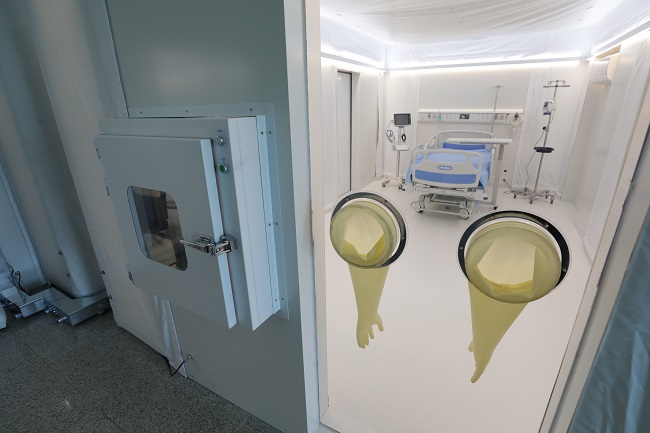 MCM Utilized at Residential Treatment Center in Gyeonggi
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM) developed by the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics was installed at special residential treatment center in Gyeonggi Province on September 13.
The MCM is an isolate negative pressure unit fitted with high-quality medical equipment, developed by Professor Taek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative. This is also a part of the Korean Disease Control Package Development Project from last July.
In January, a ward with four beds for critical care was installed at the Korea Institute for Radiological & Medical Sciences in Seoul for a trial operation, and two mild cases were treated there. It was also implemented as an isolated negative pressure unit in the Daejeon Konyang University Hospital emergency room in June, and has treated 138 cases since.
The special residential treatment center installed in the Gyeonggi Provincial Academy gymnasium, which consists of 28 beds in 14 rooms (double occupancy) and a multipurpose room (for X-rays and treatment), is to remain open through October 10. Unlike existing treatment centers that have quarantined COVID-19 patients for two weeks, the Gyeonggi MCM will act as a self-treatment-associated short-term treatment center. While in self-treatment, patients showing symptoms requiring special attention will be moved to the MCM, followed by short-term hospitalization of 1-3 days for observation before further measures are taken.
Patients can be treated using the MCM’s own treatment capacities, including in-person and oxygen treatment, X-rays, and IVs. There are individual bathrooms in each room, and the pressure, ventilation, and the automatic opening and closing of the entrance can be centrally monitored and controlled. Patients showing symptoms during treatment will be moved to a specially designated hospital for critical care, and will return to the self-treatment center if no further abnormalities are reported.
The Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center’s Ansung Hospital will take charge of operating the special treatment center. Each day, one or two doctors, three nurses, two nursing assistants, one administrative staff member, two or three disinfection specialists, and a medical imaging engineer will work in three shifts. There will also be about 20 additional specially designated staff members including KAIST researchers, firefighters, and police officers.
The MCM was internationally recognized as an excellent medical facility not only for its functionality, economic feasibility, and utility, but also for its unique design and aesthetics. It received two Best of Best awards at the Red Dot Award in product design and Communication Design in user interface.
By running this special treatment center, KAIST will conduct research on how to build an optimized model for efficient negative pressure medical units. This research is expected to lead to advances in waste water treatment systems, mobile bathrooms optimized for infectious cases, and MCM user interfaces for electronic devices, etc.
Professor Taek-Jin Nam, the general director of the project and design, said “if there is a gymnasium available, we can convert it into a special treatment center fitted with a waste water treatment system, and pressure equipment in two weeks even without additional infrastructure.”
The head of the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative Choongsik Bae said, “our MCM research started in July of last year, and in just over a year, it has become a successful and innovative case that has undergone trials and become commercialized in a short period of time.” He added, “In response to COVID-19, KAIST is conducting research and empirical studies, not just in relation to the MCM, but in other areas of disease control as well.”
Based on the excellent disease control technologies developed by KAIST research teams, the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics is conducting technology transfers and industrialization, and is developing a Korean disease control package model
2021.09.15 View 12663
MCM Utilized at Residential Treatment Center in Gyeonggi
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM) developed by the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics was installed at special residential treatment center in Gyeonggi Province on September 13.
The MCM is an isolate negative pressure unit fitted with high-quality medical equipment, developed by Professor Taek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative. This is also a part of the Korean Disease Control Package Development Project from last July.
In January, a ward with four beds for critical care was installed at the Korea Institute for Radiological & Medical Sciences in Seoul for a trial operation, and two mild cases were treated there. It was also implemented as an isolated negative pressure unit in the Daejeon Konyang University Hospital emergency room in June, and has treated 138 cases since.
The special residential treatment center installed in the Gyeonggi Provincial Academy gymnasium, which consists of 28 beds in 14 rooms (double occupancy) and a multipurpose room (for X-rays and treatment), is to remain open through October 10. Unlike existing treatment centers that have quarantined COVID-19 patients for two weeks, the Gyeonggi MCM will act as a self-treatment-associated short-term treatment center. While in self-treatment, patients showing symptoms requiring special attention will be moved to the MCM, followed by short-term hospitalization of 1-3 days for observation before further measures are taken.
Patients can be treated using the MCM’s own treatment capacities, including in-person and oxygen treatment, X-rays, and IVs. There are individual bathrooms in each room, and the pressure, ventilation, and the automatic opening and closing of the entrance can be centrally monitored and controlled. Patients showing symptoms during treatment will be moved to a specially designated hospital for critical care, and will return to the self-treatment center if no further abnormalities are reported.
The Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center’s Ansung Hospital will take charge of operating the special treatment center. Each day, one or two doctors, three nurses, two nursing assistants, one administrative staff member, two or three disinfection specialists, and a medical imaging engineer will work in three shifts. There will also be about 20 additional specially designated staff members including KAIST researchers, firefighters, and police officers.
The MCM was internationally recognized as an excellent medical facility not only for its functionality, economic feasibility, and utility, but also for its unique design and aesthetics. It received two Best of Best awards at the Red Dot Award in product design and Communication Design in user interface.
By running this special treatment center, KAIST will conduct research on how to build an optimized model for efficient negative pressure medical units. This research is expected to lead to advances in waste water treatment systems, mobile bathrooms optimized for infectious cases, and MCM user interfaces for electronic devices, etc.
Professor Taek-Jin Nam, the general director of the project and design, said “if there is a gymnasium available, we can convert it into a special treatment center fitted with a waste water treatment system, and pressure equipment in two weeks even without additional infrastructure.”
The head of the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative Choongsik Bae said, “our MCM research started in July of last year, and in just over a year, it has become a successful and innovative case that has undergone trials and become commercialized in a short period of time.” He added, “In response to COVID-19, KAIST is conducting research and empirical studies, not just in relation to the MCM, but in other areas of disease control as well.”
Based on the excellent disease control technologies developed by KAIST research teams, the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics is conducting technology transfers and industrialization, and is developing a Korean disease control package model
2021.09.15 View 12663 -
 KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 9734
KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 9734 -
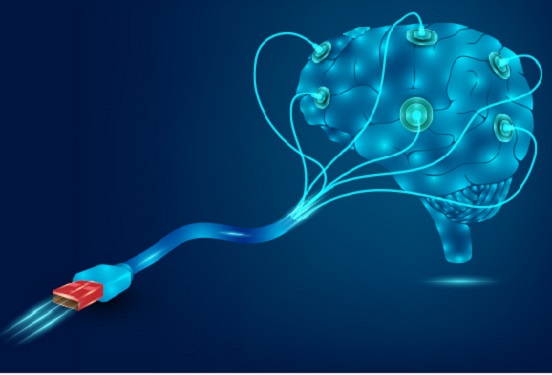 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 12718
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 12718 -
 KPC4IR Leads the Global Blockchain Standards Via Korea Innovation Studies
The Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) at KAIST will play a leading role in the Global Standards Mapping Initiative (GSMI) 2.0 as the Chair of Working Group on South Korea at the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC). The GBBC, a Swiss-based non-profit consortium, established the GSMI to map blockchain technology ecosystem, established the GSMI to map blockchain and digital asset standards and regulation globally. The initial release of the GSMI mapped data and outputs from ons, 185 jurisdictions, nearly 400 industry groups, and over 30 technical standard-setting entities.
The GSMI Working Group on South Korea is the only group that will investigate the country-level innovation of blockchain and digital asset alongside six Korean blockchain associations: The GSMI Working Group on South Korea is the only group that will investigate the country-level innovation of blockchain and digital asset alongside six Korean blockchain associations: the Korea Blockchain Association, the Korea Society of Blockchain, Blockchain & Law, the Open Blockchain and DID Association, the Korea Blockchain Startup Association, and the Korea Blockchain Industry Promotion Association. Individual members also joined from the Inter-American Development Bank, Blockchain Labs, and GOPAX.
The GSMI Working Group on South Korea, chaired by KAIST, will leverage their experience in blockchain adoption to assist in setting global standards for the ecosystem. The Group will also highlight how South Korea can be a testbed for ITC adoption and open the door to a blockchain-ready world.
GSMI 2.0 is spearheaded by nine working groups chaired by institutions, such as the World Economic Forum and the GBBC, Ernst & Young, HM Revenue and Customs, Accenture, and Hyperledger - Linux Foundation. Each of the Working Groups will be supported by sixteen fellows from eight fellow program partners. KAIST student Yujin Bang is the South Korea Working Group fellow. The GBBC and the WEF already published the first volume of the GSMI in October 2020 in collaboration with world-leading institutions, including KAIST, MIT Media Lab, and Accenture.
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim said, “The designation of KAIST is the result of continued collaborations with the WEF. The participation of this working group will help Korea’s global leadership with blockchain standards.”
2021.05.18 View 8559
KPC4IR Leads the Global Blockchain Standards Via Korea Innovation Studies
The Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) at KAIST will play a leading role in the Global Standards Mapping Initiative (GSMI) 2.0 as the Chair of Working Group on South Korea at the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC). The GBBC, a Swiss-based non-profit consortium, established the GSMI to map blockchain technology ecosystem, established the GSMI to map blockchain and digital asset standards and regulation globally. The initial release of the GSMI mapped data and outputs from ons, 185 jurisdictions, nearly 400 industry groups, and over 30 technical standard-setting entities.
The GSMI Working Group on South Korea is the only group that will investigate the country-level innovation of blockchain and digital asset alongside six Korean blockchain associations: The GSMI Working Group on South Korea is the only group that will investigate the country-level innovation of blockchain and digital asset alongside six Korean blockchain associations: the Korea Blockchain Association, the Korea Society of Blockchain, Blockchain & Law, the Open Blockchain and DID Association, the Korea Blockchain Startup Association, and the Korea Blockchain Industry Promotion Association. Individual members also joined from the Inter-American Development Bank, Blockchain Labs, and GOPAX.
The GSMI Working Group on South Korea, chaired by KAIST, will leverage their experience in blockchain adoption to assist in setting global standards for the ecosystem. The Group will also highlight how South Korea can be a testbed for ITC adoption and open the door to a blockchain-ready world.
GSMI 2.0 is spearheaded by nine working groups chaired by institutions, such as the World Economic Forum and the GBBC, Ernst & Young, HM Revenue and Customs, Accenture, and Hyperledger - Linux Foundation. Each of the Working Groups will be supported by sixteen fellows from eight fellow program partners. KAIST student Yujin Bang is the South Korea Working Group fellow. The GBBC and the WEF already published the first volume of the GSMI in October 2020 in collaboration with world-leading institutions, including KAIST, MIT Media Lab, and Accenture.
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim said, “The designation of KAIST is the result of continued collaborations with the WEF. The participation of this working group will help Korea’s global leadership with blockchain standards.”
2021.05.18 View 8559 -
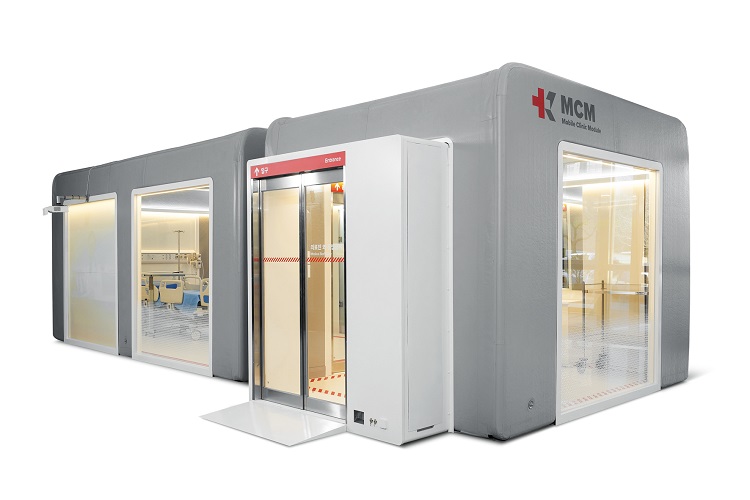 Mobile Clinic Module Wins Red Dot and iF Design Awards
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM), an inflatable negative pressure ward building system developed by the Korea Aid for Respiratory Epidemic (KARE) initiative at KAIST, gained international acclaim by winning the prestigious Red Dot Design Award and iF Design Award.
The MCM was recognized as one of the Red Dot Product Designs of the Year. It also won four iF Design Awards in communication design, interior architecture, user interface, and user experience. Winning the two most influential design awards demonstrates how product design can make a valuable contribution to help contain pandemics and reflects new consumer trends for dealing with pandemics.
Designed to be patient friendly, even in the extreme medical situations such as pandemics or triage, the MCM is the result of collaborations among researchers in a variety of fields including mechanical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, medical hospitals, and engineering companies. The research team was led by Professor Tek-Jin Nam from the Department of Industrial Design.
The MCM is expandable, moveable, and easy to store through a combination of negative pressure frames, air tents, and multi-functional panels. Positive air pressure devices supply fresh air from outside the tent. An air pump and controller maintain air beam pressure, while filtering exhausted air from inside. An internal air information monitoring system efficiently controls inside air pressure and purifies the air. It requires only one-fourth of the volume of existing wards and takes up approximately 40% of their weight. The unit can be transported in a 40-foot container truck.
MCMs are now located at the Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences and Jeju Vaccine Center and expect to be used at many other facilities. KARE is developing antiviral solutions and devices such as protective gear, sterilizers, and test kits to promptly respond to the pandemic. More than 100 researchers at KAIST are collaborating with industry and clinical hospitals to develop antiviral technologies that will improve preventive measures, diagnoses, and treatments.
Professor Nam said, “Our designers will continue to identify the most challenging issues, and try to resolve them by realizing user-friendly functions. We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms. We look forward to the MCM upgrading epidemic management resources around the globe.”
(END)
2021.04.21 View 10835
Mobile Clinic Module Wins Red Dot and iF Design Awards
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM), an inflatable negative pressure ward building system developed by the Korea Aid for Respiratory Epidemic (KARE) initiative at KAIST, gained international acclaim by winning the prestigious Red Dot Design Award and iF Design Award.
The MCM was recognized as one of the Red Dot Product Designs of the Year. It also won four iF Design Awards in communication design, interior architecture, user interface, and user experience. Winning the two most influential design awards demonstrates how product design can make a valuable contribution to help contain pandemics and reflects new consumer trends for dealing with pandemics.
Designed to be patient friendly, even in the extreme medical situations such as pandemics or triage, the MCM is the result of collaborations among researchers in a variety of fields including mechanical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, medical hospitals, and engineering companies. The research team was led by Professor Tek-Jin Nam from the Department of Industrial Design.
The MCM is expandable, moveable, and easy to store through a combination of negative pressure frames, air tents, and multi-functional panels. Positive air pressure devices supply fresh air from outside the tent. An air pump and controller maintain air beam pressure, while filtering exhausted air from inside. An internal air information monitoring system efficiently controls inside air pressure and purifies the air. It requires only one-fourth of the volume of existing wards and takes up approximately 40% of their weight. The unit can be transported in a 40-foot container truck.
MCMs are now located at the Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences and Jeju Vaccine Center and expect to be used at many other facilities. KARE is developing antiviral solutions and devices such as protective gear, sterilizers, and test kits to promptly respond to the pandemic. More than 100 researchers at KAIST are collaborating with industry and clinical hospitals to develop antiviral technologies that will improve preventive measures, diagnoses, and treatments.
Professor Nam said, “Our designers will continue to identify the most challenging issues, and try to resolve them by realizing user-friendly functions. We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms. We look forward to the MCM upgrading epidemic management resources around the globe.”
(END)
2021.04.21 View 10835 -
 KAIST Teams Up with Yozma Group to Nurture Startups
KAIST has joined hands with Israeli venture capital investor Yozma Group to help campus-based startups grow and build success. The two signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on joint technology value creation initiatives at the signing ceremony that was held at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon on April 8.
Under the MOU, Yozma Group will make investments and implement acceleration programs for startups established by KAIST professors, graduates, and students, as well as those invested in by the university.
Yozma Group already launched a $70 million fund to help grow companies in Korea and Israel. Yozma Group will use the fund as well as its global acceleration know-how and network of over 400 R&D centers across Israel to help promising KAIST startups enter overseas markets.
Moreover, Yozma Group also plans to discover and support KAIST startups that need technology from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel’s leading multidisciplinary basic research institution in natural and exact sciences.
KAIST is also in talks to locate Yozma Group’s branch office on the university’s campus to ensure seamless collaborations.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee explained to Yozma Group’s Founder and Chairman Yigal Erlich and Head of Asia Pacific Won-Jae Lee at the MOU signing ceremony that “startup and technology commercialization are the crucial areas where KAIST will make innovations.”
“Cooperation with Yozma Group will help KAIST startups transform their ideas and technologies into real businesses and build a global presence,” he added.
Yozma Group started as Yozma Fund, created in conjunction with the Israeli government in 1993 to support the globalization of Israeli startups and to foster the growth of Israel’s venture capital industry. The Fund, which was privatized in 1998, has supported 97 Israeli tech ventures joining the Nasdaq, leading Israel to become a global innovation hub that has the third-most companies listed on the Nasdaq.
(END)
2021.04.20 View 8270
KAIST Teams Up with Yozma Group to Nurture Startups
KAIST has joined hands with Israeli venture capital investor Yozma Group to help campus-based startups grow and build success. The two signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on joint technology value creation initiatives at the signing ceremony that was held at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon on April 8.
Under the MOU, Yozma Group will make investments and implement acceleration programs for startups established by KAIST professors, graduates, and students, as well as those invested in by the university.
Yozma Group already launched a $70 million fund to help grow companies in Korea and Israel. Yozma Group will use the fund as well as its global acceleration know-how and network of over 400 R&D centers across Israel to help promising KAIST startups enter overseas markets.
Moreover, Yozma Group also plans to discover and support KAIST startups that need technology from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel’s leading multidisciplinary basic research institution in natural and exact sciences.
KAIST is also in talks to locate Yozma Group’s branch office on the university’s campus to ensure seamless collaborations.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee explained to Yozma Group’s Founder and Chairman Yigal Erlich and Head of Asia Pacific Won-Jae Lee at the MOU signing ceremony that “startup and technology commercialization are the crucial areas where KAIST will make innovations.”
“Cooperation with Yozma Group will help KAIST startups transform their ideas and technologies into real businesses and build a global presence,” he added.
Yozma Group started as Yozma Fund, created in conjunction with the Israeli government in 1993 to support the globalization of Israeli startups and to foster the growth of Israel’s venture capital industry. The Fund, which was privatized in 1998, has supported 97 Israeli tech ventures joining the Nasdaq, leading Israel to become a global innovation hub that has the third-most companies listed on the Nasdaq.
(END)
2021.04.20 View 8270 -
 Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 14892
Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 14892 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 33553
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 33553 -
 Provost Kwang Hyung Lee Elected as the 17th President of KAIST
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee was selected as the 17th president of KAIST during a vote of the KAIST Board of Trustees on February 18. He will succeed President Sung-Chul Shin, whose four-year term concludes on February 22.
President-elect Lee, 67, was among the three final candidates who were nominated by the Presidential Search Committee. Upon the selection, President-elect Lee said he will take up new challenges to transform KAIST into the most relevant research university in the world, fostering talents who can work with emerging technologies while pushing for innovative R&D initiatives that will benefit all of humanity.
President-elect Lee is a futurologist who pioneered multidisciplinary studies and research at KAIST. He advocated that the convergence of information, biology, and nano-technologies would be critical for future industries, playing a crucial role in establishing the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2001 and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy in 2013. He then served as the inaugural head of both faculties.
President-elect Lee has extensive administrative experience at KAIST, serving as Associate Vice President of the International Office, and Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs since early 2001. He is also serving as a member of the Korea Presidential Education Committee.
An ardent champion of entrepreneurship and startups, he has advised the first generations of KAIST startup entrepreneurs such as Nexon, Idis, Neowiz, and Olaworks. President-elect Lee, drawn to creative thinking and flipped learning, is famous for watching TV upside down. Such pioneering ideas and his unusual thinking style were modeled in the ‘eccentric professor’ role featured on the TV hit drama of ‘KAIST’ from 1999 to 2000.
An alumnus who earned his MS in industrial engineering at KAIST in 1980 after completing his undergraduate studies at Seoul National University, President-elect Lee joined the KAIST faculty in 1985 upon receiving his PhD in computer science from INSA de Lyon in France.
A computer scientist as well as fuzzy theorist whose research area extends to AI, bioinformatics, fuzzy intelligent systems, and foresight methods, Professor Lee has published more than 70 papers in international journals and textbooks on system programming, fuzzy set theory and its applications, and three-dimensional creativity. He also invented a fuzzy elevator, subway operation controller, and AI transportation controller.
A fellow at the Korea Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, he was decorated by the Korean government and the French government in recognition of the innovative education and research initiatives he has pursued.
2021.02.18 View 10382
Provost Kwang Hyung Lee Elected as the 17th President of KAIST
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee was selected as the 17th president of KAIST during a vote of the KAIST Board of Trustees on February 18. He will succeed President Sung-Chul Shin, whose four-year term concludes on February 22.
President-elect Lee, 67, was among the three final candidates who were nominated by the Presidential Search Committee. Upon the selection, President-elect Lee said he will take up new challenges to transform KAIST into the most relevant research university in the world, fostering talents who can work with emerging technologies while pushing for innovative R&D initiatives that will benefit all of humanity.
President-elect Lee is a futurologist who pioneered multidisciplinary studies and research at KAIST. He advocated that the convergence of information, biology, and nano-technologies would be critical for future industries, playing a crucial role in establishing the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2001 and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy in 2013. He then served as the inaugural head of both faculties.
President-elect Lee has extensive administrative experience at KAIST, serving as Associate Vice President of the International Office, and Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs since early 2001. He is also serving as a member of the Korea Presidential Education Committee.
An ardent champion of entrepreneurship and startups, he has advised the first generations of KAIST startup entrepreneurs such as Nexon, Idis, Neowiz, and Olaworks. President-elect Lee, drawn to creative thinking and flipped learning, is famous for watching TV upside down. Such pioneering ideas and his unusual thinking style were modeled in the ‘eccentric professor’ role featured on the TV hit drama of ‘KAIST’ from 1999 to 2000.
An alumnus who earned his MS in industrial engineering at KAIST in 1980 after completing his undergraduate studies at Seoul National University, President-elect Lee joined the KAIST faculty in 1985 upon receiving his PhD in computer science from INSA de Lyon in France.
A computer scientist as well as fuzzy theorist whose research area extends to AI, bioinformatics, fuzzy intelligent systems, and foresight methods, Professor Lee has published more than 70 papers in international journals and textbooks on system programming, fuzzy set theory and its applications, and three-dimensional creativity. He also invented a fuzzy elevator, subway operation controller, and AI transportation controller.
A fellow at the Korea Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, he was decorated by the Korean government and the French government in recognition of the innovative education and research initiatives he has pursued.
2021.02.18 View 10382