COVID-19
-
 Krafton Matches Alumni Donations to Raise 11 Billion KRW for SW Developers
Alumni donations from the School of Computing, including Baemin and Devsisters, continue to grow
Alumni from the KAIST School of Computing who are current and former developers at the leading game company Krafton, established by KAIST alumna Byung-Gyu Chang, made an agreement to help raise 11 billion KRW during a ceremony on June 4. The funds raised in the matching grant will be used to nurture software developers.
Krafton Chairman Chang donated 10 billion won last January. His donation inspired other alumni working at Krafton as well as its former developers. Eleven KAIST alumni raised 5.5 billion KRW in two months and discussed the matching grant idea with Chairman Chang.
The Krafton matching grant ceremony was attended by President Kwang Hyung Lee, Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu, Krafton Chairman Byung-gyu Chang, and KAIST alumnus from Krafton Seung-woo Shin. Other alumni donors including Krafton CEO Changhan Kim joined the ceremony online.
Krafton CEO Changhan Kim said, “Just as our alma mater played an important role in growing our company, we hope that our donation could help support good developers. This will not only help our company, but advance our industry.”
KAIST and Krafton also signed a business agreement to foster competitive developers. Krafton said it plans to continue giving back to society through the matching grant program.
Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu thanked Chairman Chang and alumni who took part in the fund raising, saying, “To take the lead in rapidly changing computer technology, we desperately need more top students, faculty members, and facilities. We need more resources and infrastructure for interdisciplinary research.”
The School of Computing has seen significant growth recently. Its number of undergraduate students has increased from 450 in 2016 to more than 900 in 2021. With this donation, the school will expand its current buildings to provide diverse educational and mentoring programs in more spacious facilities.
Seung-woo Shin (Class of ’92), who joined Krafton’s matching grant, said, “I have always been thankful for the people I met and what I learned at KAIST. I was moved by the idea of giving back to the school.”
Seong-jung Ryu (Class of ’97) said, “This donation reminded me of the good times I had back then. I thought it was crucial that the department’s facilities be extended, so I naturally wanted to take part.”
Alumni donations, especially from the School of Computing, have also continued to grow more recently. Woowa Brothers Corp. CEO Beom-Jun Kim, the developer of the meal delivery app ‘Baemin’ donated 100 million KRW in April. Baemin became the most used app in the country during the COVID-19 pandemic.
He explained, “I have been thinking about ways to give something to the next generation, rather than ‘paying back’ those who helped me in the past.”
Encouraged by Baemin’s donation, alumni couple Ha-Yeon Seo and Dong-Hun Hahn from the School of Computing and eleven alumni engineers working at Devsisters Corp. also followed suit.
2021.06.09 View 11117
Krafton Matches Alumni Donations to Raise 11 Billion KRW for SW Developers
Alumni donations from the School of Computing, including Baemin and Devsisters, continue to grow
Alumni from the KAIST School of Computing who are current and former developers at the leading game company Krafton, established by KAIST alumna Byung-Gyu Chang, made an agreement to help raise 11 billion KRW during a ceremony on June 4. The funds raised in the matching grant will be used to nurture software developers.
Krafton Chairman Chang donated 10 billion won last January. His donation inspired other alumni working at Krafton as well as its former developers. Eleven KAIST alumni raised 5.5 billion KRW in two months and discussed the matching grant idea with Chairman Chang.
The Krafton matching grant ceremony was attended by President Kwang Hyung Lee, Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu, Krafton Chairman Byung-gyu Chang, and KAIST alumnus from Krafton Seung-woo Shin. Other alumni donors including Krafton CEO Changhan Kim joined the ceremony online.
Krafton CEO Changhan Kim said, “Just as our alma mater played an important role in growing our company, we hope that our donation could help support good developers. This will not only help our company, but advance our industry.”
KAIST and Krafton also signed a business agreement to foster competitive developers. Krafton said it plans to continue giving back to society through the matching grant program.
Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu thanked Chairman Chang and alumni who took part in the fund raising, saying, “To take the lead in rapidly changing computer technology, we desperately need more top students, faculty members, and facilities. We need more resources and infrastructure for interdisciplinary research.”
The School of Computing has seen significant growth recently. Its number of undergraduate students has increased from 450 in 2016 to more than 900 in 2021. With this donation, the school will expand its current buildings to provide diverse educational and mentoring programs in more spacious facilities.
Seung-woo Shin (Class of ’92), who joined Krafton’s matching grant, said, “I have always been thankful for the people I met and what I learned at KAIST. I was moved by the idea of giving back to the school.”
Seong-jung Ryu (Class of ’97) said, “This donation reminded me of the good times I had back then. I thought it was crucial that the department’s facilities be extended, so I naturally wanted to take part.”
Alumni donations, especially from the School of Computing, have also continued to grow more recently. Woowa Brothers Corp. CEO Beom-Jun Kim, the developer of the meal delivery app ‘Baemin’ donated 100 million KRW in April. Baemin became the most used app in the country during the COVID-19 pandemic.
He explained, “I have been thinking about ways to give something to the next generation, rather than ‘paying back’ those who helped me in the past.”
Encouraged by Baemin’s donation, alumni couple Ha-Yeon Seo and Dong-Hun Hahn from the School of Computing and eleven alumni engineers working at Devsisters Corp. also followed suit.
2021.06.09 View 11117 -
 Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 11535
Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 11535 -
 Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 15766
Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 15766 -
 The Educational ‘Metaverse’ Is Coming
The universities best equipped with digital infrastructure and savvy human resources will emerge as the new leaders − no matter where they are, says Kwang Hyung Lee
It goes without saying that the Covid-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on the education sector. Approximately 1.6 billion students from 192 countries, or 91 per cent of the world’s student population, have experienced educational disruptions.
As we all know, this disruption led to online education hastily emerging as an important new platform. However, approximately 29 percent of young people worldwide, about 364 million individuals, are not online. In many ways, the digital divide is now wider than ever.
We do, however, have an opportunity to ensure that the integration of emerging technologies is further accelerated and that online delivery becomes an integral component of education. This should, in theory, lead to more inclusive and creative pedagogical solutions.
The entire world has effectively taken part in an educational experiment, and at KAIST we were able to confirm that blended education worked effectively for our students. It made up for the long-standing pedagogical shortfalls of the one-way delivery of knowledge and made it possible to shift to a learner-centric model, giving us a great opportunity to unlock the creativity and collaborative minds of our students. Education tailored to students’ individual levels will not only help them accumulate knowledge but improve their ability to use it.
A recent survey in South Korea found that 96 per cent of Seoul citizens believed that the pandemic widened the existing learning gap, but 74 per cent said that schools should carry out a blended form of education using both remote and in-person classes. The feedback from KAIST students on our online classes gives us a glimpse into the new paths we need to take.
From last March, we offered 60 per cent real-time classes via Zoom and 40 per cent through our pre-recorded learning management system. Our students were satisfied with the real-time classes in which they could interact face to face with professors. The blended class format combining real-time and pre-recorded content received very satisfactory evaluations. The problem, however, came with lab classes via Zoom. Students expressed their dissatisfaction with the passive and indirect learning experiences.
Developing online tools or technologies that can enable scientific experiments, engineering prototyping and other hands-on activities remains a challenge. However, we can begin to address these issues using complementary technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, image recognition and eye-tracking technologies.
The barriers to access to these new experiences are both complex and pervasive, yet there are ways we can pull together to disrupt these barriers at a global level in the hope of fostering inclusive growth.
For instance, the virtual campus will become a reality at the Kenya-KAIST campus, which will open by September 2023 in the Konza Technopolis, 60km outside Nairobi.
There, we aim to go beyond online education by creating a “metaverse” that provides assistance for running classes and creates an immersive learning experience that runs the gamut of campus activities while utilising the latest digital technologies.
Following a feasibility study of the Kenya campus that took place five years ago, we planned to utilise Mooc courses created by KAIST professors. Using online content there will help mitigate the educational gap between the two institutions, plus it will reduce the need for many students and faculty to make the long commute from the capital to the campus. Although students are expected to live on campus, they will probably engage in other activities in Nairobi and want to take classes wherever they are.
Since it will take some time to select and recruit an excellent group of faculty members, we feel it will be more effective to use online lecture platforms to deliver standardised and qualified content.
It has been posited that the fast adoption of online education will affect international students’ enrolment in universities, which will lead to reductions in revenue. However, we expect that students will choose a university that offers more diverse and interactive metaverse experiences on top of academic and global experiences. The time has come to rebuild the curriculum and infrastructure for the world of the metaverse. We can’t go back to the way things were before.
Universities around the world are now on the same starting line. They need to innovate and pioneer new approaches and tools that can enable all sorts of campus activities online. They should carve out their own distinct metaverse that is viable for human interaction and diverse technological experiences that promote students’ creativity and collaborative minds.
The universities best equipped with digital infrastructure and savvy human resources will emerge as the new leaders − no matter where they are.
Successful education needs the full support of communities and equal access to opportunities. Technological breakthroughs must be used to benefit everyone. To this end, the private and public sectors need to collaborate to bring about inclusive learning opportunities and help shore up global resilience against this and any future pandemics. The hope is that such disruption will bring about new technology and knowledge that we can leverage to reshape the future of education.
ⓒ Source: Times Higher Education (THE)
2021.05.10 View 9375
The Educational ‘Metaverse’ Is Coming
The universities best equipped with digital infrastructure and savvy human resources will emerge as the new leaders − no matter where they are, says Kwang Hyung Lee
It goes without saying that the Covid-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on the education sector. Approximately 1.6 billion students from 192 countries, or 91 per cent of the world’s student population, have experienced educational disruptions.
As we all know, this disruption led to online education hastily emerging as an important new platform. However, approximately 29 percent of young people worldwide, about 364 million individuals, are not online. In many ways, the digital divide is now wider than ever.
We do, however, have an opportunity to ensure that the integration of emerging technologies is further accelerated and that online delivery becomes an integral component of education. This should, in theory, lead to more inclusive and creative pedagogical solutions.
The entire world has effectively taken part in an educational experiment, and at KAIST we were able to confirm that blended education worked effectively for our students. It made up for the long-standing pedagogical shortfalls of the one-way delivery of knowledge and made it possible to shift to a learner-centric model, giving us a great opportunity to unlock the creativity and collaborative minds of our students. Education tailored to students’ individual levels will not only help them accumulate knowledge but improve their ability to use it.
A recent survey in South Korea found that 96 per cent of Seoul citizens believed that the pandemic widened the existing learning gap, but 74 per cent said that schools should carry out a blended form of education using both remote and in-person classes. The feedback from KAIST students on our online classes gives us a glimpse into the new paths we need to take.
From last March, we offered 60 per cent real-time classes via Zoom and 40 per cent through our pre-recorded learning management system. Our students were satisfied with the real-time classes in which they could interact face to face with professors. The blended class format combining real-time and pre-recorded content received very satisfactory evaluations. The problem, however, came with lab classes via Zoom. Students expressed their dissatisfaction with the passive and indirect learning experiences.
Developing online tools or technologies that can enable scientific experiments, engineering prototyping and other hands-on activities remains a challenge. However, we can begin to address these issues using complementary technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, image recognition and eye-tracking technologies.
The barriers to access to these new experiences are both complex and pervasive, yet there are ways we can pull together to disrupt these barriers at a global level in the hope of fostering inclusive growth.
For instance, the virtual campus will become a reality at the Kenya-KAIST campus, which will open by September 2023 in the Konza Technopolis, 60km outside Nairobi.
There, we aim to go beyond online education by creating a “metaverse” that provides assistance for running classes and creates an immersive learning experience that runs the gamut of campus activities while utilising the latest digital technologies.
Following a feasibility study of the Kenya campus that took place five years ago, we planned to utilise Mooc courses created by KAIST professors. Using online content there will help mitigate the educational gap between the two institutions, plus it will reduce the need for many students and faculty to make the long commute from the capital to the campus. Although students are expected to live on campus, they will probably engage in other activities in Nairobi and want to take classes wherever they are.
Since it will take some time to select and recruit an excellent group of faculty members, we feel it will be more effective to use online lecture platforms to deliver standardised and qualified content.
It has been posited that the fast adoption of online education will affect international students’ enrolment in universities, which will lead to reductions in revenue. However, we expect that students will choose a university that offers more diverse and interactive metaverse experiences on top of academic and global experiences. The time has come to rebuild the curriculum and infrastructure for the world of the metaverse. We can’t go back to the way things were before.
Universities around the world are now on the same starting line. They need to innovate and pioneer new approaches and tools that can enable all sorts of campus activities online. They should carve out their own distinct metaverse that is viable for human interaction and diverse technological experiences that promote students’ creativity and collaborative minds.
The universities best equipped with digital infrastructure and savvy human resources will emerge as the new leaders − no matter where they are.
Successful education needs the full support of communities and equal access to opportunities. Technological breakthroughs must be used to benefit everyone. To this end, the private and public sectors need to collaborate to bring about inclusive learning opportunities and help shore up global resilience against this and any future pandemics. The hope is that such disruption will bring about new technology and knowledge that we can leverage to reshape the future of education.
ⓒ Source: Times Higher Education (THE)
2021.05.10 View 9375 -
 COVID-Update: KAIST on High Alert amid Spring Resurgence
COVID-19 Task Force responds 24-7 and ISSS provides returning international students with a comfort package during 14-day mandatory quarantine
In response to the upsurge of COVID-19 cases in the proximate college districts in Daejeon, KAIST announced the enforcement of stricter health and safety regulations. Korean health authorities expected another surge of COVID-19 cases this spring as Korea’s daily new COVID-19 cases have rebounded to the high 600s and over 700 in April, which is the most in over three months.
New guidelines issued on April 5 banned faculty, staff, and students from engaging in off-campus activities and utilizing external public facilities. Such facilities include, but are not limited to, bars, cafes, clubs, gyms, karaoke rooms, PC rooms, restaurants, and other crowded indoor spaces. All class and research activities, work meetings, and school events were moved exclusively online, and working from home and flexible working hours were highly encouraged in order to minimize face-to-face interactions on campus. In particular, having meals outside of KAIST cafeterias in groups of two or more was prohibited, while food delivery and take-outs were allowed.
Executive Vice President and Provost Seung Seob Lee said in a letter to the KAIST community on April 5 that “the school considers the risk of the current situation to be very high, likely the highest since the outbreak of COVID-19.” Provost Lee then called for more team efforts to contain the current phase of the pandemic and asked everyone to do their part.
The school installed new temperature scanners equipped with hand sanitizer dispensers in front of the dormitory entrances to further control the spread of the disease on campus, following confirmed COVID-19 cases among dormitory residents.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues with no clear end in sight, the Task Force for the Prevention of COVID-19 and the International Scholar and Student Services (ISSS) Team at KAIST are working around the clock to reduce the risk of infection spread not only within the campus, but also coming from outside the campus.
Under strict health and safety guidelines, KAIST has allowed international students to come back to campus. Currently about 600 international students, mostly graduate students reside on campus. All returning students should complete the mandatory 14-day self-quarantine required by the Korean government at their own expense.
The KAIST COVID-19 Task Force is in charge of enacting on-campus health and safety guidelines, responding to reports and inquiries from the KAIST community 24-7, and controlling outsider access, among other responsibilities.
The ISSS Team requires returning international students to fill out an entry authorization form and receive approval from the KAIST COVID-19 Task Force prior to returning to campus from their home countries. Once students arrive at their designated quarantine facility, the KAIST ISSS Team sends care packages, which includes some toiletries, instant food, a multipot, a thermometer, and other daily necessities. During the quarantine period, returning students are also advised to follow the directions given by government officials and to coordinate with the ISSS Team. The team also provides useful Korean phrases for international students to help them with communication.
The self-quarantine period ends at 12 p.m. 14 days after arrival. Within two days of finishing the 14 days of self-isolation, these students are required to undergo a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for COVID-19 at the nearest health center. After confirmed negative, they are allowed to move into on-campus accommodations. KAIST will maintain the current method of remote education and distancing methods until further notice.
(END)
2021.04.16 View 10609
COVID-Update: KAIST on High Alert amid Spring Resurgence
COVID-19 Task Force responds 24-7 and ISSS provides returning international students with a comfort package during 14-day mandatory quarantine
In response to the upsurge of COVID-19 cases in the proximate college districts in Daejeon, KAIST announced the enforcement of stricter health and safety regulations. Korean health authorities expected another surge of COVID-19 cases this spring as Korea’s daily new COVID-19 cases have rebounded to the high 600s and over 700 in April, which is the most in over three months.
New guidelines issued on April 5 banned faculty, staff, and students from engaging in off-campus activities and utilizing external public facilities. Such facilities include, but are not limited to, bars, cafes, clubs, gyms, karaoke rooms, PC rooms, restaurants, and other crowded indoor spaces. All class and research activities, work meetings, and school events were moved exclusively online, and working from home and flexible working hours were highly encouraged in order to minimize face-to-face interactions on campus. In particular, having meals outside of KAIST cafeterias in groups of two or more was prohibited, while food delivery and take-outs were allowed.
Executive Vice President and Provost Seung Seob Lee said in a letter to the KAIST community on April 5 that “the school considers the risk of the current situation to be very high, likely the highest since the outbreak of COVID-19.” Provost Lee then called for more team efforts to contain the current phase of the pandemic and asked everyone to do their part.
The school installed new temperature scanners equipped with hand sanitizer dispensers in front of the dormitory entrances to further control the spread of the disease on campus, following confirmed COVID-19 cases among dormitory residents.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues with no clear end in sight, the Task Force for the Prevention of COVID-19 and the International Scholar and Student Services (ISSS) Team at KAIST are working around the clock to reduce the risk of infection spread not only within the campus, but also coming from outside the campus.
Under strict health and safety guidelines, KAIST has allowed international students to come back to campus. Currently about 600 international students, mostly graduate students reside on campus. All returning students should complete the mandatory 14-day self-quarantine required by the Korean government at their own expense.
The KAIST COVID-19 Task Force is in charge of enacting on-campus health and safety guidelines, responding to reports and inquiries from the KAIST community 24-7, and controlling outsider access, among other responsibilities.
The ISSS Team requires returning international students to fill out an entry authorization form and receive approval from the KAIST COVID-19 Task Force prior to returning to campus from their home countries. Once students arrive at their designated quarantine facility, the KAIST ISSS Team sends care packages, which includes some toiletries, instant food, a multipot, a thermometer, and other daily necessities. During the quarantine period, returning students are also advised to follow the directions given by government officials and to coordinate with the ISSS Team. The team also provides useful Korean phrases for international students to help them with communication.
The self-quarantine period ends at 12 p.m. 14 days after arrival. Within two days of finishing the 14 days of self-isolation, these students are required to undergo a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for COVID-19 at the nearest health center. After confirmed negative, they are allowed to move into on-campus accommodations. KAIST will maintain the current method of remote education and distancing methods until further notice.
(END)
2021.04.16 View 10609 -
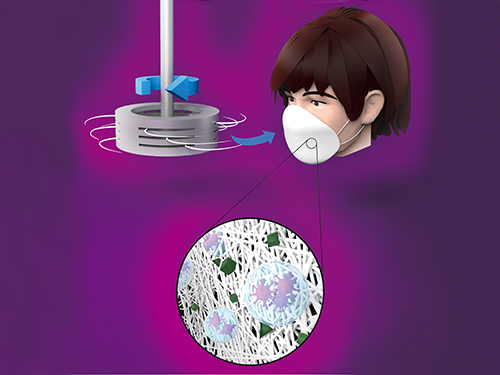 Centrifugal Multispun Nanofibers Put a New Spin on COVID-19 Masks
KAIST researchers have developed a novel nanofiber production technique called ‘centrifugal multispinning’ that will open the door for the safe and cost-effective mass production of high-performance polymer nanofibers. This new technique, which has shown up to a 300 times higher nanofiber production rate per hour than that of the conventional electrospinning method, has many potential applications including the development of face mask filters for coronavirus protection.
Nanofibers make good face mask filters because their mechanical interactions with aerosol particles give them a greater ability to capture more than 90% of harmful particles such as fine dust and virus-containing droplets.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the growing demand in recent years for a better kind of face mask. A polymer nanofiber-based mask filter that can more effectively block harmful particles has also been in higher demand as the pandemic continues.
‘Electrospinning’ has been a common process used to prepare fine and uniform polymer nanofibers, but in terms of safety, cost-effectiveness, and mass production, it has several drawbacks. The electrospinning method requires a high-voltage electric field and electrically conductive target, and this hinders the safe and cost-effective mass production of polymer nanofibers.
In response to this shortcoming, ‘centrifugal spinning’ that utilizes centrifugal force instead of high voltage to produce polymer nanofibers has been suggested as a safer and more cost-effective alternative to the electrospinning. Easy scalability is another advantage, as this technology only requires a rotating spinneret and a collector.
However, since the existing centrifugal force-based spinning technology employs only a single rotating spinneret, productivity is limited and not much higher than that of some advanced electrospinning technologies such as ‘multi-nozzle electrospinning’ and ‘nozzleless electrospinning.’ This problem persists even when the size of the spinneret is increased.
Inspired by these limitations, a research team led by Professor Do Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a centrifugal multispinning spinneret with mass-producibility, by sectioning a rotating spinneret into three sub-disks. This study was published as a front cover article of ACS Macro Letters, Volume 10, Issue 3 in March 2021.
Using this new centrifugal multispinning spinneret with three sub-disks, the lead author of the paper PhD candidate Byeong Eun Kwak and his fellow researchers Hyo Jeong Yoo and Eungjun Lee demonstrated the gram-scale production of various polymer nanofibers with a maximum production rate of up to 25 grams per hour, which is approximately 300 times higher than that of the conventional electrospinning system. The production rate of up to 25 grams of polymer nanofibers per hour corresponds to the production rate of about 30 face mask filters per day in a lab-scale manufacturing system.
By integrating the mass-produced polymer nanofibers into the form of a mask filter, the researchers were able to fabricate face masks that have comparable filtration performance with the KF80 and KF94 face masks that are currently available in the Korean market. The KF80 and KF94 masks have been approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea to filter out at least 80% and 94% of harmful particles respectively.
“When our system is scaled up from the lab scale to an industrial scale, the large-scale production of centrifugal multispun polymer nanofibers will be made possible, and the cost of polymer nanofiber-based face mask filters will also be lowered dramatically,” Kwak explained.
This work was supported by the KAIST-funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2020.
Publication:
Byeong Eun Kwak, Hyo Jeong Yoo, Eungjun Lee, and Do Hyun Kim. (2021) Large-Scale Centrifugal Multispinning Production of Polymer Micro- and Nanofibers for Mask Filter Application with a Potential of Cospinning Mixed Multicomponent Fibers. ACS Macro Letters, Volume No. 10, Issue No. 3, pp. 382-388. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.0c00829
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dohyun.kim@kaist.edu
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https:/kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2021.04.12 View 13221
Centrifugal Multispun Nanofibers Put a New Spin on COVID-19 Masks
KAIST researchers have developed a novel nanofiber production technique called ‘centrifugal multispinning’ that will open the door for the safe and cost-effective mass production of high-performance polymer nanofibers. This new technique, which has shown up to a 300 times higher nanofiber production rate per hour than that of the conventional electrospinning method, has many potential applications including the development of face mask filters for coronavirus protection.
Nanofibers make good face mask filters because their mechanical interactions with aerosol particles give them a greater ability to capture more than 90% of harmful particles such as fine dust and virus-containing droplets.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the growing demand in recent years for a better kind of face mask. A polymer nanofiber-based mask filter that can more effectively block harmful particles has also been in higher demand as the pandemic continues.
‘Electrospinning’ has been a common process used to prepare fine and uniform polymer nanofibers, but in terms of safety, cost-effectiveness, and mass production, it has several drawbacks. The electrospinning method requires a high-voltage electric field and electrically conductive target, and this hinders the safe and cost-effective mass production of polymer nanofibers.
In response to this shortcoming, ‘centrifugal spinning’ that utilizes centrifugal force instead of high voltage to produce polymer nanofibers has been suggested as a safer and more cost-effective alternative to the electrospinning. Easy scalability is another advantage, as this technology only requires a rotating spinneret and a collector.
However, since the existing centrifugal force-based spinning technology employs only a single rotating spinneret, productivity is limited and not much higher than that of some advanced electrospinning technologies such as ‘multi-nozzle electrospinning’ and ‘nozzleless electrospinning.’ This problem persists even when the size of the spinneret is increased.
Inspired by these limitations, a research team led by Professor Do Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a centrifugal multispinning spinneret with mass-producibility, by sectioning a rotating spinneret into three sub-disks. This study was published as a front cover article of ACS Macro Letters, Volume 10, Issue 3 in March 2021.
Using this new centrifugal multispinning spinneret with three sub-disks, the lead author of the paper PhD candidate Byeong Eun Kwak and his fellow researchers Hyo Jeong Yoo and Eungjun Lee demonstrated the gram-scale production of various polymer nanofibers with a maximum production rate of up to 25 grams per hour, which is approximately 300 times higher than that of the conventional electrospinning system. The production rate of up to 25 grams of polymer nanofibers per hour corresponds to the production rate of about 30 face mask filters per day in a lab-scale manufacturing system.
By integrating the mass-produced polymer nanofibers into the form of a mask filter, the researchers were able to fabricate face masks that have comparable filtration performance with the KF80 and KF94 face masks that are currently available in the Korean market. The KF80 and KF94 masks have been approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea to filter out at least 80% and 94% of harmful particles respectively.
“When our system is scaled up from the lab scale to an industrial scale, the large-scale production of centrifugal multispun polymer nanofibers will be made possible, and the cost of polymer nanofiber-based face mask filters will also be lowered dramatically,” Kwak explained.
This work was supported by the KAIST-funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2020.
Publication:
Byeong Eun Kwak, Hyo Jeong Yoo, Eungjun Lee, and Do Hyun Kim. (2021) Large-Scale Centrifugal Multispinning Production of Polymer Micro- and Nanofibers for Mask Filter Application with a Potential of Cospinning Mixed Multicomponent Fibers. ACS Macro Letters, Volume No. 10, Issue No. 3, pp. 382-388. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.0c00829
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dohyun.kim@kaist.edu
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https:/kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2021.04.12 View 13221 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 31609
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 31609 -
 KAIST Celebrates 50-Year Anniversary with 2,712 New Graduates via 2021 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST is proud to announce the graduation of 2,712 students, including 668 PhDs and 1,331 master’s degree recipients. The pandemic could not stop the university from recognizing each graduate's remarkable and original achievements. A pandemic-proof blended commencement ceremony was held on Friday, February 19, and livestreamed to the graduates and their loved ones.
KAIST decided to take extra precautions to protect graduates and other attendees’ health and well-being.
For the virtual ceremony, only 83 out of the 2,712 graduates were invited to attend the ceremony in person. Graduates were divided into four groups to attend at four different places in Daejeon and Seoul campuses and watch the ceremony via Zoom. No family members or friends of the graduates were allowed to participate at the campus, but happily cheered the graduates via YouTube.
This year’s valedictorian, Hyun-Young Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, received the Award of the Minister of Science and ICT. Salutorian Yeh-Lin Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the Award of the KAIST Board of Trustees, while the recipient of the KAIST Presidential Award was Min-Jae Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering. The Award of the KAIST Development Foundation Chairman and the KAIST Alumni Association Presidential Award were conferred to Kyung-Tae Kim from the Department of Physics and Min-Woo Jung from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, respectively.
President Sung-Chul Shin, Chairman of the Board of Trustees Woo Sik Kim, and a very limited number of faculty members and administrative staff officiated the commencement ceremony from the KAIST Auditorium.
President Shin applauded the graduates’ hard work and dedication in his commencement speech. He also delivered a very special congratulatory message to the bachelor’s degree awardees.
“This year’s commencement is especially meaningful for me. I was appointed as the 16th president of KAIST on February 23, 2017, and met you for the first time on February 28 at the matriculation ceremony. We promised each other—as freshmen and as the first alumnus president—to do our best for the next four years,” President Shin recalled.
He added, “I have done my best to keep my promise, and now my term will end on February 22. Of course, the past four years were even more precious because you were all a part of it.”
In conclusion, President Shin said, “I am proud of you for keeping your end of the promise. Thank you for becoming who you are today. I have high hopes for the bright future that you will be shaping for KAIST and our society.”
The livestream ceremony is archived for viewing on KAIST's Official YouTube Channel.
(END)
2021.02.19 View 9419
KAIST Celebrates 50-Year Anniversary with 2,712 New Graduates via 2021 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST is proud to announce the graduation of 2,712 students, including 668 PhDs and 1,331 master’s degree recipients. The pandemic could not stop the university from recognizing each graduate's remarkable and original achievements. A pandemic-proof blended commencement ceremony was held on Friday, February 19, and livestreamed to the graduates and their loved ones.
KAIST decided to take extra precautions to protect graduates and other attendees’ health and well-being.
For the virtual ceremony, only 83 out of the 2,712 graduates were invited to attend the ceremony in person. Graduates were divided into four groups to attend at four different places in Daejeon and Seoul campuses and watch the ceremony via Zoom. No family members or friends of the graduates were allowed to participate at the campus, but happily cheered the graduates via YouTube.
This year’s valedictorian, Hyun-Young Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, received the Award of the Minister of Science and ICT. Salutorian Yeh-Lin Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the Award of the KAIST Board of Trustees, while the recipient of the KAIST Presidential Award was Min-Jae Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering. The Award of the KAIST Development Foundation Chairman and the KAIST Alumni Association Presidential Award were conferred to Kyung-Tae Kim from the Department of Physics and Min-Woo Jung from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, respectively.
President Sung-Chul Shin, Chairman of the Board of Trustees Woo Sik Kim, and a very limited number of faculty members and administrative staff officiated the commencement ceremony from the KAIST Auditorium.
President Shin applauded the graduates’ hard work and dedication in his commencement speech. He also delivered a very special congratulatory message to the bachelor’s degree awardees.
“This year’s commencement is especially meaningful for me. I was appointed as the 16th president of KAIST on February 23, 2017, and met you for the first time on February 28 at the matriculation ceremony. We promised each other—as freshmen and as the first alumnus president—to do our best for the next four years,” President Shin recalled.
He added, “I have done my best to keep my promise, and now my term will end on February 22. Of course, the past four years were even more precious because you were all a part of it.”
In conclusion, President Shin said, “I am proud of you for keeping your end of the promise. Thank you for becoming who you are today. I have high hopes for the bright future that you will be shaping for KAIST and our society.”
The livestream ceremony is archived for viewing on KAIST's Official YouTube Channel.
(END)
2021.02.19 View 9419 -
 KAIST International Symposium Highlights the Value of Science through Global Collaboration
The presidents of three premier science and technology universities shared their belief that universities should move forward to embrace social changes while maintaining the importance of academics for future generations during the KAIST International Symposium on February 16.
The symposium, one of the events to celebrate KAIST’s 50th anniversary, highlighted the future role of universities over the next 50 years by hosting a panel featuring ETH Zurich President Joël Mesot, Caltech President Thomas Rosenbaum, and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin. Members of the foreign diplomatic corps representing seven countries also explored the new model of global collaboration in the second session.
President Rosenbaum of Caltech said that even though society is changing, the role of universities will not be different since the value of knowledge will always be important. He said that universities must embrace change.
He said that universities should move forward fearlessly if they believe it would impact wider society positively. He added that universities should also be courageous enough to take a new path based on longer-term perspectives and lessons learned from successes. One of the roles of universities is to establish various hypotheses and possible prospects, raise doubts, and go forward with a strong will for the future generations to come.
He cited LIGO (the Laser Inerferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory), as a good example of a successful university-research collaboration. LIGO is funded by the National Science Foundation in the US and operated by Caltech and MIT. Approximately 1300 scientists from around the world, including the Max Planck Society in Germany and the Science and Technology Facilities Council in the UK, participate in the LIGO Scientific Collaboration. In 2019, the international team of scientists detected the collision of two black holes with masses about 142 times the mass of the sun in the most massive collision ever detected. MIT Physicist Rainer Weiss shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with Professor Barry Barish and Professor Kip Thorn from the Department of Physics at Caltech in recognition of their contribution to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves.
President Mesot of ETH Zurich stressed that universities should foster young talents well versed with creative thinking and entrepreneurship in this new era. He also said that COVID-19 has reaffirmed the importance of science and global collaborations beyond borders to address global challenges such as pandemics. President Mesot said COVID-19 has taught us the value of science and R&D, adding that the roll-out of a vaccine in only one year would have been impossible without the decades-long R&D foundation that universities and industries have established.
He also gave the example of the MRI as a reason universities should provide strong basic science research foundation. In 1944 in the US, Dr. Isidor Isaac Rabi won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance. The MRI research inspired many ETH professors for further studies and led them to win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1952 for their MRI basic theory and in 1991 the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with the development of high-resolution spectroscopy. “The MRI first started 80 years ago and still applies in today’s medicine. We should focus on research which will keep such value,” President Mesot said.
Meanwhile President Shin also said that the age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution has been deemed the "winner takes all" era. At this highly competitive time, R&D activities are more meaningful if they produce the world’s best, first, and only outcomes.
“We aim to achieve excellence in research with long-term innovative research support systems. We will conduct R&D activities that will lead the megatrends of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: hyper-connectivity, super-intelligence, and meta-convergence. In addition, we will double down to conduct forward-looking flagship research that will enhance the happiness and prosperity of all humanity in the areas of global warming, infectious diseases, bio-medicine, energy and environment, smart technology, and post-AI.”
Responding to one of the student’s question about what mindsets are expected of students enrolled in government-funded national universities, President Mesot made three suggestions. First, they should remember that they are privileged, so they should give back their talents to society. They should also be patient with what they are doing even when they don’t achieve the desired results. Lastly, they should remain open to new ideas and be flexible when encountering disruptions.
Seven diplomats stationing in Korea including Rob Rapson, US Charge d’Affairs ad Interim Rob Rapson, UAE Ambassador Abdulla Saif Al Nuaimi, Kenyan Ambassador Mwende Mwinzi, Danish Ambassador Einar Jensen, Pakistani Ambassador Mumtaz Zahar Baloch, Egyptian Ambassador Haem Fahmy, and UK Ambassador Simon Smith joined the second session themed KAIST for the Global Community.
They all agreed that KAIST is one of the shining examples of successful international collaboration stemming from the international aid loan from USAID. Five decades later, KAIST now is working to help the Kenyan government to establish Kenya KAIST with a 95-million US funding from the Korea Exim Bank.
While stressing the importance of global collaboration for inclusive growth in the global community, the seven diplomats gave their insights on the newly transforming global environment intertwined with COVID-19 and the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In the face of global changes caused by emerging technologies and carbon neutrality, the ambassadors expressed a strong desire to make collaborations between KAIST and their countries to propel new innovations in industry and education in their countries.
2021.02.17 View 9258
KAIST International Symposium Highlights the Value of Science through Global Collaboration
The presidents of three premier science and technology universities shared their belief that universities should move forward to embrace social changes while maintaining the importance of academics for future generations during the KAIST International Symposium on February 16.
The symposium, one of the events to celebrate KAIST’s 50th anniversary, highlighted the future role of universities over the next 50 years by hosting a panel featuring ETH Zurich President Joël Mesot, Caltech President Thomas Rosenbaum, and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin. Members of the foreign diplomatic corps representing seven countries also explored the new model of global collaboration in the second session.
President Rosenbaum of Caltech said that even though society is changing, the role of universities will not be different since the value of knowledge will always be important. He said that universities must embrace change.
He said that universities should move forward fearlessly if they believe it would impact wider society positively. He added that universities should also be courageous enough to take a new path based on longer-term perspectives and lessons learned from successes. One of the roles of universities is to establish various hypotheses and possible prospects, raise doubts, and go forward with a strong will for the future generations to come.
He cited LIGO (the Laser Inerferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory), as a good example of a successful university-research collaboration. LIGO is funded by the National Science Foundation in the US and operated by Caltech and MIT. Approximately 1300 scientists from around the world, including the Max Planck Society in Germany and the Science and Technology Facilities Council in the UK, participate in the LIGO Scientific Collaboration. In 2019, the international team of scientists detected the collision of two black holes with masses about 142 times the mass of the sun in the most massive collision ever detected. MIT Physicist Rainer Weiss shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with Professor Barry Barish and Professor Kip Thorn from the Department of Physics at Caltech in recognition of their contribution to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves.
President Mesot of ETH Zurich stressed that universities should foster young talents well versed with creative thinking and entrepreneurship in this new era. He also said that COVID-19 has reaffirmed the importance of science and global collaborations beyond borders to address global challenges such as pandemics. President Mesot said COVID-19 has taught us the value of science and R&D, adding that the roll-out of a vaccine in only one year would have been impossible without the decades-long R&D foundation that universities and industries have established.
He also gave the example of the MRI as a reason universities should provide strong basic science research foundation. In 1944 in the US, Dr. Isidor Isaac Rabi won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance. The MRI research inspired many ETH professors for further studies and led them to win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1952 for their MRI basic theory and in 1991 the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with the development of high-resolution spectroscopy. “The MRI first started 80 years ago and still applies in today’s medicine. We should focus on research which will keep such value,” President Mesot said.
Meanwhile President Shin also said that the age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution has been deemed the "winner takes all" era. At this highly competitive time, R&D activities are more meaningful if they produce the world’s best, first, and only outcomes.
“We aim to achieve excellence in research with long-term innovative research support systems. We will conduct R&D activities that will lead the megatrends of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: hyper-connectivity, super-intelligence, and meta-convergence. In addition, we will double down to conduct forward-looking flagship research that will enhance the happiness and prosperity of all humanity in the areas of global warming, infectious diseases, bio-medicine, energy and environment, smart technology, and post-AI.”
Responding to one of the student’s question about what mindsets are expected of students enrolled in government-funded national universities, President Mesot made three suggestions. First, they should remember that they are privileged, so they should give back their talents to society. They should also be patient with what they are doing even when they don’t achieve the desired results. Lastly, they should remain open to new ideas and be flexible when encountering disruptions.
Seven diplomats stationing in Korea including Rob Rapson, US Charge d’Affairs ad Interim Rob Rapson, UAE Ambassador Abdulla Saif Al Nuaimi, Kenyan Ambassador Mwende Mwinzi, Danish Ambassador Einar Jensen, Pakistani Ambassador Mumtaz Zahar Baloch, Egyptian Ambassador Haem Fahmy, and UK Ambassador Simon Smith joined the second session themed KAIST for the Global Community.
They all agreed that KAIST is one of the shining examples of successful international collaboration stemming from the international aid loan from USAID. Five decades later, KAIST now is working to help the Kenyan government to establish Kenya KAIST with a 95-million US funding from the Korea Exim Bank.
While stressing the importance of global collaboration for inclusive growth in the global community, the seven diplomats gave their insights on the newly transforming global environment intertwined with COVID-19 and the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In the face of global changes caused by emerging technologies and carbon neutrality, the ambassadors expressed a strong desire to make collaborations between KAIST and their countries to propel new innovations in industry and education in their countries.
2021.02.17 View 9258 -
 Ushering in a New Era at the 50th Innoversary Ceremony
President Moon Jae-In declares KAIST the future of Korea
KAIST reaffirmed its goal of becoming an institute that can serve the world for the next century, marking its 50th anniversary on February 16. The KAIST community and distinguished guests gathered online during the official ceremony to commemorate KAIST’s anniversary and envisioned ways to serve the world, a major shift from its founding mission focusing on national growth.
The ceremony celebrated the legacy of KAIST, which has become a trailblazer by fostering the most competent scientists and engineers and making breakthroughs which led to the nation becoming a global high-tech leader.
President Moon Jae-In applauded KAIST as “the future of Korea” in his online congratulatory message, saying that “KAIST has made us feel proud when the nation stays ahead in science and technology. The dream of KAIST has been the dream of Korea. The passion of KAIST has been the passion of Korea. KAIST is the future of Korea.”
“KAIST has overcome challenges and created innovations for advancing the nation, from the first internet network to launching our first satellite in the early 80s to the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM), a negative pressure ward module in response to COVID-19. Whenever the nation faced a challenge, KAIST was there.”
President Moon also asked KAIST researchers to find sustainable ways to balance nature and humanity in this time of climate change and the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum Dr.Klaus Schwab also congratulated, saying "KAIST is a leader in ensuring social inclusion. Founded with the support of USAID, today it is paying it forward and sharing the same support through the Kenya-KAIST project."
The ceremony first brought Dr. KunMo Chung to the stage, the man who proposed the idea of founding the first advanced science and technology institute in Korea. His proposal to the then administrator of USAID John Hannah resulted in the Korean government meriting a 6 million USD loan for to start KAIST. He was the only Korean member of the USAID feasibility study team led by Dr. Frederick Terman, the former vice president of Stanford University. Dr. Chung wrote the Terman Report, which gave a green light to the establishment of KAIST in Korea in 1970.
Dr. Chung said the nation’s strong desire to escape from poverty through the advancement of science and technology was thoroughly realized by KAIST. “The Terman Report’s vision was perfectly realized. Now it’s time to envision the next dream of KAIST for another century.”
President Sung-Chul Shin said in his anniversary speech that KAIST has now transformed into a university that will serve the all of humanity by advancing science and technology while fostering new talents best fit for the new global environment. President Shin said that to fulfill KAIST’s second dream, the university will drive innovation in the five major areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future strategy, under the C3 spirit of a Challenging spirit, Creativity, and Caring minds.
“In the next 50 years, KAIST hopes to fulfill the 10-10-10 Dream, that is, to have 10 Singularity Professors who have produced world-class achievements, 10 Decacorn startups valued at 10 trillion won, and global campuses in 10 countries.”
Then, four young KAIST professors who are conducting research in the flagship fields of mobility, new materials, post-AI, and bio-medicine presented their research vision and gave speeches. Professor Hae-Won Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Jihyeon Yeom from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering said the advent of new mobility combined with robotics and new nano-materials scaled down into spintronics, ‘KAISTronic materials’, will provide new momentum for the industry and the wellbeing of humanity. Professor Kijung Shin from the Graduate School of AI spoke on the new future transformed by quantum computers. Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering predicted a future in which cancer will no longer be a terminal disease and digital cells and the digitization of bio-medicine will significantly improve our quality of life. He said the combination of anti-aging and reverse aging studies will make a difference in our lives.
After the official ceremony, KAIST’s administrative leadership including President Shin and Dr. Kun-Mo Chung attended a ceremony to dedicate the sky lounge at the Academic Cultural Complex as the John Hannah Hall. Terman Hall, located in the Creative Learning Building, was dedicated in 2004 in honor of Dr. Frederick Terman.
2021.02.17 View 13261
Ushering in a New Era at the 50th Innoversary Ceremony
President Moon Jae-In declares KAIST the future of Korea
KAIST reaffirmed its goal of becoming an institute that can serve the world for the next century, marking its 50th anniversary on February 16. The KAIST community and distinguished guests gathered online during the official ceremony to commemorate KAIST’s anniversary and envisioned ways to serve the world, a major shift from its founding mission focusing on national growth.
The ceremony celebrated the legacy of KAIST, which has become a trailblazer by fostering the most competent scientists and engineers and making breakthroughs which led to the nation becoming a global high-tech leader.
President Moon Jae-In applauded KAIST as “the future of Korea” in his online congratulatory message, saying that “KAIST has made us feel proud when the nation stays ahead in science and technology. The dream of KAIST has been the dream of Korea. The passion of KAIST has been the passion of Korea. KAIST is the future of Korea.”
“KAIST has overcome challenges and created innovations for advancing the nation, from the first internet network to launching our first satellite in the early 80s to the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM), a negative pressure ward module in response to COVID-19. Whenever the nation faced a challenge, KAIST was there.”
President Moon also asked KAIST researchers to find sustainable ways to balance nature and humanity in this time of climate change and the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum Dr.Klaus Schwab also congratulated, saying "KAIST is a leader in ensuring social inclusion. Founded with the support of USAID, today it is paying it forward and sharing the same support through the Kenya-KAIST project."
The ceremony first brought Dr. KunMo Chung to the stage, the man who proposed the idea of founding the first advanced science and technology institute in Korea. His proposal to the then administrator of USAID John Hannah resulted in the Korean government meriting a 6 million USD loan for to start KAIST. He was the only Korean member of the USAID feasibility study team led by Dr. Frederick Terman, the former vice president of Stanford University. Dr. Chung wrote the Terman Report, which gave a green light to the establishment of KAIST in Korea in 1970.
Dr. Chung said the nation’s strong desire to escape from poverty through the advancement of science and technology was thoroughly realized by KAIST. “The Terman Report’s vision was perfectly realized. Now it’s time to envision the next dream of KAIST for another century.”
President Sung-Chul Shin said in his anniversary speech that KAIST has now transformed into a university that will serve the all of humanity by advancing science and technology while fostering new talents best fit for the new global environment. President Shin said that to fulfill KAIST’s second dream, the university will drive innovation in the five major areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future strategy, under the C3 spirit of a Challenging spirit, Creativity, and Caring minds.
“In the next 50 years, KAIST hopes to fulfill the 10-10-10 Dream, that is, to have 10 Singularity Professors who have produced world-class achievements, 10 Decacorn startups valued at 10 trillion won, and global campuses in 10 countries.”
Then, four young KAIST professors who are conducting research in the flagship fields of mobility, new materials, post-AI, and bio-medicine presented their research vision and gave speeches. Professor Hae-Won Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Jihyeon Yeom from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering said the advent of new mobility combined with robotics and new nano-materials scaled down into spintronics, ‘KAISTronic materials’, will provide new momentum for the industry and the wellbeing of humanity. Professor Kijung Shin from the Graduate School of AI spoke on the new future transformed by quantum computers. Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering predicted a future in which cancer will no longer be a terminal disease and digital cells and the digitization of bio-medicine will significantly improve our quality of life. He said the combination of anti-aging and reverse aging studies will make a difference in our lives.
After the official ceremony, KAIST’s administrative leadership including President Shin and Dr. Kun-Mo Chung attended a ceremony to dedicate the sky lounge at the Academic Cultural Complex as the John Hannah Hall. Terman Hall, located in the Creative Learning Building, was dedicated in 2004 in honor of Dr. Frederick Terman.
2021.02.17 View 13261 -
 COVID-Update: Spring 2021 Classes Continue Online
KAIST announced that its spring 2021 classes will also be online as the pandemic continues into the new year. The spring semester will begin on March 1.
Executive Vice President and Provost Kwang Hyung Lee said in a letter to the KAIST community on January 15 that nearly all classes in the 2021 spring semester will be held online. However, a very limited number of lab classes and other classes that require on-site practice and demonstrations will be offered either in-person or in a blended format. In addition, graduate courses above the 600 level and graduate courses in the College of Business at the Seoul campus will be allowed to conduct in-person or blended classes under very strict social distancing guidelines.
Provost Lee said that the university will be revert back to in-person classes as soon as the government eases the social distancing guidelines. As of February 4, the nation is under Level 2.5 in Seoul and its metropolitan areas, while other regions are at Level 2. Level 2.5 prohibits the gathering of 10 or more people, and Levels 1 and 2 require gatherings to be fewer than 50 people. At Level 3, all classes will be held online.
Test management is another challenge. Regarding mid-term and final exams, the university plans to give more flexibility to professors. Professors may give additional assignments instead of a mid-term exam. Open-book exams and real-time exams through Zoom will be another option. However, some classes that require in-person tests in some graduate courses will be allowed as long as they follow very strict social distancing guidelines.
2021.02.04 View 5833
COVID-Update: Spring 2021 Classes Continue Online
KAIST announced that its spring 2021 classes will also be online as the pandemic continues into the new year. The spring semester will begin on March 1.
Executive Vice President and Provost Kwang Hyung Lee said in a letter to the KAIST community on January 15 that nearly all classes in the 2021 spring semester will be held online. However, a very limited number of lab classes and other classes that require on-site practice and demonstrations will be offered either in-person or in a blended format. In addition, graduate courses above the 600 level and graduate courses in the College of Business at the Seoul campus will be allowed to conduct in-person or blended classes under very strict social distancing guidelines.
Provost Lee said that the university will be revert back to in-person classes as soon as the government eases the social distancing guidelines. As of February 4, the nation is under Level 2.5 in Seoul and its metropolitan areas, while other regions are at Level 2. Level 2.5 prohibits the gathering of 10 or more people, and Levels 1 and 2 require gatherings to be fewer than 50 people. At Level 3, all classes will be held online.
Test management is another challenge. Regarding mid-term and final exams, the university plans to give more flexibility to professors. Professors may give additional assignments instead of a mid-term exam. Open-book exams and real-time exams through Zoom will be another option. However, some classes that require in-person tests in some graduate courses will be allowed as long as they follow very strict social distancing guidelines.
2021.02.04 View 5833 -
 Highly Deformable Piezoelectric Nanotruss for Tactile Electronics
With the importance of non-contact environments growing due to COVID-19, tactile electronic devices using haptic technology are gaining traction as new mediums of communication.
Haptic technology is being applied in a wide array of fields such as robotics or interactive displays. haptic gloves are being used for augmented information communication technology. Efficient piezoelectric materials that can convert various mechanical stimuli into electrical signals and vice versa are a prerequisite for advancing high-performing haptic technology.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong confirmed the potential of tactile devices by developing ceramic piezoelectric materials that are three times more deformable. For the fabrication of highly deformable nanomaterials, the research team built a zinc oxide hollow nanostructure using proximity field nanopatterning and atomic layered deposition. The piezoelectric coefficient was measured to be approximately 9.2 pm/V and the nanopillar compression test showed an elastic strain limit of approximately 10%, which is more than three times greater than that of the bulk zinc oxide one.
Piezoelectric ceramics have a high piezoelectric coefficient with a low elastic strain limit, whereas the opposite is true for piezoelectric polymers. Therefore, it has been very challenging to obtain good performance in both high piezoelectric coefficients as well as high elastic strain limits. To break the elastic limit of piezoelectric ceramics, the research team introduced a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls.
According to the Griffith criterion, the fracture strength of a material is inversely proportional to the square root of the preexisting flaw size. However, a large flaw is less likely to occur in a small structure, which, in turn, enhances the strength of the material. Therefore, implementing the form of a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls can extend the elastic limit of the material. Furthermore, a monolithic 3D structure can withstand large strains in all directions while simultaneously preventing the loss from the bottleneck. Previously, the fracture property of piezoelectric ceramic materials was difficult to control, owing to the large variance in crack sizes. However, the research team structurally limited the crack sizes to manage the fracture properties.
Professor Hong’s results demonstrate the potential for the development of highly deformable ceramic piezoelectric materials by improving the elastic limit using a 3D hollow nanostructure. Since zinc oxide has a relatively low piezoelectric coefficient compared to other piezoelectric ceramic materials, applying the proposed structure to such components promised better results in terms of the piezoelectric activity.
“With the advent of the non-contact era, the importance of emotional communication is increasing. Through the development of novel tactile interaction technologies, in addition to the current visual and auditory communication, mankind will enter a new era where they can communicate with anyone using all five senses regardless of location as if they are with them in person,” Professor Hong said.
“While additional research must be conducted to realize the application of the proposed designs for haptic enhancement devices, this study holds high value in that it resolves one of the most challenging issues in the use of piezoelectric ceramics, specifically opening new possibilities for their application by overcoming their mechanical constraints.
The research was reported in Nano Energy and supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korea Research Foundation, and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.02.02 View 11381
Highly Deformable Piezoelectric Nanotruss for Tactile Electronics
With the importance of non-contact environments growing due to COVID-19, tactile electronic devices using haptic technology are gaining traction as new mediums of communication.
Haptic technology is being applied in a wide array of fields such as robotics or interactive displays. haptic gloves are being used for augmented information communication technology. Efficient piezoelectric materials that can convert various mechanical stimuli into electrical signals and vice versa are a prerequisite for advancing high-performing haptic technology.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong confirmed the potential of tactile devices by developing ceramic piezoelectric materials that are three times more deformable. For the fabrication of highly deformable nanomaterials, the research team built a zinc oxide hollow nanostructure using proximity field nanopatterning and atomic layered deposition. The piezoelectric coefficient was measured to be approximately 9.2 pm/V and the nanopillar compression test showed an elastic strain limit of approximately 10%, which is more than three times greater than that of the bulk zinc oxide one.
Piezoelectric ceramics have a high piezoelectric coefficient with a low elastic strain limit, whereas the opposite is true for piezoelectric polymers. Therefore, it has been very challenging to obtain good performance in both high piezoelectric coefficients as well as high elastic strain limits. To break the elastic limit of piezoelectric ceramics, the research team introduced a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls.
According to the Griffith criterion, the fracture strength of a material is inversely proportional to the square root of the preexisting flaw size. However, a large flaw is less likely to occur in a small structure, which, in turn, enhances the strength of the material. Therefore, implementing the form of a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls can extend the elastic limit of the material. Furthermore, a monolithic 3D structure can withstand large strains in all directions while simultaneously preventing the loss from the bottleneck. Previously, the fracture property of piezoelectric ceramic materials was difficult to control, owing to the large variance in crack sizes. However, the research team structurally limited the crack sizes to manage the fracture properties.
Professor Hong’s results demonstrate the potential for the development of highly deformable ceramic piezoelectric materials by improving the elastic limit using a 3D hollow nanostructure. Since zinc oxide has a relatively low piezoelectric coefficient compared to other piezoelectric ceramic materials, applying the proposed structure to such components promised better results in terms of the piezoelectric activity.
“With the advent of the non-contact era, the importance of emotional communication is increasing. Through the development of novel tactile interaction technologies, in addition to the current visual and auditory communication, mankind will enter a new era where they can communicate with anyone using all five senses regardless of location as if they are with them in person,” Professor Hong said.
“While additional research must be conducted to realize the application of the proposed designs for haptic enhancement devices, this study holds high value in that it resolves one of the most challenging issues in the use of piezoelectric ceramics, specifically opening new possibilities for their application by overcoming their mechanical constraints.
The research was reported in Nano Energy and supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korea Research Foundation, and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.02.02 View 11381