flexible
-
 KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
Source: IDTechEX, Feb. 28, 2011
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
28 Feb 2011
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by researchers at KAIST (Korea Advance Institute of Science & Technology).
The research, led by KAIST"s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of "Advanced Materials".
Professor Bae"s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae"s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, "Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further."
http://www.printedelectronicsworld.com/articles/kaist_paves_the_way_to_commercialize_flexible_display_screens_00003144.asp?sessionid=1
2011.03.01 View 16285
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
Source: IDTechEX, Feb. 28, 2011
KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
28 Feb 2011
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by researchers at KAIST (Korea Advance Institute of Science & Technology).
The research, led by KAIST"s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of "Advanced Materials".
Professor Bae"s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae"s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, "Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further."
http://www.printedelectronicsworld.com/articles/kaist_paves_the_way_to_commercialize_flexible_display_screens_00003144.asp?sessionid=1
2011.03.01 View 16285 -
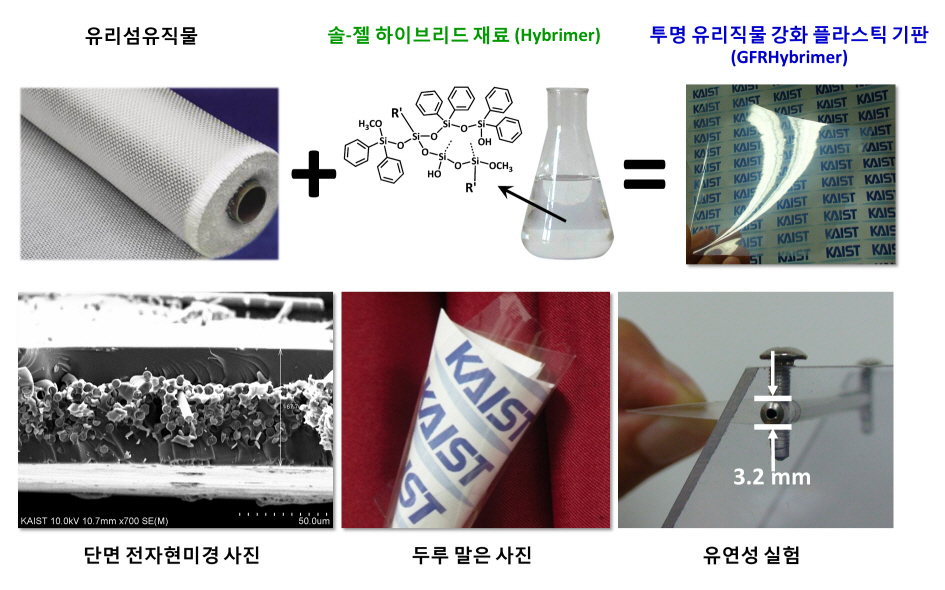 KAIST developed a plastic film board less sensitive to heat.
The research result was made the cover of magazine, Advanced Materials and is accredited to paving the way to commercialize flexible display screens and solar power cells.
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by Korean researchers.
The research, led by KAIST’s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of ‘Advanced Materials’ which is the leading magazine in the field of materials science.
Professor Bae’s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae’s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, “Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further.”
2011.01.05 View 17027
KAIST developed a plastic film board less sensitive to heat.
The research result was made the cover of magazine, Advanced Materials and is accredited to paving the way to commercialize flexible display screens and solar power cells.
Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by Korean researchers.
The research, led by KAIST’s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. The research result was printed as the cover paper of ‘Advanced Materials’ which is the leading magazine in the field of materials science.
Professor Bae’s team developed a hybrid material with the same properties as fiber glass. With the material, they created a transparent, plastic film sheet resistant to heat. Transparent plastic film sheets were used by researchers all over the world to develop devices such as flexible displays or solar power cells that can be fit into various living spaces. However, plastic films are heat sensitive and tend to expand as temperature increases, thereby making it difficult to produce displays or solar power cells.
The new transparent, plastic film screen shows that heat expansion index (13ppm/oC) similar to that of glass fiber (9ppm/oC) due to the presence of glass fibers; its heat resistance allows to be used for displays and solar power cells over 250oC.
Professor Bae’s team succeeded in producing a flexible thin plastic film available for use in LCD or AMOLED screens and thin solar power cells.
Professor Bae commented, “Not only the newly developed plastic film has superior qualities, compared to the old models, but also it is cheap to produce, potentially bringing forward the day when flexible displays and solar panels become commonplace. With the cooperation of various industries, research institutes and universities, we will strive to improve the existing design and develop it further.”
2011.01.05 View 17027 -
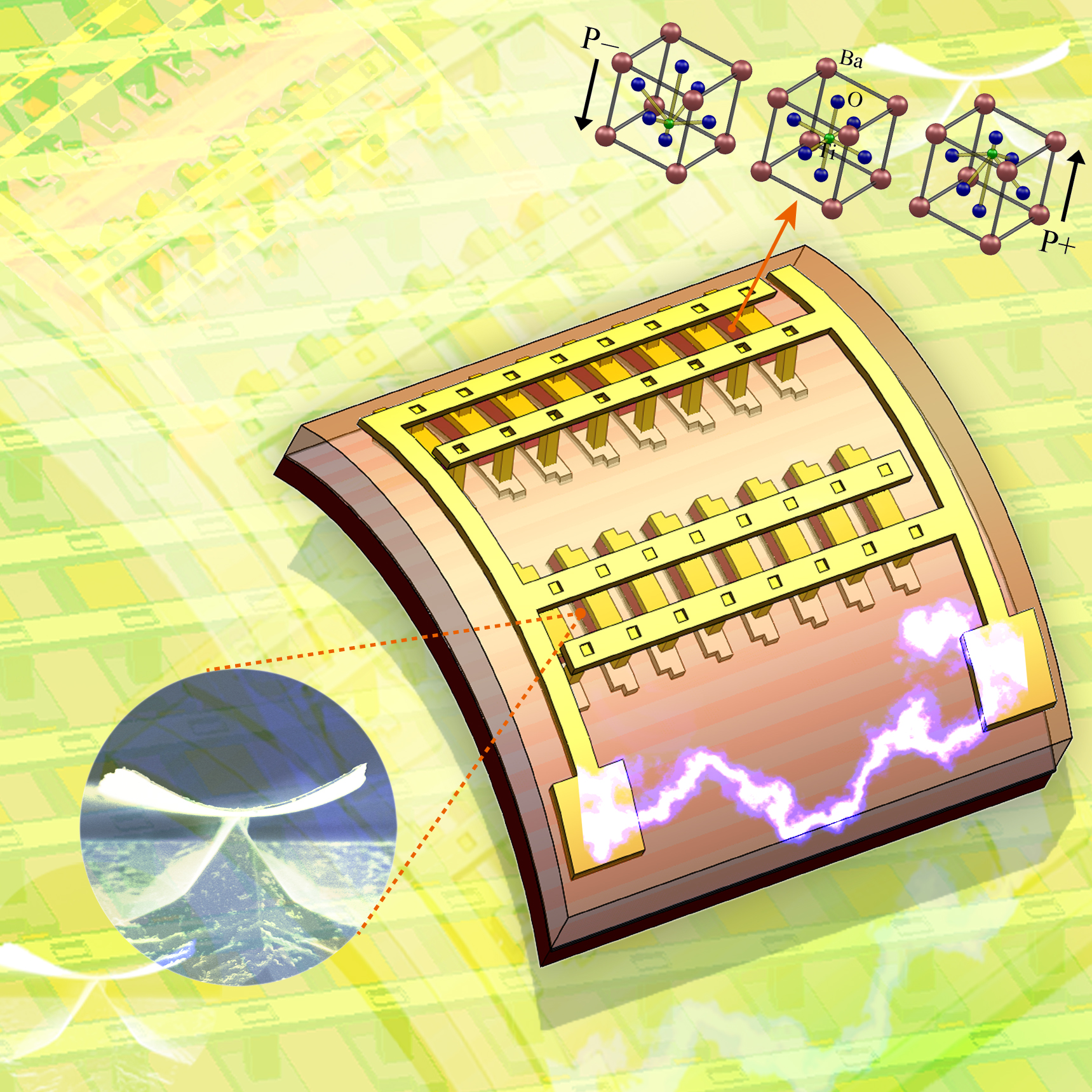 The KAIST & GIT team developed a power generation technology using bendable thin film nano-materials.
Figure description: Flexible thin film nanomaterials produce electricity.
Can a heart implanted micro robot operate permanently?
Can cell phones and tiny robots implanted in the heart operate permanently without having their batteries charged?
It might sound like science fiction, but these things seem to be possible in the near future. The team of Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) and Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Institute of Technology, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) has developed new forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology using the freely bendable piezoelectric ceramic thin film nano-materials that can convert tiny movements of the human body (such as heart beats and blood flow) into electrical energy.
The piezoelectric effect refers to voltage generation when pressure or bending strength is applied to piezoelectric materials. The ceramics, containing a perovskite structure, have a high piezoelectric efficiency. Until now, it has been very difficult to use these ceramic materials to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to their brittle property.
The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a bio-eco-friendly ceramic thin film nanogenerator that is freely bendable without breakdown.
Nanogenerator technology, a power generating system without wires or batteries, combines nanotechnology with piezoelectrics that can be used not only in personal mobile electronics but also in bio-implantable sensors or as an energy source for micro robots. Energy sources in nature (wind, vibration, and sound) and biomechanical forces produced by the human body (heart beats, blood flow, and muscle contraction/relaxation) can infinitely produce nonpolluting energy. (Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw)
Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST) was involved in the first co-invention of “High Performance Flexible Single Crystal Electronics” during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This nanogenerator technology, based on the previous invention, utilized the similar protocol of transferring ceramic thin film nano-materials on flexible substrates and produced voltage generation between electrodes.
Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Tech, inventor of the nanogenerator) said, “This technology can be used to turn on an LED by slightly modifying circuits and operate touchable flexible displays. In addition, thin film nano-materials (‘barium titanate’) of this research have the property of both high efficiency and lead-free bio compatibility, which can be used in future medical applications.” This result is published in November online issue of ‘Nano Letters’ ACS journal.
<Video>
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw
Thin Film Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces.
2010.11.23 View 17344
The KAIST & GIT team developed a power generation technology using bendable thin film nano-materials.
Figure description: Flexible thin film nanomaterials produce electricity.
Can a heart implanted micro robot operate permanently?
Can cell phones and tiny robots implanted in the heart operate permanently without having their batteries charged?
It might sound like science fiction, but these things seem to be possible in the near future. The team of Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) and Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Institute of Technology, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) has developed new forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology using the freely bendable piezoelectric ceramic thin film nano-materials that can convert tiny movements of the human body (such as heart beats and blood flow) into electrical energy.
The piezoelectric effect refers to voltage generation when pressure or bending strength is applied to piezoelectric materials. The ceramics, containing a perovskite structure, have a high piezoelectric efficiency. Until now, it has been very difficult to use these ceramic materials to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to their brittle property.
The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a bio-eco-friendly ceramic thin film nanogenerator that is freely bendable without breakdown.
Nanogenerator technology, a power generating system without wires or batteries, combines nanotechnology with piezoelectrics that can be used not only in personal mobile electronics but also in bio-implantable sensors or as an energy source for micro robots. Energy sources in nature (wind, vibration, and sound) and biomechanical forces produced by the human body (heart beats, blood flow, and muscle contraction/relaxation) can infinitely produce nonpolluting energy. (Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw)
Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST) was involved in the first co-invention of “High Performance Flexible Single Crystal Electronics” during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This nanogenerator technology, based on the previous invention, utilized the similar protocol of transferring ceramic thin film nano-materials on flexible substrates and produced voltage generation between electrodes.
Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Tech, inventor of the nanogenerator) said, “This technology can be used to turn on an LED by slightly modifying circuits and operate touchable flexible displays. In addition, thin film nano-materials (‘barium titanate’) of this research have the property of both high efficiency and lead-free bio compatibility, which can be used in future medical applications.” This result is published in November online issue of ‘Nano Letters’ ACS journal.
<Video>
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw
Thin Film Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces.
2010.11.23 View 17344 -
 International Workshop on EEWS 2010 was held.
On October 7 and 8th at Fusion Hall of KI Building, KAIST, the 2010 International Workshop on EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) was held.
The third to be held, forty national and international academic professionals including Mark Shannon, professor at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Domen Kazunari, Tokyo University professor, Dong Sub Kim, CTO of SK Energy and Doyoung Seung, Senior Vice President of GS Caltex, participated at this year’s workshop.
In twelve sessions, themes including Artificial Photosynthesis, Wireless Power Transfer, Green Aviation, Safe Nuclear Fuel Reuse, Fuel Cells in Action, LED 2.0, Foundation of Energy-Water Nexus, and Flexible Battery & Solar Cell were presented and discussed.
“Through this workshop, current EEWS policy and research progress from different countries and the future of related technologies will be foreseen,” said Jae Kyu Lee, Dean of KAIST EEWS Initiative. “I hope it became an opportunity to create cooperative relationships with leading researchers.”
EEWS is a research project conducted by KAIST to solve global issues that mankind faces today such as depletion of energy, environmental pollution, water shortage, and sustainability.
2010.10.15 View 19313
International Workshop on EEWS 2010 was held.
On October 7 and 8th at Fusion Hall of KI Building, KAIST, the 2010 International Workshop on EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) was held.
The third to be held, forty national and international academic professionals including Mark Shannon, professor at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Domen Kazunari, Tokyo University professor, Dong Sub Kim, CTO of SK Energy and Doyoung Seung, Senior Vice President of GS Caltex, participated at this year’s workshop.
In twelve sessions, themes including Artificial Photosynthesis, Wireless Power Transfer, Green Aviation, Safe Nuclear Fuel Reuse, Fuel Cells in Action, LED 2.0, Foundation of Energy-Water Nexus, and Flexible Battery & Solar Cell were presented and discussed.
“Through this workshop, current EEWS policy and research progress from different countries and the future of related technologies will be foreseen,” said Jae Kyu Lee, Dean of KAIST EEWS Initiative. “I hope it became an opportunity to create cooperative relationships with leading researchers.”
EEWS is a research project conducted by KAIST to solve global issues that mankind faces today such as depletion of energy, environmental pollution, water shortage, and sustainability.
2010.10.15 View 19313 -
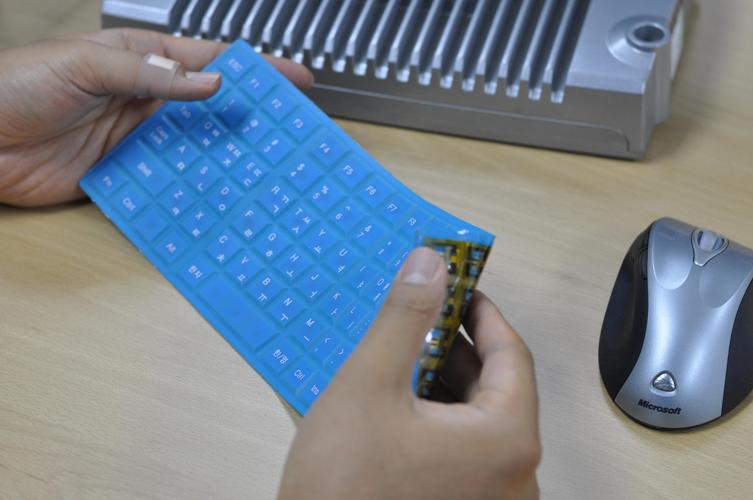 KAIST has developed a powerless and wireless keyboard that can be folded and easily carried around.
The KAIST Institute for Information Technology Convergence (KIITC) has developed the next generation keyboard that does not need power and wires.
The powerless/wireless keyboard developed by KIITC is flexible, foldable, portable, and compact, making the possession of keyboard easier and more convenient.
The idea of this technology was derived from "Idea Contest for Future Device" opened by KIITC in 2007, and Future Device Team (Team Leader: Dr. Sungkwan Jung) of KIITC embodied the idea and developed full-flexible powerless/wireless keyboard by using the passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to support the convenient data input for daily mobile life.
Through the technology, KAIST expects to realize ubiquitous computing and communication environment, open a new market for foldable keyboards, and secure the competitiveness of mobile devices industries in the world market.
KIITC has also successfully transferred the technology of powerless/wireless keyboard to Hanyang Demitech for commercialization.
2010.08.12 View 14264
KAIST has developed a powerless and wireless keyboard that can be folded and easily carried around.
The KAIST Institute for Information Technology Convergence (KIITC) has developed the next generation keyboard that does not need power and wires.
The powerless/wireless keyboard developed by KIITC is flexible, foldable, portable, and compact, making the possession of keyboard easier and more convenient.
The idea of this technology was derived from "Idea Contest for Future Device" opened by KIITC in 2007, and Future Device Team (Team Leader: Dr. Sungkwan Jung) of KIITC embodied the idea and developed full-flexible powerless/wireless keyboard by using the passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to support the convenient data input for daily mobile life.
Through the technology, KAIST expects to realize ubiquitous computing and communication environment, open a new market for foldable keyboards, and secure the competitiveness of mobile devices industries in the world market.
KIITC has also successfully transferred the technology of powerless/wireless keyboard to Hanyang Demitech for commercialization.
2010.08.12 View 14264 -
 Prof. Choi Unveils Method to Improve Emission Efficiency of OLED
A KAIST research team led by Prof. Kyung-Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science discovered the surface plasmon-enhanced spontaneous emission based on an organic light-emitting device (OLED), a finding expected to improve OLED"s emission efficiency, KAIST authorities said on Thursday (July 9).
For surface plasmon localization, silver nanoparticles were thermally deposited in a high vacuum on cathode. Since plasmons provide a strong oscillator decay channel, time-resolved photoluninescene (PL) results displayed a 1.75-fold increased emission rate, and continuous wave PL results showed a twofold enhanced intensity.
"The method using surface plasmon represents a new technology to enhance the emission efficiency of OLED. It is expected to greatly contribute to the development of new technologies in OLED and flexible display, as well as securing original technology," Prof. Choi said.
The finding was published in the April issue of Applied Physics Letters and the June 25 issue of Optics Express. It will be also featured as the research highlight of the August issue of Nature Photonics and Virtual Journal of Ultrafast Science.
2009.07.09 View 22857
Prof. Choi Unveils Method to Improve Emission Efficiency of OLED
A KAIST research team led by Prof. Kyung-Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science discovered the surface plasmon-enhanced spontaneous emission based on an organic light-emitting device (OLED), a finding expected to improve OLED"s emission efficiency, KAIST authorities said on Thursday (July 9).
For surface plasmon localization, silver nanoparticles were thermally deposited in a high vacuum on cathode. Since plasmons provide a strong oscillator decay channel, time-resolved photoluninescene (PL) results displayed a 1.75-fold increased emission rate, and continuous wave PL results showed a twofold enhanced intensity.
"The method using surface plasmon represents a new technology to enhance the emission efficiency of OLED. It is expected to greatly contribute to the development of new technologies in OLED and flexible display, as well as securing original technology," Prof. Choi said.
The finding was published in the April issue of Applied Physics Letters and the June 25 issue of Optics Express. It will be also featured as the research highlight of the August issue of Nature Photonics and Virtual Journal of Ultrafast Science.
2009.07.09 View 22857 -
 KAIST to hold International Workshop on Flexible Displays
The 2009 KAIST International Workshop on Flexible Displays will take place at the Electrical Engineering Building on June 25, university sources said on Tuesday (June 23).
The workshop organized by the Center for Advanced Flexible Display Convergence (CAFDC) will explore the status and future vision of flexible and transparent plasma displays, which are among the key technologies for the development of the next-generation displays. There will be also discussions about technologies to realize the large-scale flexible and transparent display which is regarded as the display of the future.
Among the speakers are some of the most prominent figures in the field. Gary Eden from University of Illinois, Prof. Kunihide Tachibana from Kyoto University, and Carol Wedding, the president of Imaging Systems Tech., USA and several other well-known professors and engineers will participate in the workshop.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, CAFDC chair, said: "The workshop will provide an excellent opportunity to examine the flexible and transparent plasma display technologies. It will also be a good chance to explore large-scale flexible and transparent displays from various technical viewpoints."
2009.06.24 View 21164
KAIST to hold International Workshop on Flexible Displays
The 2009 KAIST International Workshop on Flexible Displays will take place at the Electrical Engineering Building on June 25, university sources said on Tuesday (June 23).
The workshop organized by the Center for Advanced Flexible Display Convergence (CAFDC) will explore the status and future vision of flexible and transparent plasma displays, which are among the key technologies for the development of the next-generation displays. There will be also discussions about technologies to realize the large-scale flexible and transparent display which is regarded as the display of the future.
Among the speakers are some of the most prominent figures in the field. Gary Eden from University of Illinois, Prof. Kunihide Tachibana from Kyoto University, and Carol Wedding, the president of Imaging Systems Tech., USA and several other well-known professors and engineers will participate in the workshop.
Professor Kyung-Cheol Choi, CAFDC chair, said: "The workshop will provide an excellent opportunity to examine the flexible and transparent plasma display technologies. It will also be a good chance to explore large-scale flexible and transparent displays from various technical viewpoints."
2009.06.24 View 21164 -
 International Workshop on Flexible Displays Held on Aug. 21-22
An international workshop on flexible displays will be held at KAIST on Aug. 21-22.
The workshop organized by Center for Advanced Flexible Display Convergence (CAFDC) in KAIST is designed to share ideas on the latest research developments and explore future trends in organic displays. Organic displays made from organic light-emitting diode (OLED) materials have recently made a real impact in consumer electronics and emerged as one of the most important technologies in the development of next-generation flexible displays.
"The workshop is expected to provide an important opportunity to showcase latest technological developments using organic light-emitting diode and examine them from the perspectives of the next-generation flexible display," said Dr. Kyung-Cheol Choi, KAIST professor of electrical engineering and computer science who heads the CAFDC.
The event will feature some of the world-renowned scholars in organic display including Prof. Stephen R. Forrest of the University of Michigan, Prof. Bernard Kippelen of Georgia Tech, and Prof. Takao Someya of the University of Tokyo, as theme presenters. It will also draw a slew of domestic scholars in the industry and academia.
2008.08.22 View 17584
International Workshop on Flexible Displays Held on Aug. 21-22
An international workshop on flexible displays will be held at KAIST on Aug. 21-22.
The workshop organized by Center for Advanced Flexible Display Convergence (CAFDC) in KAIST is designed to share ideas on the latest research developments and explore future trends in organic displays. Organic displays made from organic light-emitting diode (OLED) materials have recently made a real impact in consumer electronics and emerged as one of the most important technologies in the development of next-generation flexible displays.
"The workshop is expected to provide an important opportunity to showcase latest technological developments using organic light-emitting diode and examine them from the perspectives of the next-generation flexible display," said Dr. Kyung-Cheol Choi, KAIST professor of electrical engineering and computer science who heads the CAFDC.
The event will feature some of the world-renowned scholars in organic display including Prof. Stephen R. Forrest of the University of Michigan, Prof. Bernard Kippelen of Georgia Tech, and Prof. Takao Someya of the University of Tokyo, as theme presenters. It will also draw a slew of domestic scholars in the industry and academia.
2008.08.22 View 17584