Science
-
 KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 6581
KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 6581 -
 KAIST Opens Newly Expanded Center for Contemplative Research in Collaboration with Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 2nd that it would hold an opening ceremony for the expanded KAIST Center for Contemplative Research (Director Wan Doo Kim) at the Creativity Learning Building on its Daejeon campus on January 3 (Friday).
Established in 2018 with the mission of "integrating meditation and science for the happiness and prosperity of humanity," the KAIST Center for Contemplative Research has been expanding its scope of research into the neuroscience of meditation and training empathetic educators who will lead the field of meditation science in collaboration with the Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department, which was established in 2022.
Supported by the Plato Academy Foundation and with funding from SK Discovery for the facility’s expansion, the center now occupies an extended space on the 5th floor of the Creativity Learning Center. The new facilities include: ▲ Advanced Research Equipment ▲ Meditation Science Laboratories ▲ VR/XR-Based Meditation Experience Rooms ▲ A Large Digital Art Meditation Hall ▲ Personal Meditation Halls.
Particularly, the center plans to conduct next-generation meditation research using cutting-edge technologies such as: ▲ Brain-Computer Interface Technology ▲ Meditation Wearable Devices ▲ Metaverse-Based Meditation Environments.
The opening ceremony, scheduled for the morning of January 3 (Friday), was attended by key figures, including Plato Academy Foundation Chairman Chang-Won Choi, MindLab CEO Professor Seong-Taek Cho, Bosung Group Vice President Byung-Chul Lee, and KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee.
The event began with a national moment of silence to honor the victims of the recent Jeju Air passenger accident. It included a progress report by the center director, a lecture by Professor Jaeseung Jeong, panel discussions, and more.
Following a tour of the expanded facilities, the center hosted a 20-minute hands-on meditation science session using *Looxid Labs EEG devices for the first 50 participants.
*Looxid Labs EEG Device: A real-time brainwave measurement device developed by KAIST startup Looxid Labs that enables users to experience efficient and AI-powered data-driven meditation science practice (Looxid Labs website: https://looxidlabs.com/).
During the ceremony, Director of the Center for Contemplative Research Wan Doo Kim presented on "The Mission, Vision, and Future of the KAIST Center for Contemplative Research." Yujin Lee, a combined master’s and doctoral researcher from the Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department, shared insights on "The Latest Trends in Meditation Science Research."
A panel discussion and Q&A session on "The Convergence of Meditation and Brain and Cognitive Sciences" followed featuring Professors Jaeseung Jeong, HyungDong Park (Brain and Cognitive Sciences), and Jiyoung Park (Digital Humanities and Social Sciences).
Director Wan Doo Kim commented, “With this expanded opening, we aim to offer advanced meditation programs integrating brain and cognitive sciences and cutting-edge technology not only to KAIST members but also to the general public interested in meditation. We will continue to dedicate ourselves to interdisciplinary research between meditation and science.”
2025.01.03 View 4897
KAIST Opens Newly Expanded Center for Contemplative Research in Collaboration with Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 2nd that it would hold an opening ceremony for the expanded KAIST Center for Contemplative Research (Director Wan Doo Kim) at the Creativity Learning Building on its Daejeon campus on January 3 (Friday).
Established in 2018 with the mission of "integrating meditation and science for the happiness and prosperity of humanity," the KAIST Center for Contemplative Research has been expanding its scope of research into the neuroscience of meditation and training empathetic educators who will lead the field of meditation science in collaboration with the Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department, which was established in 2022.
Supported by the Plato Academy Foundation and with funding from SK Discovery for the facility’s expansion, the center now occupies an extended space on the 5th floor of the Creativity Learning Center. The new facilities include: ▲ Advanced Research Equipment ▲ Meditation Science Laboratories ▲ VR/XR-Based Meditation Experience Rooms ▲ A Large Digital Art Meditation Hall ▲ Personal Meditation Halls.
Particularly, the center plans to conduct next-generation meditation research using cutting-edge technologies such as: ▲ Brain-Computer Interface Technology ▲ Meditation Wearable Devices ▲ Metaverse-Based Meditation Environments.
The opening ceremony, scheduled for the morning of January 3 (Friday), was attended by key figures, including Plato Academy Foundation Chairman Chang-Won Choi, MindLab CEO Professor Seong-Taek Cho, Bosung Group Vice President Byung-Chul Lee, and KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee.
The event began with a national moment of silence to honor the victims of the recent Jeju Air passenger accident. It included a progress report by the center director, a lecture by Professor Jaeseung Jeong, panel discussions, and more.
Following a tour of the expanded facilities, the center hosted a 20-minute hands-on meditation science session using *Looxid Labs EEG devices for the first 50 participants.
*Looxid Labs EEG Device: A real-time brainwave measurement device developed by KAIST startup Looxid Labs that enables users to experience efficient and AI-powered data-driven meditation science practice (Looxid Labs website: https://looxidlabs.com/).
During the ceremony, Director of the Center for Contemplative Research Wan Doo Kim presented on "The Mission, Vision, and Future of the KAIST Center for Contemplative Research." Yujin Lee, a combined master’s and doctoral researcher from the Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department, shared insights on "The Latest Trends in Meditation Science Research."
A panel discussion and Q&A session on "The Convergence of Meditation and Brain and Cognitive Sciences" followed featuring Professors Jaeseung Jeong, HyungDong Park (Brain and Cognitive Sciences), and Jiyoung Park (Digital Humanities and Social Sciences).
Director Wan Doo Kim commented, “With this expanded opening, we aim to offer advanced meditation programs integrating brain and cognitive sciences and cutting-edge technology not only to KAIST members but also to the general public interested in meditation. We will continue to dedicate ourselves to interdisciplinary research between meditation and science.”
2025.01.03 View 4897 -
 KAIST Awarded Presidential Commendation for Contributions in Software Industry
- At the “25th Software Industry Day” celebration held in the afternoon on Monday, December 2nd, 2024 at Yangjae L Tower in Seoul
- KAIST was awarded the “Presidential Commendation” for its contributions for the advancement of the Software Industry in the Group Category
- Korea’s first AI master’s and doctoral degree program opened at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI
- Focus on training non-major developers through SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle", Machine Learning Engineer Bootcamp, etc., talents who can integrate development and collaboration, and advanced talents in the latest AI technologies.
- Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI received Prime Minister’s Commendation for his contributions for the advancement of the software industry.
< Photo 1. Professor Kyung-soo Kim, the Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget (second from the left) and the Manager of Planning Team, Mr. Sunghoon Jung, stand at the stage after receiving the Presidential Commendation as KAIST was selected as one of the groups that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the "25th Software Industry Day" celebration. >
“KAIST has been leading the way in achieving the grand goal of fostering 1 million AI talents in Korea by services that pan from providing various educational opportunities, from developing the capabilities of experts with no computer science specialty to fostering advanced professionals. I would like to thank all members of KAIST community who worked hard to achieve the great feat of receiving the Presidential Commendations.” (KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on December 3rd that it was selected as a group that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the “2024 Software Industry Day” celebration held at the Yangjae El Tower in Seoul on the 2nd of December and received a presidential commendation.
The “Software Industry Day”, hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the National IT Industry Promotion Agency and the Korea Software Industry Association, is an event designed to promote the status of software industry workers in Korea and to honor their achievements.
Every year, those who have made significant contributions to policy development, human resource development, and export growth for industry revitalization are selected and awarded the ‘Software Industry Development Contribution Award.’
KAIST was recognized for its contribution to developing a demand-based, industrial field-centric curriculum and fostering non-major developers and convergence talents with the goal of expanding software value and fostering excellent human resources.
< Photo 2. Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-soo Kim receiving the commendation as the representative of KAIST >
Specifically, it first opened the SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle" to foster convergent program developers equipped with the abilities to handle both the computer coding and human interactions for collaborations. This is a non-degree program that provides intensive study and assignments for 5 months for graduates and intellectuals without prior knowledge of computer science.
KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI opened and operated Korea’s first master's and doctoral degree program in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, it planned a “Machine Learning Engineers’ Boot Camp” and conducted lectures and practical training for a total of 16 weeks on the latest AI technologies such as deep learning basics and large language models. It aims to strengthen the practical capabilities of start-up companies while lowering the threshold for companies to introduce AI technology.
Also, KAIST was selected to participate in the 1st and 2nd stages of the Software-centered University Project and has been taking part in the project since 2016. Through this, it was highly evaluated for promoting curriculum based on latest technology, an autonomous system where students directly select integrated education, and expansion of internships.
< Photo 3. Professor Minjoon Seo of Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI, who received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry on the same day >
At the awards ceremony that day, Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI also received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry. Professor Seo was recognized for his leading research achievements in the fields of AI and natural language processing by publishing 28 papers in top international AI conferences over the past four years.
At the same time, he was noted for his contributions to enhancing the originality and innovation of language model research, such as △knowledge encoding, △knowledge access and utilization, and △high-dimensional inference performance, and for demonstrating leadership in the international academic community.
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST stated, “Our university will continue to do its best to foster software talents with global competitiveness through continuous development of cutting-edge curriculum and innovative degree systems.”
2024.12.03 View 7526
KAIST Awarded Presidential Commendation for Contributions in Software Industry
- At the “25th Software Industry Day” celebration held in the afternoon on Monday, December 2nd, 2024 at Yangjae L Tower in Seoul
- KAIST was awarded the “Presidential Commendation” for its contributions for the advancement of the Software Industry in the Group Category
- Korea’s first AI master’s and doctoral degree program opened at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI
- Focus on training non-major developers through SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle", Machine Learning Engineer Bootcamp, etc., talents who can integrate development and collaboration, and advanced talents in the latest AI technologies.
- Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI received Prime Minister’s Commendation for his contributions for the advancement of the software industry.
< Photo 1. Professor Kyung-soo Kim, the Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget (second from the left) and the Manager of Planning Team, Mr. Sunghoon Jung, stand at the stage after receiving the Presidential Commendation as KAIST was selected as one of the groups that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the "25th Software Industry Day" celebration. >
“KAIST has been leading the way in achieving the grand goal of fostering 1 million AI talents in Korea by services that pan from providing various educational opportunities, from developing the capabilities of experts with no computer science specialty to fostering advanced professionals. I would like to thank all members of KAIST community who worked hard to achieve the great feat of receiving the Presidential Commendations.” (KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on December 3rd that it was selected as a group that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the “2024 Software Industry Day” celebration held at the Yangjae El Tower in Seoul on the 2nd of December and received a presidential commendation.
The “Software Industry Day”, hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the National IT Industry Promotion Agency and the Korea Software Industry Association, is an event designed to promote the status of software industry workers in Korea and to honor their achievements.
Every year, those who have made significant contributions to policy development, human resource development, and export growth for industry revitalization are selected and awarded the ‘Software Industry Development Contribution Award.’
KAIST was recognized for its contribution to developing a demand-based, industrial field-centric curriculum and fostering non-major developers and convergence talents with the goal of expanding software value and fostering excellent human resources.
< Photo 2. Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-soo Kim receiving the commendation as the representative of KAIST >
Specifically, it first opened the SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle" to foster convergent program developers equipped with the abilities to handle both the computer coding and human interactions for collaborations. This is a non-degree program that provides intensive study and assignments for 5 months for graduates and intellectuals without prior knowledge of computer science.
KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI opened and operated Korea’s first master's and doctoral degree program in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, it planned a “Machine Learning Engineers’ Boot Camp” and conducted lectures and practical training for a total of 16 weeks on the latest AI technologies such as deep learning basics and large language models. It aims to strengthen the practical capabilities of start-up companies while lowering the threshold for companies to introduce AI technology.
Also, KAIST was selected to participate in the 1st and 2nd stages of the Software-centered University Project and has been taking part in the project since 2016. Through this, it was highly evaluated for promoting curriculum based on latest technology, an autonomous system where students directly select integrated education, and expansion of internships.
< Photo 3. Professor Minjoon Seo of Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI, who received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry on the same day >
At the awards ceremony that day, Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI also received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry. Professor Seo was recognized for his leading research achievements in the fields of AI and natural language processing by publishing 28 papers in top international AI conferences over the past four years.
At the same time, he was noted for his contributions to enhancing the originality and innovation of language model research, such as △knowledge encoding, △knowledge access and utilization, and △high-dimensional inference performance, and for demonstrating leadership in the international academic community.
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST stated, “Our university will continue to do its best to foster software talents with global competitiveness through continuous development of cutting-edge curriculum and innovative degree systems.”
2024.12.03 View 7526 -
 KAIST Secures Core Technology for Ultra-High-Resolution Image Sensors
A joint research team from Korea and the United States has developed next-generation, high-resolution image sensor technology with higher power efficiency and a smaller size compared to existing sensors. Notably, they have secured foundational technology for ultra-high-resolution shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors, an area currently dominated by Sony, paving the way for future market entry.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of November that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Inha University and Yale University in the U.S., has developed an ultra-thin broadband photodiode (PD), marking a significant breakthrough in high-performance image sensor technology.
This research drastically improves the trade-off between the absorption layer thickness and quantum efficiency found in conventional photodiode technology. Specifically, it achieved high quantum efficiency of over 70% even in an absorption layer thinner than one micrometer (μm), reducing the thickness of the absorption layer by approximately 70% compared to existing technologies.
A thinner absorption layer simplifies pixel processing, allowing for higher resolution and smoother carrier diffusion, which is advantageous for light carrier acquisition while also reducing the cost. However, a fundamental issue with thinner absorption layers is the reduced absorption of long-wavelength light.
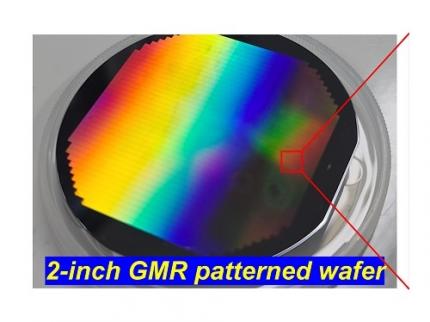
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor integrated on the Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) structure proposed in this study (left), a photograph of the fabricated wafer, and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the periodic patterns (right) >
The research team introduced a guided-mode resonance (GMR) structure* that enables high-efficiency light absorption across a wide spectral range from 400 nanometers (nm) to 1,700 nanometers (nm). This wavelength range includes not only visible light but also light the SWIR region, making it valuable for various industrial applications.
*Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) Structure: A concept used in electromagnetics, a phenomenon in which a specific (light) wave resonates (forming a strong electric/magnetic field) at a specific wavelength. Since energy is maximized under these conditions, it has been used to increase antenna or radar efficiency.
The improved performance in the SWIR region is expected to play a significant role in developing next-generation image sensors with increasingly high resolutions. The GMR structure, in particular, holds potential for further enhancing resolution and other performance metrics through hybrid integration and monolithic 3D integration with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-based readout integrated circuits (ROIC).
< Figure 2. Benchmark for state-of-the-art InGaAs-based SWIR pixels with simulated EQE lines as a function of TAL variation. Performance is maintained while reducing the absorption layer thickness from 2.1 micrometers or more to 1 micrometer or less while reducing it by 50% to 70% >
The research team has significantly enhanced international competitiveness in low-power devices and ultra-high-resolution imaging technology, opening up possibilities for applications in digital cameras, security systems, medical and industrial image sensors, as well as future ultra-high-resolution sensors for autonomous driving, aerospace, and satellite observation.
Professor Sang Hyun Kim, the lead researcher, commented, “This research demonstrates that significantly higher performance than existing technologies can be achieved even with ultra-thin absorption layers.”
< Figure 3. Top optical microscope image and cross-sectional scanning electron microscope image of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor fabricated on the GMR structure (left). Improved quantum efficiency performance of the ultra-thin image sensor (red) fabricated with the technology proposed in this study (right) >
The results of this research were published on 15th of November, in the prestigious international journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6), with Professor Dae-Myung Geum of Inha University (formerly a KAIST postdoctoral researcher) and Dr. Jinha Lim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Yale University) as co-first authors. (Paper title: “Highly-efficient (>70%) and Wide-spectral (400 nm -1700 nm) sub-micron-thick InGaAs photodiodes for future high-resolution image sensors”)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.11.22 View 6864
KAIST Secures Core Technology for Ultra-High-Resolution Image Sensors
A joint research team from Korea and the United States has developed next-generation, high-resolution image sensor technology with higher power efficiency and a smaller size compared to existing sensors. Notably, they have secured foundational technology for ultra-high-resolution shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors, an area currently dominated by Sony, paving the way for future market entry.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of November that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Inha University and Yale University in the U.S., has developed an ultra-thin broadband photodiode (PD), marking a significant breakthrough in high-performance image sensor technology.
This research drastically improves the trade-off between the absorption layer thickness and quantum efficiency found in conventional photodiode technology. Specifically, it achieved high quantum efficiency of over 70% even in an absorption layer thinner than one micrometer (μm), reducing the thickness of the absorption layer by approximately 70% compared to existing technologies.
A thinner absorption layer simplifies pixel processing, allowing for higher resolution and smoother carrier diffusion, which is advantageous for light carrier acquisition while also reducing the cost. However, a fundamental issue with thinner absorption layers is the reduced absorption of long-wavelength light.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor integrated on the Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) structure proposed in this study (left), a photograph of the fabricated wafer, and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the periodic patterns (right) >
The research team introduced a guided-mode resonance (GMR) structure* that enables high-efficiency light absorption across a wide spectral range from 400 nanometers (nm) to 1,700 nanometers (nm). This wavelength range includes not only visible light but also light the SWIR region, making it valuable for various industrial applications.
*Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) Structure: A concept used in electromagnetics, a phenomenon in which a specific (light) wave resonates (forming a strong electric/magnetic field) at a specific wavelength. Since energy is maximized under these conditions, it has been used to increase antenna or radar efficiency.
The improved performance in the SWIR region is expected to play a significant role in developing next-generation image sensors with increasingly high resolutions. The GMR structure, in particular, holds potential for further enhancing resolution and other performance metrics through hybrid integration and monolithic 3D integration with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-based readout integrated circuits (ROIC).
< Figure 2. Benchmark for state-of-the-art InGaAs-based SWIR pixels with simulated EQE lines as a function of TAL variation. Performance is maintained while reducing the absorption layer thickness from 2.1 micrometers or more to 1 micrometer or less while reducing it by 50% to 70% >
The research team has significantly enhanced international competitiveness in low-power devices and ultra-high-resolution imaging technology, opening up possibilities for applications in digital cameras, security systems, medical and industrial image sensors, as well as future ultra-high-resolution sensors for autonomous driving, aerospace, and satellite observation.
Professor Sang Hyun Kim, the lead researcher, commented, “This research demonstrates that significantly higher performance than existing technologies can be achieved even with ultra-thin absorption layers.”
< Figure 3. Top optical microscope image and cross-sectional scanning electron microscope image of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor fabricated on the GMR structure (left). Improved quantum efficiency performance of the ultra-thin image sensor (red) fabricated with the technology proposed in this study (right) >
The results of this research were published on 15th of November, in the prestigious international journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6), with Professor Dae-Myung Geum of Inha University (formerly a KAIST postdoctoral researcher) and Dr. Jinha Lim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Yale University) as co-first authors. (Paper title: “Highly-efficient (>70%) and Wide-spectral (400 nm -1700 nm) sub-micron-thick InGaAs photodiodes for future high-resolution image sensors”)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.11.22 View 6864 -
 KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
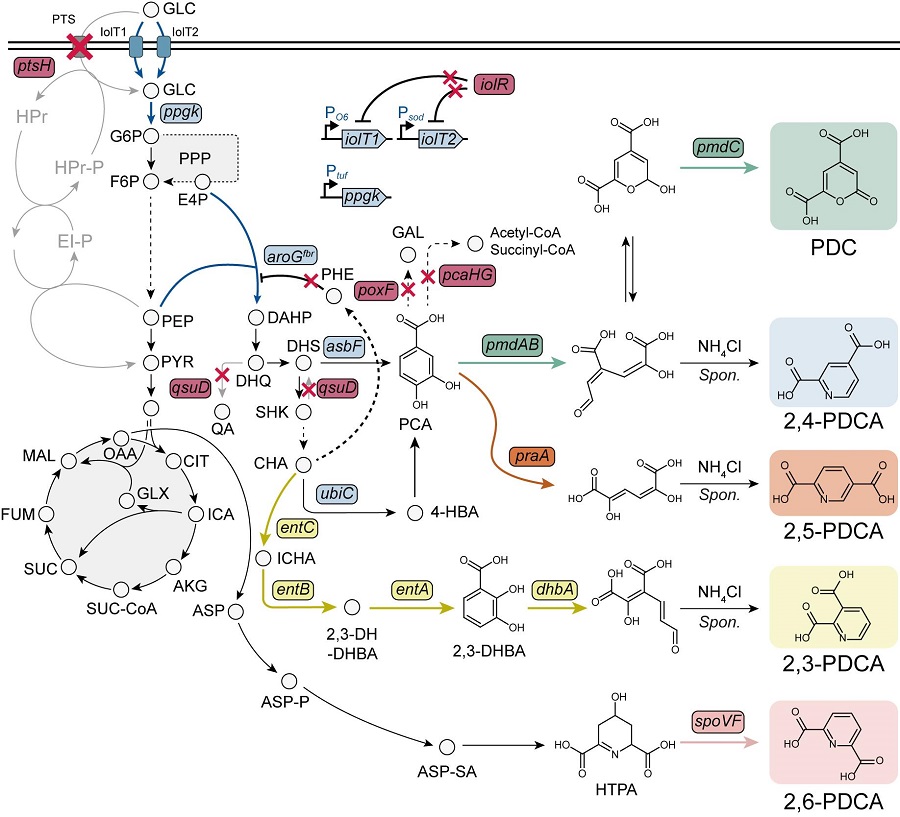
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 10389
KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 10389 -
 A heated battle of science and sports, who is the winner of this year's KA-PO War?
< Photos from KAIST-POSTECH Science War (photographed by Student Junhyeok Park of KAIST Freshman Course) >
The future leaders of science at KAIST and POSTECH (President Seong Keun Kim) held their annual science and sporting event at POSTECH for two days from September 20th to 21st. The 'KAIST-POSTECH Science War (hereafter KA-PO War)' is a festival consisting of science and sports games and various side events to promote exchange and cooperation between the two universities. It is also known by the nickname 'Science War'.
KA-PO War consists of △Science Games △e-Sports △Athletics, and the two universities compete in a total of 7 events including hacking competitions, artificial intelligence programming (AI), science quizzes, League of Legends (LOL), baseball, basketball, and soccer. In particular, the 9-hour ‘hacking competition’ and the ‘AI programming’ competition, which pits the AI design strategies of the two universities against each other, are famous for its competitions that are not easily seen at other universities.
The future science leaders of KAIST and POSTECH competed with their brains and physical strength even in the rain, and in the competition where the university that wins more than 4 out of 7 events wins, KAIST won with a score of 6 to 1 after fierce matches.
In addition, for this KAIST competition, Byeong-cheol Kim, the CEO of POSTECH Holdings and an alumnus of the Department of Industrial Management at POSTECH, donated 10 million won for the preparation of this event.
< Photos from KA-PO War site (photographed by Student Junhyeok Park of KAIST Freshman Course) >
KA-PO War Director Henry Kwon (KAIST Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering) said, “I would like to thank the planning team and supporters who worked hard to make it a successful event. This year’s KA-PO War shined even brighter because of the students from both universities who cheered passionately and played games despite the hot weather and rain. I hope this will be an opportunity to further strengthen the bond and sense of belonging among engineering students.”
KA-PO War Preparatory Committee Chairman Sa-joon Hong (POSTECH Department of Physics) said, “As if to manifest this year’s motto, ‘BLAST,’ the intense heat swept through the competition, and regardless of the outcome, the students from both universities took away unforgettable and precious memories.”
As a kind of student festival jointly held between the two universities, which have been held annually since 2002, KAIST-POSTECH Science Wars is held under a different name each year depending on the venue. This year, it was held at POSTECH, thus called ‘KA-PO War.’
2024.09.19 View 3810
A heated battle of science and sports, who is the winner of this year's KA-PO War?
< Photos from KAIST-POSTECH Science War (photographed by Student Junhyeok Park of KAIST Freshman Course) >
The future leaders of science at KAIST and POSTECH (President Seong Keun Kim) held their annual science and sporting event at POSTECH for two days from September 20th to 21st. The 'KAIST-POSTECH Science War (hereafter KA-PO War)' is a festival consisting of science and sports games and various side events to promote exchange and cooperation between the two universities. It is also known by the nickname 'Science War'.
KA-PO War consists of △Science Games △e-Sports △Athletics, and the two universities compete in a total of 7 events including hacking competitions, artificial intelligence programming (AI), science quizzes, League of Legends (LOL), baseball, basketball, and soccer. In particular, the 9-hour ‘hacking competition’ and the ‘AI programming’ competition, which pits the AI design strategies of the two universities against each other, are famous for its competitions that are not easily seen at other universities.
The future science leaders of KAIST and POSTECH competed with their brains and physical strength even in the rain, and in the competition where the university that wins more than 4 out of 7 events wins, KAIST won with a score of 6 to 1 after fierce matches.
In addition, for this KAIST competition, Byeong-cheol Kim, the CEO of POSTECH Holdings and an alumnus of the Department of Industrial Management at POSTECH, donated 10 million won for the preparation of this event.
< Photos from KA-PO War site (photographed by Student Junhyeok Park of KAIST Freshman Course) >
KA-PO War Director Henry Kwon (KAIST Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering) said, “I would like to thank the planning team and supporters who worked hard to make it a successful event. This year’s KA-PO War shined even brighter because of the students from both universities who cheered passionately and played games despite the hot weather and rain. I hope this will be an opportunity to further strengthen the bond and sense of belonging among engineering students.”
KA-PO War Preparatory Committee Chairman Sa-joon Hong (POSTECH Department of Physics) said, “As if to manifest this year’s motto, ‘BLAST,’ the intense heat swept through the competition, and regardless of the outcome, the students from both universities took away unforgettable and precious memories.”
As a kind of student festival jointly held between the two universities, which have been held annually since 2002, KAIST-POSTECH Science Wars is held under a different name each year depending on the venue. This year, it was held at POSTECH, thus called ‘KA-PO War.’
2024.09.19 View 3810 -
 KAIST Develops Microbial Liquid Egg Substitute
A team of researchers published a paper on developing a substitute for eggs using microorganisms, grabbing international attention. It is expected that the development of egg substitutes using non-animal raw materials will solve the problems of factory farming, which causes problems like increased emission of greenhouse gas and waste, and contribute to building a sustainable food system that allows easy protein intake.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the Biological Process Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering have published a paper on the development of an "Eco-Friendly Liquid Egg Substitute Derived from Microorganisms."
Eggs play a crucial role in various culinary applications due to their unique physicochemical properties such as gelling, foaming, and emulsifying, while also providing essential nutrients. However, traditional egg production is not only unethical and resource-intensive but also has significant environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and waste issues. Additionally, factors such as wars and trade regulations have led to significant increases in egg prices, highlighting food security concerns. In response to these issues, there has been growing interest in egg substitutes made from non-animal sources to establish a sustainable food system.
Although there has been progress in developing non-animal protein-based egg substitutes, no substitute has been able to fully replicate the essential functional properties of liquid eggs, such as gelling and foaming, while also providing complete nutrition. In this context, the research team aimed to develop a liquid egg substitute using microbial biomass, which has a protein content comparable to that of meat per unit dry mass. Various microorganisms, such as yeast, Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria, and other probiotics, have been proven safe through long-term human consumption. Microbial biomass requires fewer resources like water and land during production, and possesses high-quality nutrients, making it a promising sustainable food resource.
< Figure 1. Comparison of heat treatment results of microbial pellets and microbial lysates >
However, the semi-solid microbial biomass recovered through microbial cultivation was observed to turn liquid upon heating, unlike liquid egg. To address this, the research team devised a microbial lysate by breaking down the cell walls and cell membranes of microorganisms, which correspond to the eggshell. They found that the microbial lysate's proteins coagulated when heated and formed a gel similar to that of liquid egg. The gel formed from the heated microbial lysate was found to have microscopic structures and physical properties similar to those of boiled eggs. The addition of microbial-derived edible enzymes or plant-based materials allowed for the adjustment of its properties, enabling the creation of various textures.
Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated that the microbial lysate could form stable foams widely used in baking, such as meringues (made from egg whites). They successfully baked meringue cookies using this lysate, showing its potential as a functional liquid egg substitute.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, "This substitute has excellent nutritional components, making it suitable for regular food consumption. It is especially promising as emergency food for long-term space travel, wartime situations, and other emergencies. More importantly, it contributes to securing a sustainable food system."
< Figure 2. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
< Figure 3. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
The paper was published online in the journal npj Science of Food, issued by Nature.
- Paper Title: Microbial lysates repurposed as liquid egg substitutes
- Authors: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Da-Hee Ahn, Seok Yeong Jung, YuHyun Lee, and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT's project for developing eco-friendly chemical technologies to replace petroleum (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and the Rural Development Administration's Agricultural Microorganisms Project Group (Director: Professor Pan-sik Jang, Seoul National University) for developing protein production technology from inorganic substances through microbial metabolic system control (Project Leader: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST).
2024.07.05 View 7762
KAIST Develops Microbial Liquid Egg Substitute
A team of researchers published a paper on developing a substitute for eggs using microorganisms, grabbing international attention. It is expected that the development of egg substitutes using non-animal raw materials will solve the problems of factory farming, which causes problems like increased emission of greenhouse gas and waste, and contribute to building a sustainable food system that allows easy protein intake.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the Biological Process Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering have published a paper on the development of an "Eco-Friendly Liquid Egg Substitute Derived from Microorganisms."
Eggs play a crucial role in various culinary applications due to their unique physicochemical properties such as gelling, foaming, and emulsifying, while also providing essential nutrients. However, traditional egg production is not only unethical and resource-intensive but also has significant environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and waste issues. Additionally, factors such as wars and trade regulations have led to significant increases in egg prices, highlighting food security concerns. In response to these issues, there has been growing interest in egg substitutes made from non-animal sources to establish a sustainable food system.
Although there has been progress in developing non-animal protein-based egg substitutes, no substitute has been able to fully replicate the essential functional properties of liquid eggs, such as gelling and foaming, while also providing complete nutrition. In this context, the research team aimed to develop a liquid egg substitute using microbial biomass, which has a protein content comparable to that of meat per unit dry mass. Various microorganisms, such as yeast, Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria, and other probiotics, have been proven safe through long-term human consumption. Microbial biomass requires fewer resources like water and land during production, and possesses high-quality nutrients, making it a promising sustainable food resource.
< Figure 1. Comparison of heat treatment results of microbial pellets and microbial lysates >
However, the semi-solid microbial biomass recovered through microbial cultivation was observed to turn liquid upon heating, unlike liquid egg. To address this, the research team devised a microbial lysate by breaking down the cell walls and cell membranes of microorganisms, which correspond to the eggshell. They found that the microbial lysate's proteins coagulated when heated and formed a gel similar to that of liquid egg. The gel formed from the heated microbial lysate was found to have microscopic structures and physical properties similar to those of boiled eggs. The addition of microbial-derived edible enzymes or plant-based materials allowed for the adjustment of its properties, enabling the creation of various textures.
Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated that the microbial lysate could form stable foams widely used in baking, such as meringues (made from egg whites). They successfully baked meringue cookies using this lysate, showing its potential as a functional liquid egg substitute.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, "This substitute has excellent nutritional components, making it suitable for regular food consumption. It is especially promising as emergency food for long-term space travel, wartime situations, and other emergencies. More importantly, it contributes to securing a sustainable food system."
< Figure 2. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
< Figure 3. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
The paper was published online in the journal npj Science of Food, issued by Nature.
- Paper Title: Microbial lysates repurposed as liquid egg substitutes
- Authors: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Da-Hee Ahn, Seok Yeong Jung, YuHyun Lee, and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT's project for developing eco-friendly chemical technologies to replace petroleum (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and the Rural Development Administration's Agricultural Microorganisms Project Group (Director: Professor Pan-sik Jang, Seoul National University) for developing protein production technology from inorganic substances through microbial metabolic system control (Project Leader: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST).
2024.07.05 View 7762 -
 KAIST and Merck Sign MOU to Boost Biotech Innovation
< (From left) KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee and Merck CEO Matthias Heinzel >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Merck Life Science (CEO Matthias Heinzel) on May 29 to foster innovation and technology creation in advanced biotechnology.
Since May of last year, the two institutions have been discussing multidimensional innovation programs and will now focus on industry-academia cooperation to tackle bioindustry challenges with this MOU as a foundation.
KAIST will conduct joint research projects in various advanced biotechnology fields, such as synthetic biology, mRNA, cell line engineering, and organoids, using the chemical and biological portfolios provided by Merck.
Additionally, KAIST will establish an Experience Lab in collaboration with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. This lab will support the discovery and analysis of candidate substances in materials science and biology.
Programs to enhance researchers' capabilities will also be offered. Scholarships for graduate students and awards for professors will be implemented. Researchers will have opportunities to participate in global academic events and educational programs hosted by Merck, such as the Curious 2024 Future Insight Conference and the Innovation Cup.
M Ventures, a venture capital subsidiary of Merck Group, will collaborate with KAIST's startup institute to support technology commercialization and continue to develop their startup ecosystem.
The signing ceremony at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon was attended by the CEO of Merck Life Science and the President of KAIST along with representatives from both institutions.
Matthias Heinzel, a member of the Executive Board of Merck and CEO Life Science, said, “This agreement with KAIST is a significant step toward accelerating the development of the life science industry both in Korea and globally. Advancing life science research and fostering the next generation of scientists is essential for discovering new medicines to meet global health needs.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee responded, “We are pleased to share a vision for scientific advancement with Merck, a leading global technology company. We anticipate that this partnership will strengthen the connection between Merck’s life science business and the global scientific community.”
In March, Merck, a global science and technology company with over 350 years of history, announced a plan to invest 430 billion KRW (€300 million) to build a bioprocessing center in Daejeon, where KAIST is located. This is Merck's largest investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
2024.05.30 View 8973
KAIST and Merck Sign MOU to Boost Biotech Innovation
< (From left) KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee and Merck CEO Matthias Heinzel >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Merck Life Science (CEO Matthias Heinzel) on May 29 to foster innovation and technology creation in advanced biotechnology.
Since May of last year, the two institutions have been discussing multidimensional innovation programs and will now focus on industry-academia cooperation to tackle bioindustry challenges with this MOU as a foundation.
KAIST will conduct joint research projects in various advanced biotechnology fields, such as synthetic biology, mRNA, cell line engineering, and organoids, using the chemical and biological portfolios provided by Merck.
Additionally, KAIST will establish an Experience Lab in collaboration with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. This lab will support the discovery and analysis of candidate substances in materials science and biology.
Programs to enhance researchers' capabilities will also be offered. Scholarships for graduate students and awards for professors will be implemented. Researchers will have opportunities to participate in global academic events and educational programs hosted by Merck, such as the Curious 2024 Future Insight Conference and the Innovation Cup.
M Ventures, a venture capital subsidiary of Merck Group, will collaborate with KAIST's startup institute to support technology commercialization and continue to develop their startup ecosystem.
The signing ceremony at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon was attended by the CEO of Merck Life Science and the President of KAIST along with representatives from both institutions.
Matthias Heinzel, a member of the Executive Board of Merck and CEO Life Science, said, “This agreement with KAIST is a significant step toward accelerating the development of the life science industry both in Korea and globally. Advancing life science research and fostering the next generation of scientists is essential for discovering new medicines to meet global health needs.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee responded, “We are pleased to share a vision for scientific advancement with Merck, a leading global technology company. We anticipate that this partnership will strengthen the connection between Merck’s life science business and the global scientific community.”
In March, Merck, a global science and technology company with over 350 years of history, announced a plan to invest 430 billion KRW (€300 million) to build a bioprocessing center in Daejeon, where KAIST is located. This is Merck's largest investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
2024.05.30 View 8973 -
 The World’s First Hacking-preventing Cryptographic Semiconductor Chip
With the dramatic increase in the amount of information exchanged between components or devices in the 5G/6G era, such as for the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous driving, hacking attacks are becoming more sophisticated. Consequently, enhancing security functions is essential for safely transmitting data between and among devices.
On February 29th, a KAIST research team led by Professors Yang-gyu Choi and Seung-tak Ryu from the School of Electrical Engineering announced the successful development of the world's first security cryptographic semiconductor.
The team has developed the Cryptoristor, a cryptographic transistor based on FinFET technology, produced through a 100% silicon-compatible process, for the first time in the world. Cryptoristor is a random number generator (RNG) with unparalleled characteristics, featuring a unique structure comprising a single transistor and a distinctive mechanism.
In all security environments, including artificial intelligence, the most crucial element is the RNG. In the most commonly used security chip, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the RNG is a core component, occupying approximately 75% of the total chip area and more than 85% of its energy consumption. Hence, there is an urgent need for the development of low-power/ultra-small RNGs suitable for mobile or IoT devices.
Existing RNGs come with limitations as they lack compatibility with silicon CMOS processes and circuit-based RNGs occupy a large surface area.
In contrast, the team’s newly developed Cryptoristor, a cryptographic semiconductor based on a single-component structure, consumes and occupies less than .001 of the power and area compared to the current chips being used. Utilizing the inherent randomness of FinFETs, fabricated on a Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) substrate with an insulating layer formed beneath the silicon, the team developed an RNG that unpredictably produces zeroes and ones.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of the security cryptographic transistor device. >
Generally speaking, preventing hackers from predicting the encrypted algorithms during data exchanges through mobile devices is pivotal. Therefore, this method ensures unpredictability by generating random sequences of zeroes and ones that change every time.
Moreover, while the Cryptoristor-based RNG research is the world's first of its kind without any international implementation cases, it shares the same transistor structure as existing logic or memory components. This enables 100% production through rapid mass production processes using existing semiconductor facilities at a low cost.
Seung-il Kim, a PhD student who led the research, explained the significance of the study, stating, "As a cryptographic semiconductor, the ultra-small/low-power random number generator enhances security through its distinctive unpredictability, supporting safe hyperconnectivity with secure transmissions between chips or devices. Particularly, compared to previous research, it offers excellent advantages in terms of energy consumption, integration density, and cost, making it suitable for IoT device environments."
This research, with master’s student Hyung-jin Yoo as the co-author, was officially published in the online edition of Science Advances, a sister journal of Science, in February 2024 (research paper title: Cryptographic transistor for true random number generator with low power consumption).
This research received support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project and the Core Technology Development Project for the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory.
2024.03.07 View 9985
The World’s First Hacking-preventing Cryptographic Semiconductor Chip
With the dramatic increase in the amount of information exchanged between components or devices in the 5G/6G era, such as for the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous driving, hacking attacks are becoming more sophisticated. Consequently, enhancing security functions is essential for safely transmitting data between and among devices.
On February 29th, a KAIST research team led by Professors Yang-gyu Choi and Seung-tak Ryu from the School of Electrical Engineering announced the successful development of the world's first security cryptographic semiconductor.
The team has developed the Cryptoristor, a cryptographic transistor based on FinFET technology, produced through a 100% silicon-compatible process, for the first time in the world. Cryptoristor is a random number generator (RNG) with unparalleled characteristics, featuring a unique structure comprising a single transistor and a distinctive mechanism.
In all security environments, including artificial intelligence, the most crucial element is the RNG. In the most commonly used security chip, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), the RNG is a core component, occupying approximately 75% of the total chip area and more than 85% of its energy consumption. Hence, there is an urgent need for the development of low-power/ultra-small RNGs suitable for mobile or IoT devices.
Existing RNGs come with limitations as they lack compatibility with silicon CMOS processes and circuit-based RNGs occupy a large surface area.
In contrast, the team’s newly developed Cryptoristor, a cryptographic semiconductor based on a single-component structure, consumes and occupies less than .001 of the power and area compared to the current chips being used. Utilizing the inherent randomness of FinFETs, fabricated on a Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) substrate with an insulating layer formed beneath the silicon, the team developed an RNG that unpredictably produces zeroes and ones.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of the security cryptographic transistor device. >
Generally speaking, preventing hackers from predicting the encrypted algorithms during data exchanges through mobile devices is pivotal. Therefore, this method ensures unpredictability by generating random sequences of zeroes and ones that change every time.
Moreover, while the Cryptoristor-based RNG research is the world's first of its kind without any international implementation cases, it shares the same transistor structure as existing logic or memory components. This enables 100% production through rapid mass production processes using existing semiconductor facilities at a low cost.
Seung-il Kim, a PhD student who led the research, explained the significance of the study, stating, "As a cryptographic semiconductor, the ultra-small/low-power random number generator enhances security through its distinctive unpredictability, supporting safe hyperconnectivity with secure transmissions between chips or devices. Particularly, compared to previous research, it offers excellent advantages in terms of energy consumption, integration density, and cost, making it suitable for IoT device environments."
This research, with master’s student Hyung-jin Yoo as the co-author, was officially published in the online edition of Science Advances, a sister journal of Science, in February 2024 (research paper title: Cryptographic transistor for true random number generator with low power consumption).
This research received support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project and the Core Technology Development Project for the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory.
2024.03.07 View 9985 -
 A Korean research team develops a new clinical candidate for fatty liver disease
A team of Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a new drug candidate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) acting on peripheral tissues. To date, there has not been an optimal treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and this discovery is expected to set the grounds for the development of new drugs that can safely suppress both liver fat accumulation and liver fibrosis at the same time.
A joint research team led by Professor Jin Hee Ahn from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) and Professor Hail Kim from the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering developed a new chemical that can suppress disease-specific protein (HTR2A) through years of basic research. The team also revealed to have verified its efficacy and safety through preclinical tests (animal tests) at JD Bioscience Inc., a start-up company founded by Professor Ahn.
Although NAFLD has a prevalence rate as high as 20-30%, and about 5% of the global adult population suffers from NASH, there are no commercial drugs targeting them to date. NAFLD is a chronic disease that starts from the fatty liver and progresses into steatohepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The mortality rate of patients increases with accompanied cardiovascular diseases and liver-related complications, and appropriate treatment in the early stage is hence necessary.
< Figure 1. Strategy and history of 5HT2A antagonists. Library and rational design for the development of compound 11c as a potent 5HT2A antagonist. Previous research efforts were discontinued due to limited oral absorption and safety. A therapeutic candidate to overcome this problem was identified and phase 1 clinical trials are currently in progress. >
The new synthetic chemical developed by the joint GIST-KAIST research is an innovative drug candidate that shows therapeutic effects on NASH based on a dual action mechanism that inhibits the accumulation of fat in the liver and liver fibrosis by suppressing the serotonin receptor protein 5HT2A.
The research team confirmed its therapeutic effects in animal models for NAFLD and NASH, in which hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis* caused by fat accumulation in the liver were suppressed simultaneously by 50-70%.
*fibrosis: stiffening of parts of the liver, also used as a major indicator to track the prognosis of steatosis
The research team explained that the material was designed with optimal polarity and lipid affinity to minimize its permeability across the blood-brain barrier. It therefore does not affect the brain, and causes little side effects in the central nervous system (CNS) such as depression and suicidal ideations, while demonstrating excellent inhibition on its target protein present in tissues outside brain (IC50* = 14 nM). The team also demonstrated its superior efficacy in improving liver fibrosis when compared to similar drugs in the phase 3 clinical trial.
*IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration): the concentration at which a chemical suppresses 50% of a particular biological function
< Figure 2. GM-60106 (11c)'s effect on obesity: When GM-60106 was administered to an obese animal model (mice) for 2 months, body weight, body fat mass, and blood sugar were significantly reduced (a-d). In addition, the steatohepatitis level (NAFLD Activity Score) and the expression of genes of the treated mice involved in adipogenesis along with blood/liver fat decreased (e-h) >
Based on the pharmacological data obtained through preclinical trials, the team evaluated the effects of the drug on 88 healthy adults as part of their phase 1 clinical trial, where the side effects and the safe dosage of a drug are tested against healthy adults. Results showed no serious side effects and a good level of drug safety.
In addition, a preliminary efficacy evaluation on eight adults with steatohepatitis is currently underway.
Professor Jin Hee Ahn said, “The aim of this research is to develop a treatment for NASH with little side effects and guaranteed safety by developing a new target. The developed chemical is currently going through phase 1 of the global clinical trial in Australia through JD Bioscience Inc., a bio venture company for innovative drug development.” he added, “The candidate material the research team is currently developing shows not only a high level of safety and preventative effects by suppressing fat accumulation in the liver, but also a direct therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis. This is a strength that distinguishes our material from other competing drugs.”
< Figure 3. Efficacy of GM-60106 (11c) on liver fibrosis: When GM-60106 was administered to a steatohepatitis model (mice) for 3 months, the expression of genes associated with tissue fibrosis was significantly reduced (b-c). As a result of a detailed analysis of the tissues of the animal model, it was confirmed that the rate of tissue fibrosis was reduced and the expression rate of genes related to tissue fibrosis and inflammation was also significantly reduced (e-h). >
Professor Hail Kim from KAIST said, “Until now, this disease did not have a method of treatment other than weight control, and there has been no attempt to develop a drug that can be used for non-obese patients.” He added, “Through this research, we look forward to the development of various treatment techniques targeting a range of metabolic diseases including NASH that do not affect the weight of the patient.”
This study, conducted together by the research teams led by Professor Ahn from GIST and Professor Kim from KAIST, as well as the research team from JD Bioscience Inc., was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National New Drug Development Project. The results of this research were published by Nature Communications on January 20.
The team also presented the results of their clinical study on the candidate material coded GM-60106 targeting metabolic abnormality-related MASH* at NASH-TAG Conference 2024, which was held in Utah for three days starting on January 4, which was selected as an excellent abstract.
*MASH (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis): new replacement term for NASH
2024.02.21 View 10744
A Korean research team develops a new clinical candidate for fatty liver disease
A team of Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a new drug candidate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) acting on peripheral tissues. To date, there has not been an optimal treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and this discovery is expected to set the grounds for the development of new drugs that can safely suppress both liver fat accumulation and liver fibrosis at the same time.
A joint research team led by Professor Jin Hee Ahn from Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) and Professor Hail Kim from the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering developed a new chemical that can suppress disease-specific protein (HTR2A) through years of basic research. The team also revealed to have verified its efficacy and safety through preclinical tests (animal tests) at JD Bioscience Inc., a start-up company founded by Professor Ahn.
Although NAFLD has a prevalence rate as high as 20-30%, and about 5% of the global adult population suffers from NASH, there are no commercial drugs targeting them to date. NAFLD is a chronic disease that starts from the fatty liver and progresses into steatohepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The mortality rate of patients increases with accompanied cardiovascular diseases and liver-related complications, and appropriate treatment in the early stage is hence necessary.
< Figure 1. Strategy and history of 5HT2A antagonists. Library and rational design for the development of compound 11c as a potent 5HT2A antagonist. Previous research efforts were discontinued due to limited oral absorption and safety. A therapeutic candidate to overcome this problem was identified and phase 1 clinical trials are currently in progress. >
The new synthetic chemical developed by the joint GIST-KAIST research is an innovative drug candidate that shows therapeutic effects on NASH based on a dual action mechanism that inhibits the accumulation of fat in the liver and liver fibrosis by suppressing the serotonin receptor protein 5HT2A.
The research team confirmed its therapeutic effects in animal models for NAFLD and NASH, in which hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis* caused by fat accumulation in the liver were suppressed simultaneously by 50-70%.
*fibrosis: stiffening of parts of the liver, also used as a major indicator to track the prognosis of steatosis
The research team explained that the material was designed with optimal polarity and lipid affinity to minimize its permeability across the blood-brain barrier. It therefore does not affect the brain, and causes little side effects in the central nervous system (CNS) such as depression and suicidal ideations, while demonstrating excellent inhibition on its target protein present in tissues outside brain (IC50* = 14 nM). The team also demonstrated its superior efficacy in improving liver fibrosis when compared to similar drugs in the phase 3 clinical trial.
*IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration): the concentration at which a chemical suppresses 50% of a particular biological function
< Figure 2. GM-60106 (11c)'s effect on obesity: When GM-60106 was administered to an obese animal model (mice) for 2 months, body weight, body fat mass, and blood sugar were significantly reduced (a-d). In addition, the steatohepatitis level (NAFLD Activity Score) and the expression of genes of the treated mice involved in adipogenesis along with blood/liver fat decreased (e-h) >
Based on the pharmacological data obtained through preclinical trials, the team evaluated the effects of the drug on 88 healthy adults as part of their phase 1 clinical trial, where the side effects and the safe dosage of a drug are tested against healthy adults. Results showed no serious side effects and a good level of drug safety.
In addition, a preliminary efficacy evaluation on eight adults with steatohepatitis is currently underway.
Professor Jin Hee Ahn said, “The aim of this research is to develop a treatment for NASH with little side effects and guaranteed safety by developing a new target. The developed chemical is currently going through phase 1 of the global clinical trial in Australia through JD Bioscience Inc., a bio venture company for innovative drug development.” he added, “The candidate material the research team is currently developing shows not only a high level of safety and preventative effects by suppressing fat accumulation in the liver, but also a direct therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis. This is a strength that distinguishes our material from other competing drugs.”
< Figure 3. Efficacy of GM-60106 (11c) on liver fibrosis: When GM-60106 was administered to a steatohepatitis model (mice) for 3 months, the expression of genes associated with tissue fibrosis was significantly reduced (b-c). As a result of a detailed analysis of the tissues of the animal model, it was confirmed that the rate of tissue fibrosis was reduced and the expression rate of genes related to tissue fibrosis and inflammation was also significantly reduced (e-h). >
Professor Hail Kim from KAIST said, “Until now, this disease did not have a method of treatment other than weight control, and there has been no attempt to develop a drug that can be used for non-obese patients.” He added, “Through this research, we look forward to the development of various treatment techniques targeting a range of metabolic diseases including NASH that do not affect the weight of the patient.”
This study, conducted together by the research teams led by Professor Ahn from GIST and Professor Kim from KAIST, as well as the research team from JD Bioscience Inc., was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National New Drug Development Project. The results of this research were published by Nature Communications on January 20.
The team also presented the results of their clinical study on the candidate material coded GM-60106 targeting metabolic abnormality-related MASH* at NASH-TAG Conference 2024, which was held in Utah for three days starting on January 4, which was selected as an excellent abstract.
*MASH (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis): new replacement term for NASH
2024.02.21 View 10744 -
 World-renowned Soprano Sumi Jo and Broadcom CEO Hock Tan awarded honorary doctorate from KAIST
< (From left) Sumi Jo, Distinguished Visiting Professor at the Graduate School of Culture and Technology, and Broadcom President and CEO Hock Tan >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that it awarded honorary doctorates to world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo, a distinguished visiting professor at the Graduate School of Culture and Technology, and the President and Chief Executive Officer of Broadcom Inc., Hock Tan, at the graduation ceremony held on the 16th of February, 2024.
Professor Sumi Jo, who received an honorary doctorate in science and technology, was appointed as a visiting professor at KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology in 2021 and established the "Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center" and have been involved in research providing valuable feedback on projects to put on stage performances utilizing AI-orchestrated musical ensemble technology and research on virtual voices using vocal synthesis technology, as well as participating in the demonstration of the technological performance showcased at KAIST. Also, she held a special lecture and a talk concert for KAIST students, sharing her experience as a celebrated soprano on the world stage and having honest conversations with students.
KAIST said, “The doctorate is being awarded in recognition of her contributions that is broadening the spectrum of research in the field of science and technology to lead the digital era by suggesting a direction for future
science and technology to take led by culture. Also, her significant contribution to promoting necessary internationalization capabilities helps KAIST as it is growing into a world-class university through new academic challenges.”
< Professor Sumi Jo (left), who received an honorary doctorate in science and technology, and President Kwang-Hyung Lee >
Professor Sumi Jo, who debuted as Gilda in the opera in 1986, has performed with world-class conductors such as Herbert von Karajan, Georg Solti, Zubin Mehta, and James Levine. She has released over 40 full-length albums and continues to excel in all areas of vocal performances, including film scores, songs, and musicals.
Professor Sumi Jo said, “When I received a proposal from President Kwang-Hyung Lee of KAIST to convey what I experienced and felt on the world stage to students of science at KAIST under the topic of ‘Music and My Life,’ questions started to swirl inside of me.”
She continued, “Singing on stage is about ‘expressing,’ and it is a comprehensive artistic process that unfolding the artist’s inner self (expression) and showing it (presentation) in a way that the audience can best feel it through
methods such as sound, lighting, and directing. And I realized that, I was singing all my life in an environment where science and technology coexisted with culture and art.”
“When I worked with the students here at KAIST, I came to realize that when scientific and technologically talented people are set free to really enjoy their ideas and explore them on their own terms, their insight become sharper and their creativity become richer,” she said. She went on to add, “I am proud to be able to join the graduates at the ceremony and would like to express my gratitude for awarding me the honorary doctorate.”
< (From left) President Hock Tan, who received the honorary doctorate in engineering, Mrs. Lya Trung Tan, and President Kwang-Hyung Lee >
Hock Tan received an honorary doctorate in engineering. He is a highly successful businessman who demonstrated entrepreneurship based on a profound understanding of science and technology, which transformed Broadcom into a global enterprise in technology that provides semiconductor and software solutions.
Broadcom has achieved advancement and technological innovation in the semiconductor industry tailored to computer and telecommunication networks, and is evaluated as having played a major role in bringing about the digital transformation movement that is now encompassing the global communities.
Tan attributes the secret to his success to ‘the considerate decision made by the university to award him the scholarship which enabled him to pursue his degree’ and ‘the great team members working with him’..’ Also, he is well-known as a person who considers giving back to society his most important mission.
To support effective medical treatment and identification of the cause of autism, Tan has made large donations to MIT and Harvard University since 2017 several times, and during the COVID-19 pandemic, he reinforced his support to improve the treatment of workers at community medical institutions and non-profit organizations. He also founded the Broadcom Foundation, which supports science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education programs for students in and outside the United States.
KAIST said, “We are awarding CEO Hock Tan the honorary doctorate in recognition of his contribution to KAIST’s emergence as a world-class university, as he emphasized the importance of convergence research and
internationalization of KAIST during his time serving as an overseas member of the KAIST President's Advisory Council from 2006 to 2013, while providing policy advices built on his experiences of innovations from various parts around the world.”
Tan emphasized, “KAIST has been vital to Korea’s advancement in the global economy. (KAIST) remains a source of technological innovation,” and that, “It is truly an honor to be recognized by an institution with such a distinguished record of excellence in science, engineering and research.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Professor Sumi Jo’s exploration into the future of performing arts through science and technology helps to expand KAIST’s scope and enhance our creative capabilities, while the dedication and humane efforts Hock Tan demonstrates as he contributes to digital innovation through corporate management and engages in various social contribution activities serves as a superb example to all members of KAIST.”
He continued, “These two have lived out the values of challenge and innovation and became examples for many, and we are very pleased to welcome them as the newest members of the KAIST family. On behalf of all members of KAIST, I deliver our sincere congratulations.”
2024.02.17 View 12159
World-renowned Soprano Sumi Jo and Broadcom CEO Hock Tan awarded honorary doctorate from KAIST
< (From left) Sumi Jo, Distinguished Visiting Professor at the Graduate School of Culture and Technology, and Broadcom President and CEO Hock Tan >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that it awarded honorary doctorates to world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo, a distinguished visiting professor at the Graduate School of Culture and Technology, and the President and Chief Executive Officer of Broadcom Inc., Hock Tan, at the graduation ceremony held on the 16th of February, 2024.
Professor Sumi Jo, who received an honorary doctorate in science and technology, was appointed as a visiting professor at KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology in 2021 and established the "Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center" and have been involved in research providing valuable feedback on projects to put on stage performances utilizing AI-orchestrated musical ensemble technology and research on virtual voices using vocal synthesis technology, as well as participating in the demonstration of the technological performance showcased at KAIST. Also, she held a special lecture and a talk concert for KAIST students, sharing her experience as a celebrated soprano on the world stage and having honest conversations with students.
KAIST said, “The doctorate is being awarded in recognition of her contributions that is broadening the spectrum of research in the field of science and technology to lead the digital era by suggesting a direction for future
science and technology to take led by culture. Also, her significant contribution to promoting necessary internationalization capabilities helps KAIST as it is growing into a world-class university through new academic challenges.”
< Professor Sumi Jo (left), who received an honorary doctorate in science and technology, and President Kwang-Hyung Lee >
Professor Sumi Jo, who debuted as Gilda in the opera in 1986, has performed with world-class conductors such as Herbert von Karajan, Georg Solti, Zubin Mehta, and James Levine. She has released over 40 full-length albums and continues to excel in all areas of vocal performances, including film scores, songs, and musicals.
Professor Sumi Jo said, “When I received a proposal from President Kwang-Hyung Lee of KAIST to convey what I experienced and felt on the world stage to students of science at KAIST under the topic of ‘Music and My Life,’ questions started to swirl inside of me.”
She continued, “Singing on stage is about ‘expressing,’ and it is a comprehensive artistic process that unfolding the artist’s inner self (expression) and showing it (presentation) in a way that the audience can best feel it through
methods such as sound, lighting, and directing. And I realized that, I was singing all my life in an environment where science and technology coexisted with culture and art.”
“When I worked with the students here at KAIST, I came to realize that when scientific and technologically talented people are set free to really enjoy their ideas and explore them on their own terms, their insight become sharper and their creativity become richer,” she said. She went on to add, “I am proud to be able to join the graduates at the ceremony and would like to express my gratitude for awarding me the honorary doctorate.”
< (From left) President Hock Tan, who received the honorary doctorate in engineering, Mrs. Lya Trung Tan, and President Kwang-Hyung Lee >
Hock Tan received an honorary doctorate in engineering. He is a highly successful businessman who demonstrated entrepreneurship based on a profound understanding of science and technology, which transformed Broadcom into a global enterprise in technology that provides semiconductor and software solutions.
Broadcom has achieved advancement and technological innovation in the semiconductor industry tailored to computer and telecommunication networks, and is evaluated as having played a major role in bringing about the digital transformation movement that is now encompassing the global communities.
Tan attributes the secret to his success to ‘the considerate decision made by the university to award him the scholarship which enabled him to pursue his degree’ and ‘the great team members working with him’..’ Also, he is well-known as a person who considers giving back to society his most important mission.
To support effective medical treatment and identification of the cause of autism, Tan has made large donations to MIT and Harvard University since 2017 several times, and during the COVID-19 pandemic, he reinforced his support to improve the treatment of workers at community medical institutions and non-profit organizations. He also founded the Broadcom Foundation, which supports science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education programs for students in and outside the United States.
KAIST said, “We are awarding CEO Hock Tan the honorary doctorate in recognition of his contribution to KAIST’s emergence as a world-class university, as he emphasized the importance of convergence research and
internationalization of KAIST during his time serving as an overseas member of the KAIST President's Advisory Council from 2006 to 2013, while providing policy advices built on his experiences of innovations from various parts around the world.”
Tan emphasized, “KAIST has been vital to Korea’s advancement in the global economy. (KAIST) remains a source of technological innovation,” and that, “It is truly an honor to be recognized by an institution with such a distinguished record of excellence in science, engineering and research.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Professor Sumi Jo’s exploration into the future of performing arts through science and technology helps to expand KAIST’s scope and enhance our creative capabilities, while the dedication and humane efforts Hock Tan demonstrates as he contributes to digital innovation through corporate management and engages in various social contribution activities serves as a superb example to all members of KAIST.”
He continued, “These two have lived out the values of challenge and innovation and became examples for many, and we are very pleased to welcome them as the newest members of the KAIST family. On behalf of all members of KAIST, I deliver our sincere congratulations.”
2024.02.17 View 12159 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops Sweat-Resistant Wearable Robot Sensor
New electromyography (EMG) sensor technology that allows the long-term stable control of wearable robots and is not affected by the wearer’s sweat and dead skin has gained attention recently. Wearable robots are devices used across a variety of rehabilitation treatments for the elderly and patients recovering from stroke or trauma.
A joint research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE) and Professor Jung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME) announced on January 23rd that they have successfully developed a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor that can electrically sense physiological signals at a high level without being affected by the state of the user’s skin.
For wearable robots to recognize the intentions behind human movement for their use in rehabilitation treatment, they require a wearable electrophysiological sensor that gives precise EMG measurements. However, existing sensors often show deteriorating signal quality over time and are greatly affected by the user’s skin conditions. Furthermore, the sensor’s higher mechanical hardness causes noise since the contact surface is unable to keep up with the deformation of the skin. These shortcomings limit the reliable, long-term control of wearable robots.
< Figure 1. Design and working concept of the Stretchable microNeedle Adhesive Patch (SNAP). (A) Schematic illustration showing the overall system configuration and application of SNAP. (B) Exploded view schematic diagram of a SNAP, consisting of stretchable serpentine interconnects, Au-coated Si microneedle, and ECA made of Ag flakes–silicone composite. (C) Optical images showing high mechanical compliance of SNAP. >
However, the recently developed technology is expected to allow long-term and high-quality EMG measurements as it uses a stretchable and adhesive conducting substrate integrated with microneedle arrays that can easily penetrate the stratum corneum without causing discomfort. Through its excellent performance, the sensor is anticipated to be able to stably control wearable robots over a long period of time regardless of the wearer’s changing skin conditions and without the need for a preparation step that removes sweat and dead cells from the surface of their skin.
The research team created a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor by integrating microneedles into a soft silicon polymer substrate. The hard microneedles penetrate through the stratum corneum, which has high electrical resistance. As a result, the sensor can effectively lower contact resistance with the skin and obtain high-quality electrophysiological signals regardless of contamination. At the same time, the soft and adhesive conducting substrate can adapt to the skin’s surface that stretches with the wearer’s movement, providing a comfortable fit and minimizing noise caused by movement.
< Figure 2. Demonstration of the wireless Stretchable microNeedle Adhesive Patch (SNAP) system as an Human-machine interfaces (HMI) for closed-loop control of an exoskeleton robot. (A) Illustration depicting the system architecture and control strategy of an exoskeleton robot. (B) The hardware configuration of the pneumatic back support exoskeleton system. (C) Comparison of root mean square (RMS) of electromyography (EMG) with and without robotic assistance of pretreated skin and non-pretreated skin. >
To verify the usability of the new patch, the research team conducted a motion assistance experiment using a wearable robot. They attached the microneedle patch on a user’s leg, where it could sense the electrical signals generated by the muscle. The sensor then sent the detected intention to a wearable robot, allowing the robot to help the wearer lift a heavy object more easily.
Professor Jae-Woong Jung, who led the research, said, “The developed stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor can stability detect EMG signals without being affected by the state of a user’s skin. Through this, we will be able to control wearable robots with higher precision and stability, which will help the rehabilitation of patients who use robots.”
The results of this research, written by co-first authors Heesoo Kim and Juhyun Lee, who are both Ph.D. candidates in the KAIST School of EE, were published in Science Advances on January 17th under the title “Skin-preparation-free, stretchable microneedle adhesive patches for reliable electrophysiological sensing and exoskeleton robot control”.
This research was supported by the Bio-signal Sensor Integrated Technology Development Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Electronic Medicinal Technology Development Project, and the Step 4 BK21 Project.
2024.01.30 View 9649
KAIST Research Team Develops Sweat-Resistant Wearable Robot Sensor
New electromyography (EMG) sensor technology that allows the long-term stable control of wearable robots and is not affected by the wearer’s sweat and dead skin has gained attention recently. Wearable robots are devices used across a variety of rehabilitation treatments for the elderly and patients recovering from stroke or trauma.
A joint research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE) and Professor Jung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME) announced on January 23rd that they have successfully developed a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor that can electrically sense physiological signals at a high level without being affected by the state of the user’s skin.
For wearable robots to recognize the intentions behind human movement for their use in rehabilitation treatment, they require a wearable electrophysiological sensor that gives precise EMG measurements. However, existing sensors often show deteriorating signal quality over time and are greatly affected by the user’s skin conditions. Furthermore, the sensor’s higher mechanical hardness causes noise since the contact surface is unable to keep up with the deformation of the skin. These shortcomings limit the reliable, long-term control of wearable robots.
< Figure 1. Design and working concept of the Stretchable microNeedle Adhesive Patch (SNAP). (A) Schematic illustration showing the overall system configuration and application of SNAP. (B) Exploded view schematic diagram of a SNAP, consisting of stretchable serpentine interconnects, Au-coated Si microneedle, and ECA made of Ag flakes–silicone composite. (C) Optical images showing high mechanical compliance of SNAP. >
However, the recently developed technology is expected to allow long-term and high-quality EMG measurements as it uses a stretchable and adhesive conducting substrate integrated with microneedle arrays that can easily penetrate the stratum corneum without causing discomfort. Through its excellent performance, the sensor is anticipated to be able to stably control wearable robots over a long period of time regardless of the wearer’s changing skin conditions and without the need for a preparation step that removes sweat and dead cells from the surface of their skin.
The research team created a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor by integrating microneedles into a soft silicon polymer substrate. The hard microneedles penetrate through the stratum corneum, which has high electrical resistance. As a result, the sensor can effectively lower contact resistance with the skin and obtain high-quality electrophysiological signals regardless of contamination. At the same time, the soft and adhesive conducting substrate can adapt to the skin’s surface that stretches with the wearer’s movement, providing a comfortable fit and minimizing noise caused by movement.
< Figure 2. Demonstration of the wireless Stretchable microNeedle Adhesive Patch (SNAP) system as an Human-machine interfaces (HMI) for closed-loop control of an exoskeleton robot. (A) Illustration depicting the system architecture and control strategy of an exoskeleton robot. (B) The hardware configuration of the pneumatic back support exoskeleton system. (C) Comparison of root mean square (RMS) of electromyography (EMG) with and without robotic assistance of pretreated skin and non-pretreated skin. >
To verify the usability of the new patch, the research team conducted a motion assistance experiment using a wearable robot. They attached the microneedle patch on a user’s leg, where it could sense the electrical signals generated by the muscle. The sensor then sent the detected intention to a wearable robot, allowing the robot to help the wearer lift a heavy object more easily.
Professor Jae-Woong Jung, who led the research, said, “The developed stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor can stability detect EMG signals without being affected by the state of a user’s skin. Through this, we will be able to control wearable robots with higher precision and stability, which will help the rehabilitation of patients who use robots.”
The results of this research, written by co-first authors Heesoo Kim and Juhyun Lee, who are both Ph.D. candidates in the KAIST School of EE, were published in Science Advances on January 17th under the title “Skin-preparation-free, stretchable microneedle adhesive patches for reliable electrophysiological sensing and exoskeleton robot control”.
This research was supported by the Bio-signal Sensor Integrated Technology Development Project by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Electronic Medicinal Technology Development Project, and the Step 4 BK21 Project.
2024.01.30 View 9649