Mobile
-
 KAIST Professor Sung-Ju Lee Appointed a Technical Program Chair of INFOCOM
Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the Department of Computer Science at KAIST has been appointed to serve as a technical program chair of IEEE INFOCOME. The computer communication conference, started in 1982, is influential in the research fields of the Internet, wireless, and data centers.
Professor Lee is the first Korean to serve as a program chair. He has been acknowledged for his work in network communications. In the 34th conference, which will be held next year, he will take part in selecting 650 experts in the field to become members and supervise the evaluation of around 1,600 papers.
Professor Lee is the leading researcher in the field of wireless mobile network systems. He is a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and served as the general chair of the 20th Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) SIGMOBILE Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing & Networking (MobiCom 2014). He is on the editorial boards of IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) and IEEE Internet of Things Journals.
Professor Lee said, “I hope to continue the traditions of the conference, as well as integrating research from various areas of network communication. I will strive to create a program with high technology transfer probability.”
The 34th IEEE INFOCOM will take place in San Francisco in April 2016.
2015.07.02 View 9914
KAIST Professor Sung-Ju Lee Appointed a Technical Program Chair of INFOCOM
Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the Department of Computer Science at KAIST has been appointed to serve as a technical program chair of IEEE INFOCOME. The computer communication conference, started in 1982, is influential in the research fields of the Internet, wireless, and data centers.
Professor Lee is the first Korean to serve as a program chair. He has been acknowledged for his work in network communications. In the 34th conference, which will be held next year, he will take part in selecting 650 experts in the field to become members and supervise the evaluation of around 1,600 papers.
Professor Lee is the leading researcher in the field of wireless mobile network systems. He is a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and served as the general chair of the 20th Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) SIGMOBILE Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing & Networking (MobiCom 2014). He is on the editorial boards of IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) and IEEE Internet of Things Journals.
Professor Lee said, “I hope to continue the traditions of the conference, as well as integrating research from various areas of network communication. I will strive to create a program with high technology transfer probability.”
The 34th IEEE INFOCOM will take place in San Francisco in April 2016.
2015.07.02 View 9914 -
 KAIST & the Classic 500 Co Sign for Mobile Healthcare Research
KAIST and The Classic 500 Co., Ltd., an elder care provider based in Seoul, signed a memorandum of understanding to expand medical services by cooperating on the research of medical services and IT on March 24, 2015.
Twenty people from the two institutions, including President Steve Kang, Dong-Hyun Bak, CEO of The Classic 500 and Mun-Sul Jeong, a former KAIST Chairman of the Board, attended the signing ceremony.
Under the agreement, the two institutions will cooperate on mobile healthcare research and the development of a telemedicine system. They will also research and develop a system to better serve society with medical services.
The Classic 500, established by Konkuk University in Korea, provides nursing care services and assisted living facilities for senior citizens.
2015.03.26 View 9627
KAIST & the Classic 500 Co Sign for Mobile Healthcare Research
KAIST and The Classic 500 Co., Ltd., an elder care provider based in Seoul, signed a memorandum of understanding to expand medical services by cooperating on the research of medical services and IT on March 24, 2015.
Twenty people from the two institutions, including President Steve Kang, Dong-Hyun Bak, CEO of The Classic 500 and Mun-Sul Jeong, a former KAIST Chairman of the Board, attended the signing ceremony.
Under the agreement, the two institutions will cooperate on mobile healthcare research and the development of a telemedicine system. They will also research and develop a system to better serve society with medical services.
The Classic 500, established by Konkuk University in Korea, provides nursing care services and assisted living facilities for senior citizens.
2015.03.26 View 9627 -
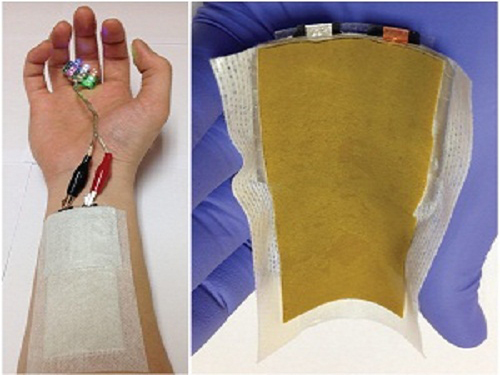 KAIST Develops a Credit-Card-Thick Flexible Lithium Ion Battery
Since the battery can be charged wirelessly, useful applications are expected including medical patches and smart cards.
Professor Jang Wook Choi at KAIST’s Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) and Dr. Jae Yong Song at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science jointly led research to invent a flexible lithium ion battery that is thinner than a credit card and can be charged wirelessly.
Their research findings were published online in Nano Letters on March 6, 2015. Lithium ion batteries are widely used today in various electronics including mobile devices and electronic cars. Researchers said that their work could help accelerate the development of flexible and wearable electronics.
Conventional lithium ion batteries are manufactured based on a layering technology, stacking up anodes, separating films, and cathodes like a sandwich, which makes it difficult to reduce their thickness. In addition, friction arises between layers, making the batteries impossible to bend. The coating films of electrodes easily come off, which contributes to the batteries’ poor performance.
The research team abandoned the existing production technology. Instead, they removed the separating films, layered the cathodes and anodes collinearly on a plane, and created a partition between electrodes to eliminate potential problems, such as short circuits and voltage dips, commonly present in lithium ion batteries.
After more than five thousand consecutive flexing experiments, the research team confirmed the possibility of a more flexible electrode structure while maintaining the battery performance comparable to the level of current lithium ion batteries.
Flexible batteries can be applied to integrated smart cards, cosmetic and medical patches, and skin adhesive sensors that can control a computer with voice commands or gesture as seen in the movie “Iron Man.”
Moreover, the team has successfully developed wireless-charging technology using electromagnetic induction and solar batteries.
They are currently developing a mass production process to combine this planar battery technology and printing, to ultimately create a new paradigm to print semiconductors and batteries using 3D printers.
Professor Choi said, “This new technology will contribute to diversifying patch functions as it is applicable to power various adhesive medical patches.”
Picture 1: Medical patch (left) and flexible secondary battery (right)
Picture 2: Diagram of flexible battery
Picture 3: Smart card embedding flexible battery
2015.03.24 View 13712
KAIST Develops a Credit-Card-Thick Flexible Lithium Ion Battery
Since the battery can be charged wirelessly, useful applications are expected including medical patches and smart cards.
Professor Jang Wook Choi at KAIST’s Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) and Dr. Jae Yong Song at the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science jointly led research to invent a flexible lithium ion battery that is thinner than a credit card and can be charged wirelessly.
Their research findings were published online in Nano Letters on March 6, 2015. Lithium ion batteries are widely used today in various electronics including mobile devices and electronic cars. Researchers said that their work could help accelerate the development of flexible and wearable electronics.
Conventional lithium ion batteries are manufactured based on a layering technology, stacking up anodes, separating films, and cathodes like a sandwich, which makes it difficult to reduce their thickness. In addition, friction arises between layers, making the batteries impossible to bend. The coating films of electrodes easily come off, which contributes to the batteries’ poor performance.
The research team abandoned the existing production technology. Instead, they removed the separating films, layered the cathodes and anodes collinearly on a plane, and created a partition between electrodes to eliminate potential problems, such as short circuits and voltage dips, commonly present in lithium ion batteries.
After more than five thousand consecutive flexing experiments, the research team confirmed the possibility of a more flexible electrode structure while maintaining the battery performance comparable to the level of current lithium ion batteries.
Flexible batteries can be applied to integrated smart cards, cosmetic and medical patches, and skin adhesive sensors that can control a computer with voice commands or gesture as seen in the movie “Iron Man.”
Moreover, the team has successfully developed wireless-charging technology using electromagnetic induction and solar batteries.
They are currently developing a mass production process to combine this planar battery technology and printing, to ultimately create a new paradigm to print semiconductors and batteries using 3D printers.
Professor Choi said, “This new technology will contribute to diversifying patch functions as it is applicable to power various adhesive medical patches.”
Picture 1: Medical patch (left) and flexible secondary battery (right)
Picture 2: Diagram of flexible battery
Picture 3: Smart card embedding flexible battery
2015.03.24 View 13712 -
 Qualcomm Innovation Award Recognizes 20 KAIST Students
The
award provides research fellowships, worth of USD 100,000, to 20 KAIST graduate
students
With an audience of 100 people present,
KAIST held a ceremony for the Qualcomm Innovation Award 2015 at the Information
Technology Convergence building on campus on March 12, 2015.
The Qualcomm Innovation Award, established
in 2010, is a fellowship that supports innovative science and engineering master’s
and doctoral students at KAIST. Qualcomm donated USD 100,000 to KAIST, stipulating that it be used to foster a creative research environment for graduate
students.
To select the recipients, KAIST formed an award committee chaired
by Professor Soo-Young Lee of the Department of Electrical Engineering and accepted research proposals until late January.
The award committee first selected 37
proposals from 75 papers submitted and then chose the final 20 research
proposals on March 12, 2015 after presentation evaluations. The presentations had to show promise of innovation and creativity; prospective influence on wireless communications
and mobile industry; and the prospect of being implemented.
Each recipient received a USD 4,500 research
fellowship along with an opportunity to present their research findings at a
workshop where Qualcomm engineers and other distinguished individuals of the industry
will attend.
Previously, Qualcomm has donated
research fellowships to KAIST graduate students in 2011 and 2013.
2015.03.19 View 11169
Qualcomm Innovation Award Recognizes 20 KAIST Students
The
award provides research fellowships, worth of USD 100,000, to 20 KAIST graduate
students
With an audience of 100 people present,
KAIST held a ceremony for the Qualcomm Innovation Award 2015 at the Information
Technology Convergence building on campus on March 12, 2015.
The Qualcomm Innovation Award, established
in 2010, is a fellowship that supports innovative science and engineering master’s
and doctoral students at KAIST. Qualcomm donated USD 100,000 to KAIST, stipulating that it be used to foster a creative research environment for graduate
students.
To select the recipients, KAIST formed an award committee chaired
by Professor Soo-Young Lee of the Department of Electrical Engineering and accepted research proposals until late January.
The award committee first selected 37
proposals from 75 papers submitted and then chose the final 20 research
proposals on March 12, 2015 after presentation evaluations. The presentations had to show promise of innovation and creativity; prospective influence on wireless communications
and mobile industry; and the prospect of being implemented.
Each recipient received a USD 4,500 research
fellowship along with an opportunity to present their research findings at a
workshop where Qualcomm engineers and other distinguished individuals of the industry
will attend.
Previously, Qualcomm has donated
research fellowships to KAIST graduate students in 2011 and 2013.
2015.03.19 View 11169 -
 'Dr. M,' Mobile Healthcare Showroom Opened at KI
Portable and wearable computers have made the way we manage our health easier and potentially more effective. Researchers from six departments and one graduate school at KAIST collaborated and conducted a one-year project called the “Mobile Healthcare Innovation” to develop a mobile healthcare system. Their research results are on exhibit on campus at the “Dr. M Showroom” which was open on March 13, 2015.
Located on the second floor of the College of Information and Electrical Engineering building, the showroom displays the entirety of mobile healthcare system developed during 2014, from the collection of biological data through smart sensors to analyzing big data to provide customized healthcare models for patients.
Standing in for a mobile doctor, Dr. M is a networked medical service system provided through the Internet of Things (IoC), wearable electronics, smart home, and smart car. Under this care, people can monitor their health on a daily basis at any-time and place, helping them to lower the risk of serious health problems. Patients who have chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular illness can inform doctors of their health status in real time. Moreover, people living in remote regions can receive quality medical services without traveling long distances.
At the showroom, about 40 convergence technologies are displayed, including biological sensors, low-power communication devices, IoC technology, big data, disease analysis, and prediction technology, presenting how these technologies are connected and worked systematically. For example, all the data earned from biological sensors are analyzed to produce relevant user information. Once abnormalities are discovered, the results would be sent immediately to medical staff for treatment.
As part of Dr. M, KAIST has been implementing the establishment of a “Mobile Healthcare Campus,” distributing small, wearable wristbands to 100 students. The wristbands read students’ biological signals and send them to researchers for monitoring. In addition, KAIST plans to collaborate with local hospitals, nursing care centers, communications, and mobile healthcare service providers for the commercialization of Dr. M system.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Department, who has led the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project said, “One of the great advantages Dr. M can offer is the capability to customize healthcare service based on individuals and ages. For individuals in their twenties, for example, healthcare services such as skincare and diet programs will be more relevant whereas blood pressure monitoring for patients in their fifties and early diagnosis for the recurrence of diseases for those in their seventies. If we define human history in terms of major technology advancements, the first big one was computation, communication for the second, and I think ubiquitous healthcare will be the third one. We will continue to develop Dr. M in collaboration with medical and research organizations.”
A total of 32 professors from the Departments of Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Industrial and Systems Engineering, Industrial Design, Web Science, Knowledge Service Engineering, and the Information Security Graduate School participated in the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project.
2015.03.17 View 11274
'Dr. M,' Mobile Healthcare Showroom Opened at KI
Portable and wearable computers have made the way we manage our health easier and potentially more effective. Researchers from six departments and one graduate school at KAIST collaborated and conducted a one-year project called the “Mobile Healthcare Innovation” to develop a mobile healthcare system. Their research results are on exhibit on campus at the “Dr. M Showroom” which was open on March 13, 2015.
Located on the second floor of the College of Information and Electrical Engineering building, the showroom displays the entirety of mobile healthcare system developed during 2014, from the collection of biological data through smart sensors to analyzing big data to provide customized healthcare models for patients.
Standing in for a mobile doctor, Dr. M is a networked medical service system provided through the Internet of Things (IoC), wearable electronics, smart home, and smart car. Under this care, people can monitor their health on a daily basis at any-time and place, helping them to lower the risk of serious health problems. Patients who have chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular illness can inform doctors of their health status in real time. Moreover, people living in remote regions can receive quality medical services without traveling long distances.
At the showroom, about 40 convergence technologies are displayed, including biological sensors, low-power communication devices, IoC technology, big data, disease analysis, and prediction technology, presenting how these technologies are connected and worked systematically. For example, all the data earned from biological sensors are analyzed to produce relevant user information. Once abnormalities are discovered, the results would be sent immediately to medical staff for treatment.
As part of Dr. M, KAIST has been implementing the establishment of a “Mobile Healthcare Campus,” distributing small, wearable wristbands to 100 students. The wristbands read students’ biological signals and send them to researchers for monitoring. In addition, KAIST plans to collaborate with local hospitals, nursing care centers, communications, and mobile healthcare service providers for the commercialization of Dr. M system.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Department, who has led the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project said, “One of the great advantages Dr. M can offer is the capability to customize healthcare service based on individuals and ages. For individuals in their twenties, for example, healthcare services such as skincare and diet programs will be more relevant whereas blood pressure monitoring for patients in their fifties and early diagnosis for the recurrence of diseases for those in their seventies. If we define human history in terms of major technology advancements, the first big one was computation, communication for the second, and I think ubiquitous healthcare will be the third one. We will continue to develop Dr. M in collaboration with medical and research organizations.”
A total of 32 professors from the Departments of Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Industrial and Systems Engineering, Industrial Design, Web Science, Knowledge Service Engineering, and the Information Security Graduate School participated in the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project.
2015.03.17 View 11274 -
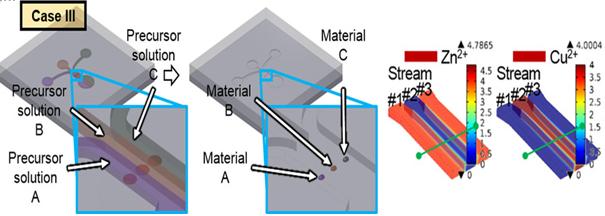 KAIST Develops Subminiature, Power-Efficient Air Pollution Sensing Probe
Professor Inkyu Park and his research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have developed a subminiature, power-efficient air-pollution sensing probe that can be applied to mobile devices. Their research findings were published online in the January 30th issue of Scientific Reports.
As air pollution has increased, people have taken greater interest in health care. The developed technology could allow people to measure independently the air pollution level of their surrounding environments.
Previous instruments used to measure air pollution levels were bulky and consumed a lot of power. They also often produced inaccurate results when measuring air pollution in which different toxic gases were mixed. These problems could not be resolved with existing semiconductor manufacturing process.
Using local temperature field control technology, Professor Park’s team succeeded in integrating multiple heterogeneous nanomaterials and fitting them onto a small, low-power electronic chip. This microheating sensor can heat microscale regions through local hydrothermal synthesis. Because it requires a miniscale amount of nanomaterials to manufacture, the sensor is most suitable for mobile devices.
Professor Park said, “Our research will contribute to the development of convergence technology in such field as air pollution sensing probes, biosensors, electronic devices, and displays.”
The team's research was supported by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Figure 1 – The Concept of Multiple Nanomaterial Device and Numerical Simulation Results of Precursor Solutions
Figure 2 - Multiple Nanomaterial Manufactured in a Microscale Region
2015.02.27 View 11960
KAIST Develops Subminiature, Power-Efficient Air Pollution Sensing Probe
Professor Inkyu Park and his research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have developed a subminiature, power-efficient air-pollution sensing probe that can be applied to mobile devices. Their research findings were published online in the January 30th issue of Scientific Reports.
As air pollution has increased, people have taken greater interest in health care. The developed technology could allow people to measure independently the air pollution level of their surrounding environments.
Previous instruments used to measure air pollution levels were bulky and consumed a lot of power. They also often produced inaccurate results when measuring air pollution in which different toxic gases were mixed. These problems could not be resolved with existing semiconductor manufacturing process.
Using local temperature field control technology, Professor Park’s team succeeded in integrating multiple heterogeneous nanomaterials and fitting them onto a small, low-power electronic chip. This microheating sensor can heat microscale regions through local hydrothermal synthesis. Because it requires a miniscale amount of nanomaterials to manufacture, the sensor is most suitable for mobile devices.
Professor Park said, “Our research will contribute to the development of convergence technology in such field as air pollution sensing probes, biosensors, electronic devices, and displays.”
The team's research was supported by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Figure 1 – The Concept of Multiple Nanomaterial Device and Numerical Simulation Results of Precursor Solutions
Figure 2 - Multiple Nanomaterial Manufactured in a Microscale Region
2015.02.27 View 11960 -
 KAIST's Thermoelectric Generator on Glass Fabric Receives the Grand Prize at the Netexplo Forum 2015
The forum announced top ten IT innovations expected to change the world and selected the grand prize on February 4, 2014.
Established in 2007 by Martine Bidegain and Thierry Happe in partnership with the French Senate and the French Ministry for the Digital Economy, the Netexplo Observatory is an independent global organization that studies the impact of digital technology and innovation on society and business.
Every year, the Netexplo Observatory hosts an international conference, the Netexplo Forum, in Paris, France, which surveys digital innovation worldwide. The 8th forum was held in partnership with the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) on February 4-5, 2015, at the UNESCO House in Paris.
Prior to the conference, the Netexplo Forum 2015 named the top ten most promising digital technologies that will greatly impact the world.
Among them was Professor Byung Jin Cho’s research on a wearable thermoelectric generator (http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2014-04/tkai-tgo041014.php). The generator was selected as the most innovative technology this year.
Professor Cho of KAIST’s Electrical Engineering Department developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator that is extremely light and flexible and that produces electricity from the heat of the human body. This technology can be applied widely to wearable computers and mobile devices.
The full list of innovations follows below:
Wearable Thermo-Element, South Korea: The human body becomes a source of energy for mobile devices.
W.Afate 3D-printer, Togo: An environmentally friendly fablab that makes a low-cost 3D-printer from recycling electronic components.
Slack, USA: By combining email, Skype, and file-sharing and social networks, internal communication becomes much easier and simpler.
PhotoMath, Croatia: A free app that enables smartphone users to solve mathematical problems simply by scanning the mathematical texts.
Kappo, Chile: Connected cyclists produce and transmit useful data for urban planning to make the city more bike-friendly.
Branching Minds, USA: An improved learning process for students in difficulty through a personalized approach.
Baidu Kuai Sou, China: Smart chopsticks that can check food hazards.
SCio, Israel: A pocket molecular sensor with various applications and data
Rainforest Connection, USA: Fighting deforestation with recycled smartphones
Sense Ebola Followup, Nigeria: A mobile tool to help contain Ebola
For more details on the wearable thermos-element which received the 2015 Netexplo Award, please go to https://www.netexplo.org/en/intelligence/innovation/wearable-thermo-element.
Pictures 1 and 2: A high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Picture 3: Senator Catherine Morin-Desailly (left) of the French Parliament presents the 2015 Netexplo Award to Professor Byung Jin Cho (right) on February 4, 2015 at the UNESCO House in Paris.
Credit of Loran Dhérines
Picture 4: Professor Byung Jin Cho (left) poses with Dr. Joël de Rosnay (right).
Credit of Loran Dhérines
2015.02.06 View 15768
KAIST's Thermoelectric Generator on Glass Fabric Receives the Grand Prize at the Netexplo Forum 2015
The forum announced top ten IT innovations expected to change the world and selected the grand prize on February 4, 2014.
Established in 2007 by Martine Bidegain and Thierry Happe in partnership with the French Senate and the French Ministry for the Digital Economy, the Netexplo Observatory is an independent global organization that studies the impact of digital technology and innovation on society and business.
Every year, the Netexplo Observatory hosts an international conference, the Netexplo Forum, in Paris, France, which surveys digital innovation worldwide. The 8th forum was held in partnership with the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) on February 4-5, 2015, at the UNESCO House in Paris.
Prior to the conference, the Netexplo Forum 2015 named the top ten most promising digital technologies that will greatly impact the world.
Among them was Professor Byung Jin Cho’s research on a wearable thermoelectric generator (http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2014-04/tkai-tgo041014.php). The generator was selected as the most innovative technology this year.
Professor Cho of KAIST’s Electrical Engineering Department developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator that is extremely light and flexible and that produces electricity from the heat of the human body. This technology can be applied widely to wearable computers and mobile devices.
The full list of innovations follows below:
Wearable Thermo-Element, South Korea: The human body becomes a source of energy for mobile devices.
W.Afate 3D-printer, Togo: An environmentally friendly fablab that makes a low-cost 3D-printer from recycling electronic components.
Slack, USA: By combining email, Skype, and file-sharing and social networks, internal communication becomes much easier and simpler.
PhotoMath, Croatia: A free app that enables smartphone users to solve mathematical problems simply by scanning the mathematical texts.
Kappo, Chile: Connected cyclists produce and transmit useful data for urban planning to make the city more bike-friendly.
Branching Minds, USA: An improved learning process for students in difficulty through a personalized approach.
Baidu Kuai Sou, China: Smart chopsticks that can check food hazards.
SCio, Israel: A pocket molecular sensor with various applications and data
Rainforest Connection, USA: Fighting deforestation with recycled smartphones
Sense Ebola Followup, Nigeria: A mobile tool to help contain Ebola
For more details on the wearable thermos-element which received the 2015 Netexplo Award, please go to https://www.netexplo.org/en/intelligence/innovation/wearable-thermo-element.
Pictures 1 and 2: A high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Picture 3: Senator Catherine Morin-Desailly (left) of the French Parliament presents the 2015 Netexplo Award to Professor Byung Jin Cho (right) on February 4, 2015 at the UNESCO House in Paris.
Credit of Loran Dhérines
Picture 4: Professor Byung Jin Cho (left) poses with Dr. Joël de Rosnay (right).
Credit of Loran Dhérines
2015.02.06 View 15768 -
 KAIST Co-owns the HEVC Patent Portfolio License
MPEG LA, LLC, a firm based in Denver, Colorado, which licenses patent pools covering essential patents required for the use of video coding technology, such as MPEG-2, MPEG-4 Visual (Part 2), and HEVC/H.264, announced the availability of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Patent Portfolio License on September 29, 2014.
The HEVC standard, also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is necessary to improve video coding and transmission efficiency for the Internet, televisions, and mobile gadgets with increased speed and capacity.
Through the portfolio license, users can easily obtain patent rights required for the HEVC standard in a single transaction, instead of negotiating separate licenses from multiple patent holders.
A total of 23 enterprises currently own essential HEVC patents. KAIST is the only Korean university among the joint patent owners. Collaborating with the Korea Broadcasting System (KBS) and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST developed one of the core patents.
For a link to a press release distributed by MPEG LA, LLC, please see:
MPEG LA, LLC, September 29, 2014
"MPEG LA, LLC Offers HEVC Patent Portfolio License"
http://www.mpegla.com/main/Pages/Media.aspx
2014.10.02 View 14723
KAIST Co-owns the HEVC Patent Portfolio License
MPEG LA, LLC, a firm based in Denver, Colorado, which licenses patent pools covering essential patents required for the use of video coding technology, such as MPEG-2, MPEG-4 Visual (Part 2), and HEVC/H.264, announced the availability of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Patent Portfolio License on September 29, 2014.
The HEVC standard, also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is necessary to improve video coding and transmission efficiency for the Internet, televisions, and mobile gadgets with increased speed and capacity.
Through the portfolio license, users can easily obtain patent rights required for the HEVC standard in a single transaction, instead of negotiating separate licenses from multiple patent holders.
A total of 23 enterprises currently own essential HEVC patents. KAIST is the only Korean university among the joint patent owners. Collaborating with the Korea Broadcasting System (KBS) and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST developed one of the core patents.
For a link to a press release distributed by MPEG LA, LLC, please see:
MPEG LA, LLC, September 29, 2014
"MPEG LA, LLC Offers HEVC Patent Portfolio License"
http://www.mpegla.com/main/Pages/Media.aspx
2014.10.02 View 14723 -
 Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 10668
Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 10668 -
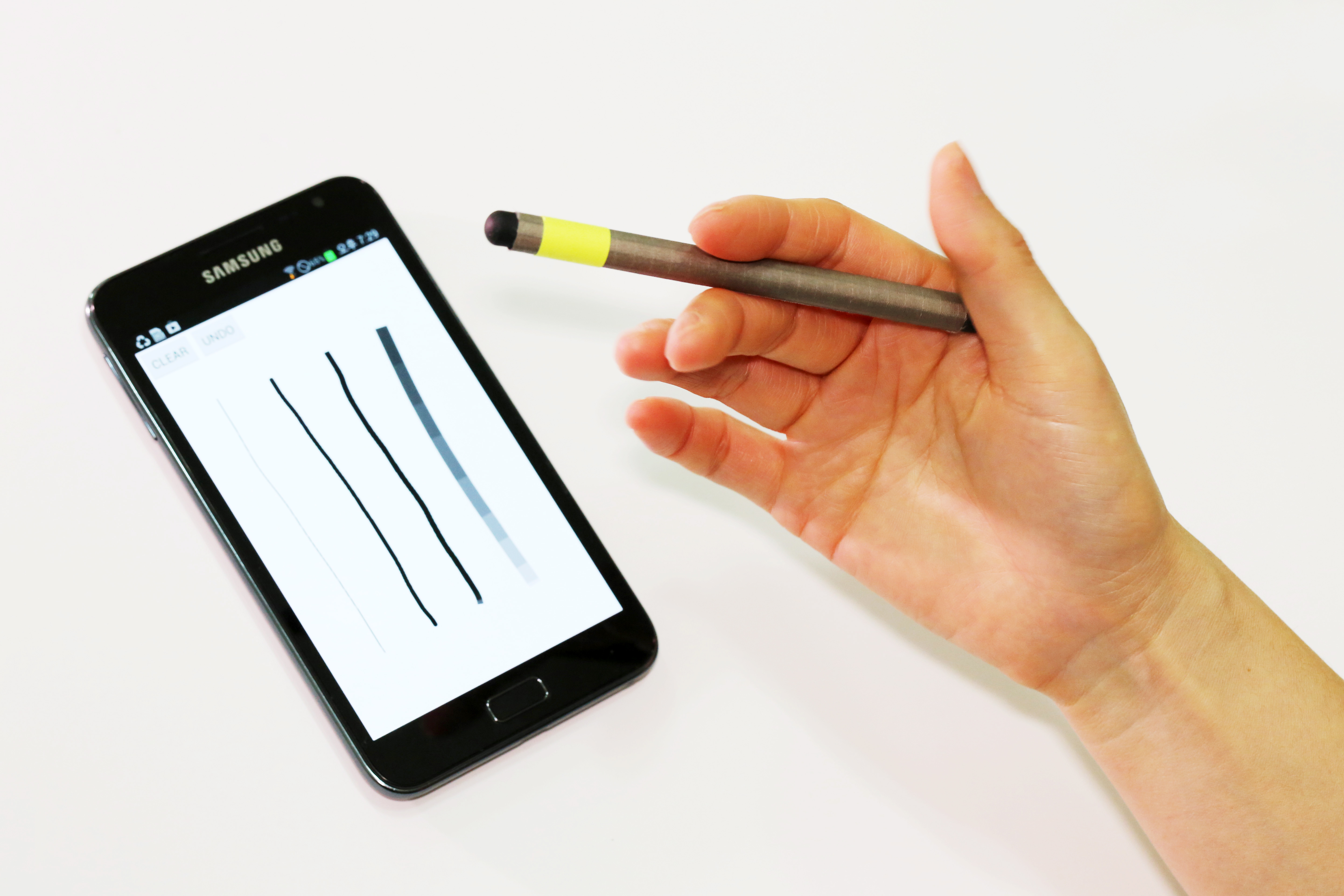 A magnetic pen for smartphones adds another level of conveniences
Utilizing existing features on smartphones, the MagPen provides users with a compatible and simple input tool regardless of the type of phones they are using.
A doctoral candidate at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a magnetically driven pen interface that works both on and around mobile devices. This interface, called the MagPen, can be used for any type of smartphones and tablet computers so long as they have magnetometers embedded in.
Advised by Professor Kwang-yun Wohn of the Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST, Sungjae Hwang, a Ph.D. student, created the MagPen in collaboration with Myung-Wook Ahn, a master"s student at the GSCT of KAIST, and Andrea Bianchi, a professor at Sungkyunkwan University.
Almost all mobile devices today provide location-based services, and magnetometers are incorporated in the integrated circuits of smartphones or tablet PCs, functioning as compasses. Taking advantage of built-in magnetometers, Hwang"s team came up with a technology that enabled an input tool for mobile devices such as a capacitive stylus pen to interact more sensitively and effectively with the devices" touch screen. Text and command entered by a stylus pen are expressed better on the screen of mobile devices than those done by human fingers.
The MagPen utilizes magnetometers equipped with smartphones, thus there is no need to build an additional sensing panel for a touchscreen as well as circuits, communication modules, or batteries for the pen. With an application installed on smartphones, it senses and analyzes the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet embedded in a standard capacitive stylus pen.
Sungjae Hwang said, "Our technology is eco-friendly and very affordable because we are able to improve the expressiveness of the stylus pen without requiring additional hardware beyond those already installed on the current mobile devices. The technology allows smartphone users to enjoy added convenience while no wastes generated."
The MagPen detects the direction at which a stylus pen is pointing; selects colors by dragging the pen across smartphone bezel; identifies pens with different magnetic properties; recognizes pen-spinning gestures; and estimates the finger pressure applied to the pen.
Notably, with its spinning motion, the MagPen expands the scope of input gestures recognized by a stylus pen beyond its existing vocabularies of gestures and techniques such as titling, hovering, and varying pressures. The tip of the pen switches from a pointer to an eraser and vice versa when spinning. Or, it can choose the thickness of the lines drawn on a screen by spinning.
"It"s quite remarkable to see that the MagPen can understand spinning motion. It"s like the pen changes its living environment from two dimensions to three dimensions. This is the most creative characteristic of our technology," added Sungjae Hwang.
Hwang"s initial research result was first presented at the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces organized by the Association for Computing Machinery and held on March 19-22 in Santa Monica, the US.
In the next month of August, the research team will present a paper on the MagPen technology, entitled "MagPen: Magnetically Driven Pen Interaction On and Around Conventional Smartphones" and receive an Honorable Mention Award at the 15th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services (MobileHCI 2013) to be held in Germany.
In addition to the MagPen, Hwang and his team are conducting other projects to develop different types of magnetic gadgets (collectively called "MagGetz") that include the Magnetic Marionette, a magnetic cover for a smartphone, which offers augmented interactions with the phone, as well as magnetic widgets such as buttons and toggle interface.
Hwang has filed ten patents for the MagGetz technology.
Youtube Links: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NkPo2las7wc, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J9GtgyzoZmM
2013.07.25 View 12798
A magnetic pen for smartphones adds another level of conveniences
Utilizing existing features on smartphones, the MagPen provides users with a compatible and simple input tool regardless of the type of phones they are using.
A doctoral candidate at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a magnetically driven pen interface that works both on and around mobile devices. This interface, called the MagPen, can be used for any type of smartphones and tablet computers so long as they have magnetometers embedded in.
Advised by Professor Kwang-yun Wohn of the Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST, Sungjae Hwang, a Ph.D. student, created the MagPen in collaboration with Myung-Wook Ahn, a master"s student at the GSCT of KAIST, and Andrea Bianchi, a professor at Sungkyunkwan University.
Almost all mobile devices today provide location-based services, and magnetometers are incorporated in the integrated circuits of smartphones or tablet PCs, functioning as compasses. Taking advantage of built-in magnetometers, Hwang"s team came up with a technology that enabled an input tool for mobile devices such as a capacitive stylus pen to interact more sensitively and effectively with the devices" touch screen. Text and command entered by a stylus pen are expressed better on the screen of mobile devices than those done by human fingers.
The MagPen utilizes magnetometers equipped with smartphones, thus there is no need to build an additional sensing panel for a touchscreen as well as circuits, communication modules, or batteries for the pen. With an application installed on smartphones, it senses and analyzes the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet embedded in a standard capacitive stylus pen.
Sungjae Hwang said, "Our technology is eco-friendly and very affordable because we are able to improve the expressiveness of the stylus pen without requiring additional hardware beyond those already installed on the current mobile devices. The technology allows smartphone users to enjoy added convenience while no wastes generated."
The MagPen detects the direction at which a stylus pen is pointing; selects colors by dragging the pen across smartphone bezel; identifies pens with different magnetic properties; recognizes pen-spinning gestures; and estimates the finger pressure applied to the pen.
Notably, with its spinning motion, the MagPen expands the scope of input gestures recognized by a stylus pen beyond its existing vocabularies of gestures and techniques such as titling, hovering, and varying pressures. The tip of the pen switches from a pointer to an eraser and vice versa when spinning. Or, it can choose the thickness of the lines drawn on a screen by spinning.
"It"s quite remarkable to see that the MagPen can understand spinning motion. It"s like the pen changes its living environment from two dimensions to three dimensions. This is the most creative characteristic of our technology," added Sungjae Hwang.
Hwang"s initial research result was first presented at the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces organized by the Association for Computing Machinery and held on March 19-22 in Santa Monica, the US.
In the next month of August, the research team will present a paper on the MagPen technology, entitled "MagPen: Magnetically Driven Pen Interaction On and Around Conventional Smartphones" and receive an Honorable Mention Award at the 15th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services (MobileHCI 2013) to be held in Germany.
In addition to the MagPen, Hwang and his team are conducting other projects to develop different types of magnetic gadgets (collectively called "MagGetz") that include the Magnetic Marionette, a magnetic cover for a smartphone, which offers augmented interactions with the phone, as well as magnetic widgets such as buttons and toggle interface.
Hwang has filed ten patents for the MagGetz technology.
Youtube Links: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NkPo2las7wc, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J9GtgyzoZmM
2013.07.25 View 12798 -
 KAIST and JAIT Sign MOU
KAIST and JAIT (Jeonbuk Institute of Automotive Technology) signed a MOU for the training and development of future automobile technology.
JAIT is the domestic front runner in automobile research and the MOU will allow KAIST to participate with JAIT on research and development of automobile technology.
Research on future vehicle technology, transportation system using electric transport system, cooperation in education, research and development, and international business, and knowledge transfer are all part of the MOU.
2012.11.29 View 8258
KAIST and JAIT Sign MOU
KAIST and JAIT (Jeonbuk Institute of Automotive Technology) signed a MOU for the training and development of future automobile technology.
JAIT is the domestic front runner in automobile research and the MOU will allow KAIST to participate with JAIT on research and development of automobile technology.
Research on future vehicle technology, transportation system using electric transport system, cooperation in education, research and development, and international business, and knowledge transfer are all part of the MOU.
2012.11.29 View 8258 -
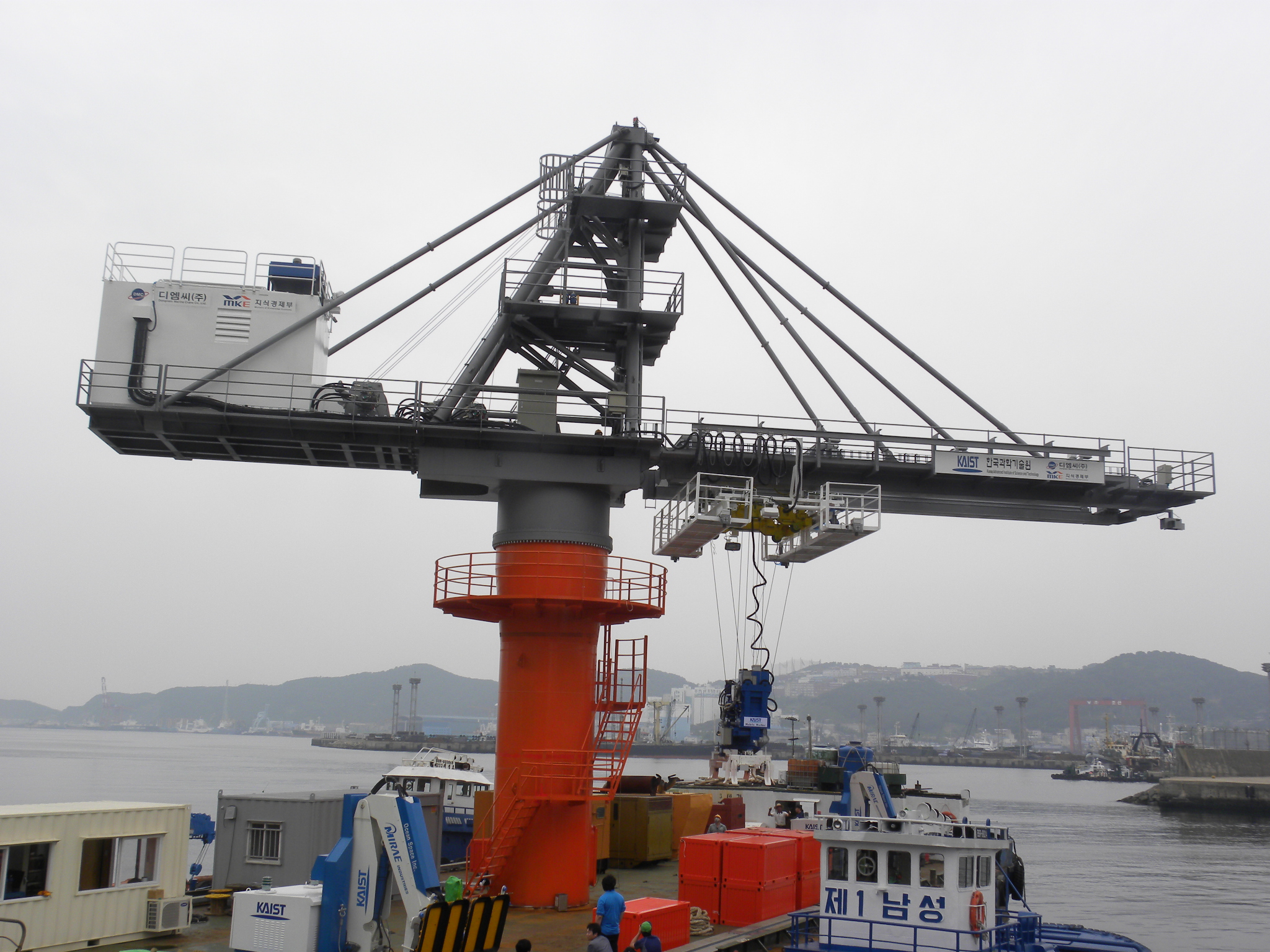 Mobile Harbor delivers the goods for container ships at sea by Reuters TV
Reuters TV introduced the Mobile Harbor showcase that was held on June 29, 2011 in Busan, Korea. For the article, please follow the link:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tuADd3DqCQg
2011.07.11 View 7192
Mobile Harbor delivers the goods for container ships at sea by Reuters TV
Reuters TV introduced the Mobile Harbor showcase that was held on June 29, 2011 in Busan, Korea. For the article, please follow the link:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tuADd3DqCQg
2011.07.11 View 7192