GO
-
 3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 6752
3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 6752 -
 Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 13630
Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 13630 -
 T-GPS Processes a Graph with Trillion Edges on a Single Computer
Trillion-scale graph processing simulation on a single computer presents a new concept of graph processing
A KAIST research team has developed a new technology that enables to process a large-scale graph algorithm without storing the graph in the main memory or on disks. Named as T-GPS (Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation) by the developer Professor Min-Soo Kim from the School of Computing at KAIST, it can process a graph with one trillion edges using a single computer.
Graphs are widely used to represent and analyze real-world objects in many domains such as social networks, business intelligence, biology, and neuroscience. As the number of graph applications increases rapidly, developing and testing new graph algorithms is becoming more important than ever before. Nowadays, many industrial applications require a graph algorithm to process a large-scale graph (e.g., one trillion edges). So, when developing and testing graph algorithms such for a large-scale graph, a synthetic graph is usually used instead of a real graph. This is because sharing and utilizing large-scale real graphs is very limited due to their being proprietary or being practically impossible to collect.
Conventionally, developing and testing graph algorithms is done via the following two-step approach: generating and storing a graph and executing an algorithm on the graph using a graph processing engine.
The first step generates a synthetic graph and stores it on disks. The synthetic graph is usually generated by either parameter-based generation methods or graph upscaling methods. The former extracts a small number of parameters that can capture some properties of a given real graph and generates the synthetic graph with the parameters. The latter upscales a given real graph to a larger one so as to preserve the properties of the original real graph as much as possible.
The second step loads the stored graph into the main memory of the graph processing engine such as Apache GraphX and executes a given graph algorithm on the engine. Since the size of the graph is too large to fit in the main memory of a single computer, the graph engine typically runs on a cluster of several tens or hundreds of computers. Therefore, the cost of the conventional two-step approach is very high.
The research team solved the problem of the conventional two-step approach. It does not generate and store a large-scale synthetic graph. Instead, it just loads the initial small real graph into main memory. Then, T-GPS processes a graph algorithm on the small real graph as if the large-scale synthetic graph that should be generated from the real graph exists in main memory. After the algorithm is done, T-GPS returns the exactly same result as the conventional two-step approach.
The key idea of T-GPS is generating only the part of the synthetic graph that the algorithm needs to access on the fly and modifying the graph processing engine to recognize the part generated on the fly as the part of the synthetic graph actually generated.
The research team showed that T-GPS can process a graph of 1 trillion edges using a single computer, while the conventional two-step approach can only process of a graph of 1 billion edges using a cluster of eleven computers of the same specification. Thus, T-GPS outperforms the conventional approach by 10,000 times in terms of computing resources. The team also showed that the speed of processing an algorithm in T-GPS is up to 43 times faster than the conventional approach. This is because T-GPS has no network communication overhead, while the conventional approach has a lot of communication overhead among computers.
Professor Kim believes that this work will have a large impact on the IT industry where almost every area utilizes graph data, adding, “T-GPS can significantly increase both the scale and efficiency of developing a new graph algorithm.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP).
Publication:
Park, H., et al. (2021) “Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation based on Top-Down Graph Upscaling,” Presented at the IEEE ICDE 2021 (April 19-22, 2021, Chania, Greece)
Profile:
Min-Soo Kim
Associate Professor
minsoo.k@kaist.ac.kr
http://infolab.kaist.ac.kr
School of Computing
KAIST
2021.05.06 View 8583
T-GPS Processes a Graph with Trillion Edges on a Single Computer
Trillion-scale graph processing simulation on a single computer presents a new concept of graph processing
A KAIST research team has developed a new technology that enables to process a large-scale graph algorithm without storing the graph in the main memory or on disks. Named as T-GPS (Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation) by the developer Professor Min-Soo Kim from the School of Computing at KAIST, it can process a graph with one trillion edges using a single computer.
Graphs are widely used to represent and analyze real-world objects in many domains such as social networks, business intelligence, biology, and neuroscience. As the number of graph applications increases rapidly, developing and testing new graph algorithms is becoming more important than ever before. Nowadays, many industrial applications require a graph algorithm to process a large-scale graph (e.g., one trillion edges). So, when developing and testing graph algorithms such for a large-scale graph, a synthetic graph is usually used instead of a real graph. This is because sharing and utilizing large-scale real graphs is very limited due to their being proprietary or being practically impossible to collect.
Conventionally, developing and testing graph algorithms is done via the following two-step approach: generating and storing a graph and executing an algorithm on the graph using a graph processing engine.
The first step generates a synthetic graph and stores it on disks. The synthetic graph is usually generated by either parameter-based generation methods or graph upscaling methods. The former extracts a small number of parameters that can capture some properties of a given real graph and generates the synthetic graph with the parameters. The latter upscales a given real graph to a larger one so as to preserve the properties of the original real graph as much as possible.
The second step loads the stored graph into the main memory of the graph processing engine such as Apache GraphX and executes a given graph algorithm on the engine. Since the size of the graph is too large to fit in the main memory of a single computer, the graph engine typically runs on a cluster of several tens or hundreds of computers. Therefore, the cost of the conventional two-step approach is very high.
The research team solved the problem of the conventional two-step approach. It does not generate and store a large-scale synthetic graph. Instead, it just loads the initial small real graph into main memory. Then, T-GPS processes a graph algorithm on the small real graph as if the large-scale synthetic graph that should be generated from the real graph exists in main memory. After the algorithm is done, T-GPS returns the exactly same result as the conventional two-step approach.
The key idea of T-GPS is generating only the part of the synthetic graph that the algorithm needs to access on the fly and modifying the graph processing engine to recognize the part generated on the fly as the part of the synthetic graph actually generated.
The research team showed that T-GPS can process a graph of 1 trillion edges using a single computer, while the conventional two-step approach can only process of a graph of 1 billion edges using a cluster of eleven computers of the same specification. Thus, T-GPS outperforms the conventional approach by 10,000 times in terms of computing resources. The team also showed that the speed of processing an algorithm in T-GPS is up to 43 times faster than the conventional approach. This is because T-GPS has no network communication overhead, while the conventional approach has a lot of communication overhead among computers.
Professor Kim believes that this work will have a large impact on the IT industry where almost every area utilizes graph data, adding, “T-GPS can significantly increase both the scale and efficiency of developing a new graph algorithm.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP).
Publication:
Park, H., et al. (2021) “Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation based on Top-Down Graph Upscaling,” Presented at the IEEE ICDE 2021 (April 19-22, 2021, Chania, Greece)
Profile:
Min-Soo Kim
Associate Professor
minsoo.k@kaist.ac.kr
http://infolab.kaist.ac.kr
School of Computing
KAIST
2021.05.06 View 8583 -
 KAIST and Google Partner to Develop AI Curriculum
Two KAIST professors, Hyun Wook Ka from the School of Transdisciplinary Studies and Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, were recipients of Google Education Grants that will support the development of new AI courses integrating the latest industrial technology. This collaboration is part of the KAIST-Google Partnership, which was established in July 2019 with the goal of nurturing AI talent at KAIST.
The two proposals -- Professor Ka’s ‘Cloud AI-Empowered Multimodal Data Analysis for Human Affect Detection and Recognition’ and Professor Jang’s ‘Learning Smart Factory with AI’-- were selected by the KAIST Graduate School of AI through a school-wide competition held in July. The proposals then went through a final review by Google and were accepted. The two professors will receive $7,500 each for developing AI courses using Google technology for one year.
Professor Ka’s curriculum aims to provide a rich learning experience for students by providing basic knowledge on data science and AI and helping them obtain better problem solving and application skills using practical and interdisciplinary data science and AI technology.
Professor Jang’s curriculum is designed to solve real-world manufacturing problems using AI and it will be field-oriented. Professor Jang has been managing three industry-academic collaboration centers in manufacturing and smart factories within KAIST and plans to develop his courses to go beyond theory and be centered on case studies for solving real-world manufacturing problems using AI.
Professor Jang said, “Data is at the core of smart factories and AI education, but there is often not enough of it for the education to be effective. The KAIST Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory has a testbed for directly acquiring data generated from real semiconductor automation equipment, analyzing it, and applying algorithms, which enables truly effective smart factory and AI education.”
KAIST signed a partnership with Google in July 2019 to foster global AI talent and is operating various programs to train AI experts and support excellent AI research for two years.
The Google AI Focused Research Award supports world-class faculty performing cutting-edge research and was previously awarded to professors Sung Ju Hwang from the Graduate School of AI and Steven Whang from the School of Electrical Engineering along with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) credits. These two professors have been collaborating with Google teams since October 2018 and recently extended their projects to continue through 2021.
In addition, a Google Ph.D. Fellowship was awarded to Taesik Gong from the School of Computing in October this year, and three Student Travel Grants were awarded to Sejun Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, Chulhyung Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, and Sangyun Lee from the School of Computing earlier in March. Five students were also recommended for the Google Internship program in March.
(END)
2020.12.11 View 13914
KAIST and Google Partner to Develop AI Curriculum
Two KAIST professors, Hyun Wook Ka from the School of Transdisciplinary Studies and Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, were recipients of Google Education Grants that will support the development of new AI courses integrating the latest industrial technology. This collaboration is part of the KAIST-Google Partnership, which was established in July 2019 with the goal of nurturing AI talent at KAIST.
The two proposals -- Professor Ka’s ‘Cloud AI-Empowered Multimodal Data Analysis for Human Affect Detection and Recognition’ and Professor Jang’s ‘Learning Smart Factory with AI’-- were selected by the KAIST Graduate School of AI through a school-wide competition held in July. The proposals then went through a final review by Google and were accepted. The two professors will receive $7,500 each for developing AI courses using Google technology for one year.
Professor Ka’s curriculum aims to provide a rich learning experience for students by providing basic knowledge on data science and AI and helping them obtain better problem solving and application skills using practical and interdisciplinary data science and AI technology.
Professor Jang’s curriculum is designed to solve real-world manufacturing problems using AI and it will be field-oriented. Professor Jang has been managing three industry-academic collaboration centers in manufacturing and smart factories within KAIST and plans to develop his courses to go beyond theory and be centered on case studies for solving real-world manufacturing problems using AI.
Professor Jang said, “Data is at the core of smart factories and AI education, but there is often not enough of it for the education to be effective. The KAIST Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory has a testbed for directly acquiring data generated from real semiconductor automation equipment, analyzing it, and applying algorithms, which enables truly effective smart factory and AI education.”
KAIST signed a partnership with Google in July 2019 to foster global AI talent and is operating various programs to train AI experts and support excellent AI research for two years.
The Google AI Focused Research Award supports world-class faculty performing cutting-edge research and was previously awarded to professors Sung Ju Hwang from the Graduate School of AI and Steven Whang from the School of Electrical Engineering along with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) credits. These two professors have been collaborating with Google teams since October 2018 and recently extended their projects to continue through 2021.
In addition, a Google Ph.D. Fellowship was awarded to Taesik Gong from the School of Computing in October this year, and three Student Travel Grants were awarded to Sejun Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, Chulhyung Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, and Sangyun Lee from the School of Computing earlier in March. Five students were also recommended for the Google Internship program in March.
(END)
2020.12.11 View 13914 -
 Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 12622
Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 12622 -
 Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13045
Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13045 -
 Quantum Classifiers with Tailored Quantum Kernel
Quantum information scientists have introduced a new method for machine learning classifications in quantum computing. The non-linear quantum kernels in a quantum binary classifier provide new insights for improving the accuracy of quantum machine learning, deemed able to outperform the current AI technology.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee from the School of Electrical Engineering, proposed a quantum classifier based on quantum state fidelity by using a different initial state and replacing the Hadamard classification with a swap test. Unlike the conventional approach, this method is expected to significantly enhance the classification tasks when the training dataset is small, by exploiting the quantum advantage in finding non-linear features in a large feature space.
Quantum machine learning holds promise as one of the imperative applications for quantum computing. In machine learning, one fundamental problem for a wide range of applications is classification, a task needed for recognizing patterns in labeled training data in order to assign a label to new, previously unseen data; and the kernel method has been an invaluable classification tool for identifying non-linear relationships in complex data.
More recently, the kernel method has been introduced in quantum machine learning with great success. The ability of quantum computers to efficiently access and manipulate data in the quantum feature space can open opportunities for quantum techniques to enhance various existing machine learning methods.
The idea of the classification algorithm with a nonlinear kernel is that given a quantum test state, the protocol calculates the weighted power sum of the fidelities of quantum data in quantum parallel via a swap-test circuit followed by two single-qubit measurements (see Figure 1). This requires only a small number of quantum data operations regardless of the size of data. The novelty of this approach lies in the fact that labeled training data can be densely packed into a quantum state and then compared to the test data.
The KAIST team, in collaboration with researchers from the University of KwaZulu-Natal (UKZN) in South Africa and Data Cybernetics in Germany, has further advanced the rapidly evolving field of quantum machine learning by introducing quantum classifiers with tailored quantum kernels.This study was reported at npj Quantum Information in May.
The input data is either represented by classical data via a quantum feature map or intrinsic quantum data, and the classification is based on the kernel function that measures the closeness of the test data to training data.
Dr. Daniel Park at KAIST, one of the lead authors of this research, said that the quantum kernel can be tailored systematically to an arbitrary power sum, which makes it an excellent candidate for real-world applications.
Professor Rhee said that quantum forking, a technique that was invented by the team previously, makes it possible to start the protocol from scratch, even when all the labeled training data and the test data are independently encoded in separate qubits.
Professor Francesco Petruccione from UKZN explained, “The state fidelity of two quantum states includes the imaginary parts of the probability amplitudes, which enables use of the full quantum feature space.”
To demonstrate the usefulness of the classification protocol, Carsten Blank from Data Cybernetics implemented the classifier and compared classical simulations using the five-qubit IBM quantum computer that is freely available to public users via cloud service. “This is a promising sign that the field is progressing,” Blank noted.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41534-020-0272-6
-Profile
Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee
rhee.jk@kaist.ac.kr
Professor, School of Electrical Engineering
Director, ITRC of Quantum Computing for AIKAIST
Daniel Kyungdeock Parkkpark10@kaist.ac.krResearch Assistant ProfessorSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2020.07.07 View 13403
Quantum Classifiers with Tailored Quantum Kernel
Quantum information scientists have introduced a new method for machine learning classifications in quantum computing. The non-linear quantum kernels in a quantum binary classifier provide new insights for improving the accuracy of quantum machine learning, deemed able to outperform the current AI technology.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee from the School of Electrical Engineering, proposed a quantum classifier based on quantum state fidelity by using a different initial state and replacing the Hadamard classification with a swap test. Unlike the conventional approach, this method is expected to significantly enhance the classification tasks when the training dataset is small, by exploiting the quantum advantage in finding non-linear features in a large feature space.
Quantum machine learning holds promise as one of the imperative applications for quantum computing. In machine learning, one fundamental problem for a wide range of applications is classification, a task needed for recognizing patterns in labeled training data in order to assign a label to new, previously unseen data; and the kernel method has been an invaluable classification tool for identifying non-linear relationships in complex data.
More recently, the kernel method has been introduced in quantum machine learning with great success. The ability of quantum computers to efficiently access and manipulate data in the quantum feature space can open opportunities for quantum techniques to enhance various existing machine learning methods.
The idea of the classification algorithm with a nonlinear kernel is that given a quantum test state, the protocol calculates the weighted power sum of the fidelities of quantum data in quantum parallel via a swap-test circuit followed by two single-qubit measurements (see Figure 1). This requires only a small number of quantum data operations regardless of the size of data. The novelty of this approach lies in the fact that labeled training data can be densely packed into a quantum state and then compared to the test data.
The KAIST team, in collaboration with researchers from the University of KwaZulu-Natal (UKZN) in South Africa and Data Cybernetics in Germany, has further advanced the rapidly evolving field of quantum machine learning by introducing quantum classifiers with tailored quantum kernels.This study was reported at npj Quantum Information in May.
The input data is either represented by classical data via a quantum feature map or intrinsic quantum data, and the classification is based on the kernel function that measures the closeness of the test data to training data.
Dr. Daniel Park at KAIST, one of the lead authors of this research, said that the quantum kernel can be tailored systematically to an arbitrary power sum, which makes it an excellent candidate for real-world applications.
Professor Rhee said that quantum forking, a technique that was invented by the team previously, makes it possible to start the protocol from scratch, even when all the labeled training data and the test data are independently encoded in separate qubits.
Professor Francesco Petruccione from UKZN explained, “The state fidelity of two quantum states includes the imaginary parts of the probability amplitudes, which enables use of the full quantum feature space.”
To demonstrate the usefulness of the classification protocol, Carsten Blank from Data Cybernetics implemented the classifier and compared classical simulations using the five-qubit IBM quantum computer that is freely available to public users via cloud service. “This is a promising sign that the field is progressing,” Blank noted.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41534-020-0272-6
-Profile
Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee
rhee.jk@kaist.ac.kr
Professor, School of Electrical Engineering
Director, ITRC of Quantum Computing for AIKAIST
Daniel Kyungdeock Parkkpark10@kaist.ac.krResearch Assistant ProfessorSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2020.07.07 View 13403 -
 Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 19507
Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 19507 -
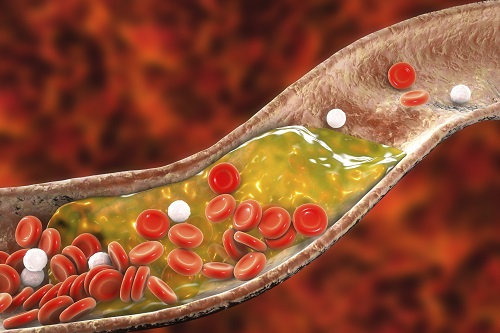 New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 15194
New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 15194 -
 KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 15989
KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 15989 -
 Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10201
Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10201 -
 KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research
Google has agreed to support KAIST students and professors in the fields of AI research and education. President Sung-Chul Shin and Google Korea Country Director John Lee signed the collaboration agreement during a ceremony on July 19 at KAIST.
Under the agreement, Google will fund the Google AI-Focused Research Awards Program, the PhD Fellowship Program, and Student Travel Grants for KAIST. In addition, Google will continue to provide more academic and career building opportunities for students, including Google internship programs.
KAIST and Google has been collaborating for years. Professor Steven Whang at the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Ju Hwang at the School of Computing won the AI-Focused Award in 2018 and conduct their researches on "Improving Generalization and Reliability of Any Deep Neural Networks" and "Automatic and Acitionable Model Analysis for TFX," respectively. Outstanding PhD students have been recognized through the PhD Fellowship Program. However, this new collaboration agreement will focus on research, academic development, and technological innovation in AI.
Google plans to support research in the fields of deep learning, cloud machine learning, and voice technologies. Google will fund the development of two educational programs based on Google open source technology each year for two years that will be used in the new AI Graduate School opening for the fall semester.
John Lee of Google Korea said, “This partnership lays a solid foundation for deeper collaboration.” President Shin added, “This partnership will not only advance Korea’s global competitiveness in AI-powered industries but also contribute to the global community by nurturing talents in this most extensive discipline.”
2019.07.22 View 9619
KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research
Google has agreed to support KAIST students and professors in the fields of AI research and education. President Sung-Chul Shin and Google Korea Country Director John Lee signed the collaboration agreement during a ceremony on July 19 at KAIST.
Under the agreement, Google will fund the Google AI-Focused Research Awards Program, the PhD Fellowship Program, and Student Travel Grants for KAIST. In addition, Google will continue to provide more academic and career building opportunities for students, including Google internship programs.
KAIST and Google has been collaborating for years. Professor Steven Whang at the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Ju Hwang at the School of Computing won the AI-Focused Award in 2018 and conduct their researches on "Improving Generalization and Reliability of Any Deep Neural Networks" and "Automatic and Acitionable Model Analysis for TFX," respectively. Outstanding PhD students have been recognized through the PhD Fellowship Program. However, this new collaboration agreement will focus on research, academic development, and technological innovation in AI.
Google plans to support research in the fields of deep learning, cloud machine learning, and voice technologies. Google will fund the development of two educational programs based on Google open source technology each year for two years that will be used in the new AI Graduate School opening for the fall semester.
John Lee of Google Korea said, “This partnership lays a solid foundation for deeper collaboration.” President Shin added, “This partnership will not only advance Korea’s global competitiveness in AI-powered industries but also contribute to the global community by nurturing talents in this most extensive discipline.”
2019.07.22 View 9619