THE
-
 Dopant properties of silicon nanowires investigated
Professor Chang Kee Joo
Professor Kee Joo Chang’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has successfully unearthed the properties of boron and phosphorous dopants in silicon nanowires, a material expected to be used in next generation semiconductors. The research team was the first in the world to investigate the movement of boron and phosphorous (impurities or ‘dopants’ added for electrical flow) in oxidized silicon nanowires and study the mechanism behind its deactivation.
It is nearly impossible to develop a silicon based semiconductor thinner than 10nm, even using the most advanced modern technology. However, the thickness of silicon nanowires are within the nano level and hence, allows a higher degree of integration in semiconductors.
For silicon nanowires to carry electricity, small amounts of boron and phosphorous need to be added (‘doping’ process). Compared to silicon, nanowires are harder to create due to the difficulties in the doping process as well as the control of electrical conduction properties.
Professor Chang’s research team improved upon the existing simple model by applying revolutionary quantum simulation theory to create a realistic core-shell atomic model. This research successfully investigated the cause of the escape of boron dopants from the silicon core during oxidation. It was also found that although phosphorous dopants do not escape as oxides, they form electrically deactivated pairs which decreases the efficiency. These phenomena were attributed to the film shape of the nano-wires, which increases the relative surface area compared to a same volume of silicon.
The research results were published in the online September edition of the world renowned Nano Letters.
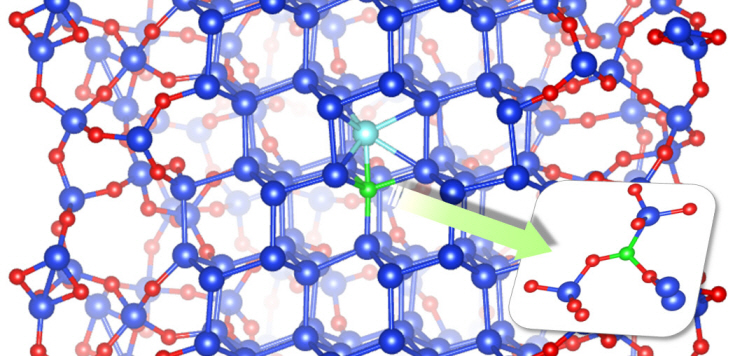
Figure: The longitudinal section diagram of the Silicon/oxide core-shell model
2012.11.28 View 9165
Dopant properties of silicon nanowires investigated
Professor Chang Kee Joo
Professor Kee Joo Chang’s research team from the Department of Physics at KAIST has successfully unearthed the properties of boron and phosphorous dopants in silicon nanowires, a material expected to be used in next generation semiconductors. The research team was the first in the world to investigate the movement of boron and phosphorous (impurities or ‘dopants’ added for electrical flow) in oxidized silicon nanowires and study the mechanism behind its deactivation.
It is nearly impossible to develop a silicon based semiconductor thinner than 10nm, even using the most advanced modern technology. However, the thickness of silicon nanowires are within the nano level and hence, allows a higher degree of integration in semiconductors.
For silicon nanowires to carry electricity, small amounts of boron and phosphorous need to be added (‘doping’ process). Compared to silicon, nanowires are harder to create due to the difficulties in the doping process as well as the control of electrical conduction properties.
Professor Chang’s research team improved upon the existing simple model by applying revolutionary quantum simulation theory to create a realistic core-shell atomic model. This research successfully investigated the cause of the escape of boron dopants from the silicon core during oxidation. It was also found that although phosphorous dopants do not escape as oxides, they form electrically deactivated pairs which decreases the efficiency. These phenomena were attributed to the film shape of the nano-wires, which increases the relative surface area compared to a same volume of silicon.
The research results were published in the online September edition of the world renowned Nano Letters.
Figure: The longitudinal section diagram of the Silicon/oxide core-shell model
2012.11.28 View 9165 -
 3D contents using our technology
Professor Noh Jun Yong’s research team from KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology has successfully developed a software program that improves the semiautomatic conversation rate efficiency of 3D stereoscopic images by 3 times.
This software, named ‘NAKiD’, was first presented at the renowned Computer Graphics conference/exhibition ‘Siggraph 2012’ in August and received intense interest from the participants.
The ‘NAKiD’ technology is forecasted to replace the expensive imported equipment and technology used in 3D filming.
For multi-viewpoint no-glasses 3D stereopsis, two cameras are needed to film the image. However, ‘NAKiD’ can easily convert images from a single camera into a 3D image, greatly decreasing the problems in the film production process as well as its cost.
There are 2 methods commonly used in the production of 3D stereoscopic images; filming using two cameras and the 3D conversion using computer software.
The use of two cameras requires expensive equipment and the filmed images need further processing after production. On the other hand, 3D conversion technology does not require extra devices in the production process and can also convert the existing 2D contents into 3D, a main reason why many countries are focusing on the development of stereoscopic technology.
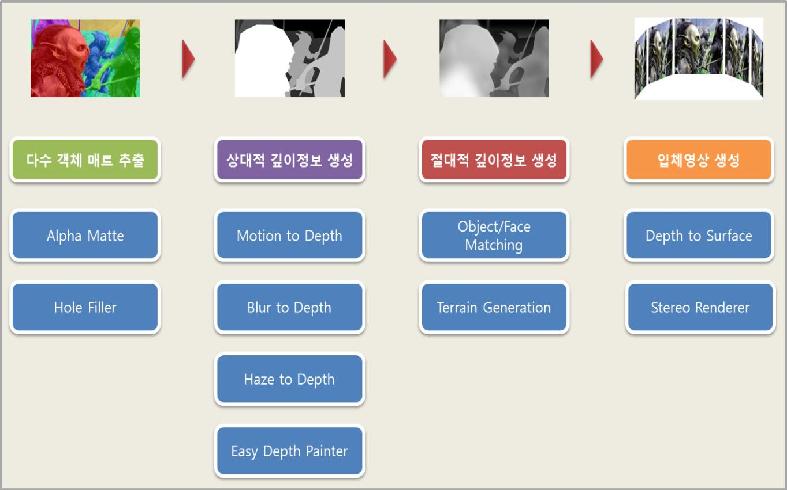
Stereoscopic conversion is largely divided in to 3 steps; object separation, formation of depth information and stereo rendering. Professor Noh’s teams focused on the optimization of each step to increase the efficiency of the conversion system.
Professor Noh’s research team first increased the separation accuracy to the degree of a single hair and created an algorithm that automatically fills in the background originally covered by the separated object.
The team succeeded in the automatic formation of depth information using the geographic or architectural characteristic and vanishing points. For the stereo rendering process, the team decreased the rendering time by reusing the rendered information of one side, rather than the traditional method of rendering the left and right images separately.
Professor Noh said that ‘although 3D TVs are becoming more and more commercialized, there are not enough programs that can be watched in 3D’ and that ‘stereoscopic conversion technology is receiving high praise in the field of graphics because it allows the easy production of 3D contents with small cost’.
2012.10.20 View 11317
3D contents using our technology
Professor Noh Jun Yong’s research team from KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology has successfully developed a software program that improves the semiautomatic conversation rate efficiency of 3D stereoscopic images by 3 times.
This software, named ‘NAKiD’, was first presented at the renowned Computer Graphics conference/exhibition ‘Siggraph 2012’ in August and received intense interest from the participants.
The ‘NAKiD’ technology is forecasted to replace the expensive imported equipment and technology used in 3D filming.
For multi-viewpoint no-glasses 3D stereopsis, two cameras are needed to film the image. However, ‘NAKiD’ can easily convert images from a single camera into a 3D image, greatly decreasing the problems in the film production process as well as its cost.
There are 2 methods commonly used in the production of 3D stereoscopic images; filming using two cameras and the 3D conversion using computer software.
The use of two cameras requires expensive equipment and the filmed images need further processing after production. On the other hand, 3D conversion technology does not require extra devices in the production process and can also convert the existing 2D contents into 3D, a main reason why many countries are focusing on the development of stereoscopic technology.
Stereoscopic conversion is largely divided in to 3 steps; object separation, formation of depth information and stereo rendering. Professor Noh’s teams focused on the optimization of each step to increase the efficiency of the conversion system.
Professor Noh’s research team first increased the separation accuracy to the degree of a single hair and created an algorithm that automatically fills in the background originally covered by the separated object.
The team succeeded in the automatic formation of depth information using the geographic or architectural characteristic and vanishing points. For the stereo rendering process, the team decreased the rendering time by reusing the rendered information of one side, rather than the traditional method of rendering the left and right images separately.
Professor Noh said that ‘although 3D TVs are becoming more and more commercialized, there are not enough programs that can be watched in 3D’ and that ‘stereoscopic conversion technology is receiving high praise in the field of graphics because it allows the easy production of 3D contents with small cost’.
2012.10.20 View 11317 -
 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony Held
The 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony was held at Seoul KAIST Campus.
Recipients of the award included former congressmen Kim Young Sun and Lee Jeong Hyuk, and Kim Boo Kyung researcher at Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute also representing Vooz Ltd. that created the character POOCA.
The Intellectual Property Rights Award is given to an individual or a group that succeeded in utilizing, protecting, creating, and establishment of its foundation including patent, copyright, and brand. Intellectual Property Rights is viewed as of importance for future national competitiveness.
The Award is organized by the Korea Patent Attorneys Association, the Korea Association of Intellectual Property Services, and KAIST and are respectively core institutions in the training of Intellectual Property Rights Experts and the creation, utilization, and the protection of intellectual property.
In addition the Award is also co-organized by the KAIST Graduate School of Intellectual Property Rights (established in cooperation with KAIST and the Korean Intellectual Property Office) and the total 20 million Won of prize money is funded by Korea Institute of Intellectual Strategy and Kim Ok Lan Foundation.
The Award Ceremony was held with a special lecture by the recipients.
It was stressed that the evaluation process was carried out with that the decision is a silent message to the society and is also a type of market signal.
Director Ko Gi Seok (Presidential Council on Intellectual Property) revealed that the candidates’ impact on the strength of national intellectual property rights was thoroughly scrutinized.
In the criteria of Creation of Intellectual Property, ETRI received the award in recognition of the institution’s successful patenting and commercializing of products of Korean R&D.
ETRI created a total of 251 International Patents in cooperation with ITU, ISO, IEE, etc. and also participated in a total of 9 International Standard Patent Pool, showing its active Intellectual Property management.
Such efforts ranked ETRI 1st in the United States Patent Evaluation performed by the US Patent Board in 2011 out of 237 institutions.
In addition Recipient of the Intellectual Property Utilization criteria, VOOZ ltd.’s Kim Boo Kyung promised the free use of their character POOCA in ETRI’s automated Korean-English translator. Researcher Kim Boo Kyung was rewarded with the award in recognition of his contribution to the domestic economy and realization of the commercialization of a copy right through licensing.
Former congressman Kim Young Son received an Award in the Foundation criteria in recognition of his efforts in the establishment of the Presidential Council on Intellectual Property and the Basic Blueprints for the Intellectual Property Law.
Former congressman Lee Jeong Hyuk received the same award in recognition of standardization and streamlining Intellectual Property Rights Policies. His realization and pursuit of the establishment of a balanced growth based on law for the competitiveness of businesses was the driving force behind his accomplishments.
2012.10.16 View 13092
2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony Held
The 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony was held at Seoul KAIST Campus.
Recipients of the award included former congressmen Kim Young Sun and Lee Jeong Hyuk, and Kim Boo Kyung researcher at Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute also representing Vooz Ltd. that created the character POOCA.
The Intellectual Property Rights Award is given to an individual or a group that succeeded in utilizing, protecting, creating, and establishment of its foundation including patent, copyright, and brand. Intellectual Property Rights is viewed as of importance for future national competitiveness.
The Award is organized by the Korea Patent Attorneys Association, the Korea Association of Intellectual Property Services, and KAIST and are respectively core institutions in the training of Intellectual Property Rights Experts and the creation, utilization, and the protection of intellectual property.
In addition the Award is also co-organized by the KAIST Graduate School of Intellectual Property Rights (established in cooperation with KAIST and the Korean Intellectual Property Office) and the total 20 million Won of prize money is funded by Korea Institute of Intellectual Strategy and Kim Ok Lan Foundation.
The Award Ceremony was held with a special lecture by the recipients.
It was stressed that the evaluation process was carried out with that the decision is a silent message to the society and is also a type of market signal.
Director Ko Gi Seok (Presidential Council on Intellectual Property) revealed that the candidates’ impact on the strength of national intellectual property rights was thoroughly scrutinized.
In the criteria of Creation of Intellectual Property, ETRI received the award in recognition of the institution’s successful patenting and commercializing of products of Korean R&D.
ETRI created a total of 251 International Patents in cooperation with ITU, ISO, IEE, etc. and also participated in a total of 9 International Standard Patent Pool, showing its active Intellectual Property management.
Such efforts ranked ETRI 1st in the United States Patent Evaluation performed by the US Patent Board in 2011 out of 237 institutions.
In addition Recipient of the Intellectual Property Utilization criteria, VOOZ ltd.’s Kim Boo Kyung promised the free use of their character POOCA in ETRI’s automated Korean-English translator. Researcher Kim Boo Kyung was rewarded with the award in recognition of his contribution to the domestic economy and realization of the commercialization of a copy right through licensing.
Former congressman Kim Young Son received an Award in the Foundation criteria in recognition of his efforts in the establishment of the Presidential Council on Intellectual Property and the Basic Blueprints for the Intellectual Property Law.
Former congressman Lee Jeong Hyuk received the same award in recognition of standardization and streamlining Intellectual Property Rights Policies. His realization and pursuit of the establishment of a balanced growth based on law for the competitiveness of businesses was the driving force behind his accomplishments.
2012.10.16 View 13092 -
 2012 Times Higher Education Ranks KAIST a Record High of 68th
KAIST was evaluated as the 68th best university by the Times Higher Education, a English University Evaluation Body.
The 2012 evaluation is 29 places higher than the 2011 evaluation.
As a side note, KAIST was ranked a record high of 63rd in the world by Quacquarelli Symonds’ 2012 QS World University Evaluation.
2012.10.16 View 8081
2012 Times Higher Education Ranks KAIST a Record High of 68th
KAIST was evaluated as the 68th best university by the Times Higher Education, a English University Evaluation Body.
The 2012 evaluation is 29 places higher than the 2011 evaluation.
As a side note, KAIST was ranked a record high of 63rd in the world by Quacquarelli Symonds’ 2012 QS World University Evaluation.
2012.10.16 View 8081 -
 College of Cultural Sciences Announces Results for 6th Best Paper Award
The College of Cultural Sciences cohosts with the EFL Program the Best Paper Award each semester. The Best Paper Awards went to Jo Hyeong Chan and Oh Shin Ah undergraduate students. The Best Paper Award was established in 2009 in order to encourage and improve the English writing skills of undergraduate students.
The College of Humanities and Social Sciences opened up 69 English courses in Spring of 2012 and 14 papers were recommended by the respective professors as ‘best papers’. Out of these papers 2 were selected for First Prize and 4 were selected as Honorable Mentions. The two recipients’ papers were recommended by Professor Park Woo Seok (Topics in Philosophy).
2012.10.16 View 8549
College of Cultural Sciences Announces Results for 6th Best Paper Award
The College of Cultural Sciences cohosts with the EFL Program the Best Paper Award each semester. The Best Paper Awards went to Jo Hyeong Chan and Oh Shin Ah undergraduate students. The Best Paper Award was established in 2009 in order to encourage and improve the English writing skills of undergraduate students.
The College of Humanities and Social Sciences opened up 69 English courses in Spring of 2012 and 14 papers were recommended by the respective professors as ‘best papers’. Out of these papers 2 were selected for First Prize and 4 were selected as Honorable Mentions. The two recipients’ papers were recommended by Professor Park Woo Seok (Topics in Philosophy).
2012.10.16 View 8549 -
 Professor Moon Song Chun appointed representative director of European IT society
Professor Moon Song Chun from the College of business at KAIST was appointed as the representative director of Asia for the European IR society EUROMICRO at its 35th general meeting in Lille, France.
Professor Moon is highly regarded in his work in popularization of IT in 3rd world countries and has published the largest number of papers in the history of EUROMICRO. For the next two years, Professor Moon will work to introduce Asia’s IT capabilities to the world and to increase the recognition of the society in the region.
Professor Moon, who is also known as the first Computer Science Doctor (PhD) in Korea, has worked to popularize IT by initiating IT volunteer services in Africa, the Middle East, Central and South America, South East Asia and Eastern Europe. He has also helped in the recognition of Korea’s IT capacity, working as a Korean Delegate for the UN International Y2K Cooperation Center, a Distinguished Scholar at Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and a Visiting Scholar at Cambridge University.
2012.09.25 View 9859
Professor Moon Song Chun appointed representative director of European IT society
Professor Moon Song Chun from the College of business at KAIST was appointed as the representative director of Asia for the European IR society EUROMICRO at its 35th general meeting in Lille, France.
Professor Moon is highly regarded in his work in popularization of IT in 3rd world countries and has published the largest number of papers in the history of EUROMICRO. For the next two years, Professor Moon will work to introduce Asia’s IT capabilities to the world and to increase the recognition of the society in the region.
Professor Moon, who is also known as the first Computer Science Doctor (PhD) in Korea, has worked to popularize IT by initiating IT volunteer services in Africa, the Middle East, Central and South America, South East Asia and Eastern Europe. He has also helped in the recognition of Korea’s IT capacity, working as a Korean Delegate for the UN International Y2K Cooperation Center, a Distinguished Scholar at Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and a Visiting Scholar at Cambridge University.
2012.09.25 View 9859 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 10623
Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 10623 -
 Professor Yoon Dong Ki becomes first Korean to Receive the Michi Nakata Prize
Professor Yoon Dong Ki (Graduate School of Nano Science and Technology) became the first Korean to receive the Michi Nakata Prize from the International Liquid Crystal Society.
The Awards Ceremony was held on the 23rd of August in Mainz, Germany in the 24th Annual International Liquid Crystal Conference.
The Michi Nakata Prize was initiated in 2008 and is rewarded every two years to a young scientist that made a ground breaking discovery or experimental result in the field of liquid crystal. Professor Yoon is the first Korean recipient of the Michi Nakata Prize.
Professor Yoon is the founder of the patterning field that utilizes the defect structure formed by smectic displays. He succeeded in large scale patterning complex chiral nano structures that make up bent-core molecules.
Professor Yoon’s experimental accomplishment was published in the Advanced Materials magazine and the Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. and also as the cover dissertation of Liquid Crystals magazine.
Professor Yoon is currently working on Three Dimensional Nano Patterning of Supermolecular Liquid Crystal and is part of the World Class University organization.
2012.09.11 View 14247
Professor Yoon Dong Ki becomes first Korean to Receive the Michi Nakata Prize
Professor Yoon Dong Ki (Graduate School of Nano Science and Technology) became the first Korean to receive the Michi Nakata Prize from the International Liquid Crystal Society.
The Awards Ceremony was held on the 23rd of August in Mainz, Germany in the 24th Annual International Liquid Crystal Conference.
The Michi Nakata Prize was initiated in 2008 and is rewarded every two years to a young scientist that made a ground breaking discovery or experimental result in the field of liquid crystal. Professor Yoon is the first Korean recipient of the Michi Nakata Prize.
Professor Yoon is the founder of the patterning field that utilizes the defect structure formed by smectic displays. He succeeded in large scale patterning complex chiral nano structures that make up bent-core molecules.
Professor Yoon’s experimental accomplishment was published in the Advanced Materials magazine and the Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. and also as the cover dissertation of Liquid Crystals magazine.
Professor Yoon is currently working on Three Dimensional Nano Patterning of Supermolecular Liquid Crystal and is part of the World Class University organization.
2012.09.11 View 14247 -
 Jellyfish removal robot developed
Professor Myung Hyun’s research team from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST has developed a jellyfish removal robot named ‘JEROS’ (JEROS: Jellyfish Elimination RObotic Swarm).
With jellyfish attacks around the south-west coast of Korea becoming a serious problem, causing deaths and operational losses (around 3 billion won a year), Professor Myung’s team started the development of this unmanned automatic jellyfish removal system 3 years ago.
JEROS floats on the surface of the water using two long cylindrical bodies. Motors are attached to the bodies such that the robot can move back and forth as well as rotate on water. A camera and GPS system allows the JEROS to detect jellyfish swarm as well as plan and calculate its work path relative to its position.
The jellyfish are removed by a submerged net that sucks them up using the velocity created by the unmanned sailing. Once caught, the jellyfish are pulverized using a special propeller.
JEROS is estimated to be 3 times more economical than manual removal. Upon experimentation, it showed a removal rate of 400kg per hour at 6 knots. To reach similar effectiveness as manual net removal, which removes up to 1 ton per hour, the research team designed the robot such that 3 or more individual robots could be grouped together and controlled as one.
The research team has finished conducting removal tests in Gunsan and Masan and plan to commercialize the robot next April after improving the removal technology. JEROS technology can also be used for a wide range of purposes such as patrolling and guarding, preventing oil spills or removing floating waste. This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology since 2010.
2012.08.29 View 13598
Jellyfish removal robot developed
Professor Myung Hyun’s research team from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST has developed a jellyfish removal robot named ‘JEROS’ (JEROS: Jellyfish Elimination RObotic Swarm).
With jellyfish attacks around the south-west coast of Korea becoming a serious problem, causing deaths and operational losses (around 3 billion won a year), Professor Myung’s team started the development of this unmanned automatic jellyfish removal system 3 years ago.
JEROS floats on the surface of the water using two long cylindrical bodies. Motors are attached to the bodies such that the robot can move back and forth as well as rotate on water. A camera and GPS system allows the JEROS to detect jellyfish swarm as well as plan and calculate its work path relative to its position.
The jellyfish are removed by a submerged net that sucks them up using the velocity created by the unmanned sailing. Once caught, the jellyfish are pulverized using a special propeller.
JEROS is estimated to be 3 times more economical than manual removal. Upon experimentation, it showed a removal rate of 400kg per hour at 6 knots. To reach similar effectiveness as manual net removal, which removes up to 1 ton per hour, the research team designed the robot such that 3 or more individual robots could be grouped together and controlled as one.
The research team has finished conducting removal tests in Gunsan and Masan and plan to commercialize the robot next April after improving the removal technology. JEROS technology can also be used for a wide range of purposes such as patrolling and guarding, preventing oil spills or removing floating waste. This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology since 2010.
2012.08.29 View 13598 -
 First Annual CanSat Idea Exhibition held
The Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology held the ‘CanSat’ Exhibition in order to increase interest and understanding of satellites in primary, secondary, and high school level students.
The exhibition, hosted by KAIST Satellite Research Center and funded by Korea Aerospace Institute, was held in SaeJeong City.
90 primary, secondary school teams, 57 high school teams, and 14 university teams submitted their applications for participation. Of these teams 20 primary, secondary school teams, 5 high school teams, and 5 university teams were selected after thorough document valuation and presentation assessment.
The 20 primary, secondary school teams participated in the science camp to gain firsthand experience in the construction and launch of a simple satellite system.
The high school and university teams were evaluated by the level of completion of the task given and the level of creativity involved.
The CanSat Exhibition has been held in aerospace powerhouses and this was the first time such an exhibition was held in Korea.
2012.08.21 View 10642
First Annual CanSat Idea Exhibition held
The Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology held the ‘CanSat’ Exhibition in order to increase interest and understanding of satellites in primary, secondary, and high school level students.
The exhibition, hosted by KAIST Satellite Research Center and funded by Korea Aerospace Institute, was held in SaeJeong City.
90 primary, secondary school teams, 57 high school teams, and 14 university teams submitted their applications for participation. Of these teams 20 primary, secondary school teams, 5 high school teams, and 5 university teams were selected after thorough document valuation and presentation assessment.
The 20 primary, secondary school teams participated in the science camp to gain firsthand experience in the construction and launch of a simple satellite system.
The high school and university teams were evaluated by the level of completion of the task given and the level of creativity involved.
The CanSat Exhibition has been held in aerospace powerhouses and this was the first time such an exhibition was held in Korea.
2012.08.21 View 10642 -
 Graduate School of Culture and Technology Begins Mobile Science Classroom
KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology plans visits to elementary schools without the facilities to facilitate hands on science education.
The Graduate School of Culture and Technology planned the ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involving three elementary schools during the summer holidays.
The ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involves increasing interest and artistic sensitivity through experience based science education.
The program is composed of two separate programs in consideration to the level of participating students.
The beginner level program includes: code making, writing secret letters, sticker decorating program and the moderate level program includes: making wipers using complex pulley system, catapult design using elasticity, and puppet show using joints to animate.
The programs will be taught by masters and doctorate program candidates from the KAIST Youth Culture and Technology Experience Center.
*STEAM: And integrated education system including Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics.
2012.07.26 View 10030
Graduate School of Culture and Technology Begins Mobile Science Classroom
KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology plans visits to elementary schools without the facilities to facilitate hands on science education.
The Graduate School of Culture and Technology planned the ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involving three elementary schools during the summer holidays.
The ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involves increasing interest and artistic sensitivity through experience based science education.
The program is composed of two separate programs in consideration to the level of participating students.
The beginner level program includes: code making, writing secret letters, sticker decorating program and the moderate level program includes: making wipers using complex pulley system, catapult design using elasticity, and puppet show using joints to animate.
The programs will be taught by masters and doctorate program candidates from the KAIST Youth Culture and Technology Experience Center.
*STEAM: And integrated education system including Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics.
2012.07.26 View 10030 -
 Systems biology demystifies the resistance mechanism of targeted cancer medication
Korean researchers have found the fundamental resistance mechanism of the MEK inhibitor, a recently highlighted chemotherapy method, laying the foundation for future research on overcoming cancer drug resistance and improving cancer survival rates. This research is meaningful because it was conducted through systems biology, a fusion of IT and biotechnology.
The research was conducted by Professor Gwang hyun Cho’s team from the Department of Biology at KAIST and was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
The research was published as the cover paper for the June edition of the Journal of Molecular Cell Biology (Title: The cross regulation between ERK and PI3K signaling pathways determines the tumoricidal efficacy of MEK inhibitor).
Targeted anticancer medication targets certain molecules in the signaling pathway of the tumor cell and not only has fewer side effects than pre-existing anticancer medication, but also has high clinical efficacy. The technology also allows the creation of personalized medication and has been widely praised by scientists worldwide.
However, resistances to the targeted medication have often been found before or during the clinical stage, eventually causing the medications to fail to reach the drug development stage. Moreover, even if the drug is effective, the survival rate is low and the redevelopment rate is high.
An active pathway in most tumor cells is the ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases) signaling pathway. This pathway is especially important in the development of skin cancer or thyroid cancer, which are developed by the mutation of the BRAF gene inside the path. In these cases, the MEK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases) inhibitor is an effective treatment because it targets the pathway itself. However, the built-up resistance to the inhibitor commonly leads to the redevelopment of cancer.
Professor Cho’s research team used large scale computer simulations to analyze the fundamental resistance mechanism of the MEK inhibitor and used molecular cell biological experiments as well as bio-imaging* techniques to verify the results.
* Bio-imaging: Checking biological phenomena at the cellular and molecular levels using imagery
The research team used different mutational variables, which revealed that the use of the MEK inhibitor reduced the transmission of the ERK signal but led to the activation of another signaling pathway (the PI3K signaling pathway), reducing the effectiveness of the medication. Professor Cho’s team also found that this response originated from the complex interaction between the signaling matter as well as the feedback network structure, suggesting that the mix of the MEK inhibitor with other drugs could improve the effects of the targeted anticancer medication.
Professor Cho stated that this research was the first of its kind to examine the drug resistivity against the MEK inhibitor at the systematic dimension and showed how the effects of drugs on the signaling pathways of cells could be predicted using computer simulation. It also showed how basic research on signaling networks can be applied to clinical drug use, successfully suggesting a new research platform on overcoming resistance to targeting medication using its fundamental mechanism.
2012.07.06 View 13448
Systems biology demystifies the resistance mechanism of targeted cancer medication
Korean researchers have found the fundamental resistance mechanism of the MEK inhibitor, a recently highlighted chemotherapy method, laying the foundation for future research on overcoming cancer drug resistance and improving cancer survival rates. This research is meaningful because it was conducted through systems biology, a fusion of IT and biotechnology.
The research was conducted by Professor Gwang hyun Cho’s team from the Department of Biology at KAIST and was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
The research was published as the cover paper for the June edition of the Journal of Molecular Cell Biology (Title: The cross regulation between ERK and PI3K signaling pathways determines the tumoricidal efficacy of MEK inhibitor).
Targeted anticancer medication targets certain molecules in the signaling pathway of the tumor cell and not only has fewer side effects than pre-existing anticancer medication, but also has high clinical efficacy. The technology also allows the creation of personalized medication and has been widely praised by scientists worldwide.
However, resistances to the targeted medication have often been found before or during the clinical stage, eventually causing the medications to fail to reach the drug development stage. Moreover, even if the drug is effective, the survival rate is low and the redevelopment rate is high.
An active pathway in most tumor cells is the ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases) signaling pathway. This pathway is especially important in the development of skin cancer or thyroid cancer, which are developed by the mutation of the BRAF gene inside the path. In these cases, the MEK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases) inhibitor is an effective treatment because it targets the pathway itself. However, the built-up resistance to the inhibitor commonly leads to the redevelopment of cancer.
Professor Cho’s research team used large scale computer simulations to analyze the fundamental resistance mechanism of the MEK inhibitor and used molecular cell biological experiments as well as bio-imaging* techniques to verify the results.
* Bio-imaging: Checking biological phenomena at the cellular and molecular levels using imagery
The research team used different mutational variables, which revealed that the use of the MEK inhibitor reduced the transmission of the ERK signal but led to the activation of another signaling pathway (the PI3K signaling pathway), reducing the effectiveness of the medication. Professor Cho’s team also found that this response originated from the complex interaction between the signaling matter as well as the feedback network structure, suggesting that the mix of the MEK inhibitor with other drugs could improve the effects of the targeted anticancer medication.
Professor Cho stated that this research was the first of its kind to examine the drug resistivity against the MEK inhibitor at the systematic dimension and showed how the effects of drugs on the signaling pathways of cells could be predicted using computer simulation. It also showed how basic research on signaling networks can be applied to clinical drug use, successfully suggesting a new research platform on overcoming resistance to targeting medication using its fundamental mechanism.
2012.07.06 View 13448